Abstract
This research evaluated the recovery and reuse of dolomitic calcareous amendment saturated with nutrients adsorbed from hydroponic effluent as a soil improver and its impact on the agronomic performance of Phaseolus vulgaris. Initially, the dolomitic calcareous amendment (DCA) was saturated with nutrients from the hydroponic effluent through adsorption tests. The characterization of the DCA was conducted before and after nutrient saturation to verify its composition. Soil analysis was carried out prior to the trial, and a completely randomized experimental design was applied with four treatments and five replications, totaling 20 experimental units for each soil type (sandy and clayey): T1 (control), T2 (raw dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCA), T3 (saturated dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCAS), and T4 (granulated dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCAG). Agronomic performance parameters of Phaseolus vulgaris were assessed to determine nutrient availability to the plant: number of pods, pod length (cm), number of seeds per pod, and weight of 100 seeds (g). Data normality was verified using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and results were analyzed using ANOVA and mean comparisons through Tukey’s test (p < 0.05) using InfoStat software 2020I. Additionally, plant tissue was analyzed to determine nutrient absorption in the seeds, and both soil types were analyzed after harvest. Adsorption results indicated that the DCA retained phosphorus, manganese, calcium, and zinc. According to the characterization, DCA primarily consisted of calcium and magnesium carbonates; following the saturation process, an increase in carbonate groups was observed due to calcium adsorption from the hydroponic effluent. Results in both soil types showed no significant differences in pod number, pod length, or seeds per pod, except for the weight of 100 seeds in sandy soil, where T1, T2, and T3 differed significantly from T4. Based on references, the phosphorus content in the harvested seeds from T3 in sandy soil is classified as sufficient. The findings demonstrate the potential of recovering and reusing nutrients from hydroponic effluent using DCA and transforming it into a value-added agricultural input for soil improvement, presenting a promising alternative for more sustainable and efficient agriculture.
1. Introduction
The risk of phosphate rock supply shortage for fertilizer production and the need to control eutrophication in water bodies are valid reasons to pursue treatment techniques capable of capturing and recovering phosphorus from effluents. Adsorption is a highly selective and efficient technique for phosphate adsorption and recovery from water and wastewater, which may serve as secondary phosphorus sources [1]. In this regard, Boeykens et al. [2] demonstrated that dolomitic calcareous amendment (DCA) is an efficient phosphate adsorbent in aqueous solutions containing other contaminants. This amendment, composed of CaMg(CO3)2, is widely present in sedimentary rocks and also occurs in some igneous [3] and metamorphic rocks [4]. This natural adsorbent is widely used in construction, glass manufacturing, cement production, rubber industries, agricultural soil amendment production, ammonia removal from gases, and heavy metal removal from wastewater [5,6,7].
Following the research by Boeykens et al. [2], Piol et al. [8] studied phosphate desorption processes to recover and reuse DCA as an adsorbent in water treatment, assessing its final disposal potential as a soil amendment by applying desorbed phosphate as fertilizer. They evaluated phosphate bioavailability from the saturated amendment at the lab scale in an artificial environment, using native microorganisms from Buenos Aires (Argentina) to release phosphate in the plant rhizosphere. The extracts were used in Lactuca sativa growth experiments, showing no phytotoxic effects and promoting plant development.
According to Bacelo et al. [1], some materials—especially those of biological origin and those based on non-toxic metals such as calcium, magnesium, or iron—can be used directly as fertilizers after being saturated with phosphate. In this regard, Delgado et al. [9] investigated fertilization of fava bean cultivation using compost from urban waste, known as urbabono. The experiment was conducted in a greenhouse with 12 L pots, incorporating two soil types: sandy (92% sand) and clayey (35% clay and 37% silt), with different treatments: control (no fertilization), mineral fertilizer (N-P-K), and organic fertilizer (urbabono). The authors concluded that urbabono could be considered a viable alternative for fava bean cultivation in both soil types without negatively affecting nutrient balance or yield and even improving seed quality.
In Paraguay, the production and commercialization of lettuce grown through hydroponic systems is a rapidly growing sector. However, hydroponic cultivation requires large amounts of water and chemical fertilizers to optimize plant growth. As a result, this type of agriculture generates high concentrations of point-source pollution, especially nitrogen, phosphorus, and other chemicals used in nutrient solutions. Therefore, alternatives must be sought to treat and/or reuse residual nutrient solutions. Current technologies for treating hydroponic effluents, such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis, are effective [10] but involve high operational and maintenance costs. Additionally, other authors note that the inherent variability of hydroponic effluents—affected by crop type, environment, and season—warrants further systematic investigation. Accordingly, some have studied phosphorus recovery from hydroponic waste solutions via chemical precipitation (NaOH), confirming the technical feasibility of phosphorus recovery from hydroponic effluents [11].
The aforementioned context opens the possibility for further studies involving nutrient recovery and recycling from hydroponic effluent using DCA, given its proven capacity to capture phosphate from water. All of this aligns with the need to optimize resource use and generate useful, applicable knowledge based on circular economy principles. Therefore, the aim of this research was to evaluate the recovery and reuse of nutrients from hydroponic effluent as an agricultural amendment (both corrective and fertilizer) in soils and its impact on the agronomic performance of Phaseolus vulgaris. The reuse of by-products—specifically, DCAS—represents a key step toward a more sustainable agricultural future.
Agronomic Performance of Beans
Gonçalves et al. [12] determined the physical properties of Carioca bean seeds cultivated under field conditions, reporting an average weight of 24.9188 g per 100 seeds. Additionally, the same authors classified the seeds as follows: small seeds (<15 g/100 seeds), medium seeds (15.1–20 g/100 seeds), large seeds (20.1–25 g/100 seeds), and very large seeds (>25.1 g/100 seeds).
Another author studied the physical, chemical, nutritional, and technological properties of beans from different color groups. The cultivars selected for evaluation were Pérola and BRS Estilo (commercial group Rioca), IPR Uirapuru and BRS Esteio (black commercial group), and BRS Agreste and BRS Pitanga (special commercial group). The cultivation was carried out in June 2014 at the experimental fields of Embrapa Arroz e Feijão at the Capivara farm in Santo Antônio de Goiás (GO), Brazil. Regarding the 100-seed weight, results ranged from 19.38 g for IPR Uirapuru to 25.28 g for Pérola [13].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DCA Saturation
The dolomitic calcareous amendment (DCA) was obtained from a specialized supplier in Ciudad del Este, Paraguay. The material was sieved using U.S.A. Standard Testing Sieve (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA), Specification A.S.T.M.E-11, 50 and 270 mesh [14].
Figure 1 details the procedure to concentrate (saturate) nutrients onto the DCA. Initially, the hydroponic effluent was analyzed to identify and quantify the nutrients present in the sample. Effluent samples were collected from a lettuce production system. The analyses followed standard methods for water and wastewater testing [15]. Phosphorus was determined using method 4500-P E (Ascorbic Acid Method), while other nutrients were measured by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (Method 3111 B—Air-acetylene direct flame method). The pH was determined using the electrometric method 4500-H+ B.

Figure 1.
Flowchart for nutrient concentration onto DCA.
Based on the adsorbent/solution ratio used by Boeykens et al. [2], batch tests were performed in triplicate by mixing 3.00 g of DCA with 50.0 mL of hydroponic effluent in a plastic container. The mixture remained in contact for 24 h under constant shaking (160 rpm, temperature 25 ± 2 °C) to allow sufficient nutrient adsorption and DCA saturation. Afterward, the mixture was filtered, and the resulting solution was analyzed to determine which nutrients and in what proportions had been retained on the DCA surface. This evaluation was performed by comparing the composition of the final solution with that of the initial solution. The nutrient removal percentages were calculated using Equation (1).
where and are the initial and final concentrations (mg/L), respectively [16].
2.2. Characterization of the DCA
Once the adsorbent was saturated, the materials (raw dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCA and saturated dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCAS) were characterized to verify their composition. The identification of constituent phases was conducted by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a multipurpose EMPYREN–PANalytical diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical, Enigma Business Park, Grovewood Road, Malvern WR14 1XZ, UK). The equipment was configured with a monochromator and slits (1, 1, 0, 3), operating at 40 kV and 20 mA current. The scanning speed was 1°/min, with a 2θ angle range of 5–60°, and Cu-Kα radiation with a wavelength of 0.15418 nm. The data obtained were analyzed using X’Pert HighScore Plus®—PANalytical® software version 3.0.0, which identified the crystalline phases of the samples. In addition, calcium oxide (CaO), magnesium oxide (MgO), and neutralizing value (NV) were evaluated according to the Official Manual of Analytical Methods for Mineral, Organic, Organomineral Fertilizers and Soil Amendments in Brazil (2014): Chapter V—(B) Particle Size Analysis, (C) Items 3 and 4.3 for MgO and CaO, respectively (AAS method).
2.3. Soil Treatment and Agronomic Performance of Phaseolus vulgaris
Soils were collected from agricultural land at a depth of 0–20.0 cm in two locations in Paraguay. The clayey soil sample (37.44% sand, 26.64% silt, and 35.92% clay) was collected in the district of Minga Guazú, Paraguay (Latitude 25°29′23.7″ S, Longitude 54°51′23.0″ W), and the sandy soil sample (81.60% sand, 5.36% silt, and 13.04% clay) was collected in the district of Yhú, Paraguay (Latitude 25°08′39.4″ S, Longitude 55°51′49.4″ W). The Minga Guazú soil corresponds to the Oxisol order, while the Yhú soil is classified as Argisol [17].
Both soil types were analyzed prior to the experiment, following the EMBRAPA methodology [18].
Initial soil properties for the clayey soil were: pH 5.00; aluminum: 0.30 cmolc/dm3; calcium: 3.20 cmolc/dm3; magnesium: 2.34 cmolc/dm3; potassium: 0.64 cmolc/dm3; CEC (Cation Exchange Capacity): 11.84 cmolc/dm3; phosphorus: 4.77 mg/dm3. For the sandy soil: pH 4.55; aluminum: 0.70 cmolc/dm3; calcium: 0.24 cmolc/dm3; magnesium: 0.11 cmolc/dm3; potassium: 0.05 cmolc/dm3; CEC: 4.49 cmolc/dm3; phosphorus: 3.11 mg/dm3 [19].
The reuse of DCA saturated with nutrients was evaluated using a completely randomized design, with four treatments and five replicates, totaling 20 experimental units for each soil type (sandy and clayey). The treatments were T1 (Control): Soil without DCA; T2 (DCA): Soil with raw DCA; T3 (DCAS): Soil with saturated DCA; and T4 (DCAG): Soil with granulated DCA.
Experimental units were installed under a 50% white shade net. The granulated DCA was supplied by the company BM Brasilminas (Guarulhos, Brazil).
The amendment doses were calculated based on the soil analysis results, considering soil texture class differences. Additionally, it was considered that one hectare of soil with a depth of 20 cm weighs approximately 2,000,000 kg [20]. Thus, the amendment dose for 2000 g of soil was calculated using the base saturation method, applying Equation (2) [21].
RC is the calcareous requirement in kg/ha; V2 is the desired base saturation for Phaseolus vulgaris (70%), V1 is the percentage of current base saturation of the soil, and CEC is the cation exchange capacity in cmolc/dm3 (provided in the analysis report).
The amendment doses calculated were 2747 kg/ha for sandy soil and 2122 kg/ha for clayey soil. These amounts were weighed and homogenously mixed into the soils. Then, they were placed in polyethylene bags (25.0 cm × 20.0 cm) for 90 days. During this period, enough deionized water (to avoid calcium interference) was added to maintain soil moisture and allow amendment reactions. This condition was maintained throughout the experimental phase, with the bag openings covered to prevent water loss by evaporation. Soil moisture was monitored daily using a portable meter.
After soil correction, fertilization was applied based on prior soil analysis results, taking into account textural class differences and crop requirements. Fertilizer doses applied were: clayey soil (N:20; P:105; K:30 kg/ha) and sandy soil (N:20; P:105; K:80 kg/ha).
After correction and fertilization, Phaseolus vulgaris seeds were sown to verify nutrient availability. Later, plant tissue was analyzed to determine nutrient absorption in the seeds. The variety sown was Habilla 40, a local Paraguayan determinate-growth variety. Plants are erect, averaging 35–37 cm in height, with violet flowers. The growth cycle is 95 days, and the seeds are cream-colored with mottled patterns [22]. Seeds were sown on 20 March 2023, placing four seeds per hole at a depth of 1.0 cm. Most seeds had germinated within a week. Thinning was performed on 12 April 2023, leaving two plants per pot. The removed plants were returned to the soil. Irrigation was applied regularly to maintain soil moisture near field capacity.
Pest and disease control was managed using appropriate products. Pests from germination to flowering included whiteflies, leaf beetles, leafhoppers, stink bugs, and thrips. A broad-spectrum insecticide from the neonicotinoid family (75 g thiamethoxam) was used. During flowering, caterpillars mainly targeted leaves and pods; they were controlled with emamectin benzoate 30 insecticide.
Cercospora fungus infections were treated with a systemic and mesostemic foliar fungicide containing trifloxystrobin and prothioconazole.
Harvest began on 7 June 2023, as some pods had dried. The final harvest was completed on 26 June 2023. Agronomic performance parameters evaluated were the number of pods, pod length (cm), number of seeds per pod, and weight of 100 seeds (g).
After harvest, soils from the pots were collected and dried to analyze pH (in water), exchangeable aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and available phosphorus to assess changes in these properties after 177 days from amendment and fertilization. Results were compared with initial values obtained before the trial.
Data normality was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and results were evaluated using analysis of variance and Tukey’s test (p < 0.05) with InfoStat software 2020I.
2.4. Analysis of Phaseolus vulgaris Seeds
The Phaseolus vulgaris seeds were analyzed to evaluate the amount of nutrients absorbed by the plant. Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium parameters were analyzed to conform to the EMBRAPA methodology [18].
3. Results and Discussion
Table 1 presents the mean and standard deviation of the initial and final nutrient concentrations after contact with the DCA, as well as the nutrient removal percentages obtained from the tests. The initial and final pH values of the sample were 8.01 and 8.22, respectively.

Table 1.
Initial and final nutrient concentrations and removal percentages.
According to Table 1, the DCA retained phosphorus, manganese, calcium, and zinc—macro- and micronutrients essential for plant development. The phosphorus removal result is consistent with that obtained by Boeykens et al. [2], who achieved approximately 74% phosphorus elimination.
3.1. DCA Characterization
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Component Identification
The XRD analysis of the raw dolomitic calcareous amendment (DCA) shown in Figure 2a reveals that its main components are calcium and magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2), and calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonate (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2), consistent with Walker et al. [23], who reported that DCA may contain iron traces. According to Soares et al. [24], iron in DCA is associated with orthoclase and certain amorphous minerals.
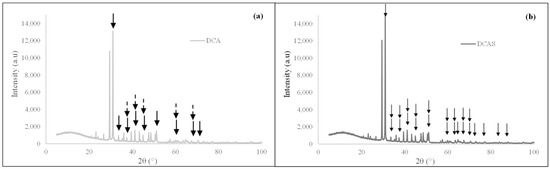
Figure 2.
Diffractograms of (a) raw dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCA and (b) nutrient-saturated dolomitic calcareous amendment—DCAS.  Represents calcium and magnesium carbonate: (CaMg(CO3)2.
Represents calcium and magnesium carbonate: (CaMg(CO3)2.  Represents calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonate: (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2).
Represents calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonate: (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2).
 Represents calcium and magnesium carbonate: (CaMg(CO3)2.
Represents calcium and magnesium carbonate: (CaMg(CO3)2.  Represents calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonate: (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2).
Represents calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonate: (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2).
In Figure 2b, nutrient adsorption from hydroponic effluent increased the intensity of peaks found in the DCA diffractogram, shifting the peaks related to calcium, magnesium, and iron carbonates (Ca(Mg,Fe)(CO3)2). Additionally, XRD analysis of the DCAS detected calcium and magnesium oxides, whose concentrations are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical and granulometric characteristics of the amendments.
Considering that DCA typically contains around 21.6% Ca and 13.1% Mg [25], Table 2 shows that the Ca content in DCA exceeds the expected value. Moreover, all parameters measured in DCAS were higher than in DCA, notably 38.74% CaO and 99.92% NV.
3.2. Agronomic Performance of Phaseolus vulgaris
The statistical analysis results for the agronomic performance of Phaseolus vulgaris are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Agronomic performance of Phaseolus vulgaris.
As shown in Table 3, no significant differences were found in pod number, pod length, or seeds per pod across treatments in both soil types, except for the 100-seed weight in sandy soil. In this case, T1, T2, and T3 showed significantly higher values than T4. However, no significant differences were observed for this parameter in clayey soil.
According to [22], the average number of pods per plant is six, with an average length of 9 cm. These values were not achieved in the present study, possibly due to the limitations of pot cultivation.
In the study by Delgado et al. [9] on Vicia faba fertilized with urban waste compost, the number of seeds per pod in sandy soil was three across treatments, while in clayey soil, the values were 3, 2, and 3, respectively. These results align with those of the present study, where the number of seeds per pod ranged between 2 and 3.
Regarding the 100-seed weight, the value obtained in T4 for sandy soil was low (15.00 g) compared to T1, T2, and T3 (24.80, 23.80, and 24.80 g, respectively). These results fall within the range reported by [13], where 100-seed weights varied between 19.38 and 25.28 g for the cultivars IPR Uirapuru and Pérola.
The values obtained in T1 and T3 for the sandy soil and in T3 for the clayey soil are similar to those reported by Gonçalves et al. [12], who recorded an average weight of 24.9188 g in the evaluated seeds. The values obtained in the present study are noteworthy, considering that the referenced authors conducted their research under field conditions.
Likewise, it is worth highlighting that the values from T1, T2, and T3 in the sandy soil, as well as those from all treatments applied to the clayey soil, were higher than those reported by Salinas et al. [26], whose field study aimed to determine the most efficient chemical fertilizer applications in terms of growth and yield of Phaseolus vulgaris crops in a region located in northeastern Paraguay. They found that the best value for the weight of 100 seeds was 18.54 g, using NPK combined with micronutrients.
Regarding seed classification, and based on the criteria mentioned by Gonçalves et al. [12], the seeds evaluated in T4 for sandy soil are considered small. In contrast, the seeds from the other treatments were classified as large.
3.3. Nutrient Content in Phaseolus vulgaris Seeds
In Figure 3a, the nitrogen content in seeds from T3 (DCAS) grown in sandy soil stands out, reaching 31.43 g/kg. Delgado et al. [9], who studied the fertilization of a fava bean crop using compost from urban waste (urbabono), obtained 3.66% and 3.71% nitrogen in the harvested seeds from sandy and clayey soils, respectively. In this regard, the results obtained in the present study are similar to those reported in the cited reference, considering that the nitrogen concentration in the seeds falls within the 3% range.
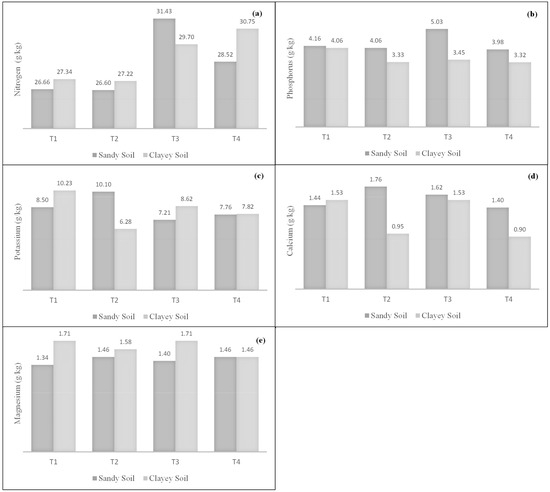
Figure 3.
Concentrations of (a) nitrogen, (b) phosphorus, (c) potassium, (d) calcium, and (e) magnesium in Phaseolus vulgaris seeds across treatments: T1 (control), T2 (DCA), T3 (DCAS), and T4 (DCAG).
According to Figure 3b, the results obtained in sandy soil stand out, where higher phosphorus levels were recorded in the seeds. The highest value, 5.03 g/kg, was observed in T3 (saturated dolomitic calcareous amendment). This result aligns with the agronomic performance data, particularly the 100-seed weight for this treatment, which was the highest and classified the seeds as large. Moreover, this finding correlates with the previously observed data, as there is a direct relationship between nitrogen and phosphorus uptake: the higher the nitrogen content, the greater the phosphorus absorption by plants due to increased phosphorus solubility.
In Figure 3c, the highest potassium content in seeds was found primarily in those harvested from clayey soil, particularly in T1, T3, and T4, with levels of 10.23, 8.62, and 7.82 g/kg, respectively. The greater the colloidal content, the higher the fertility due to increased nutrient retention capacity. Therefore, the clay fraction tends to present a higher potassium content. In sandy soil, T2 yielded the highest potassium content in the seeds, reaching 10.10 g/kg. Nevertheless, the potassium concentrations obtained in this study are higher than those reported by Smith et al. [27], who assessed the impact of drought on productivity and nutrient concentrations in the leaves and seed tissues of common beans grown in the field. The potassium concentration reported by the authors was 3 mg/g (equivalent to 3 g/kg).
Figure 3c shows that the highest potassium content present in the grains was found mainly in those harvested in clay soil, in this case, those obtained in T1, T3, and T4, respectively. The levels were 10.23, 8.62, and 7.82 g/kg for these treatments. The more colloid, the higher the fertility since there is a greater nutrient storage capacity. Therefore, the clay fraction has the highest potassium content. In T2, a higher potassium content was detected in the grains obtained from sandy soil, reaching 10.10 g/kg of this nutrient. However, the potassium concentration referred to by Smith et al. [27] was 3.00 mg/g (equivalent to 3.00 g/kg), the levels obtained in the present study higher.
In Figure 3e, the highest magnesium concentrations were observed in seeds harvested from clayey soil, as this soil type contains higher levels of exchangeable magnesium. Clayey soils are effective at retaining nutrients due to their negative charge, which attracts positively charged cations such as magnesium. The highest concentration of this element was 1.71 g/kg, recorded in both T1 and T3.
The sufficiency ranges in seeds for the elements studied are: N (58.63–62.32 g/kg), P (4.93–5.52 g/kg), K (24.80–28.05 g/kg), Ca (13.07–14.35 g/kg), and Mg (4.67–5.31 g/kg) [28]. Based on these standards, the nutrient levels found in this study are considered low for N, K, Ca, and Mg. Phosphorus levels were also mostly low, except for T3 in sandy soil, which was classified as sufficient.
3.4. Soil Chemical Properties During the Experiment
Figure 4 shows the post-harvest levels of pH, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus in both sandy and clayey soils. These values were compared with initial levels to evaluate the impact of each treatment.
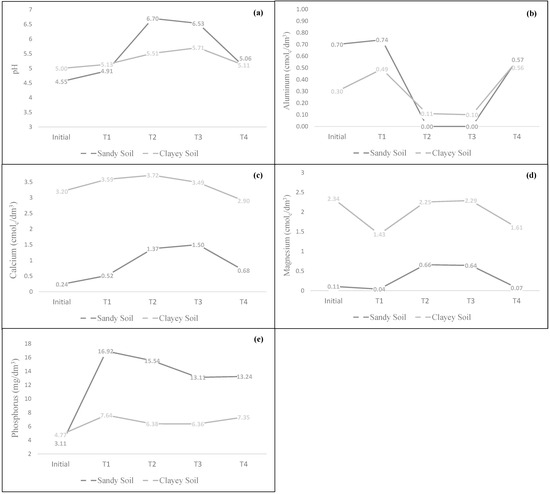
Figure 4.
(a) Soil pH, (b) aluminum (cmolc/dm3), (c) calcium (cmolc/dm3), (d) magnesium (cmolc/dm3), and (e) phosphorus (mg/dm3) under the treatments: T1 (control), T2 (DCA), T3 (DCAS), and T4 (DCAG), after the harvest of Phaseolus vulgaris.
Figure 4a shows that the initial pH in sandy soil was 4.55 (very high acidity), increasing to 6.70 and 6.53 in treatments T2 and T3, respectively. Based on these pH values, the acidity is classified as very low and low, respectively [29]. A similar trend was observed in clayey soil, where the pH was also higher than the initial value. The initial pH was 5.00 (high acidity), increasing to 5.51 and 5.71 (high and low acidity) in T2 and T3, respectively.
Figure 4b shows that aluminum content in both sandy and clayey soils followed a similar pattern: in T1 and T4, values remained above the initial levels, which were 0.30 cmolc/dm3 (low toxicity) for clayey soil and 0.70 cmolc/dm3 (toxic) for sandy soil. However, in T2 and T3 for sandy soil, aluminum was not analytically detected. According to references, aluminum levels are efficiently reduced 18 months after the application of dolomitic lime and silicates [30]. Based on classification scales, aluminum levels in T2 and T3 for sandy soil are considered non-toxic [29]; the aluminum content in T2 (0.11 cmolc/dm3) for clayey soil is slightly toxic, while in T3 (0.10 cmolc/dm3) it is considered non-toxic. The increase in Al levels in T1 and T4 may be attributed to the chemical fertilization applied in the different treatments [31].
Regarding calcium content, Figure 4c shows that in sandy soil, the initial level of 0.24 cmolc/dm3 (classified as low) increased to 0.52, 1.37, 1.50, and 0.68 cmolc/dm3 in T1, T2, T3, and T4, respectively. Nonetheless, considering these values, calcium levels are still classified as low [18]. The same figure shows that in clayey soil, the initial calcium level (classified as medium) increased in T1, T2, and T3, with values of 3.59, 3.72, and 3.49 cmolc/dm3, respectively. These calcium levels are classified as medium [18,29]. As a corrective agent that reacts slowly in the soil, DCA provides a prolonged residual effect [25].
Regarding magnesium, the initial values for sandy and clayey soils are classified as very low and high, respectively. Figure 4d shows that magnesium content follows a similar trend, with a slight decrease observed in T1 and T4, while the values for T2 and T3 remained similar across both soil types. The magnesium concentrations obtained in sandy soil are classified as very low (in T1 and T4) and medium (in T2 and T3), whereas in clayey soil, the levels are considered high [18]. In general, Oxisols have a limited capacity to retain essential plant nutrients such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Magnesium leaching may be related to the formation of inorganic ion pairs with NO3−, HCO3−, OH−, Cl−, and SO42− resulting from mineral fertilization [32].
In Figure 4e, the highest phosphorus levels were recorded in T1, with values of 16.92 and 7.64 mg/dm3 for sandy and clayey soils, respectively. According to the literature, the sandier the soil, the lower the phosphorus content [33] since sandy soils typically contain around 70% sand, making them highly permeable with low water retention capacity, low organic matter content, and low ion adsorption. This reference contrasts with the findings of the present study, as the figure highlights a strong phosphorus reaction in sandy soils. The phosphorus concentrations obtained after the harvest of Phaseolus vulgaris are classified as very high in sandy soils and high in clayey soils [18,29].
In general, after the harvest of the bean seeds, the results of the chemical property analysis indicated that pH levels and calcium content in both sandy and clayey soils continued to improve; consequently, the aluminum levels in T3 for both soil types are classified as non-toxic to plants.
4. Conclusions
In the nutrient adsorption tests of hydroponic effluent using DCA, it was confirmed that the material retains phosphorus, manganese, calcium, and zinc—macro- and micronutrients essential for plant development.
The characterization of the amendments confirmed the predominant presence of calcium and magnesium carbonates in the analyzed samples. In the saturated amendment (DCAS), an increase in carbonate groups, CaO, MgO, and neutralizing value was observed due to calcium adsorption from the hydroponic effluent—calcium being one of the main components of soil acidity correction materials.
Regarding the agronomic parameters of beans, the results for both soil types—across treatments and the control—showed no significant differences in pod number, pod length, or seeds per pod, except in the 100-seed weight in sandy soil, where values in T1, T2, and T3 differed significantly from T4.
In terms of nutrient uptake by the bean seeds, T3 in sandy soil stood out, with phosphorus content classified as sufficient according to reference standards.
After the harvest of the bean seeds, the analysis of chemical properties indicated that pH levels and calcium content in both sandy and clayey soils remained above the initial values recorded before treatment application, especially in T2 and T3, demonstrating a residual effect of DCA and DCAS. Consequently, aluminum levels remained below initial values. Notably, aluminum levels in T3 for both soil types remained within a range that does not represent toxicity to plants.
The results demonstrate the feasibility of recovering nutrients from hydroponic effluent using DCA and transforming them into a resource through their efficient reuse as a soil amendment. This represents a promising alternative for the cultivation of beans (Habilla 40) and for the proper disposal of hydroponic system effluents, whose discharge into water bodies could otherwise lead to eutrophication and environmental degradation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.E.S.L.; methodology, L.E.S.L. and S.A.T.; validation, M.N.P., J.P.F. and A.C.F.; formal analysis, L.E.S.L. and S.A.T.; investigation, L.E.S.L., P.G.G.A. and S.A.T.; resources, L.E.S.L. and S.A.T.; data curation, L.E.S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.E.S.L.; writing—review and editing, S.A.T. and M.N.P.; visualization, L.E.S.L., S.A.T. and M.N.P.; supervision, J.P.F. and A.C.F.; project administration, L.E.S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
https://dspace.unila.edu.br/items/296b01ce-4f99-43f7-a919-c79cc19736f8 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bacelo, H.; Pintor, M.A.; Santos, S.C.R.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeykens, S.P.; Piol, M.N.; Samudio Legal, L.; Saralegui, A.B.; Vázquez, C. Eutrophication decrease: Phosphate adsorption processes in presence of nitrates. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquemyn, C.; Huysmans, M.; Hunt, D.; Casini, G.; Swennen, R. Multi-scale three-dimensional distribution of fracture- and igneous intrusion-controlled hydrothermal dolomite from digital outcrop model, Latemar platform, Dolomites, northern Italy. AAPG Bull. 2015, 99, 957–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.K.; Eiler, J.M.; Nabelek, P.I. Clumped isotope thermometry of calcite and dolomite in a contact metamorphic environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 197, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirambides, A. Industrial applications of the dolomite from potamia, Thassos Island, N. Aegean Sea, Greece. Mater. Struct. 2001, 34, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, P.; Liska, M. Lea’s Chemistry of Cement and Concrete, 5th ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, B. Chapter 10—Cleaning of Product Gas. In Gasification, Biomass Gasification, Pyrolysis and Torrefaction, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piol, M.N.; Paricoto, M.; Saralegui, A.B.; Basack, S.; Vullo, D.; Boeykens, S.P. Dolomite used in phosphate water treatment: Desorption processes, recovery, reuse and final disposition. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Interempresas; Delgado, M.M.; Álvarez, C.; Martínez, S.; Gabriel, J.L. Fertilización de un Cultivo de Haba con Compost Procedente de Residuos Urbanos: Urbabono. 2020. Available online: https://www.interempresas.net/Grandes-cultivos/Articulos/316251-Fertilizacion-de-un-cultivo-de-haba-con-compost-procedente-de-residuos-urbanos-Urbabono.html (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Koide, S.; Satta, N. Separation Performance of Ion-exchange Membranes for Electrolytes in Drainage Nutrient Solutions subjected to Electrodialysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 87, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, S.; Hagare, D.; Maheshwari, B. Phosphorus recovery from hydroponics waste nutrient solution and its economic potential. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 209, 107710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.C.; Mota, D.C.D.; Oliveira, C.M.; Montalvão, M.L.; Santos, A.F.S.; Lopes, E.F. Propriedades físicas de grãos de feijão carioca (Phaseolus vulgaris). In A Produção do Conhecimento nas Ciências Agrárias e Ambientais; Atena: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J. Propriedades Físicas, Químicas, Nutricionais e Tecnológicas de Feijões (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) de Diferentes Grupos de cor. Master’s Thesis, Coordenação do Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, da Escola de Agronomia, da Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiânia, Brasil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- A.S.T.M.E-11; Standard Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WEF (Water Environment Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Waters and Wastewaters, 23rd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R., Eaton, A., Clesceri, L., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, J.H.; Martínez, O.M.; Fernández, L.M. Remoción de contaminantes en aguas residuales industriales empleando carbón activado de pino pátula. Avances 2013, 10, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- López, O.; González, E.; De Llamas, P.; Molinas, A.; Franco, S.; García, S.; Ríos, E. Estudio de Reconocimiento de Suelos, Capacidad de uso de la Tierra y Propuesta de Ordenamiento Territorial Preliminar de la Región Oriental del Paraguay; Proyecto de Racionalización del uso de la tierra SSERNMA/MAG/Banco Mundial: Asunción, Paraguay, 1995; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, F.C. Manual de Análises Químicas de Solos, Plantas e Fertilizantes, 2nd ed.; Embrapa Informação Tecnológica: Brasilia, Brasil, 2009; p. 627. [Google Scholar]
- Legal, L.E.S.; Trinidad, S.A.; Frigo, J.P.; Furtado, A.C. Reuso da dolomita saturada por nutrientes como corretivo em solos agrícolas. Cad. Pedagog. 2023, 20, 1066–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, D.R. Interpretación del Análisis de Suelo y Recomendaciones de Fertilizantes Para la Caña de Azúcar; Centro De Investigación De La Caña De Azúcar De Colombia: Florida, Colombia, 1993; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.; Silva, M.; Guilherme, L.R. Acidez do Solo e Calagem, 3rd ed.; ANDA: São Paulo, Brazil, 1991; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Casaccia, R. Cultivo de la Habilla; Dirección de Investigación Agraria, Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganaderia: Asunción, Paraguay, 1991; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.M.; Hansen, L.; Hanna, J.A.; Allen, S.J. Kinetics of a reactive dye adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.A.L.; Do Nascimento, R.M.; Paskocimas, C.A.; Castro, R.J.S. Avaliação da adição de dolomita em massa de cerâmica de revestimento de queima vermelha. Cerâmica 2014, 60, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, J.; Molina, E. Acidez y Encalado de los Suelos, 1st ed.; International Plant Nutrition Institute IPNI: Quito, Ecuador, 1999; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, D.; Barreto, S.; Colmán, J.M.; Meza, W.; Recalde, S.; Lezcano, I. Rendimiento de Habilla Negra (Paseolus vulgaris L.) Influenciado por la Aplicación de Fertilizantes Químicos. Cienc. Lat. Rev. Cient. Multidiscip. 2023, 7, 4934–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Veneklaas, E.; Polania, J.; Rao, I.M.; Beebe, S.E.; Merchant, A. Field drought conditions impact yield but not nutritional quality of the seed in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesquita, M.A.M.; Silveira, P.M.; Leandro, W.M.; Flores, R.A.; Maranhão, D.D.C. DRIS Standards for nutritional evaluation of Phaseolus vulgaris in Cerrado, Goiás state, Brazil. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Meneghetti, A.M. Manual de Procedimentos de Amostragem e Análise Química de Plantas, Solo e Fertilizantes; EDUTFPR: Curitiba, Brazil, 2018; p. 252. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral Castro, G.; Costa Crusciol, C. Effects of surface application of dolomitic calcareous and calcium-magnesium silicate on soybean and maize in rotation with green manure in a tropical región. Soil Plant Nutr. 2015, 74, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis Pires, A.; Henrique Monnerat, P.; Marciano, C.R.; Da Rocha Pinho, L.; Daré Zampirolli, P.; Castro Carriello Rosa, R.; Almeida Muniz, R. Efeito da adubação alternativa do maracujazeiro amarelo nas características químicas e físicas do solo. Acta Sci. Agron. 2009, 31, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crusciol, C.A.C.; Garcia, R.A.; Castro, G.S.A.; Rosolem, C.A. Nitrate role in basic cation leaching under no-till. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2011, 35, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, V.A. Física do Solo, 3rd ed.; Universidade de Passo Fundo: São José, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).