Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matters and Correlations Among Them in Different Functional Areas of a Typical Mining City in Northwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Source Identification Methods
2.4.1. Positive Matrix Factorization
2.4.2. Air Mass Dispersion Analysis
2.5. Risk Assessment
3. Results
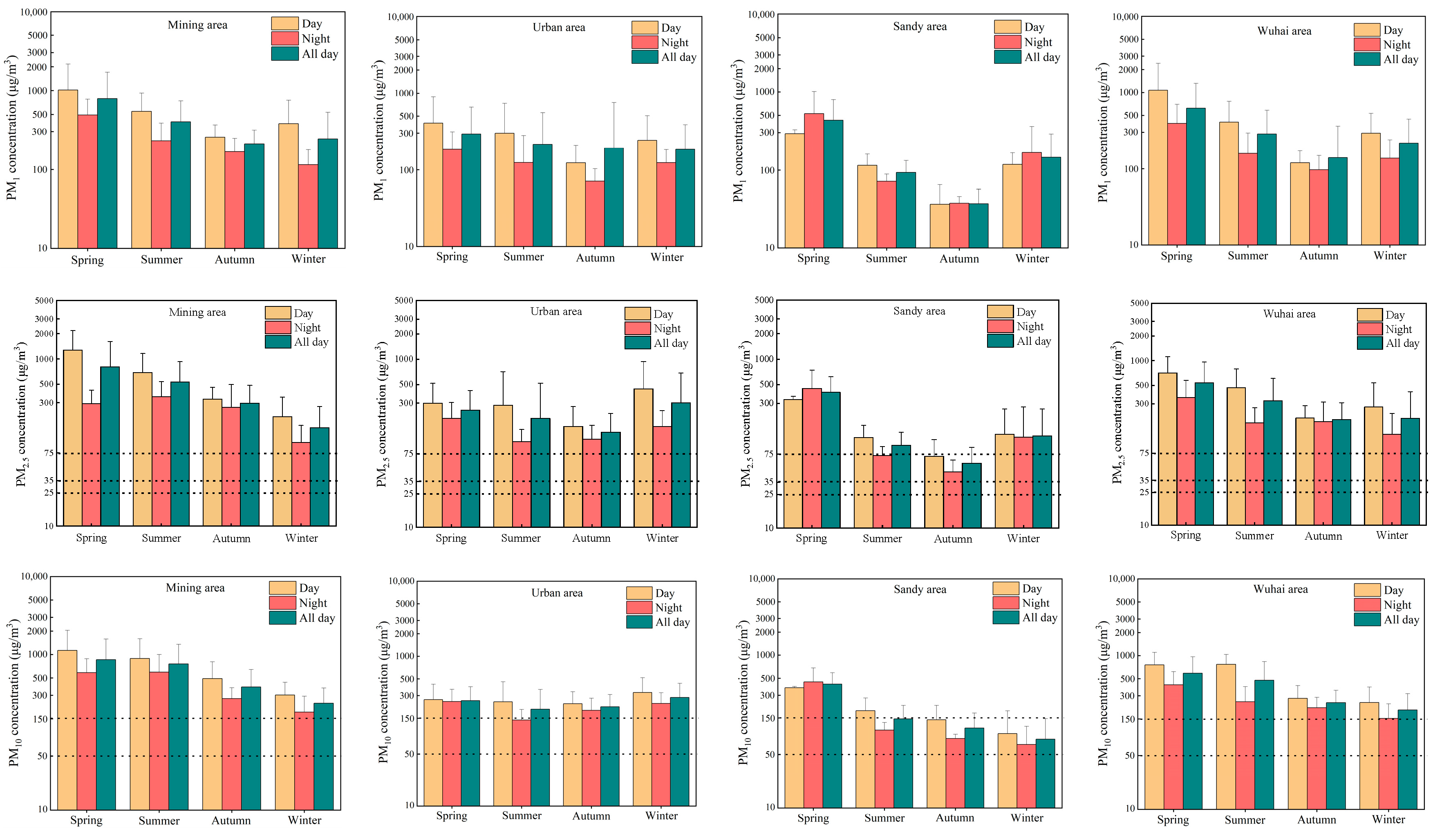
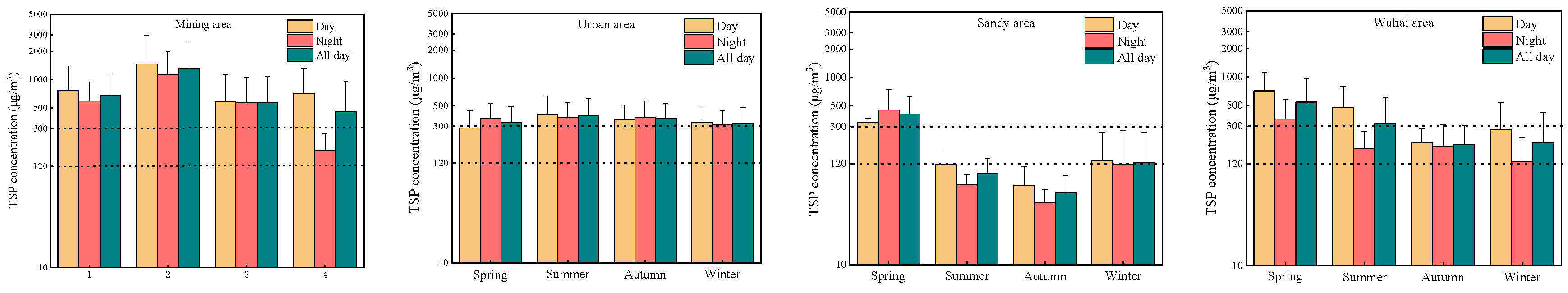
3.1. Distribution of PM Concentrations in Different Functional Areas
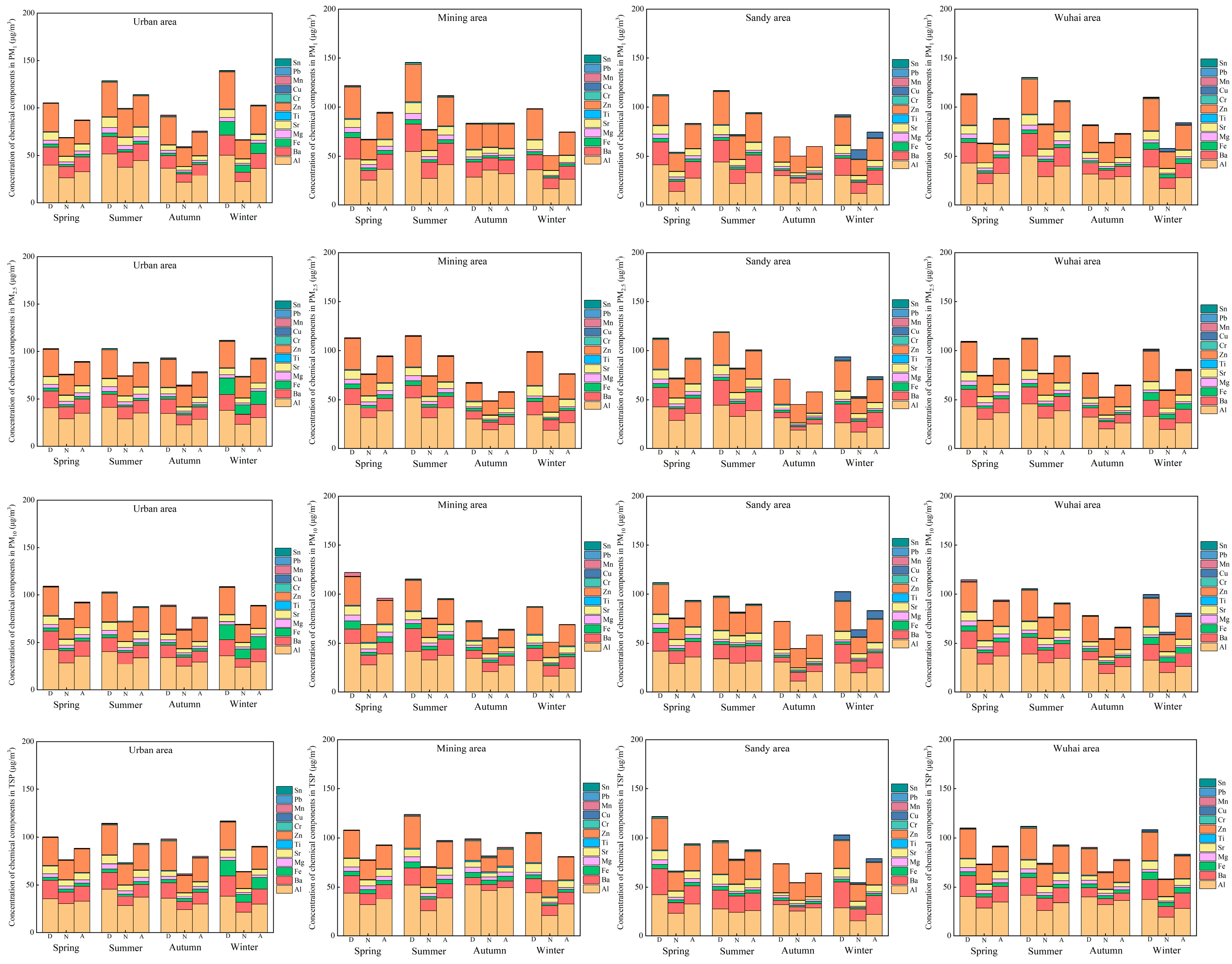
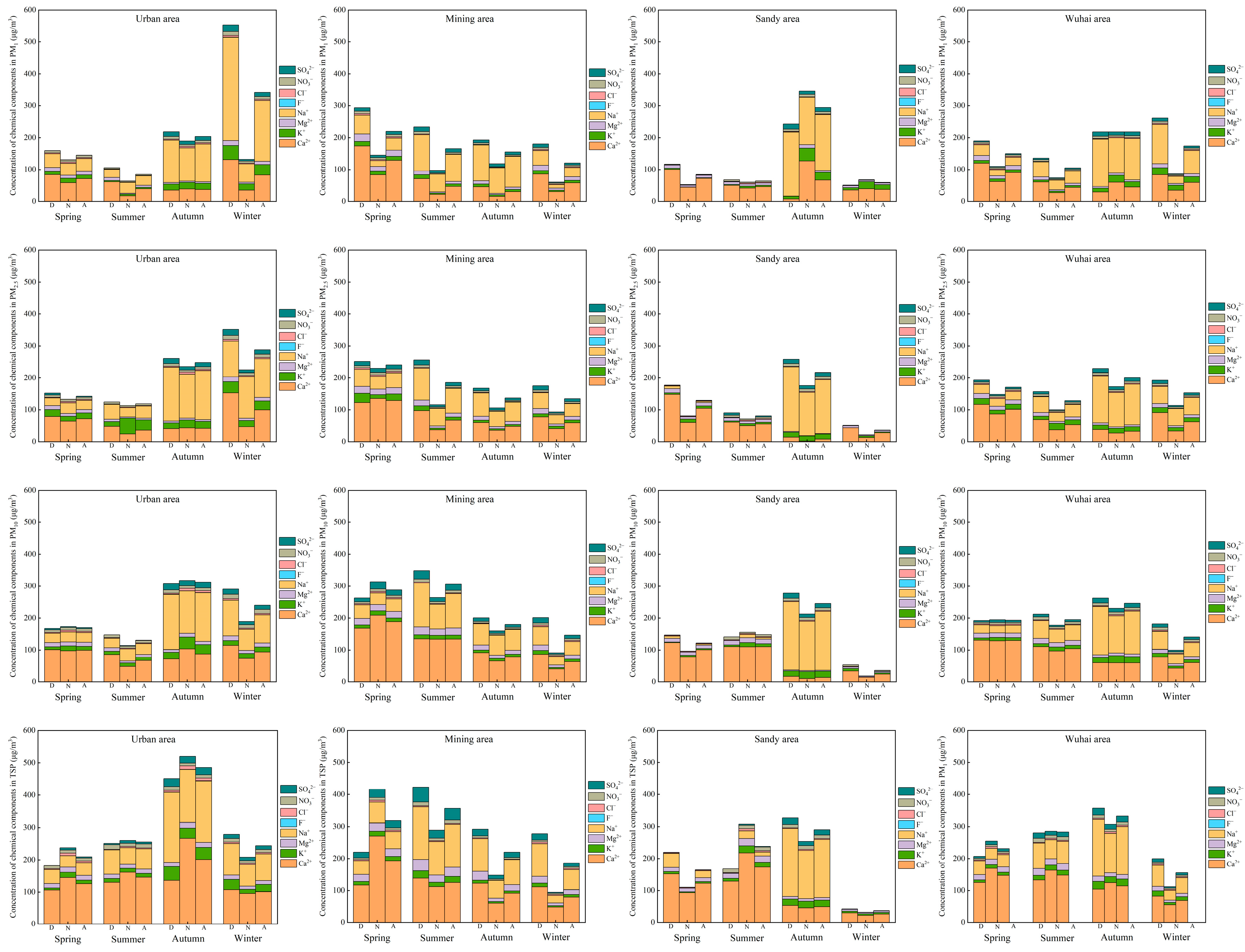
3.2. Distribution of the Chemical Composition of PM in Different Functional Areas
3.2.1. Elemental Distribution
3.2.2. Distribution of Water-Soluble Ions
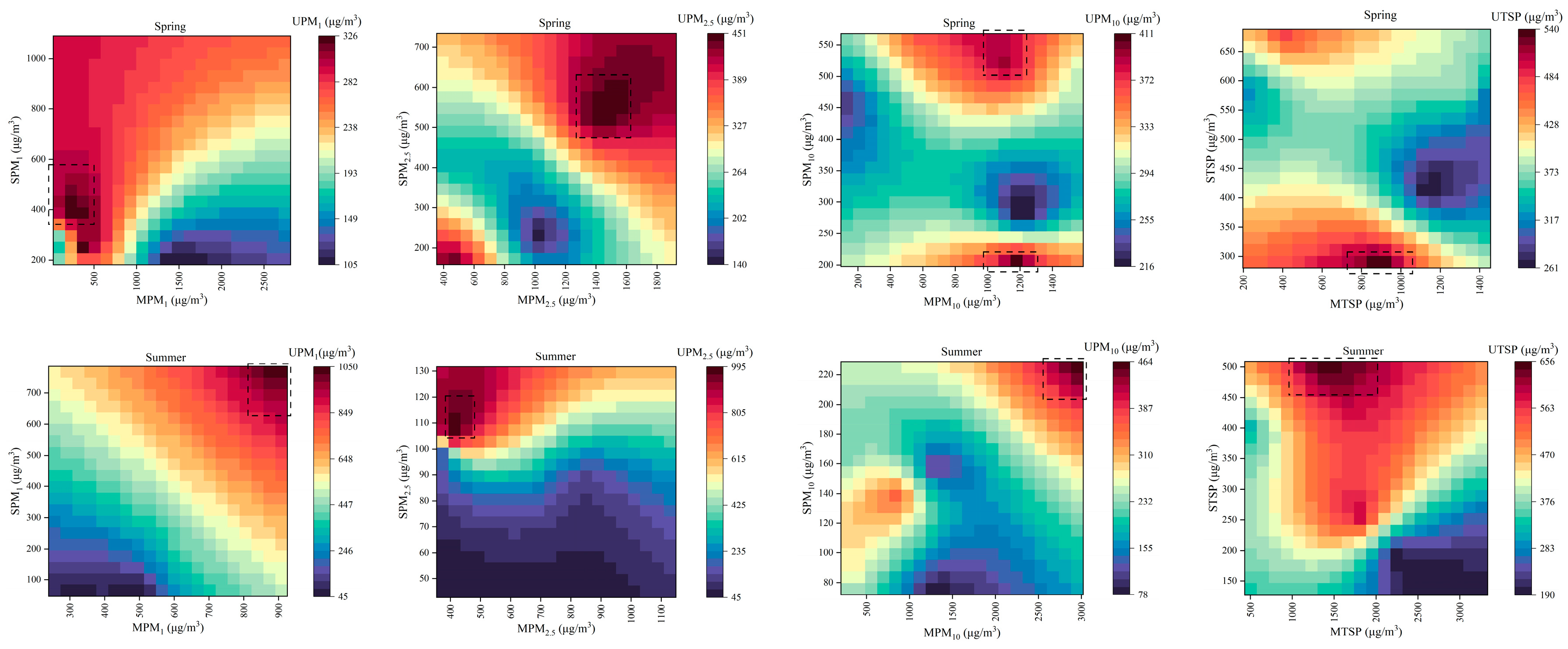
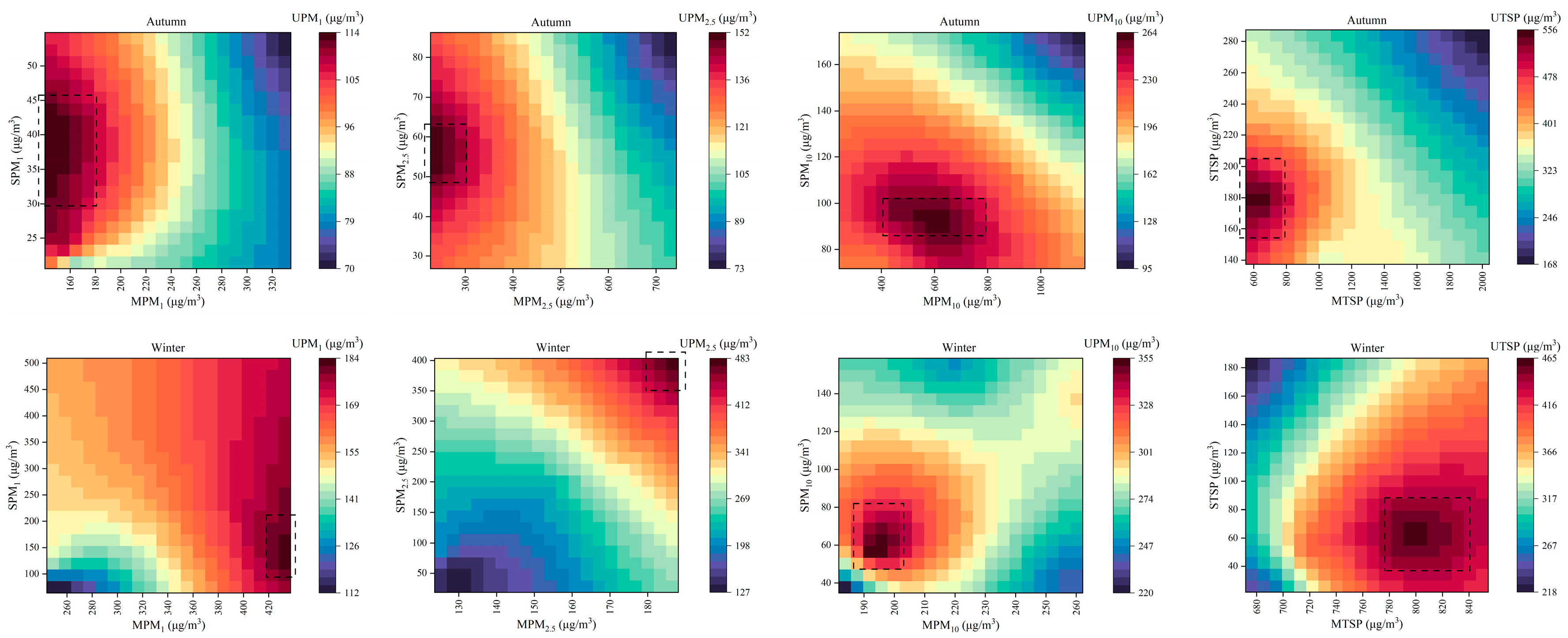
3.3. Spatiotemporal Correlation and Effect of PM Concentrations
3.3.1. Correlation Among PM Concentrations in Different Functional Areas
3.3.2. Correlation Between PM Concentrations During the Day and at Night
3.3.3. Effects of PM Concentrations in Different Functional Areas
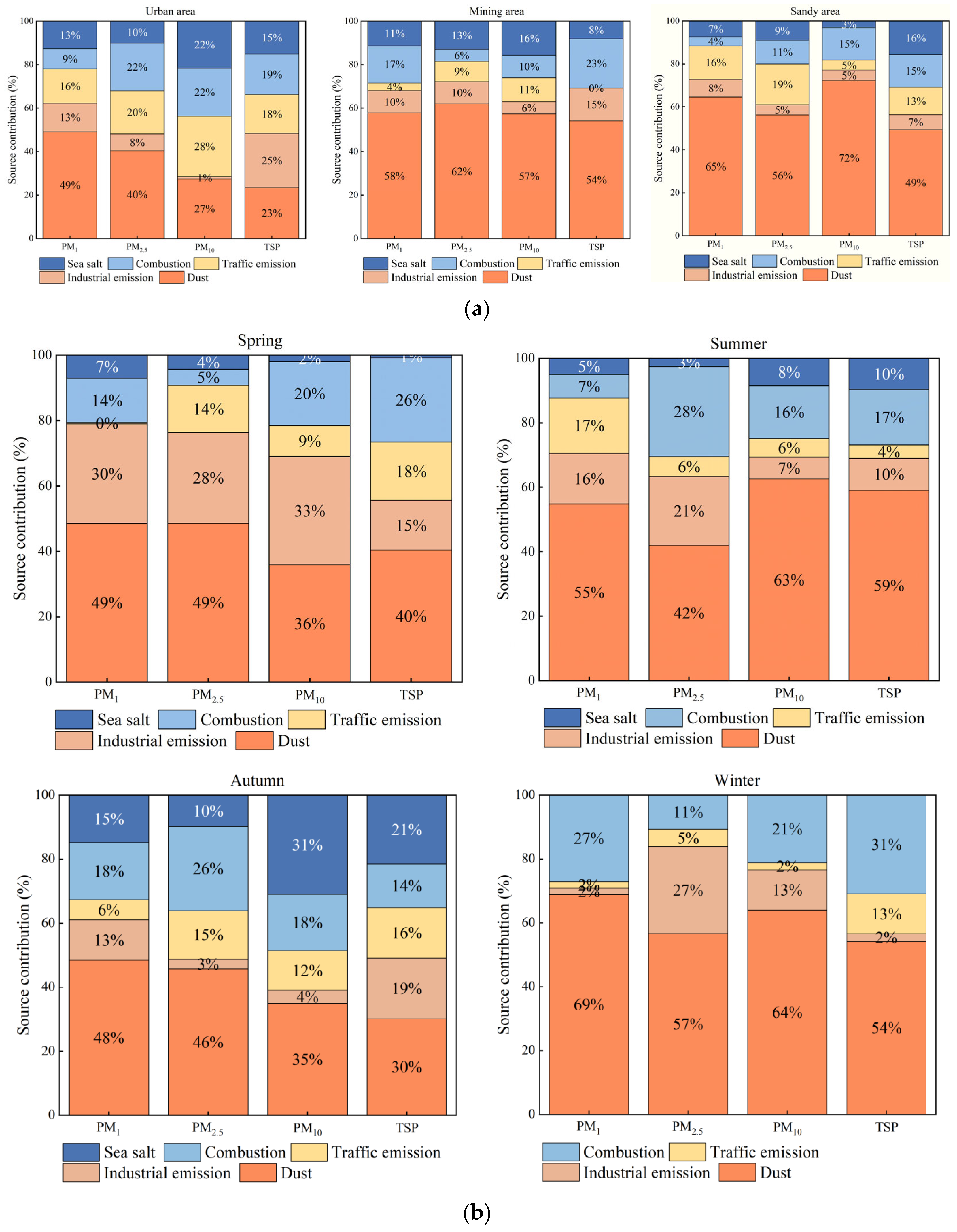
3.4. Analysis of Pollutant Sources
3.4.1. Source Apportionment Using PMF
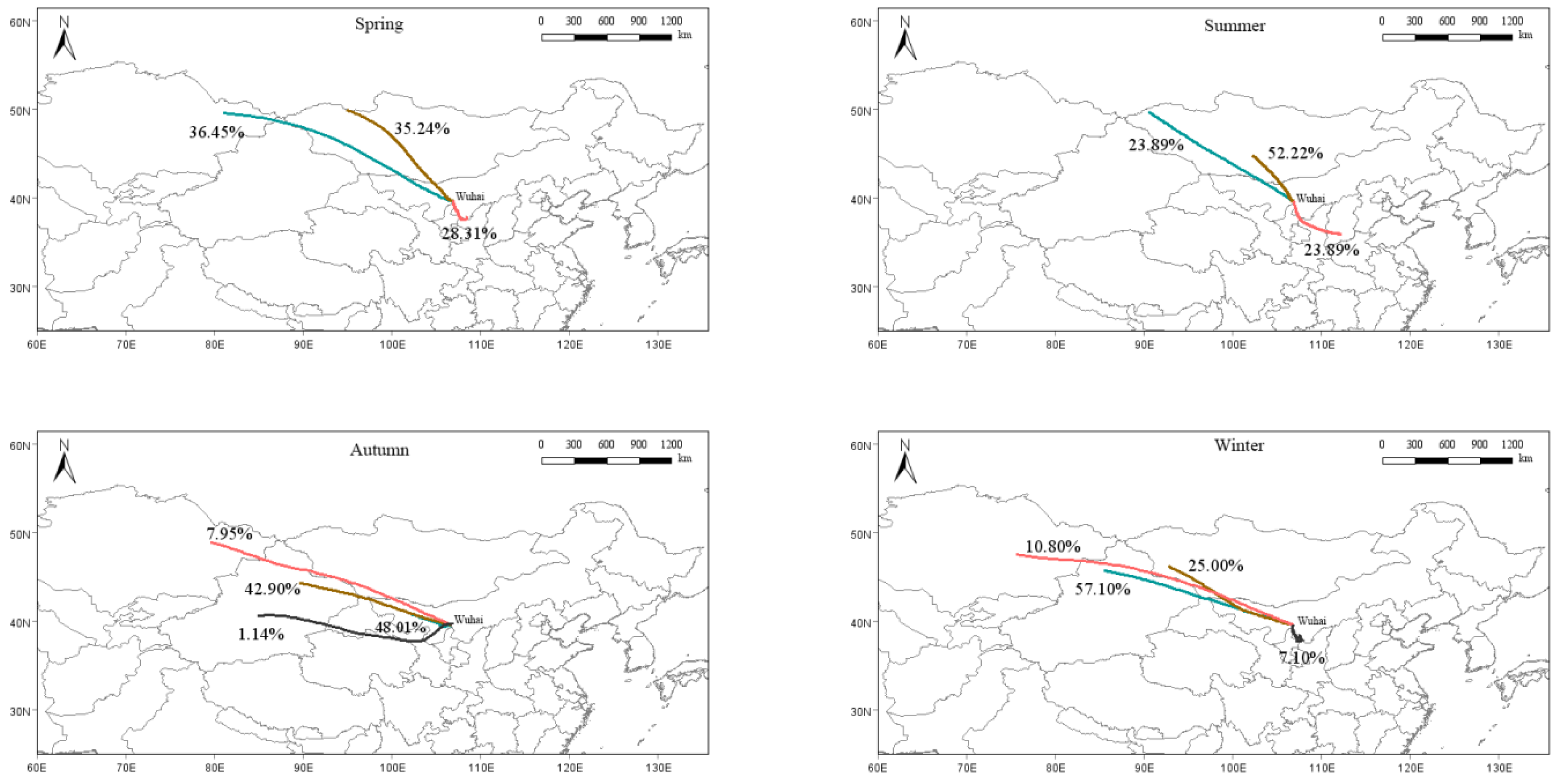
3.4.2. Backward Trajectories Cluster
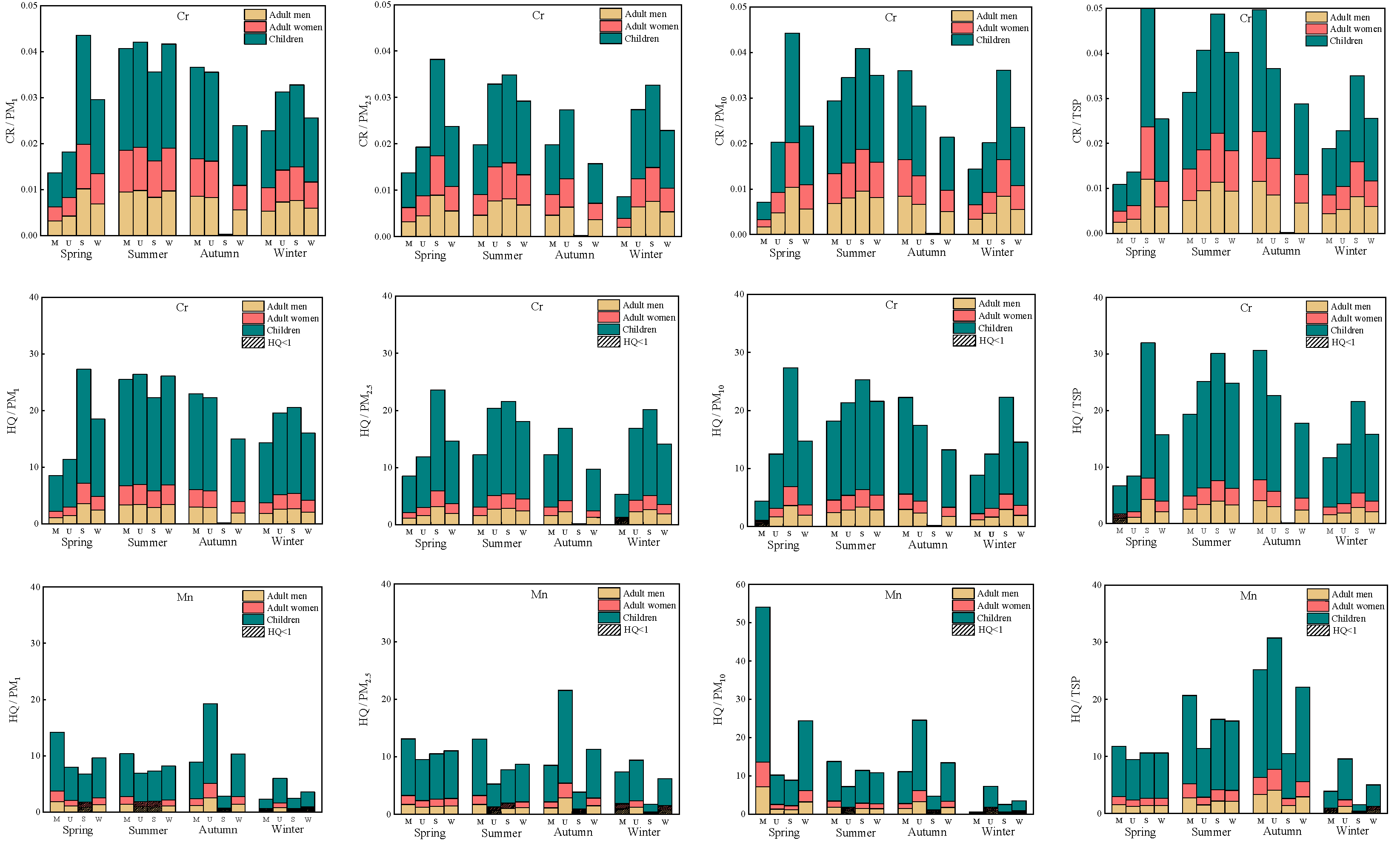
3.5. Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric PM and Its Components
4.2. Spatiotemporal Correlation of Atmospheric Pollutants
4.3. Sources and Effects of Atmospheric Pollutants
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.C.; Wu, J.J.; Qiang, L.; Wang, F.L.; Cheng, Y.F. Sediment instability caused by gas production from hydrate-bearing sediment in northern south China sea by horizontal wellbore: Sensitivity analysis. Nat. Resour. Res. 2025, 34, 1667–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Agrawal, V.; McGrath, S.; Hakala, J.A.; Lopano, C.; Goodman, A. Geochemical controls on CO2 interactions with deep subsurface shales: Implications for geologic carbon sequestration. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1278–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishtiaq, M.; Jehan, N.; Khan, S.A.; Muhammad, S.; Saddique, U.; Iftikhar, B.; Zahidullah. Potential harmful elements in coal dust and human health risk assessment near the mining areas in Cherat, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14666–14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshukov, T.; Legoshchin, K.; Yakovenko, O.; Bach, S.; Russakov, D.; Dimakova, D.; Vdovina, E.; Baranova, E.; Avdeev, K.; Kolpina, E.; et al. Fractional composition and toxicity coal-rock of PM10-PM0.1 dust near an opencast coal mining area and coal-fired power station. Sustainability 2023, 14, 16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Verdin, A.; Escande, F.; Saint-Georges, F.; Cazier, F.; Mulliez, P.; Courcot, D.; Shirali, P.; Gosset, P.; Garçon, G. In vitro short-term exposure to air pollution PM2.5-0.3 induced cell cycle alterations and genetic instability in a human lung cell coculture mode. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Huang, K.; Xie, M.J.; Deng, C.R.; Zou, Z.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, Y.L. First long-term and near real-time measurement of trace elements in China’s urban atmosphere: Temporal variability, source apportionment and precipitation effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11793–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ji, D.S.; He, J.; Kong, S.F.; Wang, Y.S. In situ continuous observation of hourly elements in PM2.5 in urban Beijing, China: Occurrence levels, temporal variation, potential source regions and health risks. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaymon, I.D.; Mei, X.D.; Yang, S.J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Schauer, J.J.; Zhang, Y.X. PM2.5 in Abuja, Nigeria: Chemical characterization, source apportionment, temporal variations, transport pathways and the health risks assessment. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.D. Land use and transportation interaction implications on public health and quality of life. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2000, 20, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.D.; Sallis, J.F.; Conway, T.L.; Chapman, J.E.; Saelens, B.E.; Bachman, W. Many pathways from land use to health: Associations between neighborhood walkability and active transportation, body mass index, and air quality. J. Am. Plann. Assoc. 2006, 72, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.E.; Yoon, D.K.; Bae, H.J. Evaluating the effect of compact urban form on air quality in Korea. Environ. Plan. B-Urban 2019, 46, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.P.; Patra, A.K.; Kolluru, S.S.R. Spatial and temporal variation of respirable particles around a surface coal mine in India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Cheng, R.; Jing, M.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yan, J.; Lin, C.S.; Wu, Y.F.; et al. Source-specific health risk analysis on particulate trace elements: Coal combustion and traffic emission as major contributors in wintertime Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10967–10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Qiao, B.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Yang, F.M.; Jiang, X. Characteristics and sources of trace elements in PM2.5 in two megacities in Sichuan basin of southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.F.; Luo, B.; Simayi, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; He, J.M.; Xie, S.D. Spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 elemental composition over China and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, W.Z. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 in China based on ground-level observations for 190 cities. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, T.L.; Xu, X.D.; Han, H.; Wang, H.L.; Shu, Z.Z. Atmospheric transport drives regional interactions of ozone pollution in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 830, 154634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Ge, X.L.; Sonya, C.; Ye, J.H.; Lei, Y.L.; Chen, M.D.; Zhang, Q. Influence of regional emission controls on the chemical composition, sources, and size distributions of submicron aerosols: Insights from the 2014 Nanjing Youth Olympic Games. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 807, 150869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 777-2015; Ambient Air and Waste Gas from Stationary Sources Emission-Determination of Metal Elements in Ambient Particle Matter-Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Chinese Research Academy Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2015.
- HJ 800-2016; Ambient Air-Determination of the Water Soluble Cations (Li+, Na+, NH4+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+) from Atmospheric Particlesion Chromatography. Chinese Research Academy Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 799-2016; Ambient Air-Determination of the Water Soluble Anions (F−, Cl−, Br−, NO2−, NO3−, PO43−, SO32−, SO42−) from Atmospheric Particles Ion Chromatography. Chinese Research Academy Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Li, Q.Q.; Gong, D.C.; Wang, H.; Wang Yu Han, S.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, S.; Yu, P.F.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, B.G. Rapid increase in atmospheric glyoxal and methylglyoxal concentrations in Lhasa, Tibetan Plateau: Potential sources and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shen, Z.J.; Zhang, P.P.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.L. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils around the gangue heap of coal mine based on APCS-MLR and PMF receptor model. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2192–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.S.; Zhao, T.N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wu, H.X.; Hu, P. Source apportionment and health risk due to PM10 and TSP at the surface workings of an underground coal mine in the arid desert region of Northwestern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 803, 149901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.N.; Wang, R.S.; Ai, X.F.; Wang, M.W.; Sun, T.; Jiang, Q.N. Coupling effects of sandstorm and dust from coal bases on the atmospheric environment of Northwest China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q. MeteoInfo: GIS software for meteorological data visualization and analysis. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 21, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ashbaugh, L. The impact of trajectory starting heights on the MURA trajectory source apportionment (TSA) method. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7022–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, A.; Symons, J.M.; Kleissl, J.; Wang, L.; Parlange, M.B.; Ondov, J.; Breysse, P.N.; Diette, G.B.; Eggleston, P.A.; Buckley, T.J. Impact of the 2002 Canadian forest fires on particulate matter air quality in Baltimore City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). 2005. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/69477/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_chi.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. Chinese Research Academy Environmental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Luo, H.; Zhou, W.; Jiskani, I.M.; Wang, Z. Analyzing characteristics of particulate matter pollution in open-pit coal mines: Implications for green mining. Energies 2021, 14, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Jiskani, I.M.; Luo, H.; Ao, Z.; Mvula, E.M. Annual dust pollution characteristics and its prevention and control for environmental protection in surface mines. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 825, 153949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J. Study on Dust Distribution and Diffusion Mechanism in Open Pit Coal Mine. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.F.; Li, W.J. Emission characteristics and individual particle analysis of metals in fine particles emitted from residential coal burning. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.C.; Hsieh, L.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Tsai, Y.I. Characterization of PM2.5 fugitive metal in the workplaces and the surrounding environment of a secondary aluminum smelter. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6884–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L. Characteristics and Source Analysis of Dust Pollution in Jinan City. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, F.; Viana, M.; Richard, A.; Furger, M.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Nava, S.; Lucarelli, F.; Bukowiecki, N.; Alastuey, A.; Reche, C.; et al. Size and time-resolved roadside enrichment of atmospheric particulate pollutants. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2917–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoratos, T.; Martini, G. Brake wear particle emissions: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2491–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altıntas, Y.; Kaygısız, Y.; Öztürk, E.; Aksöz, S.; Keşlioğlu, K.; Maraşlı, N. The measurements of electrical and thermal conductivity variations with temperature and phonon component of the thermal conductivity in Sn-Cd-Sb, Sn-In-Cu, Sn-Ag-Bi and Sn-Bi-Zn alloys. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Z.; Gaga, E.O.; Taşpınar, F.; Arı, A.; Pekey, B.; Pekey, H.; Dögeroglu, T.; Üzmez, Ö.Ö. Atmospheric ambient trace element concentrations of PM10 at urban and sub-urban sites: Source apportionment and health risk estimation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledoux, F.; Kfoury, A.; Delmaire, G.; Roussel, G.; Zein, A.E.; Courcot, D. Contributions of local and regional anthropogenic sources of metals in PM2.5 at an urban site in northern France. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, H.L. Size distributions and source apportionment of soluble ions in aerosol in Nanjing. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yan, C.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Ma, J.J.; Li, W.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, Y. PM2.5-bound elements in Hebei province, China: Pollution levels, source apportionment and health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, Q.; Su, F.C.; Wang, Q.; Yu, X.; Kang, P.R.; Zhang, R.Q.; Tang, X.Y. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 between heavily polluted days and other days in Zhengzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 66, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.X.; Huang, T.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Mo, J.Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.X.; Li, J.X.; Lian, L.L.; Ma, J.M. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM1 and PM2.5 in a national coal chemical industrial base of the golden energy triangle, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H.; Duan, L.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.L.; Chai, F.H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yun, Y.R. Chemical composition and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Lanzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, R.J.; Chen, W.D.; Han, Y.M.; Xu, H.M.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Long-term trends in visibility and impacts of aerosol composition on visibility impairment in Baoji, China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 149, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawichai, S.; Bootdee, S.; Sillapapiromsuk, S.; Janta, R. Epidemiological study on health risk assessment of exposure to PM2.5-bound toxic metals in the industrial metropolitan of Rayong, Thailand. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Bajar, S.; Gupta, S.; Vijayan, N.; Sharma, S.K. Evaluating health risks of PM2.5-bound heavy elements in Faridabad, Haryana (India): An industrial perspective. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Shen, Y.; Xu, B.; Shen, J.; Jin, L.; Yao, L.; Kuang, B.Y.; Xu, Z.N.; Pei, X.Y.; Tang, Q.; et al. Characteristics, sources, and health risks of PM2.5-bound trace metals in northern Zhejiang Province: The effects of meteorological variables based on machine learning. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wan, M.; Pang, X.L.; Yao, L.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, W.J.; Zhu, J.N.; Zhang, C.W. Chemical characterization, source identifcation, and health risk assessment of atmospheric fine particulate matter in winter in Hangzhou Bay. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinara, P.; Chuersuwan, N.; Pongkiatkul, P.; Chanpiwat, P.; Jiamjaras-rangsi, W. Quantifying the noncarcinogenic and carcinogenic risks resulting from the inhalation of PM2.5-bound metals: A multicity analysis and implications for public health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Song, W.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Fan, M.Y. Specific sources of health risks caused by size-resolved PM-bound metals in a typical coal-burning city of Northern China during the winter haze event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of heavy metals in size-fractionated atmospheric particulate matters and associated health risk assessment based on the respiratory deposition. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penttinen, P.; Timonen, K.L.; Tiittanen, P.; Mirme, A.; Ruuskanen, J.; Pekkanen, J. Ultrafine particles in urban air and respiratory health among adult asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Ma, C.; Zhan, S. Modeling particulate matter emissions during mineral loading process under weak wind simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, C.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Zhang, R.; Chi, K.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Lin, S.H.; Hsu, S.C. Characteristics of trace metals in traffic-derived particles in Hsuehshan Tunnel, Taiwan: Size distribution, potential source, and fingerprinting metal ratio. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4117–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillon, M.C.; Monfort, E.; Escrig, A.; Celades, I.; Guerra, L.; Busani, G.; Sterni, A.; Querol, X. Air quality comparison between two European ceramic tile clusters. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, S.; Han, B.; Bai, Z.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Receptor modeling of PM2.5, PM10 and TSP in different seasons and long-range transport analysis at a coastal site of Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4681–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Sun, Y.; An, Z. The variation of characteristics and formation mechanisms of aerosols in dust, haze, and clear days in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6579–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, N.J.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.Y.; Xiao, H.W. Chemical characterization and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 from a plateau city of Kunming at different seasons. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.P.; Zhang, F.W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Characterization of water-soluble inorganic ions in size-segregated aerosols in coastal city, Xiamen. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcculloch, A.; Aucott, M.L.; Benkovitz, C.M.; Graedel, T.E.; Kleiman, G.; Midgley, P.M.; Li, Y.F. Global emissions of hydrogen chloride and chloromethane from coal combustion, incineration and industrial activities: Reactive Chlor ine Emissions Inventory. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliani, E.; Nicola, M.; Jonathan, G.; Tara, K.B.; Zoe, K.S.; Iain, J.B. Measurement of diesel combustion-related air pollution downwind of an experimental unconventional natural gas operations site. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 189, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.D.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Jin, M.J.; Han, S.J.; Zhao, J.S.; Zhang, R.Q.; Yan, Q.S. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological and health risk assessment of atmospheric PM2.5 in a living area of Zhengzhou City. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4774–4782. [Google Scholar]
- DB11/T 656-2009; Environmental Site Assessment Guideline. Beijing Municipal Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision: Beijing, China, 2009.
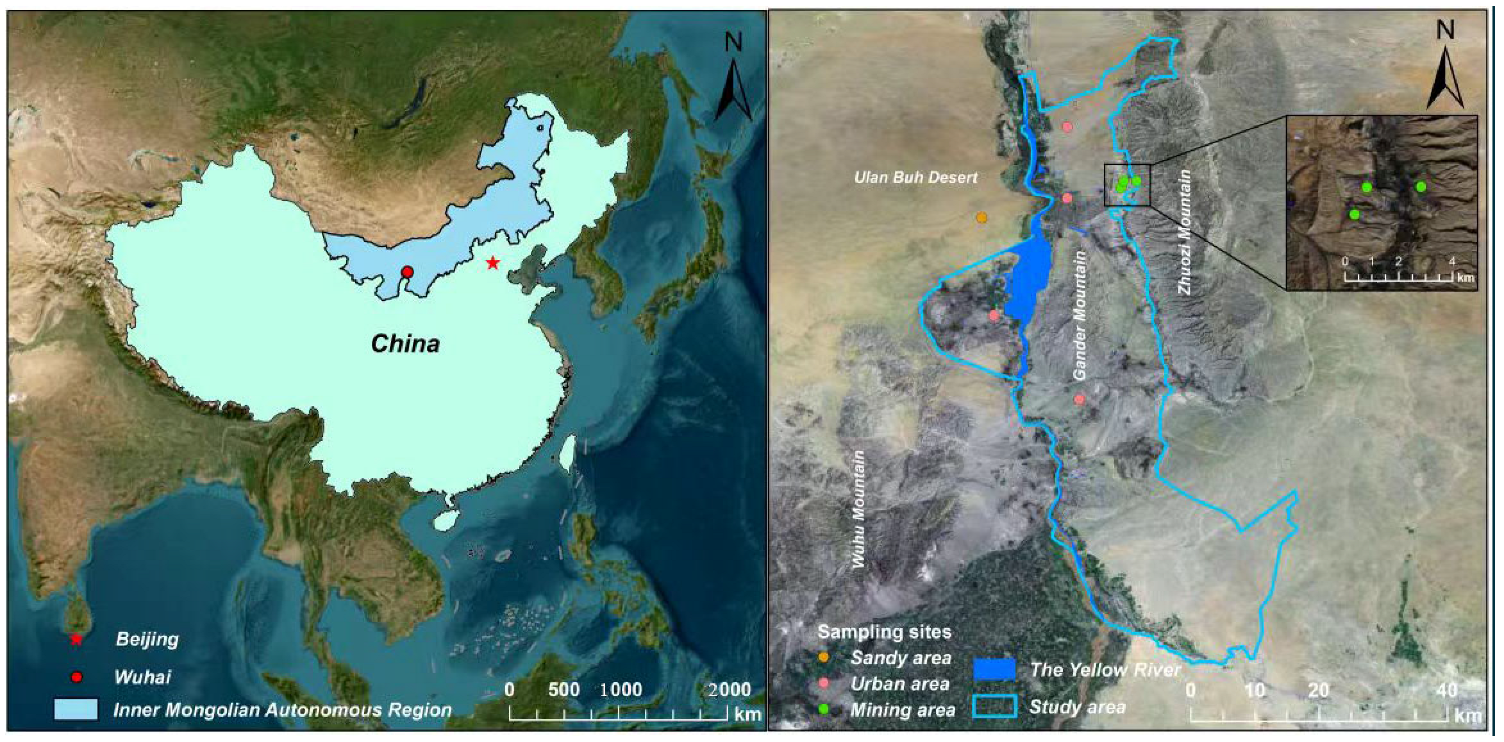
| Sampling Points | Longitude | Latitude | Production Activities | Pavement Condition | Distance to Mining Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mining area | 106.91 | 39.71 | Mining activities such as blasting, excavation, loading and unloading, transportation, etc. | Gravel–sand–dirt–coal–dust pavement | |
| 106.89 | 39.71 | ||||
| 106.89 | 39.70 | ||||
| Urban area | 106.81 | 39.69 | Predominantly human residential activity with high traffic volume. | Concrete hardened pavement | 6.95 km |
| 106.71 | 39.52 | 25.18 km | |||
| 106.83 | 39.41 | 32.69 km | |||
| 106.81 | 39.79 | 12.13 km | |||
| Sandy area | 106.69 | 39.66 | Sparse residential population and low traffic volume. | Concrete hardened pavement | 17.7 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, T.; Gao, J.; Zheng, C.; Wang, M. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matters and Correlations Among Them in Different Functional Areas of a Typical Mining City in Northwestern China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135945
Liu Y, Wang R, Zhao T, Gao J, Zheng C, Wang M. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matters and Correlations Among Them in Different Functional Areas of a Typical Mining City in Northwestern China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135945
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yun, Ruoshui Wang, Tingning Zhao, Jun Gao, Chenghao Zheng, and Mengwei Wang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matters and Correlations Among Them in Different Functional Areas of a Typical Mining City in Northwestern China" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135945
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, R., Zhao, T., Gao, J., Zheng, C., & Wang, M. (2025). Spatiotemporal Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matters and Correlations Among Them in Different Functional Areas of a Typical Mining City in Northwestern China. Sustainability, 17(13), 5945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135945





