Dynamic Evaluation of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Driver Configurational Identification in China: A Sustainable Forestry Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Super-Efficient SBM Model
2.2. Malmquist–Luenberger Index
2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
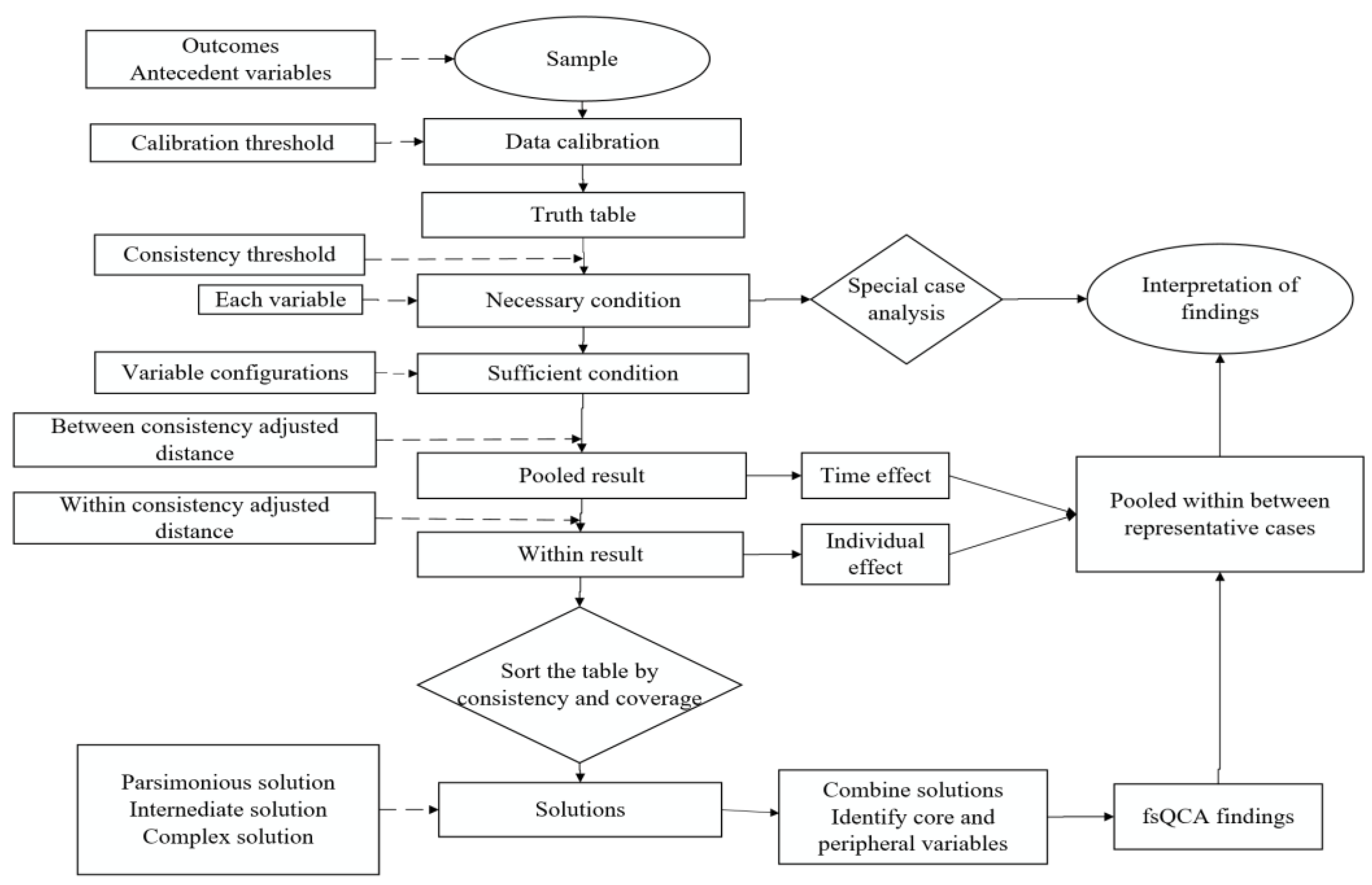
2.4. Dynamic fsQCA
3. Indicators and Data
3.1. Indicator Selection
3.1.1. Evaluation Indicators Selection of FCSE
Input Indicators
Output Indicators
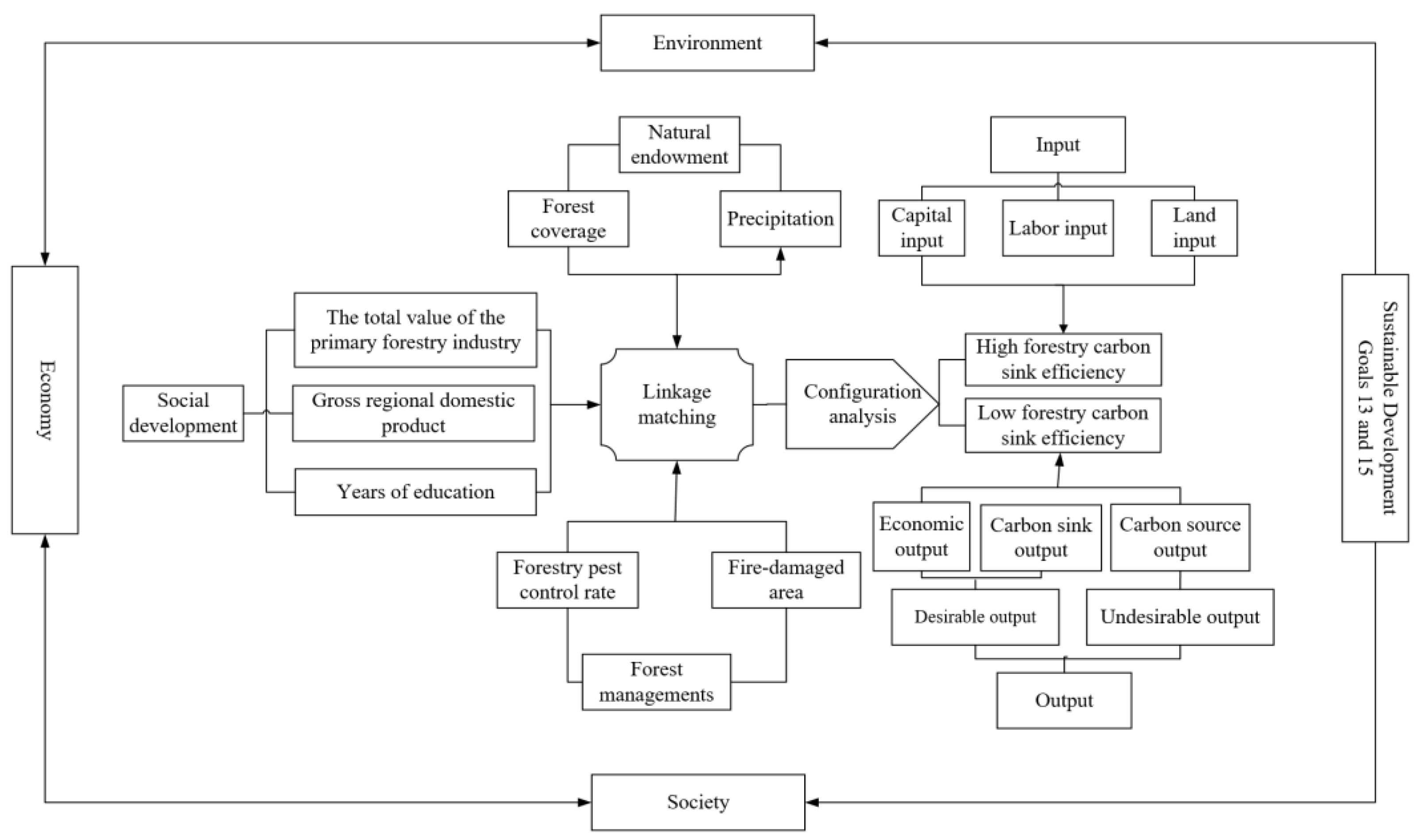
3.2. Influencing Factors and Theoretical Analysis of FCSE
- (1)
- Natural endowment
- (2)
- Social development
- (3)
- Forest management
3.3. Data Sources
3.4. Data Calibration
4. Results
4.1. Efficiency Evaluation for Forest Carbon Sinks in China
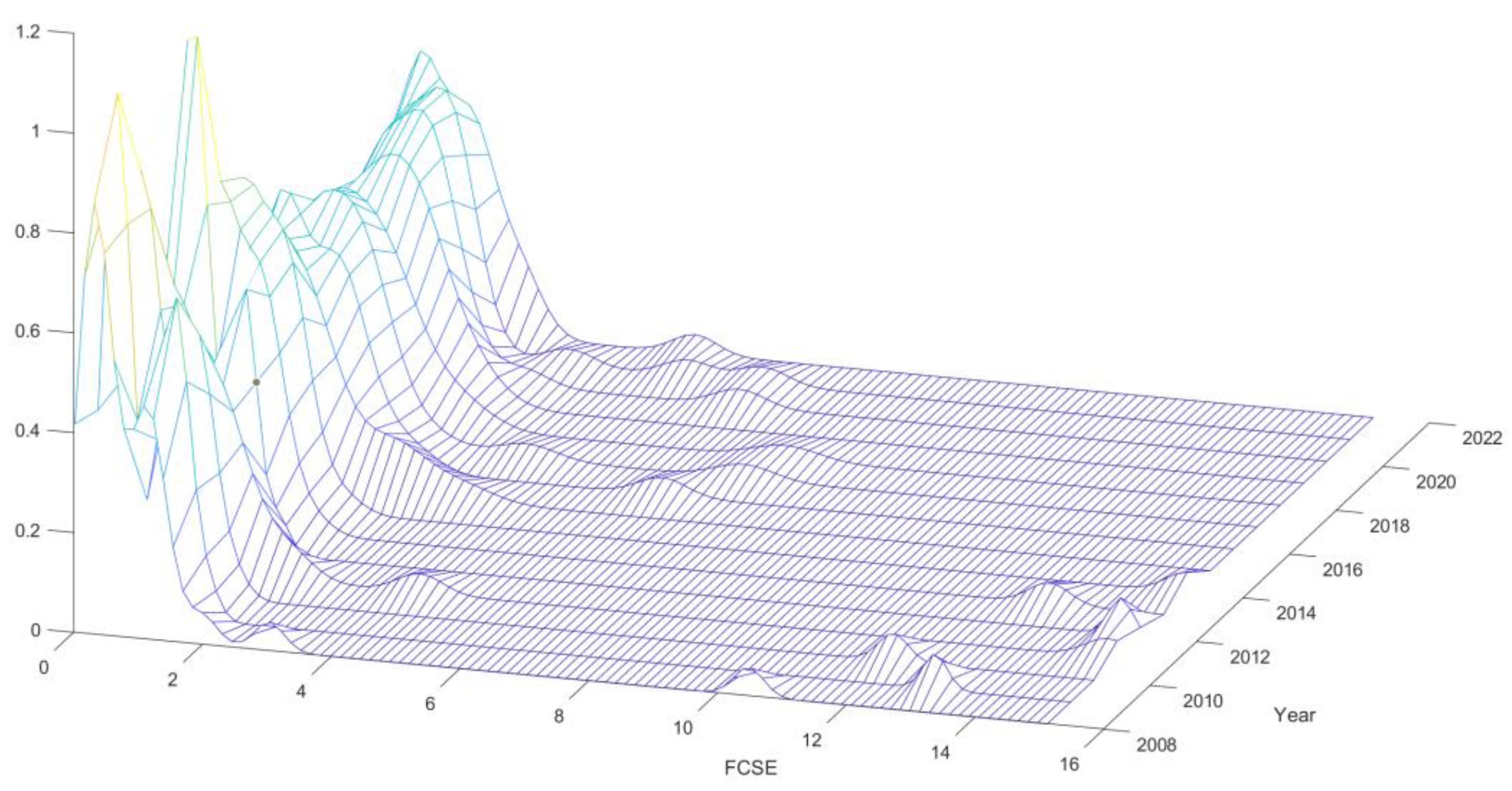
4.1.1. Analysis of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency in China
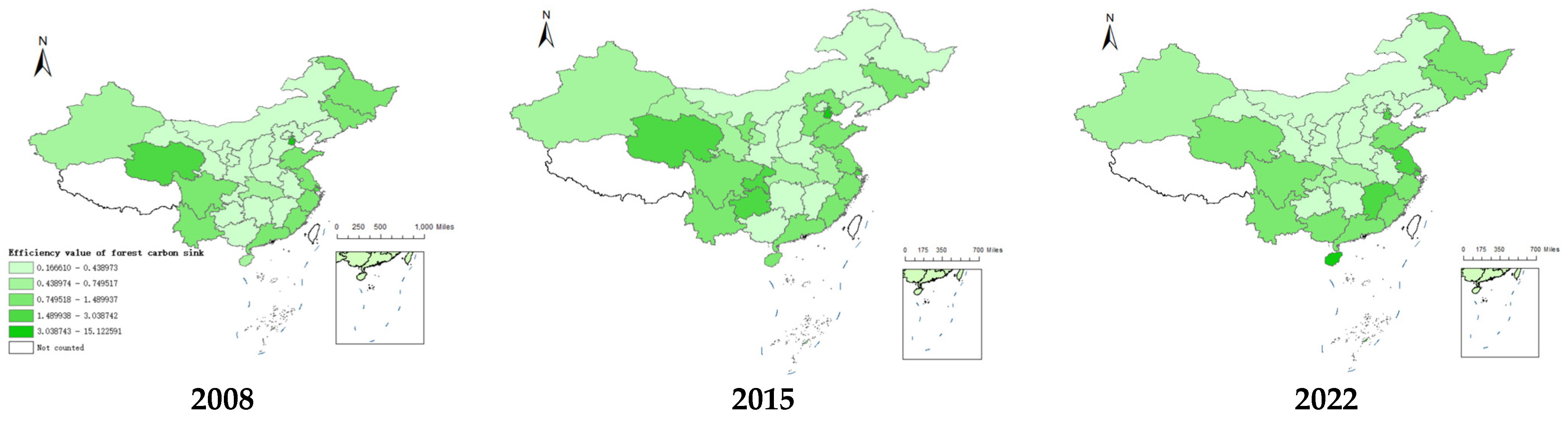
4.1.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency
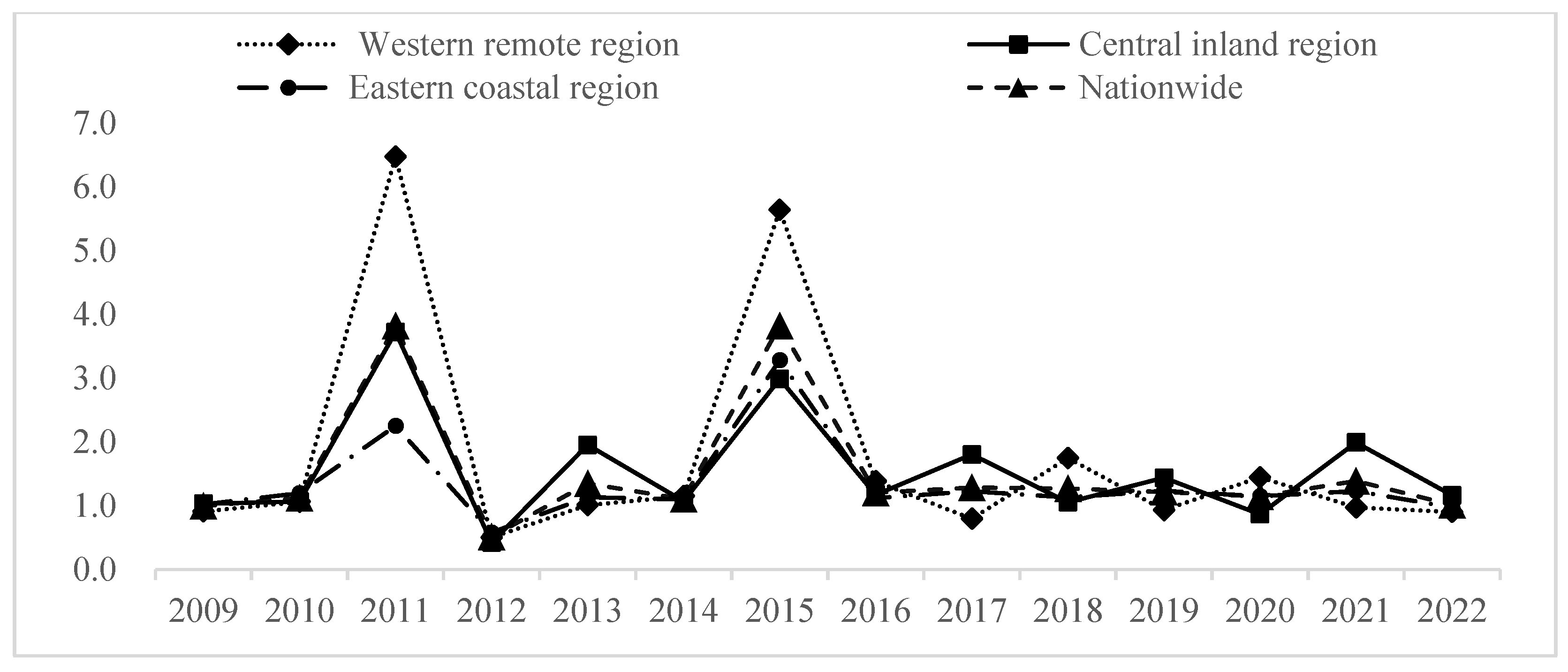
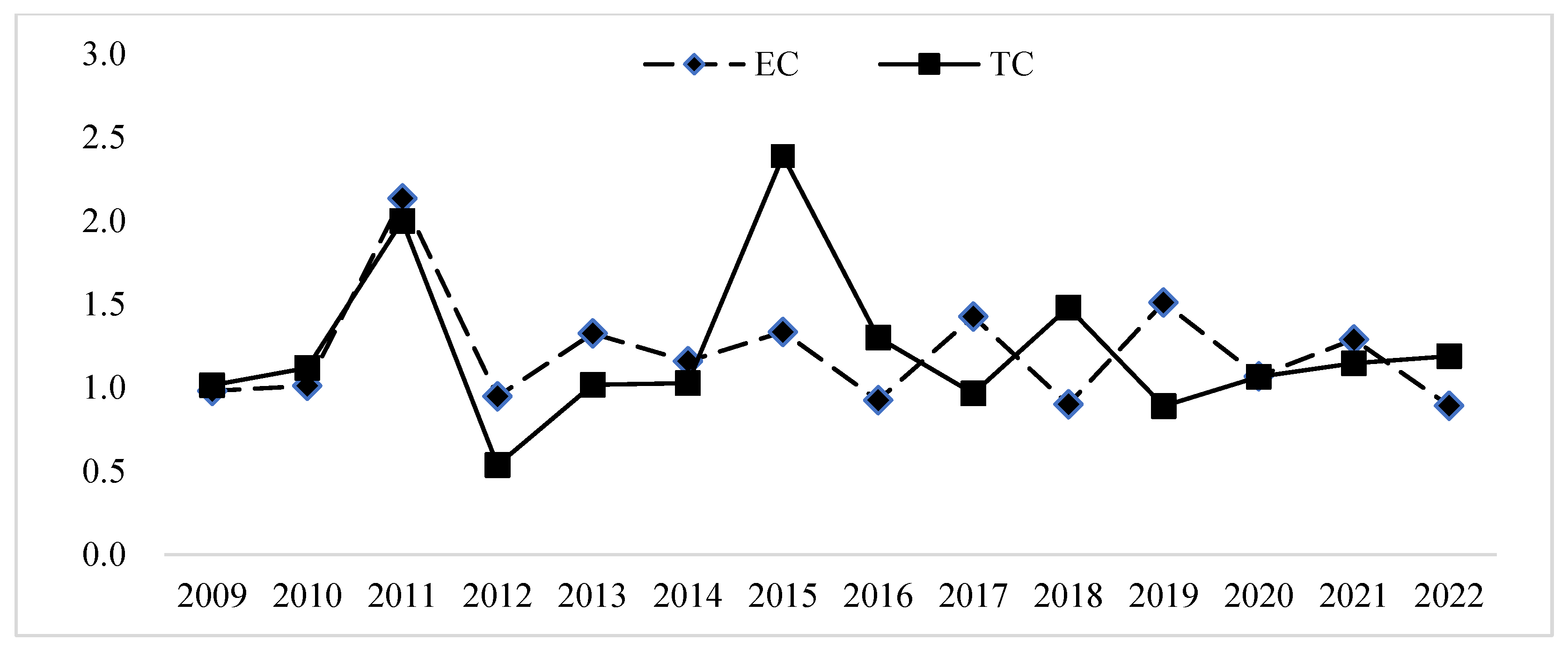
4.1.3. Decomposition of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency Factors
4.1.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Test of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency
4.2. Analysis of Driving Factors of China’s Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency
4.2.1. Necessity Analysis
4.2.2. Configuration Analysis
4.2.3. Pooled Results
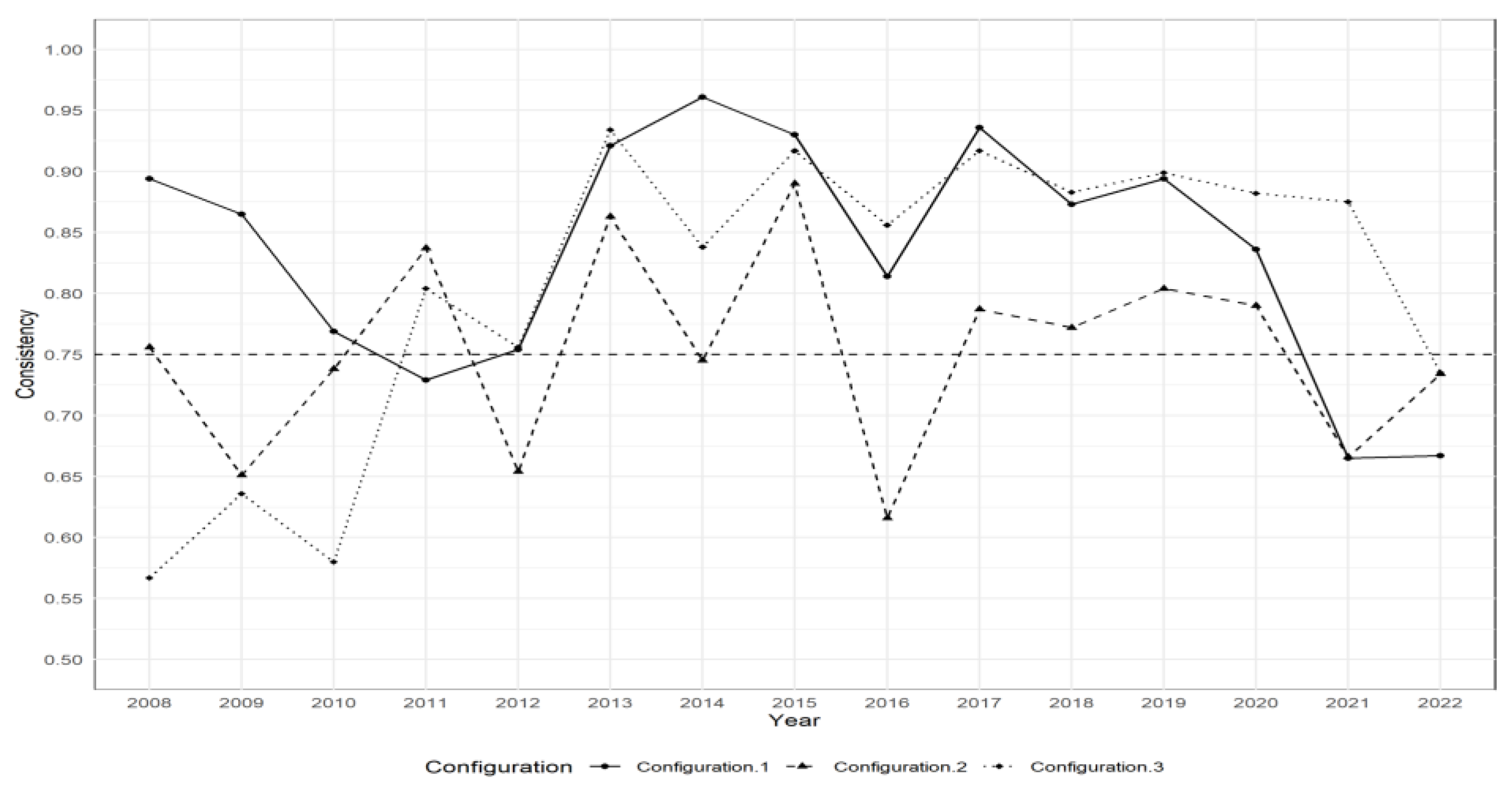
4.2.4. Between Result
4.2.5. Within Results
4.2.6. Robustness Test
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Mechanism Explanation of China’s FCSE
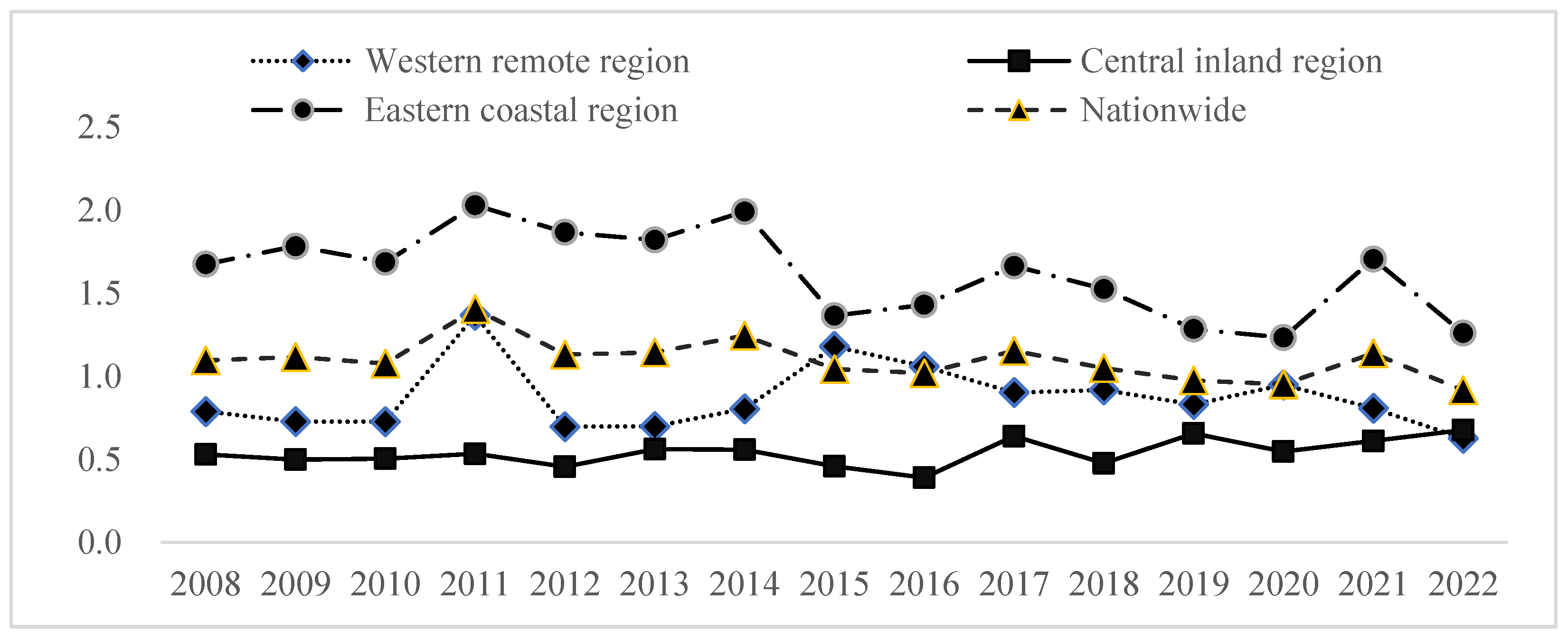
5.1.1. Efficiency Level and Spatial Distribution
5.1.2. Mechanism Analysis of Insignificant Spatial Autocorrelation
5.2. Driving Path of FCSE: Multiple Concurrent Mechanisms from the Configuration Perspective
5.2.1. Core Variables and Path Heterogeneity
5.2.2. Double-Edged Sword Effect of Disaster Management
5.2.3. Time Effect and Regional Adaptation
5.3. Policy Implications
5.4. Theoretical Contributions and Limitations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- From 2008 to 2022, the average value of China’s FCSE was 1.1, showing a “high and stable” feature. Technological progress (TC mean 1.21) was the core driving force of sustainable efficiency improvement, but the imbalance of EC among regions restricts long-term sustainability. In terms of spatial distribution, FCSE exhibits a U-shaped gradient pattern with dual peaks in eastern and southwestern regions, showing no significant spatial autocorrelation but demonstrating distinct spatial dispersion characteristics.
- (2)
- Three heterogeneous paths based on the dynamic fsQCA revealed that Configuration 1 involves the coupling of abundant precipitation with economic development, which is suitable for the eastern high urbanization region. Configuration 2 comprises a multi-factor linkage of precipitation, education, pest control, and fire area, demonstrating cross-regional adaptation. Configuration 3 is driven by the combined influence of precipitation and the total value of the primary forestry industry, facilitating the ecological and economic transformation of central China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Case | Causal Combination | Index | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
| case 1 | X3/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.178 | 0.219 | 0.323 | 0.411 | 0.59 | 0.616 | 0.602 | 0.567 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.778 | 0.717 | 0.673 | 0.665 | 0.564 | 0.572 | 0.55 | 0.528 | ||
| case 2 | X3/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.111 | 0.142 | 0.224 | 0.334 | 0.456 | 0.562 | 0.636 | 0.725 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.562 | 0.565 | 0.497 | 0.617 | 0.568 | 0.552 | 0.541 | 0.596 | ||
| case 3 | ~X3/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.904 | 0.866 | 0.791 | 0.689 | 0.6 | 0.534 | 0.509 | 0.508 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.459 | 0.455 | 0.457 | 0.529 | 0.438 | 0.528 | 0.595 | 0.698 | ||
| case 4 | ~X3/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.958 | 0.928 | 0.871 | 0.775 | 0.678 | 0.576 | 0.481 | 0.368 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.583 | 0.59 | 0.609 | 0.548 | 0.7 | 0.62 | 0.535 | 0.405 | ||
| case 5 | X4/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.321 | 0.353 | 0.428 | 0.488 | 0.591 | 0.561 | 0.546 | 0.552 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.838 | 0.798 | 0.726 | 0.737 | 0.624 | 0.616 | 0.589 | 0.611 | ||
| case 6 | X4/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.1 | 0.123 | 0.194 | 0.28 | 0.356 | 0.433 | 0.513 | 0.521 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.311 | 0.335 | 0.399 | 0.39 | 0.531 | 0.518 | 0.527 | 0.462 | ||
| case 7 | ~X4/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.736 | 0.706 | 0.646 | 0.596 | 0.556 | 0.561 | 0.562 | 0.515 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.405 | 0.4 | 0.398 | 0.474 | 0.379 | 0.476 | 0.548 | 0.573 | ||
| case 8 | ~X4/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.948 | 0.926 | 0.867 | 0.811 | 0.748 | 0.679 | 0.6 | 0.561 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.626 | 0.634 | 0.647 | 0.593 | 0.721 | 0.627 | 0.557 | 0.501 | ||
| case 9 | X5/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.054 | 0.311 | 0.207 | 0.284 | 0.297 | 0.361 | 0.548 | 0.629 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.305 | 0.525 | 0.383 | 0.562 | 0.397 | 0.473 | 0.575 | 0.653 | ||
| case 10 | X5/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.145 | 0.278 | 0.339 | 0.33 | 0.418 | 0.471 | 0.549 | 0.525 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.977 | 0.568 | 0.758 | 0.6 | 0.79 | 0.672 | 0.548 | 0.437 | ||
| case 11 | ~X5/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.996 | 0.744 | 0.869 | 0.798 | 0.843 | 0.75 | 0.569 | 0.458 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.493 | 0.46 | 0.521 | 0.564 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 0.57 | 0.546 | ||
| case 12 | ~X5/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.897 | 0.768 | 0.724 | 0.759 | 0.681 | 0.63 | 0.574 | 0.583 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.532 | 0.574 | 0.525 | 0.494 | 0.578 | 0.517 | 0.547 | 0.557 | ||
| case 13 | X6/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.393 | 0.494 | 0.482 | 0.313 | 0.3 | 0.323 | 0.402 | 0.404 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.52 | 0.503 | 0.522 | 0.389 | 0.521 | 0.438 | 0.419 | 0.407 | ||
| case 14 | ~X6/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.709 | 0.571 | 0.593 | 0.763 | 0.783 | 0.785 | 0.712 | 0.709 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.657 | 0.675 | 0.658 | 0.594 | 0.693 | 0.666 | 0.653 | 0.564 | ||
| case 15 | X7/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.649 | 0.671 | 0.625 | 0.645 | 0.547 | 0.548 | 0.591 | 0.544 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.493 | 0.479 | 0.501 | 0.512 | 0.474 | 0.517 | 0.517 | 0.611 | ||
| case 16 | X7/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.635 | 0.663 | 0.601 | 0.751 | 0.522 | 0.584 | 0.7 | 0.514 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.578 | 0.572 | 0.583 | 0.549 | 0.639 | 0.6 | 0.582 | 0.462 | ||
| case 17 | ~X7/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.444 | 0.395 | 0.485 | 0.332 | 0.571 | 0.53 | 0.419 | 0.567 |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.602 | 0.592 | 0.61 | 0.462 | 0.641 | 0.56 | 0.494 | 0.499 | ||
| Case | Causal Combination | Index | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| case 1 | X3/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.551 | 0.654 | 0.618 | 0.659 | 0.667 | 0.688 | 0.699 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.454 | 0.537 | 0.519 | 0.618 | 0.604 | 0.594 | 0.527 | |||
| case 2 | X3/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.746 | 0.812 | 0.673 | 0.69 | 0.712 | 0.686 | 0.691 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.504 | 0.519 | 0.413 | 0.437 | 0.443 | 0.505 | 0.691 | |||
| case 3 | ~X3/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.509 | 0.397 | 0.428 | 0.375 | 0.379 | 0.354 | 0.343 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.674 | 0.735 | 0.587 | 0.655 | 0.66 | 0.601 | 0.535 | |||
| case 4 | ~X3/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.316 | 0.255 | 0.378 | 0.362 | 0.356 | 0.37 | 0.352 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.406 | 0.359 | 0.476 | 0.403 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.531 | |||
| case 5 | X4/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.552 | 0.556 | 0.576 | 0.68 | 0.633 | 0.681 | 0.739 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.522 | 0.543 | 0.481 | 0.633 | 0.564 | 0.541 | 0.506 | |||
| case 6 | X4/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.578 | 0.717 | 0.732 | 0.698 | 0.796 | 0.836 | 0.797 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.562 | 0.415 | 0.481 | 0.497 | 0.528 | |||
| case 7 | ~X4/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.502 | 0.518 | 0.476 | 0.372 | 0.418 | 0.367 | 0.311 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.551 | 0.707 | 0.658 | 0.659 | 0.751 | 0.75 | 0.613 | |||
| case 8 | ~X4/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.478 | 0.382 | 0.324 | 0.382 | 0.278 | 0.228 | 0.255 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.509 | 0.394 | 0.412 | 0.432 | 0.34 | 0.349 | 0.486 | |||
| case 9 | X5/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.739 | 0.719 | 0.898 | 0.712 | 0.797 | 0.807 | 0.821 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.632 | 0.656 | 0.61 | 0.665 | 0.662 | 0.616 | 0.546 | |||
| case 10 | X5/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.52 | 0.572 | 0.673 | 0.647 | 0.699 | 0.761 | 0.76 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.431 | 0.395 | 0.42 | 0.385 | 0.394 | 0.434 | 0.489 | |||
| case 11 | ~X5/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.334 | 0.336 | 0.147 | 0.342 | 0.271 | 0.259 | 0.232 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.418 | 0.51 | 0.328 | 0.603 | 0.571 | 0.591 | 0.5 | |||
| case 12 | ~X5/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.556 | 0.501 | 0.376 | 0.438 | 0.401 | 0.326 | 0.296 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.674 | 0.574 | 0.772 | 0.492 | 0.572 | 0.558 | 0.616 | |||
| case 13 | X6/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.319 | 0.634 | 0.622 | 0.712 | 0.71 | 0.708 | 0.695 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.395 | 0.461 | 0.481 | 0.411 | 0.48 | 0.481 | 0.5 | |||
| case 14 | ~X6/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.752 | 0.462 | 0.43 | 0.392 | 0.422 | 0.381 | 0.373 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.615 | 0.488 | 0.542 | 0.47 | 0.423 | 0.441 | 0.578 | |||
| case 15 | X7/Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.352 | 0.509 | 0.458 | 0.378 | 0.432 | 0.352 | 0.408 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.493 | 0.617 | 0.511 | 0.52 | 0.649 | 0.759 | 0.671 | |||
| case 16 | X7/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.453 | 0.496 | 0.535 | 0.617 | 0.431 | 0.214 | 0.305 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.616 | 0.455 | 0.548 | 0.541 | 0.439 | 0.345 | 0.485 | |||
| case 17 | ~X7/~Y | Between to Pooled consistency | 0.627 | 0.583 | 0.523 | 0.452 | 0.655 | 0.85 | 0.793 | |
| Between to Pooled coverage | 0.484 | 0.473 | 0.47 | 0.317 | 0.439 | 0.495 | 0.565 | |||
References
- Wang, J.; Shi, K.; Hu, M. Measurement of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors Empirical Evidence from China. Forests 2022, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, E.; Sun, Y. Study on the effect of development strategy on forestry ecological efficiency in western China. China For. Econ. 2024, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, C. Research on management efficiency evaluation of provincial forestry system based on network DEA model. South. For. Sci. 2019, 48, 47–52, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, Y. Effects of financial support and forest rights reform on forestry production efficiency in the background of ecological civilization construction. Issues For. Econ. 2019, 39, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, G.; Huang, C.; Yuan, B. Spatial and temporal evolution of forest carbon sink efficiency in China: Based on a three-stage superefficiency SBM-DEA model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6769–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Li, C.; Li, H. Evaluation of forest management efficiency and heterogeneity based on dynamic DEA. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ning, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y. Government forestry input and output efficiency comparison of China and the United States. For. Resour. Manag. 2013, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Lin, Q.; Su, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J. Chinese forestry technical efficiency under the multiple target and its convergence analysis. World For. Res. 2014, 27, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Yao, S. Estimation and analysis of technical efficiency of forestry production in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 23, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Xu, J.; Su, S.; Liu, Z. After the collective forest right system reform in southern collective forest area output efficiency study. J. For. Econ. 2014, 4, 109–113, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Qu, Z.; Deng, Y. Spatial convergence and differentiation of technical efficiency of forestry production at provincial level in China. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, Q. Study on the spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing factors of forestry production efficiency in China. J. Northwest For. Coll. 2017, 32, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarski, W.; Prędki, A.; Kaliszewski, A. Efficiency and factors influencing it in forest districts in southern Poland: Application of Data Envelopment Analysis. For. Policy Econ. 2021, 130, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Man, H. Analysis of the Efficiency of Forest Carbon Sinks and Its Influencing Factors—Evidence the from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, Y. Based on super efficiency of SBM model of performance evaluation of Chinese forestry industry research. J. Chin. For. Econ. 2022, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Xue, L.; Li, Z. Forestry carbon sequestration economic benefit evaluation and regional coordination analysis. J. Stat. Decis. 2017, 2, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yin, S. Empirical study on ecological efficiency of forestry industry: Based on panel data analysis of 15 provinces. For. Econ. 2016, 38, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Shi, Y. Heilongjiang state-owned forest forestry ecological construction efficiency analysis. J. For. Econ. Probl. 2022, 42, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Di, F. Input and output efficiency of the Yangtze river economic belt wisdom forestry construction research. China For. Econ. 2023, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Sun, J.; Cai, X. China forestry green total factor productivity of space-time evolution analysis. J. Agric. For. Econ. Manag. 2022, 21, 320–330. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Bai, J.; Bao, Q. An empirical study on forestry production technical efficiency and its influencing factors in Inner Mongolia: Based on stochastic frontier production function. For. Econ. 2017, 39, 89–94, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of SBM-Malmquist measure and temporal and spatial characteristics of ecological security efficiency in forestry industry. Res. Sci. Technol. Manag. 2019, 39, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Spatial and temporal distribution, regional differences and dynamic evolution of forest green total factor productivity in the Yellow River Basin. Stat. Theory Pract. 2024, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, S. Spatial convergence and differentiation characteristics of ecological efficiency of forestry carbon sink: Evidence from China. Geosyst. Geoenviron. 2024, 3, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. Analysis of factors that influence forest vegetation carbon storage by using the VAR model: A case study in Shanxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quan, Y.; Wen, Y.; Cui, X. Study on the impact and path of digital economy on forestry carbon sink increment: Based on the moderated intermediary effect model. For. Econ. 2023, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Huo, L.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Ke, Y. Analysis of forest carbon sequestration and its influencing factors in Hainan Province under the “two mountains” concept. For. Econ. Issues 2024, 44, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, A.; Peng, C.; Zhao, S.; Ci, L. Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998. Science 2001, 292, 2320–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, R.; Piper, S.; Heimann, M. Global and hemispheric CO2 sinks deduced from changes in atmospheric O2 Concentration. Nature 1996, 381, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, W.; Hao, G.; Yan, H.; Lu, Y.; Yasmeen, R. The Impact of Climate Change on China’s Forestry Efficiency and Total Factor Productivity Change. Forests 2023, 14, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, G. Analysis of plant carbon storage in Chinese forest ecosystems and its influencing factors. Geoscience 2004, 24, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Ren, Y. Can carbon sink insurance and financial subsidies improve the carbon sequestration capacity of forestry? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, J. Forest carbon sink in China: Linked drivers and long short-term memory network-based prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigneault, A.; Favero, A. Global forest management, carbon sequestration and bioenergy supply under alternative shared socioeconomic pathways. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, D. The role of forest management on forest carbon sinks and impact analysis. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 3654–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, M.; Sun, X.; Qie, X.; Wang, Y. Measurement of green innovation efficiency in Chinese listed energy-intensive enterprises based on the three stage Super-SBM model. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 97, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuag, Y.; Fare, R. Productivity and Undesirable Outputs: A Directional Distance Function Approach. Microeconomics 1997, 51, 29–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, J. What Is a Concept? Two Definitions and Their Research Implications; Mimeo, Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ragin, C.C.; Strand, S.I. Using Qualitative Comparative Analysis to Study Causal Order Comment on Caren and Panofsky (2005). Sociol. Methods Res. 2008, 36, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch, W. Rethinking the “time blind Zone” of QCA method: Finding “time” for public management research. Chin. Adm. Manag. 2023, 33, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Deng, L.; Li, Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of carbon emission efficiency in agriculture and forestry in China under the “dual carbon” target. For. Econ. 2024, 46–48, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Luo, X.; Wu, X. Efficiency of China’s four big forest carbon sequestration: Measuring, driving factors and convergence. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Ge, J. Carbon sinks and output of China’s forestry sector:an ecological economic development perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. The evaluation indicator of ecological development transition in China’s regional economy. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; He, X. China forestry carbon sequestration potential analysis. China For. Econ. 2022, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Chen, Z. Analyses the role of forest management on forest carbon sink and influence. Low Carbon World 2019, 9, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, S. Evaluation of forest carbon sink potential and forest health status in Lishui City based on second-class forest resources survey data. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2024, 52, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; GAO, C.; Lei, G. Empirical analyses of forestry industry agglomeration and eco-efficiency: Based on panel data test on 15 Provinces in China. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Han, W. Evaluation and prediction of synergistic relationship between high-level protection of forestry ecology and high-quality development of forestry economy. For. Econ. Issues 2024, 44, 284–294. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.; Cheng, W.; Liu, X. Assessment of agricultural ecological compensation intention and payment level based on conditional value assessment method: A case study of Yongdeng County, Gansu Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 4, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dai, J.; Zhou, W. Effect of heterogeneous human capital on farmers’ economic forest management behavior: An analysis based on the adjustment effect of the policy of returning farmland to forest. For. Econ. 2023, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S. Forest management and improve the function of forest carbon sequestration strategy. J. Chin. For. Econ. 2019, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Y. Government research institutions of science and technology resources allocation efficiency factors affecting Configuration analysis. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2022, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Liu, Q.; Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Wu, X. The impacts of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle: A review. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Jia, Q. Impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems in Northeast China. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2013, 4, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, J. Long-term equilibrium and short-term dynamic relationship between forest carbon sequestration and economic growth: Based on China’s provincial panel data from 1998 to 2010. J. Nat. Resour. 2013, 28, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Luo, X.; Li, R.; Yu, Z. Region differences and dynamic evolution of forest carbon sink in China. J. CAU 2018, 23, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, P.; Liang, L.; Zeng, F. Differences in carbon sink potential between urban agglomerations are decreasing: Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Wagemann, C. Set-Theoretic Methods for the Social Sciences: A Guide to Qualitative Comparative Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.; Arino, A. A general approach to panel data set-theoretic research. J. Adv. Manag. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2016, 1, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Fan, Z.; Du, Y. Technical management capability, attention allocation and local government website construction: A Configuration analysis based on TOE framework. Manag. World 2019, 35, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihoux, B.; Ragin, C. Configurational Comparative Methods: Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) and Related Techniques; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Jia, L. Configuration perspective and Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA): A New approach to management research. Manag. World 2017, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Du, Y. Organization and management research in QCA method of application: Orientation, strategy and direction. J. Manag. 2019, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, D. The Configuration and Path of Factors Affecting the Development of Science-based Industries: A QCA Analysis Based on the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry in 31 Provinces of Mainland China. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2022, 33, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Gong, Z.; Bu, Y. Forest Quality Dynamic Change and Its Driving Factors Accompanied by Forest Transition in China. Forests 2021, 6, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, M.; Pi, S.; Lu, S. Research on the relationship between reverse transnational M&A integration Configuration and M&A integration performance of Chinese enterprises. J. Manag. 2019, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oana, I.; Schneider, C. A robustness test protocol for applied QCA: Going to the and R software application. Sociol. Methods Res. 2021, 53, 1030476263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Natural disasters and economic development drive forest dynamics and transition in China. For. Policy Econ. 2017, 76, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Index | Indicator Interpretation (Units) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Labor | Year-end employment in the forestry sector | People |
| Land | Forest area | 103 hm2 | |
| Capital | Total amount of investment in fixed assets | 103 CNY | |
| Desirable output | Economy | Total value of the primary forestry industry | 103 CNY |
| Carbon sink | Forest carbon sink | Ton | |
| Undesirable output | Carbon source | Carbon dioxide emissions | Ton |
| Variable | Mean | S.D | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Year-end employment in the forestry sector | 39,273.35 | 55,711.91 | 496 | 234,181 |
| Forest area | 706.89 | 615.11 | 1.89 | 2614.85 | |
| Total amount of investment in fixed assets | 600,253.98 | 1,196,293.74 | 518 | 10,861,358 | |
| Desirable output | Total value of the primary forestry industry | 19,313,982.53 | 27,734,177.82 | 23,999 | 374,085,252 |
| Forest carbon sink | 49,112 | 59,618.34 | 38.51 | 228,537.41 | |
| Undesirable output | Carbon dioxide emissions | 153.24 | 110.36 | 5.33 | 777.16 |
| Category | Index (Abbreviation) | Indicator Description (Units) | Indicator Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural endowment | Forest coverage (FC) Precipitation (PRE) | Ratio of forest area to total land area (%) | + + |
| Total annual precipitation (mm) | |||
| Social development | Total value of the primary forestry industry (TPFI) | Total forestry primary industry (104 CNY) | + |
| Gross regional domestic product (GDP) | 108 CNY | + | |
| Year of education (YOE) | Years of education for forestry practitioners (years) | + | |
| Forest management | Forestry pest control rate (FPCR) | % | + |
| Fire-damaged area (FDA) | Area of forest destroyed by fire (ha) | - |
| Variable | Descriptive Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D | Min | Max | ||
| Result variable | FCSE | 1.10 | 1.78 | 0.02 | 15.12 |
| Condition variable | FC | 32.71 | 17.89 | 2.97 | 66.84 |
| PRE | 916.76 | 514.64 | 55.90 | 2432.6 | |
| TPFI | 6,233,096.32 | 5,369,863.45 | 23284 | 24,215,489 | |
| GDP | 24,171.51 | 21,873.23 | 896.9 | 129,118.6 | |
| YOE | 14.21 | 0.71 | 10.56 | 15.67 | |
| FPCR | 76.66 | 21.87 | 8.45 | 100 | |
| FDA | 695.96 | 1799.63 | 0.15 | 17780.99 | |
| Variable Category | Variable | Full Member | Crossover Point | Full Non-Member |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome variable | FCSE | 1.202 | 0.653 | 0.339 |
| Antecedent variable | FC | 46.068 | 35.155 | 16.723 |
| PRE | 1279.1 | 822.625 | 491.725 | |
| TPFI | 9,061,203 | 4,771,543 | 2,018,558 | |
| GDP | 31,460.75 | 17,569.2 | 9937.6 | |
| YOE | 14.76 | 14.328 | 13.729 | |
| FPCR | 93.848 | 82.895 | 66.67 | |
| FDA | 578.708 | 133.97 | 29.222 |
| Region | FCSE Change Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ML | EC | TC | |
| Beijing | 0.82 | 0.71 | 1.15 |
| Tianjin | 0.54 | 0.37 | 1.45 |
| Hebei | 1.15 | 1.01 | 1.14 |
| Shanxi | 0.94 | 0.59 | 1.59 |
| Inner Mongolia | 1.04 | 0.65 | 1.6 |
| Liaoning | 0.81 | 0.76 | 1.07 |
| Jilin | 1.46 | 1.12 | 1.3 |
| Heilongjiang | 1.27 | 0.99 | 1.28 |
| Shanghai | 1.29 | 1.1 | 1.17 |
| Jiangsu | 1.53 | 1.56 | 0.98 |
| Chekiang | 0.38 | 0.4 | 0.94 |
| Anhui | 1.08 | 0.79 | 1.37 |
| Fujian | 1.08 | 0.97 | 1.12 |
| Jiangxi | 1.3 | 1.69 | 0.77 |
| Shandong | 0.9 | 0.8 | 1.12 |
| Henan | 0.82 | 0.66 | 1.24 |
| Hubei | 1.44 | 1.16 | 1.24 |
| Hunan | 1.11 | 1.05 | 1.06 |
| Guangdong | 1.20 | 1.00 | 1.20 |
| Guangxi | 1.18 | 1.00 | 1.18 |
| Hainan | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.98 |
| Chongqing | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.03 |
| Sichuan | 1.07 | 0.96 | 1.11 |
| Guizhou | 1.34 | 1.26 | 1.06 |
| Yunnan | 1.01 | 0.93 | 1.09 |
| Shanxi | 1.14 | 1.01 | 1.13 |
| Gansu | 0.81 | 0.31 | 2.60 |
| Qinghai | 1.03 | 0.97 | 1.06 |
| Ningxia | 0.35 | 0.75 | 0.46 |
| Xinjiang | 0.52 | 0.45 | 1.16 |
| Western remote region | 1.00 | 0.83 | 1.21 |
| Central inland region | 1.23 | 0.97 | 1.27 |
| Eastern coastal region | 0.99 | 0.88 | 1.12 |
| Mean value | 1.09 | 0.90 | 1.21 |
| Year | Moran’s I | p | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | −0.07 | 0.27 | −0.61 |
| 2009 | −0.07 | 0.21 | −0.8 |
| 2010 | −0.08 | 0.15 | −1.06 |
| 2011 | −0.08 | 0.2 | −0.85 |
| 2012 | −0.07 | 0.17 | −0.95 |
| 2013 | −0.07 | 0.15 | −1.05 |
| 2014 | −0.07 | 0.12 | −1.16 |
| 2015 | −0.05 | 0.45 | −0.13 |
| 2016 | −0.09 | 0.25 | −0.68 |
| 2017 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.75 |
| 2018 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.96 |
| 2019 | −0.04 | 0.49 | −0.03 |
| 2020 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.68 |
| 2021 | −0.01 | 0.41 | 0.23 |
| 2022 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 1.61 |
| Variable | High FCSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled Con | Pooled Cov | Between Con Adjusted Distance | Within Con Adjusted Distance | |
| FC | 0.56 | 0.584 | 0.085 | 0.679 |
| ~FC | 0.516 | 0.525 | 0.106 | 0.69 |
| PRE | 0.575 | 0.601 | 0.089 | 0.644 |
| ~PRE | 0.493 | 0.501 | 0.115 | 0.69 |
| TPFI | 0.547 | 0.566 | 0.336 | 0.529 |
| ~TPFI | 0.531 | 0.545 | 0.366 | 0.61 |
| GDP | 0.557 | 0.588 | 0.226 | 0.633 |
| ~GDP | 0.514 | 0.517 | 0.247 | 0.621 |
| YOE | 0.566 | 0.589 | 0.524 | 0.5 |
| ~YOE | 0.508 | 0.518 | 0.558 | 0.575 |
| FPCR | 0.616 | 0.621 | 0.119 | 0.529 |
| ~FPCR | 0.468 | 0.493 | 0.187 | 0.569 |
| PDA | 0.507 | 0.541 | 0.23 | 0.575 |
| ~PDA | 0.572 | 0.569 | 0.192 | 0.581 |
| Variable | Configuration Analysis—High | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration 1 | Configuration 2 | Configuration 3 | |
| Forest coverage | ⮾ | ||
| Precipitation | ● | ● | ● |
| Total value of the primary forestry industry | ⮾ | ● | |
| Gross regional domestic product | ● | ||
| Year of education | ● | ||
| Forestry pest control rate | ● | ||
| Fire-damaged area | ● | ● | |
| Consistency | 0.824 | 0.828 | 0.753 |
| PRI | 0.755 | 0.768 | 0.534 |
| Coverage | 0.175 | 0.179 | 0.091 |
| Unique coverage | 0.078 | 0.102 | 0.000 |
| Between consistency adjusted distance | 0.123 | 0.162 | 0.115 |
| Within consistency adjusted distance | 0.374 | 0.328 | 0.311 |
| Overall consistency | 0.822 | ||
| Overall PRI | 0.771 | ||
| Overall coverage | 0.318 | ||
| Region | Configuration 1 | Configuration 2 | Configuration 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern coastal region | 0.31 | 0.272 | 0.164 |
| Central inland region | 0.327 | 0.203 | 0.363 |
| Western remote region | 0.117 | 0.249 | 0.198 |
| Variable | The Frequency Is 4 | The Frequency Is 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration 1 | Configuration 2 | Configuration 3 | Configuration 1 | Configuration 2 | |
| FC | ⊗ | ||||
| PRE | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| TPFI | ⊗ | ● | ⊗ | ||
| GDP | ● | ● | |||
| YOE | ● | ● | |||
| FPCR | ● | ● | |||
| FDA | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Consistency | 0.824 | 0.828 | 0.753 | 0.824 | 0.828 |
| PRI | 0.755 | 0.768 | 0.534 | 0.755 | 0.768 |
| Coverage | 0.175 | 0.179 | 0.091 | 0.175 | 0.179 |
| Unique coverage | 0.078 | 0.102 | 0 | 0.038 | 0.126 |
| Between consistency adjusted distance | 0.822 | 0.827 | |||
| Within consistency adjusted distance | 0.771 | 0.776 | |||
| Overall consistency | 0.318 | 0.3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, C. Dynamic Evaluation of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Driver Configurational Identification in China: A Sustainable Forestry Perspective. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135931
Ding Y, Zhao J, Li C. Dynamic Evaluation of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Driver Configurational Identification in China: A Sustainable Forestry Perspective. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135931
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yingyiwen, Jing Zhao, and Chunhua Li. 2025. "Dynamic Evaluation of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Driver Configurational Identification in China: A Sustainable Forestry Perspective" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135931
APA StyleDing, Y., Zhao, J., & Li, C. (2025). Dynamic Evaluation of Forest Carbon Sink Efficiency and Its Driver Configurational Identification in China: A Sustainable Forestry Perspective. Sustainability, 17(13), 5931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135931





