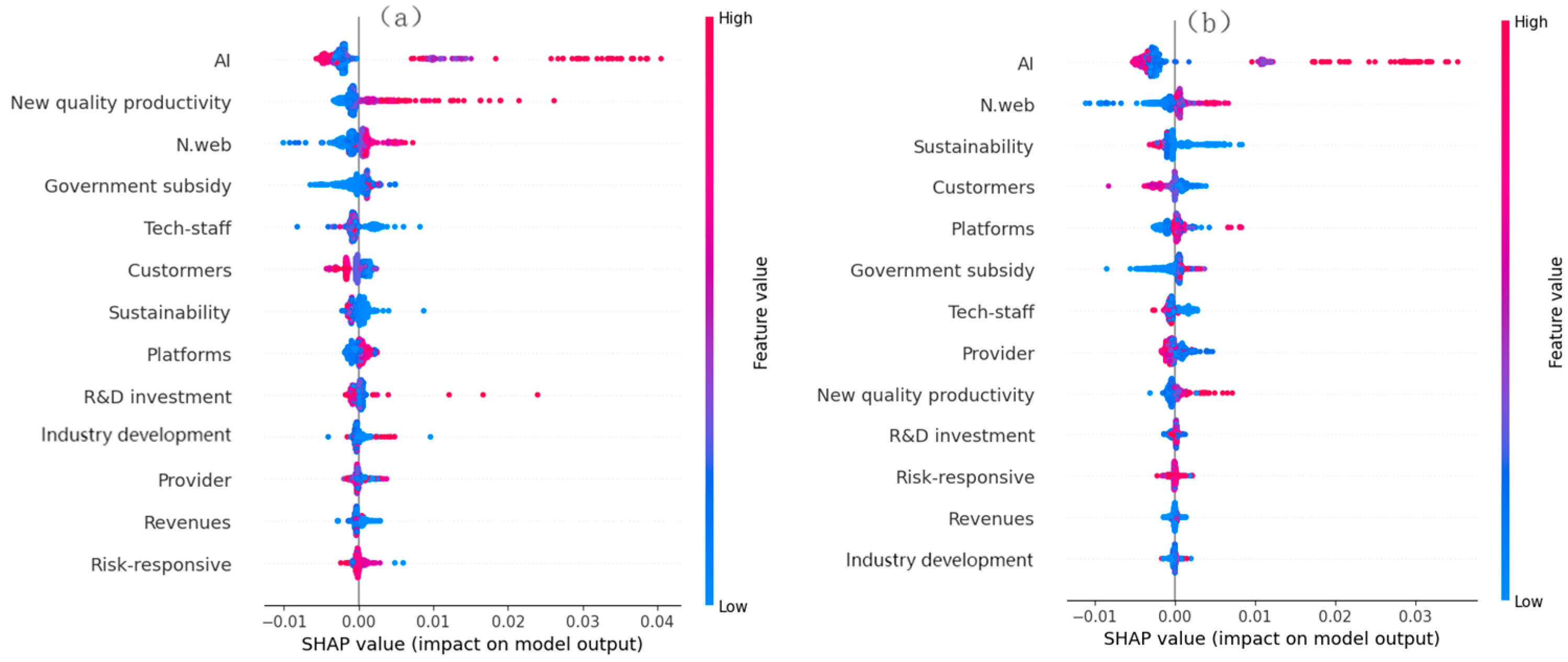
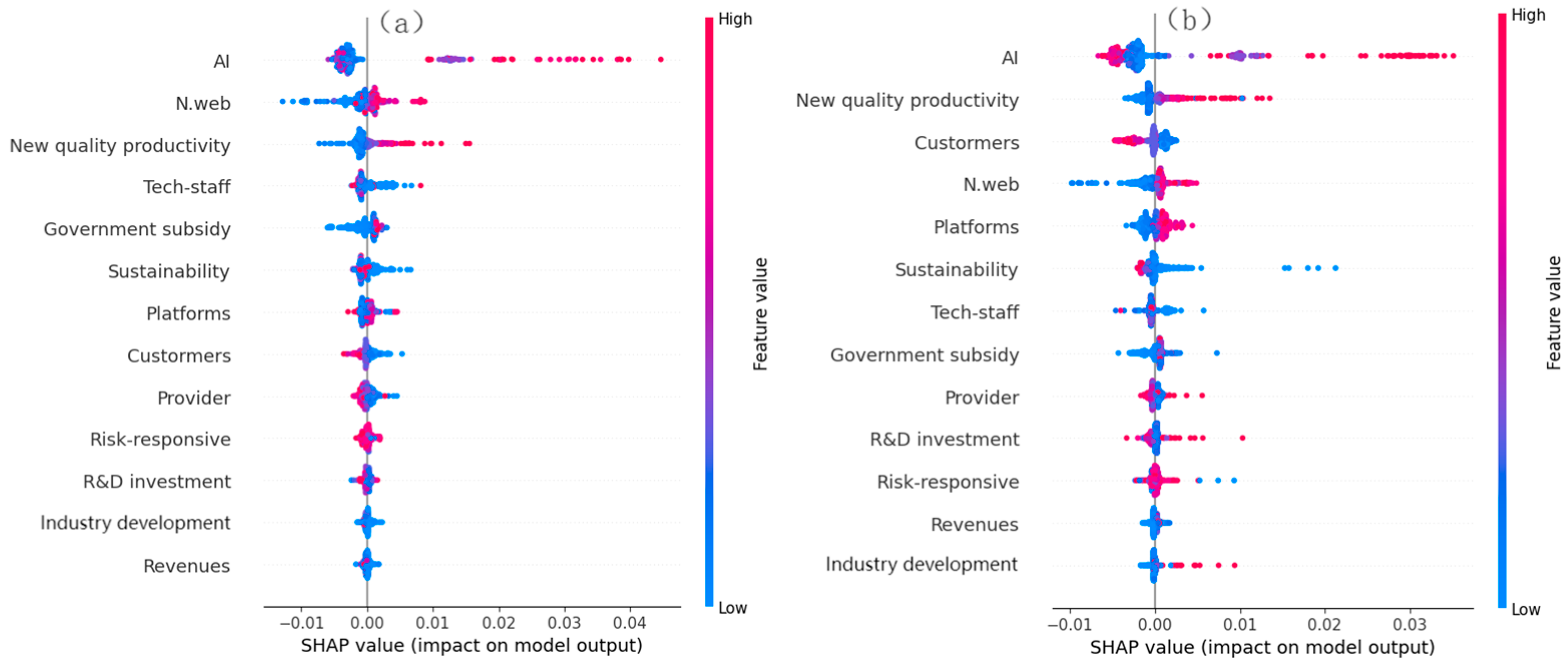
2.1. Literature Review
In the context of the digital economy, digital technology as a new production factor is comprehensively influencing and participating in innovation activities, promoting the improvement of the traditional innovation ecological theory (Li et al., 2022; Nambisan et al., 2017) [
5,
6]. Digital transformation has expanded the theory of innovation ecosystems, prompting scholars to reflect on digital innovation ecosystems.
Existing studies mainly focus on the connotation characteristics and functional positioning of digital innovation ecosystems in detail. In regard to connotation characteristics, extant research has demonstrated that the digital innovation ecosystem, in the context of digital technology, exhibits not only the dynamic nature of an innovation ecosystem and resource heterogeneity (Chae, 2019) [
7]. It also has important characteristics such as participant diversification, resource sharing, and efficient production (Ma et al., 2022; Purbasari et al., 2023) [
8,
9]. These new characteristics will enhance the synergy between multiple actors, promote the linkage and reorganization of factors, and also lead to fundamental changes in the basic structure of relationships and operating rules in the innovation ecosystem (Benitez et al., 2020) [
10]. With respect to functional positioning, digital innovation ecosystems have the capacity to facilitate the optimal allocation of resources and the empowerment of digital technologies by reshaping the behavioral relationships between participating entities (Chae, 2019) [
7]. Huang and Mao (2024) introduced energetics into the framework of digital innovation ecosystems [
3]. Wang et al. (2024) found that there are coordination dilemmas such as risk sharing and competing stakeholders in digital innovation ecosystems [
11]. Digital innovation ecosystems have the potential to promote enterprise digital transformation by accelerating the integration of manufacturing and digital technologies, thereby enhancing the value of products and services [
11].
The pervasive implementation of digital technology has precipitated the digital transformation process of enterprises (Hanelt et al., 2021) [
12]. In the context of the ongoing digital transformation, the significance of enterprise digital transformation in various fields has become increasingly evident. Different industries have launched in-depth studies on enterprise digital transformation based on their characteristics and needs. Existing research mainly focuses on the connotation characteristics and realization methods of enterprise digital transformation. First, regarding the connotative characteristics of enterprise digital transformation. Browder et al. (2024) suggest that enterprise digital transformation is the process by which enterprises use digital technology to continuously improve their business operations [
13]. The goal of transformation is to realize enhanced customer experience, create new business models, etc. According to Berghaus and Back (2016) [
14], enterprise digital transformation includes not only process digital transformation focused on efficiency but also digital capability transformation focused on enhancing product innovation. The digital transformation of enterprises is a complex value-enhancing process, specifically going through the development stages of digital conversion, digital upgrading, and digital transformation (Verhoef et al., 2021) [
15]. Digital technology has emerged as the primary catalyst for enterprise digital transformation; disruptive innovation is an important condition, and improving productivity and realizing value creation is the purpose of transformation (Zhu and Li, 2023) [
16]. Secondly, about the realization of enterprise-based transformation. Digital technology is an important condition to support the digital transformation of enterprises, and digital components, digital platforms, and digital infrastructure construction are the core components of digital technology [
6]. Both the cognitive ability and attitude of enterprise organizations are key factors in promoting enterprise digital transformation. Among them, the digital technology application ability, innovation ability, and organizational relationship of the enterprise participating subjects are the driving elements to achieve enterprise digital transformation (Troise, 2022) [
17]. The digital economy is characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and ambiguity in the development environment. Enterprises must pay close attention to the volatile environmental changes in technology and markets to effectively realize digital transformation (Chen and Tian, 2022) [
18].
In summary, existing studies have conducted preliminary discussions on digital innovation ecosystems and enterprise digital transformation. The research value of the digital innovation ecosystem and enterprise digital transformation is fully affirmed. However, existing research lacks a systematic analysis of the intrinsic mechanisms of digital innovation ecosystems affecting the digital transformation of enterprises. This has resulted in a paucity of effective theoretical guidance and practical basis for enterprises in the process of utilizing digital innovation ecosystems to achieve digital transformation. In particular, there is a dearth of research on the application of digital innovation ecosystems to specific industry contexts. Therefore, the present study takes digital creative enterprises as its research object, conducts a profound analysis of the development level of their digital innovation ecosystem, and reveals the driving path and achievement logic of their constituent elements for enterprise digital transformation. The objective of this study is to provide a scientific foundation and reference point for the systematic promotion of digital transformation in enterprises.
2.2. Theoretical Hypotheses
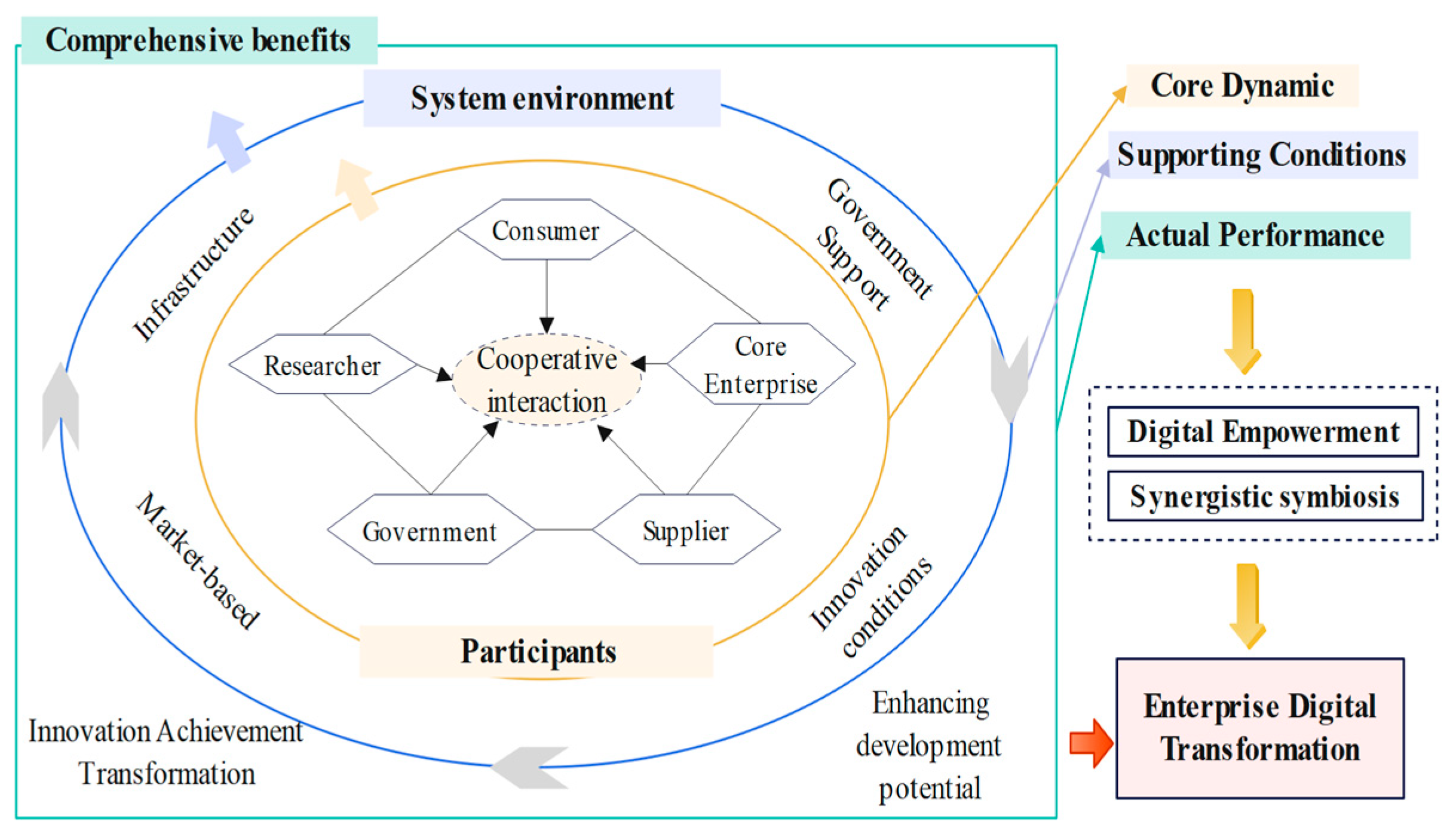
The digital innovation ecosystem refers to a complex system in which multiple participants in a specific market, technology, and policy environment jointly promote innovative development through resource sharing and technological cooperation. The objective of the digital innovation ecosystem is to integrate resources and promote open collaboration through digital means, ultimately achieving value creation with the support of the system environment. In accordance with the aforementioned definitions and extant research findings [
3], the present study principally analyzes the three constituent elements of digital innovation ecosystems: participants, system environment, and comprehensive benefits (see
Figure 1). In the context of the digital economy, diverse participants such as core enterprises, researchers, consumers, and producers carry out collaborative cooperation and jointly promote the achievement of digital transformation of enterprises with the support of policy, market, and innovation environment empowerment and comprehensive benefits.
First, the digital innovation ecosystem consists of multiple participants, including core enterprises, researchers, consumers, suppliers, and governments, which are interconnected and collaborate across boundaries to promote the digital transformation of enterprises (Huang et al., 2023) [
19]. For example, digital technology providers are an important source of technology for the digital innovation ecosystem. They continue to develop and provide advanced technologies, such as big data analytics, cloud computing, and blockchain, to provide technical support for the digital transformation of digital creative enterprises. Government departments improve the basic conditions for the digital transformation of enterprises by formulating industrial policies, tax incentives, financial subsidies, and other measures (Cai and Yu, 2022) [
20]. Digital creative enterprises that possess both innovative capabilities and significant resource advantages are well-positioned to leverage the cluster effects, thereby encouraging and enabling both upstream and downstream enterprises to participate in and achieve digital transformation.
Second, the digital innovation ecosystem can provide the necessary development environment and basic conditions for the digital transformation of enterprises. The openness and sharing of the technological environment can make it easier for enterprises to access and apply new technologies and accelerate the process of digital transformation (Pronchakov et al., 2022) [
21]. Changes in the market environment have stimulated the intrinsic motivation of digital creative enterprises for digital transformation, driving them to continuously realize innovative transformation and comprehensive development. A standardized market order has been demonstrated to be conducive to the healthy development of the entire digital innovation ecosystem. It is imperative to provide a stable institutional guarantee for the digital transformation of enterprises.
Finally, the digital innovation ecosystem, by leveraging the synergistic effect of multiple subjects and environmental safeguards, brings multifaceted and comprehensive benefits to the digital transformation of digital creative enterprises and further promotes the sustainable transformation and development of enterprises. Improvements in system effectiveness increase market share and profitability and provide sustained momentum for digital transformation (Li et al., 2023) [
22]. In an ecosystem, enterprises can utilize shared infrastructure, market channels, and other resources to reduce unit costs. The realization of economies of scale enhances the development strength of digital creative enterprises. Enterprises have more resources to invest in innovation in the process of digital transformation, which in turn accelerates the realization of transformation. Based on the above analysis, the following research hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 1 (H1). The digital innovation ecosystems can effectively drive the digital transformation of enterprises.
Dynamic capability refers to the ability of an enterprise to adapt to rapidly changing environments and create new competitive advantages by integrating, building, and reconfiguring internal and external resources. Its core is the dynamic process of enterprises continuously perceiving market opportunities, seizing opportunities, and rapidly transforming to achieve innovation (Teece, 1997) [
23]. Innovation capability is defined as the ability of an enterprise to create new products, services, and technologies by integrating internal and external resources. Absorption capacity is defined as the ability of an enterprise to identify, acquire, and digest external knowledge and transform it into its applications. Coordinative capacity is defined as a company’s ability to optimize the combination of existing resources and improve operational efficiency. Dynamic capabilities provide a new perspective for gaining a deeper understanding of the driving mechanisms of digital innovation ecosystems for enterprise digital transformation. Firstly, it is imperative to acknowledge that innovation capability represents a pivotal attribute for enterprises, as it pertains to their capacity for technological innovation and the subsequent implementation of these innovations (Wang and Ahmed, 2007; Crossan and Apaydin, 2010) [
24,
25]. Enterprises with strong innovation capabilities can proactively explore the application scenarios of new technologies in the digital innovation ecosystem. By applying them to the production and optimization of creative content, they can further accelerate the realization of digital transformation. Second, Strategic coordination capability serves as a critical dynamic capability that enables enterprises to achieve competitive advantage and sustain growth (Wang et al., 2015) [
26]. The digital innovation ecosystem is in a constantly changing environment. The ability to coordinate is also an important manifestation of an enterprise’s dynamic capabilities. It enables enterprises to flexibly adjust their strategic decisions under different environmental conditions. Ultimately, it ensures that the enterprise always stays on the right track in the digital transformation process. Third, enterprises with strong learning and absorptive capacities are better able to understand and transform knowledge from other actors in the ecosystem (Schilke, 2014) [
27]. Enterprises transform assimilated knowledge and resources into innovation capabilities, thereby enhancing resource conversion efficiency. This process provides critical technological support for accelerating digital transformation.
Hypothesis 2 (H2). Dynamic capabilities play a moderating role in the process whereby the digital innovation ecosystem drives enterprise digital transformation.