Abstract
Surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous generators (SPMSGs) are well suited for wind power applications mainly because of their high power density, low cogging torque, and effective thermal management. This study proposes an eccentric Halbach PM array pole shape to enhance the power generation capability of SPMSGs specifically designed for low-speed wind power generation. The topology of the proposed eccentric Halbach PM arrangement is optimized using a genetic algorithm. Two-dimensional finite element simulations indicate that the eccentric Halbach configuration significantly improves flux focusing and magnetic field distribution. Compared to the conventional design, the proposed structure exhibits a substantial increase in electromotive force with reduced total harmonic distortion. Cogging torque is reduced by 48.6%, supporting improved starting and low-speed operation. Under on-load, the proposed design delivers higher average torque with reduced ripple, contributing to smoother operation. At a rated speed, the output power increases by 25%, with consistently higher power generation capability across a wide range of load conditions. Additionally, the proposed generator achieves higher efficiency across all operating speeds. These findings confirm the effectiveness of the eccentric Halbach array configuration in improving the power generation capability of SPMSG, thereby reinforcing its applicability to low-speed wind energy systems aligned with long-term sustainability objectives.
1. Introduction
Wind power generation has attracted growing interest in recent years as the global demand for clean and sustainable energy continues to rise [1,2,3]. Among various generator technologies, permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSGs) have become a leading choice for wind turbines because of their high power density, high efficiency, and minimal maintenance requirements compared to conventional brushed and induction machines [4,5,6,7,8]. Within this category, surface-mounted permanent magnet (SPM) generators, in which permanent magnets (PMs) are mounted directly on the rotor surface, are widely employed in wind energy systems. Their favorable characteristics, including high output capability, low cogging torque, simple mechanical construction, and efficient thermal management, make them particularly well suited for such applications [9,10,11]. Over the past decade, numerous efforts have focused on improving the performance of SPM generators, with key objectives including increased power output, reduced cogging torque, minimized total harmonic distortion (THD), and improved efficiency. These enhancements are typically pursued through strategic modifications to the machine’s structural geometry, PM shape and arrangement, and winding configuration.
Modifying the structural parameters of PM generators plays a critical role in enhancing their electromagnetic performance, particularly in wind power applications. Such modifications directly affect the magnetic flux distribution, the coupling between the stator and rotor, magnetic reluctance paths, and associated losses. These factors collectively influence key performance metrics, such as torque production, efficiency, and harmonic content. In parallel, improvements in winding configuration can further enhance machine performance by strengthening magnetic coupling, reducing spatial and temporal harmonics, minimizing copper losses, and lowering back-EMF distortion. Given that PMs serve as the primary excitation source in these machines, changes in their shape or spatial arrangement offer additional avenues for optimization. By tailoring the magnet arrangement, it is possible to concentrate flux more effectively in the air gap, reduce leakage, improve magnet utilization, and suppress undesirable harmonic components, all of which contribute to improved overall performance. Numerous studies have explored the impact of modifying PM shape or arrangement to enhance the electromagnetic performance of PM machines. In [12,13], the authors investigated the use of non-uniform magnet pole shapes in SPM machines, demonstrating notable improvements in cogging torque, EMF, and output power compared to conventional uniform pole designs. Similarly, Amin et al. [14] examined various magnet shapes for low-speed PMSGs and found that triangular-shaped magnets yielded higher EMF and output power than other configurations, highlighting the strong correlation between magnet geometry and electromagnetic behavior. In [15], the influence of magnet shape on cogging torque and THD in PMSGs for wind turbines was assessed, showing that appropriate shaping can significantly reduce both cogging and THD, ultimately improving overall efficiency. Lubis et al. [16] studied the effect of magnet thickness and rotational speed, demonstrating their combined influence on output power maximization. Petrov et al. [17] proposed a non-uniform magnet pole arc angle, which resulted in enhanced output power, while the authors of [18] introduced a design methodology based on optimizing the mechanical pole arc coefficient. The latter maintained constant PM volume while increasing the effective magnetic field, leading to improved power output. In [19], Haraguchi et al. optimized the ratio of magnet width to pole pitch, identifying a rotor structure for surface-mounted PMSGs that offers minimal losses and maximum efficiency at the same rated power. Gu et al. [20] further advanced this area by applying an unequal tooth segmentation strategy to PMs, reporting a 4.6% increase in output torque and higher fundamental back-EMF. Recently, the authors of [21] demonstrated that implementing the E-core and C-core techniques in the SFPM generator can achieve higher PM utilization, lower cogging torque, and greater efficiency in such a generator. Finally, Jabbari et al. [22] introduced an eccentric pole shape that enhanced magnet utilization and electromagnetic performance, resulting in a significant increase in output power. These studies collectively demonstrate that targeted modifications to PM shape and arrangement can lead to substantial gains in torque, efficiency, and power output.
Segmenting PMs has proven to be an effective strategy for enhancing the output performance of PM machines [23,24,25]. Dividing the magnet into smaller segments allows for greater control over flux distribution in the air gap, which can lead to increased torque production and improved power density. In addition, segmentation helps suppress harmonic components in the magnetic field, thereby reducing torque ripple and acoustic noise. Among various segmented configurations, the Halbach array has drawn particular attention due to its ability to concentrate the magnetic field on one side while significantly weakening it on the other. This directional enhancement improves flux utilization and reduces leakage flux, making it especially advantageous for surface-mounted PM generators. Several studies have confirmed the effectiveness of this technique. For example, in 2016, a five-segment Halbach array was applied to a surface-mounted PM wind generator designed for a 3 MW wind turbine, resulting in significantly higher output power, albeit with a slight compromise in efficiency [26]. In a later study, Ni et al. [27] optimized Halbach-array-based SPM machines and demonstrated notable improvements in torque density. Duan et al. [28] further compared three Halbach configurations, i.e., traditional, uneven, and soft-magnetic, within a four-pole PM machine. The results showed that while the traditional Halbach array enhanced air-gap flux density, the uneven and soft magnetic variations delivered superior torque performance. These findings reinforce the value of Halbach-array-based segmentation in advancing the design of high-performance PMSGs for wind power applications. In [29], Gul et al. introduced an advanced double-stator, single-rotor topology for SPM generators, targeting cost minimization through structural optimization. The proposed design was evaluated using a single-objective genetic algorithm (GA), indicating explicit reduction in overall manufacturing cost. In [30], Öztürk et al. presented a cost-effective strategy for minimizing cogging torque in SPM generators by optimizing key design parameters, including the skew angle, pole embrace, and pole arc angle. Their single-objective optimization indicated that the optimized configuration achieved a cogging torque reduction of approximately 90%. More recently, Yazdanpanah et al. [31] proposed an analytical design methodology incorporating sensitivity analysis and GA-based optimization for both inner and outer rotor PMSGs intended for wind turbine applications. Their results contributed to a significant reduction in generator cost, underscoring the economic viability of the approach. Based on the literature surveys, we hypothesize that combining a Halbach PM array with an eccentric PM pole shape offers strong potential for enhancing the electromagnetic performance of SPM generators, particularly in wind power applications. The eccentric pole shape improves the magnetic field distribution and effectively reduces cogging torque, while the Halbach array increases air-gap flux density on the stator side and suppresses flux leakage toward the rotor, thereby enhancing the induced voltage and output power. To the best of our knowledge, this specific combination of Halbach magnetization and eccentric PM geometry has not yet been reported, representing a meaningful research gap in the development of PMSGs. This study addresses that gap by proposing and optimizing an eccentric Halbach-array-based SPM generator tailored for wind energy systems. The analysis in this paper aims to investigate whether the magnetic field distribution of a Halbach PM array can be further improved by incorporating an eccentric PM shape and to evaluate the extent of performance enhancement in SPM generators achieved through this combined configuration. A single-objective optimization framework is employed to refine key design parameters, aiming to simultaneously enhance output power, reduce cogging torque, and improve overall electromagnetic performance through 2D finite element simulations.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces the topology of the proposed SPM generator. Section 3 outlines the design and optimization process. Section 4 presents the electromagnetic performance analysis based on two-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA). Finally, Section 5 concludes this study with key findings and observations.
2. Machine Topology
A 12-phase, 48-slot/22-pole-pair SPM generator, adopted from [32], was selected as a conventional structure for benchmarking purposes because of its superior power generation capability among low-speed wind generators, as illustrated in Figure 1a. The machine model was enclosed within a sufficiently large surrounding air region, and a Dirichlet boundary condition was applied at the outer boundary by setting the magnetic vector potential to zero. The conventional design features concentrated armature windings and rotor-mounted PMs arranged with alternating polarity on the surface. The proposed SPM generator, shown in Figure 1b, incorporates both a Halbach array configuration and eccentric PM shaping. It is initialized by applying a segmented Halbach array to each rotor pole, dividing a single magnet into three segments. The central segment maintains the conventional radial magnetization, while the two side magnets are tilted at adjustable angles, which are subject to optimization, as illustrated in Figure 2. This arrangement aims to intensify magnetic flux at the pole edges and reduce flux leakage, thereby enhancing overall power density. It should be noted that the pole arc angle is preserved throughout the modification process.
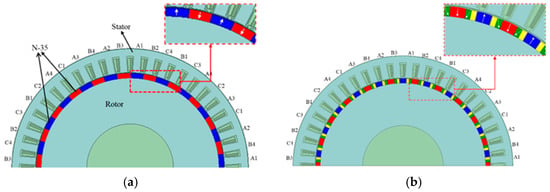
Figure 1.
Topology of 48 slots/22 pole-pair SPM generators. (a) Benchmark structure, created by the authors based on the dimensional specifications reported in [32]. (b). Proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator.
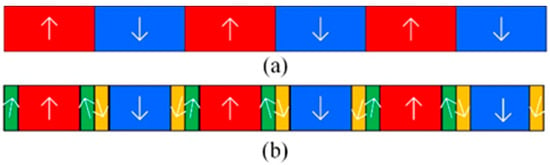
Figure 2.
Configuration of surface-mounted PMs. (a) Conventional PM arrangement. (b) Halbach PM array.
Following the transformation of the conventional structure into a Halbach PM array configuration, the rotor poles were further modified into an eccentric shape, as illustrated in Figure 3. This modification is based on the hypothesis that an eccentric PM shape can improve the magnetic field distribution within the machine. Specifically, the design aims to retain high magnetic field intensity in regions where it is functionally required while reducing the flux in areas where such intensity is unnecessary. This targeted redistribution of the magnetic field is intended to enhance flux utilization and overall electromagnetic performance. As illustrated in Figure 3, point O denotes the common center of both the inner and outer arc surfaces in the conventional pole design. In the eccentric pole configuration, O remains the center of the inner arc, while the center of the outer arc is shifted to a new position, O’. The magnet height is denoted by hm, and Rr represents the inner radius of the rotor. For the conventional structure, the outer radius is defined as Rm, whereas in the eccentric configuration, the outer radius becomes R0, with the eccentricity defined by the offset distance d between O and O’. The specifications of the design parameters used for comparison between the conventional SPM generator and the optimal structure of the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator are summarized in Table 1.
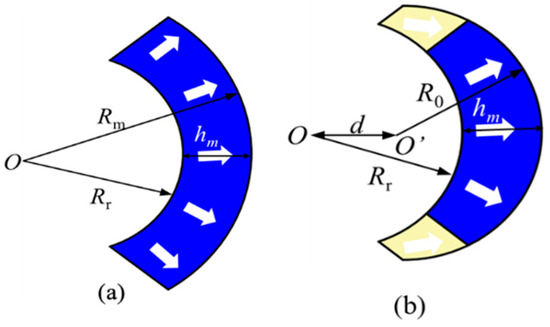
Figure 3.
Shape of PM pole. (a) Conventional pole shape. (b) Eccentric pole shape.

Table 1.
Structural parameters of the conventional and the proposed optimal SPM generators.
3. Design Optimization
To enhance the power generation capability of the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator for wind power applications, a GA was employed to optimize the key design parameters. The design and optimization process comprises four main steps, as illustrated in Figure 4 and detailed below.
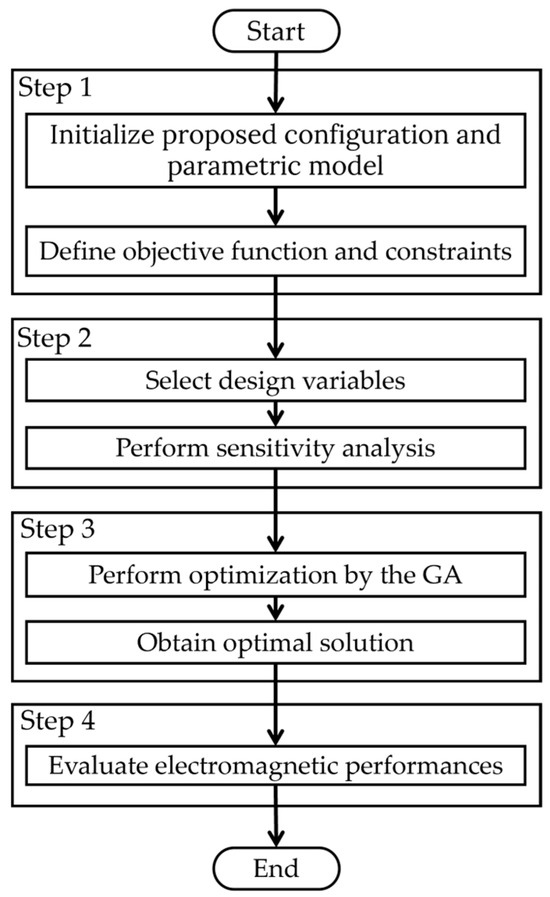
Figure 4.
Flowchart of the optimization design process.
- Step 1: Define the objective function and design constraints.
- Step 2: Define the design variables and then perform a sensitivity analysis to determine their impact on the objective function.
- Step 3: Optimize the design variables using the GA.
- Step 4: Evaluate the performance of the optimized structure.
3.1. Objective Function and Constraints
As the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator is specifically designed for wind power generation, the objective function is prioritized to maximize power output. The optimization is subject to the following constraints:
- (1)
- The optimization is conducted under identical operating conditions, with a rated speed of 500 rpm and a resistive load of 58 Ω.
- (2)
- The stator geometry, outer and inner rotor diameters, stack length, and shaft dimensions are kept consistent with those of the conventional design.
- (3)
- All structural components of the proposed generator are constructed using the same materials as those employed in the conventional machine.
- (4)
- The total PM volume in the proposed design does not exceed that of the benchmark structure.
3.2. Design Variables and Sensitivity Analysis
The design variables of the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator illustrated in Figure 5 were selected based on their direct influence on the spatial configuration of the Halbach permanent magnet array and the geometric characteristics of the eccentric PM shape. It comprises the arc span of the central magnet, αCPM, the magnetization angle of the side magnets, MSPM, and the radial distance between the eccentric pole center and the center of convention pole shape, d. The sensitivity analysis results shown in Figure 6 indicate that d exhibits the highest sensitivity index with respect to the objective function, followed by αCPM and MSPM. Based on these sensitivity indices, appropriate variation ranges for each design variable were defined to guide the optimization process. These ranges are summarized in Table 2, reflecting sensitivity-based constraints that ensure effective exploration of the design space.
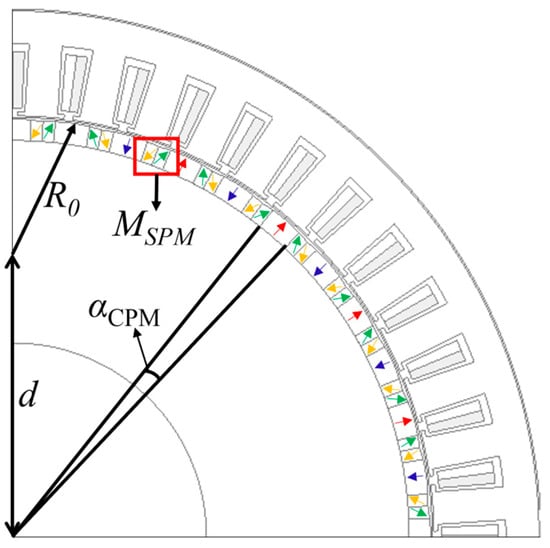
Figure 5.
Design variables.
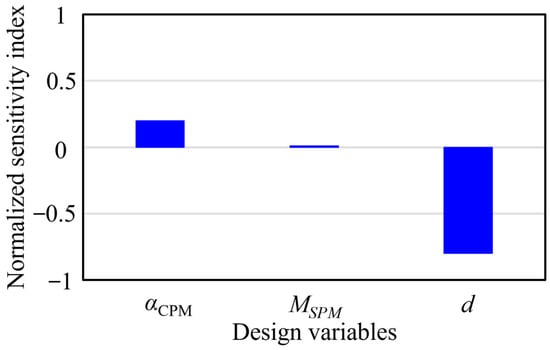
Figure 6.
Sensitivity of the design variables on the output power.

Table 2.
Range of design variables.
3.3. Optimization Using a Genetic Algorithm
The design variables of the proposed SPM generator were optimized using a GA. The GA parameters were set as follows: a population size of 600, a mutation probability of 0.85, and a crossover probability of 0.02. The optimization process was carried out over 508 generations to ensure convergence and stability of the solution. Table 3 presents both the initial and optimized values of the design parameters. The optimization results indicate that the proposed generator achieves an output power of 23.3 kW at rated conditions, representing a 25% improvement over the conventional design.

Table 3.
Initial and optimal values of design variables.
4. Performance Evaluation
This section presents a comparative analysis of the optimized SPM generator and the conventional design based on 2D FEA. Both machines were evaluated at a rated speed of 500 rpm under no-load and on-load conditions. The key performance characteristics examined include magnetic flux distribution, no-load EMF, cogging torque, electromagnetic torque, torque ripple, power generation capability, losses, and efficiency.
4.1. No-Load Performance
Magnetic field distribution is a key indicator of magnet utilization in PM machines and is directly linked to the generator’s power generation capability. Figure 7 presents the magnetic flux distribution for both the conventional and proposed structures. In the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator, the flux exhibits a well-formed pole-to-pole circulation pattern with improved symmetry and a noticeably smoother path compared to the conventional design. The shortened and more uniform flux circulation in the rotor of the proposed structure suggests reduced magnetic reluctance and improved flux utilization. This enhancement is expected to contribute to lower cogging torque and enhanced utilization of PM, ultimately supporting improvements in EMF and power generation capability. These observations confirm the effectiveness of the proposed geometry in improving the key performance of low-speed SPM generators.
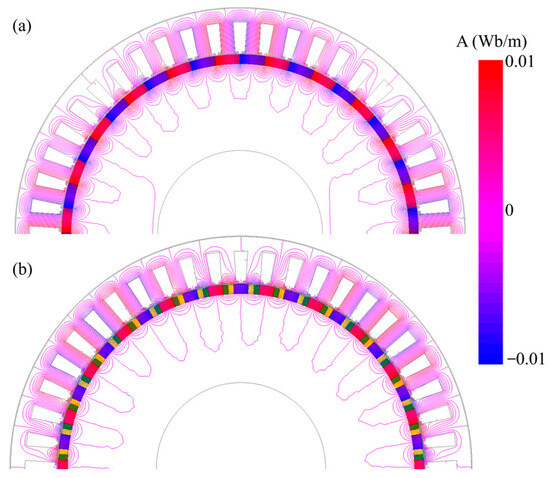
Figure 7.
Open-circuit flux distribution of (a) conventional and (b) proposed SPM generators.
Figure 8 compares the no-load EMF waveforms of the two structures. The proposed generator demonstrates a more sinusoidal waveform with an increase in the fundamental RMS voltage from 320.7 V to 344.8 V. Additionally, the THD is reduced from 18.7% to 12.9%. These improvements in waveform quality and EMF magnitude further support the potential of the proposed design to enhance power generation performance.
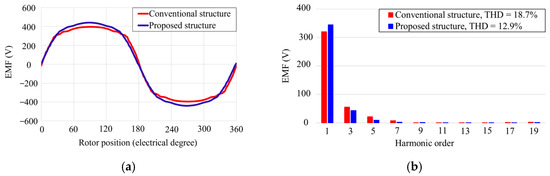
Figure 8.
Comparison of the open-circuit phase back-EMF profile between conventional and proposed SPM generators. (a) Waveforms. (b) Harmonics.
Cogging torque is a critical performance factor for permanent magnet generators, particularly in low-speed wind power applications where smooth starting and stable operation are essential. It is therefore considered one of the key performance indicators. Figure 9 presents a comparison of the cogging torque profiles between the proposed and conventional SPM generators. The proposed design shows a significant reduction in peak-to-peak cogging torque, decreasing from 3.7 N·m to 1.9 N·m, which represents a 48.6% improvement. This reduction is mainly attributed to the combination of the eccentric pole geometry and the optimized Halbach magnetization pattern, both of which reduce the magnetic field concentration at the pole edges.
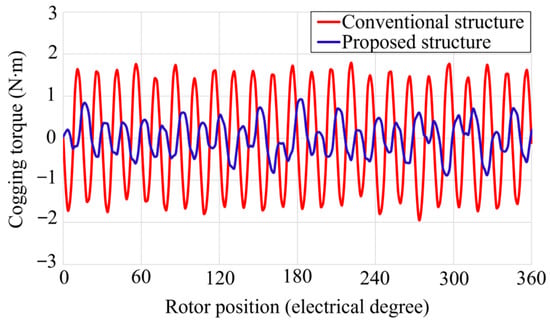
Figure 9.
Comparison of cogging torque waveforms.
4.2. On-Load Generation Performances
This section evaluates the performance of the proposed and conventional SPM generators under on-load conditions at a rated speed of 500 rpm. The power generation capability was analyzed at a rated resistive load of 58 ohms per phase, as well as under varying load conditions. The electromagnetic torque characteristics, shown in Figure 10, indicate that the proposed SPM generator produces 22% higher torque compared to the conventional design, along with a 2.6 times reduction in torque ripple. This improvement is attributed to the enhanced air-gap magnetic flux density achieved through the Halbach PM arrangement and eccentric pole shaping, which together improve flux concentration.
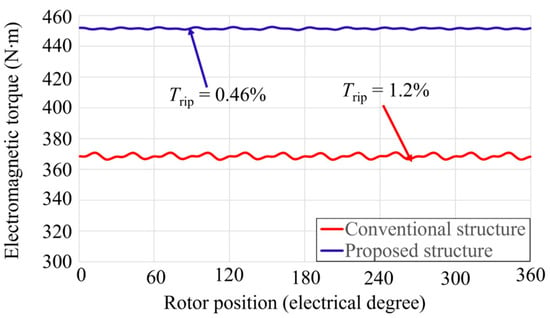
Figure 10.
Comparison of on-load electromagnetic torque waveforms between the conventional and proposed designs at a rated speed of 500 rpm.
Table 4 summarizes the comparative performance of both generators under the rated resistive load. The proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator delivers higher phase voltage and current, resulting in a 25% increase in output power. In terms of magnet utilization, the proposed design achieves 26.3% higher power output per unit volume of PM compared to the conventional structure. Although the proposed generator exhibits increased iron and magnet losses due to higher flux density in the core and magnets, and higher copper loss resulting from increased phase current, its overall efficiency remains superior to that of the conventional design. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed configuration in improving power density and performance while maintaining efficient operation.

Table 4.
Performance comparison at a rated speed of 500 rpm and a resistive load of 58 Ω.
To evaluate the power generation capability of the proposed eccentric Halbach array SPM generator, its output power across various loads and efficiency over a range of operating speeds were evaluated, as shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12, respectively. The results in Figure 11 demonstrate that the proposed generator consistently delivers higher output power than the conventional structure across the entire load range, confirming its superior power generation capability under varying load conditions.
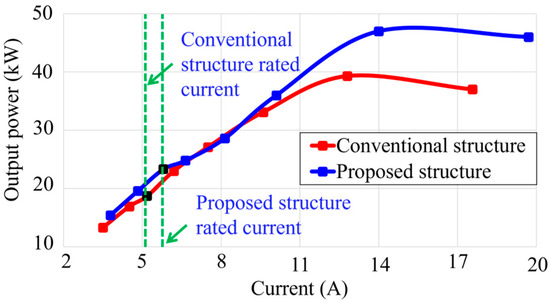
Figure 11.
Comparison of output power at different load currents at 500 rpm.
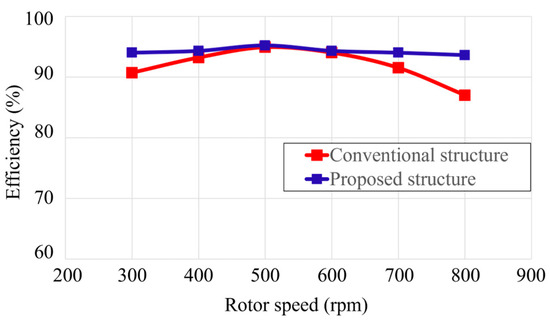
Figure 12.
Comparison of efficiency at various rotor speeds under a rated load of 58 Ω.
Figure 12 presents an efficiency comparison of both generators at different rotor speeds, evaluated under the rated resistive load of 58 Ω. The proposed generator maintains higher efficiency than the conventional design throughout all speeds. These findings validate the effectiveness of the eccentric Halbach array technique in enhancing power generation capability. Hence, the proposed design demonstrates strong potential as a high-performance solution for low-speed wind power generation. Improved generator performance enables better wind resource utilization and reduces land and infrastructure needs, thus supporting a cleaner energy transition and advancing sustainability goals. Future work should include comprehensive experimental validation to substantiate the analytical results. Additionally, the increased production costs associated with the customized Halbach array configuration and eccentric PM shaping warrant careful economic assessment during the design optimization process.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes an eccentric Halbach PM array pole shape to enhance the power generation capability of SPM generators specifically designed for low-speed wind power generation. The Halbach array is first applied to a conventional PM pole to improve flux focusing and reduce magnetic leakage. The eccentric PM shape is subsequently introduced to further enhance the magnetic field distribution. A genetic algorithm is employed to optimize the design parameters through 2D finite element simulations. The results confirm that the proposed design improves flux concentration and electromagnetic performance across the machine. Compared to the conventional structure, the proposed SPM generator achieves a 7.5% increase in electromotive force and a 7.5% reduction in total harmonic distortion. Cogging torque is reduced by 48.6%, significantly improving starting and low-speed operation. Under load, the generator delivers 22% higher average torque with 2.6 times lower ripple, contributing to smoother performance. At rated conditions, the output power improves by 25%, with consistently higher generation across various load levels. Importantly, the power per magnet volume increases by 26.3%, indicating better PM utilization. These improvements are consistent with the design assumptions involving the utilization of the Halbach array and eccentric PM shape. Although the design exhibits slightly higher losses, it maintains superior efficiency across all speed ranges. It should be noted that higher manufacturing costs for Halbach arrays and eccentric PMs present a practical limitation. These findings validate the effectiveness of the eccentric Halbach PM array in enhancing power generation capability and position the proposed SPMSG as a promising candidate for low-speed wind energy applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.M.T. and P.K.; methodology, Z.M.T.; software, Z.M.T.; data curation, Z.M.T.; formal analysis, Z.M.T., P.S., N.F., A.S. and P.K.; writing—original draft, Z.M.T.; validation, P.K.; supervision, P.K.; funding acquisition, P.K.; writing—review and editing, P.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received funding support from the Fundamental Fund of Khon Kaen University from National Science, Research and Innovation Fund or NSRF, Thailand.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhende, C.N.; Mishra, S.; Malla, S.G. Permanent magnet synchronous generator-based standalone wind energy supply system. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2011, 2, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder, H.; Ferreira, J.A.; Jensen, B.B.; Abrahamsen, A.B.; Atallah, K.; McMahon, R.A. Trends in wind turbine generator systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zuo, Y.; Chau, K.T.; Zhao, W.; Lee, C.H.T. Modern electric machines and drives for wind power generation: A review of opportunities and challenges. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2021, 15, 1864–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.D.S.; Reis, M.R.C.; Araujo, W.R.H.; Martins, M.S.R.; Ribeiro, L.E.B.; Rodrigues, C.G.; Coimbra, A.P.; Calixto, W.P.; Castaldo, P. Enhancement of the Performance of Switched Reluctance Generators in Low Wind Speed Conditions Using Advanced Tracking Techniques. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 5541150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo, J.; Martínez, J.; Probst, O. Experimental study of a small wind turbine for low- and medium-wind regimes. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 33, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. Overview of stator-permanent magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5087–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, F.; Jin, Z. Maximum power point tracking strategy for large-scale wind generation systems considering wind turbine dynamics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissayan, C.; Seangwong, P.; Chamchuen, S.; Fernando, N.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. Modeling and optimal configuration design of flux-barrier for torque improvement of rotor flux switching permanent magnet machine. Energies 2022, 15, 8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Liang, P.; Pei, Y.; Cheng, S. Magnet shape optimization of surface-mounted permanent-magnet motors to reduce harmonic iron losses. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lin, H. Comparative study of surface-mounted and interior permanent-magnet motors for high-speed applications. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hua, W. Design and analysis of surface-mounted permanent-magnet field-modulation machine for achieving high power factor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 4375–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, C.; Geng, Q.; Yan, Y. Modeling and analyzing of surface-mounted permanent-magnet synchronous machines with optimized magnetic pole shape. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of a novel surface-mounted permanent magnet motor with hybrid magnets for low cost and low torque pulsation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Madanzadeh, S.; Khan, S.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Akhtar, F.; Ro, J.-S. Effect of the magnet shape on the performance of coreless axial flux permanent magnet synchronous generator. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, E.; Dalcalı, A. Effects of magnet shapes on total harmonic distortion and cogging torque in a permanent magnet synchronous generator for wind turbines. Clean Energy 2023, 7, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, A.; Aini, Z. Analysis of the Effect of Magnetic Thickness and Rotating Speed on PMSG 24 Slot 16 Pole Characteristics. PROtek J. Ilm. Tek. Elektro 2023, 10, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, I.; Niemelä, M.; Ponomarev, P.; Pyrhönen, J. Rotor surface ferrite permanent magnets in electrical machines: Advantages and limitations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5314–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wang, D. A novel design method of permanent magnet synchronous generator from perspective of permanent magnet material saving. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 32, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, H.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M. Suitable design of a PMSG for a small-scale wind power generator. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 15–18 November 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Wang, K.; Cao, R.; Liu, C. Design of five phase SPM machine considering third harmonic current injection. In Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Seangwong, P.; Fernando, N.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. E-Core and C-Core switched flux permanent magnet generators for wind power generation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138590–138601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A. An analytical expression for magnet shape optimization in surface-mounted permanent magnet machines. Math. Comput. Appl. 2018, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Optimization design of halbach permanent magnet motor based on multi-objective sensitivity. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2020, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jing, L.; Qu, R.; Li, D. Analysis and application of discrete Halbach magnet array with unequal arc lengths and unequally changed magnetization directions. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2017, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Seangwong, P.; Fernando, N.; Jongudomkarn, J.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. A novel double stator hybrid-excited flux reversal permanent magnet machine with Halbach arrays for electric vehicle traction applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 113255–113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshibani, S.; Dutta, R.; Agelidis, V.G. Optimization of a MW Halbach PMSG for wind turbine applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 1963–1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Wang, Q. Optimum split ratio in surface-mounted permanent magnet machines with pieced Halbach magnet array. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Lu, H.; Zhao, C.; Shen, H. Influence of different Halbach arrays on performance of permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA 2020), Dalian, China, 27–29 June 2020; pp. 994–998. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, W.; Gao, Q.; Lenwari, W. Optimal design of a 5-MW double-stator single-rotor PMSG for offshore direct drive wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 56, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Dalcalı, A.; Çelik, E.; Sakar, S. Cogging torque reduction by optimal design of PM synchronous generator for wind turbines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17593–17600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, R.; Mortazavizadeh, S.; Salehian, M.; Campos-Gaona, D.; Anaya-Lara, O. Design optimization of inner and outer-rotor PMSGs for X-ROTOR wind turbines. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2024, 18, 2605–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Hua, W.; Soulard, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, M. Electromagnetic performance comparison between 12-phase switched flux and surface-mounted PM machines for direct-drive wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).