Leaf–Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry and Adaptation in Karst Plant Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Setting
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Determination of Plant Functional Characteristics and Soil Samples
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
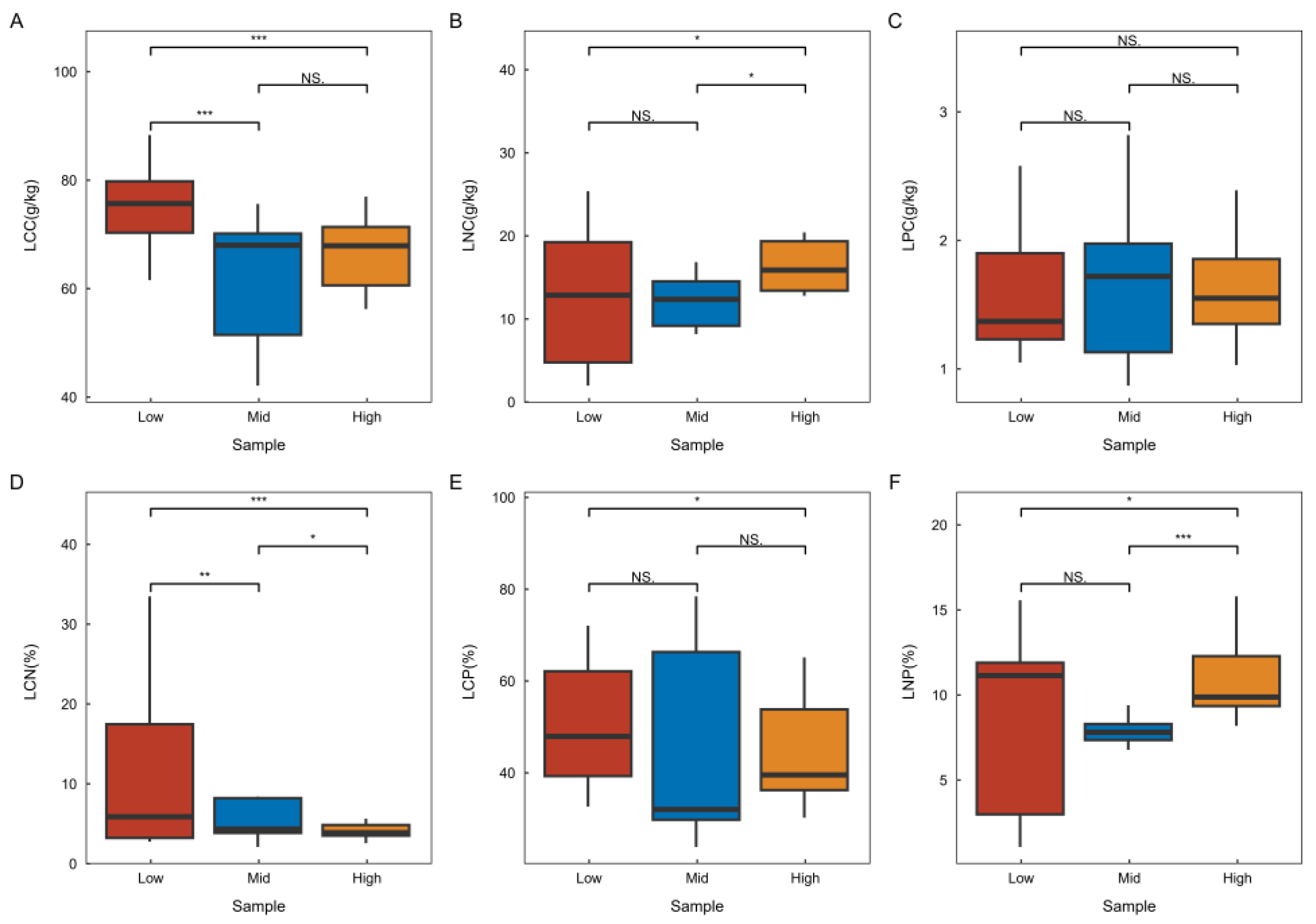
3.1. Chemometric Characteristics of Leaves Across Different Latitude Gradients
3.2. Soil Stoichiometry Characteristics Across Different Latitude Gradients
3.3. Variation in Leaf and Soil Stoichiometry Across Different Latitude Gradients
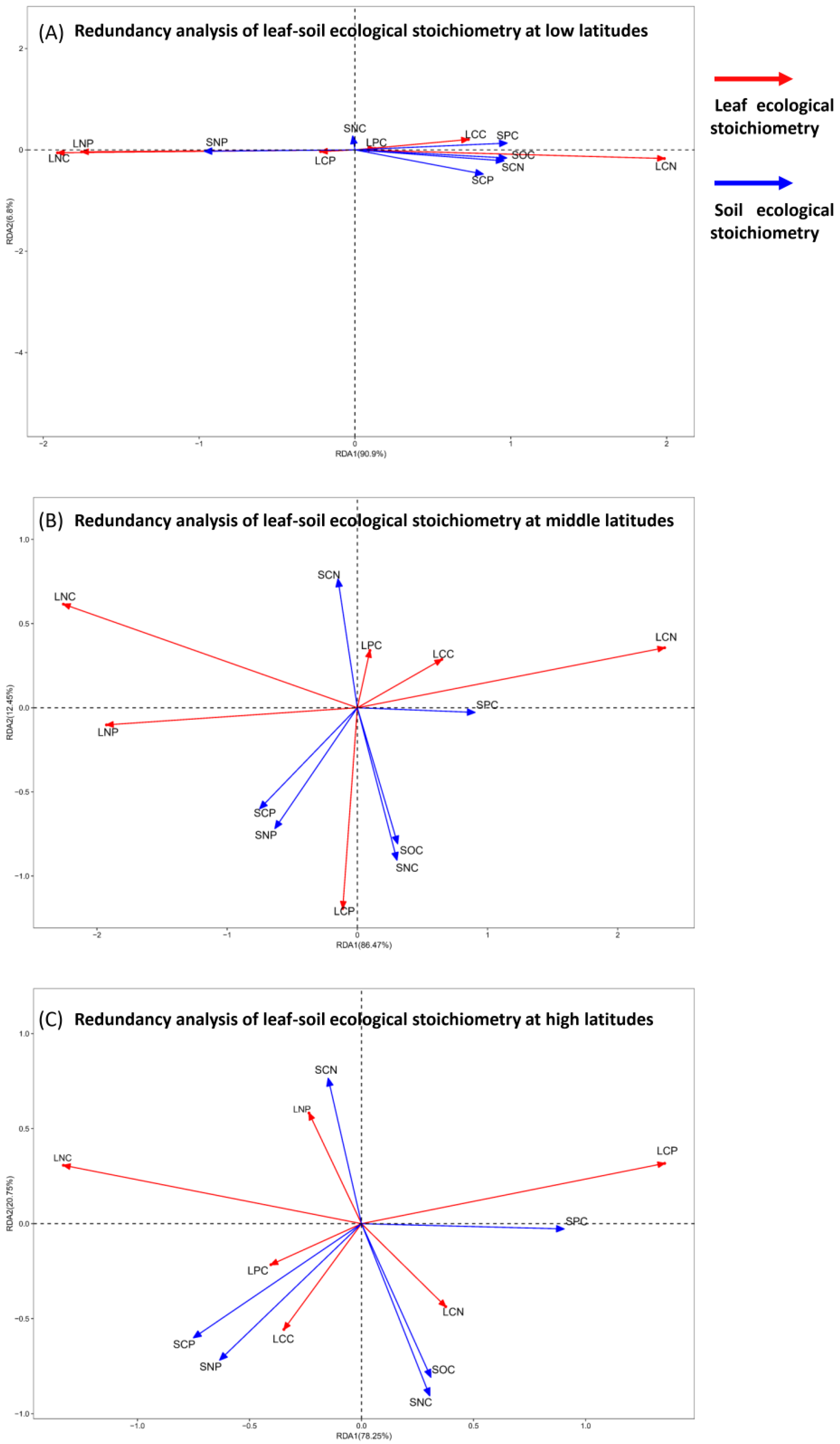
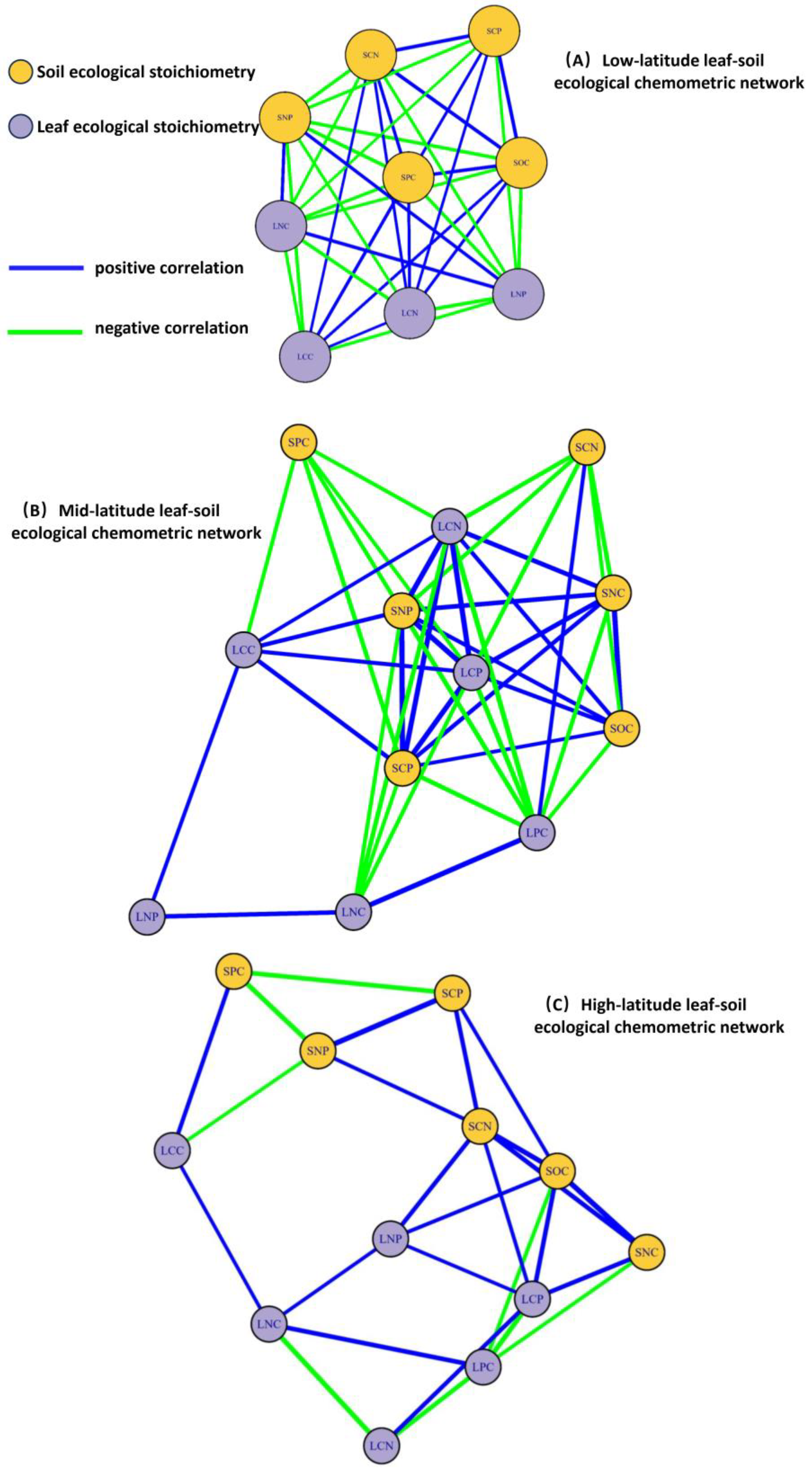
3.4. Correlation Between Leaf and Soil Stoichiometry Across Different Latitude Gradients
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Uptake and Utilization by Plant Leaves Across Different Latitude Gradients
4.2. Changes in Soil Stoichiometry Across Different Latitude Gradients
4.3. Chemometric Relationships Between Plant Leaves and Soil Across Different Latitude Gradients
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Gong, Y.; Lafleur, P.; Wu, Y. Patterns and drivers of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry in Southern China’s grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, M.; Preece, C. Bryophyte C: N: P stoichiometry, biogeochemical niches and elementome plasticity driven by environment and coexistence. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Jin, Q.; Huang, J.F.; Hei, J.; Lin, S.Y.; Huang, Z.; Hou, N.; Wang, W.Q. Characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and their ecological stoichiometric ratios in different habitats of East Lake Wetland, Fuzhou. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 21, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.Y. Stoichiometry characteristics of soil nutrient elements and its influencing factors in typical in karst rocky desertification ecosystems, southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 6580–6593. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.L.; Yu, Y.H.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhong, X.P. Contents and ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil nutrients under different land utilization forms in stony desertification area. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 31, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Yu, L.F.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y.N.; Yan, L.B. C: N: P stoichiometry of leaf-litter-soil continuum in secondary forests of the rocky desertification regions of the karst plateau. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2020, 26, 681–688. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Yu, G.R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar]
- Guittar, J.; Goldberg, D.; Klanderud, K.; Telford, R.J.; Vandvik, V. Can trait patterns along gradients predict plant community responses to climate change? Ecology 2016, 97, 2791–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Li, T.; He, B.; Feng, M.; Liang, K. Effects of vegetation succession on topsoil C, N, and P contents and stoichiometry following agricultural abandonment in a representative karst trough valley. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 192, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Li, Y.B.; Li, R.L. Karst rocky desertification: Formation background, evolution and comprehensive taming. Quat. Sci. 2003, 23, 657–666. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Yan, X.Y.; Xie, J.Q.; Hou, M.T.; Chen, D.M.; Zang, L.P.; Liu, Q.F.; Sui, M.Z.; Zhang, G.Q. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests. Biodiv. Sci. 2024, 32, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Zhou, G.; Zu, L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Sui, G.; He, Y.; Liu, Q. Multi-Trophic Species Diversity Contributes to the Restoration of Soil Multifunctionality in Degraded Karst Forests through Cascading Effects. Forests. 2024, 15, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Z.; He, J.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, J.; et al. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiv. Sci. 2009, 17, 533–548. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 2017-2011; Determination of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium in Plants. Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2011.
- LY/T1228-2015; Determination of Nitrogen in Forest Soil. Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2015.
- LY/T 1232-2015; Phosphorus Determination Methods of Forest Soils. Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Agren, G.I. The C: N: P stoichiometry of autotrophs–theory and observations. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, G.D.; Wang, W.D.; Xu, Z.L.; Jin, Y.Y.; Bai, Y.Y. C, N, P stoichiometric characteristics of tree, shrub, herb leaves and soil in Kanas natural forests of Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecolo. Sin. 2023, 43, 8749–8758. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.J.; Yu, G.R.; Jiang, C.M.; Fang, H.J.; Sun, X.M. Stoichiometric characteristics of leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus of 102 dominant species in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect of East China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Prentice, I.C.; Wright, I.J.; Evans, B.J.; Togashi, H.F.; Caddy-Retalic, S.; Mclnerney, F.A.; Sparrow, B.; Leitch, E.; Lowe, A.J. Components of leaf-trait variation along environmental gradients. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.; Niklas, K.J.; Han, W.; Kattge, J.; Rich, P.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, H.; et al. Global leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry and their scaling exponent. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Reich, P.B.; Schmid, B.; Shrestha, N.; Feng, X.; Lyu, T.; Maitner, B.S.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, D.; et al. Leaf size of woody dicots predicts ecosystem primary productivity. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Yu, M.; Geoff Wang, G.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, X.R. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across forty-two woody species in Southeast China. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 44, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mam, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; An, S. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of robinia pseudoacacia forest soil in different latitudes of loess plateau. Acta Pedologica Sin. 2013, 50, 818–825. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.S.; Wang, L. Leaf nitrogen: Phosphorus stoichiometry across Chinese grassland biomass. Oecologia 2008, 155, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Wu, Y.; Tang, L.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, L.P.; He, J.S.; Fang, J.Y. Leaf carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across plant species in Beijing and its periphery. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2009, 45, 855–860. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, M.; An, S. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics and physical-chemical properties of soils at different latitudes on the loess plateau. J. Nat. Resou. 2015, 30, 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.W.; Chen, S.L.; Yang, Q.P.; Li, Y.C. Effects of stand density on Oligostachyum lubricum leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry and nutrient resorption. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 893–899. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Chang, S.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, H.J.; Song, C.C.; He, P.; Sun, X.J. Plant and soil ecological stoichiometry with vertical zonality on the northern slope of the middle Tianshan Mountains. Acta Ecolo. Sin. 2016, 36, 4363–4372. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Hu, T.; Wang, J.; Gong, Y.; Luo, C. Seasonal variation of soil nitrogen pools and microbes under natural evergreen broadleaved forest and its artificial regeneration forests in Southern Sichuan Province, China. Acta Ecolo. Sin. 2011, 31, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, M.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X. Ecostoichiometric characteristics of dominant plant leaves-soil ecology in different communities of desert steppe in Yanchi county, Ningxia. Acta Agrectir. Sin. 2021, 29, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
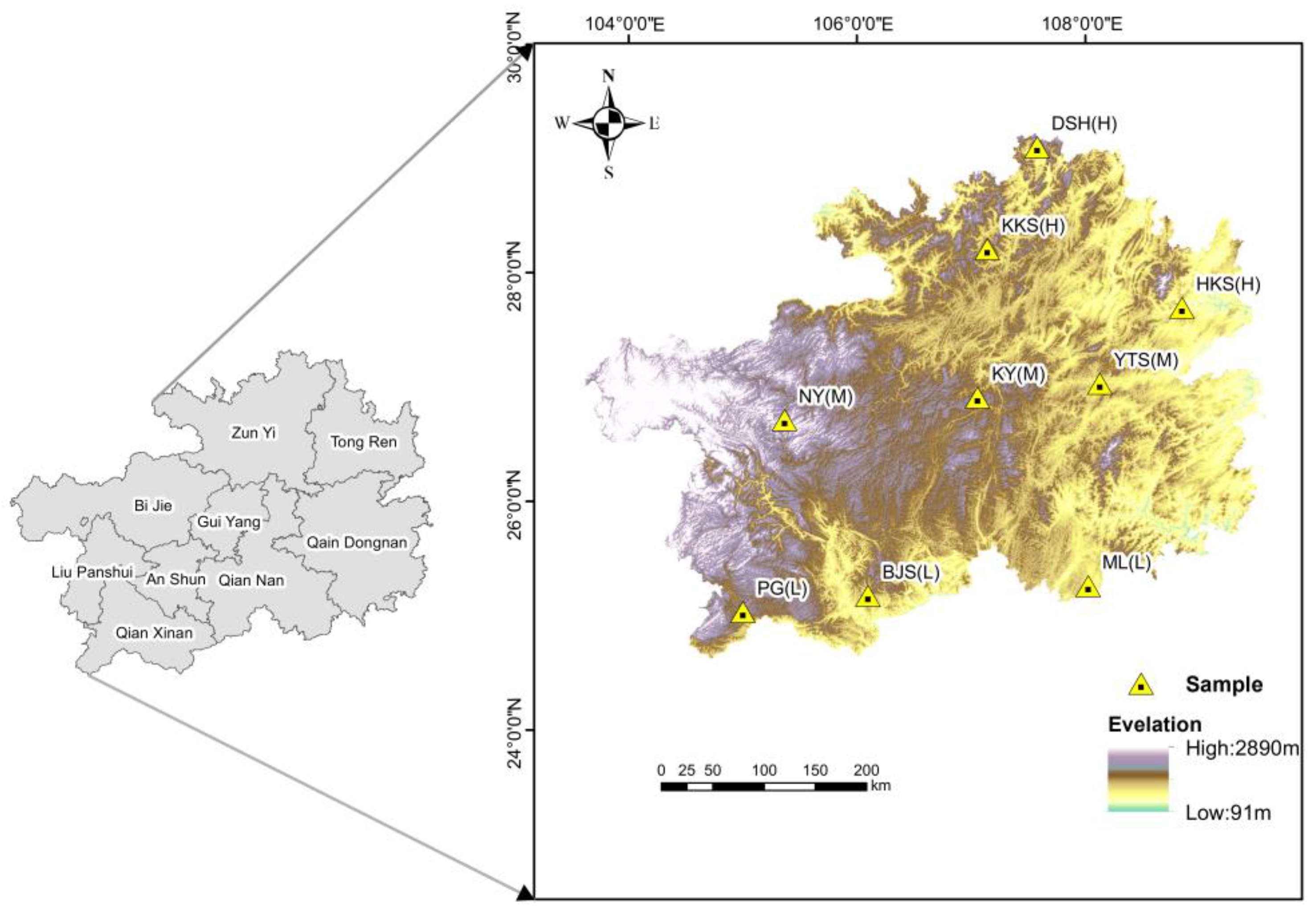

| Latitude | Sample | Dominant Species | Coverage (%) | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | ML | Cornus wilsoniana, Lindera communis, Nandina domestica, Selaginella tamariscina | 95 | 646.32 |
| PG | Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia, Cinnamomum glanduliferum, Callicarpa macrophylla Vahl | 76 | 1152.3 | |
| BJS | Quercus acutissima, Albizia julibrissin, Arytera littoralis | 78 | 752.06 | |
| Middle | KY | Cunninghamia lanceolata, Cyclobalanopsis myrsinifolia, Castanea seguinii Dode | 72 | 1095.21 |
| YTS | Liquidambar formosana, Rhus chinensis, Styrax confuses, Pteridium aquilinum | 82 | 835.61 | |
| NY | Betula luminifera, Lithocarpus glaber | 84 | 1818.32 | |
| High | KKS | Cunninghamia lanceolata, Fagus longipetiolata Seem, Eurya japonica Thunb | 91 | 1498.61 |
| HKS | Cunninghamia lanceolata, Liquidambar formosana Hance, Symplocos sumuntia, Camellia oleifera | 85 | 685.11 | |
| DSH | Fagus longipetiolata, Cunninghamia lanceolata, Woonyoungia septentrionali, Synedrella nodiflora | 93 | 1239.5 |
| Type | Longitude | Factors | Maximum | Minimum | Mean Value | Fold | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | Low | LCC | 88.32 | 61.58 | 75.25 | 1.43 | 7.94 | 10.55 |
| LNC | 25.38 | 1.98 | 12.52 | 12.82 | 7.41 | 59.19 | ||
| LPC | 2.58 | 1.05 | 1.58 | 2.46 | 0.43 | 27.22 | ||
| LCN | 33.48 | 2.77 | 10.23 | 12.09 | 8.22 | 80.35 | ||
| LCP | 72.06 | 32.65 | 50.79 | 2.21 | 13.44 | 26.46 | ||
| LNP | 15.57 | 1.07 | 8.53 | 14.55 | 4.82 | 56.51 | ||
| Mid | LCC | 75.62 | 42.12 | 61.59 | 1.80 | 11.51 | 18.69 | |
| LNC | 32.14 | 8.20 | 13.71 | 3.92 | 6.87 | 50.11 | ||
| LPC | 2.82 | 0.87 | 1.65 | 3.24 | 0.58 | 35.15 | ||
| LCN | 8.41 | 2.1 | 5.29 | 4.00 | 2.21 | 41.78 | ||
| LCP | 78.44 | 23.86 | 42.98 | 3.29 | 19.59 | 45.58 | ||
| LNP | 11.38 | 6.78 | 8.16 | 1.68 | 1.27 | 15.56 | ||
| High | LCC | 76.97 | 56.23 | 66.40 | 1.37 | 6.45 | 9.71 | |
| LNC | 29.48 | 12.84 | 17.21 | 2.30 | 4.99 | 28.99 | ||
| LPC | 2.39 | 1.03 | 1.61 | 2.32 | 0.37 | 22.98 | ||
| LCN | 5.49 | 2.57 | 4.08 | 2.14 | 0.92 | 22.55 | ||
| LCP | 65.15 | 30.23 | 43.43 | 2.16 | 10.86 | 25.01 | ||
| LNP | 15.53 | 8.26 | 10.81 | 1.88 | 2.22 | 20.54 | ||
| Soil | Low | SOC | 72.89 | 8.64 | 24.84 | 8.44 | 21.34 | 85.91 |
| SNC | 5.28 | 2.69 | 3.96 | 1.96 | 0.63 | 15.91 | ||
| SPC | 1.83 | 0.53 | 0.92 | 3.45 | 0.43 | 46.74 | ||
| SCN | 26.32 | 2.73 | 6.61 | 9.64 | 6.60 | 99.85 | ||
| SCP | 59.37 | 16.17 | 23.64 | 3.67 | 11.37 | 48.10 | ||
| SNP | 7.27 | 1.85 | 5.07 | 3.93 | 1.78 | 35.11 | ||
| Mid | SOC | 25.53 | 4.64 | 13.90 | 5.50 | 5.60 | 40.29 | |
| SNC | 7.55 | 1.42 | 4.17 | 5.32 | 2.06 | 49.40 | ||
| SPC | 2.15 | 0.38 | 0.97 | 5.66 | 0.70 | 72.16 | ||
| SCN | 4.74 | 2.78 | 3.54 | 1.71 | 0.60 | 16.95 | ||
| SCP | 38.08 | 6.70 | 19.79 | 5.68 | 11.18 | 56.49 | ||
| SNP | 12.23 | 2.02 | 6.03 | 6.05 | 4.09 | 67.83 | ||
| High | SOC | 13.76 | 5.12 | 9.54 | 2.69 | 2.24 | 23.48 | |
| SNC | 3.82 | 1.87 | 2.91 | 2.04 | 0.50 | 17.18 | ||
| SPC | 0.90 | 0.39 | 0.63 | 2.31 | 0.16 | 25.40 | ||
| SCN | 3.63 | 2.65 | 3.24 | 1.37 | 0.28 | 8.64 | ||
| SCP | 25.82 | 7.67 | 16.25 | 3.37 | 5.25 | 32.31 | ||
| SNP | 7.44 | 2.77 | 4.95 | 2.69 | 1.40 | 28.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Tian, T.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, H. Leaf–Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry and Adaptation in Karst Plant Communities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135790
Wang Y, Fan Z, Tian T, Deng Y, Zhao H. Leaf–Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry and Adaptation in Karst Plant Communities. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135790
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Zuhong Fan, Tian Tian, Ying Deng, and Hong Zhao. 2025. "Leaf–Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry and Adaptation in Karst Plant Communities" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135790
APA StyleWang, Y., Fan, Z., Tian, T., Deng, Y., & Zhao, H. (2025). Leaf–Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Ecological Stoichiometry and Adaptation in Karst Plant Communities. Sustainability, 17(13), 5790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135790






