Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Patterns on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Taihang Mountains of Hebei Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
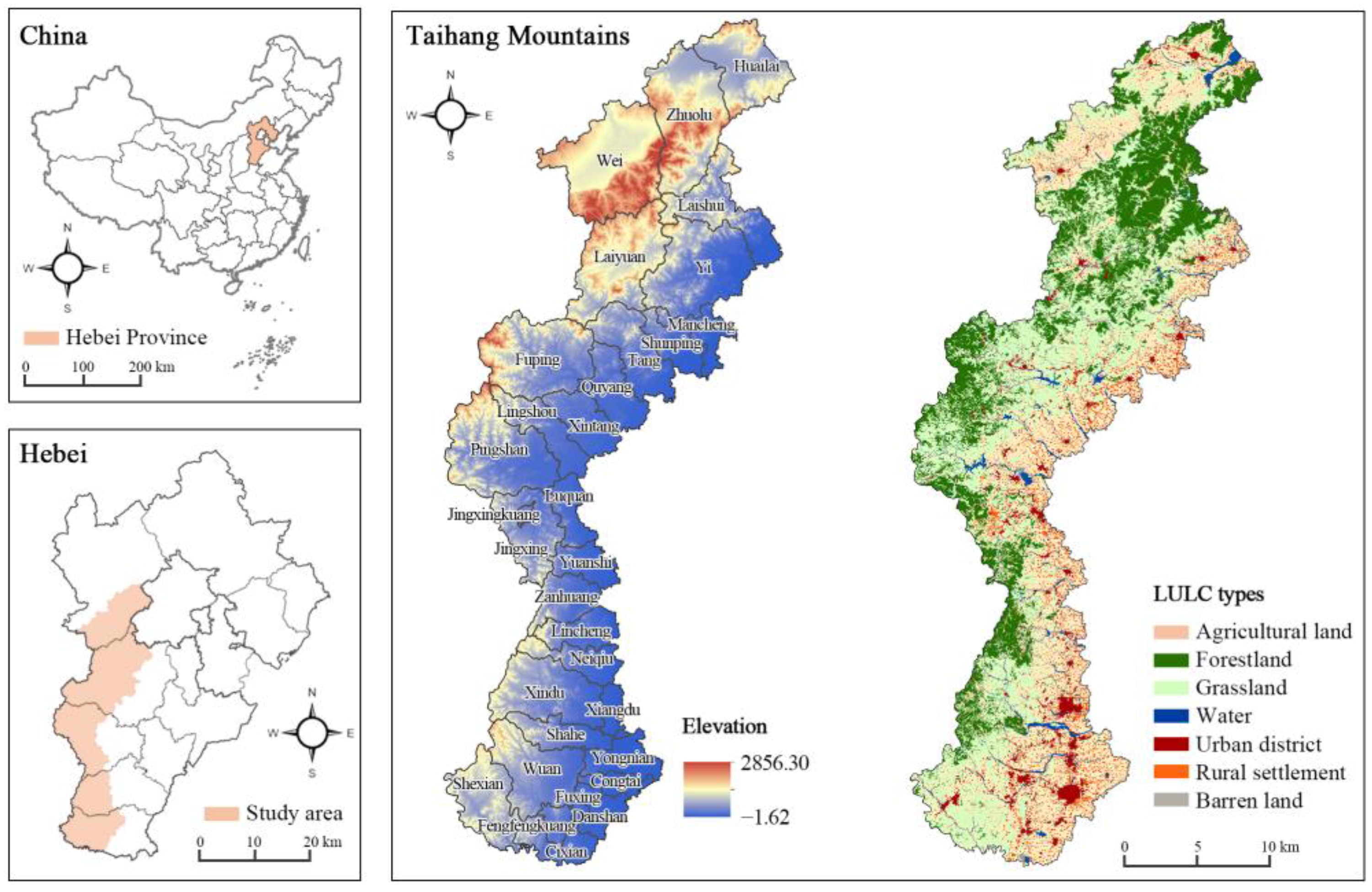
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Theoretical Framework
2.3. Data Sources
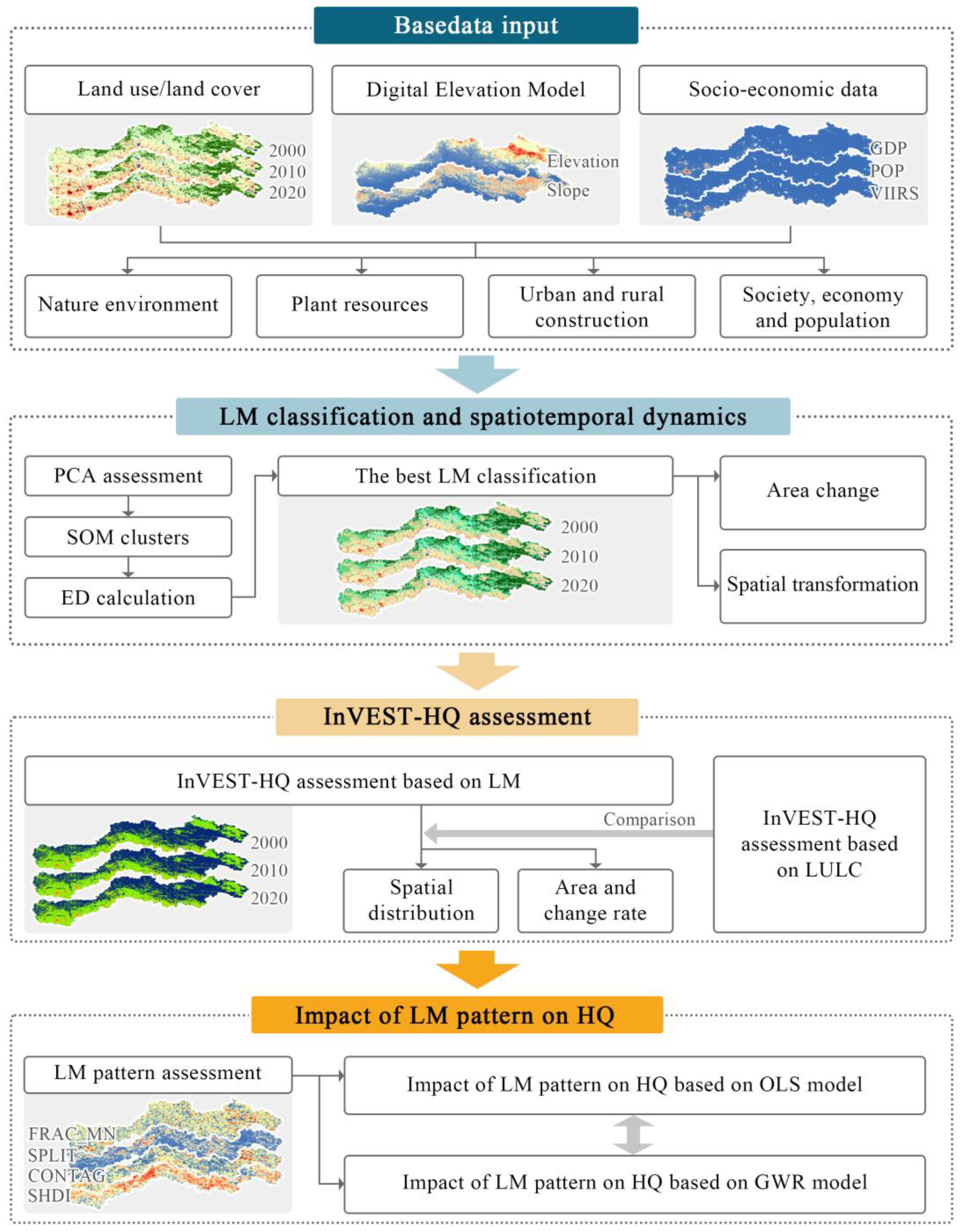
2.4. Research Method
2.4.1. Landscape Mosaic Classification
- Index system
- 2.
- PCA assessment
- 3.
- SOM cluster and ED assessment
2.4.2. Habitat Quality Evaluation
2.4.3. Landscape Mosaic Pattern Metrics
2.4.4. OLS and GWR Model
3. Results
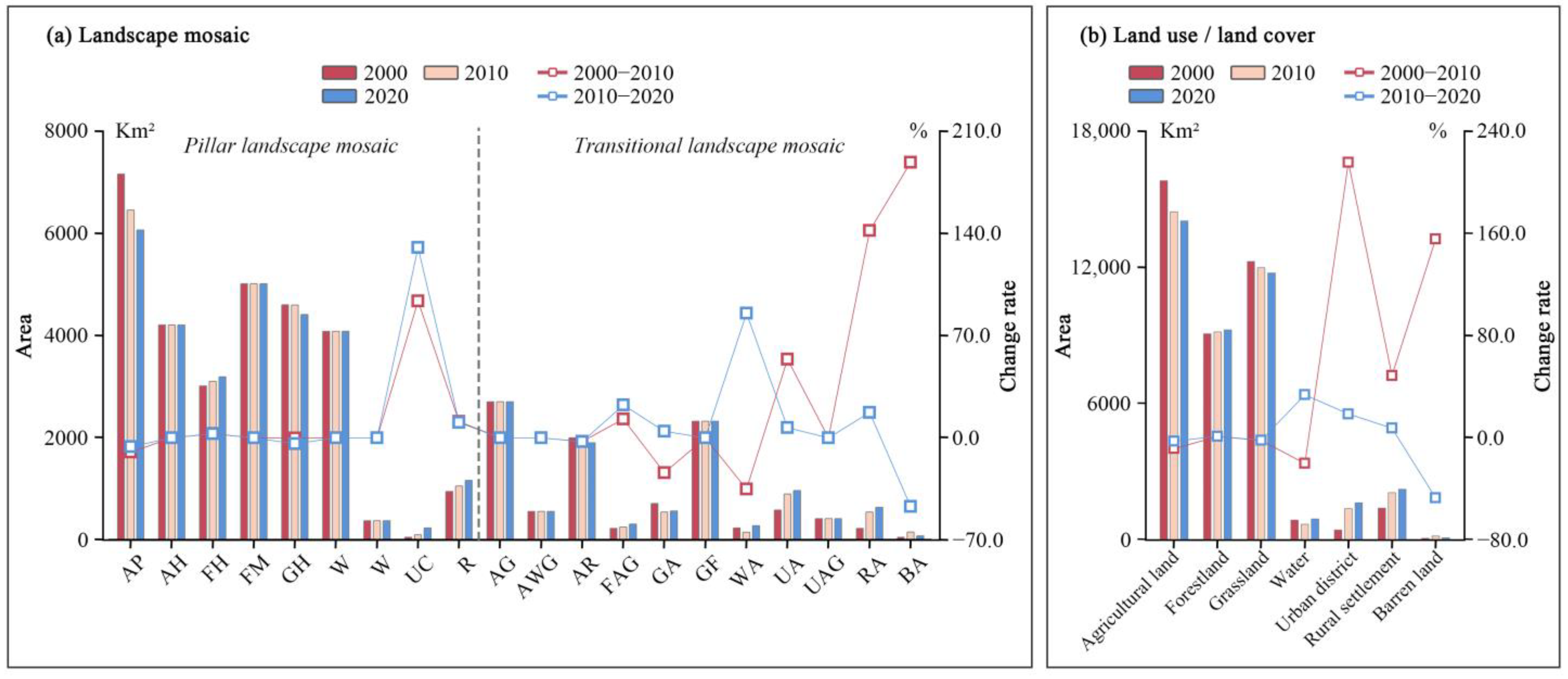
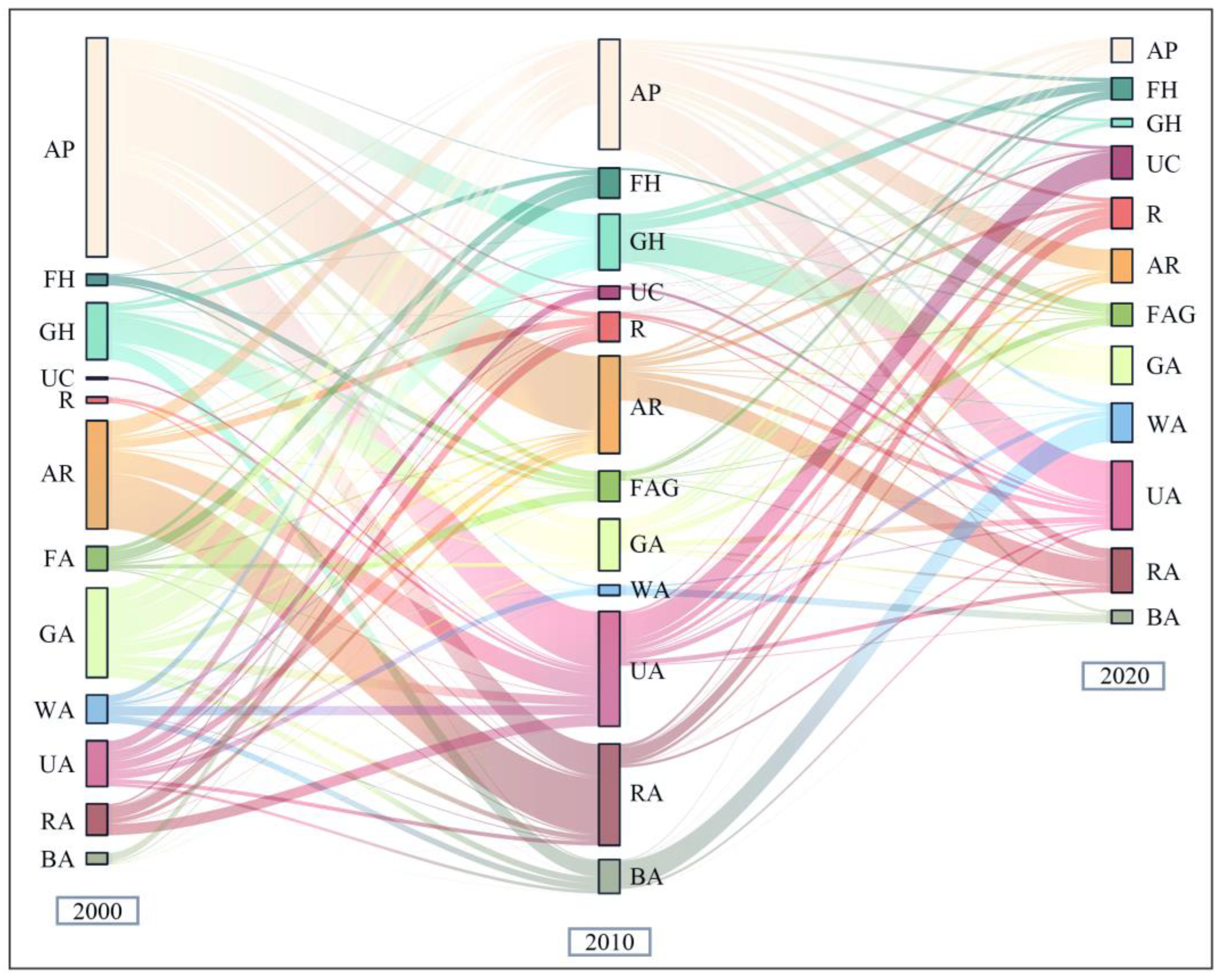
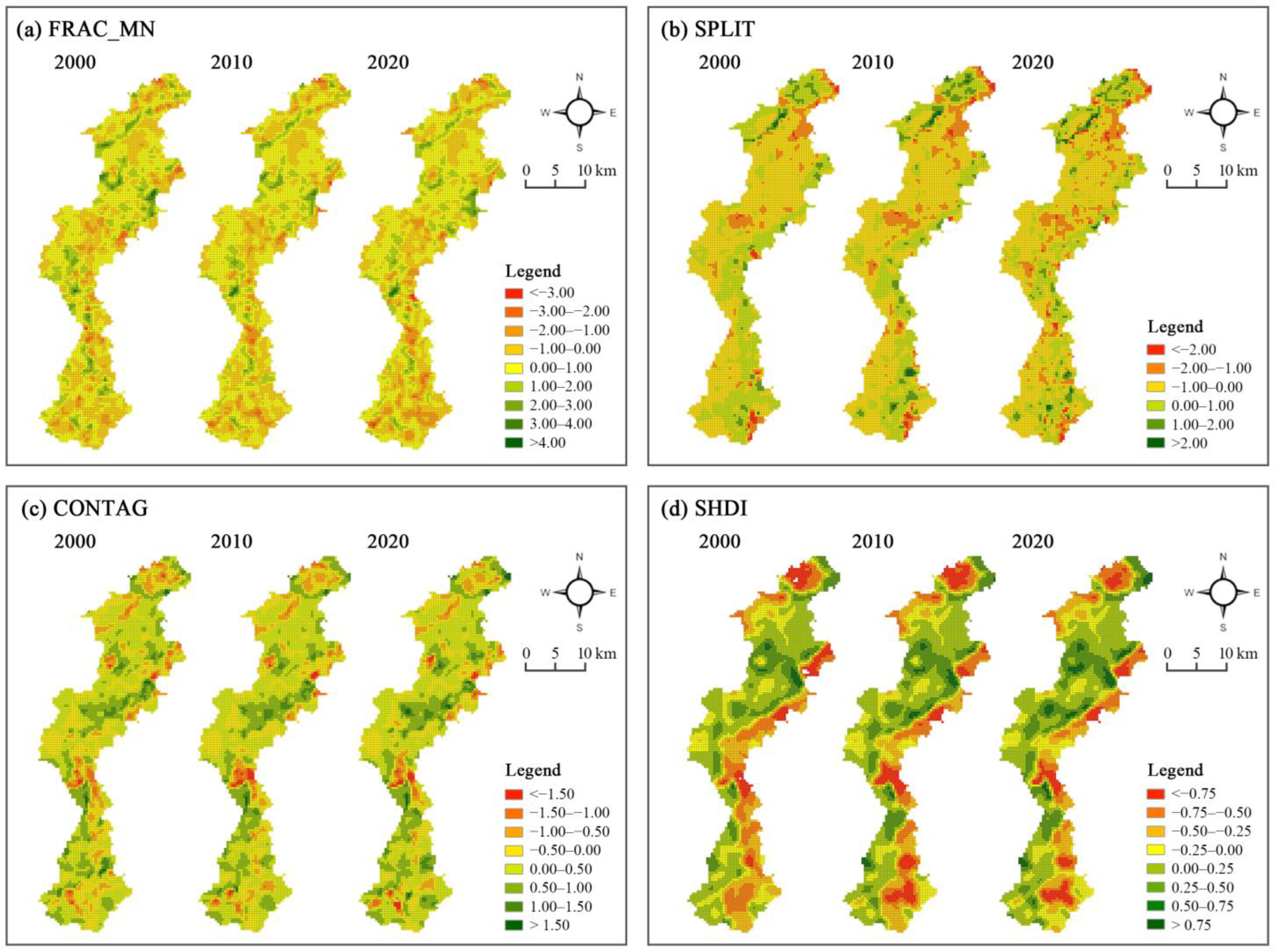
3.1. Classification of and Changes in Landscape Mosaic
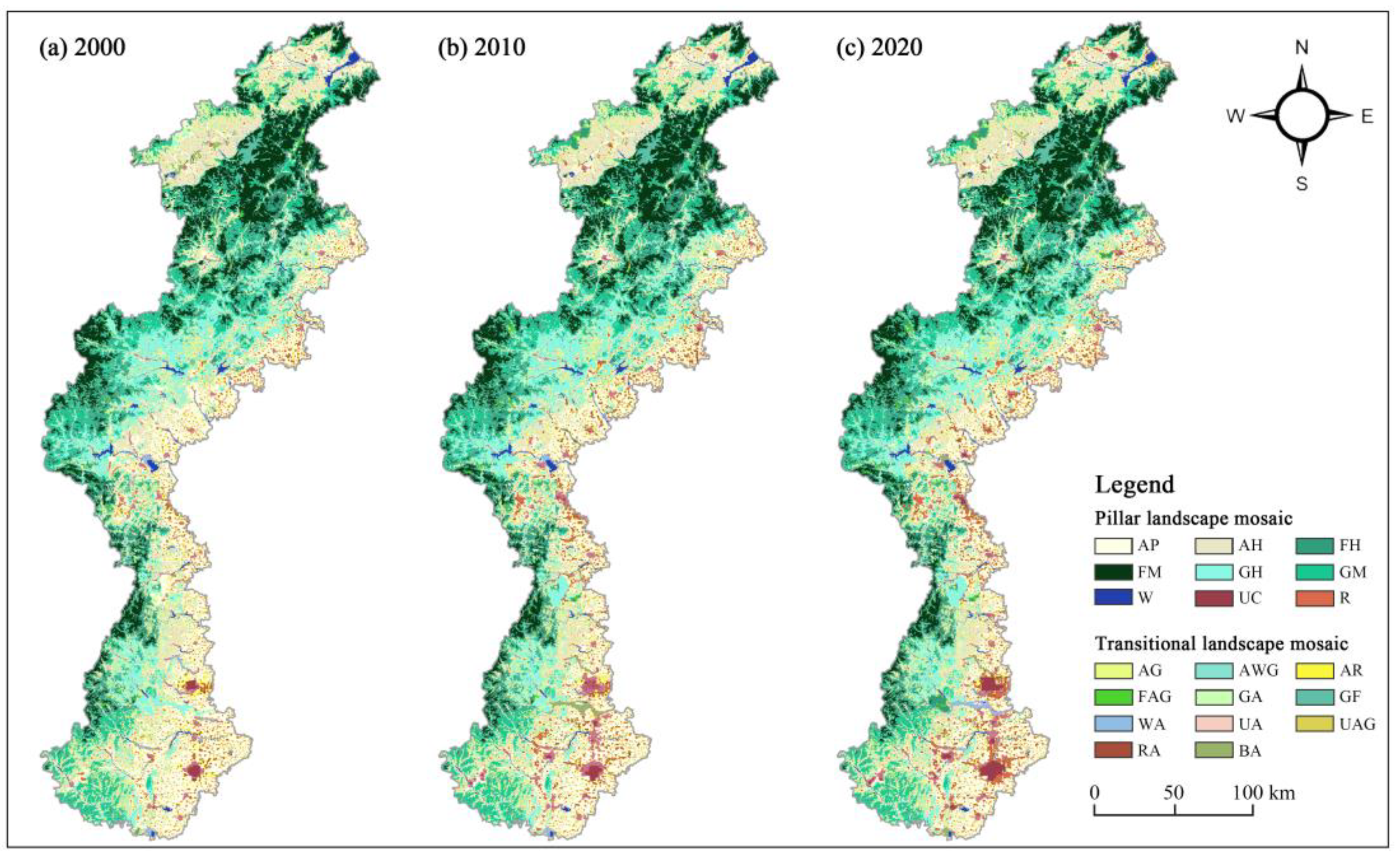
3.1.1. Classification of Landscape Mosaic
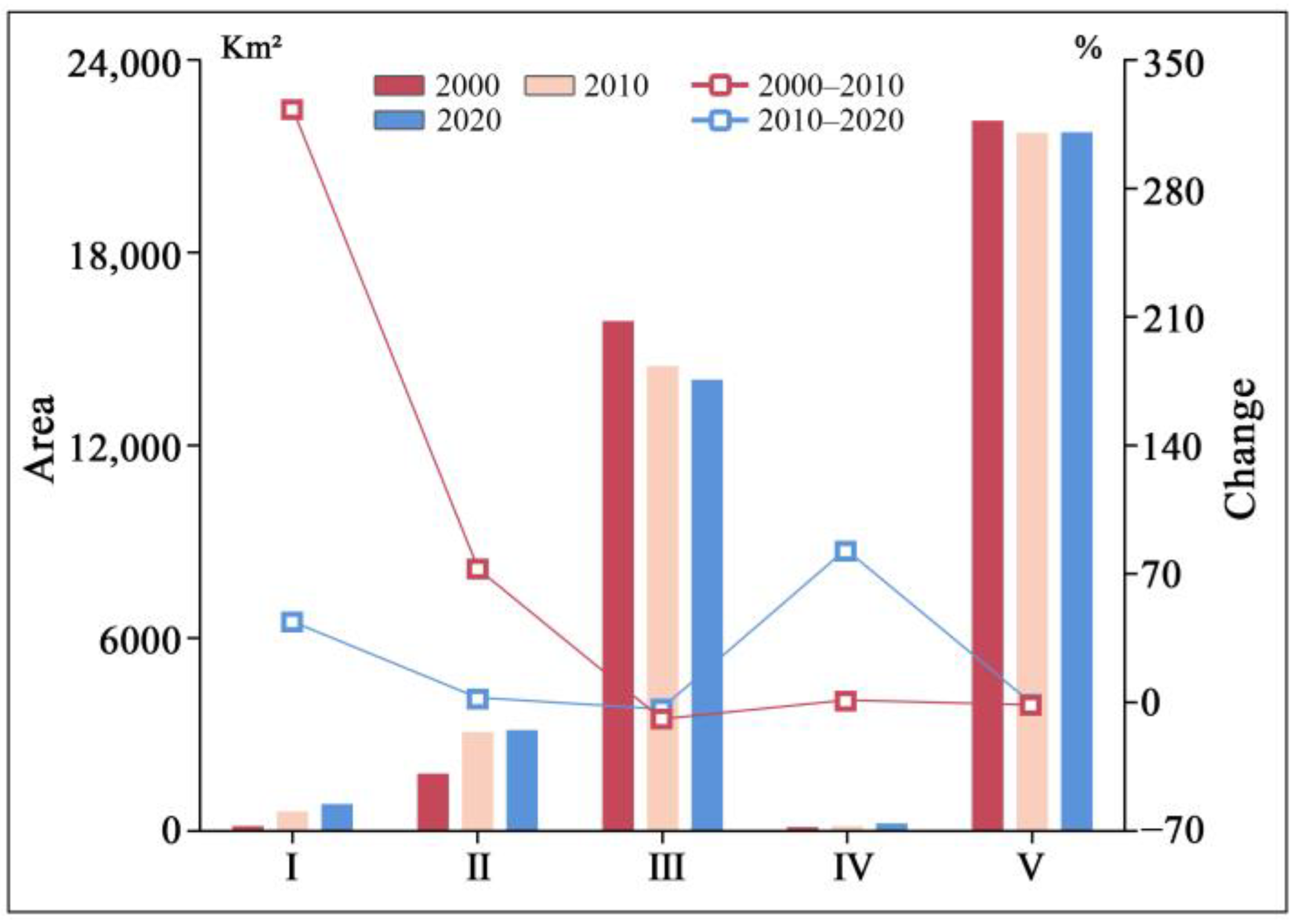
3.1.2. Area Change of Landscape Mosaic
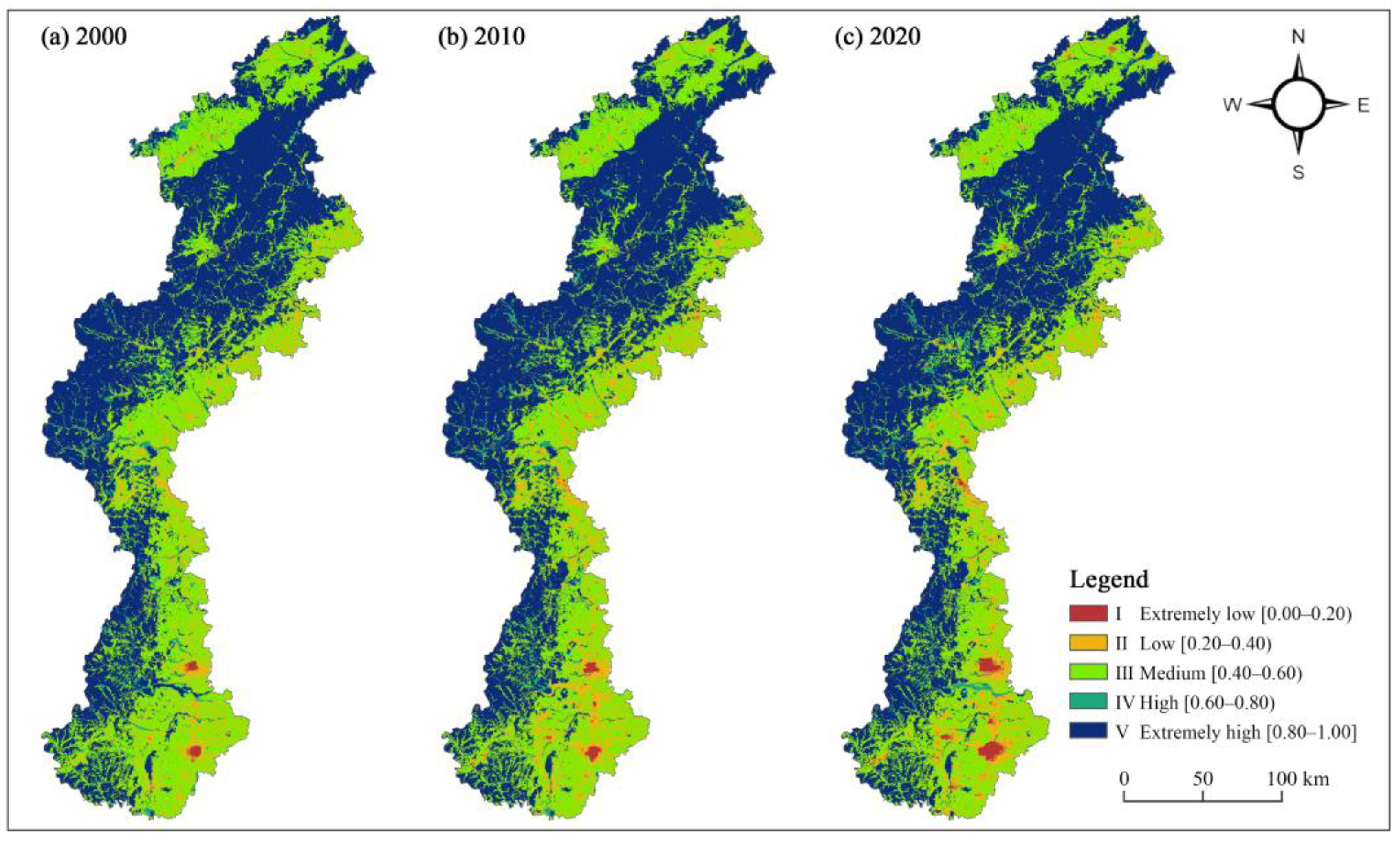
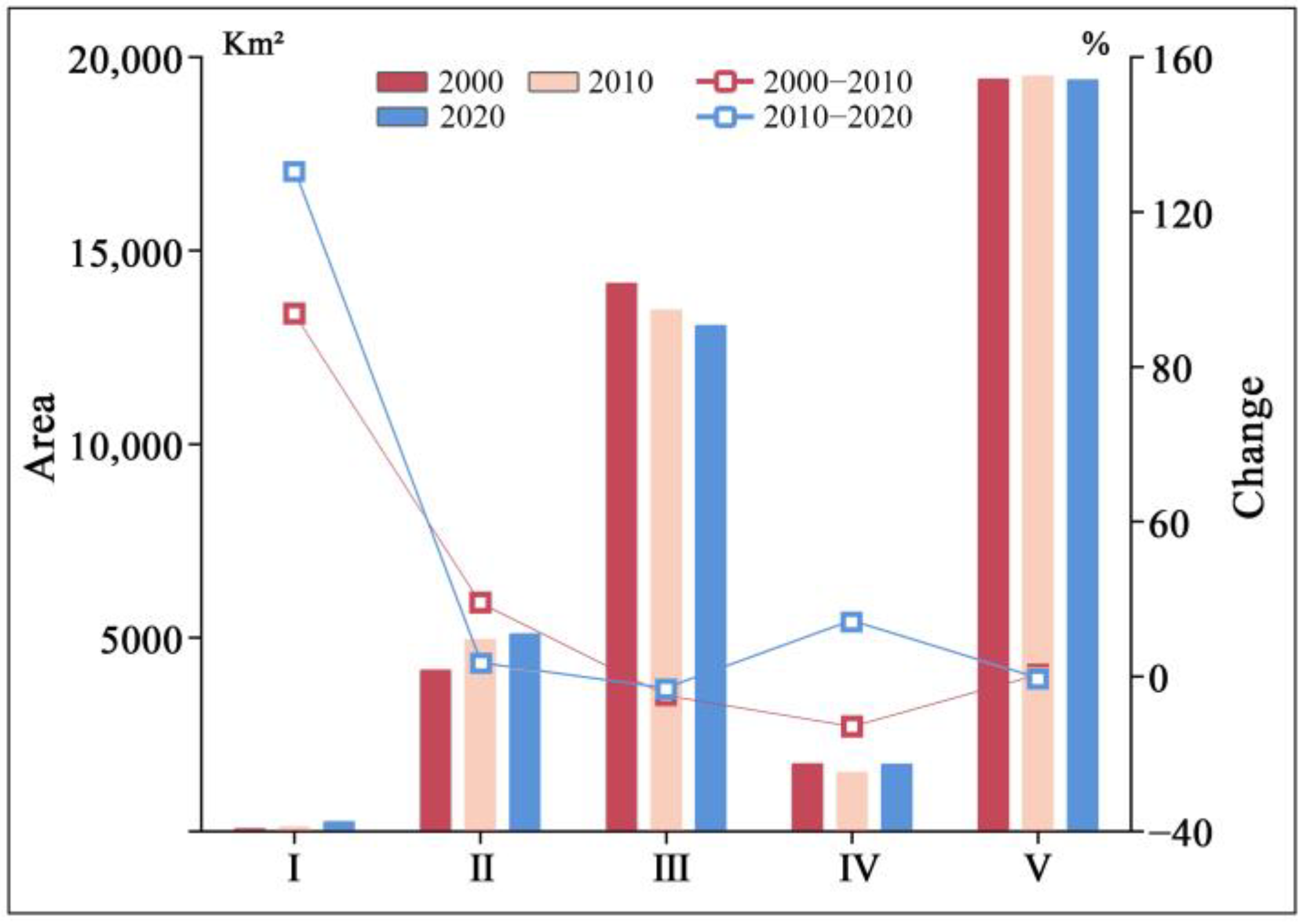
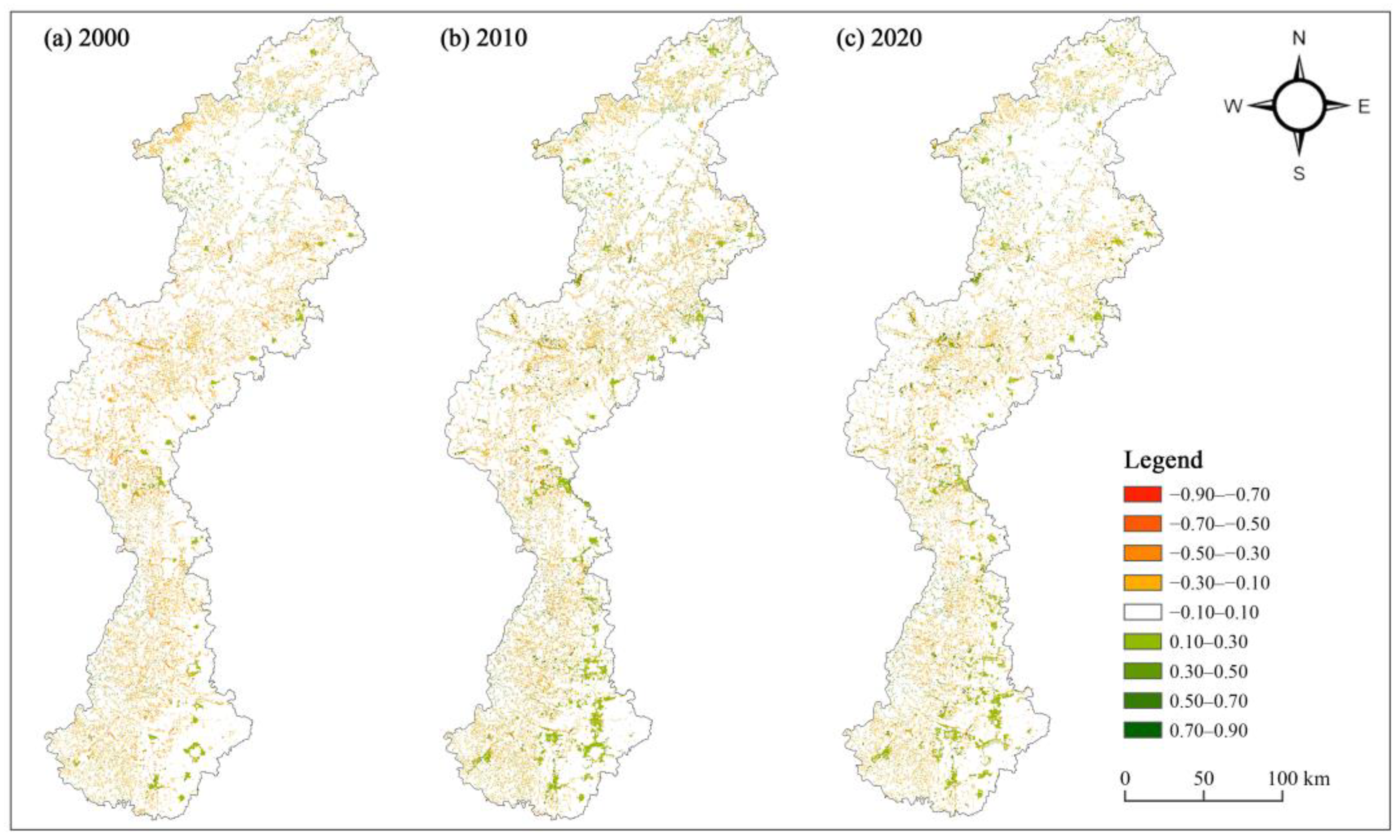
3.2. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Habitat Quality
3.3. Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Pattern on Habitat Quality Based on OLS Model
3.4. Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Pattern on Habitat Quality Based on GWR Model
4. Discussion
4.1. LM Classification Method Integrating PCA-SOM-ED Composite Model
4.2. InVEST-HQ Model Assessment Using LM Instead of LULC
4.3. Targeted Development Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Type | Abbreviations | LM Name | General Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLM | AP | Arable landscape in plains | The landscape exhibits a continuous high-density texture of farmland, interspersed with a limited number of rural residential areas and agricultural facilities. |
| AH | Arable landscape in hillsides | The composition of LULC is identical to that of AP. The primary distinction lies in its geographical location, situated on a hillside with a specific slope. | |
| FH | Forest landscape in hillsides | Forest landscape predominantly consists of trees and shrubs, primarily located in hilly regions. A limited number of these landscapes can be found near urban areas, where they depend on green spaces such as forest parks and nature reserves. | |
| FM | Forest landscape in deep mountain areas | Forest landscape situated in a mountainous region characterized by steeper terrain and predominantly retains a natural state. | |
| GH | Grass landscape in hillsides | Grass landscape encompasses both natural and artificial grassland features. It includes a limited extent of cultivated land, woodlands, and rural settlements, all located within a hillside zone. | |
| GM | Grass landscape in mountain areas | Grass landscape situated in a mountainous region characterized by steeper terrain and predominantly retains a natural state. | |
| W | Water landscape | The relatively concentrated rivers, lakes, and reservoirs represent valuable surface water resources within the study area. | |
| UC | Urban core landscape | Urban landscapes characterized by a continuous urban fabric demonstrate the highest levels of population density within the study area, alongside average GDP and average light DN values. | |
| R | Rural settlement landscape | In urban and rural built-up areas, where impervious surfaces and farmland intermingle, population density, average GDP, and nighttime light intensity are relatively low. | |
| TLM | AG | Arable land–grassland transitional area | Landscape characterized by farmland and grassland elements, typically situated at the peripheries of rural settlements. |
| AWG | Arable land–water–grassland transitional area | Landscape characterized by the predominance of farmland, water bodies, and grassland, situated on the rural periphery of the valley. | |
| AR | Arable land–rural settlement transitional area | Situated on the periphery of cities and villages, the area features relatively clustered rural residential zones at its core, creating a landscape characterized by the intermingling of farmland and rural housing. | |
| FAG | Forest–arable land–grass transitional area | Landscape characterized by a combination of cultivated land, woodland, and grassland. This type of landscape occurs only under specific terrain conditions. | |
| GA | Grass–arable land transitional area | The landscape texture is consistent with that of AG; however, the primary distinguishing factor is the shift in the dominant element type from farmland to grassland. | |
| GF | Grass–forestland transitional area | Landscape space transitions between woodland and grassland, typically found in steeper mountainous terrain. | |
| WA | Water–arable land transitional area | Landscape situated on both banks of the river, where farmland is relatively concentrated. Although it occupies a small area within the study region, it is widely distributed. | |
| UA | Urban–arable land transitional area | Landscape adjacent to urban built-up regions, which reflects the spatial characteristics associated with the periphery of urban development. | |
| UAG | Urban–arable–grassland transitional area | Landscape exhibits a similar formation mechanism to that of UA. A significant distinction lies in the heightened presence of industrial buildings, which act as impermeable surfaces within the landscape. | |
| RA | Rural–arable land transitional area | This region is characterized by a transitional landscape comprising rural settlements and agricultural land. It generally commences from location R and extends outward in a “finger-like” configuration along transportation routes or waterways. The population and socio-economic conditions of this area are surpassed only by those of location R. | |
| BA | Barren–arable land transitional area | Bare soil and wasteland constitute the primary landscape features of this spatial type, with a limited presence of farmland landscapes in the region. |
| Landscape Mosaic Type | Area (km2) | Area (%) | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 7157.88 | 0.18 | 177.93 | 2.25 | 0.39 | 74.79 | 0.34 | 1.80 | 0.07 | 0.76 | 1.85 | 0.16 | 4.47 | 56.96 |
| AH | 4205.25 | 0.11 | 593.16 | 6.15 | 0.26 | 72.79 | 2.11 | 4.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 1.27 | 2.43 |
| FH | 3016.98 | 0.08 | 741.43 | 20.83 | 0.24 | 10.63 | 83.43 | 5.57 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 1.80 |
| FM | 5014.53 | 0.13 | 1210.16 | 28.71 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 97.21 | 2.37 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.87 |
| GH | 4601.25 | 0.12 | 385.81 | 15.22 | 0.32 | 4.72 | 0.84 | 93.90 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 4.90 |
| GM | 4081.59 | 0.10 | 832.36 | 24.18 | 0.04 | 2.29 | 3.51 | 94.13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.49 |
| W | 379.80 | 0.01 | 276.58 | 1.94 | 85.59 | 7.73 | 0.52 | 3.73 | 2.07 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 2.75 | 7.88 |
| UC | 52.65 | 0.01 | 88.46 | 2.42 | 0.01 | 10.73 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 87.75 | 1.28 | 20.90 | 105.80 | 7928.93 |
| R | 950.58 | 0.02 | 196.18 | 2.29 | 0.23 | 31.29 | 0.50 | 1.89 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 65.81 | 0.18 | 5.07 | 67.17 |
| AG | 2706.48 | 0.07 | 546.47 | 12.94 | 0.26 | 49.39 | 2.24 | 47.71 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.01 | 1.13 | 3.88 |
| AWG | 558.18 | 0.01 | 378.04 | 7.84 | 34.96 | 39.40 | 4.43 | 19.64 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 1.96 | 5.61 |
| AR | 2001.51 | 0.05 | 243.70 | 3.49 | 0.47 | 71.50 | 1.27 | 4.80 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 21.47 | 0.23 | 4.74 | 81.96 |
| FAG | 225.45 | 0.01 | 776.40 | 16.33 | 2.81 | 28.47 | 38.90 | 25.06 | 2.73 | 0.46 | 1.58 | 0.06 | 1.16 | 26.44 |
| GA | 715.77 | 0.02 | 445.97 | 11.25 | 1.72 | 29.19 | 3.15 | 63.14 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.79 | 0.16 | 2.03 | 45.88 |
| GF | 2323.71 | 0.06 | 1037.75 | 25.33 | 0.05 | 1.80 | 42.14 | 55.98 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 1.10 |
| WA | 234.00 | 0.01 | 174.87 | 1.72 | 71.22 | 24.96 | 1.34 | 1.35 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 4.46 | 81.87 |
| UA | 586.80 | 0.01 | 163.70 | 2.53 | 10.15 | 43.01 | 0.37 | 2.41 | 040 | 42.30 | 1.36 | 2.50 | 17.76 | 1048.30 |
| UAG | 516.43 | 0.01 | 391.62 | 10.31 | 1.69 | 42.52 | 9.90 | 31.25 | 0.08 | 12.47 | 2.09 | 0.14 | 3.27 | 75.81 |
| RA | 225.09 | 0.01 | 131.49 | 1.96 | 0.58 | 45.71 | 0.43 | 1.06 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 51.98 | 0.70 | 10.10 | 266.60 |
| BA | 54.00 | 0.01 | 756.00 | 3.84 | 0.67 | 25.83 | 1.67 | 4.88 | 64.98 | 0.21 | 1.78 | 0.16 | 3.70 | 57.68 |
| Landscape Mosaic Type | Area (km2) | Area (%) | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 6455.61 | 0.16 | 177.98 | 2.14 | 0.26 | 92.91 | 0.33 | 1.43 | 0.02 | 3.19 | 1.87 | 0.34 | 3.86 | 287.16 |
| AH | 4205.25 | 0.11 | 593.16 | 6.15 | 0.17 | 92.91 | 2.15 | 3.92 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 7.80 |
| FH | 3103.74 | 0.08 | 745.39 | 20.68 | 0.12 | 10.09 | 83.52 | 5.44 | 0.03 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 7.70 |
| FM | 5014.53 | 0.13 | 1210.16 | 28.71 | 0.01 | 0.37 | 97.18 | 2.37 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 1.83 |
| GH | 4597.65 | 0.12 | 393.45 | 15.05 | 0.30 | 4.17 | 0.79 | 93.29 | 0.02 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.02 | 1.06 | 16.32 |
| GM | 4091.59 | 0.10 | 832.36 | 24.18 | 0.02 | 2.26 | 3.57 | 93.99 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 6.45 |
| W | 379.80 | 0.01 | 276.58 | 1.94 | 78.71 | 8.11 | 1.28 | 4.49 | 6.01 | 1.17 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 2.94 | 56.39 |
| UC | 101.97 | 0.01 | 137.50 | 2.32 | 0.69 | 6.65 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 92.24 | 0.28 | 15.84 | 74.20 | 11,534.82 |
| R | 1057.14 | 0.03 | 196.28 | 2.37 | 0.08 | 14.53 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 93.32 | 0.48 | 8.75 | 332.78 |
| AG | 2706.48 | 0.07 | 546.47 | 12.94 | 0.22 | 48.91 | 2.24 | 47.68 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.72 | 0.01 | 1.08 | 11.94 |
| AWG | 556.18 | 0.01 | 378.04 | 7.84 | 33.52 | 39.17 | 4.24 | 18.35 | 1.79 | 1.37 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 2.30 | 37.81 |
| AR | 1952.01 | 0.05 | 256.52 | 3.59 | 0.32 | 59.73 | 1.09 | 3.82 | 0.06 | 2.74 | 32.23 | 0.40 | 4.93 | 305.20 |
| FAG | 254.61 | 0.01 | 746.67 | 17.22 | 1.21 | 20.55 | 44.43 | 23.26 | 0.33 | 7.63 | 2.58 | 0.13 | 0.93 | 83.49 |
| GA | 544.32 | 0.01 | 450.03 | 12.56 | 0.96 | 24.12 | 4.52 | 59.12 | 0.50 | 8.89 | 1.90 | 0.32 | 2.30 | 209.67 |
| GF | 2323.71 | 0.06 | 1037.75 | 25.33 | 0.03 | 1.75 | 42.15 | 55.86 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 2.58 |
| WA | 152.10 | 0.01 | 176.22 | 2.03 | 72.81 | 20.52 | 0.85 | 3.21 | 0.01 | 2.03 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 4.17 | 457.52 |
| UA | 902.34 | 0.02 | 164.64 | 2.62 | 3.67 | 26.16 | 0.20 | 1.10 | 1.01 | 67.16 | 0.70 | 4.61 | 19.13 | 3429.76 |
| UAG | 416.43 | 0.01 | 391.62 | 10.31 | 1.27 | 27.23 | 7.15 | 20.52 | 0.17 | 42.41 | 1.26 | 0.25 | 3.98 | 215.36 |
| RA | 544.59 | 0.01 | 165.64 | 2.45 | 0.68 | 40.03 | 0.32 | 1.90 | 0.06 | 1.87 | 55.14 | 0.84 | 8.33 | 671.94 |
| BA | 155.88 | 0.01 | 115.01 | 2.02 | 0.09 | 19.30 | 0.50 | 1.97 | 75.71 | 0.99 | 1.14 | 0.16 | 2.72 | 105.92 |
| AP | FH | GH | UC | R | AR | FAG | GA | WA | UA | RA | BA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | —— | 6.93 | 108.18 | 10.17 | 22.14 | 343.62 | 33.21 | 60.39 | 10.89 | 251.82 | 145.08 | 5.76 |
| FH | 3.69 | —— | 3.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 32.22 | 10.44 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.00 |
| GH | 12.06 | 24.84 | —— | 0.00 | 2.79 | 0.99 | 20.52 | 118.89 | 0.54 | 4.59 | 2.52 | 71.37 |
| UC | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.09 | —— | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 9.9 | 0.27 | 0.00 |
| R | 1.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.71 | —— | 0.81 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 16.11 | 8.19 | 0.27 |
| AR | 70.20 | 0.09 | 12.51 | 6.39 | 36.99 | —— | 2.97 | 8.28 | 1.17 | 101.34 | 253.44 | 0.72 |
| FAG | 21.42 | 46.17 | 5.94 | 0.09 | 1.44 | 7.38 | —— | 18.27 | 0.54 | 3.51 | 5.59 | 0.09 |
| GA | 61.56 | 59.67 | 113.85 | 0.18 | 8.46 | 17.01 | 46.35 | —— | 3.33 | 42.12 | 24.57 | 30.78 |
| WA | 33.66 | 0.00 | 1.35 | 0.36 | 1.44 | 11.61 | 0.90 | 2.88 | —— | 42.48 | 4.41 | 30.33 |
| UA | 45.81 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 37.08 | 9.90 | 38.34 | 2.88 | 11.25 | 27.81 | —— | 18.45 | 14.31 |
| RA | 9.90 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 3.96 | 52.11 | 22.05 | 0.27 | 3.06 | 0.63 | 50.67 | —— | 0.54 |
| BA | 36.36 | 0.09 | 7.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 0.09 | 2.34 | 1.89 | 1.44 | 0.36 | —— |
| AP | FH | GH | UC | R | AR | FAG | GA | WA | UA | RA | BA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | —— | 18.45 | 14.22 | 15.48 | 18.27 | 101.07 | 42.75 | 22.05 | 22.41 | 186.39 | 46.62 | 13.59 |
| FH | 0.18 | —— | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 10.62 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| GH | 31.14 | 42.66 | —— | 0.00 | 1.98 | 0.63 | 6.84 | 130.68 | 0.09 | 5.31 | 3.15 | 1.44 |
| UC | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.00 | —— | 1.08 | 0.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 14.40 | 0.36 | 0.09 |
| R | 1.35 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 1.71 | —— | 2.25 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.09 | 16.38 | 6.66 | 0.00 |
| AR | 17.82 | 0.09 | 2.16 | 10.8 | 22.41 | —— | 5.04 | 5.67 | 4.95 | 28.44 | 105.66 | 0.63 |
| FAG | 4.05 | 22.68 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 1.35 | —— | 4.86 | 4.59 | 1.71 | 4.68 | 0.00 |
| GA | 22.68 | 14.49 | 18.54 | 1.44 | 2.34 | 8.91 | 32.40 | —— | 2.34 | 27.54 | 11.70 | 6.12 |
| WA | 2.43 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 1.17 | —— | 7.29 | 1.17 | 33.84 |
| UA | 11.70 | 0.72 | 1.71 | 116.82 | 33.75 | 20.43 | 4.86 | 5.76 | 26.01 | —— | 21.78 | 4.59 |
| RA | 14.85 | 0.00 | 0.54 | 3.15 | 58.86 | 15.93 | 0.09 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 11.88 | —— | 0.00 |
| BA | 3.42 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.99 | 0.18 | 0.63 | 115.29 | 12.33 | 0.63 | —— |
| Threat Factor | Maximum Distance (km) | Weight (0.1) | Decay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural land | 1.0 | 0.50 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Urban district | 6.0 | 0.80 | Linear distance-decay |
| Rural settlement | 1.8 | 0.70 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Expressway and railroad networks | 4.0 | 0.50 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Main road network in urban district | 2.0 | 0.30 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Land Use/Land Cover Type | Habitat | Agricultural Land | Urban District | Rural Settlement | Expressway and Railroad Networks | Main Road Network in Urban District |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural land | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| Forestland | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Grassland | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Water | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Urban district | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.45 |
| Rural settlement | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.55 |
| Barren land | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.60 |

References
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.P.; Tao, W.Q.; Zhang, D.G. Ecosystem Services Assessment, Trade-Off, and Bundles in the Yellow River Basin, China. Diversity 2021, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.L.; Chen, Y.; Bu, L.Y.; Ye, Y.M. Multi-scenario analysis of habitat quality in the Yellow River delta by coupling FLUS with InVEST model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, M. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Friving Forces of Habitat Quality in Guizhou Province. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6908. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, M.M.; He, S.; Gan, M.Y.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, K. Impacts of urbanization and landscape pattern on habitat quality using OLS and GWR models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y. Evolution of habitat quality and association with land-use changes in mountainous areas: A case study of the Taihang Mountains in Hebei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Luo, J.G.; Zhang, H.; Qin, S.; Yu, M.J. Projections of land use change and habitat quality assessment by coupling climate change and development patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.N.; Wu, X.F. Influence of urban land use compact change on riparian habitat: A case study of Wuhan section of Hanjiang river small watershed. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2021, 37, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Semmens, D.J.; Clement, J.M. An application of Social Values for Ecosystem Services (SolVES) to three national forests in Colorado and Wyoming. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Semmens, D.; Villa, F.; Johnson, G.W. Quantifying and valuing ecosystem services: An application of ARIES to the San Pedro River basin, USA. In Handbook on the Economics of Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2014; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Boumans, R.; Roman, J.; Altman, I.; Kaufman, L. The Multiscale Integrated Model of Ecosystem Services (MIMES): Simulating the interactions of coupled human and natural systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.J.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.P.; Li, C.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Yi, Y.J. Investigation of the spatio-temporal dynamics in landscape variations in a shallow lake based on a new Tendency-Pattern-Service conceptual framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.Z. Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of habitat quality in Nansihu Lake basin, eastern China, from 1980 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Song, Y.Y.; Xue, D.Q. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use and Habitat Quality in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Fu, M.C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.T. Land-use change in Changli County, China: Predicting its spatio-temporal evolution in habitat quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Bi, L.L. Spatial and temporal changes of habitat quality and its influential factors in China based on the InVEST model. Forests 2023, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.D.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.H.; Lin, T.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zheng, Y. The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains. Forests 2024, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Sun, C.G.; Fan, F.L. Estimating the characteristic spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality using the invest model—A case study from Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.P.; Zhang, D.G. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Habitat Quality and Its Influencing Factros in the Yellow River Basin based on InVEST Model and GeoDetector. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liao, L.Y.; Xu, Z.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chi, M.W.; Lan, S.R.; Gan, Q.C. Interactive effects on habitat quality using InVEST and GeoDetector models in Wenzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G. Landscape Ecology: The Effect of Pattern on Process. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989, 20, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Roy, P.S.; Murthy, M.S.R.; Jha, C.S. Application of Landscape Ecology and Remote Sensing for Assessment, Monitoring and Conservation of Biodiversity. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, R.T.T.; Godron, M. Landscape Ecology; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.S.; Li, F.; Hu, D.; Larry Li, B. Understanding Eco-complexity: Social-Economic-Natural Complex Ecosystem Approach. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, Z.F.; Huang, Q.X. Characteristics and progress of land use/cover change research during 1990–2018. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveh, Z. Some Remarks on Recent Developments in Landscape Ecology as a Transdisciplinary Ecological and Geographical Science. Landsc. Ecol. 1991, 5, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Bian, Z.Y.; Ding, S.Y. Effects of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the generation and provision of ecosystem services. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 6412–6421. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.X.; Wang, C.Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Yu, M. Ecological Network Characteristics of the Functional Group of Epigaeic Arthropod in Arable Land with Different Field Margin Types. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 9, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.H.; Gao, B.H.; Dong, J.X.; Gao, L.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, L.H. Community Diversity of Arthropod in Forest-steppe Ecotone in southeast Edge of Inner Mongolia Tableland. Scientia 2008, 3, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.M.; Xin, Z.B.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Q.S. Plant Diversity and Soil Characteristics of Different Inundation Zones in An Aquaticterrestrial Ecotone, Li River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 5121–5130. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Q.Z.; Ma, K.M.; Wu, J.G.; Tang, R.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Luo, S.H.; Bao, L.; Cai, X.H. An Overview of Advances in Distributional Pattern of Urban Biodiversity. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.T.; Xie, D.B.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, W.B. Study on the Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Regional Biodiversity. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Dramstad, W.E.; Olson, J.D.; Forman, R.T.T. Landscape Ecology Principles in Landscape Architecture and Land-Use Planning; Harvard University Graduate School of Design: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenasso, M.L.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Weathers, K.C.; Jones, C.G. A Framework for a Theory of Ecological Boundaries. BioScience 2003, 53, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Hett, C.; Ramamonjisoa, B.; Messerli, P. Beyond deforestation monitoring in conservation hotspots: Analysing landscape mosaic dynamics in north-eastern Madagascar. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 68, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, M.; Hilal, M.; Sigura, M.; Antognelli, S.; Joly, D. Urban-rural-natural gradient analysis with CORINE data: An application to the metropolitan France. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 171, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumaker, N.H. Using landscape indices to predict habitat connectivity. Ecology 1996, 77, 1210–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedler, B.; Pernkopf, L.; Strasser, T.; Lang, S.; Smith, G. A composite indicator for assessing habitat quality of riparian forests derived from Earth observation data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 37, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, S.; von Wehrden, H.; Poirazidis, K.; Wesley, M.; Hochachka, W.M.; Wrbka, T.; Kati, V. Performance of methods to select landscape metrics for modelling species richness. Ecol. Model. 2015, 295, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieb, J.T.; Bennett, E.M. Landscape structure as a mediator of ecosystem service interactions. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 2863–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedler, B.; Lang, S. A spatially explicit patch model of habitat quality, integrating spatio-structural indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Norton, D.J. Mapping and analyzing landscape patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 1994, 9, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowosad, J.; Stepinski, T.F. Global inventory of landscape patterns and latent variables of landscape spatial configuration. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitters, K.H.; Wickham, J.D.; Wade, T.G. An indicator of forest dynamics using a shifting landscape mosaic. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Lv, Y.Y.; Li, M.S. Assessing Dynamic Pattern of Forest Fragmentation based on A Landscape Mosaic Indicator: A Case Study of Oregon State, USA. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.X.; Wang, L.L.; Hu, R.N.; Lu, X.N.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, G.L.; Tan, B.C. Identification of unique ecosystem service bundles in farmland-A case study in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.H.; Kang, D.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, D. Landscape classification with self-organizing map using user participation and environmental data: The case of the Seoul Metropolitan Area. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 20, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Herzog, F. Applicability of landscape metrics for the monitoring of landscape change: Issues of scale, resolution and interpretability. Ecol. Indic. 2002, 2, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Yuan, F. Assessing landscape changes and dynamics using patch analysis and GIS modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 16, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Ling, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Shen, R.; Wang, Y. How do different processes of habitat fragmentation affect habitat quality?–Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, H.; Yang, X. The spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of habitat quality in the typical region of the Lunan Economic Belt: A case study of Donggang District, Rizhao. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.B.; Rao, L.Y. Impacts of Land Use and Climate Change on Ecosystem Services in Agro-pastoral Ecotone. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5114–5124. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.L.; Xiao, C.W.; Feng, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.M. Accelerating decline of habitat quality in Chinese border areas. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, Y.Q. Exploring the spatial and temporal driving mechanisms of landscape patterns on habitat quality in a city undergoing rapid urbanization based on GTWR and MGWR: The case of Nanjing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yue, H.; Li, Z.Q. Examining the influences of air quality in China’s cities using multi-scale geographically weighted regression. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 1444–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhou, W.Q.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Yu, W.J.; Li, W.F. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N. Urbanization impact on landscape patterns in Beijing City, China: A spatial heterogeneity perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X. Response of multiple mountain ecosystem services on environmental gradients: How to respond, and where should be priority conservation? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.L.; Li, S.C.; Liu, D.H.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.L. Analysis of the driving factors of precipitation change during the development of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Batunacun; Zhen, L.; Zhuang, D.F. Assessment of land-use and land-cover change in Guangxi, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, X.; Qin, W.C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, R.; Yan, C.Z.; Wu, S.X.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Fan, F.L. A Parameter Optimized Method for InVEST Model in Sub-Pixel Scale Integrating Machine Learning Algorithm and Vegetation–Impervious Surface–Soil Model. Land 2024, 13, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Hong, S. Urban expansion patterns and their driving forces based on the center of gravity-GTWR model: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H. The application of ANN-FLUS model in reconstructing historical cropland distribution changes: A case study of Vietnam from 1885 to 2000. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.X.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhang, B.J.; Cheng, W.J. Land Use/Cover-Related Ecosystem Service Value in Fragile Eco-logical Environments: A Case Study in Hexi Region, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Xu, M.; Fu, H.P.; Wang, S.R. Classification of county natural landscape governance units for Wusheng. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. 2020, 56, 553–560. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski, A.; Bauer, D.M.; Bell, K.P.; Loftin, C.S.; Nelson, E.J. Using landscape metrics to characterize towns along an urban-rural gradient. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2937–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Wang, X.B.; Liu, S.L. Economic growth target and radical urbanization: Evidence from satellite night-light data. J. World Econ. 2021, 44, 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzari, M.; Sigura, M. Landscape sequences along the urban–rural–natural gradient: A novel geospatial approach for identification and analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 140, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Zhang, X.S.; Tong, S.; Hou, R.; Wang, Q.X.; He, J. Landscape ecological land consolidation zoning in Hubei Province based on grey constellation clustering. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.H.; Hildebrandt, H.; Van den Busch, J.L.; Heymans, C. Photometric redshift calibration with self-organising maps. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 637, A100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, F.; Gao, H.; Zhou, C.B.; Zhang, X.L. The impact of land-use change on water-related ecosystem services: A study of the Guishui River Basin, Beijing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S148–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Su, W.Z. Impacts of land-use change on habitat quality during 1985–2015 in the Taihu Lake Basin. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Capital Project. InVEST 3.15.0. Stanford University, University of Minnesota, Chinese Academy of Sciences, The Nature Conservancy, World Wildlife Fund, Stockholm Resilience Centre and the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. 2025. Available online: https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/software/invest (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Gomi, T.; Watenabe, Y.; Sakai, M. How does confounding impacts of flood and forest thinning alter benthic macroinvertebrate communities in Japanese headwater streams. Int. For. Rev. 2014, 16, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.M.; Gu, Y.F. Influence of edge effects on arthropods communities in agroforestry ecological systems. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 31, 6186–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanaraj, K.; Angadi, D.P. Analysis of urban expansion patterns through landscape metrics in an emerging metropolis of Mangaluru Community Development Block, India, During 1972–2018. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, S.B.; Sun, H.; Liu, H. Effect of Urban fringes green space fragmentation on ecosystem service value. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, D.B.; Resor, C.A.C.; Beauvais, G.P.; Kipfmueller, K.F.; Fernandes, C.I.; Baker, W. Watershed analysis of forest fragmentation by clearcuts and roads in a Wyoming forest. Landsc. Ecol. 1998, 13, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, X.; Cheng, G.D. Landscape evolution in the middle Heihe River Basin of north-west China during the last decade. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 53, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Qin, B.; Lin, Y. Assessment of the Impact of Land Use Change on Spatial Differentiation of Landscape and Ecosystem Service Values in the Case of Study the Pearl River Delta in China. Land 2021, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Skidmore, A.K.; Toxopeus, A.G.; Hao, F.H. Long-term vegetation landscape pattern with non-point source nutrient pol-lution in upper stream of Yellow River basin. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yu, Z.W.; Wang, L.C.; Vejre, H. Suitability of regional development based on ecosystem service benefits and losses: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, L. Analysis on land ecological security change and affect factors using RS and GWR in the Danjiangkou Reservoir area, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, S.; Bian, Z.X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.Q. Effects of farmland landscape pattern on spatial distribution of soil organic carbon in Lower Liaohe Plain of northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Xia, C.Y.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, J. The spatiotemporal evolution and prediction of carbon storage: A case study of urban ag-glomeration in China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Land 2022, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Stuart Chapin, F.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, H.; Zhong, T.Y. Environmental effects of land-use/cover change caused by urbanization and policies in Southwest China Karst area–A case study of Guiyang. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitters, K.; Schleeweis, K.; Costanza, J. Forest area change in the shifting landscape mosaic of the continental United States from 2001 to 2016. Land 2020, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.M.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.F. Evolution of habitat quality based on ISODATA spatial mosaic clustering analysis. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 40, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, O.P. The need for management of nature conservation sites designated under Natura 2000. J. Appl. Ecol. 1998, 35, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.B.; Wayne, R.K.; Girman, D.J.; Bruford, M.W. A role for ecotones in generating rainforest biodiversity. Science 1997, 276, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molau, U. Mountain biodiversity patterns at low and high latitudes. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2004, 33, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielgolaski, F.E.; Hofgaard, A.; Holtmeier, F.K. Sensitivity to environmental change of the treeline ecotone and its associated biodiversity in European mountains. Clim. Res. 2017, 73, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.N.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.F.; Fan, Z.M. Quantitative assessment of the habitat quality dynamics in Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, K.; Ryals, R. Nutrient cycling in agroecosystems: Balancing food and environmental objectives. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2017, 41, 761–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.A.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, J.; Bruijnzeel, A.; Mao, Z.; Yang, X.D.; Cardinael, R.; Meng, F.R.; Slide, R.C.; Seitz, S.; et al. Reductions in water, soil and nutrient losses and pesticide pollution in agroforestry practices: A review of evidence and processes. Plant Soil 2020, 453, 45–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.D.; Ding, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.H.; Qiu, P.W.; Chang, J.L.; Peng, L.; Wang, S.Q.; Hong, Y.Y.; Liu, G.J. Plant trait-environment trends and their conservation implications for riparian wetlands in the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.T.; Kennard, M.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Sui, X.Y.; Li, K.M.; Wang, G.J.; Chen, Y.F. Human disturbance and long-term changes in fish taxonomic, functional and phylogenetic diversity in the Yellow River, China. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 3711–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.X.; Kou, Z.W.; Meng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.P. Spatial and temporal characteristics of urban area expansion in Zhengzhou from 1990 to 2020. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2022, 56, 674–684. [Google Scholar]
| Data Type | Data Source/Processing | Data Format | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital elevation model | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 5 June 2024) | Raster | 30 m |
| Land use/land cover | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 10 October 2022) | Raster | 30 m |
| Nighttime light data | U.S. National Centers for Environmental Information (https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/download.html, accessed on 10 December 2024) | Raster | 500 m |
| Urban roads data | National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure (http://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 20 February 2025) | Shp | – |
| Gross domestic product | Statistical yearbooks compiled by local county-level governments, land use/land cover data from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, and Nighttime light data from the U.S. National Centers for Environmental Information | Raster | 30 m |
| Population | The Global Population Data Project (Worldpop) (https://hub.worldpop.org, accessed on 10 December 2024) and county-level demographic yearbooks compiled by local governments | Raster | 500 m |
| Type | Indicators | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nature condition | X1 Elevation | m | [65] |
| X2 Slope | ° | [65] | |
| X3 Proportion of water area | % | [65] | |
| Plant resources | X4 Proportion of agricultural land area | % | [35,66] |
| X5 Proportion of forestland area | % | [35,66] | |
| X6 Proportion of grassland area | % | [35,66] | |
| X7 Proportion of barren land area | % | [35,66] | |
| Urban and rural construction | X8 Proportion of urban district area | % | [35,66] |
| X9 Proportion of rural settlement area | % | [35,66] | |
| X10 Nighttime light intensity | w/(m2·sr·μm) | [67,68,69] | |
| Society and economy condition | X11 Population density | Person/km2 | [67,68,69] |
| X12 Gross domestic product | Million/km2 | [67,68,69] |
| Threat Factor | Abbreviations | Maximum Distance (km) | Weight (0.1) | Decay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable landscape in plains | AP | 1.0 | 0.50 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Arable landscape on hillsides | AH | 0.5 | 0.40 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Urban core landscape | UC | 11.0 | 1.00 | Linear distance-decay |
| Rural settlement landscape | R | 2.5 | 0.75 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Arable land–rural settlement transitional area | AR | 1.5 | 0.70 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Urban–arable land transitional area | UA | 6.0 | 0.85 | Linear distance-decay |
| Urban–arable–grassland transitional area | UAG | 5.0 | 0.75 | Linear distance-decay |
| Rural–arable land transitional area | RA | 1.8 | 0.70 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Expressway and railroad networks | ERRN | 4.0 | 0.50 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Main road network in urban district | EMRN | 2.0 | 0.30 | Exponential distance-decay |
| Landscape Mosaic Type | Abbreviations | Habitat | AP | AH | UC | R | AR | UA | UAG | RA | ERRN | EMRN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable landscape in plains | AP | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| Arable landscape in hillsides | AH | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.70 |
| Forest landscape in hillsides | FH | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Forest landscape in deep mountain areas | FM | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Grass landscape in hillsides | GH | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Grass landscape in mountain areas | GM | 0.85 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Water landscape | W | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Urban core landscape | UC | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.45 |
| Rural settlement landscape | R | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.55 |
| Arable land–grassland transitional area | AG | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.75 |
| Arable land–water–grassland transitional area | AWG | 0.65 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.50 | 0.80 | 0.75 |
| Arable land–rural settlement transitional area | AR | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.80 | 0.60 |
| Forest–arable land–grass transitional area | FAG | 0.70 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Grass–arable land transitional area | GA | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.80 |
| Grass–forestland transitional area | GF | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| Water–arable land transitional area | WA | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| Urban–arable land transitional area | UA | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.45 |
| Urban–arable–grassland transitional area | UAG | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.45 |
| Rural–arable land transitional area | RA | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.60 |
| Barren–arable land transitional area | BA | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.60 |
| Landscape Mosaic Type | Area (Km2) | Area (%) | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 6064.11 | 0.15 | 174.58 | 2.22 | 0.54 | 92.97 | 0.36 | 1.38 | 0.02 | 2.73 | 1.99 | 1.00 | 4.21 | 529.95 |
| AH | 4205.25 | 0.11 | 593.16 | 6.15 | 0.18 | 93.10 | 2.13 | 3.77 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 1.10 | 7.60 |
| FH | 3191.85 | 0.08 | 738.89 | 20.67 | 0.18 | 9.85 | 83.74 | 5.13 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.02 | 0.45 | 12.75 |
| FM | 5014.53 | 0.13 | 1210.16 | 28.71 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 97.18 | 2.37 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.78 |
| GH | 4411.08 | 0.11 | 385.26 | 14.92 | 0.27 | 4.16 | 0.73 | 93.19 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.74 | 0.06 | 1.08 | 34.79 |
| GM | 4081.59 | 0.10 | 832.36 | 24.18 | 0.02 | 2.25 | 3.52 | 94.00 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 5.07 |
| W | 379.80 | 0.01 | 276.58 | 1.94 | 89.13 | 5.01 | 0.37 | 2.01 | 2.91 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 3.68 | 226.97 |
| UC | 234.90 | 0.01 | 154.06 | 2.33 | 0.97 | 9.74 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.02 | 88.27 | 0.56 | 17.71 | 49.93 | 9537.51 |
| R | 1168.65 | 0.03 | 184.35 | 2.26 | 0.14 | 13.88 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 84.68 | 1.82 | 7.88 | 944.63 |
| AG | 2706.48 | 0.07 | 546.47 | 12.94 | 0.19 | 49.01 | 2.24 | 47.55 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 13.11 | 27.61 |
| AWG | 558.18 | 0.01 | 378.04 | 7.84 | 38.31 | 36.46 | 4.28 | 18.07 | 0.90 | 0.45 | 1.52 | 0.20 | 2.75 | 90.36 |
| AR | 1901.07 | 0.05 | 261.17 | 3.68 | 0.77 | 57.54 | 1.14 | 3.77 | 0.04 | 3.15 | 33.58 | 0.97 | 4.84 | 504.60 |
| FAG | 311.94 | 0.01 | 680.91 | 15.21 | 2.60 | 21.98 | 44.18 | 16.86 | 0.43 | 10.99 | 2.95 | 0.30 | 1.15 | 138.77 |
| GA | 568.44 | 0.01 | 434.09 | 12.42 | 1.44 | 23.32 | 3.93 | 60.81 | 0.20 | 8.66 | 1.65 | 0.60 | 2.30 | 297.36 |
| GF | 2323.71 | 0.06 | 1037.75 | 25.33 | 0.03 | 1.74 | 42.05 | 55.91 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 4.39 |
| WA | 281.97 | 0.01 | 171.74 | 2.27 | 71.49 | 17.29 | 2.61 | 2.72 | 1.11 | 3.82 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 3.60 | 458.02 |
| UA | 965.88 | 0.02 | 175.51 | 2.88 | 4.45 | 25.00 | 0.34 | 1.55 | 0.40 | 67.37 | 0.89 | 5.66 | 16.96 | 3010.20 |
| UAG | 416.43 | 0.01 | 391.62 | 10.31 | 0.80 | 21.26 | 5.11 | 23.93 | 0.02 | 48.50 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 3.91 | 309.55 |
| RA | 639.54 | 0.02 | 161.79 | 2.54 | 1.41 | 41.00 | 0.81 | 2.67 | 0.05 | 2.68 | 51.38 | 2.39 | 7.49 | 1196.38 |
| BA | 82.53 | 0.00 | 255.31 | 2.35 | 4.19 | 16.91 | 0.16 | 3.05 | 73.79 | 0.77 | 1.14 | 0.62 | 3.03 | 266.01 |
| Year | FRAC_MN | SPLIT | CONTAG | SHDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.860 | 0.718 | 0.058 | −0.425 |
| 2010 | 0.902 | 1.008 | 0.310 | −0.460 |
| 2020 | 0.791 | 0.921 | 0.347 | −0.499 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, J.; Hao, P.; Hao, J.; Huang, Y.; Yu, M.; Ding, K.; Zhou, Y. Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Patterns on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Taihang Mountains of Hebei Province, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5503. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125503
Feng J, Hao P, Hao J, Huang Y, Yu M, Ding K, Zhou Y. Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Patterns on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Taihang Mountains of Hebei Province, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5503. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125503
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Junming, Peizheng Hao, Jing Hao, Yinran Huang, Miao Yu, Kang Ding, and Yang Zhou. 2025. "Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Patterns on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Taihang Mountains of Hebei Province, China" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5503. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125503
APA StyleFeng, J., Hao, P., Hao, J., Huang, Y., Yu, M., Ding, K., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Impacts of Landscape Mosaic Patterns on Habitat Quality Using OLS and GWR Models in Taihang Mountains of Hebei Province, China. Sustainability, 17(12), 5503. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125503






