Teaching and Learning About the Ecological Footprint to Primary School Students: A Vehicle for Achieving the 2030 SDGs
Abstract
1. Introduction
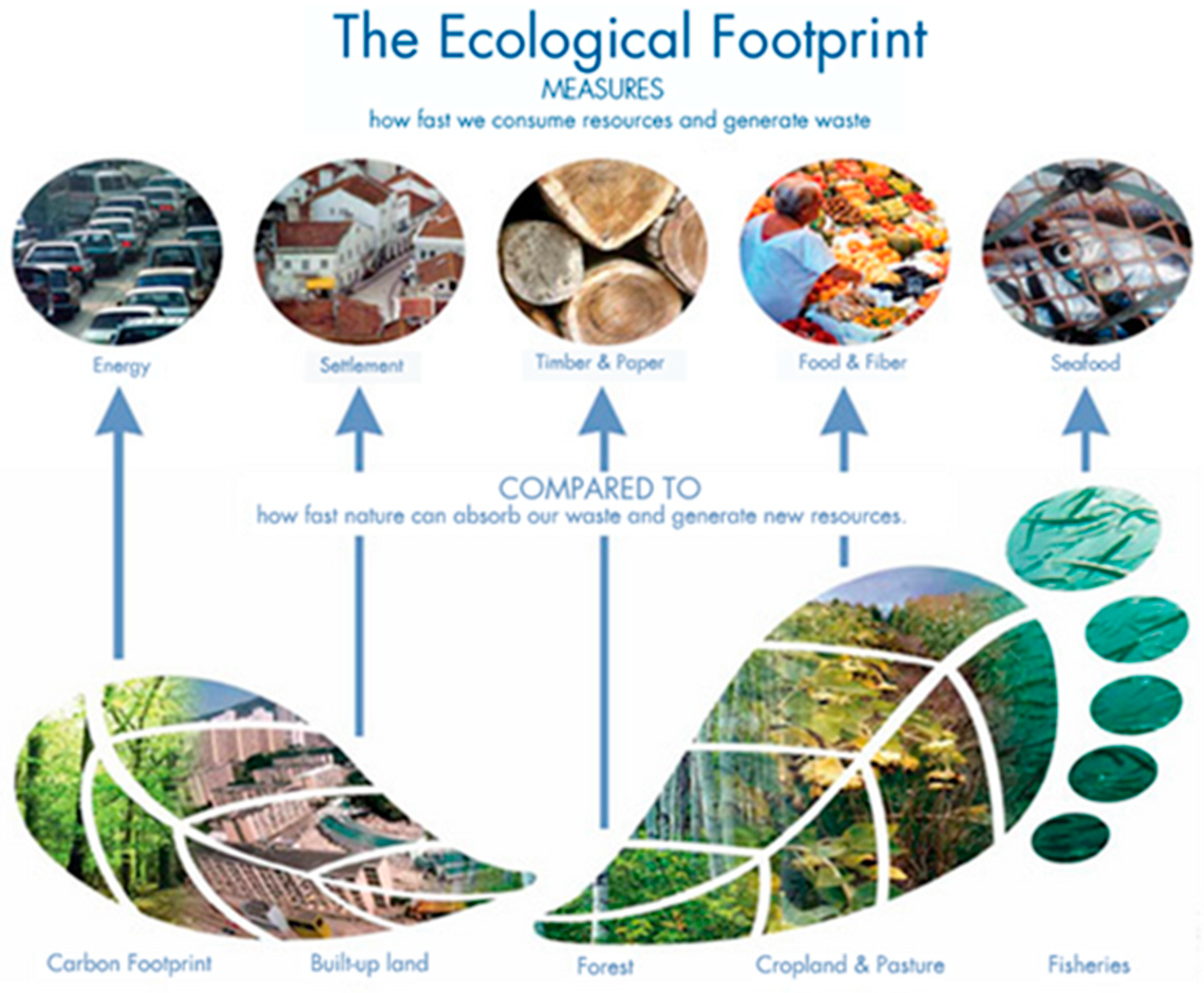
1.1. Concept of Ecological Footprint (EF)
1.2. Previous Teaching Interventions of EF
1.3. Aim of the Study and Research Questions
- To what extent primary school students’ understanding of the EF concept can be enhanced following a relevant teaching intervention?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Significance Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
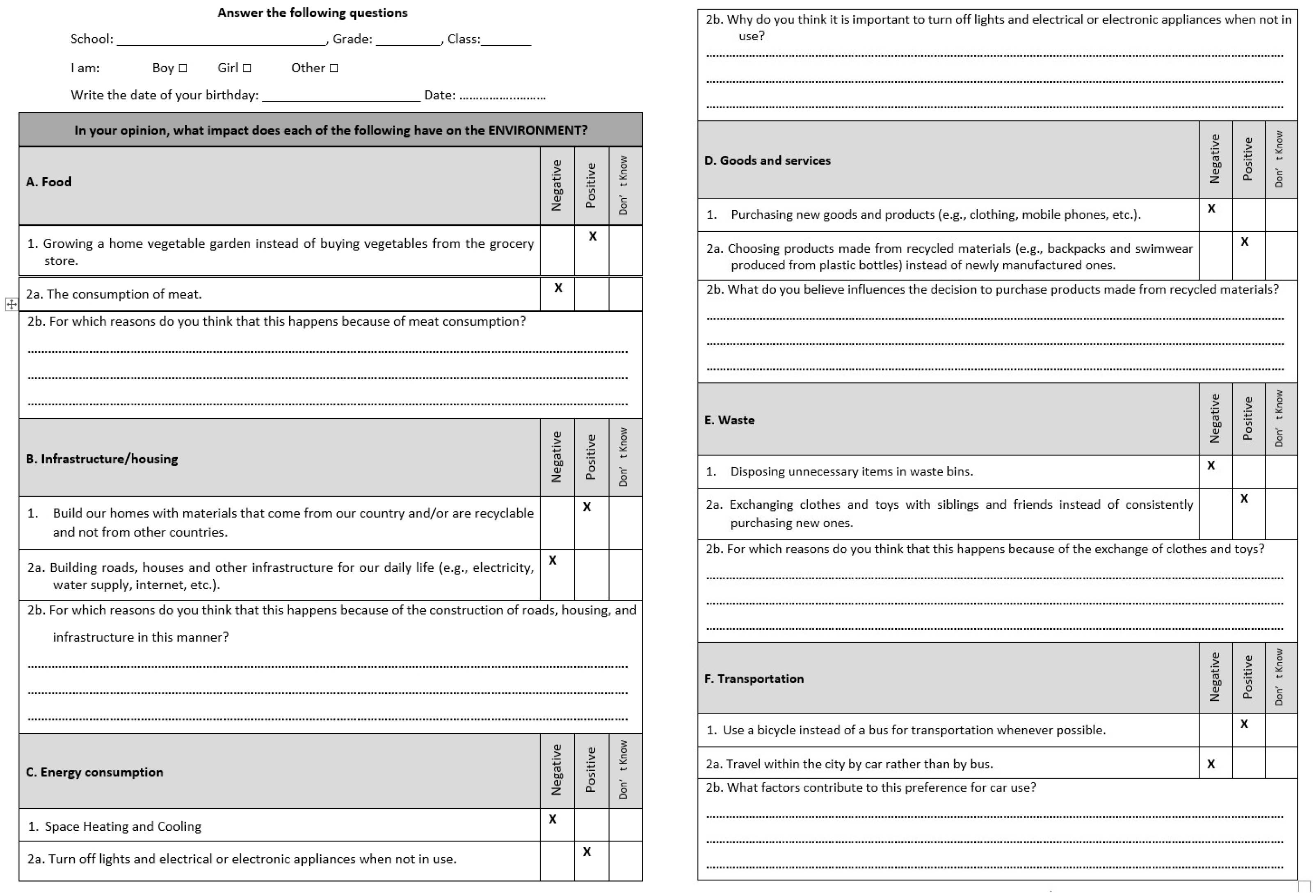
Appendix A
References
- GFN (Global Footprint Network). Footprint Futures—A Teaching Module on Human Dependence on the Biosphere 2016. Available online: https://www.footprintnetwork.org/2016/05/01/footprint-futures/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robimson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M. Ecological Footprint and Appropriated Carrying Capacity: A Tool for Planning Toward Sustainability. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Galli, A.; Giampietro, M.; Goldfinger, S.; Lazarus, E.; Lin, D.; Saltelli, A.; Muller, F. Questioning the Ecological Footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, T.; Barrett, J. A Review of the Ecological Footprint Indicator—Perceptions and Methods. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1645–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Heijungs, R.; de Snoo, G.R. Theoretical exploration for the combination of the ecological, energy, carbon, and water footprints: Overview of a footprint family. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, P.; Dasgupta, A.; Barrett, S. Population, ecological footprint and the sustainable development goals. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2023, 84, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, J.; Lundqvist, U.; Robert, K.H.; Wackernagel, M. The ecological footprint from a systems perspective of sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 1999, 6, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dzakpasu, M.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.C. Validity and utility of ecological footprint accounting: A state-of-the-art review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 32, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Galli, A. An overview on ecological footprint and sustainable development: A chat with Mathis Wackernagel. Int. J. Ecodynamics 2007, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, S.; Niccolucci, V.; Neri, E.; Cranston, G.; Galli, A.; Wackernagel, M. Sustainable development: Ecological footprint in accounting. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Management; Jorgensen, S.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 2467–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Kovshun, N.; Doroshenko, O.; Zhydyk, I.; Nalyvaiko, N.; Vashai, Y.; Skakovska, S. Global measurement of ecological footprint in the context of sustainable development. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1269, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrovatka, M. On sustainability interpretations of the Ecological Footprint. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, L.; Tian, C.; Zhu, B.; Chevallier, J. Impacts of the ecological footprint on sustainable development: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopnina, H. Education for the future? Critical evaluation of education for sustainable development goals. J. Environ. Educ. 2020, 51, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, I. Ecological footprints and sustainable development. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzevicius, J. Ecological footprint as an indicator of sustainable development. Econ. Manag. 2010, 15, 711–718. [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel, M.; Rees, W. Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth; New Society Publishers: Gabriola Island, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- GFN (Global Footprint Network). Glossary 2025a. Available online: https://www.footprintnetwork.org/resources/glossary/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- GFN (Global Footprint Network). National Footprint Accounts 2019 edition 2025b. Available online: https://data.footprintnetwork.org/?_ga=2.28364668.1543056325.1686042711-1970917240.1686042711#/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Amprazis, A.; Galanis, N.; Malandrakis, G.; Panaras, G.; Papadopoulou, P.; Panaras, G.; Galli, A. The Ecological Footprint of Greeks: Main drivers of consumption and influencing factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GFN (Global Footprint Network). How the Footprint Works 2025c. Available online: https://www.footprintnetwork.org/our-work/ecological-%20%20footprint/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Sayhan, H.; Sayhan, S.; Demirbas, O.C. Ecological footprints of primary school students and recommendations to diminish them. Am.—Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2013, 13, 521–530. [Google Scholar]
- Zeqir, V.; Shahin, B. Ecological footprint as a tool for change of individual attitudes toward the environment and better education for sustainability. Tech. Soc. Sci. J. 2022, 30, 727. [Google Scholar]
- Karakas, H. An activity to increase ecological footprint awareness of primary school teacher candidates: Educational drama. Res. Pedagog. 2019, 9, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Malandrakis, G.; Papadopoulou, P.; Gavrilakis, C.; Mogias, A. An education for sustainable development self-efficacy scale for primary pre-service teachers: construction and validation. Journ. Environm. Educ. 2019, 50, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Cebrián, G.; Regadera, E.; Fernandez, M.Y. Analysing the relationship between university students’ ecological footprint and their connection with nature and pro-environmental attitude. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Gibberd, J. Reducing students’ ecological footprints through self-developed interventions. S. Afr. J. Psychol. 2022, 52, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, O.; Aydogdu, M. Application and Evaluation of Ecological Footprint as an Environmental Education Tool. Int. Online J. Educ. Sci. 2010, 2, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cordero, E.C.; Todd, A.M.; Abellera, D. Climate change education and the ecological footprint. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, P.; Vega-Marcote, P.; Garcia Mira, R. Sustainable consumption: A teaching intervention in higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2013, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, R.; Addaney, M.; Danquah, L. The ecological footprint and environmental sustainability of students of a public university in Ghana: Developing ecologically sustainable practices. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2021, 22, 1552–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Birch, R.; Cherrett, N.; Simmons, C. An Analysis of the Policy and Educational Applications of the Ecological Footprint; Stockholm Environment Institute: Heslington York, England, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, D.; Vigoda-Gadot, E.; Haim, A. Encouraging ecological behaviors among students by using the ecological footprint as an educational tool: A quasi experimental design in a public high school in the city of Haifa. Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 19, 844–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO (United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization). UNESCO World Conference on Education for Sustainable Development: Proceedings. In Proceedings of the UNESCO World Conference on Education for Sustainable Development, Bonn, Germany, 31 March–2 April 2009; Available online: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0018/001850/185056e.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Ryu, H.; Brody, S.D. Examining the impacts of a graduate course on sustainable development using ecological footprint analysis. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2006, 7, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, G.F.M.; Vetter, A.; Martin, S. An overview of ecological footprinting and other tools and their application to the development of sustainability process: Audit and methodology at Holme Lacy College, UK. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2004, 5, 340–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Wackernagel, M.; Iha, K.; Lazarus, E. Ecological footprint: Implications for biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 173, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, M.; Bondavalli, C.; Bodini, A. Ecological footprint as a tool for local sustainability: The municipality of Piacenza (Italy) as a case study. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2009, 29, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Alferez, A.; Vidal, S.; Fernandez, M.Y.; Albareda, S. Methodological approaches to change consumption habits of future teachers in Barcelona, Spain: Reducing their personal Ecological Footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 122, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, T.M.; Dalton, C.; Loo, J.; Benakoun, L. Developing ecological footprint scenarios on university campuses: A case study of the University of Toronto at Mississauga. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2008, 9, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, L.; Davis, J. Ecological footprinting: Its potential as a tool for change in preservice teacher education. Environ. Educ. Res. 2013, 19, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetoulis, J. Assessing the Ecological impact of a university: The ecological footprint for the University of Redlands, USA. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2001, 2, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, D.; Kissinger, M.; Vigoda-Gadot, E.; Haim, A. Analyzing the ecological footprint at the institutional scale- The case of an Israeli high-school. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Reducing students’ carbon footprints using personal carbon footprint management system based on environmental behavioural theory and persuasive technology. Environ. Educ. Res. 2016, 22, 658–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.; Galli, A.; Patrizi, N.; Pulselli, F.M. Learning and teaching sustainability: The contribution of Ecological Footprint calculators. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNichol, H.; Davis, J.M.; O’Brien, K.R. An ecological footprint for an early learning centre: Identifying opportunities for early childhood sustainability education through interdisciplinary research. Environ. Educ. Res. 2011, 17, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, S.M.; Mapar, M.; Nicolau, M.; Patrizi, N.; Malandrakis, G.; Pulselli, F.M.; Nicolau, P.B.; Caeiro, S.; Niccolucci, V.; Theodossiou, N.P.; et al. Teaching sustainability within the context of everyday life: Steps toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals through the EUSTEPs Module. Front. in Educ. 2022, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Government Gazette B’ 3567/(4.8.2021) Law 3567/4-8-2021. Curriculum Framework for Skills Workshops for All Types of Schools, Kindergartens, Primary and Secondary Schools. Available online: https://www.e-nomothesia.gr/kat-ekpaideuse/protobathmia-ekpaideuse/upourgike-apophase-94236-gd4-2021.html (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Cohen, L.; Manion, L.; Morrison, K. Research Methods in Education, 5th ed.; Routledge Falmer: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, D. Doing Qualitative Research, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods, 3rd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, A.K.; Sen, G.; Aksaray, B. Examining the association of climate change worry and awareness of ecological footprint reduction behaviours with Mediterranean diet adherence and climate-friendly food choices. Br. Food J. 2024, 127, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, B.F.; Agostinho, F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Pinto, M.J.A.P.; Marroquin, M.C.; Paredes, M.D. A quantitative assessment model for students’ sustainability: Evidence from a Peruvian university. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2023, 24, 1744–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotis, E.; Arsenopoulos, A.; Kanellou, E.; Psarras, J.; Kontogiorgos, P. A multi-sourced data based framework for assisting utilities identify energy poor households: A case-study in Greece. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2020, 15, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Paravantis, J.A.; Founda, D.; Kolokotsa, D.; Michalakakou, P.; Papadopoulos, A.M.; Kontoulis, N.; Tzavali, A.; Stigka, E.; Ioannidis, Z.; et al. Financial crisis and energy consumption: A household survey in Greece. Energy Build. 2013, 65, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, W.C., Jr. Expanding our views of science education to address sustainable development, empowerment, and social transformation. Discip. Interdiscip. Sci. Educ. Res. 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wals, A.E.; Brody, M.; Dillon, J.; Stevenson, R.B. Convergence between science and environmental education. Science 2014, 344, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean Personal EF | Personal EF by Land Types | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gha/Person | Built-Up Land | Carbon Footprint | Cropland | Fishing Grounds | Forest Land | Grazing Land | |
| Greece * | 3.78 gha | 1.8% | 50.9% | 26.4% | 3.2% | 7.9% | 9.8% |
| Europe * | 4.65 gha | 2.3% | 55.3% | 21.8% | 3.9% | 12.4% | 4.3% |
| World * | 2.58 gha | 2.6% | 60.3% | 18.6% | 3.1% | 10.4% | 5% |
| Greek research ** | 3.4 gha | 1.6% | 56.2% | 24.6% | 3% | 6.9% | 7.7% |
| Session (Duration) | Topic | Main Activities | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2 × 45′) |
|
|
|
| 2 (2 × 45′) |
| HOMEWORK: Fill of the table with the weekly consumption of food CLASSWORK: Taxonomy of recorded food by:
|
|
| 3 (2 × 45′) |
| HOMEWORK: Collection of information about students’:
|
|
| 4 (2 × 45′) |
|
|
|
| 5 (2 × 45′) |
|
|
|
| Ecological Footprint Category | Students’ Main Justifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Pre Test | Post Test | |
| Food | * Animals die * Μeat is wrapped in plastic ** Eating meat is good for humans | * Animals are threatened with extinction ** Eating meat is good for humans |
| Infrastructures/Housing | * Gas emissions ** Fast transportation * Environmental pollution | ** Making human life easier ** Fast transportation * Deforestation |
| Energy | ** Making human life easier * Electricity saving | * Energy saving * Electricity saving |
| Goods/Services | * Less garbage * Factories are working less * Less environmental pollution | * Factories are working less * Less environmental pollution |
| Waste | * Less environmental pollution, * Helping other people | * Factories are working less * Fewer purchases of new things |
| Transportation | ** Faster transportation by car ** Buses produce more emissions ** Risk of catching a disease in a bus | ** Faster transportation by car * Less emissions when choosing a bus ** Risk of catching a disease in a bus |
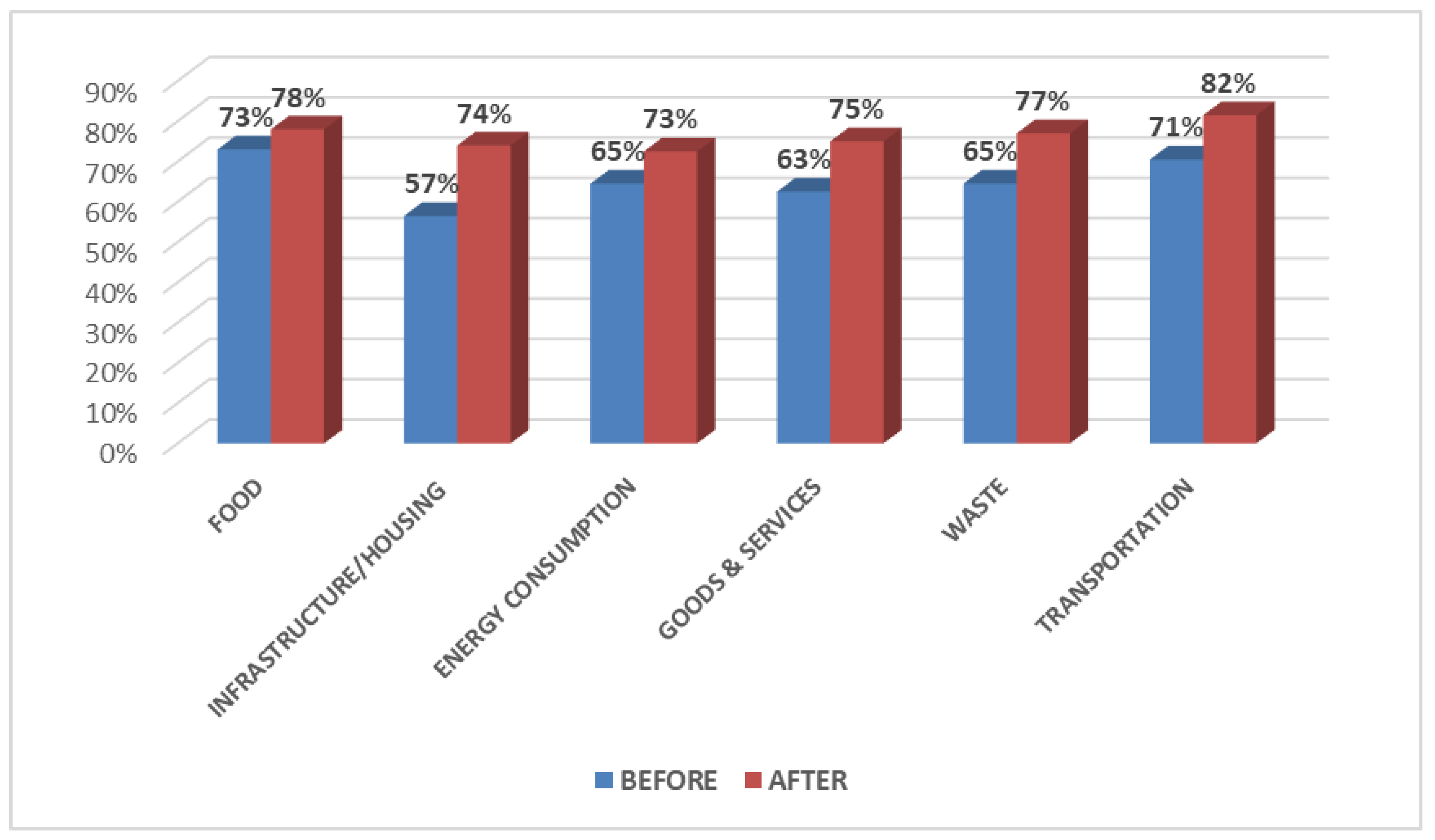
| EF Categories | Mean | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food | Pre | 1.46 | −1.241 | 0.217 |
| Post | 1.56 | |||
| Infrastructures and Housing | Pre Post | 1.13 1.48 | −4.201 | p < 0.001 |
| Energy | Pre Post | 1.29 1.45 | −2.383 | 0.019 |
| Goods and Services | Pre Post | 1.25 1.50 | −3.982 | p < 0.001 |
| Waste | Pre Post | 1.29 1.54 | 3.023 | 0.003 |
| Transportation | Pre Post | 1.41 1.63 | −2.725 | 0.007 |
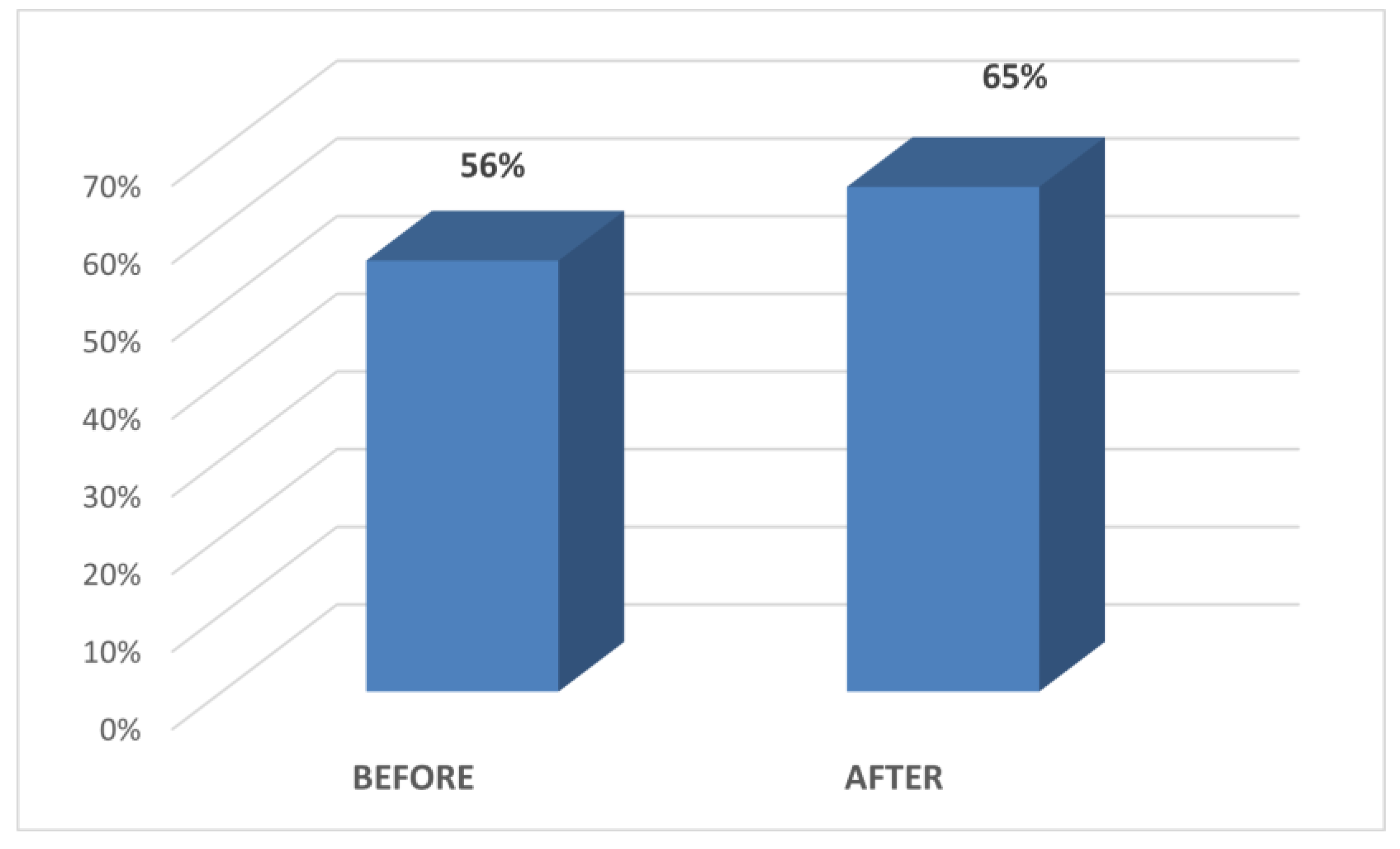
| Total EF | Pre Post | 7.85 9.17 | −5.107 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galanis, N.; Amprazis, A.; Malandrakis, G. Teaching and Learning About the Ecological Footprint to Primary School Students: A Vehicle for Achieving the 2030 SDGs. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125429
Galanis N, Amprazis A, Malandrakis G. Teaching and Learning About the Ecological Footprint to Primary School Students: A Vehicle for Achieving the 2030 SDGs. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125429
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalanis, Nikolaos, Alexandros Amprazis, and Georgios Malandrakis. 2025. "Teaching and Learning About the Ecological Footprint to Primary School Students: A Vehicle for Achieving the 2030 SDGs" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125429
APA StyleGalanis, N., Amprazis, A., & Malandrakis, G. (2025). Teaching and Learning About the Ecological Footprint to Primary School Students: A Vehicle for Achieving the 2030 SDGs. Sustainability, 17(12), 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125429







