1. Introduction
The supply chain consists of independent organizations involved in the flow of products, services, or information from a source to the consumer [
1]. Supply chain management means the harmonious management of products, services, and information, which significantly affects the competitiveness of enterprises in terms of production costs, speed of bringing the product to the market, capital needs of enterprises, and profitability. In this direction, the purpose of supply chain management is to create a seamless supply chain where regional borders are eliminated to respond to consumer demands, offer quality products and services to the market, reduce production costs, and gain a competitive advantage [
2]. However, managing today’s globalized supply chain has a complex structure due to uncertainties in economic and technological fields [
3]. The increasing scale of enterprises, diversified product portfolio, changes in the product life cycle, increasing consumer demands, the presence of many geographical locations to be served, and the large number of intermediaries cause this complexity to increase [
4]. Eliminating complexity and solving existing problems is possible with the transition from traditional understanding to digitalisation, which is a modern, global, smart, and sustainable understanding [
5]. In recent years, advanced technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain technology have been actively used in supply chain management with digitalization [
6]. Among these technologies, blockchain technology stands out as a promising technology [
7].
The combination of supply chain management and blockchain technology enables the exchange of information among supply chain members by optimizing supply chain activities. In this context, supply chain processes are accelerated and strengthened thanks to shared transactional and strategically important information [
8]. Integrating blockchain technology into the supply chain is a reliable approach to support and reorganize supply chain models and improve the quality of service provided. In short, adapting the blockchain to the supply chain ensures supply chain sustainability [
9]. With the use of blockchain in the supply chain, it is possible to monitor every stage of the supply chain and identify the sources that cause insecurity. In this way, it becomes easier to track where the product offered to the market goes within the supply chain network [
10]. At the same time, the fact that the blockchain does not belong to any person allows the digital records kept to be followed by everyone [
8]. Blockchain technology shortens transaction costs and times by removing unnecessary steps in the supply chain network [
11]. Blockchain technology plays a vital role in supply chain management thanks to its features, such as unalterability of data, traceability, and transparency [
12]. Due to its high level of applicability, blockchain technology provides benefits for businesses in business relationships in almost every supply network. It ensures cooperation with stakeholders in the supply network and increases process-added value [
13].
The new product development process consists of various interrelated activities, such as the emergence of a new product idea, designing, testing, and launching the product. The last stage of this process is the commercialization of the product. This process is a complex process that is costly, time-consuming, and requires working together with internal and external stakeholders [
14]. At this point, blockchain technology emerges as a modern form of integration that businesses can use in new product development strategies [
15]. Blockchain enables the storage of information required in the new product development process and simultaneously sharing it with other interested parties [
6]. This situation paves the way for the formation of trust between stakeholders. This technology, which enables easier communication and cooperation with suppliers, enables businesses to easily access the additional information required to develop new products [
16]. In short, during the new product development process, it ensures that the processes such as collecting, tracking, and storing the data of the supply chain proceed reliably and transparently [
15].
Blockchain technology is a developing technology. Although blockchain technology, which was born with the concept of cryptocurrency, has only recently started to be applied in the world within the scope of supply chain management, some examples of companies that use blockchain technology in supply chain management are Walmart, Nestlé, Foxconn, IBM-Food Trust Food Trust, Carrefour, Migros, and TOGG. According to the comprehensive research report prepared by Market Research Future, the blockchain market in supply chain management will show great development from 2022 to 2030 and will reach a value of approximately USD 17.15 billion by the end of 2030 [
17].
The use of blockchain technology, the importance of which is mentioned above, in supply chain management will bring many benefits. Within the scope of this study, it was tried to determine in which direction the use of blockchain technology in supply chain management affects new product development. At the same time, the opinions of purchasing managers about the supply chain process, process knowledge, and the effect of blockchain on the new product development process were obtained. It is thought that these views will guide other company managers who have not yet used blockchain technology or are new to it. In line with the main question of the research, which is the effect of the use of blockchain technology in supply chain management on new product development, the mediating role of supply chain transparency and supplier trust in the relationship between the adoption of blockchain technology and new product development variables has been tried to be determined. In this context, by selecting ISO 1000 companies as the main mass, it is one of the first studies conducted in Türkiye in this context. The fact that the studies on this subject are generally qualitative, address the difficulties and benefits of using blockchain technology in supply chain management, and that there are few studies on the adoption of blockchain technology and new product development differentiates this study from other studies. In addition, it is thought that it will contribute to the literature by combining the technology, environment, organization, and technology acceptance models, which are among the technology acceptance models for the adoption of blockchain technology, and the model created due to literature reviews. In addition to this information, companies will decide how to adapt to blockchain, which factors to pay attention to, and how to position blockchain by seeing the effect of blockchain on new product production. In line with the results obtained, the importance of technology, especially blockchain technology, will be understood, and it will be seen that it is a usable variable not only in the field of new product development but also in other production areas.
4. Results
A questionnaire form was used to test the hypotheses and the proposed theoretical model. Before conducting the field study in its entirety, the questionnaire was tested by applying it to the target audience (within the scope of the pilot study) to verify its validity and make the necessary changes. Only minor changes were made after the pilot application by checking whether the survey questions were easily understood. Then, the entire survey application was conducted.
The data obtained as a result of the survey application was analyzed with the help of SPSS 26.0 and AMOS 22.0 statistical programs. Before conducting the necessary analyses, a normality test was performed to determine whether the sample showed a normal distribution, and it was determined that the data showed a normal distribution. Descriptive statistics, explanatory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, and structural equation modeling were used in the analysis of the data. Since the research model is a model that examines cause/effect relationships, the structural equation model was preferred.
4.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Participants/Descriptive Statistics
Frequency analysis was performed to determine the demographic characteristics of the participants, and the findings are shown in
Table 4.
As seen in the table, the frequency distribution of demographic characteristics of 650 participants is as follows: Most of the participants are undergraduate graduates, 55.8%, male 60.3%, 43.1% are between the ages of 40 and 49, and 23.8% are supply chain management department managers.
4.2. Participating in Business Characteristics/Descriptive Statistics
Frequency analysis was used to determine the characteristics of participating businesses, and the findings are shown in
Table 5.
As seen in the table, the frequency distribution of findings regarding the characteristics of the participating enterprises is as follows: The field of activity of most of the participating enterprises is automotive with a rate of 27.1%, the duration of activity is 21–30 years with a rate of 28.6%, the legal structure is joint stock company with a rate of 63.2%, the number of employees is 2251–3250 with a rate of 63.2%, the duration of working with the same supplier is 16–20 years with a rate of 31.1%, the capital structure is foreign partnership with a rate of 59.1%, the market structure is both markets (domestic and international) with a rate of 67.5%, and the annual net sales revenue is between 101 million TRY and 500 million TRY with a rate of 42.8%.
4.3. Participants’ Evaluations of the Variables Forming the Research Model
The mean and standard deviation values resulting from the evaluation of the technological dimension, organizational dimension, environmental dimension, intention to adopt blockchain technology, adoption of blockchain technology, supply chain transparency, supplier trust, and new product development variables forming the research model by the participants are presented below.
The statement with the highest mean for the technological dimension variable is, “The main feature of blockchain technology is that it makes all recorded data available to all network participants almost continuously”, with a mean of 3.99. Again, the statement under the same variable, “To share data over the blockchain, supply chain members must agree on the standard processes, types and levels of detail of the data to be shared”, stands out with a mean of 3.86. In line with these two statements, it is possible to say that the participants attach importance to sharing data continuously over the blockchain network within the framework of predetermined rules in a way that all participants can see. The two statements with the highest mean for the organizational dimension variable are, “Adoption and implementation of blockchain technology requires extensive technological investments. Your company’s sufficient financial resources support such investments”, with an average of 3.89, and “Senior management is willing to allocate a budget for the implementation of blockchain technology”, with an average of 3.88, respectively. In line with these two statements with similar means, it is possible to say that the participating companies support investments in this direction by allocating a budget for investments in the adoption and implementation of blockchain technology. The two statements with the highest and the same mean for the environmental dimension variable are, “Your company needs to implement blockchain technology to become a leader in its sector”, and “Your company’s major partners demand that the company implement blockchain technologies”, with an average of 3.82. In line with these two statements, it is possible to say that the participating companies need to implement blockchain technologies to become leaders in the sector and meet the demands of their major partners in this direction. The statement with the highest mean for the intention to adopt blockchain technology variable is, “Your company plans to digitally transform its supply chain management through blockchain technologies”, with an average of 3.85. In line with this statement, it is possible to say that the participant companies plan to adopt blockchain technologies to supply chain management. The statement with the highest mean for the blockchain technology adoption variable is, “Your company’s commercial activities invest resources in blockchain-enabled supply chain applications”, with an average of 3.88. In line with this statement, it is possible to say that the participant companies invest resources in blockchain-enabled supply chain applications. The two statements with the highest mean for the supply chain transparency variable are, respectively, “Blockchain technology enables information sharing with suppliers and vendors about production, assembly, delivery, and maintenance processes”, with an average of 3.88, and “Blockchain technology enables verification and certification of product characteristics, such as indicating whether a food product is organic”, with an average of 3.87. In line with these two statements, it is possible to say that the blockchain technology of the participating companies enables the sharing of information between suppliers and sellers about the processes and the verification and certification of the features of the products. The two statements with the highest average for the supplier trust variable are “Trust is necessary for technological success”, with an average of 3.88, and “You develop good relationships with your suppliers and/or buyers by using blockchain technologies”, with an average of 3.84, respectively. In line with these two statements, it is possible to say that the participating companies can develop trust-based relationships with suppliers with the help of blockchain technology. The statement with the highest average for the new product development variable is, “Your company is rapidly developing a new product for the market by using blockchain technology in its supply chain”, with an average of 3.84. In line with this statement, it is possible to say that the participating companies can quickly introduce new products to the market with the help of blockchain technology.
4.4. Reliability Analysis Results
In order to determine the reliability levels of the scales used in the research, the necessary analyses were performed; Cronbach’s Alpha values were determined, and the results are shown in
Table 6.
It is accepted that the Cronbach Alpha values of the scales are at least 0.70 and above. Cronbach Alpha values of 0.70 and above prove that the reliability of the scales used in the study is at an acceptable level [
51]. In this study, reliability analysis was conducted for each scale in the research model. As a result of the analysis, it was seen that the reliability levels of the scales varied between 0.87 and 0.95, and it was concluded that the scales used were reliable. Confirmatory factor analysis was used to test the validity of the scales whose reliability levels were determined. Confirmatory factor analysis for the scales is included in the following section of the study.
4.5. Path Analysis Results Regarding Interactions Between Model Variables
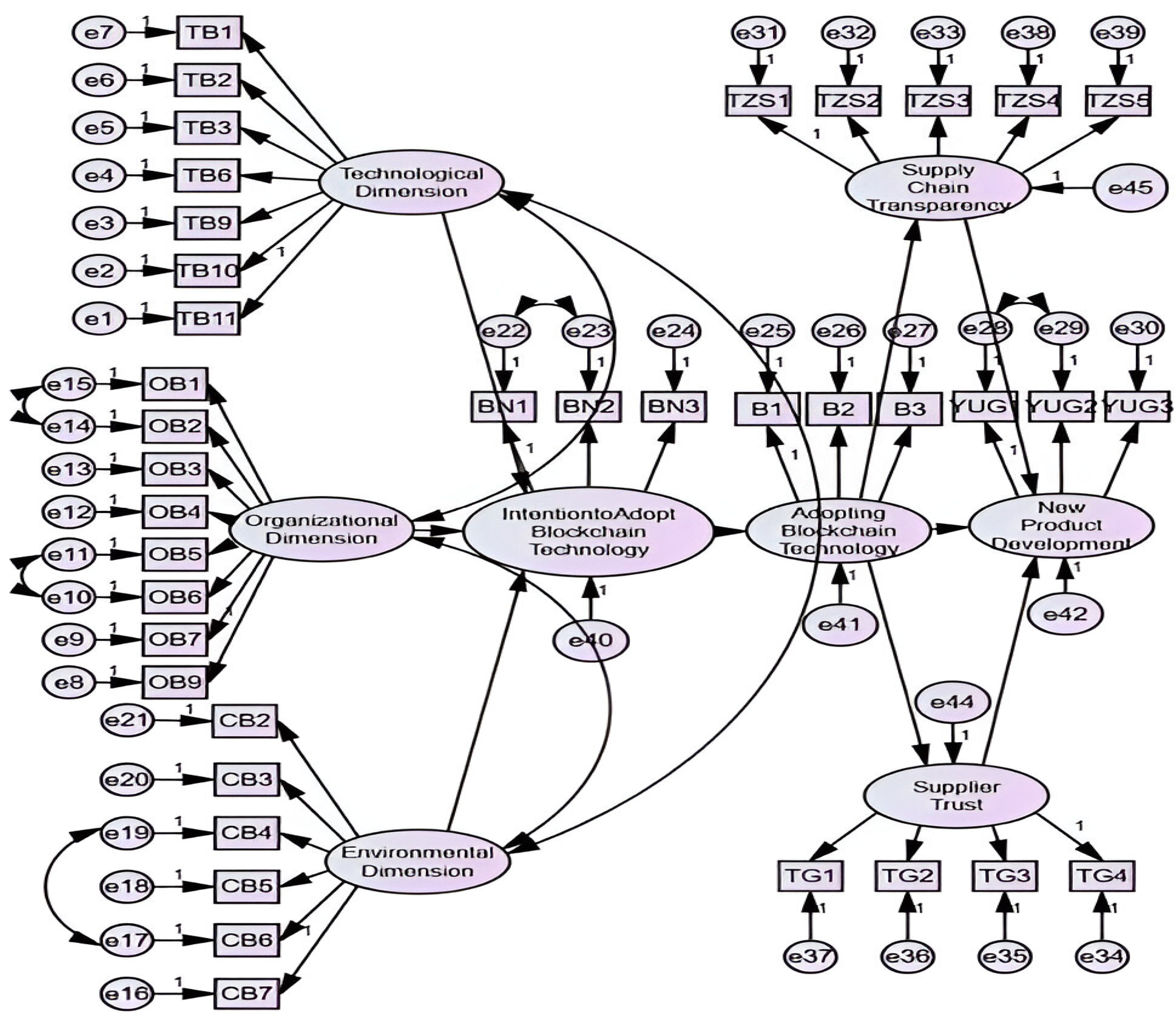
After the reliability and validity analyses of the variables forming the research model were conducted, confirmatory factor analysis was applied to the variables. As a result of confirmatory factor analysis, questions four, five, seven, and eight were removed from the technological dimension variable, question eight from the organizational dimension variable, and question one from the environmental dimension variable. Subsequently, structural equation modeling was conducted for the research model, and the path diagram is presented in
Figure 3.
The fit indices for the path analysis performed to test the hypotheses proposed are shown in
Table 7, both before and after modification.
When the fit index values of the research model were examined, it was seen that the variables in the model did not have acceptable fit values (Chi-Square/sd: 3.536 GFI: 0.818 AGFI: 0.794 RMSEA:0.063), and modifications were made by establishing a covariance connection between the first and second questions of the organizational dimension variable, as well as between the fifth and sixth questions of the organizational dimension variable, between the fourth and sixth questions of the environmental dimension variable, between the first and second questions of the intention to adopt blockchain technology variable, and between the first and second questions of the new product development variable.
After the necessary modifications were completed, it was seen that the Chi-Square/sd ratio was 2.879 below the reference value, the RMSEA value was 0.054, the GFI value was 0.850, the AGFI value was 0.829, the CFI value was 0.959, the NFI value was 0.939, and the NNFI(TLI) value was 0.956, and these values were at an acceptable level of fit. In addition, the results obtained show that the research model as a whole is statistically significant.
In order to test the hypotheses developed in line with the research purpose, the standardized coefficients, error variances, t-values, and significance levels (
p-values) for the relationships between the variables are shown in
Table 8.
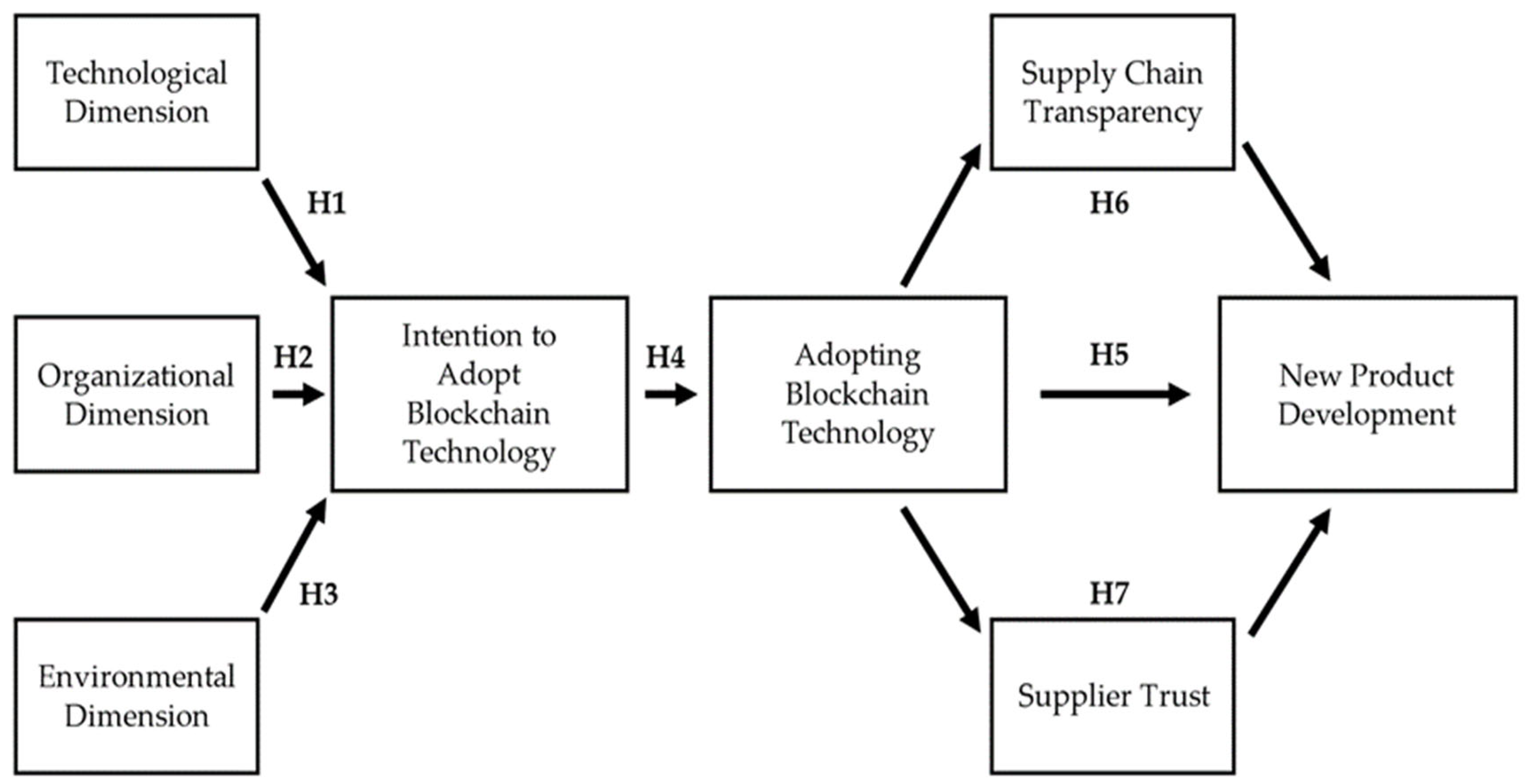
According to the results of the structural equation model analysis, the H1 hypothesis was rejected because the “Technological dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology” hypothesis was p ≥ 0.05.
Hypothesis H2 was rejected because the hypothesis “Organizational dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology” was p ≥ 0.05.
Similarly, hypothesis H3 was also rejected because the hypothesis “Environmental dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology” was p ≥ 0.05.
The intention to adopt blockchain technology has a statistically significant effect on the adoption of blockchain technology. In line with this result, hypothesis H4 was accepted (p ≤ 0.05). In other words, when the intention to adopt blockchain technology increases, the adoption of blockchain technology will also increase positively.
Adopting blockchain technology has a statistically significant effect on new product development. In line with this result, hypothesis H5 was accepted (p ≤ 0.05). In other words, when the adoption of blockchain technology increases, new product development will also increase positively.
In addition to this information, the adoption of blockchain technology has a statistically significant effect on supply chain transparency and supplier trust. Accordingly, hypotheses H6 and H8 were accepted (p ≤ 0.05). In other words, as the adoption of blockchain technology increases, supply chain transparency and supplier trust will also increase positively.
At the same time, supply chain transparency and supplier trust also have a statistically significant effect on new product development. Accordingly, hypotheses H7 and H9 were accepted (p ≤ 0.05). In other words, as supply chain transparency and supplier trust increase, new product development will also increase positively.
Accordingly, the acceptance and rejection statuses of the hypotheses of the research model are shown in
Table 9.
4.6. Testing the Madiation Effect
Mediation analysis is a widely used estimation method in research conducted in the field of social sciences. This method defines the indirect relationship between dependent and independent variables. In other words, it allows analyzing the relationship between the independent variable and the mediator variable. At this point, the mediator variable is in the position of a variable that is estimated with the independent variable and acts as the dependent variable.
In the relationship between variables, it is desired for the independent variables to have a high correlation with the dependent variables and for the independent variables to have a low correlation with each other [
96]. In line with the mediation approach of Baron and Kenny, which is called the causal steps approach, the existence of the mediator effect develops depending on 4 conditions. These conditions are as follows [
97]:
The total effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable must be statistically significant.
The independent variable must affect the mediator variable statistically significantly.
The mediator variable must affect the dependent variable statistically significantly.
If the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable decreases in the last regression, the mediation is expressed as “partial mediation”; if it disappears completely, it is expressed as “full mediation”.
4.6.1. Examining the Mediating Effect of the Supply Chain Transparency Variable
To determine the mediating role of supply chain transparency in the effect of blockchain technology adoption on new product development, Model 4 in the process macro add-on in the SPSS package program was selected, and hierarchical regression analysis was performed. The results obtained from the study are shown in
Table 10.
As seen in the table, according to the mediation effect results, in the first stage, adopting blockchain technology has a positive effect on new product development (β = 0.957); in the second stage, adopting blockchain technology has a positive effect on supply chain transparency (β = 0.882); in the third stage, supply chain transparency has a positive effect on new product development (β = 0.655). According to the mediation effect results, since the condition of not being zero between the BootLLCI values indicating a low reliability interval and the BootULCI values indicating a high reliability interval (0.455–0.638) is provided, it is seen that there is a mediation effect of supply chain transparency between adopting blockchain technology and new product development (β = 0.546). To decide on the type of mediation effect, the p-value was examined, and it was seen that the p-value was less than 0.05. Thus, it was understood that this effect was a partial mediation effect. In addition to this analysis, the existence of the mediation effect was questioned again with the Sobel test. According to the Sobel test results (p = 0.000 < 0.05), since the Z scores are greater than 1.96 (4.805 > 1.96), it has been proven again that there is a mediation effect. Based on this finding, the H6 hypothesis (Supply chain transparency variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development) has been accepted. In other words, supply chain transparency has a partial mediating role by reducing the effect of blockchain technology adoption on new product development.
4.6.2. Examining the Mediating Effect of the Supplier Trust Variable
In order to determine the mediating role of supplier trust in the effect of adopting blockchain technology on new product development, Model 4 in the Process Macro add-on in the SPSS package program was selected, and hierarchical regression analysis was performed. The results obtained from the study are shown in
Table 11.
As seen in the table, according to the mediation effect results, it was seen that in the first stage, adopting blockchain technology had a positive effect on new product development (β = 0.957); in the second stage, adopting blockchain technology had a positive effect on supplier trust (β = 0.927); in the third stage, supplier trust had a positive effect on new product development (β = 0.592). According to the mediation effect results, since the condition of not being zero between the BootLLCI values indicating low reliability interval and the BootULCI values indicating high reliability interval (0.431–0.606) was provided, it was seen that there was a mediation effect of supplier trust between adopting blockchain technology and new product development (β = 0.518). To decide on the type of mediation effect, the p-value was examined, and it was seen that the p-value was less than 0.05. Thus, it was understood that this effect was a partial mediation effect. In addition to this analysis, the existence of the mediation effect was questioned again with the Sobel test.
According to the Sobel test results (
p = 0.000 < 0.05), since the Z scores were greater than 1.96 (5.222 > 1.96), it was proven again that there was a mediation effect. Based on this finding, hypothesis H7 (Supplier trust variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development) was accepted. In other words, supplier trust played a partial mediating role by reducing the effect of blockchain technology adoption on new product development. The acceptance and rejection status of the hypotheses for the mediating variable analysis are shown in
Table 12.
5. Conclusions
In the competitive global environment, the diversity of consumer demands and the rapid change of technology push businesses to catch up with change and even innovate to survive. In this environment where competition is intense, and change is developing very quickly, achieving success in the market becomes possible by developing unique, high-quality, new features, high value-in-use, long product life cycles, and difficult-to-imitate products. Businesses catch up with the change in the market through the supply chain, respond to innovations, and transform this situation into business opportunities. In this process, many businesses benefit from information technologies to compete with their competitors by reducing costs and producing in line with consumer demands. Blockchain technology, one of the information technologies, is a promising technology used by many businesses. In this context, the blockchain technology used provides simultaneous sharing, tracking, and immutability of data among supply chain members. By using blockchain technology in supply chain management, transparency is ensured, and a sense of trust develops among stakeholders. In this way, the new product development process becomes more effective and easier for businesses. In light of this information, the purpose of the research is to determine the impact of adopting blockchain technology in supply chain management on new product development, to determine the opinions of purchasing managers on supply chain integration, process knowledge, and the role of blockchain in new product development, and to determine the mediating role of supply chain transparency and supplier trust in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development variables. The following results were obtained from the research conducted for this purpose.
The majority of the participants are male undergraduate graduates and supply chain management department managers between the ages of 40 and 49. It was determined that the field of activity of most of the participating enterprises is automotive, the duration of activity is 21–30 years, the legal structure is a joint-stock company, the number of employees is 2251–3250, the duration of working with the same supplier is 16–20 years, the capital structure is foreign partnership, the market structure is both markets (domestic and international) and the annual net sales revenue is between 101 million TRY and500 million TRY. Participants’ perceptions of the technological dimension, organizational dimension, environmental dimension, intention to adopt blockchain technology, blockchain technology adoption, supply chain transparency, supplier trust, and new product development were measured, and the statements with the highest levels of agreement are listed below.
“The main feature of blockchain technology is that it makes all recorded data available to all network participants almost continuously”.
“Adoption and implementation of blockchain technology require extensive technological investments. Your company’s sufficient financial resources support such investments”.
“Your company needs to implement blockchain technology to become a leader in its sector”.
“Your company plans to digitally transform its supply chain management through blockchain technologies”.
“Commercial activities in your company invest resources in blockchain-enabled supply chain applications”.
“Blockchain technology enables information sharing with suppliers and vendors about production, assembly, delivery, and maintenance processes”.
“Trust is necessary for technological success”.
“Your company is rapidly developing a new product for the market by using blockchain technology in its supply chain”.
It can be deduced from the above statements that the participants think that by using blockchain technology in supply chain management, data can be used in all supply processes and by all network participants and that new products can be quickly introduced to the market. In addition, the participants believe that digital transformation should be realized by having financial resources for the use of blockchain technology and by supporting such investments. At this point, the importance of trust among stakeholders for technological success is emphasized.
Validity and reliability analyses of the model created within the scope of the research were conducted. As a result of the analyses, the reliability levels of the scales belonging to the eight variables in the model were found to be high. In addition, explanatory and confirmatory factor analyses were conducted to reveal the validity of the scale. Necessary modifications were made in the confirmatory factor analysis, scale expressions not included in the fit values were removed, and structural equation analysis was used to test the hypotheses. When the research examined whether the technological dimension affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology, it was seen that the technological dimension does not affect the intention to adopt blockchain technology. Accordingly, the research’s H
1 hypothesis (H
1: Technological dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology) was rejected. When the organizational dimension affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology, it was seen that the organizational dimension does not affect the intention to adopt blockchain technology. Accordingly, the research’s H
2 hypothesis (H
2: Organizational dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology) was rejected. When the environmental dimension affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology, it was seen that the environmental dimension does not affect the intention to adopt blockchain technology. Accordingly, the research’s H
3 hypothesis (H
3: Environmental dimension positively affects the intention to adopt blockchain technology) was rejected. These results differ from the studies conducted by Mishra et al. [
98], Chittipaka et al. [
55], Shahzad et al. [
12], Hashimy et al. [
66], and Kumar Bhardwaj et al. [
4], which were obtained by scanning the theory.
In other words, these dimensions mentioned do not affect the intention to adopt blockchain technology. It can be thought that the reason for this situation is the technology acceptance models used. There is a possibility that different results may be obtained in the use of different technology models. From a different perspective, since blockchain technology is a very new technology in Turkey, the necessity of blockchain technology may be understood, but the enterprise may not be ready for this technology in terms of technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions. The same results can be encountered not only in terms of blockchain technology but also in studies conducted within the scope of the adoption of other elements of Industry 4.0. In this direction, researchers who study these topics may encounter the same results. At this point, this study can provide theoretical support to those who conduct research. In addition, the reason why the hypotheses of other studies were accepted may be because they were conducted in countries where the level of development of blockchain technology is high.
When it was examined whether the intention to adopt blockchain technology affects the adoption of blockchain technology, it was seen that the intention to adopt blockchain technology affects the adoption of blockchain technology. In this direction, the H
4 hypothesis of the research (H
4: The intention to adopt blockchain technology positively affects the adoption of blockchain technology) was accepted. This result is compatible with the studies conducted by Shahazad et al. [
12], Kamble et al. [
5], and Hashimy et al. [
66]. Adoption intention expresses the desire of businesses to use new technologies. When businesses are willing to use technology, their use of that technology is positively affected [
12].
When it was examined whether the adoption of blockchain technology affects new product development, it was seen that the adoption of blockchain technology affects new product development. In this direction, the H
5 hypothesis of the research (H
5: Adoption of blockchain technology positively affects new product development) was accepted. This result is compatible with the studies conducted by Benzidia et al. [
6], Wan et al. [
72], and Mishra et al. [
98]. The adoption of blockchain technology and its use by businesses improve innovation activities [
6]. Blockchain technology has a strong impact on new product development [
94]. The fact that studies on innovation generally concern computer science, while this research adapts innovation to production, creates originality. The adoption of blockchain by businesses positively affects new product development.
Within the scope of the research model, it was investigated whether the supply chain transparency variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development. As a result of the mediation test, it was observed that supply chain transparency has a partial mediating effect. In other words, supply chain transparency played a partial mediating role by reducing the effect of blockchain technology adoption on new product development. In this direction, the H
6 hypothesis (H
6: The supply chain transparency variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development) was accepted. This result shows that blockchain technology adoption influences supply chain transparency, and supply chain transparency has an effect on new product development. These results are consistent with the studies conducted by Rashid et al. [
61] and Yunlin [
99]. Uncertainty in supply chains is not a desired situation for businesses that are members of the chain. The importance that businesses attach to transparency affects the decisions they make. Thus, ensuring transparency in the supply chain both strengthens the relationships established with suppliers and becomes an important element in new product development [
97]. To summarize, supply chain transparency facilitates the adoption of blockchain technology and makes new product development more likely. Therefore, ensuring supply chain transparency affects the effectiveness of the blockchain technology adoption process in providing supply chain transparency and the optimal increase in new product development. Within the scope of the research model, it was examined whether the supplier trust variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development. As a result of the mediation test, it was seen that supplier trust has a partial mediating effect. In other words, supplier trust played a partial mediating role by reducing the effect of blockchain technology adoption on new product development. In this direction, the H
7 hypothesis (H
7: Supplier trust variable has a mediating role in the relationship between blockchain technology adoption and new product development) was accepted. This result shows that adopting blockchain technology affects supplier trust and supplier trust in new product development. These results are consistent with the studies conducted by Rashid et al. [
61] and Alsmadi et al. [
100].
When businesses trust their suppliers, it makes it easier for them to adopt blockchain technology and makes new product development more likely. Therefore, ensuring supplier trust affects the blockchain technology adoption process’ impact on supplier trust and the optimal increase in new product development.