Eutrophication Monitoring for Sustainable Development in Nha Trang Marine Protected Area, Vietnam
Abstract
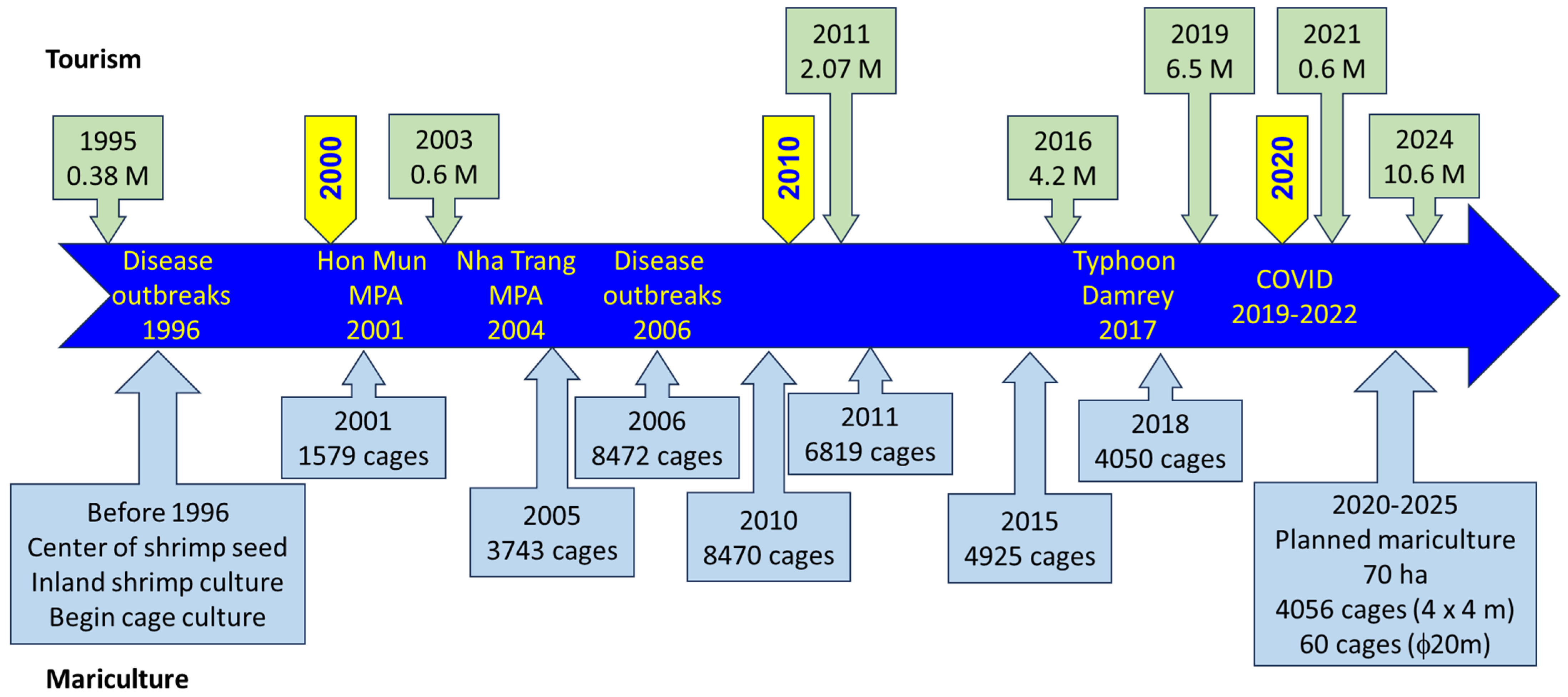
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Collection, and Analysis
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. EI Calculation
2.2.2. EI Validation
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Water Quality Parameters
3.2. Classification of Water Quality in Nha Trang Bay
4. Discussion
4.1. EI Approach
4.2. The Weighting Method in the Eutrophication Index
4.3. EI as a Tool for Water Quality Monitoring in MPAs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, C.; Carter, R.W.; Thomsen, D.C.; Smith, T.F. Monitoring and evaluation for adaptive coastal management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 89, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udy, J.; Gall, M.; Longstaff, B.; Moore, K.; Roelfsema, C.; Spooner, D.R.; Albert, S. Water quality monitoring: A combined approach to investigate gradients of change in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Clayton, T.D.; Swarzenski, P.; Brock, J.C.; Muller-Karger, F.E. Assessment of estuarine water-quality indicators using MODIS medium-resolution bands: Initial results from Tampa Bay, FL. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, S.B.; Ferreira, J.G.; Simas, T. An integrated methodology for assessment of estuarine trophic status. Ecol. Model. 2003, 169, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Bald, J.; Franco, J.; Larreta, J.; Muxika, I.; Revilla, M.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Solaun, O.; Uriarte, A.; Valencia, V. Using multiple ecosystem components, in assessing ecological status in Spanish (Basque Country) Atlantic marine waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, Á.; Franco, J.; Valencia, V.; Bald, J.; Muxika, I.; Jesús Belzunce, M.; Solaun, O. Implementation of the European water framework directive from the Basque country (northern Spain): A methodological approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.; Adams, M.; Walker, T.R. Role of sustainability in global seaports. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 202, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artiola, J.; Pepper, I.; Brusseau, M. Environmental Monitoring and Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; p. 410. [Google Scholar]
- Jingzhong, Z.; Liping, D.; Baoping, Q. Preliminary studies on eutrophication and red tide problems in Bohai Bay. Hydrobiologia 1985, 127, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R. Review of assessing methods for coastal eutrophication. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1996, 15, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cloern, J.E. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 210, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Shen, Z. A review on eutrophication research of coastal waters. Mar. Sci. 2005, 29, 53–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.G.; Lee, S.S.; Schofield, K.A.; Ridley, C.E.; Washington, B.J.; Gibbs, D.A. Response of chlorophyll a to total nitrogen and total phosphorus concentrations in lotic ecosystems: A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, P.; Padisák, J.; Koschel, R.; Krienitz, L.; Gervais, F. Chlorophyll a concentration across a trophic gradient of lakes: An estimator of phytoplankton biomass? Limnologica 2008, 38, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragih, F.S.; Djamil, H.; Juanda, J.; Mubarak, A.S.; Hasan, V.; Sihombing, A.; Satyantini, W.H. Nutrient Concentration, Water Brightness, Chlorophyll-a, and Phytoplankton Abundance as Indicators for Determining the Trophic Status of Lake Toba, North Sumatera—Indonesia. J. Aquac. Fish Health 2024, 13, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Alcântara, E.; Rodrigues, T.; Bernardo, N. Satellite estimates of euphotic zone and Secchi disk depths in a colored dissolved organic matter-dominated inland water. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.T.; Walve, J.; Andersson, A.; Karlson, B.; Kratzer, S. The Effect of Optical Properties on Secchi Depth and Implications for Eutrophication Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V. Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems a global problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Dauer, D.M. Assessing the environmental quality status in estuarine and coastal systems: Comparing methodologies and indices. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Giovanardi, F.; Montanari, G.; Rinaldi, A. Characterization of the trophic conditions of marine coastal waters with special reference to the NW Adriatic Sea: Proposal for a trophic scale, turbidity and generalized water quality index. Environmetrics 1998, 9, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’uomo, A.; Torrisi, M. The Eutrophication/Pollution Index-Diatom based (EPI-D) and three new related indices for monitoring rivers: The case study of the river Potenza (the Marches, Italy). Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2011, 145, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Fernández, J.R.; García Nieto, P.J.; Díaz Muñiz, C.; Álvarez Antón, J.C. Modeling eutrophication and risk prevention in a reservoir in the Northwest of Spain by using multivariate adaptive regression splines analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 68, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, M.; Agarwal, R.P. Stability and dynamics analysis of time delayed eutrophication ecological model based upon the Zeya reservoir. Math. Comput. Simul. 2014, 97, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, A.; Ponis, E.; Cacciatore, F.; Riccardi, E.; Pigozzi, S.; Parati, P.; Novello, M.; Ungaro, N.; Acquavita, A.; Manconi, P.; et al. A New Multi-Index Method for the Eutrophication Assessment in Transitional Waters: Large-Scale Implementation in Italian Lagoons. Environments 2022, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ye, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Integrated ecological quality assessment of the sea area adjacent to the Yellow River estuary under multiple pollutants. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1542611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEEA. Effects of Nutrient Enrichment in the Nation’s Estuaries: A Decade of Change; National Estuarine Eutrophication Assessment: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2007; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Selman, M.; Greenhalgh, S.; Diaz, R.; Sugg, Z. Eutrophication and hypoxia in coastal areas: A global assessment of the state of knowledge. In WRI Policy Note: Water Quality: Eutrophication and Hypoxia; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Zou, G.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L. Eutrophication dangers the ecological status of coastal wetlands: A quantitative assessment by composite microbial index of biotic integrity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotto, L.P.A.; Jacinto, G.S.; Villanoy, C.L. Spatiotemporal variability of hypoxia and eutrophication in Manila Bay, Philippines during the northeast and southwest monsoons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Chen, K.L.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, Q.H.; Qiu, Y.P.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, J.F. Evaluation for the ecological quality status of coastal waters in East China Sea using fuzzy integrated assessment method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, P.M.; Hieu, N.T.D.; Thao, P.T.P. Variation of water quality in Nha Trang Bay. Vietnam J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.G.; Andersen, J.H.; Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Camp, J.; Cardoso da Silva, M.; Garcés, E.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Humborg, C.; Ignatiades, L.; et al. Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maúre, E.d.R.; Terauchi, G.; Ishizaka, J.; Clinton, N.; DeWitt, M. Globally consistent assessment of coastal eutrophication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyman, N.; Tavakoly Sany, S.B.; Tajfard, M.; Hashim, R.; Rezayi, M.; Karlen, D.J. The status and characteristics of eutrophication in tropical coastal water. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1086–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.-S. A comprehensive approach to assessing eutrophication for the Guangdong coastal waters in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1280821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-K.; Chen, P.; Chen, H.-Y. Comprehensive assessment of coastal eutrophication in Taiwan and its implications for management strategy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.V. The marine environmental status in the coastal waters of south Vietnam (2002–2006). In Proceedings of the National Conference “Bien Dong 2007”, Nha Trang, Vietnam, 12–14 September 2007; pp. 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Vinh, L.T.; Kiem, D.T.; Thu, N.H.; Tam, P.H.; Ngoc, P.H. Some remarks on water environment in Nhatrang City. In Proceedings of the National Conference “Bien Dong 2007”, Nha Trang, Vietnam, 12–14 September 2007; pp. 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.M.L.; Quach, T.T.T.; Tran, A.P.; Nguyen, C.D. Assessment of water quality in coastal estuaries under the impact of an industrial zone in Hai Phong, Vietnam. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 113, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, C.T.T.; Thanh, T.; Thanh, T.D.; Vinh, V.D.; Tu, T.A. Assessment of the environmental carrying capacity of pollutants in Tam Giang-Cau Hai Lagoon (Vietnam) and solutions for the environment protection of the lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, L.H.; Kim-Hong, P.T.; Chung, T.V.; Binh, T.V.; Dung, L.T.; Ngoc, P.H.; Thu, N.H.; Thu, N.T.T.; Anh, N.T.H.; Nguyen, A.L.; et al. Environmental Concerns for Sustainable Mariculture in Coastal Waters of South-Central Vietnam. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souda, K.; Minami, T. Analysis of water pollution in Halong Bay, Vietnam using a comprehensive water quality index. Environ. Technol. 2020, 49, 209–213. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, V.D. Environmental state in Mekong Delta, South of Vietnam. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Marine Pollution, Monaco, Monaco, 5–9 October 1998; pp. 674–675. [Google Scholar]
- Pettine, M.; Casentini, B.; Fazi, S.; Giovanardi, F.; Pagnotta, R. A revisitation of TRIX for trophic status assessment in the light of the European Water Framework Directive: Application to Italian coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.T.; Hieu, N.M.; Kunzmann, A. Negative effects of fish cages on coral reefs through nutrient enrichment and eutrophication in Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 55, 102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Zhao, J.x.; Feng, Y.x.; Hu, W.p.; Yu, K.f.; Gasparon, M.; Pham, T.B.; Clark, T.R. Impact of recent coastal development and human activities on Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam: Evidence from a Porites lutea geochemical record. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuu, D.T.; Jones, P.J.S.; Ekins, P. Governance analysis of Nha Trang Bay and Cu Lao Cham Marine Protected Areas, Vietnam. Mar. Policy 2021, 127, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh-Thu, P.; Sang, H.M.; Thao, L.T.T.; Hieu, N.M.; Tram, D.T.T.; Ngoc, D.T.H.; Mien, P.T. A SWOT Analysis of Aquaculture for Sustainable Management in Coastal Waters of Ba Ria—Vung Tau Province, Vietnam. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2023, 25, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, P.Q.; Khanal, R. What next for marine ecosystem management in Vietnam: Assessment of coastal economy, climate change, and policy implication. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 25002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.T.T.; Ha, N.T.T.; Do Khanh, G.; Van Thanh, N.; Hens, L. Sustainability assessment of coastal ecosystems: DPSIR analysis for beaches at the Northeast Coast of Vietnam. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 5032–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Do, K.H.; Pham, T.T.T. Tourism in marine protected areas: A view from Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 33, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, K.S. Degradation of Coral Reefs under Complex Impact of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors with Nha Trang Bay (Vietnam) as an Example. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2023, 13, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, P.T.; Kroeze, C.; Bush, S.R.; Mol, A.P.J. Water pollution by intensive brackish shrimp farming in south-east Vietnam: Causes and options for control. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuu, D.T.; Jones, P.J.S.; Ekins, P. Development of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) in Vietnam from a coevolutionary governance perspective: Challenges of unholy alliances between the state, businesses and NGOs. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 149, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, H.H.; Huan, N.H. Distribution of dissolved and particulate organic carbon in Nha Trang—Binh Cang Bay. Collect. Mar. Res. Work. 1998, 8, 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Wright, S.W. Phytoplankton Pigments in Oceanography: Guidelines to Modern Methods; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 1997; p. 661. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, J.P.; Sinhaseni, P. The determination of ammonia and total ionic inorganic nitrogen in sea water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1957, 36, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, C.E.; Holm-Hansen, T. A salicylatehypochlorite method for determining ammonia in seawater. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.; Groenen, P.J.F.; Hastie, T.; D’Enza, A.I.; Markos, A.; Tuzhilina, E. Principal component analysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.R.; Peele, E.R.; Ammerman, J.W.; Harding, L.W.J. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 82, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, P.V.; Tuan, V.S. Characteristics of chemistry environment and possible relation to coral reef degradation in Nha Trang bay. In Proceedings of the First National Conference on Marine Biology, Nha Trang, Vietnam, 1996; Science and Technological Publishing House: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 1996; pp. 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, K.R. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature 2005, 437, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S. Eutrophication and the macroscope. In Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology; Andersen, J.H., Conley, D.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 207, pp. 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, S. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. WIREs Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.W. Coastal nitrogen pollution: A review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xu, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Seasonal nutrients variation, eutrophication pattern, and Chlorophyll a response adjacent to Guangdong coastal water, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1236609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Campillo, S.; Fernández-Palacios, J.M.; García-Lacunza, A.; García-Oliva, M.; Ibañez, H.; Navarro-Martínez, P.C.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Quispe-Becerra, J.I.; et al. Long-Term Dynamic in Nutrients, Chlorophyll a, and Water Quality Parameters in a Coastal Lagoon During a Process of Eutrophication for Decades, a Sudden Break and a Relatively Rapid Recovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. The Complex Relationships Between Increases in Fertilization of the Earth, Coastal Eutrophication and Proliferation of Harmful Algal Blooms. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Granéli, E., Turner, J.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 189, pp. 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, W.R.; Garber, J.H.; Summers, R.; Kemp, W.M. Inputs, transformations, and transport of nitrogen and phosphorus in Chesapeake Bay and selected tributaries. Estuaries 1995, 18, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading Dead Zones and Consequences for Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Water Quality Assessments—A Guide to Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring—Second Edition; UNESCO/WHO/UNEP: Cambridge, UK, 1996; p. 656. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Cochlan, W.P.; Glibert, P.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Kudela, R.M.; Parsons, M.L.; Rensel, J.E.J.; Townsend, D.W.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, A.; Ranasinghe, A.; Weisberg, S.B. Assessing ecological integrity in marine waters, using multiple indices and ecosystem components: Challenges for the future. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Wu, J.-W.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.-W.; Gao, C.; Lin, Z.-Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooday, A.J.; Jorissen, F.; Levin, L.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; Naqvi, S.W.A.; Rabalais, N.N.; Scranton, M.; Zhang, J. Historical records of coastal eutrophication-induced hypoxia. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1707–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, P.; Tian, C.; Zhang, C.; Du, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, B. Coastal eutrophication in China: Trend, sources, and ecological effects. Harmful Algae 2021, 107, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan, V.S. Biodiversity dynamics of coral reefs in Nha Trang Bay and management measures. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Marine Science and Technology: Volume 4—Marine Biology and Resources, Ha Noi, Vietnam, April 2011; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.V. Environmental status in the coastal waters of South Vietnam (1996–2002). Collect. Mar. Res. Work. 2003, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, D.; Andre, I.M.; Morel, A. Oceanic primary production 2: Estimation at global scale from satellite (Coastal Zone Color Scanner) chlorophyll. Glob. Biochem. Cycles 1996, 10, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Nath, S.S. A Strategic Reassessment of Fish Farming Potential in Africa; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.I.; Somerfield, P.J. A multivariate approach to model skill assessment. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 76, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpas, I.; Tsirtsis, G.; Karydis, M.; Kokkoris, G.D. Principal component analysis: Development of a multivariate index for assessing eutrophication according to the European water framework directive. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.K.S.; Lam, W.K.C. Development of a Marine Sediment Pollution Index. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, A.; Ebeid, M.; Soliman, A.; Halim, A.A.; Ali, A.E.; Fahmy, M. Evaluation of the water quality and the eutrophication risk in Mediterranean sea area: A case study of the Port Said Harbour, Egypt. Environ. Chall. 2022, 7, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B.B.; Haskins, J.C.; Wasson, K.; Watson, E. Identifying factors that influence expression of eutrophication in a central California estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 439, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, D. Correlation Model-Based Principal Component Analysis on the Application on Water Body Eutrophication Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Granada, Spain, 11–13 June 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tac-An, N. The Contamination Status in Coastal Zone of NhaTrang Bay. The Ecological Effects and Preventive Means; Institute of Oceanography: Nha Trang, Vietnam, 1996; p. 128. [Google Scholar]
- Tac-An, N.; Minh-Thu, P.; Cherbadji, I.I.; Propp, M.V.; Odintsov, V.S.; Propp, L.H. Primary production of coral ecosystems in the Vietnamese coastal and adjacent marine waters. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 96, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, V.T.T.; Kiem, D.T.; Ngoc, P.H.; Phu, L.H.; Tam, P.H.; Vinh, L.T. Coastal sea water quality of Nha Trang bay, Khanh Hoa, Viet Nam. J. Shipp. Ocean Eng. 2015, 5, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.T.; Kunzmann, A. The sediment load and deposition by river discharge and their relation to organochlorine pesticides pollutants in the sediment bottom of Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam. Ocean Sci. J. 2015, 50, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, V.H.; Tac-An, N.; Huong, L.H. Sediment quality assessment of some marine ports in Nha Trang Bay by biotoxycity testing. In Proceedings of the National Conference “Bien Dong 2007”, Nha Trang, Vietnam, 12–14 September 2007; pp. 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Phuong, T.T.M. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Nha Trang bay, Khanh Hoa, Viet Nam. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, Nice, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giao, N.T.; Dien, N.T.C.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nhu, T.N.; Mi, L.T.D.; Nhien, H.T.H. Evaluating Relationship between Surface Water Quality and Zooplankton Diversity in Coastal Areas of Tien Giang Province, Vietnam. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2024, 28, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, K.S.; Britayev, T.A.; Huan, N.H.; Pereladov, M.V.; Latypov, Y.Y. Influence of anthropogenic pressure and seasonal upwelling on coral reefs in Nha Trang Bay (Central Vietnam). Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Category | EI | Level | Goods and Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oligotrophic | <0.25 | I | All activities but limiting aquaculture |
| Low mesotrophic | 0.25–0.50 | II | Good for swimming, aquaculture, and biodiversity protection |
| Mesotrophic | 0.50–0.75 | III | Good for aquaculture, limiting swimming |
| High mesotrophic | 0.75–1.00 | IV | Controlling aquaculture and limiting biodiversity, but good for port activities, shipbuilding, and navigation |
| Eutrophic | 1.00–2.00 | V | Limiting aquaculture and reducing biodiversity but good for port activities, shipbuilding, and navigation |
| Polluted | 2.00–5.00 | VI | Controlling port activities and navigation; no aquaculture |
| Heavy polluted | >5.00 | VII | Limiting port activities and navigation |
| Parameter | Vietnamese environmental standard (VNES) | Criterion [63] | |
| Chl-a (mg m−3) | No data | 1–10 | |
| DIN (mgN m−3) | No data | 200–300 | |
| DIP (mgP/m−3) | 15 | 15 | |
| BOD (mg O2 L−1) | 10 | 1–3 (for COD concentration (used for comparison)) | |
| Survey Time | Number of Stations/Number of Samples | TSM (g m−3) | Chl-a (mg m−3) | DIN (mgN m−3) | DIP (mgP m−3) | BOD (mgO2 L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| December 1996 | 11/22 | 4.35 ± 4.37 | 1.33 ± 1.45 | 194 ± 154 | 31.6 ± 13.5 | 0.85 ± 0.33 |
| April 1997 | 11/22 | 1.97 ± 1.29 | 0.17 ± 0.11 | 26 ± 15 | 19.9 ± 6.1 | 0.79 ± 0.45 |
| November 1997 | 11/22 | 10.64 ± 9.47 | 0.56 ± 0.57 | 81 ± 96 | 19.1 ± 6.7 | 0.65 ± 0.18 |
| March 1998 | 11/22 | 1.76 ± 1.07 | 0.23 ± 0.13 | 107 ± 127 | 13.9 ± 10.8 | 0.86 ± 0.31 |
| April 2008 | 23/82 | 2.22 ± 1.89 | 0.50 ± 0.29 | 46 ± 73 | 8.9 ± 6.6 | 0.23 ± 0.20 |
| July 2013 | 13/45 | 1.57 ± 1.08 | 0.64 ± 0.73 | 64 ± 22 | 10.0 ± 11.3 | 0.49 ± 0.23 |
| January 2014 | 13/45 | 1.80 ± 1.92 | 0.75 ± 0.41 | 65 ± 43 | 10.4 ± 11.9 | 1.04 ± 1.18 |
| August 2019 | 13/24 | 2.50 ± 2.71 | 0.94 ± 0.60 | 99.19 ± 28.97 | 26.19 ± 14.22 | 0.37 ± 0.16 |
| November 2024 | 14/29 | 2.84 ± 1.95 | 1.92 ± 1.67 | 96.64 ± 72.18 | 16.84 ± 13.19 | 0.48 ± 0.23 |
| VNES | - | 80 | No data | No data | 15 | 10 |
| ECEI | - | No data | 1–10 | 200–300 | 15 | 1–3 |
| Period | Wi (sum Wi = 1) | EI | Status | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a | DIN | DIP | BOD | Min | Max | Average | ±SD | ||
| December 1996 | 0.264 | 0.338 | 0.041 | 0.357 | 0.30 | 2.68 | 1.07 | 0.58 | V |
| April 1997 | 0.270 | 0.263 | 0.170 | 0.297 | 0.20 | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.18 | II |
| November 1997 | 0.378 | 0.276 | 0.278 | 0.068 | 0.29 | 1.34 | 0.72 | 0.29 | III |
| March 1998 | 0.199 | 0.322 | 0.250 | 0.229 | 0.21 | 1.75 | 0.65 | 0.33 | III |
| April 2008 | 0.121 | 0.408 | 0.382 | 0.089 | 0.17 | 1.15 | 0.40 | 0.24 | II |
| July 2013 | 0.415 | 0.076 | 0.243 | 0.266 | 0.20 | 1.18 | 0.59 | 0.28 | III |
| January 2014 | 0.212 | 0.354 | 0.296 | 0.138 | 0.30 | 0.81 | 0.47 | 0.13 | II |
| August 2019 | 0.245 | 0.252 | 0.234 | 0.251 | 0.21 | 1.26 | 0.55 | 0.24 | III |
| November 2024 | 0.244 | 0.252 | 0.262 | 0.242 | 0.23 | 1.94 | 0.46 | 0.34 | II |
| Average | 0.261 | 0.282 | 0.239 | 0.215 | 0.17 | 2.68 | 0.59 | 0.20 | III |
| Environmental monitoring station | 0.121 | 0.408 | 0.382 | 0.088 | 0.16 | 1.69 | 0.58 | 0.24 | III |
| Low tide | 0.116 | 0.475 | 0.400 | 0.009 | 0.14 | 1.60 | 0.55 | 0.24 | III |
| High tide | 0.140 | 0.349 | 0.346 | 0.165 | 0.17 | 1.51 | 0.62 | 0.25 | III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minh-Thu, P.; The, H.V.; Ben, H.X.; Hieu, N.M.; Phu, L.H.; Dung, L.T.; Ngoc, P.H.; Linh, V.T.T.; Mien, P.T.; Ha, T.T.; et al. Eutrophication Monitoring for Sustainable Development in Nha Trang Marine Protected Area, Vietnam. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115128
Minh-Thu P, The HV, Ben HX, Hieu NM, Phu LH, Dung LT, Ngoc PH, Linh VTT, Mien PT, Ha TT, et al. Eutrophication Monitoring for Sustainable Development in Nha Trang Marine Protected Area, Vietnam. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115128
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinh-Thu, Phan, Ho Van The, Hoang Xuan Ben, Nguyen Minh Hieu, Le Hung Phu, Le Trong Dung, Pham Hong Ngoc, Vo Tran Tuan Linh, Pham Thi Mien, Tran Thanh Ha, and et al. 2025. "Eutrophication Monitoring for Sustainable Development in Nha Trang Marine Protected Area, Vietnam" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115128
APA StyleMinh-Thu, P., The, H. V., Ben, H. X., Hieu, N. M., Phu, L. H., Dung, L. T., Ngoc, P. H., Linh, V. T. T., Mien, P. T., Ha, T. T., Thang, N. T. X., Vinh, H. T., & Viet Ha, D. (2025). Eutrophication Monitoring for Sustainable Development in Nha Trang Marine Protected Area, Vietnam. Sustainability, 17(11), 5128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115128






