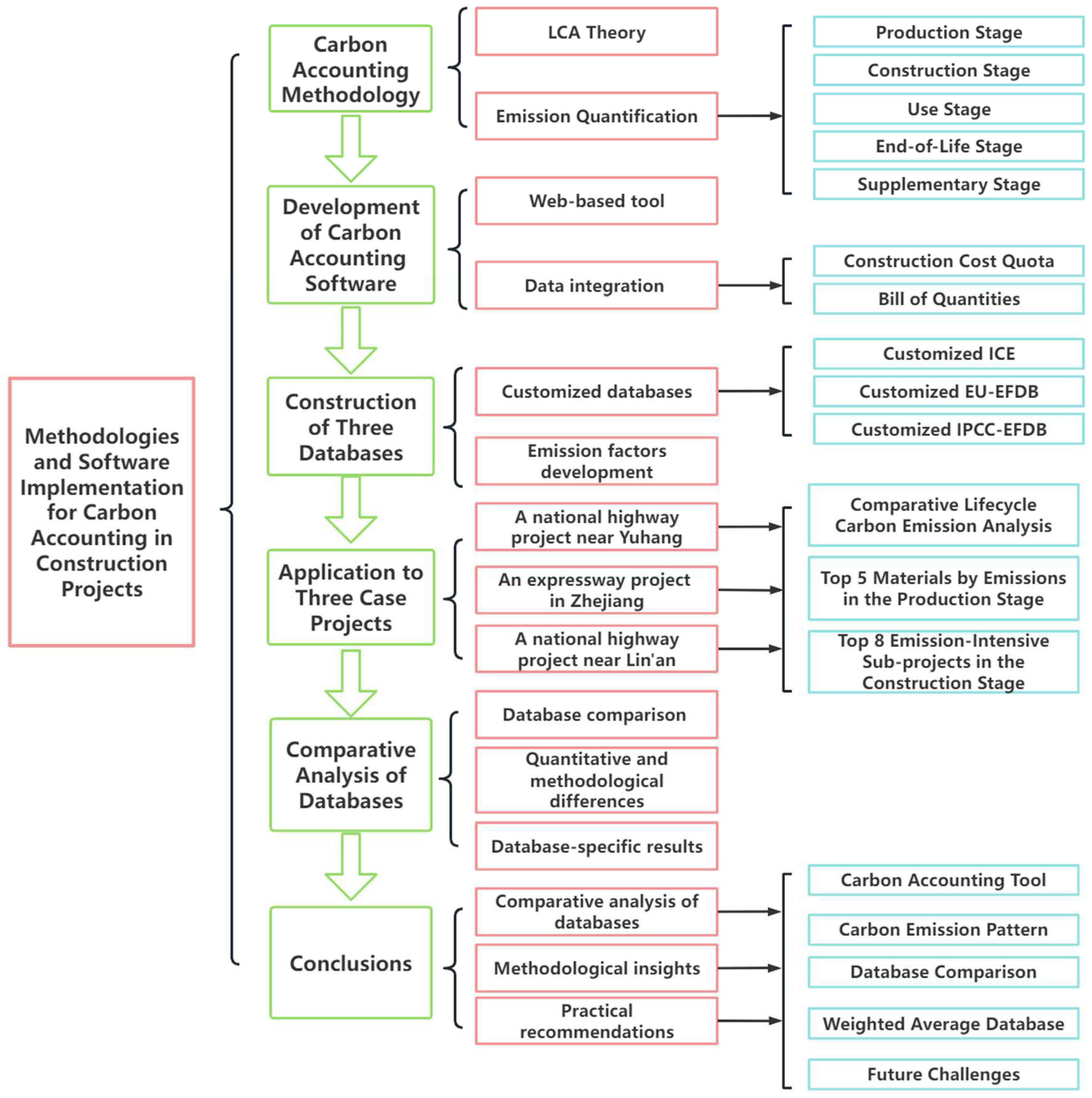
Carbon Accounting in Construction Engineering: Methodology and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Carbon Accounting Model and Database for Construction Projects
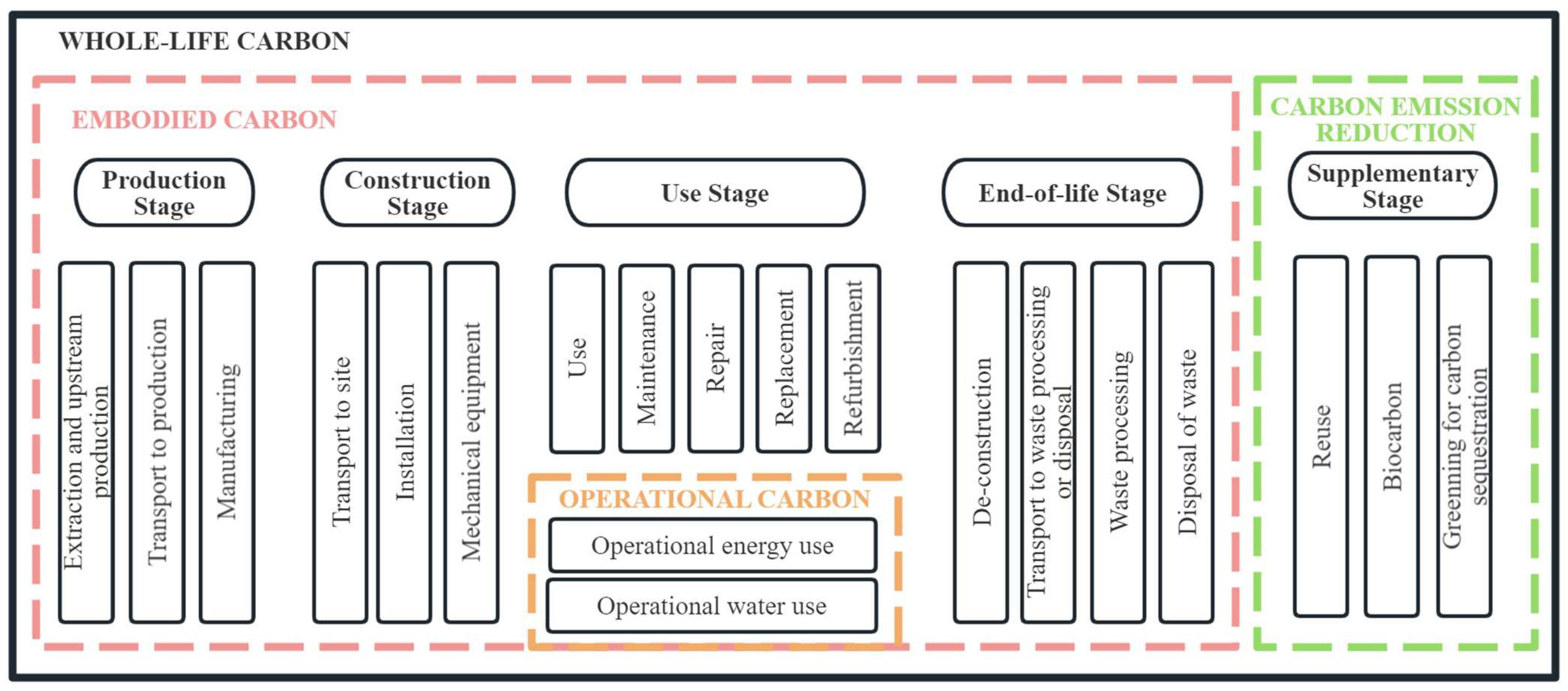
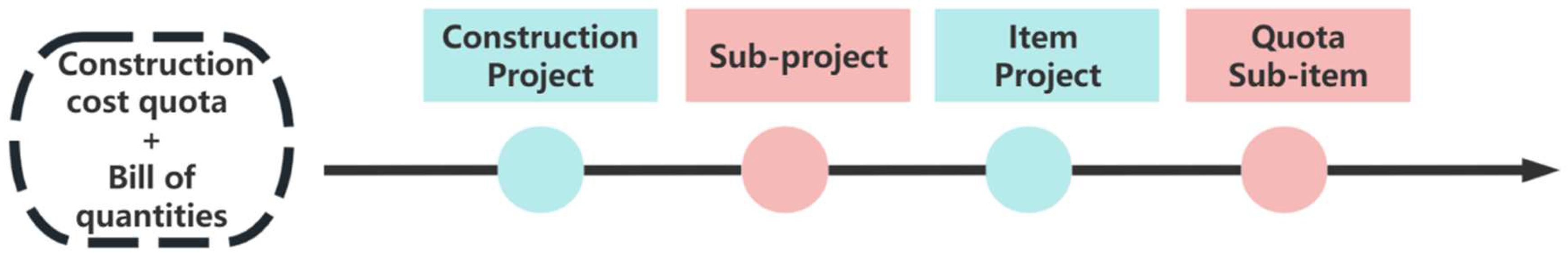
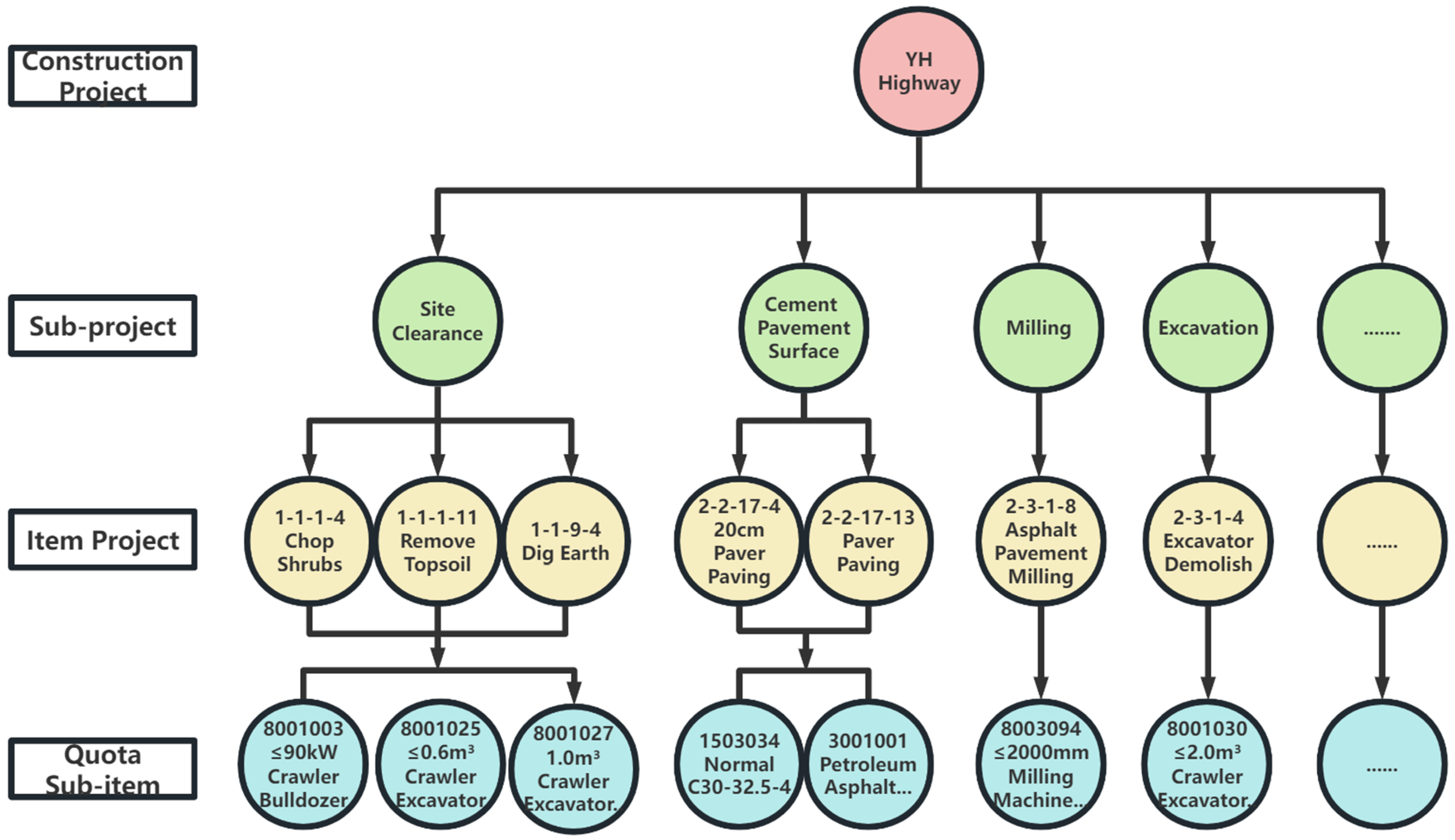
2.1. Carbon Emission Calculation Boundaries
2.2. Carbon Emission Factor Database
- Unit conversion: As different fossil energy sources are measured using different units (e.g., coal is measured in tons, natural gas in cubic meters), it was necessary to convert these into a unified thermal value unit. According to “General Rules for Calculation of the Comprehensive Energy Consumption (GB/T 2589-2020)” [51], all energy sources were converted to a standard unit of Lower Heating Value (LHV) to ensure consistency across the datasets. For instance, 1 ton of coal was converted to its equivalent LHV value in megajoules per ton (MJ/ton), and the same was done for natural gas and oil, enabling a uniform comparison of carbon emissions across different types of energy resources.
- Preliminary calculation: The carbon emission factors and carbon oxidation rates for various fossil energy sources from the IPCC-EFDB were multiplied by their respective lower heating values. This calculation is done to determine the energy content of each fossil fuel and its contribution to carbon emissions. The result was then further multiplied by 44/12 (to convert atomic carbon to molecular CO2), as this ratio represents the molecular weight conversion factor, where 44 is the molar mass of CO2 and 12 is the molar mass of carbon. This method ensures that the carbon content is properly accounted for in the form of carbon dioxide.
- Carbon emission calculation: The carbon dioxide emissions from fossil energy encompass both combustion and production processes. Both components were summed to obtain the final emission values. The formula used for the calculation is CEF = Average Lower Heating Value × Carbon Oxidation Rate × 44/12 + production stage Carbon Emission Factor. This formula was derived from the “IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories” [52] and has been widely adopted in carbon emission assessments for energy consumption. The production stage carbon emission factor account for emissions released during the extraction and transportation of fossil fuels, while the combustion process calculates emissions during energy use.
| Database | Country/Region | Content | Features | Modification Methods | Customized CEF Entries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICE | UK | Building materials, transport, construction processes, energy | Authoritative and construction-focused; limited coverage outside construction, slower updates | 1. Unit conversion (GB/T 51366-2019 [46] and Guidelines for Corporate Greenhouse Gas Emission Accounting and Reporting [53]) 2. Enhanced construction-stage calculation methods (GB/T 50854-2024 [38], JTG/T 3832-2018 [39]). 3. Added supplementary stage data | 1574 |
| EU-EFDB | Europe | Building materials, transport, agriculture, waste, energy | Broad sector coverage, real-time updates; lacks industrial production and land-use data | Same | 1605 |
| IPCC-EFDB | Global | Building materials, transport, industry, land-use, energy | Global benchmark, standardized; infrequent updates, missing recent trends | Same | 1548 |
| Stage | Item/Activity | Customized ICE | Customized EU-EFDB | Customized IPCC-EFDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Stage | Cement (per ton) | 550 | 880 | 530 |
| Construction Stage | Axial Flow Fan (per h) | 1.37 | 1.01 | 1.06 |
| Use Stage | Electricity (take the North China Region as an example, per kWh) | 0.884 | 0.901 | 0.841 |
| End-of-life Stage | Landfill (per kg) | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.011 |
| Supplementary Stage | Biocarbon (per kg) | −0.166 | −0.66 | −0.66 |
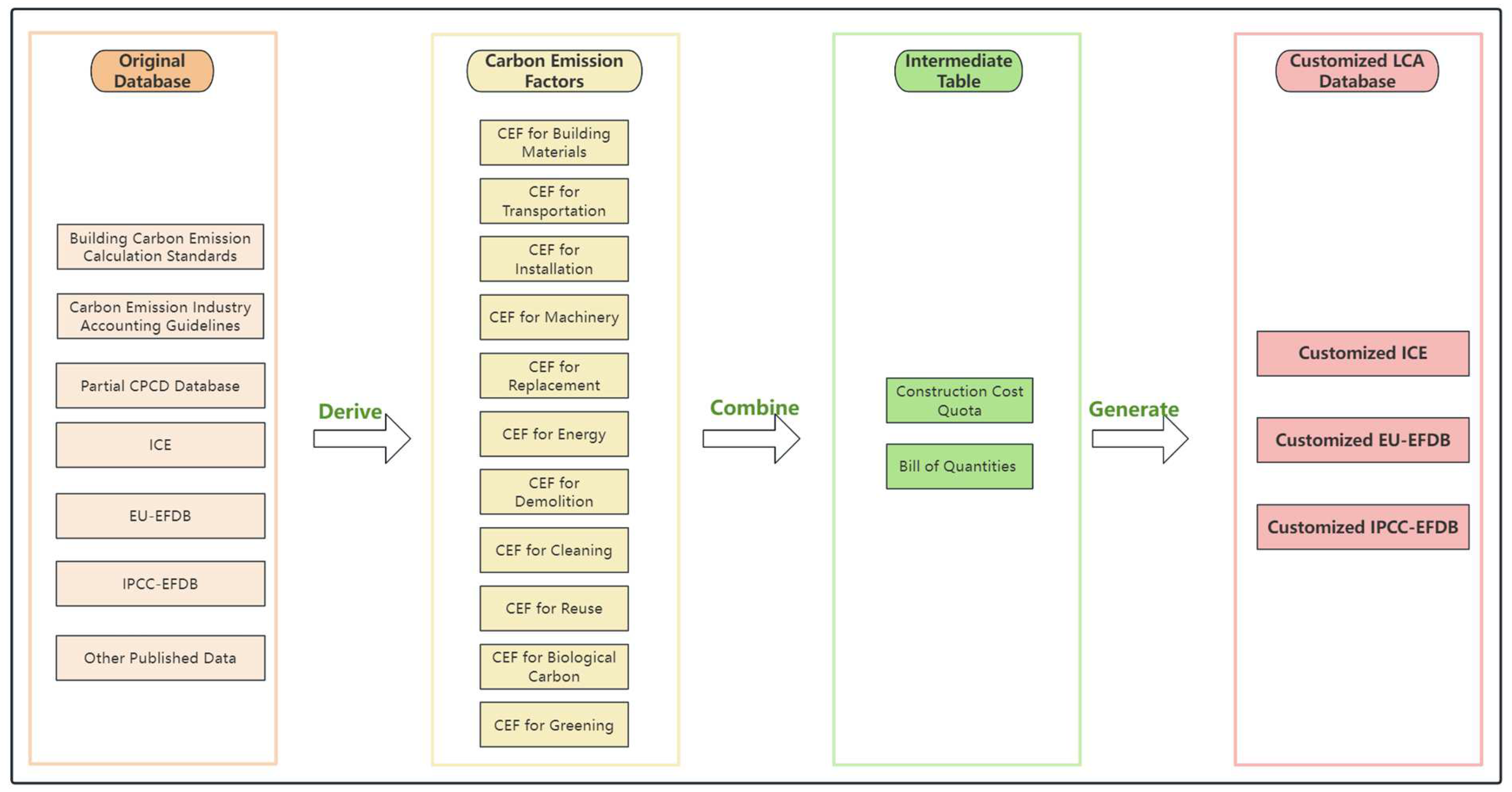
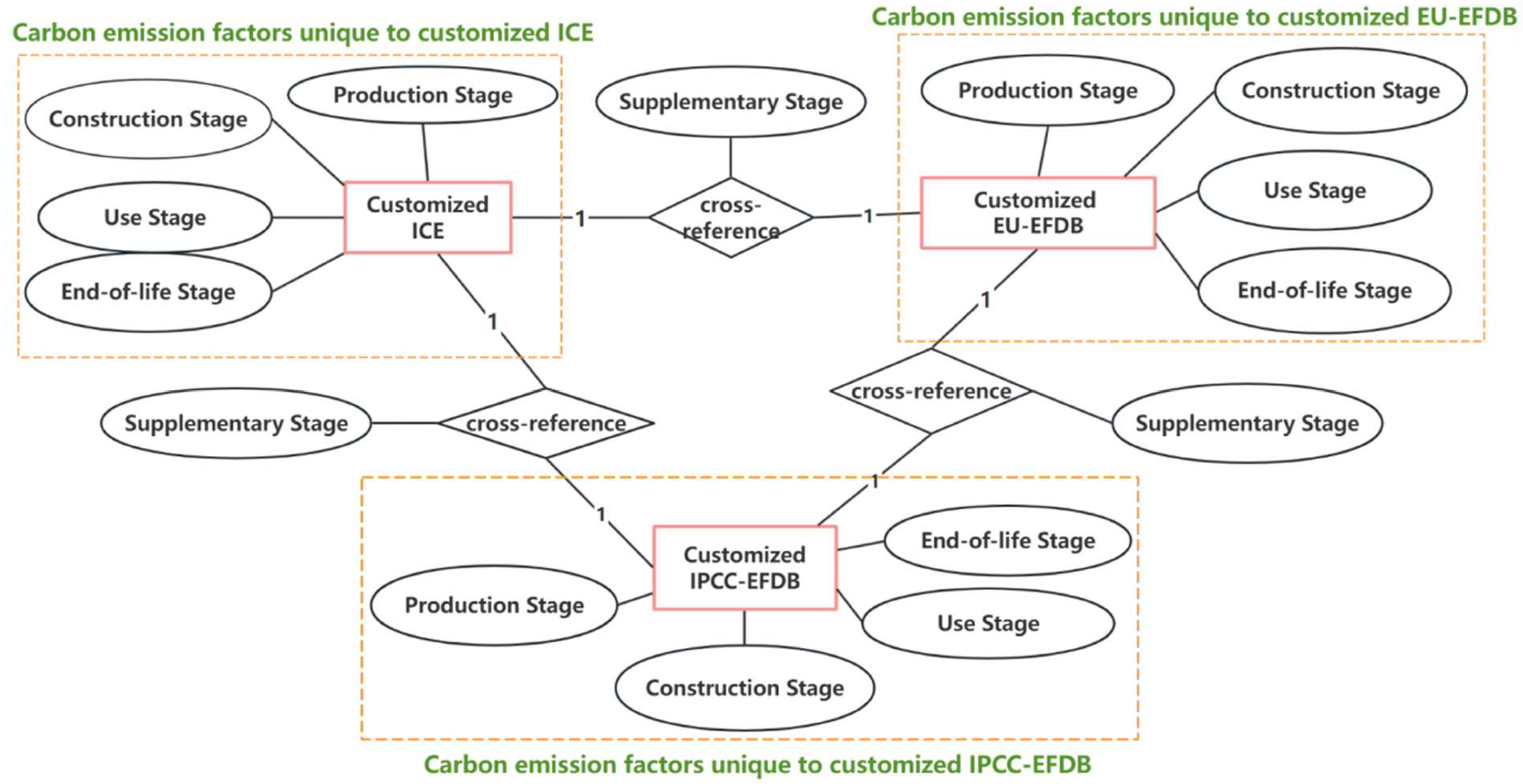
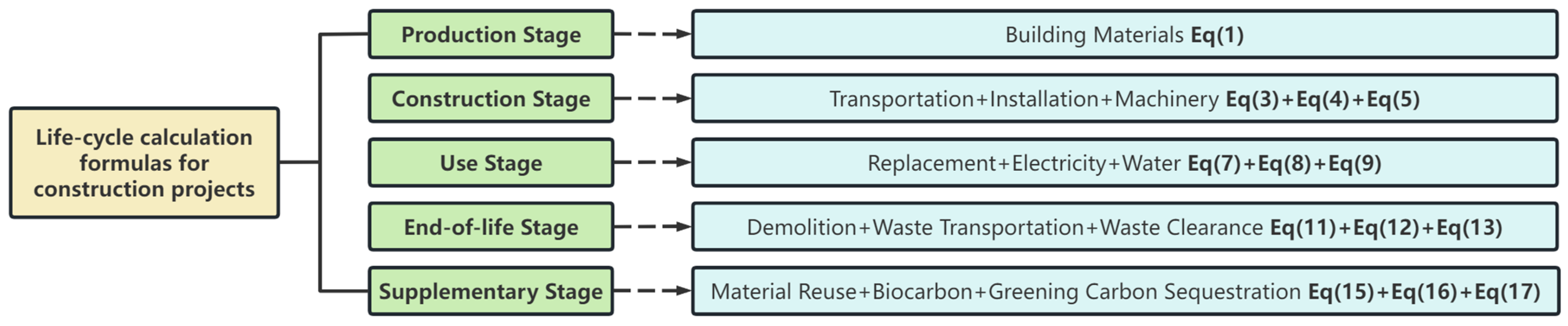
2.3. Carbon Emission Calculation Method
2.3.1. Production Stage Analysis
2.3.2. Construction Stage Analysis
2.3.3. Use Stage Analysis
2.3.4. End-of-Life Stage Analysis
2.3.5. Supplementary Stage Analysis
3. Development of Carbon Accounting Tool for Construction Project
3.1. Software Design Framework
- Importing basic project information: This module allows users to input essential project details, including project name, type, location, and timeline (start and end dates).
- Building the LCA model: This module enables users to create one or more LCA models based on the project details and scenarios.
- Selecting the LCA database: This module provides users with the option to choose from different LCA databases based on the specific needs of the project scenario: the customized ICE, the customized EU-EFDB, and the customized IPCC-EFDB.
- Whole-life-cycle carbon accounting for the construction project: This module enables users to conduct whole-life-cycle carbon accounting for multiple processes and stages of the construction project, including the production stage, construction stage, use stage, end-of-life stage, and supplementary stage.
- Data validation: This module highlights any errors in the data within the model to improve the coherence of the LCA model.
- LCA carbon footprint results overview: This module clearly presents the results of the LCA carbon accounting, including carbon emissions for each life-cycle stage, construction-stage statistics, bar and pie charts depicting emissions and their respective proportions across stages, and allows for comparison of multiple carbon accounting scenarios to identify potential carbon reduction measures.

3.2. Graphic User Interface (GUI) Design
3.3. Frontend-Backend System Integration
4. Engineering Case Studies
4.1. Project Overview
- YH Highway
- 2.
- ZJ Expressway
- 3.
- LA Highway

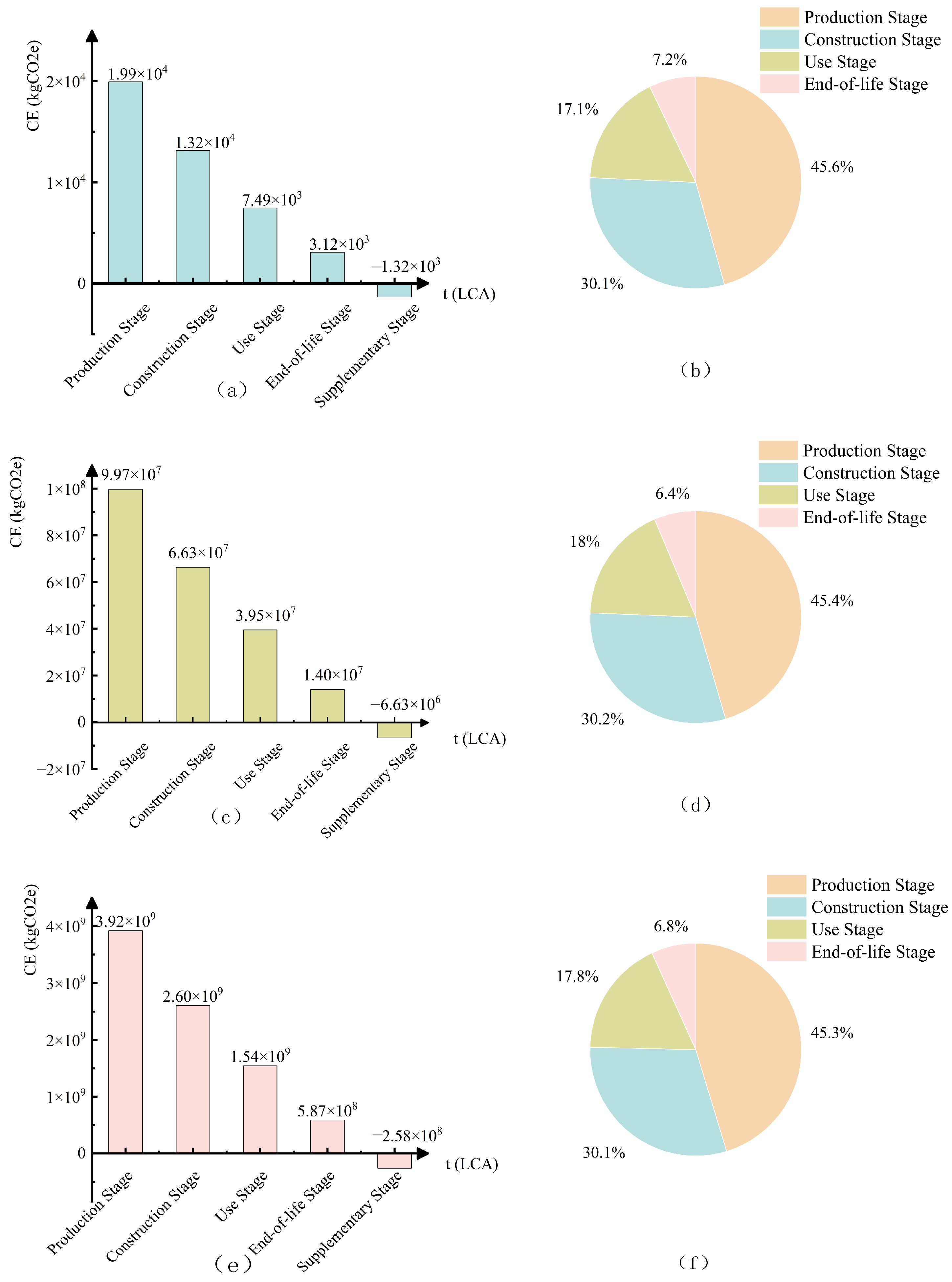
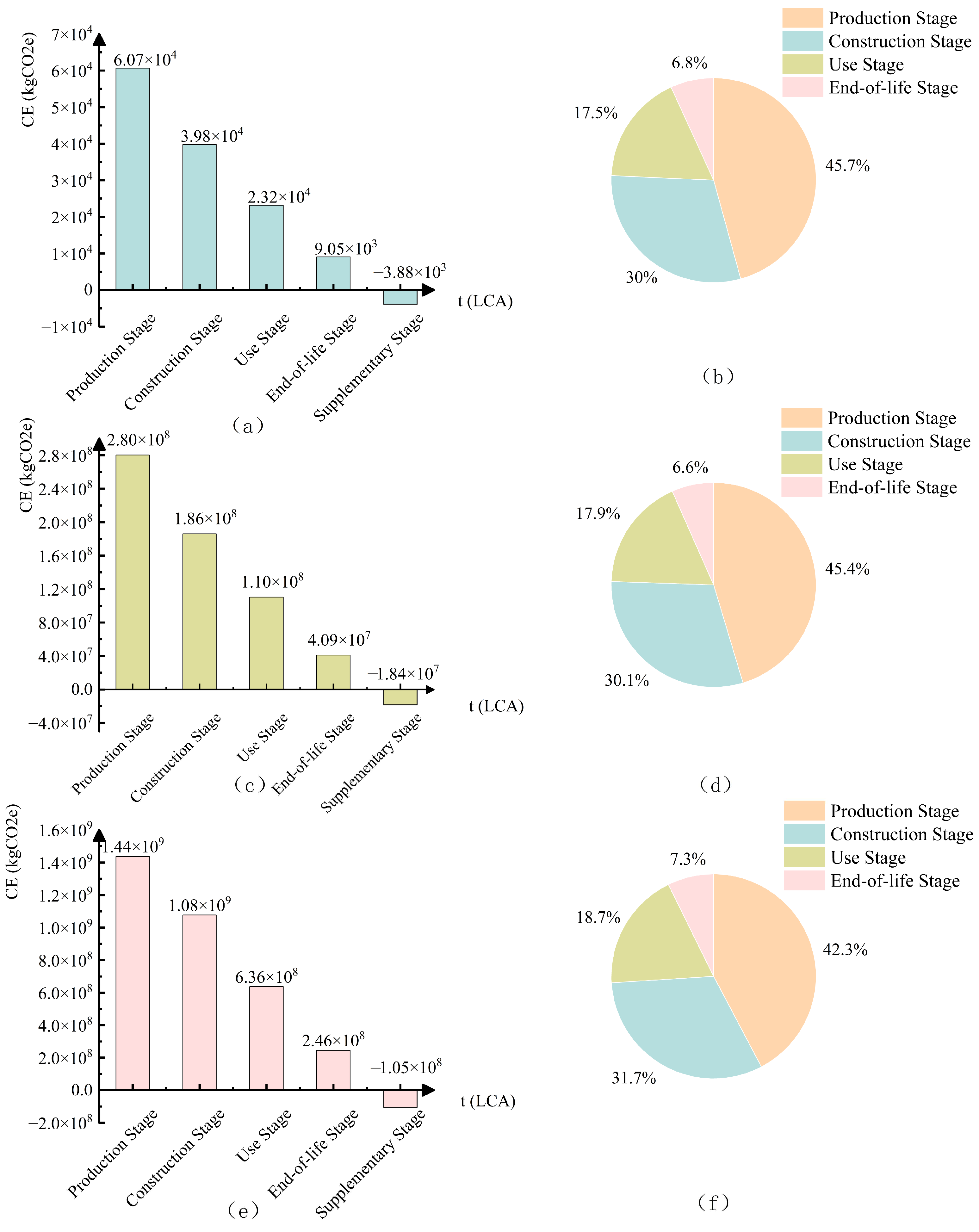
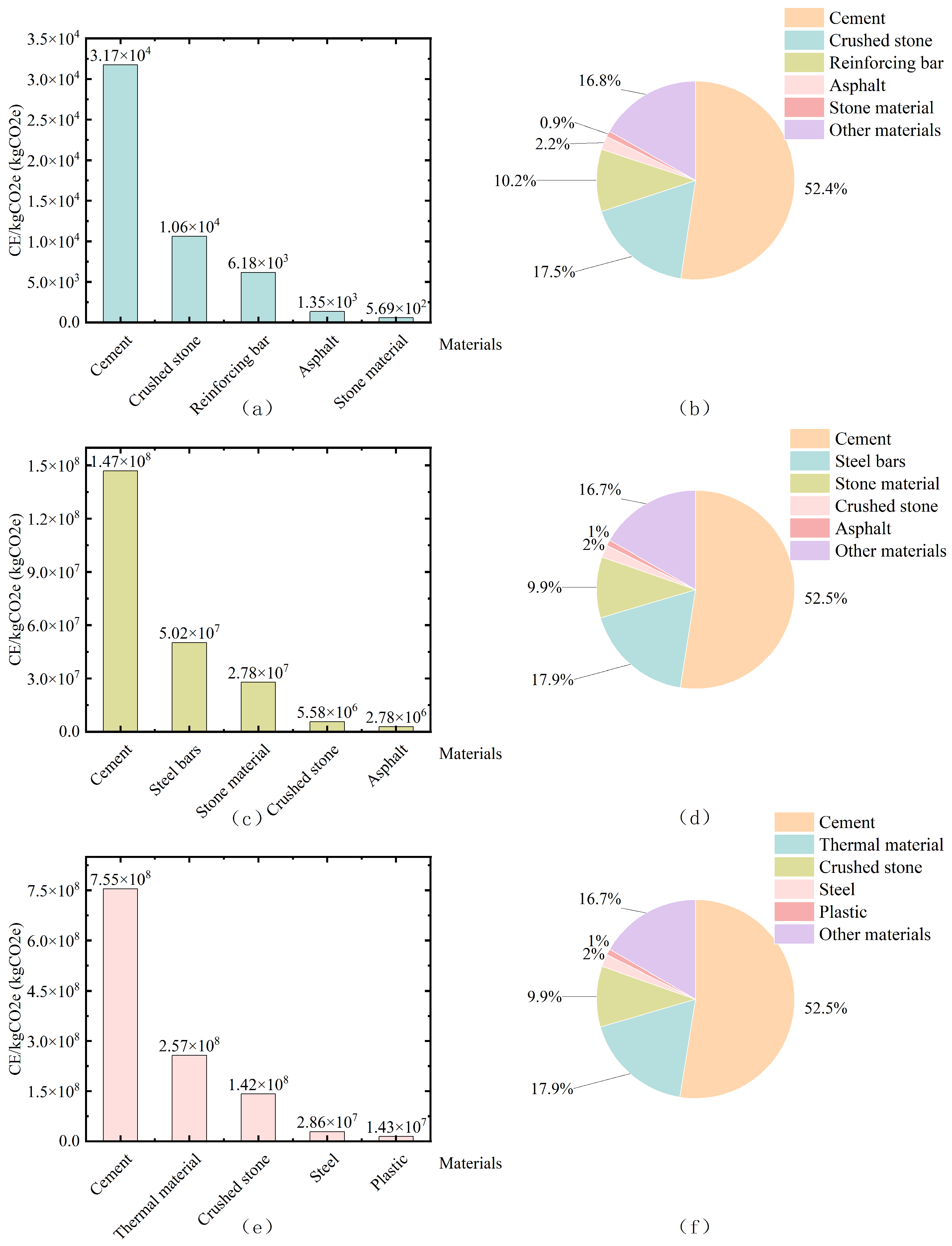
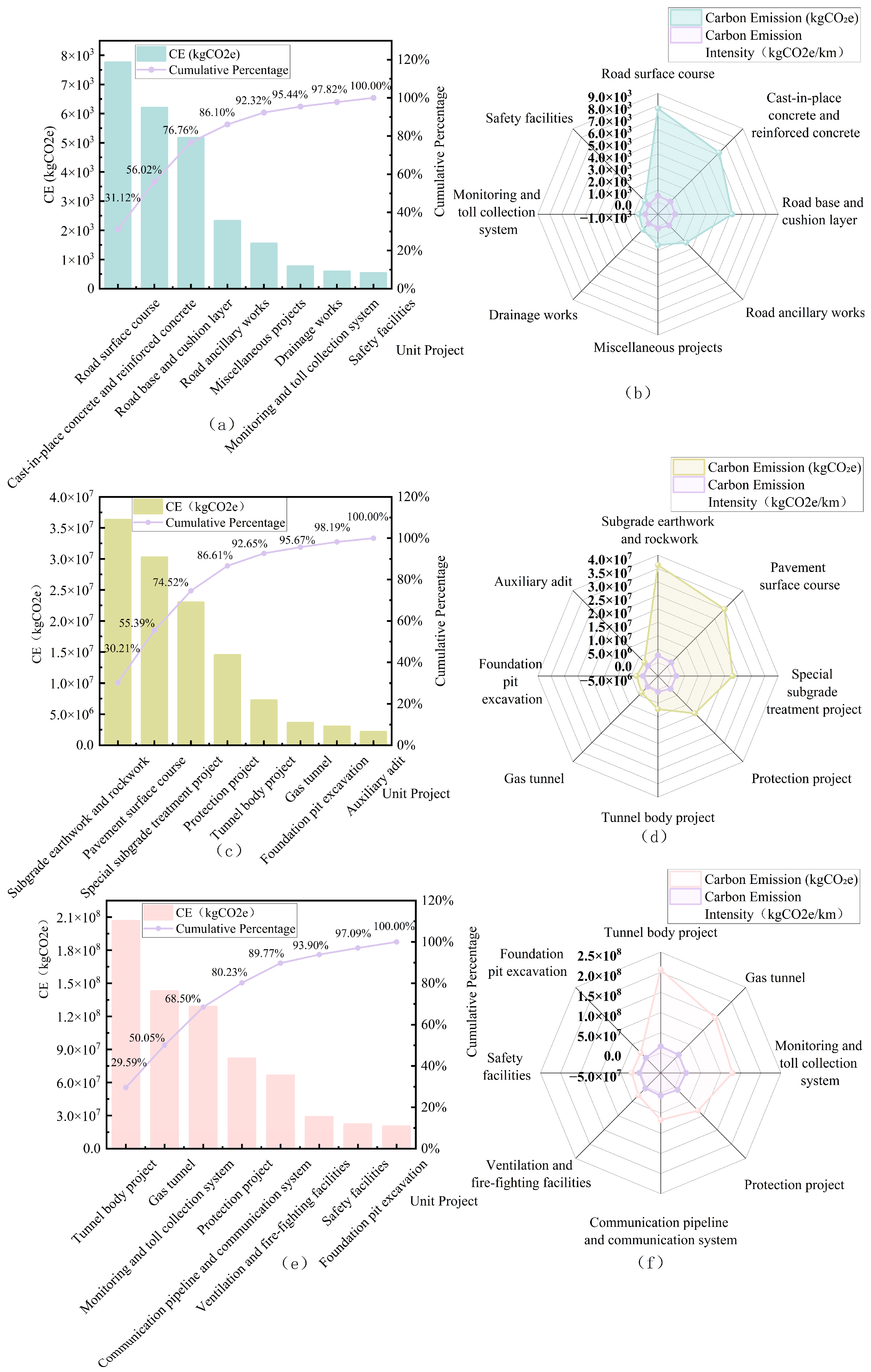
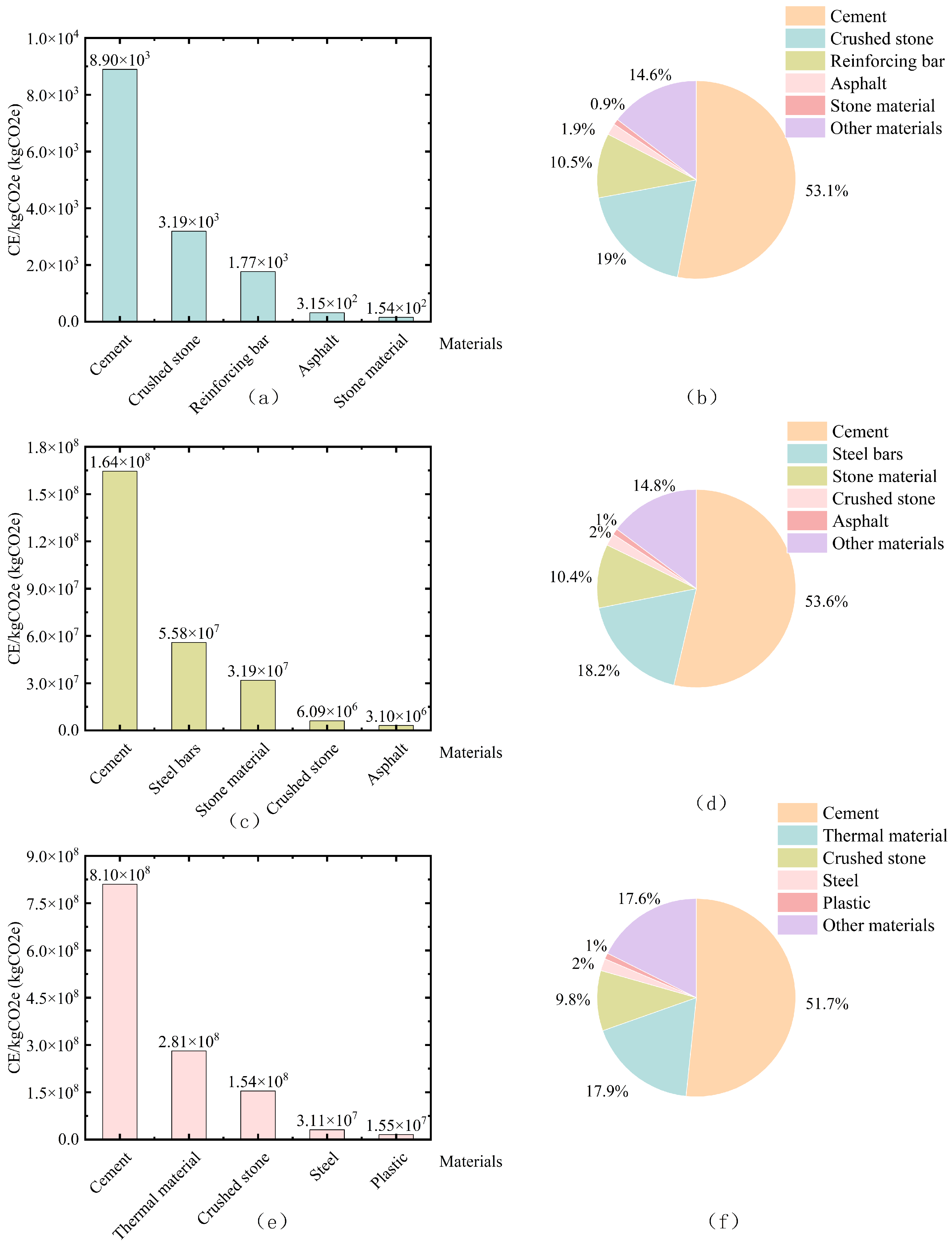
4.2. Carbon Accounting Results and Comparative Analysis
5. Comparison of Carbon Emission Estimation Based on Different Databases
5.1. Similarities in Carbon Emission Estimated by the Three Customized Databases
5.2. Differences in Carbon Emission Estimated by the Three Customized Databases
- 1.
- YH Highway (EU-EFDB > ICE > IPCC-EFDB)
- 2.
- ZJ Expressway (IPCC-EFDB > EU-EFDB > ICE)
- 3.
- LA Highway (ICE > IPCC-EFDB > EU-EFDB)
5.3. Length-Based Benchmarking of Carbon Emissions
5.4. Discussions
- 1.
- Weighed average of carbon emission databases
- 2.
- Focus on the progress of carbon monitoring technologies and industry standards in construction
- 3.
- Similar International Projects and Standards
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, A.K.; Ferreira, V.M.; Dias, A.C. Promoting decarbonisation in the construction of new buildings: A strategy to calculate the Embodied Carbon Footprint. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fu, M.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Liang, J.; Ma, R.; Xie, Q. Role of CO2 geological storage in China’s pledge to carbon peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. Energy 2023, 272, 127165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, Y. Driving factors and reduction paths dynamic simulation optimization of carbon dioxide emissions in China’s construction industry under the perspective of dual carbon targets. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 112, 107789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Azmi, A.M.; Dahlan, N.Y.; Woon, K.S. Predicting life cycle carbon emission of green office buildings via an integrated LCA—MLR framework. Energy Build. 2024, 316, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Quintana-Gallardo, A.; Audí, N.M.; Guillamón, I.G. The impact of lifespan assumptions in LCA: Comparing the replacement of building parts zversus building layers—A housing case study. Energy Build. 2025, 326, 115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucco, D.; Perrucci, G. Steel–Timber hybrid buildings: A comparative life cycle assessment study of global warning potential impacts. Sustainability 2025, 17, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, C.; Chen, L.; Qiu, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q. Using BIM and LCA to calculate the life cycle carbon emissions of inpatient building: A case study in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, M.M.; Luqman, M.; Asif, M.; Shuja, S.Z.; Qannan, M. A theoretical framework to promote LCA in the construction industry of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Azari, R.; Elnimeiri, M. A building information modeling-based life cycle assessment of the embodied carbon and environmental impacts of high-rise building structures: A case study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, C.; Bazzocchi, F. Retrofitting of the Italian precast industrial building stock. LCA Anal. Decis. Mak. Tool J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143933. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati, M.; Messadi, T.; Gu, H.; Hemmati, M. LCA operational carbon reduction based on energy strategies analysis in a mass timber building. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Xia, P.; Xia, D. Study on carbon emission measurement and influencing factors for prefabricated buildings at the materialization stage based on LCA. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, G.A.; Palaniappan, S.; Habert, G. Classification of sources of uncertainty in building LCA. Energy Build. 2024, 305, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Conventional versus modular construction methods: A comparative cradle-to-gate LCA for residential buildings. Energy Build. 2019, 204, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, M.; Huang, W. Energy consumption and carbon emissions of mixing plant in asphalt pavement construction with a case study in China and reduction measures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Dong, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Sun, W.; He, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, N.; Guo, C. Evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions in subway tunnel construction. Undergr. Space 2025, 22, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Xie, W.J.; Jim, C.Y.; Feng, F. Holistic LCA evaluation of the carbon footprint of prefabricated concrete stairs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Kim, J.I.; Chen, J. Improved framework for estimating carbon emissions from prefabricated buildings during the construction stage: Life cycle assessment and case study. Build. Environ. 2025, 272, 112599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Kong, C.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Gao, X. Research on carbon emission quantification and evaluation for prefabricated inverted arch construction in drill and blast tunnels. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.B. Sustainability of underground infrastructure—Part 1: Digitalisation-based carbon assessment and baseline for TBM tunnelling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 148, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, Y. Using LCA to research carbon footprint for precast concrete piles during the building construction stage: A China study. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitouni, S.I.; Gargab, F.Z.; Tabit, A.; Mabrouki, M.; Lamdouar, N.; Jamil, A.; Ahachad, M. A life cycle carbon dioxide equivalent emissions assessment of zero carbon building in hot semi-arid climate region: Case study. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, A.; Lyu, K.; Gocer, O.; Brambilla, A.; Prasad, D. Climate risk assessment of buildings: An analysis of operating emissions of commercial offices in Australia. Energy Build. 2024, 315, 114336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, S.K.; Munteanu, A.; De Rycke, K.; De Laet, L. Embodied greenhouse gas emissions of buildings—Machine learning approach for early stage prediction. Build. Environ. 2024, 257, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Valmayor, M.A.; Infante, J.; Carmona-González, N.; Gil-Alana, L.A. US CO2 emissions and IPCC components: Evidence of persistence using fractional integration. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 26, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Heeren, N.; Bauer, C.; Burgherr, P.; McKenna, R.; Habert, G. The impacts of future sectoral change on the greenhouse gas emissions of construction materials for Swiss residential buildings. Energy Build. 2024, 303, 113824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, I.; Rootzén, J.; Johnsson, F.; Erlandsson, M. Achieving net-zero carbon emissions in construction supply chains—A multidimensional analysis of residential building systems. Dev. Built Environ. 2021, 8, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z. Analysis of carbon emission characteristics and establishment of prediction models for residential and office buildings in China. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasvaux, S.; Habert, G.; Peuportier, B.; Chevalier, J. Comparison of generic and product-specific Life Cycle Assessment databases: Application to construction materials used in building LCA studies. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1473–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arash, M.; Hasan, K.M.A.; Golam, K. Assessing the environmental impact of building houses in remote areas: 3D printing vs. traditional construction techniques. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 102, 111968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, B.; Brady, R.; Sardag, S.; Eu, B.; Skerlos, S. Growing bricks: Assessing biocement for lower embodied carbon structures. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Jassim, M.; Ilcan, H.; Sahin, O.; Bayer, İ.R.; Sahmaran, M.; Koc, M. 3D printing of circular materials: Comparative environmental analysis of materials and construction techniques. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SinoCarbon Technology Co., Ltd. SinoCarbon. Available online: https://cloud.sinocarbon.cn/product/ecm/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Starostka-Patyk, M. New Products Design Decision Making Support by SimaPro Software on the Base of Defective Products Management. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 65, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, E. Sustainable Waste Management in Schools. Master Thesis, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, W.V.; Le, K.N.; Tran, C.N.; Wang, J.Y. A review on contemporary computational programs for Building’s life-cycle energy consumption and greenhouse-gas emissions assessment: An empirical study in Australia. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4220–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.; Zhou, Y.; Illankoon, C.; Le, K.N. A critical review on BIM and LCA integration using the ISO 14040 framework. Build. Environ. 2022, 213, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50854-2024; Standard for Quantity Calculation of Housing Construction and Decoration Projects. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- JTG/T 3832-2018; Quotations for Highway Engineering Budgeting. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Symons, K. Book review: Embodied Carbon: The Inventory of Carbon and Energy (ICE). A BSRIA Guide. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Energy 2011, 164, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Circular Ecology. Embodied Carbon—The ICE Database. Available online: https://circularecology.com/embodied-carbon-footprint-database.html (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Crippa, M.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Dentener, F.; Guizzardi, D.; Sindelarova, K.; Muntean, M.; van Dingenen, R.; Granier, C. Forty years of improvements in European air quality: Regionalpolicy-industry interactions with global impacts. Atmos. Chemi-Stry Phys. 2016, 16, 3825–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook 2023; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2023; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications/emep-eea-guidebook-2023 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Muñoz, I.; Schmidt, J.; Weidema, B.P. The indirect global warming potential of methane oxida-tion in the IPCC’s sixth assessment report. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 121002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO; UNEP. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/efdb/find_ef.php (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- GB/T 51366-2019; Standard for Building Carbon Emission Calculation. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- China City Greenhouse Gas Working Group. China Products Carbon Footprint Factors Database. Available online: https://lca.cityghg.com/pages/article-view/60 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, C.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y. AutoBPS-carbon: A tool to estimate multi-year dynamic embodied and operational carbon emissions in the building sector. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melanta, S.; Miller-Hooks, E.; Avetisyan, H.G. Carbon footprint estimation tool for transportation construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P. The Establishment of a Life-Cycle Carbon Emission Factor Database for Building and Research. Master Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 2589-2020; General Rules for Calculation of the Comprehensive Energy Consumption. State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and the Standardization Administration of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2020.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/chinese/index.html (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) Office. Guidelines for Corporate Greenhouse Gas Emission Accounting and Reporting (Trial Version). Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/201311/t20131101_963960.html (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- The Institution of Structural Engineers. How to Calculate Embodied Carbon. Available online: https://www.istructe.org/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Zib, L., III; Byrne, D.M.; Marston, L.T.; Chini, C.M. Operational carbon footprint of the U.S. water and wastewater sector’s energy consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG H10-2009; Technical Specifications of Maintenance for Highway. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- JTG 5142-2019; Technical Specifications for Maintenance of Highway Asphalt Pavement. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Regulations on the Administration of Toll Highways. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2005-05/23/content_241.htm (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Luo, Y.; Shen, J.; Liang, H.; Sun, L.; Dong, L. Carbon monitoring, reporting and verification (MRV) for cleaner built environment: Developing a solar photovoltaic blockchain tool and applications in Hong Kong’s building sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, M.; Balouktsi, M.; Saade, M.R.M. Embodied carbon emissions of buildings and how to tame them. One Earth 2023, 6, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza, G.A.; Vignisdottir, H.R.; Kristensen, T.; Ramsnes, E. Greenhouse gas emission reduction potential in road tunnels—Can we reach the European Union goals with existing materials and technologies? Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. Inc. Trenchless Technol. Res. 2024, 153, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Akhtar, A. A novel approach for environmental impact assessment of road construction projects in India. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damián, R.; Zamorano, C.I. Environmental impact assessment of high-speed railway tunnel construction: A case study for five different rock mass rating classes. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 36, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Giunta, M.; Mistretta, M.; Gulotta, T.M. Energy and Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Sustainable Pavement Materials and Technologies for Urban Roads. Sustainability 2020, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 15978-2011; Sustainability of Construction Works—Assessment of Environmental Performance of Buildings—Calculation Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- ISO 14040-2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044-2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.








| Software Name | Functionalities | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SimaPro | 1. Enhance multi-product carbon accounting across diverse impact categories. 2. Support detailed life-cycle analysis for environmental decision-making. | Starostka-Patyk et al. [34] |
| Umberto | 1. Focuse on comprehensive product system life-cycle evaluations. 2. Identify sustainability improvements for optimized system performance. | Orr et al. [35] |
| Gabi | 1. LCA calculations with detailed process breakdown. 2. Comprehensive database with efficient data retrieval. | Tam et al. [36] |
| Carbon e-Management | 1. Cloud-based SaaS model with low implementation cost. 2. One-stop solution for Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) carbon management. | SinoCarbon [33] |
| No. | Stages | Content | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Production | Carbon emissions during material extraction, processing, and manufacturing of construction components | Traditional Life-cycle Stages |
| 2 | Construction | Carbon emissions during the transportation of construction materials to the site, the installation of components, and the use of machinery | |
| 3 | Use | Carbon emissions generated through building usage, maintenance, repair, renovation, and operational electricity/water consumption | |
| 4 | End-of-life | Carbon emissions from building demolition, deconstruction, waste material transportation, and waste disposal | |
| 5 | Supplementary | Carbon benefits from material recycling (e.g., scrap steel substitution), reuse, and biogenic carbon sequestration through greening initiatives | Additional Life-cycle Stage |
| No. | Emission Type | Production Stage | Construction Stage | Use Stage | End-of-Life Stage | Supplementary Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material Production | ✓ | ||||
| 2 | Transportation | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 3 | Construction Installation | ✓ | ||||
| 4 | Machinery Equipment | ✓ | ||||
| 5 | Material Replacement | ✓ | ||||
| 6 | Structural Demolition | ✓ | ||||
| 7 | Waste Management | ✓ | ||||
| 8 | Operational Energy Use | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 9 | Reuse Sequestration | ✓ | ||||
| 10 | Biogenic Carbon Sequestration | ✓ | ||||
| 11 | Afforestation Sequestration | ✓ |
| Project Title | YH Highway | ZJ Expressway | LA Highway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Site Location | Yuhang District | Zhejiang Province | Lin’an District |
| Length | 8.673 km | 4.560 km | 62.715 km |
| Project Type | Road & Bridge & Tunnel | ||
| Project Overview | The 8.673 km dual six-lane first-class highway, including surface roads and bridges, serves as a representative case for carbon accounting in highway construction. | The 4.560 km expressway in Zhejiang Province enhances regional connectivity in the Yangtze River Delta and is key for infrastructure carbon assessment. | The 62.715 km expressway expansion involves subgrades, bridges, tunnels, and interchanges, making it suitable for validating carbon accounting in large-scale projects. |
| Stage | Metric | YH Highway | ZJ Expressway | LA Highway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | Material types involved | 49 types | 101 types | 117 types |
| Most consumed material & quantity | 32.5 Cement (5398.42 t) | 32.5 Cement (24,589.23 t) | C25 Cast-in-place Concrete (26,578.12 m3) | |
| Construction | Sub-project | 9 | 153 | 285 |
| Item project | 11 | 216 | 314 | |
| Use | Most frequent replacement material & quantity | Petroleum Asphalt (16.78 kg) | Rubble (89.11 m3) | Gravel (97.46 m3) |
| Electricity consumption | 1.99 × 107 kWh | 1.09 × 1011 kWh | 4.84 × 1011 kWh | |
| Water consumption | 4.67 × 106 m3 | 9.79 × 107 m3 | 8.97 × 108 m3 | |
| End-of-life | Predominant waste transport & distance | Road Transport (87 km) | Road Transport (169 km) | Rail Transport (187 km) |
| Supplementary | Primary carbon-sequestration plants & spacing | Camphor Tree (3–5 m) | London Planetree (2–4 m) | Huanshan Katsura Tree (5–6 m) |
| Project | Customized ICE (kgCO2e) | Customized EU-EFDB (kgCO2e) | Customized IPCC-EFDB (kgCO2e) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YH Highway | 4.25 × 104 | 1.29 × 105 | 3.50 × 104 |
| ZJ Expressway | 2.13 × 108 | 5.99 × 108 | 6.54 × 108 |
| LA Highway | 8.39 × 109 | 3.29 × 109 | 3.35 × 109 |
| Project | Total Length (km) | Total Emissions (kgCO2e) | Emissions per km (kgCO2e/km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YH Highway | 8.673 | 4.25 × 104 | 4.90 × 103 |
| ZJ Expressway | 4.560 | 2.13 × 108 | 4.67 × 107 |
| LA Highway | 62.715 | 8.39 × 109 | 1.34 × 108 |
| Project Name | Weighted Carbon Emission Value (kgCO2e) |
|---|---|
| YH Highway | 6.88 × 104 |
| ZJ Expressway | 2.71 × 108 |
| LA Highway | 5.01 × 109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Deng, W.; Jike, S.; Liu, F. Carbon Accounting in Construction Engineering: Methodology and Applications. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115090
Wu Y, Zhang C, Liu Y, Deng W, Jike S, Liu F. Carbon Accounting in Construction Engineering: Methodology and Applications. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115090
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuechen, Chaofeng Zhang, Yanzhao Liu, Wenxuan Deng, Sanpo Jike, and Fushen Liu. 2025. "Carbon Accounting in Construction Engineering: Methodology and Applications" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115090
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., Deng, W., Jike, S., & Liu, F. (2025). Carbon Accounting in Construction Engineering: Methodology and Applications. Sustainability, 17(11), 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115090





