Research on Carbon Emission Reduction and Benefit Pathways for Chinese Urban Renewal Market Players Based on a Tripartite Evolutionary Game: A Carbon Trading Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- By constructing a model from the perspective of carbon trading and fully considering the key role of the market mechanism in promoting carbon emission reduction, it more accurately reflects the strategic choices and game process of each party at different stages.
- (2)
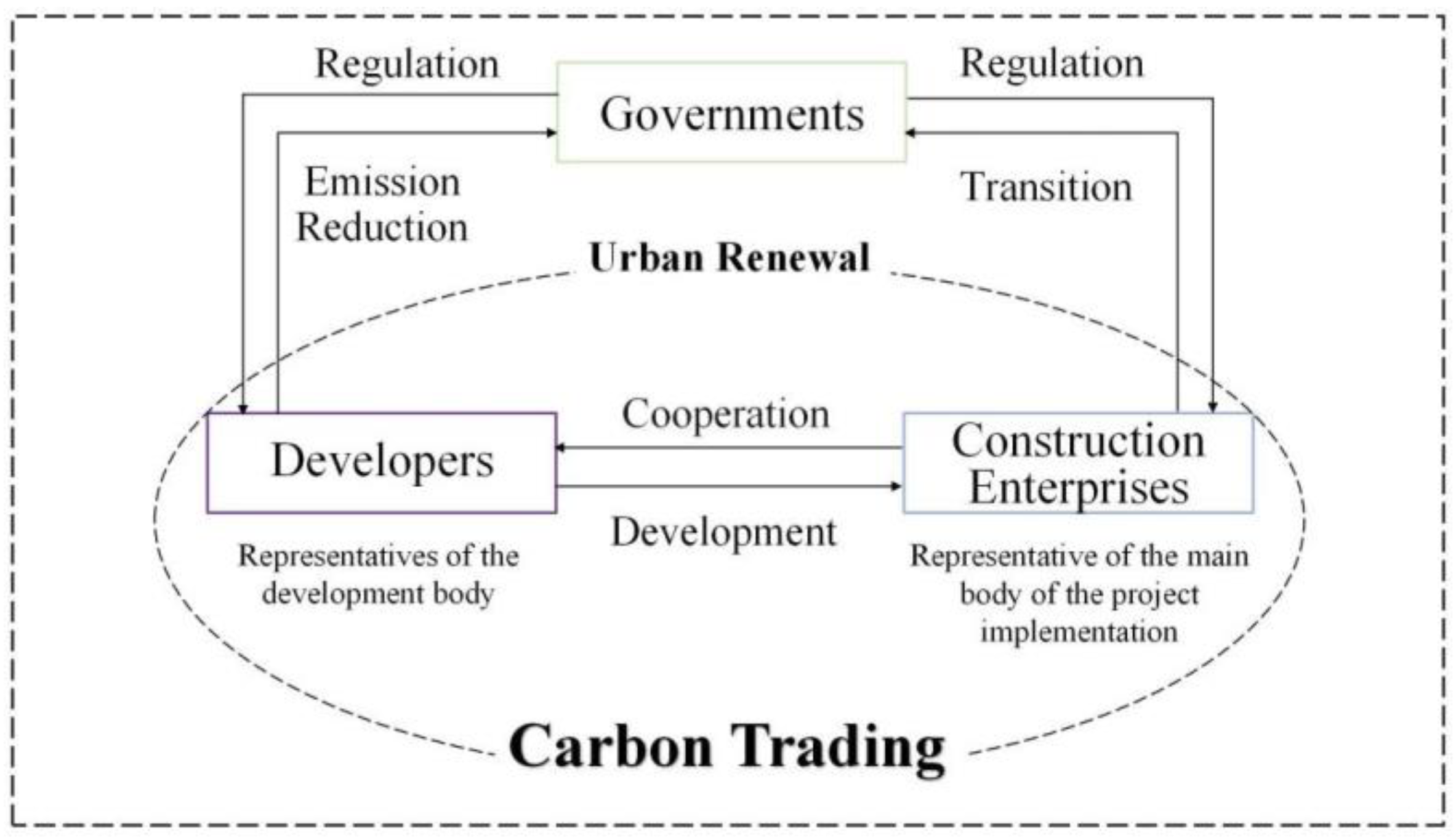
- With a particular focus on the field of urban renewal, this study analyses the roles of the government, developers, and construction enterprises and their interactions in carbon emission reduction.
- (3)
- On the basis of theoretical analyses, urban renewal is combined with carbon trading and simulating practical situations to explore new benefit possibilities for future enterprises in urban renewal, which is important for promoting sustainable urban development and achieving the dual-carbon target.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Stakeholders in Carbon Emission Reduction in Urban Renewal
2.2. Impact of Carbon Trading on Carbon Emission Reduction
2.3. Application of Evolutionary Games in Carbon Emission Reduction
3. Model Building
3.1. Basic Assumptions
3.2. Tripartite Evolutionary Game
3.2.1. Analysis of Payoff Matrix
3.2.2. Replication Dynamic Equation
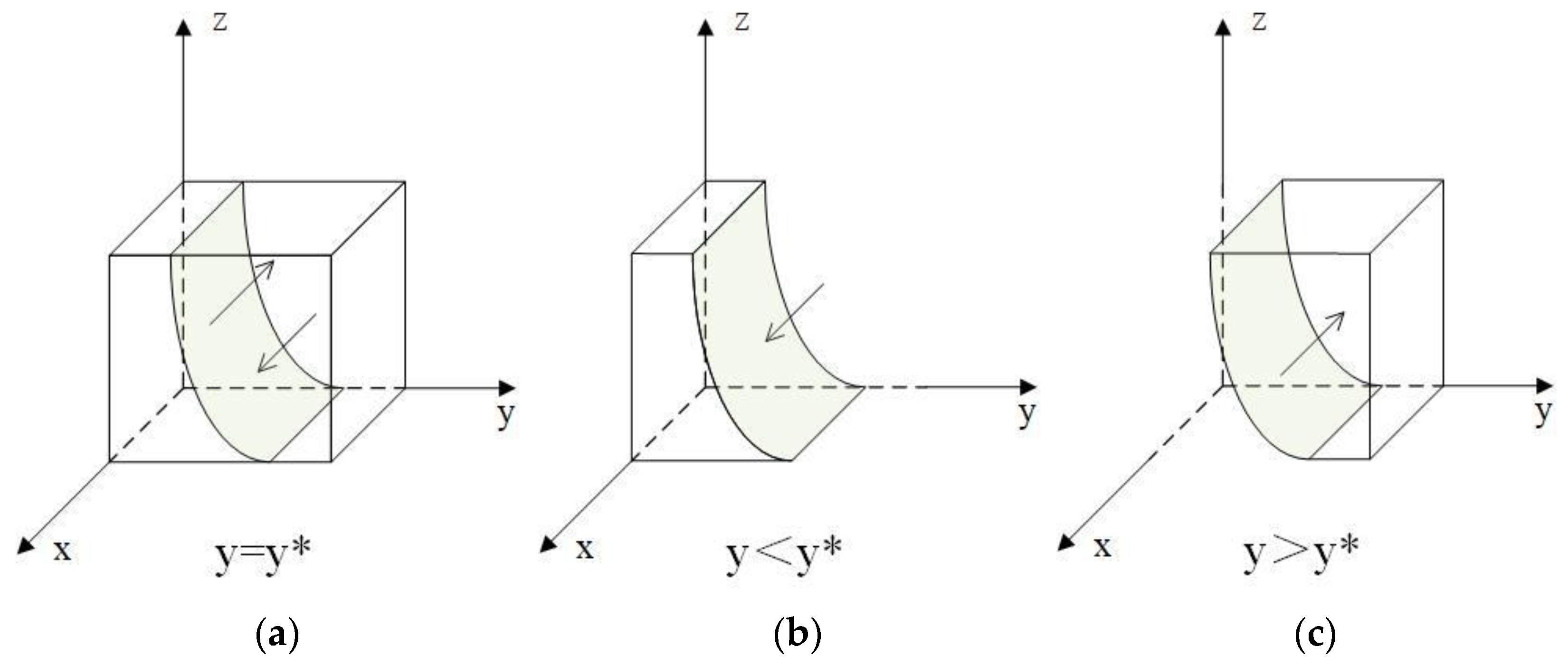
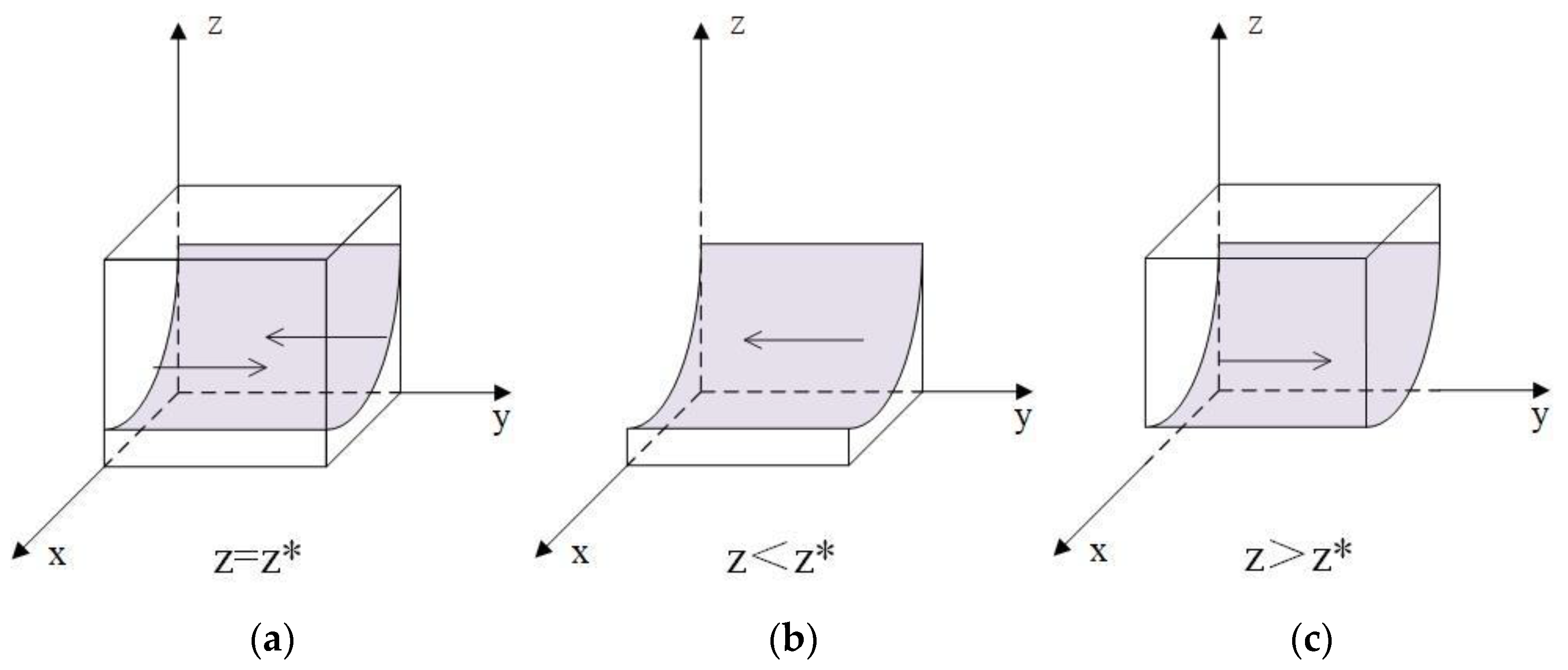
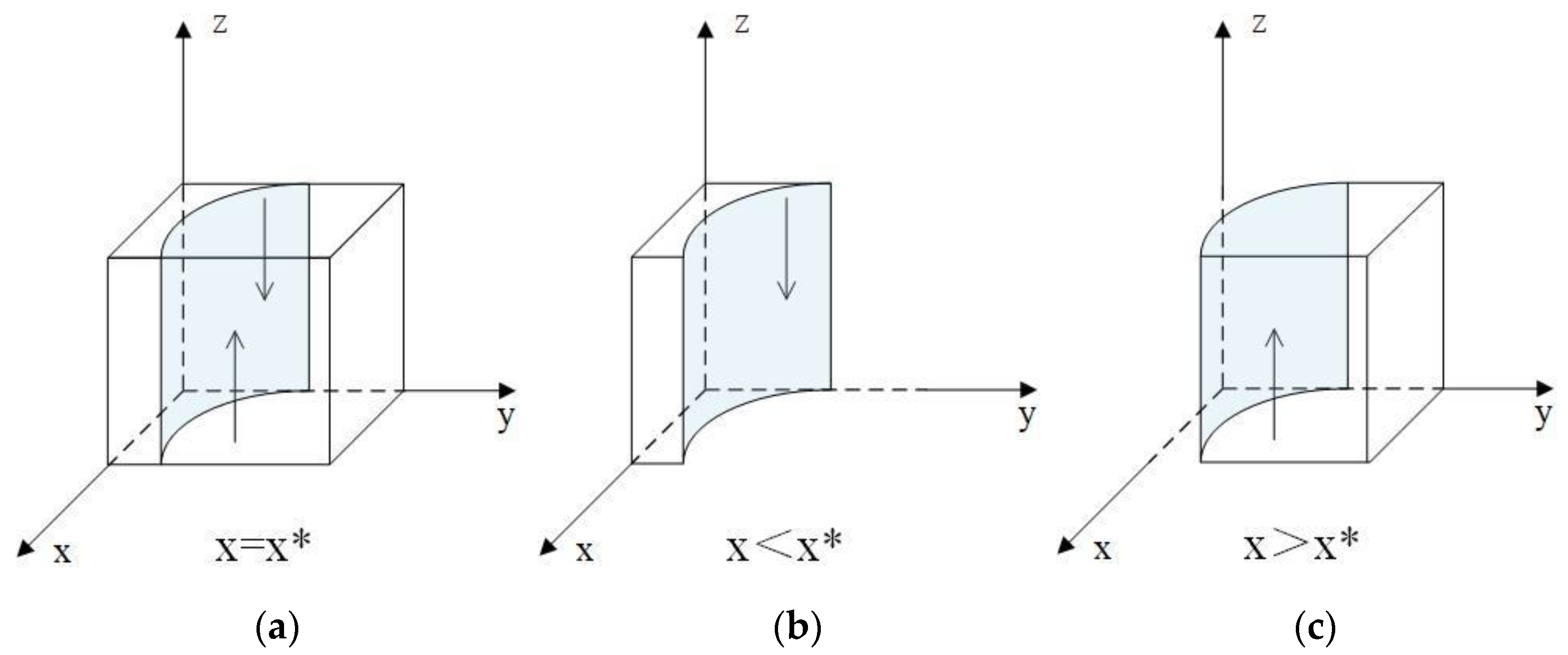
3.3. Stability Analysis of Single Subject Evolutionary Game
3.3.1. Analysis of Governments’ Strategy Stability
3.3.2. Analysis of Developers’ Strategy Stability
3.3.3. Analysis of Construction Enterprises’ Strategy Stability
3.4. Stability Analysis of Tripartite Evolutionary Game System
- (1)
- Initial stage: Due to weak awareness of emission reduction and the reliance on traditional paths and economic interests, developers and construction enterprises often lack motivation to actively and positively reduce emissions, instead adopting negative strategies in urban renewal projects. Although the government recognizes the importance of active regulation and attempts to supervise market players to reduce emissions through subsidies, the initial incremental gains cannot offset their costly inputs; in other words, R1 − R2 < C1. Moreover, developers and construction enterprises face high costs in adopting active strategies, with returns being significantly lower than traditional methods, that is, C2 > R3 − R4 + S1, C3 > R5 − R6 + S2. Given limited subsidies and weak penalties in the initial stage, governments cannot effectively motivate developers and construction enterprises, leading to inaction on their part. Therefore, the tripartite evolutionary stabilization strategy in the initial phase is E5(1,0,0). Developers and construction enterprises have adopted negative emission reduction strategies, while the government has endeavored to actively regulate but with little effect.
- (2)
- Growth stage: As government regulation intensifies, some forward-looking developers and construction enterprises may take the lead by actively investing in emission reduction and green transformation. The government typically prioritizes supporting developers who actively reduce emissions, thus creating a market demonstration effect that encourages the participation of more enterprises and guiding developers to cooperate with actively transforming construction enterprises, leading to carbon trading in urban renewal projects. At this point, R3 > R4. Developers benefit from active strategies, with subsidies and additional revenues offsetting costs, and S1 + βR7 > C2. Construction enterprises face the burden of prohibitive costs of green transformation, and they need support and assistance from the government and developers; however, limited government subsidies due to budget constraints leave them insufficiently incentivized to change, and C3 > R5 − R6 + S2. Therefore, the tripartite evolutionary stabilization strategy in the growth phase is E7(1,1,0). Developers tend to reduce emissions aggressively, while construction companies tend to take a wait-and-see approach, and governments continue to strengthen regulations and incentives.
- (3)
- Mature stage: With the increasing maturity of carbon trading policies, governments positively supervise and promote participation in carbon trading through policy guidance and financial support, and R1 − R2 > C1. Technological advancements simultaneously lower the costs to meeting carbon reduction targets, making proactive emission reduction strategies more profitable for both developers and construction enterprises; therefore, R3 − C2 + S1 > R4, R5 − C3 + S2 > R6. Their collaborative efforts create mutual benefits, with developers being able to subsidize construction enterprises’ transition costs through shared gains. At this stage, the emission reduction effectiveness of urban renewal projects is significantly improved, leading to three scenarios regarding the decision to enter the carbon trading market: First, the emission reduction volumes fall below the carbon market access standard, so it is not possible to obtain additional revenue directly through carbon trading. Second, the amount of emission reduction meets the standard; however, government incentives are insufficient to offset trading costs, and C4 > P(E2 − E1) + S3. Third, emission reductions are sufficient and profitable, and C4 < P(E2 − E1). Therefore, the tripartite evolutionary stabilization strategy at the mature phrase is E8(1,1,1), the governments regulate actively, and both developers and construction enterprises are adopting proactive emission reduction strategies and selectively participating in carbon trading.
4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Data Source
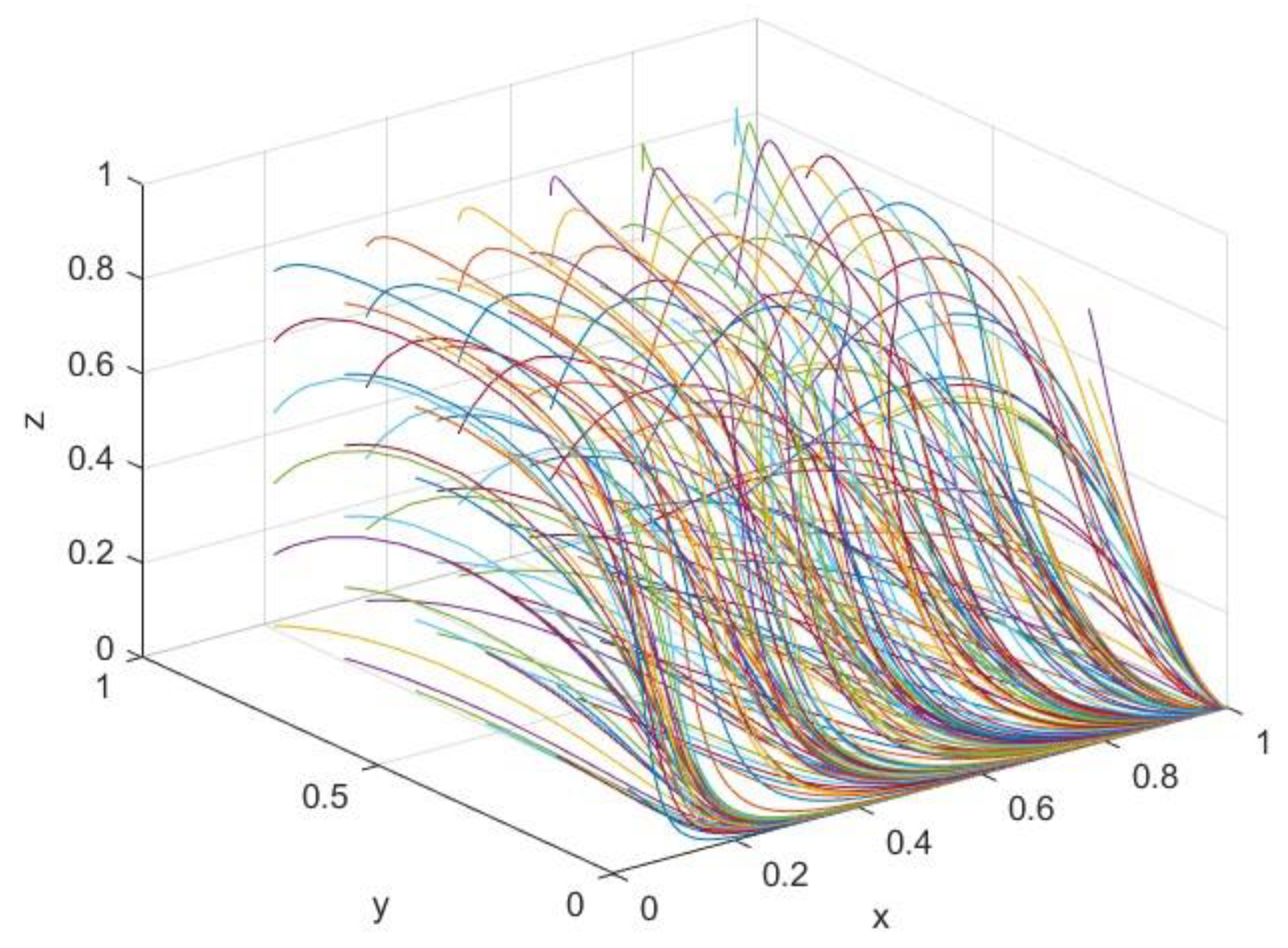
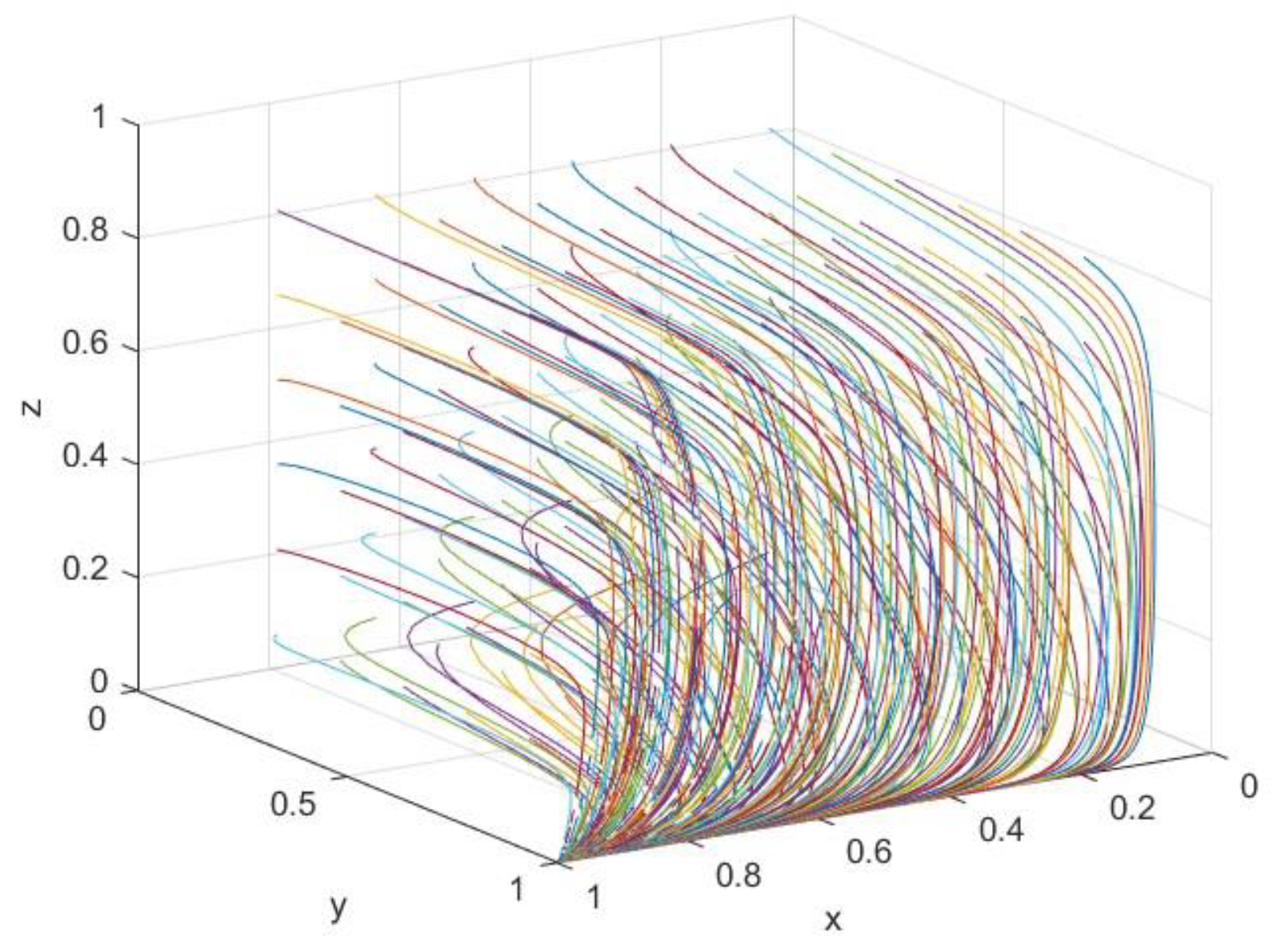
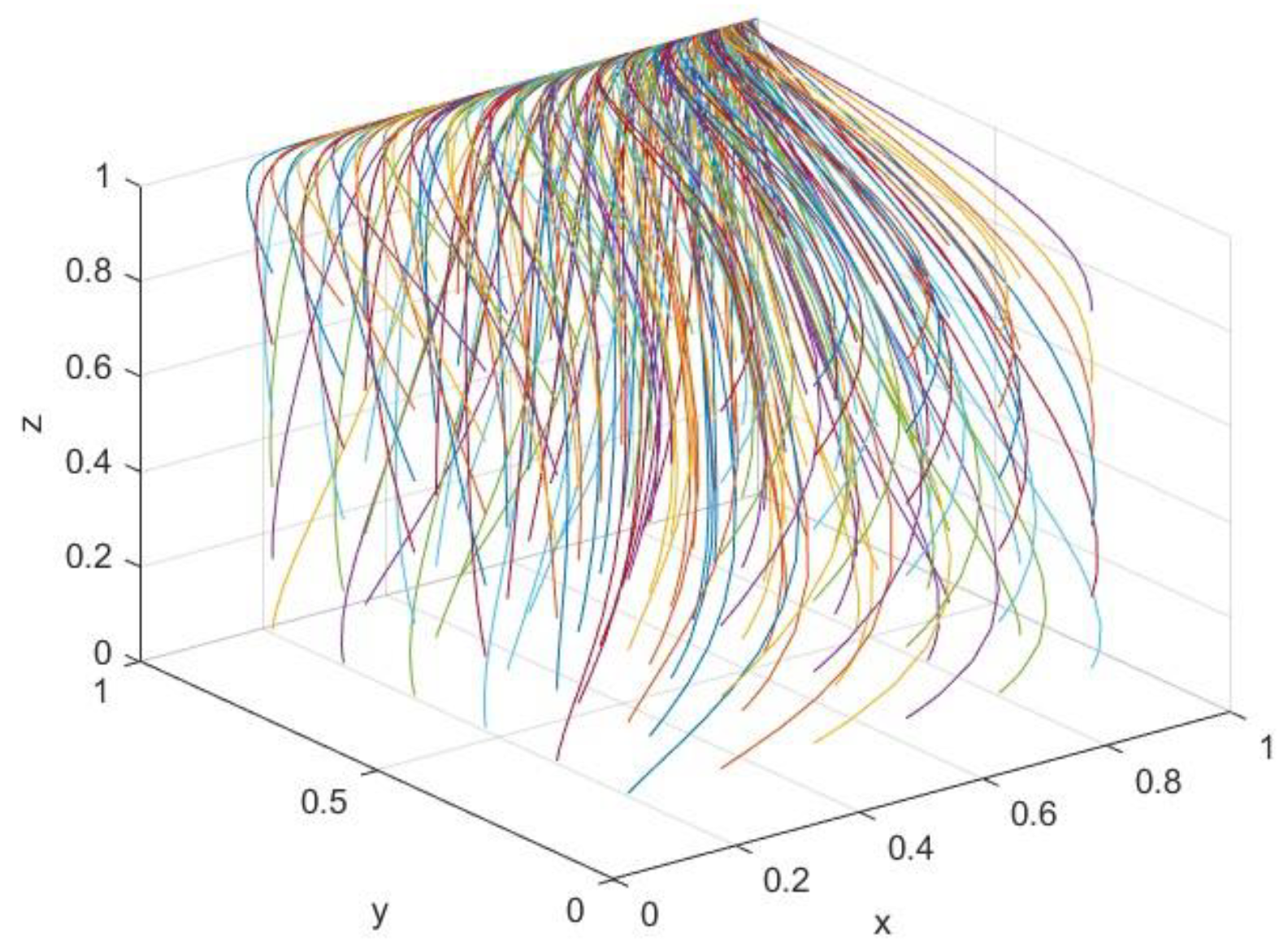
4.2. Multi-Stage Dynamic Evolution Results
4.2.1. Evolutionary Results for Stakeholders in the Initial Phase
4.2.2. Evolutionary Results for Stakeholders in the Growth Phase
4.2.3. Evolutionary Results for Stakeholders in the Mature Phase
4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
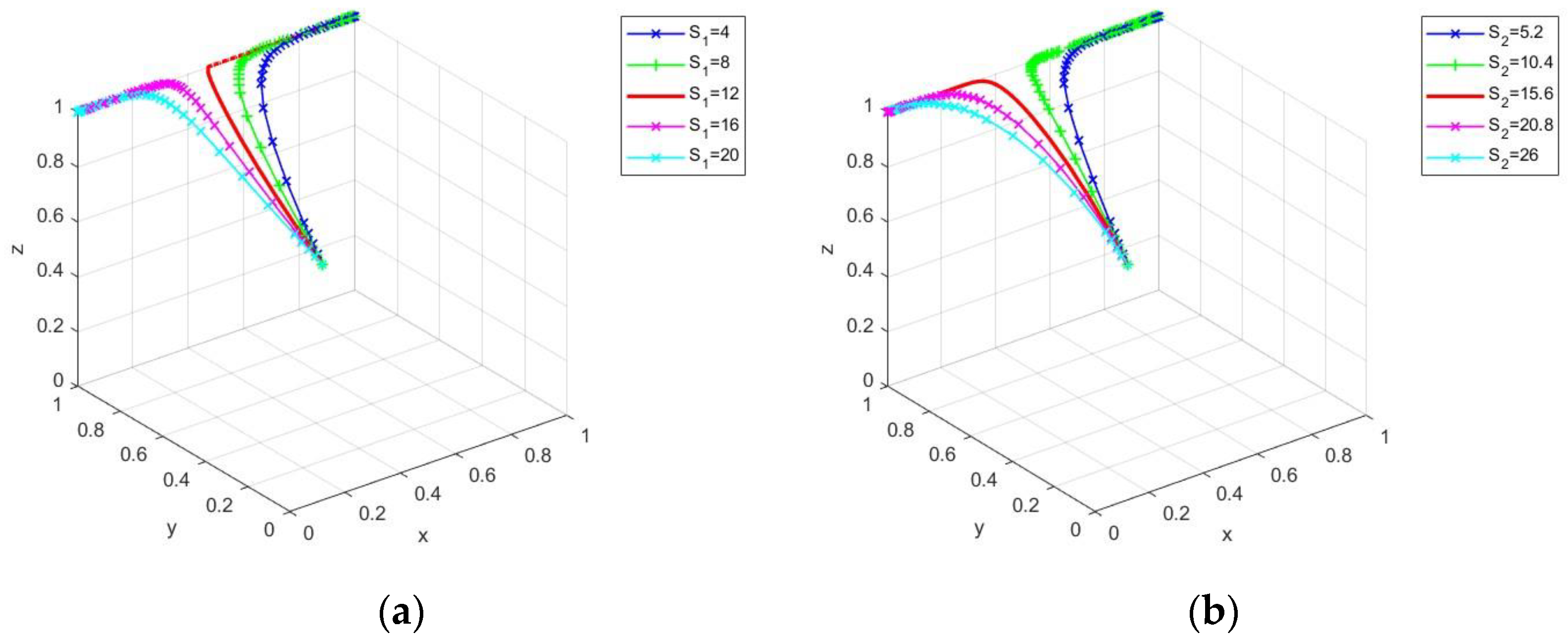
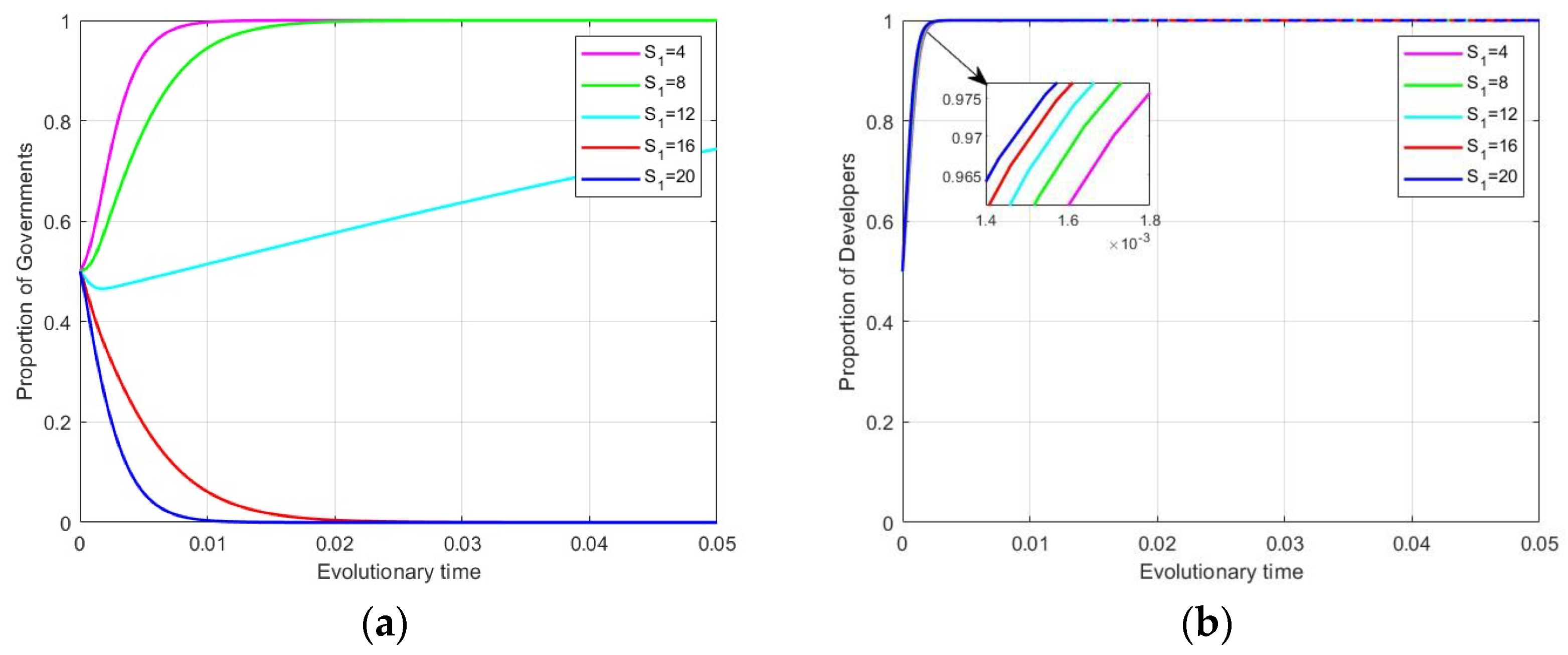
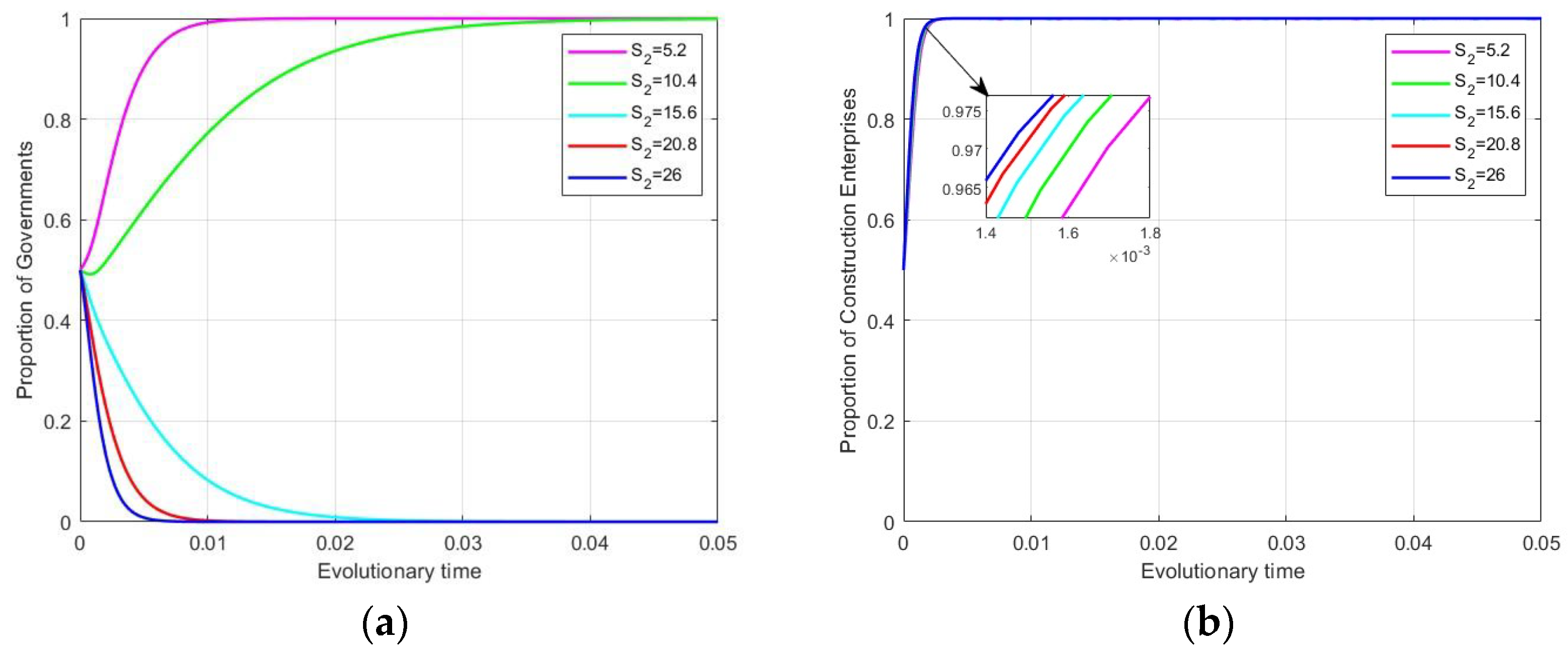
4.3.1. Impact of Government Subsidies on Evolutionary Stabilization Strategies
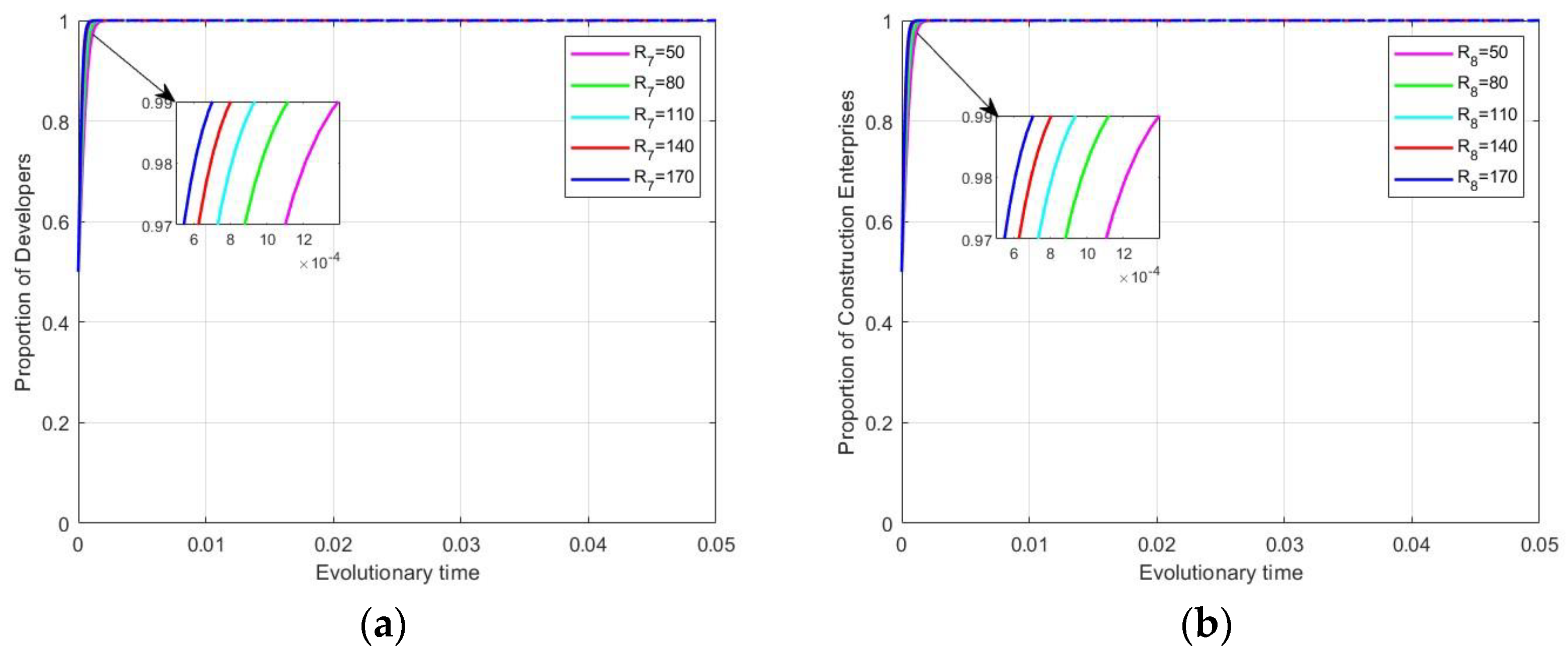
4.3.2. Impact of Government Punishments on Evolutionary Stabilization Strategies
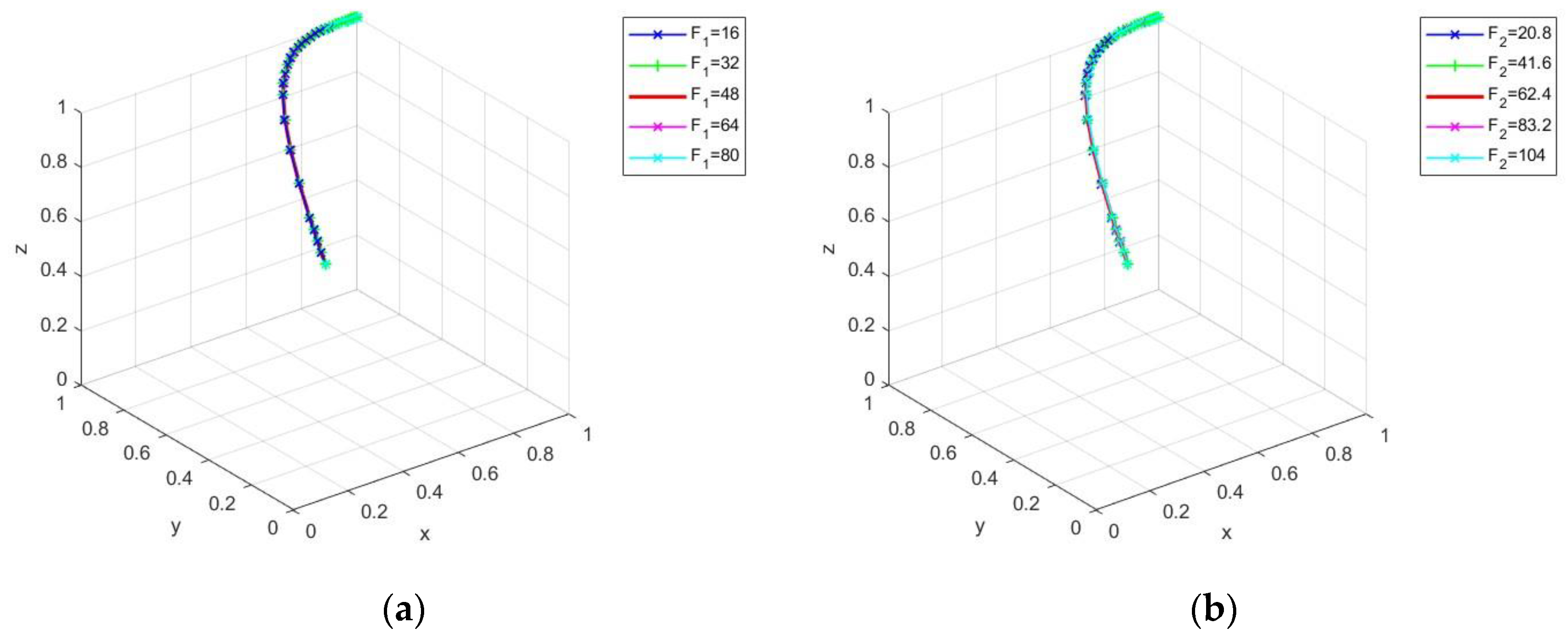
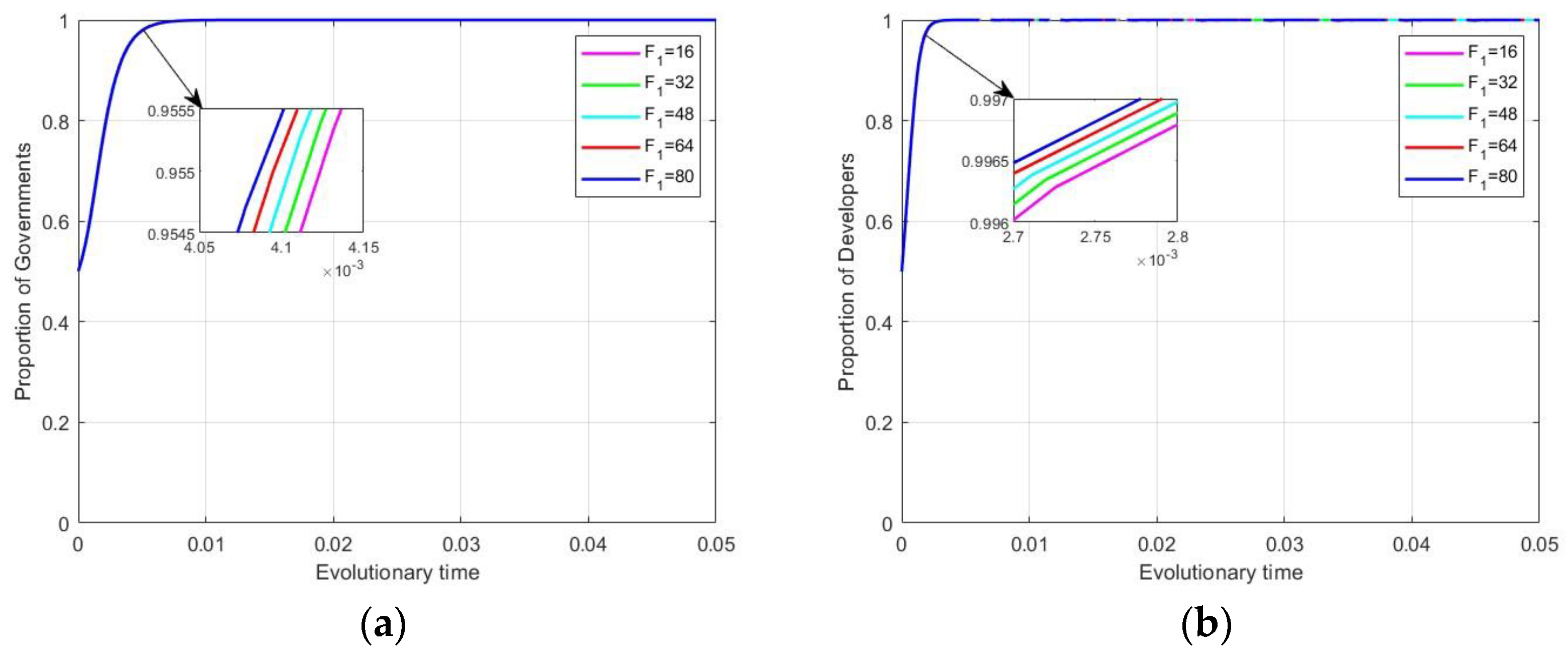
4.3.3. Impact of Additional Benefits on Evolutionary Stabilization Strategies
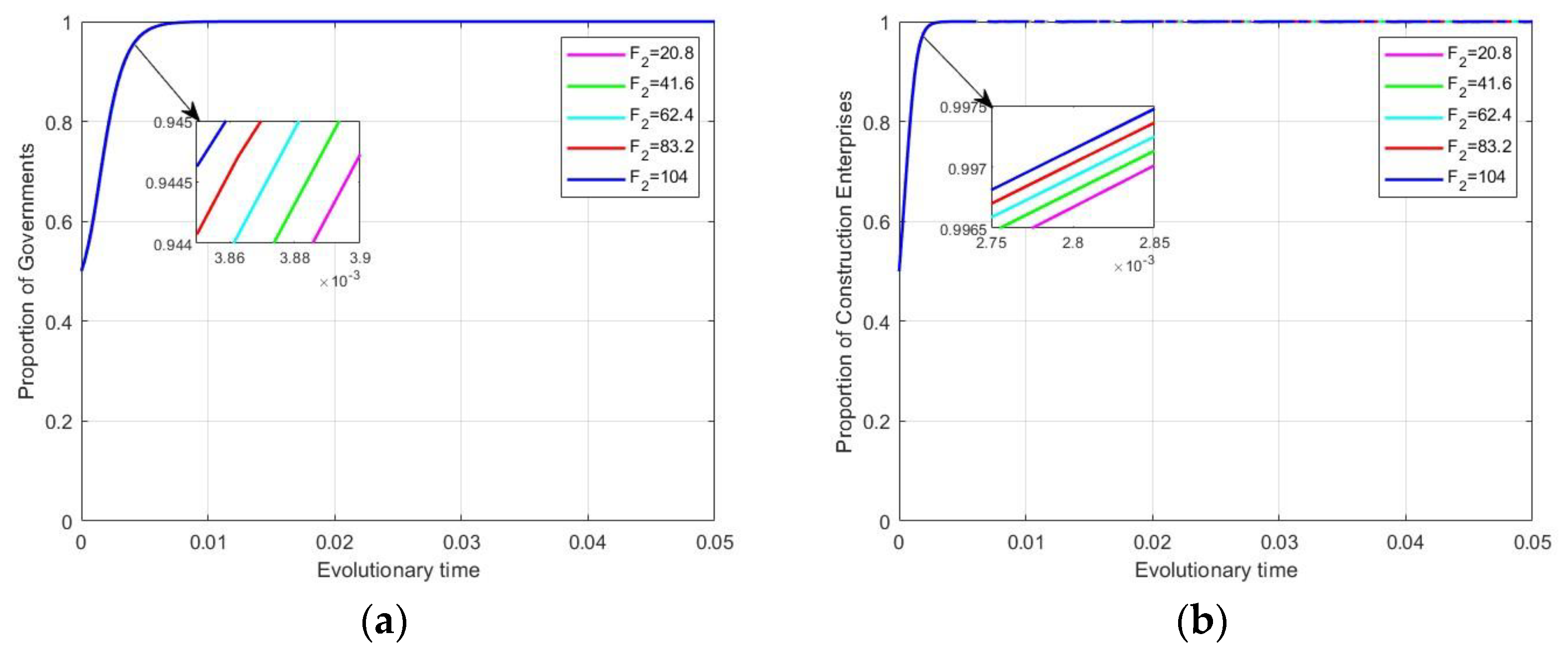
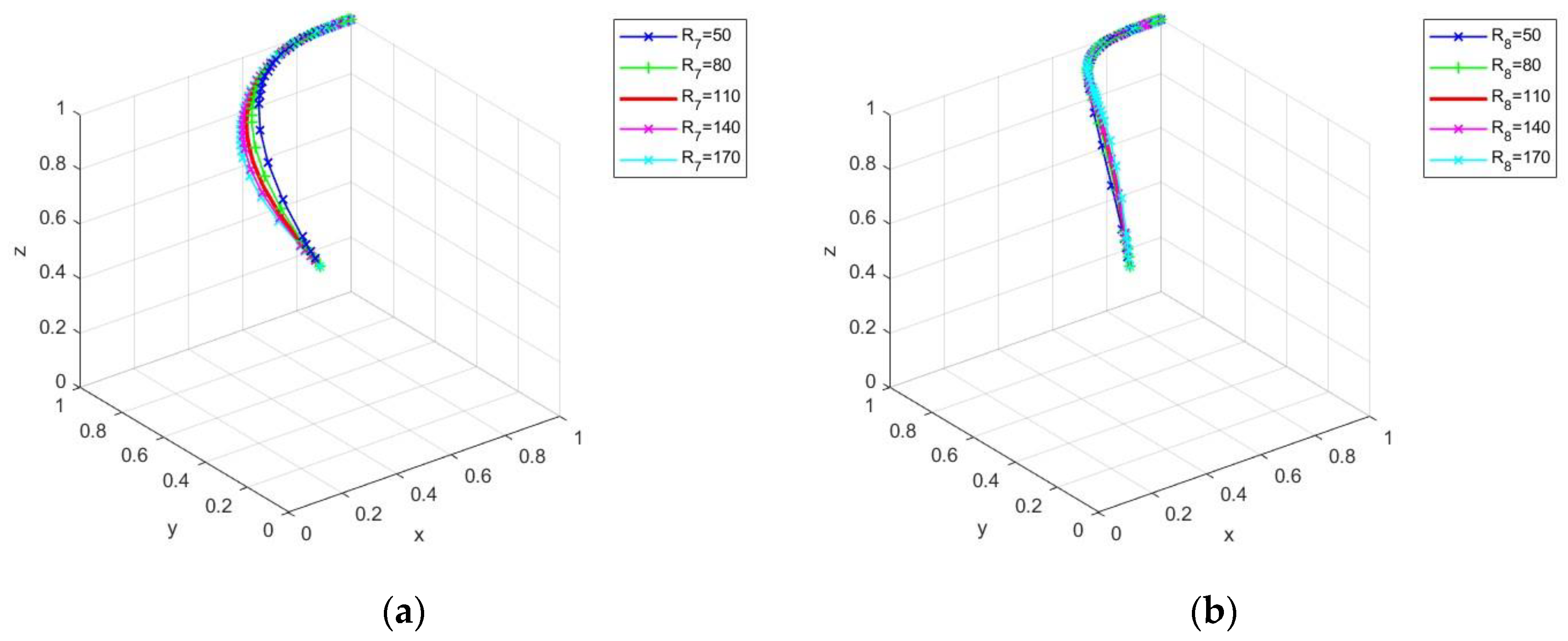
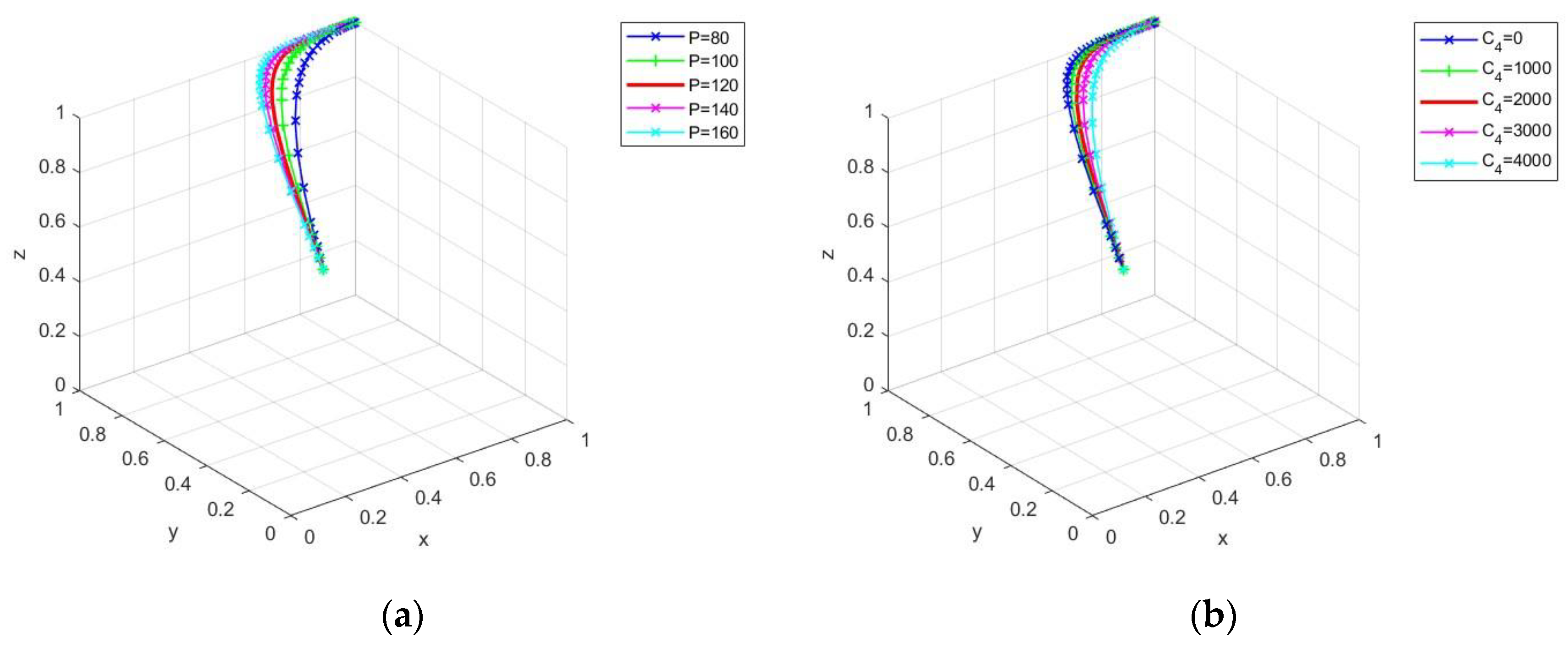
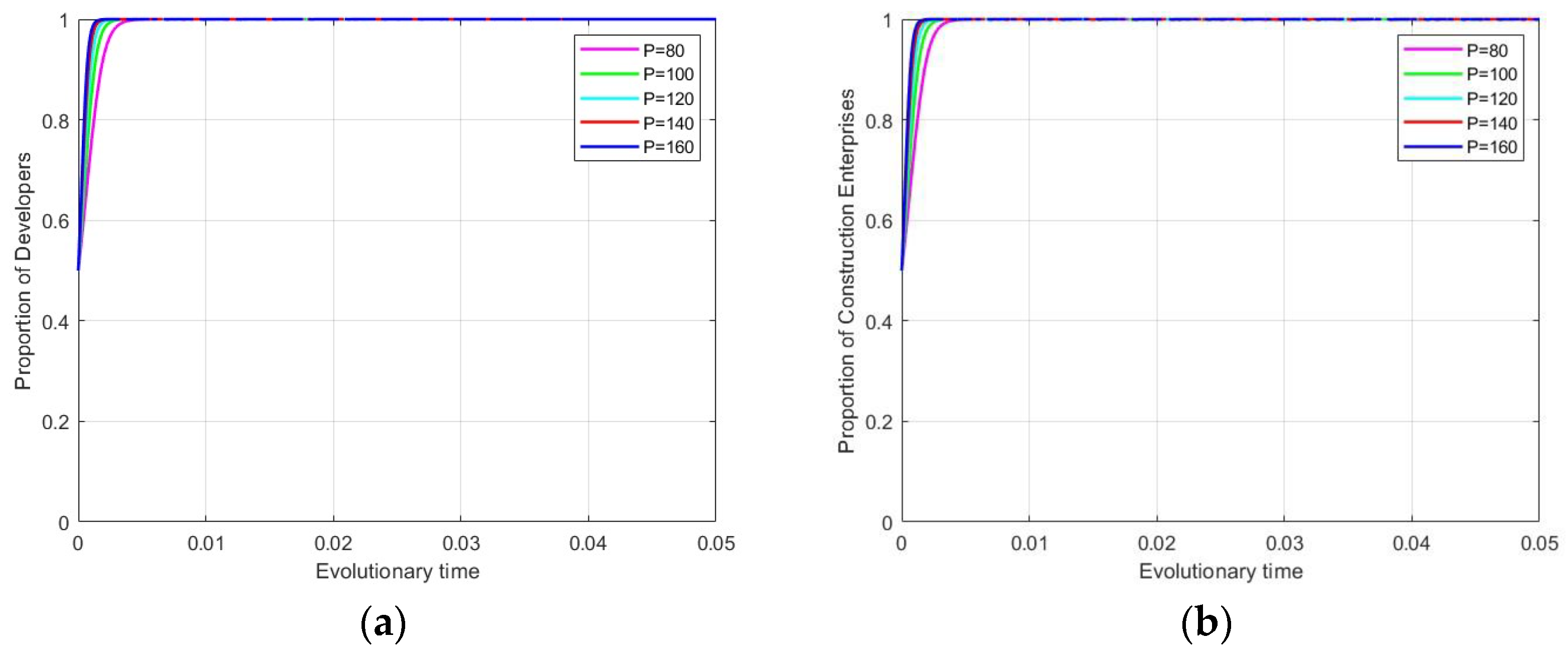
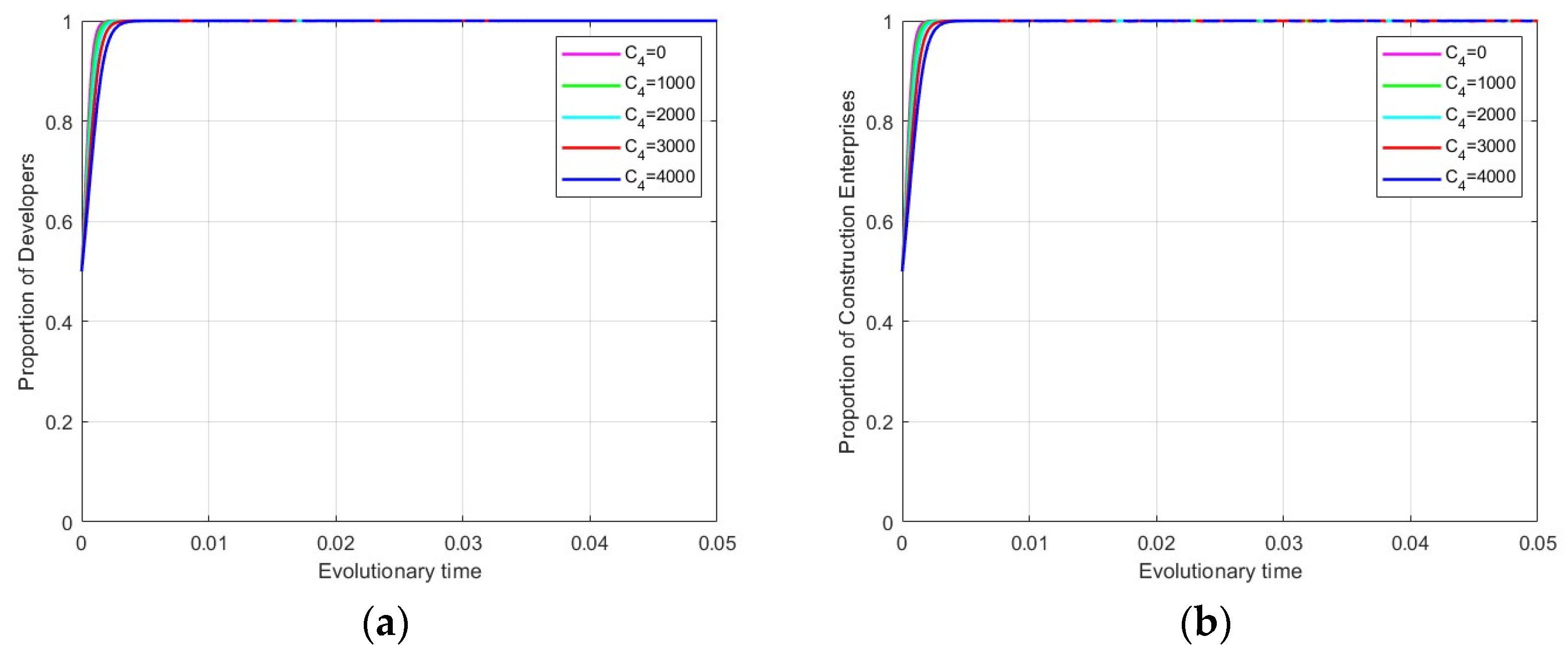
4.3.4. Impact of Carbon Trading on Evolutionary Stabilization Strategies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
- (1)
- Carbon emission reduction in urban renewal will follow the evolutionary law of the initial, growth, and mature stages, and emission reduction decisions will be made sequentially according to the order of the government, developers, and construction enterprises, which is consistent with the actual situation. Ideally, the government will actively supervise, while developers and construction enterprises will adopt active emission reduction strategies and selectively participate in carbon trading according to the amount of emission reduction required.
- (2)
- Government regulation always plays an important role. Subsidy policies and penalty mechanisms are key factors influencing decisions on carbon emission reduction in urban renewal, with the optimal subsidy rate that the government should not exceed being in the range of 20% to 30%.
- (3)
- Economic benefits are the core motivation for developers and construction enterprises to participate in carbon reduction, and continuous improvement in the carbon trading market provides a new revenue path, whose main influence mechanism is determined by the carbon market transaction participation cost and carbon market price together.
- (1)
- For governments, a dual regulatory mechanism of differentiated subsidies and stepped penalties should be established. According to the different degrees of negative emission reduction for developers and construction enterprises to set the proportion of subsidies, when the more negative party moderately increases the subsidy, the maximum subsidy ratio is no more than 30%. Regarding the emission reduction potential, there is a large difference in the emissions of the project, and the situation may need to be rectified within a specified period of time and according to the degree of its bad graded penalties. Punishment for certain factors may be needed to eliminate developers’ and construction industry enterprises’ fluky psychology, prompting them to actively take emission reduction initiatives to achieve technological transformation.
- (2)
- Developers and construction enterprises should actively respond to government incentives and seek additional benefits. Developers should prioritize investing in the research and development of technologies, such as assembled buildings and photovoltaic integration, and apply them to renovation projects with carbon reduction potential. Construction enterprises should actively innovate low-carbon construction technologies and establish real-time monitoring systems for carbon emissions to keep track of project emission reductions. Both parties should jointly sign an agreement on emission reductions to form a cooperation model of risk-sharing and benefit-sharing.
- (3)
- Carbon trading will gradually give full play to the decisive role of the market mechanism in resource allocation, improve the carbon trading rules for urban renewal projects, dynamically regulate market costs and prices, create a demonstration effect, attract more market players to participate in carbon trading, and promote the smooth operation of the market.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Feng, C. Implementation path of dual-carbon in Xiguan historical and cultural district of Guangzhou: A case study on Changhua street. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.L.; Ma, W. Evaluating carbon emissions of construction and demolition waste in building energy retrofit projects. Energy 2023, 281, 128201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X. Economic and environmental assessment of carbon emissions from demolition waste based on LCA and LCC. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Gong, X.; Yang, Y. Carbon Emission Trading Market in China: Operation Mechanism and Development Path. Ekoloji Derg. 2019, 107, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, S. Establishing the High-quality Urban Renewal System Towards the Vision of “Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality”: Changde, Hunan Province. Planners 2022, 38, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, Z. The Impact of Urban Renewal on Spatial–Temporal Changes in the Human Settlement Environment in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land 2024, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Miao, Z. Life-cycle carbon emissions (LCCE) of buildings: Implications, calculations, and reductions. Engineering 2024, 35, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Deng, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution path and driving mechanisms of sustainable urban renewal: Progress and perspective. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 1942–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sang, M.; Xu, X. How can urban regeneration reduce carbon emissions? A bibliometric review. Land 2023, 12, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Mao, C.; Huang, Z. Implementation strategies for sustainable renewal at the neighborhood level with the goal of reducing carbon emission. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Song, S. An Urban Renewal Design Method Based on Carbon Emissions and Carbon Sink Calculations: A Case Study on an Environmental Improvement Project in the Suzhou Industrial Investment Science and Technology Park. Buildings 2024, 14, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, C.M.; Ştefan, O.; Rădulescu, G.M. Management of stakeholders in urban regeneration projects. Case study: Baia-Mare, Transylvania. Sustainability 2016, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Shao, L. Research on emission reduction strategies of building materials manufacturers and real estate developers in the context of carbon trading. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 848260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, D.; Han, Z.J.; Sun, Y.P. Simulation analysis of the three-party evolutionary game of green building market players under carbon trading policy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 117591–117608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, S. Research on Environmental Protection Strategy of Urban Construction Subject Based on Evolutionary Game. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Tripartite evolutionary game analysis of carbon emission reduction behavior strategies under government regulation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zeng, X.; Wang, W. Carbon constraints and carbon emission reduction: An evolutionary game model within the energy-intensive sector. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hao, S.; Zhong, H.; Sun, Z. How to promote carbon emission reduction in buildings? Evolutionary analysis of government regulation and financial investment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, Y.; Dong, T.; Liu, B. Tripartite evolutionary game analysis on corporate carbon reduction decisions considering dual supervision under carbon trading. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 187, 109786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, F. Stakeholder management in government-led urban regeneration: A case study of the eastern suburbs in Chengdu, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörisch, J.; Schaltegger, S.; Freeman, R.E. Integrating stakeholder theory and sustainability accounting: A conceptual synthesis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiahou, X.; Li, Z.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Li, Q. Critical success factors for the implementation of urban regeneration REITs in China: A TISM–MICMAC based approach. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2024, 31, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ren, H.; Tang, J. A Framework for Assessing the Sustainability of Industrial Sites Protection and Reuse Under Stakeholders Analysis. Urban Stud. 2019, 26, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Miao, F. Evolutional Development of Public Participation in Urban Renewal: A Review of Yantian Case in Shenzhen. Urban Stud. 2015, 6, 58–62+79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Urban regeneration promotes high quality development of construction companies. Constr. Enterp. Manag. 2024, 35–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Asare, M.H. Fuzzy evaluation of comprehensive benefit in urban renewal based on the perspective of core stakeholders. Habitat Int. 2017, 66, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qian, Q.K.; Mlecnik, E.; Visscher, H.J. Critical factors for effective resident participation in neighborhood rehabilitation in Wuhan, China: From the perspectives of diverse stakeholders. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 244, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Song, J.; Bai, Y. China’s Urban Regeneration Evolution from 1949 to 2022: From the Perspective of Governance Mode. Land 2024, 13, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, T.; Luo, H.; Luo, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review of building lifecycle carbon emissions and reduction approaches. City Built Environ. 2024, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, W.Q. Towards sustainable building landscapes: A spatially explicit life-cycle analysis of carbon emissions and mitigation strategies. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Luo, K.; Zhao, L. An Operational Carbon Emission Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning Methods for Urban Residential Buildings in Guangzhou. Buildings 2024, 14, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Shen, T. Spontaneous Formation of Evolutionary Game Strategies for Long-Term Carbon Emission Reduction Based on Low-Carbon Trading Mechanism. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancalani, F.; Gnecco, G.; Metulini, R. The impact of the European Union emissions trading system on carbon dioxide emissions: A matrix completion analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechezleprêtre, A.; Nachtigall, D.; Venmans, F. The joint impact of the European Union emissions trading system on carbon emissions and economic performance. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2023, 118, 102758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, G.M.; Jafari, M.A. The efficiency of CO2 market in the phase III EU ETS: Analyzing in the context of a dynamic approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 61080–61095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, A.; Pu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Carbon market price prediction based on sequence decomposition-reconstruction-dimensionality reduction and improved deep learning model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 139063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.; Ma, X.; Shang, Y. Can China’s policy of carbon emission trading promote carbon emission reduction? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, T.; Gao, J. The effect of emission trading policy on carbon emission reduction: Evidence from an integrated study of pilot regions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Chen, Y. Innovation spillover effect of the pilot carbon emission trading policy in China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, J.; Song, Y. Impact and acting path of carbon emission trading on carbon emission intensity of construction land: Evidence from pilot areas in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, L.; Tu, J. Evolutionary Game Analysis of Governments’ and Enterprises’ Carbon-Emission Reduction. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, C.; Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Wei, W.; Zhao, M.; Xia, W. Research on evolutionary game strategy selection and simulation research of carbon emission reduction of government and enterprises under the “dual carbon” goal. Sustainability 2020, 14, 12647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Ni, W.; Ostic, D. Can carbon trading policy promote China’s decoupling of carbon emission from the perspective of technology-driven innovation? Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 893947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Li, M.W. An integrated optimization modeling approach for planning emission trading and clean-energy development under uncertainty. Renew. Energy 2014, 62, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yu, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S. Governance effects of pollution reduction and carbon mitigation of carbon emission trading policy in China. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, A. The Policy Impact of Carbon Emission Trading on Building Enterprises’ Total Factor Productivity in China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, X. Carbon emission reduction between government and heavily polluting enterprises under carbon trading mechanism based on evolutionary game analysis. J. Saf. Environ. 2023, 23, 4097–4107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, K.; He, J.; Han, C.; Liu, P. Carbon emission reduction behavior strategies in the shipping industry under government regulation: A tripartite evolutionary game analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L. Evolutionary game analysis of carbon emission reduction between government and enterprises under carbon quota trading policy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Shi, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, S. Evolutionary game analysis on improving collaboration in sustainable urban regeneration: A multiple-stakeholder perspective. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2020, 146, 04020046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y. Urban metabolism and spontaneous architectural growth: A sustainable strategy featuring participatory co-construction by multiple stakeholders. Buildings 2022, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentiss, A.M.; Foor, T.A.; Hampton, A. Testing the malthusian model: Population and storage at Housepit 54, Bridge River, British Columbia. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 18, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, W.; He, D.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; He, Z. Research on distribution strategy of logistics enterprise alliance based on three-party evolution game. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Du, L.; Tam, V.W.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Peng, C. Evolutionary game strategy of stakeholders under the sustainable and innovative business model: A case study of green building. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 333, 130136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gou, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, M. Research on the Connection Market Trading Issues of Green Certificates and CCER Based on Contribution Degree and Social Welfare. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, C. Evolutionary game model for decarbonization of shipping under green shipping corridor. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2024, 19, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, Y. Incentive-compatible mechanism for manufacturing carbon emission supervision under carbon control policies in China. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwaikat, L.N.; Ali, K.N. Green buildings cost premium: A review of empirical evidence. Energy Build. 2016, 110, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Hang, L.; Jiang, Y. Compound carbon policy for promoting low-carbon technology innovation in enterprises considering government supervision. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T. Optimal decisions and coordination of low-carbon supply chain under cap-and-trade regulation and government subsidy. J. Technol. Econ. 2024, 43, 159–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Feng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. A tripartite evolutionary game study of low-carbon innovation system from the perspective of dynamic subsidies and taxes. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Evolutionary game analysis of prefabricated buildings adoption under carbon emission trading scheme. Build. Environ. 2024, 249, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Ling, D.; Yang, Q.X.; Feng, Y.C.; Xiu, J. Central environmental protection inspection and carbon emission reduction: A tripartite evolutionary game model from the perspective of carbon neutrality. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 2139–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, C. Research on Building Carbon Emission Reduction under Differential Game. Oper. Res. Fuzziology 2024, 14, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, Q.; Shi, D. Research on the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Energy Efficiency. Financ. Trade Econ. 2024, 45, 143–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y. Life cycle carbon cost of buildings under carbon trading and carbon tax system in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morteza, A.; Chou, R.A. Distributed Matrix Multiplication: Download Rate, Randomness and Privacy Trade-Offs. In Proceedings of the 2024 60th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Urbana, IL, USA, 24–27 September 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Definition | Values |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Additional regulatory costs to governments in adopting ‘proactive regulation’ | above zero |
| C2 | Additional costs to developers adopting ‘proactive CER’ measures | above zero |
| C3 | Additional green transition costs for construction enterprises adopting ‘proactive transition’ | above zero |
| C4 | Costs to developers and construction enterprises accessing carbon market | above zero |
| R1, R2 | Corresponding revenues when government adopts ‘proactive regulation’ and ‘passive regulation’ strategy, respectively | above zero |
| R3, R4 | Benefits when developers adopt ‘proactive CER’ and ‘passive CER’ strategies | above zero |
| R5, R6 | Benefits of adopting ‘proactive transition’ and ‘passive transition’ strategies in construction enterprises | above zero |
| R7, R8 | Potential benefits that may exist for developers and construction enterprises | above zero |
| R9 | Additional benefits to government when developers and construction enterprises take initiative to participate in carbon trading | above zero |
| S1, S2 | Subsidies for developers and construction enterprises that choose proactive strategy when government adopts ‘proactive regulation’ | above zero |
| S3 | Government incentives for developers and construction enterprises to participate in carbon trading | above zero |
| F1, F2 | Penalties for developers and construction enterprises that choose negative strategy when government adopts ‘proactive regulation’ | above zero |
| L1, L2 | Losses incurred by government due to environmental pollution caused by inaction of developers and construction enterprises | above zero |
| E1, E2 | Carbon emissions with and without emission reductions in urban renewal projects | above zero |
| P | Carbon trading price | above zero |
| α | Coefficient of proportional sharing of green transition costs between developers and construction enterprises | 0 < α ≤ 1 |
| β, γ | Proportion of benefit reductions due to negative tactics of one party | 0 < β ≤ 1 0 < γ ≤ 1 |
| η | Cost-sharing coefficients for developers and construction enterprises to access carbon markets | 0 < η ≤ 1 |
| τ | Proportionate share factor of benefits from carbon trading for developers and construction enterprises | 0 < τ ≤ 1 |
| Governments (I) | Developers (II) | Construction Enterprises (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proactive Transition (z) | Passive Transition (1 − z) | ||
| Proactive regulation (x) | Proactive CER (y) | I: R1 − C1 − S1 − S2 − S3 + R9 II: R3 − C2 + S1 − αC3 + R7 − η(C4 − S3) + τP(E2 − E1) III: R5 − (1 − α)C3 − (1 − η)(C4 − S3) + (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) + S2 + R8 | I: R1 − C1 + F2 − L2 − S1 II: R3 − C2 + S1 + βR7 III: R6 − F2 |
| Passive CER (1 − y) | I: R1 − C1 + F1 − L1 − S2 II: R4 − F1 III: R5 − C3 + S2 + γR8 | I: R1 − C1 + F1 + F2 − L1 − L2 II: R4 − F1 III: R6 − F2 | |
| Passive regulation (1 − x) | Proactive CER (y) | I: R2 II: R3 − C2 − αC3 + R7 − ηC4 + τP(E2 − E1) III: R5 − (1 − α)C3 + R8 − (1 − η)C4 + (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) | I: R2 − L2 II: R3 − C2 + βR7 III: R6 |
| Passive CER (1 − y) | I: R1 − L1 II: R4 III: R5 − C3 + γR8 | I: R2 − L1 − L2 II: R4 III: R6 | |
| Equilibrium Points | Eigenvalues | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| E1(0,0,0) | R1 − C1 − R2 + F1 + F2 | R3 − C2 − R4 + βR7 | R5 − C3 − R6 + γR8 |
| E2(0,0,1) | R1 − C1 − R2 − S2 + F1 | R3 − C2 − R4 − αC3 + R7 − ηC4 + τP(E2 − E1) | −R5 + C3 + R6 − γR8 |
| E3(0,1,0) | R1 − C1 − R2 − S1 + F2 | −R3 + C2 + R4 − βR7 | R5 + R8 − R6 − (1 − α)C3 − (1 − η)C4 + (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) |
| E4(0,1,1) | R1 − C1 − R2 − S3 + R9 − S1 − S2 | −R3 + C2 + R4 + αC3 + ηC4 − τP(E2 − E1) | −R5 − R8 + R6 + (1 − α)C3 + (1 − η)C4 − (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) |
| E5(1,0,0) | −R1 + C1 + R2 − F1 − F2 | R3 − C2 − R4 + S1 + βR7 + F1 | R5 − C3 − R6 + S2 + γR8 + F2 |
| E6(1,0,1) | −R1 + C1 + R2 − F1 + S2 | R3 − C2 − R4 + S1 − αC3 + R7 + ηS3 − ηC4 + τP(E2 − E1) + F1 | −R5 + C3 + R6 − S2 − γR8 − F2 |
| E7(1,1,0) | −R1 + C1 + R2 − F2 + S1 | −R3 + C2 + R4 − S1 − βR7 − F1 | R5 + R8 − R6 + S2 + F2 + (1 − η)S3 − (1 − η)C4 + (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) − (1 − α)C3 |
| E8(1,1,1) | −R1 + C1 + R2 + S3 − R9 + S1 + S2 | −R3 + C2 + R4 − S1 + αC3 − R7 − ηS3 + ηC4 − τP(E2 − E1) − F1 | −R5 − R8 + R6 − S2 − F2 − (1 − η)S3 + (1 − η)C4 − (1 − τ)P(E2 − E1) + (1 − α)C3 |
| Stage | Initial Stage | Growth Stage | Mature Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | |||
| C1 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| C2 | 60 | 50 | 40 |
| C3 | 72 | 62 | 52 |
| C4 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| R1 | 50 | 90 | 130 |
| R2 | 62 | 32 | 12 |
| R3 | 70 | 130 | 160 |
| R4 | 96 | 75 | 50 |
| R5 | 75 | 100 | 125 |
| R6 | 82 | 62 | 42 |
| R7 | 40 | 75 | 110 |
| R8 | 40 | 75 | 110 |
| R9 | 192 | 756 | 1152 |
| S1 | 24 | 20 | 16 |
| S2 | 28.8 | 24.8 | 20.8 |
| S3 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| F1 | 24 | 40 | 48 |
| F2 | 28.8 | 49.6 | 62.4 |
| E1 | 95 | 55 | 15 |
| E2 | 107 | 97 | 87 |
| P | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| α | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| β | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Wu, T. Research on Carbon Emission Reduction and Benefit Pathways for Chinese Urban Renewal Market Players Based on a Tripartite Evolutionary Game: A Carbon Trading Perspective. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5089. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115089
Zou H, Li Y, Sun C, Wu T. Research on Carbon Emission Reduction and Benefit Pathways for Chinese Urban Renewal Market Players Based on a Tripartite Evolutionary Game: A Carbon Trading Perspective. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5089. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Han, Yuqing Li, Cong Sun, and Ting Wu. 2025. "Research on Carbon Emission Reduction and Benefit Pathways for Chinese Urban Renewal Market Players Based on a Tripartite Evolutionary Game: A Carbon Trading Perspective" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5089. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115089
APA StyleZou, H., Li, Y., Sun, C., & Wu, T. (2025). Research on Carbon Emission Reduction and Benefit Pathways for Chinese Urban Renewal Market Players Based on a Tripartite Evolutionary Game: A Carbon Trading Perspective. Sustainability, 17(11), 5089. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115089







