Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments in the Inaouène Watershed (Morocco): Indices, Statistical Methods, and Contributions to Sustainable Environmental Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
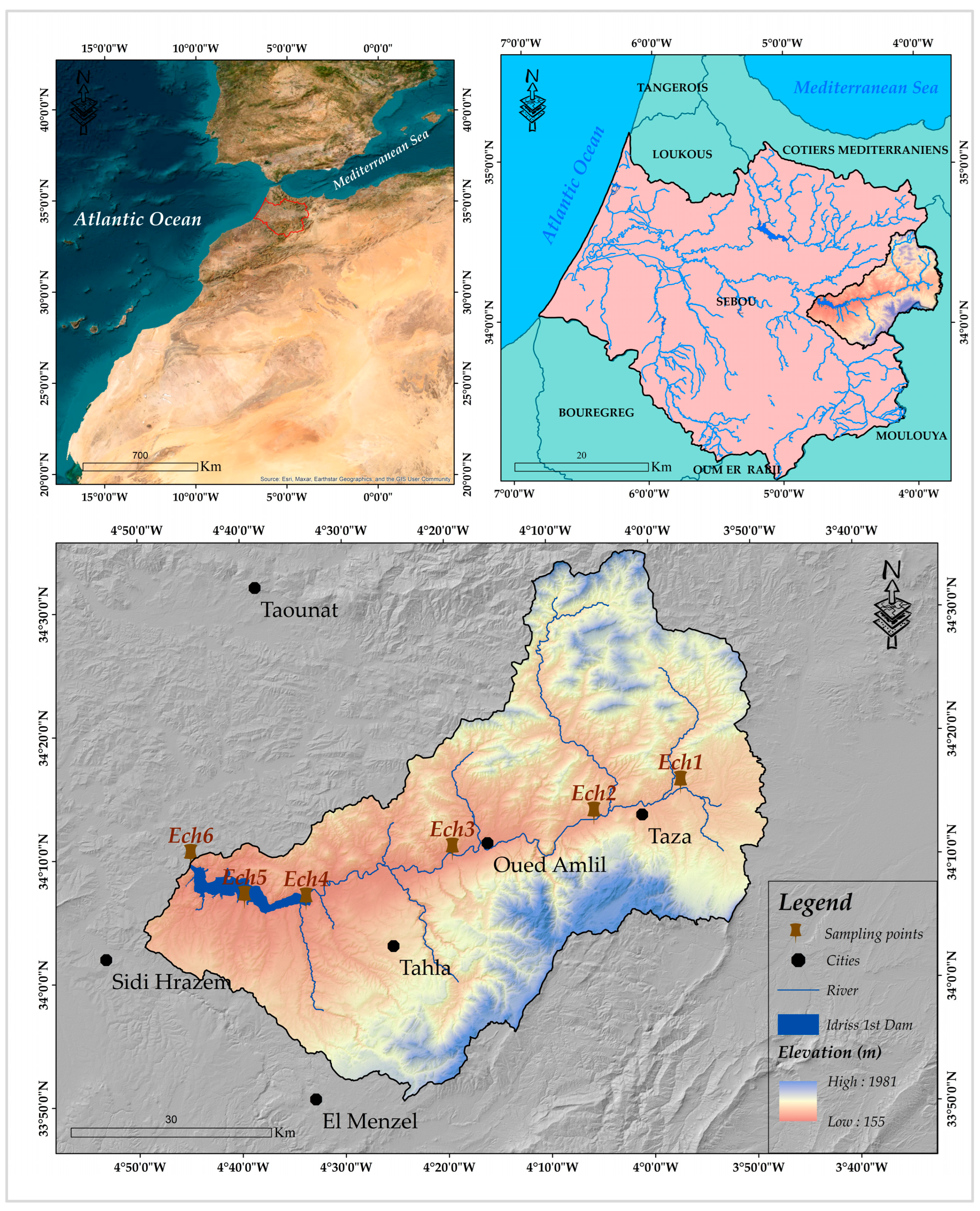
2.1. Description of the Sampling Area
- The Taza aquifer develops within highly karstified Lias limestone formations. It exhibits strong heterogeneity due to fracturing and the presence of sinkholes and underground conduits. Its recharge is rapid but irregular, making it sensitive to climatic variations.
- The Fès-Taza corridor aquifer is housed in Mio-Pliocene sedimentary formations (limestone, sandstone, marl). It ranges from unconfined to confined depending on the area, with diffuse recharge through porous materials. Its behavior is strongly influenced by local tectonics.
- The Magoussa aquifer, a semi-confined to confined system, consists of marly and sandy formations. It is characterized by low permeability and reduced transmissivity, with slow and limited recharge. Its functioning is moderate and highly dependent on the local lithological context.
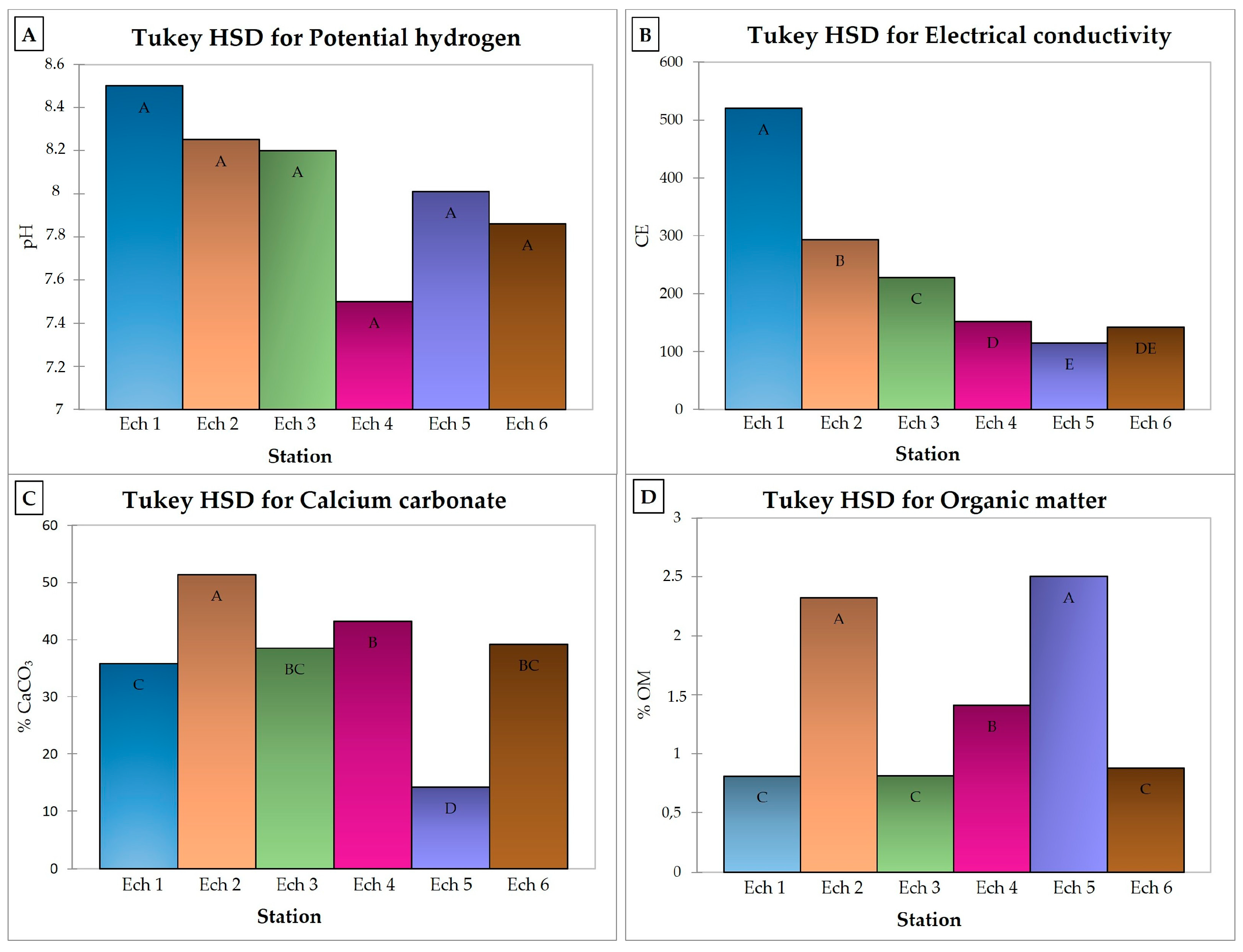
2.2. Collection and Analysis of Sediments
- Anthropogenic influences, such as urban discharges near Taza city (Ech2) and agricultural runoff from Oued Amlil (Ech3);
- Hydrological processes, including tributary confluences (Oued Larbae at Ech1, Oued Bouhlou at Ech4) and dam-induced sedimentation (Ech5);
- Contamination gradients, from the upstream reference site (Ech1, minimally impacted) to post-dam sediments (Ech6).
2.3. Pollution Indices and Contamination Levels
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
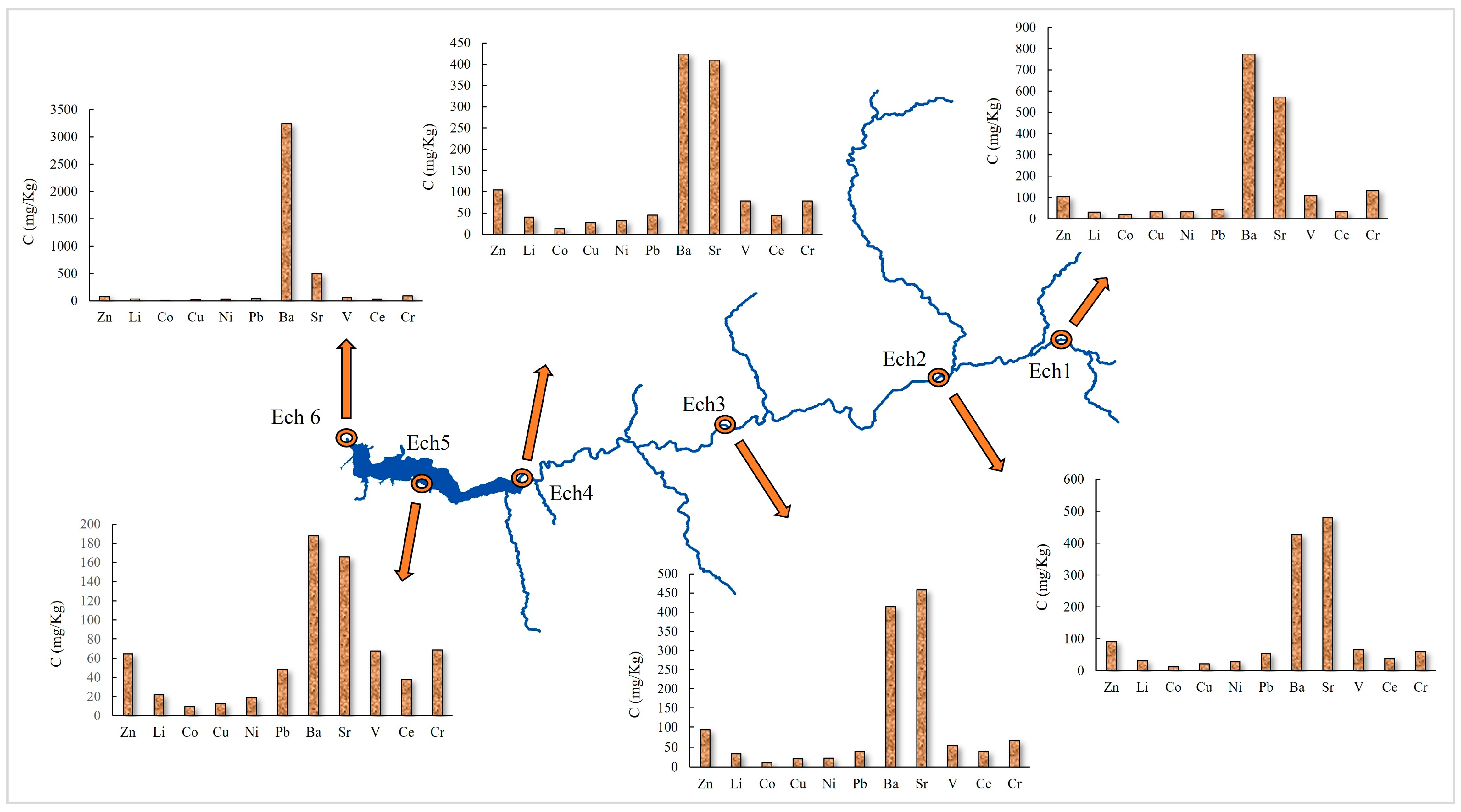
3.1. Analysis and Distribution of Heavy Metals in Sediments
3.1.1. Zinc (Zn)
3.1.2. Lithium (Li)
3.1.3. Cobalt (Co)
3.1.4. Copper (Cu)
3.1.5. Nickel (Ni)
3.1.6. Lead (Pb)
3.1.7. Barium (Ba) and Strontium (Sr)
3.1.8. Vanadium (V)
3.1.9. Cerium (Ce)
3.1.10. Chromium (Cr)
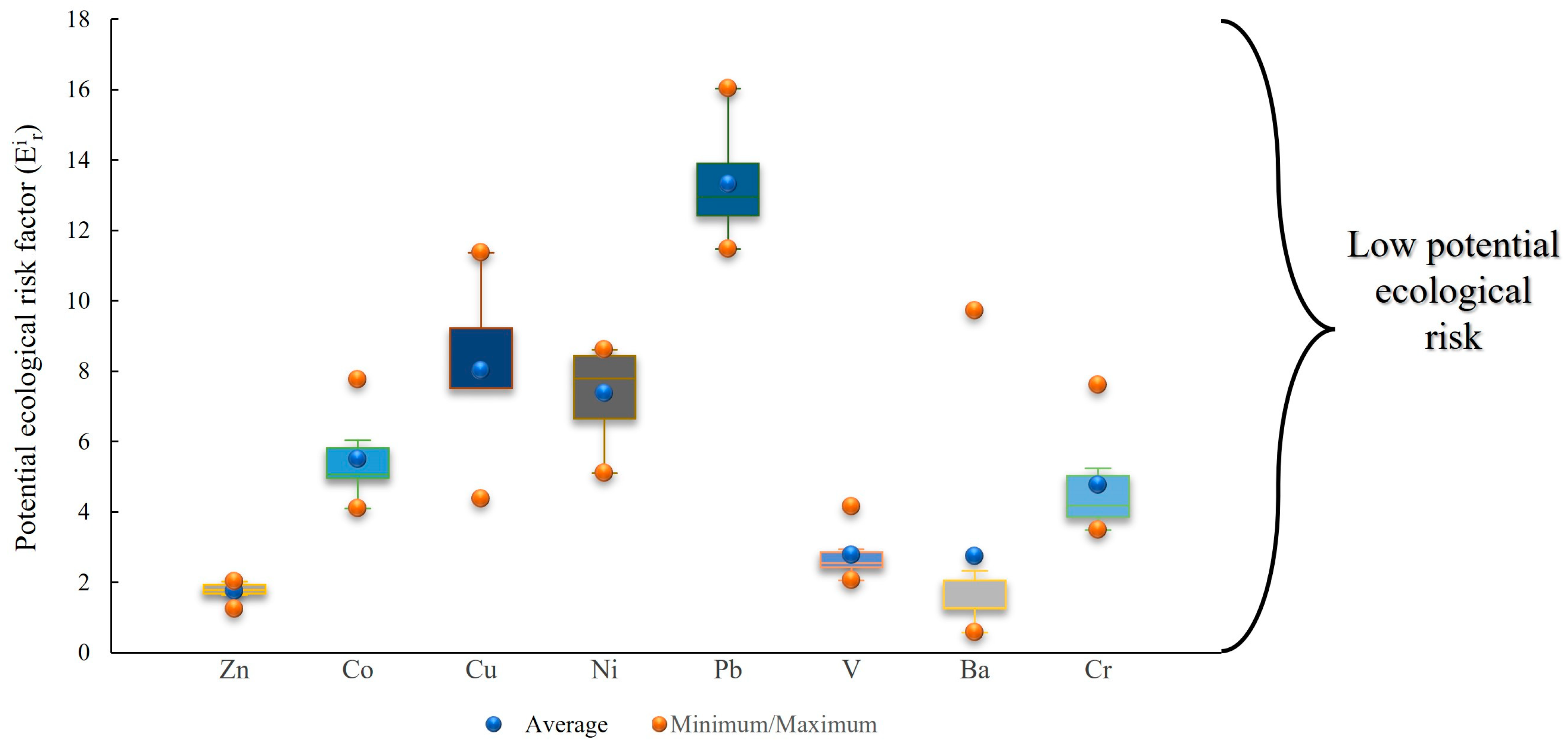
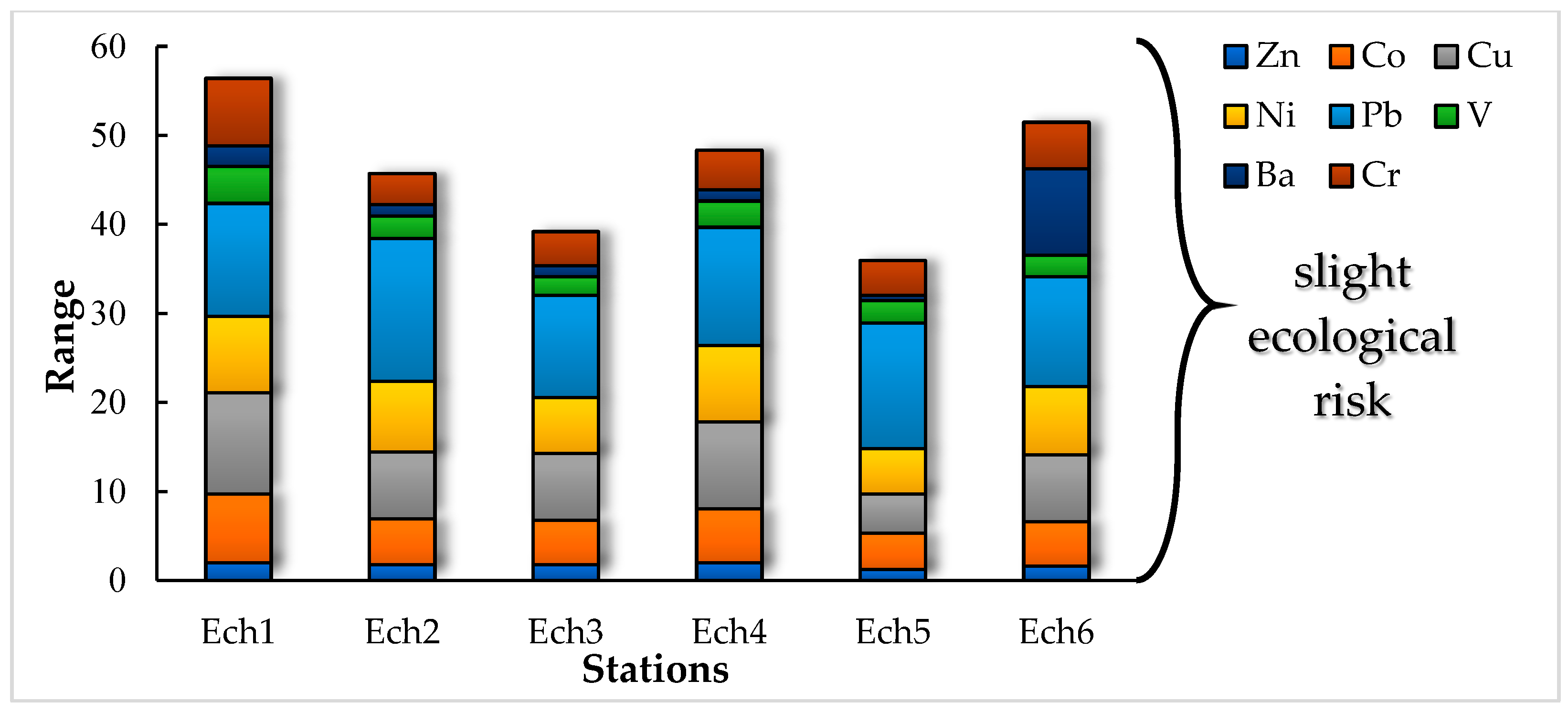
3.2. Pollution and Risk Evaluation
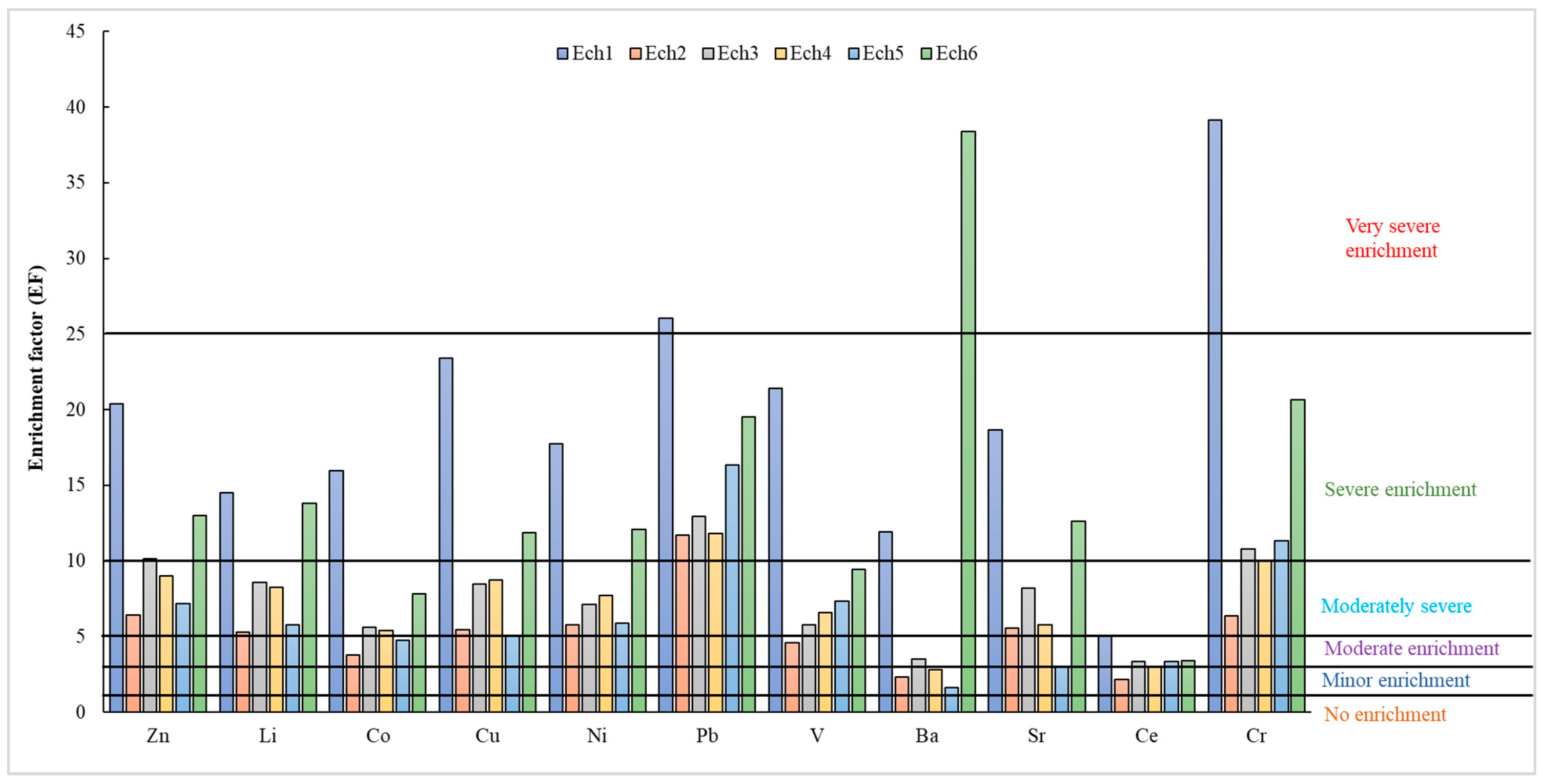
3.2.1. Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo)
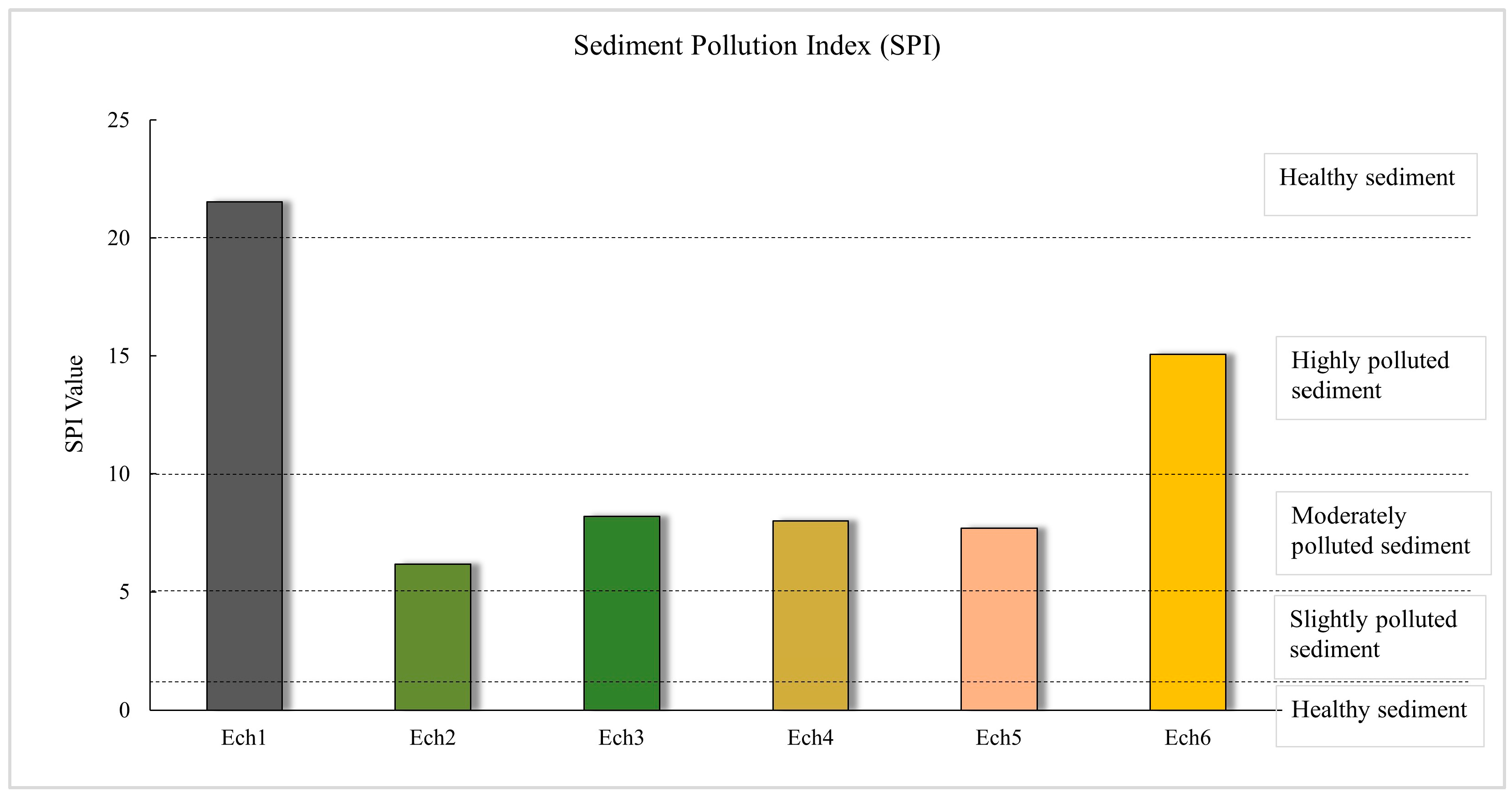
3.2.2. Enrichment Factor (EF) and Sediment Pollution Index (SPI)
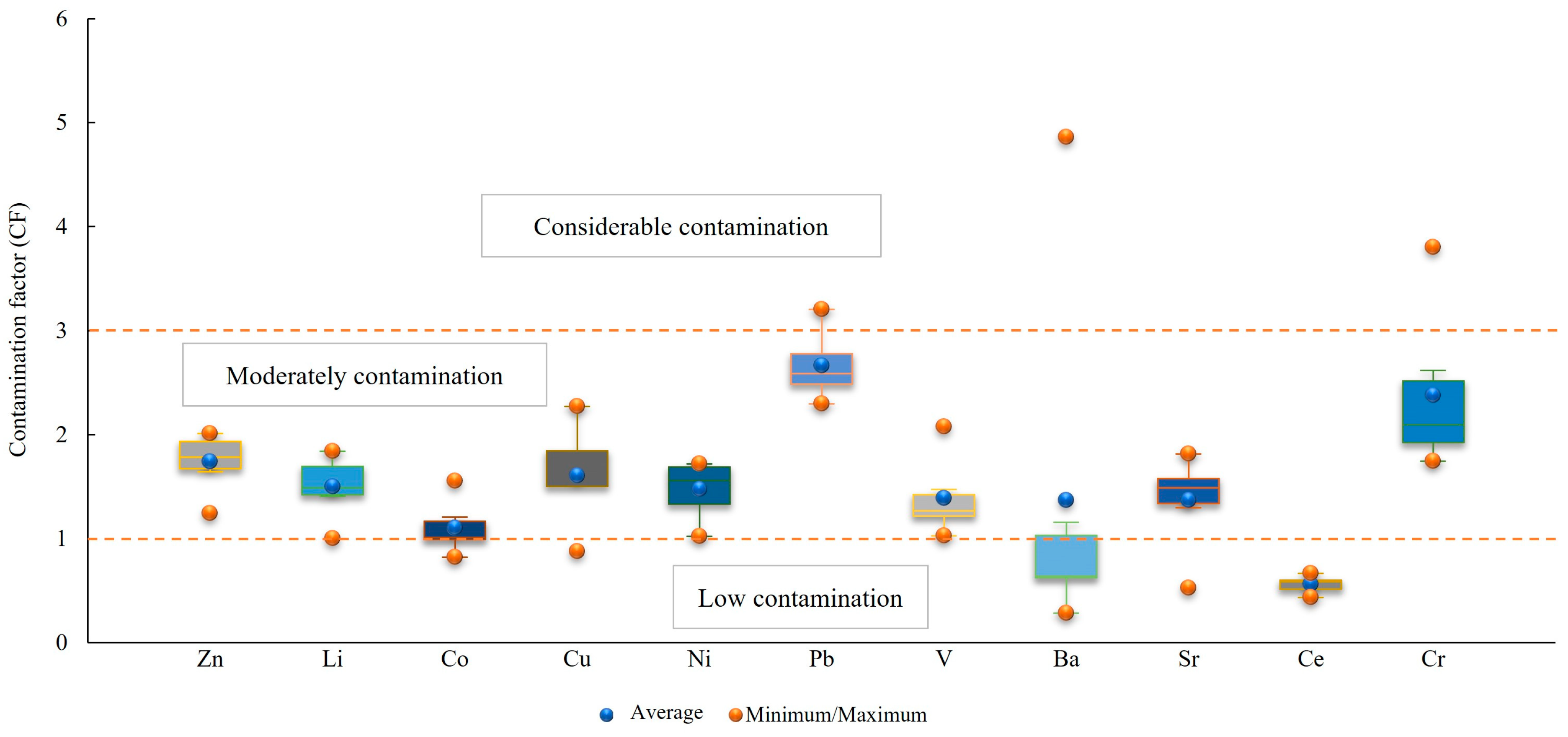
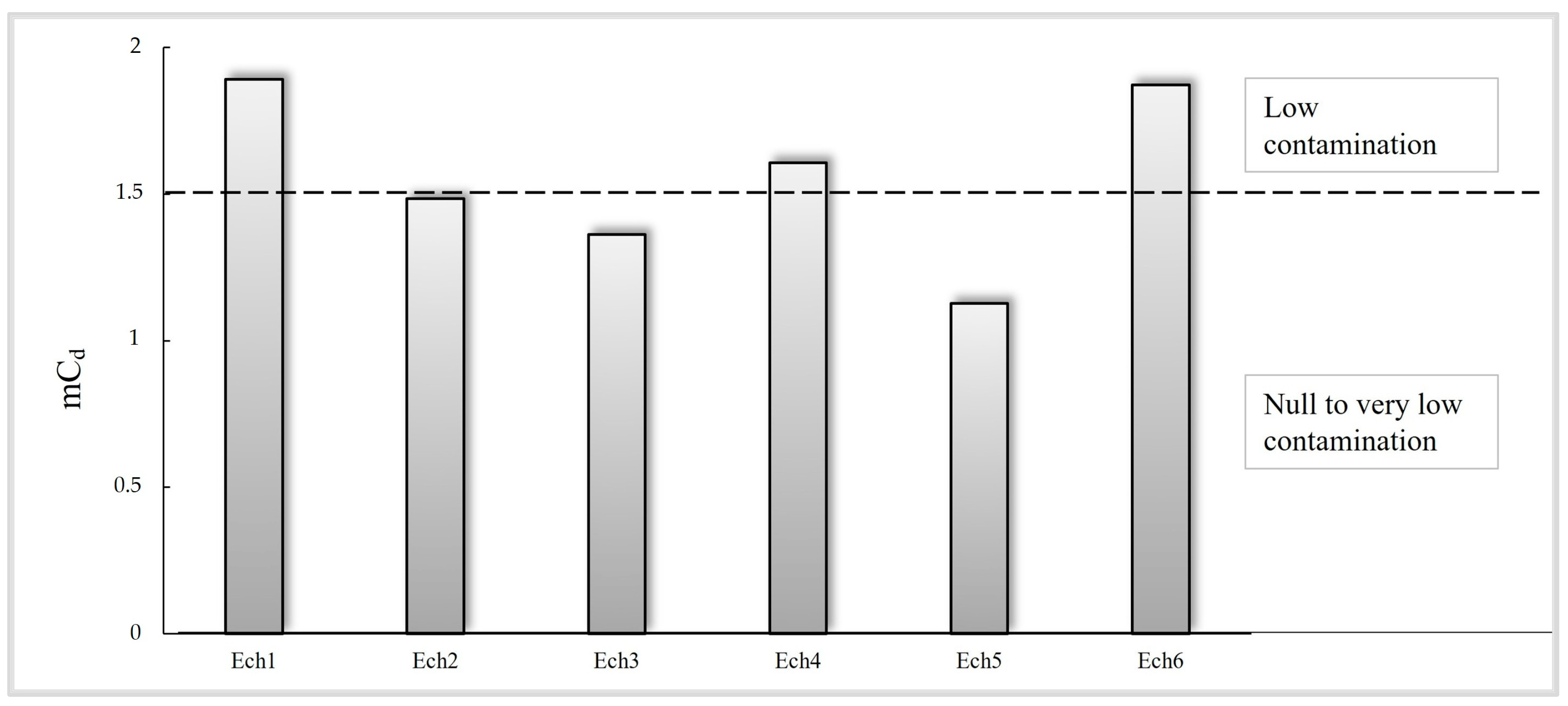
3.2.3. Contamination Factor (CF), Modified Degree of Contamination (mCd), and Pollution Load Index (PLI)
3.3. Identification of Pollution Sources
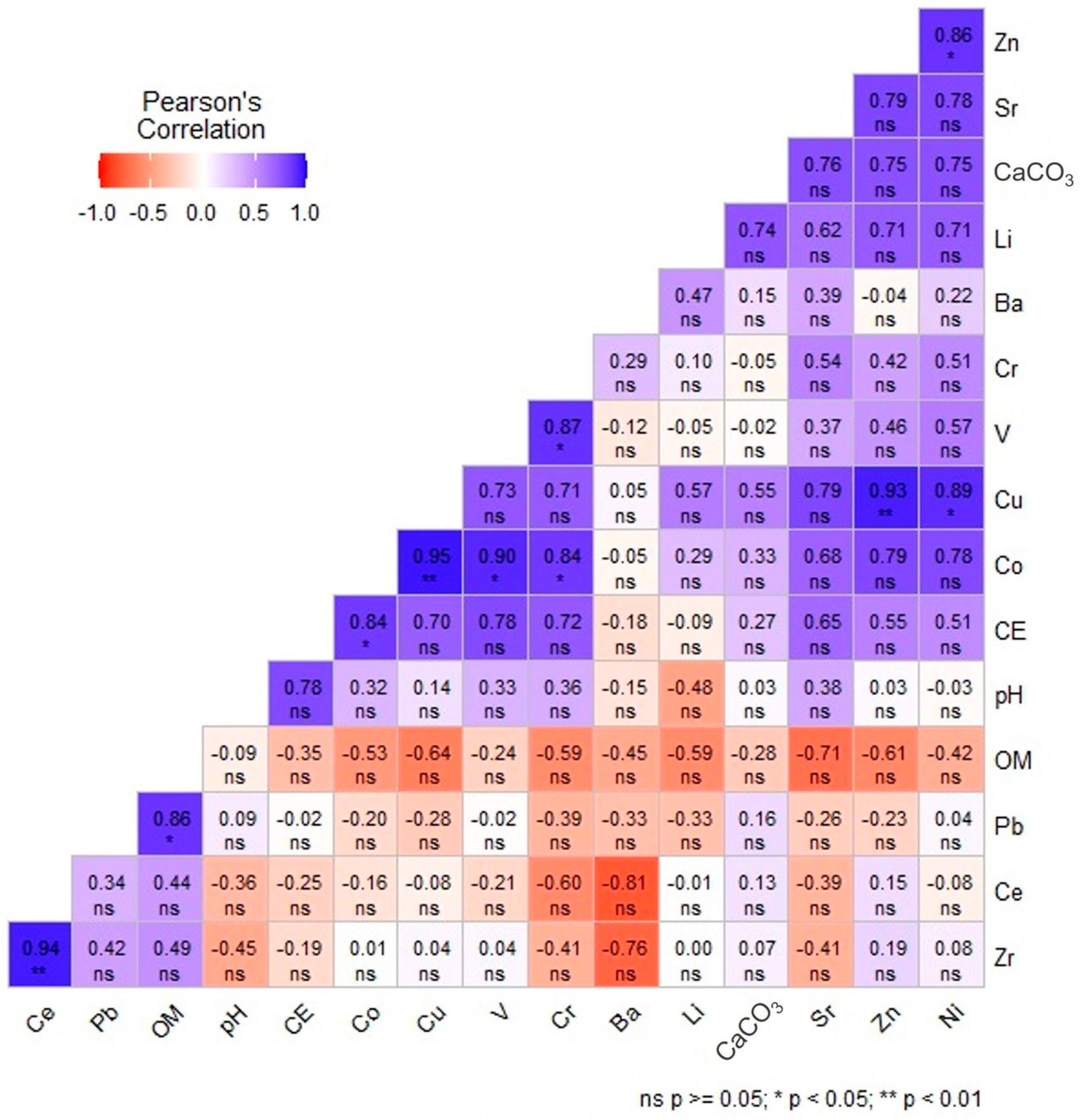
3.3.1. Correlation Matrix
3.3.2. Principal Component Analysis
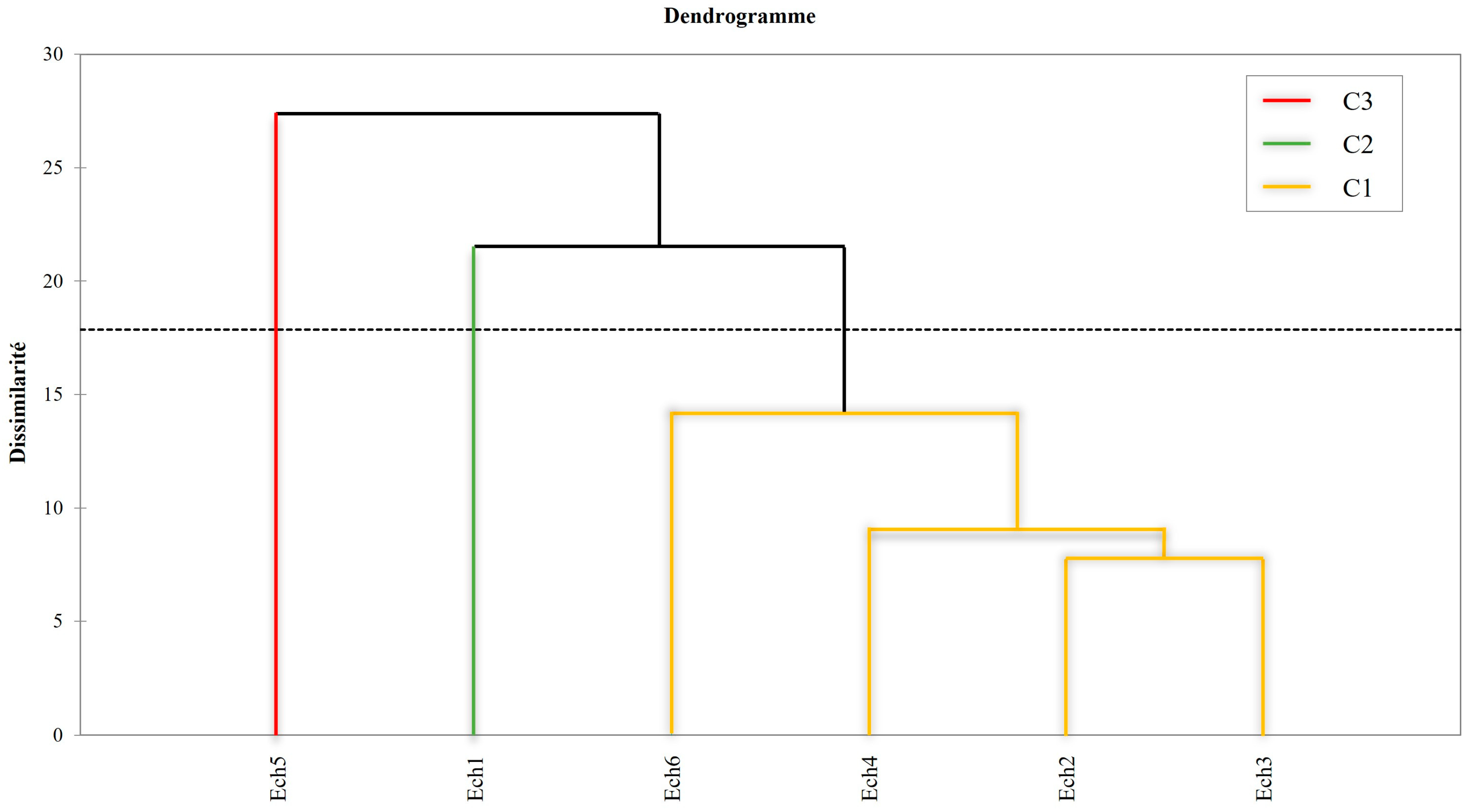
3.3.3. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guemouria, A.; Chehbouni, A.; Belaqziz, S.; Epule Epule, T.; Ait Brahim, Y.; El Khalki, E.M.; Dhiba, D.; Bouchaou, L. System Dynamics Approach for Water Resources Management: A Case Study from the Souss-Massa Basin. Water 2023, 15, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Igmoullan, B.; Namous, M.; El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; El Khalki, E.M.; Saidi, M.E.M. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS-CDR, ERA5, and SM2RAIN-ASCAT rainfall products for rainfall and drought assessment in a semi-arid watershed, Morocco. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Brahim, Y.; Bouchaou, L.; Sifeddine, A.; Beraaouz, E.H.; Wanaim, A.; Cheng, H. Hydro-climate characteristics of the karst system of Wintimdouine cave (Western High Atlas, Morocco): Monitoring and implications for paleoclimate research. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoujjati, N.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Hanich, L.; Rhoujjati, A.; Rafik, A.; Ouatiki, H.; Chehbouni, A.; Bouchaou, L. Snowpack and groundwater recharge in the Atlas mountains: New evidence and key drivers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakam, O.; Baali, A.; Azennoud, K.; El Kamel, T.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Ahouach, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of droughts and their teleconnections with large-scale climatic indices in the Lower Sebou Basin in northwestern Morocco. Acta Geogr. Slov. 2022, 62, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; El Khalki, E.M.; Najmi, A.; Bougadir, B. A Summary Analysis of Groundwater Vulnerability to Climate Variability and Anthropic Activities in the Haouz Region, Morocco. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zokm, G.M.; Okbah, M.A.; Younis, A.M. Assessment of heavy metals pollution using AVS SEM and fractionation techniques in Edku Lagoon sediments, Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2015, 50, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtkowska, M.; Bogacki, J. Assessment of trace metals contamination, species distribution, and mobility in river sediments using EDTA extraction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Grygar, T.M. A review of flood-related storage and remobilization of heavy metal pollutants in river systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotbolt, L.A.; Thomas, A.D.; Hutchinson, S.M. The use of reservoir sediments as environmental archives of catchment inputs and atmospheric pollution. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M.; Wang, F.; Caeiro, S.S. Assessing and managing sediment contamination in transitional waters. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.G.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, S.J.; Wang, Z.H. Metal pollution status in Zhelin Bay surface sediments inferred from a sequential extraction technique, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, E. Diagnostic de la Contamination Sédimentaire par les Métaux/Métalloïdes dans la rade de Toulon et Mécanismes Contrôlant leur Mobilité. Ph.D. Thesis, Université du Sud Toulon Var, Toulon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, B.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Fan, O.; Lü, C. Characteristics and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) residues along Sino-Russian boundary river. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yan, H.; Zhang, S. Heavy metal enrichment and health risk assessment of karst cave fish in Libo, Guizhou, China. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Şen, B. Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. Catena 2012, 92, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, A.R.; Monavari, S.M.; Bidhendi, G.R.; Nouri, J.; Nematpour, K. Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 147, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, M.; Choukr-Allah, R.; Bouchaou, L.; Hirich, A.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Krimissa, S.; Hssaisoune, M.; Nghira, A.; Barceló, D. Assessment of groundwater quality: Impact of natural and anthropogenic contamination in Souss-Massa River Basin. In The Souss-Massa River Basin, Morocco. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Chen, C.T.A. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.M.; Dordević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Predrag, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza River sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibak, M.; Sattari, M.; Agharokh, A.; Tahmasebi, S.; Namin, J.I. Assessing some heavy metals pollutions in sediments of the northern Persian Gulf (Bushehr province). Environ. Health Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 5, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoura, J.; Benaabidate, L.; Benbrahim, K.F. Assessment of water quality of the Inaouène River, Northern Morocco. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2015, 10, 60–66. Available online: http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Afgane, R.; Benjelloun, F.; Lahrach, A.; Daide, F. Comparative study of the physico-chemical and metallic quality of waters and sediments in the Larbaa Basin (Morocco) in the dry and wet period. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abbou, M.; Fadil, F.; El Haji, M. Évaluation de la qualité des cours d’eau de la ville de Taza utilisées dans l’irrigation des cultures maraîchères, Maroc. J. Appl. Biosci. 2014, 77, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duodu, O.G.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, A.G. Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezewudo, B.I.; Mgbenka, B.O.; Islam, M.S.; Proshad, R.; Odo, G.E. Appraisal of metal contamination in sediments of lower reaches of Niger River, Nigeria, using contamination indices and sediment quality guidelines. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 2616–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Chen, H. Border pollution reduction in China: The role of livestock environmental regulations. China Econ. Rev. 2021, 69, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.; Mondol, A.H.; Ali, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Akhtar, S.; Ahmed, A.S.S.; Bhuyan, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Islam, A.R.M.T. Assessment of As, Cr, Cd, and Pb in urban surface water from a subtropical river: Contamination, sources, and human health risk. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 191, 114960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatli, C. Sediment quality of Ergene River basin: Bio-ecological risk assessment of toxic metals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.M.; Stout, S.A.; Gunster, D.G. Ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments: Identifying sources and ecological hazard. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Martens, W.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libiad, M.; Khabbach, A.; Ennabili, A. State of riparian vegetation of streams in the watershed of the Inaouène Wadi (NW Morocco). Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- El Garouani, A.; Tribak, A. Relation entre hydrologie et climat dans le bassin versant de l’Oued Inaouène (pré-Rif marocain). In Climate Variability and Change: Proceedings of the Fifth FRIEND World Conference Held at Havana, Cuba; IAHS Publ.: Havana, Cuba, 2006; p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- ABHS. Actualisation du Plan Directeur d’Aménagement Intégré des Ressources en Eau du Bassin de Sebou. Mission II: Évaluation Quantitative des Ressources en Eau; Agence du Bassin Hydraulique de Sebou: Fes, Morocco, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AFNOR. Qualité des Sols; AFNOR Edition: Paris, France, 1994; 250p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Scott, C.A.; Yan, X. Traffic-related trace elements in soils along six highway segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence factors and spatial variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassin, P.; Baize, D.; Cambier, P.; Sterkman, T. Les éléments traces métalliques et la qualité des sols. Impact à Moyen Et à Long terme. Étude Et Gest. Des Sols 1996, 3, 298–306. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Feng, L. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in urban soil of Weinan industrial areas, Northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoubi, A.; Mejjad, N.; El Khalidi, K.; Bouchkara, M.; Fadili, A.; Chaibi, M.; Zourarah, B. Spatial Distribution and Contamination Level Assessment of Marine Sediment of the Safi Bay (Moroccan Atlantic Coast). Oceans 2023, 4, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, L.; El Okki, M.E.H.; Afri-Mehennaoui, F.Z.; Mehennaoui, S. Utilisation d’indices pour l’évaluation de la qualité des sédiments: Cas du bassin Boumerzoug (Algérie). Eur. Sci. J. 2014, 10, 336–346. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.N.; Yuan, X.Z.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yin, J.; Huang, H.J.; Liu, Z.F.; Jiang, H.W. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie-Boroon, M.H.; Toress, V.; Diaz, S.; Lazzaretto, T.; Tsang, M.; Deheyn, D.D. The geochemistry of heavy metals in the mudflat of Salinas de San Pedro Lagoon, California, USA. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Liu, X.P.; Cheng, H.F.; Zeng, E.Y.; Hu, Y.A. Heavy metal pollution in sediments of a typical mariculture zone in South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Nombela, M.A.; Vilas, F. Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ría de Vigo (NW Spain): An assessment of metal pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Müller, G.; Singh, I.B. Heavy metals in freshly deposited stream sediments of rivers associated with urbanisation of the Ganga Plain, India. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 141, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Jabbari, N. Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of pollution indices for heavy metals in North of Isfahan Province, Iran. J. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinxian, S.; Junfeng, J.; Zhongfang, Y.; Xuyin, Y.; Changping, M.; Ray, F.; Godwin, A. Geochemical behavior assessment and apportionment of heavy metal contaminants in the bottom sediments of lower reach of Changjiang River. Catena 2011, 85, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Hassani, H.; Fard Mousavi, S.B.; Jabbari, N. Evaluation of heavy metals concentration in Jajarm bauxite deposit in northeast of Iran using environmental pollution indices. Malays. J. Geosci. 2019, 3, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Q.; Xu, H.; Huang, S.; Shang, D.; Liu, R. Water quality assessment and source identification of the Shuangji River (China) using multivariate statistical methods. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulsalam, A.; Ramli, M.F.; Jamil, N.R.; Ashaari, Z.H.; Umar, D.A. Hydrochemical characteristics and identification of groundwater pollution sources in tropical savanna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; Abdel-Salam, M.A.; Ahmad, A.F.; Fathy, H.A.; Fadl, M.E.; Scopa, A. Effect of marginal-quality irrigation on accumulation of some heavy metals (Mn, Pb, and Zn) in Typic Torripsamment soils and food crops. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Akram, W.; Rashid, A.; Ullah, Z.; Shah, M.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Kamel, M.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Quality assessment of groundwater based on geochemical modelling and water quality index (WQI). Water 2022, 14, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharmar, E.; Abraham, M.; Prakash, R.; Sundaram, A.; Flores, E.S.; Canales, C.; Alam, M.A. Hydrogeochemistry and water quality assessment in the Thamirabarani River stretch by applying GIS and PCA techniques. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Adopler, A.; Tepkor, H.E.; Opoku, F.A. Comprehensive evaluation of surface water quality and potential health risk assessments of Sisa river, Kumasi. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquière, O.; Walter, J.; Chesnaux, R.; Rouleau, A. Scenarios of groundwater chemical evolution in a region of the Canadian Shield based on multivariate statistical analysis. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 246–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y. Enrichment and Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Mobility in a Coastal Quaternary Groundwater System of the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and Evaluation of Consensus-Based Sediment Quality Guidelines for Freshwater Ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Fontmorin, J.M.; Pham, H.T.; Milner, E.; Abdul, P.M.; Scott, K.; Head, I.; Yu, E.H. Zinc removal and recovery from industrial wastewater with a microbial fuel cell: Experimental investigation and theoretical prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, M.A.; Hasan, M.; Mustafa, G.; Tariq, T.; Ahmed, M.M.; Dehno, R.G.; Ghorbanpour, M. Zinc oxide nano-fertilizer differentially affects the morphological and physiological identity of redox-enzymes and biochemical attributes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheikh, B.B.; Khoukhi, Y.; Arabi, M.; Chafi, A.; Omari, A.; Benyoussef, S. The spatiotemporal variation in lead and zinc contents in the Moulouya River (northeastern Morocco). E3S Web Conf. 2024, 527, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Zain, M.; Shakoor, N.; Muhammad Arslan Ahmad, M.A.; Azeem, I.; Aziz, A.M.; Tulcan, S.X.R.; Rathore, A.; Tahir, M.; Horton, R.; et al. Global navigation of lithium in water bodies and emerging human health crisis. NPJ Clean Water 2023, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, B. Risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment at the drinking water source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, C.M.; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 797S–811S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.S.; Batley, E.G.; Hamilton, L.I.; Spadaro, A.D. Guidelines for copper in sediments with varying properties. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwegbue, M.A.C.; Emakunu, S.O.; Lari, B.; Egobueze, E.F.; Tesi, O.G.; Nwajei, E.G.; Martincigh, S.B. Risk of human exposure to metals in some household hygienic products in Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliopoulos, E.M.; Laskou, M.; Eliopoulos, G.D.; Megremi, I.; Kalatha, S.; Eliopoulos, D.G. Origin of critical metals in Fe–Ni laterites from the Balkan Peninsula: Opportunities and environmental risk. Minerals 2021, 11, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Guan, M.; Shu, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, T.; Jiang, T. Reconstruction of historical lead contamination and sources in Lake Hailing, Eastern China: A Pb isotope study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejón, P. Barium. In Heavy Metals in Soils, 1st ed.; Alloway, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, V.; Vij, S.; Sharma, K.S.; Gupta, N. Correlation of various water quality parameters and water quality index of districts of Uttarakhand. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 9, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończyk, J.; Kluziak, K.; Kołodyńska, D. Adsorption of vanadium (V) ions from aqueous solutions on different biomass-derived biochars. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcil, A.; Swami, K.R.; Gardas, R.L.; Hazrati, E.; Dembele, S. Overview on hydrometallurgical recovery of rare-earth metals from red mud. Minerals 2024, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.S.M.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium contamination and effect on environmental health and its remediation: A sustainable approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium pollution in European water, sources, health risk, and remediation strategies: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shahab, A.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Rad, S.; Jiang, J.; Yu, G.; Jiang, P.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; et al. Spatial and temporal variation of dissolved heavy metals in the Lijiang River, China: Implication of rainstorm on drinking water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68475–68486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J.; Wen, X. Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: Levels, sources, and toxic risks. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Ye, F.; Wei, G.; Li, J.; Deng, L. Source-specific ecological risk assessment and quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Pearl River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motswaiso, F.; Nakamura, K.; Watanabe, N.; Komai, T. Geochemical Investigation of Metals and Trace Elements around the Abandoned Cu-Ni Mine Site in Selibe Phikwe, Botswana. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2019, 7, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, G.; Zeng, J. Geochemical Characteristics of Strontium Isotopes in a Coastal Watershed: Implications for Anthropogenic Influenced Chemical Weathering and Export Flux. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Fu, M.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Fu, G.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y. Spatial Distribution Characteristics, Ecological Risk Assessment, and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s in Surface Sediments of the Nearshore Area of Qionghai. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1491242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Xiongzhi, X.; Keliang, C.; Islam, M.S.; Al-Mamun, M.H. Occurrence, spatial distribution, and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in surface sediments of rivers and coastal areas of the east coast of Bangladesh, north-east Bay of Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.R.; Das, S.; Panda, S. Groundwater quality monitoring by correlation, regression and hierarchical clustering analyses using WQI and PAST tools. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 16, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Gündüz, K.; Sünbül, M.R. Pollution status, potential sources, and health risk assessment of arsenic and trace metals in agricultural soils: A case study in Malatya province, Turkey. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wang, G. Experimental Study on Tailings Deposition Distribution Pattern and Sedimentation Characteristics. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 19428–19439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Enrichment Factor (EF) | Index of Geoaccumulation (Igeo) | Modified Degree of Contamination (mCd) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Pollution Intensity | Value | Pollution Level | Value | Sediment Pollution Intensity |
| EF > 50 | Extremely severe | Igeo ≥ 5 | Very highly polluted | mCd ≥ 32 | Ultra-high contamination |
| 25 ≤ EF ≤ 50 | Very severe | 4 ≤ Igeo < 5 | Highly polluted | 16 < mCd < 32 | Extremely high contamination |
| 10 ≤ EF ≤ 25 | severe | 3 ≤ Igeo < 4 | Moderately to highly polluted | 8 < mCd < 16 | Very high contamination |
| 5 ≤ EF ≤ 10 | Moderately severe | 2 ≤ Igeo < 3 | Moderately polluted | 4 < mCd < 8 | High contamination |
| 3 ≤ EF ≤ 5 | Moderate | 1 ≤ Igeo < 2 | Moderately to unpolluted | 2 < mCd < 4 | Very high contamination |
| 1 ≤ EF ≤ 3 | Minor | 0 ≤ Igeo < 1 | Unpolluted | 1.5 < mCd < 2 | Low contamination |
| EF < 1 | No enrichment | Igeo < 0 | Background concentration | mCd < 1.5 | Null to very low contamination |
| Contamination Factor (CF) | Ecological Risk Factor (Er) | Ecological Risk Index (RI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Pollution Category | Value | Risk Category | Value | Risk Category |
| CF < 1 | Low contamination | Er < 40 | No metal enrichment | RI < 150 | Low risk |
| 1 ≤ CF ≤ 3 | Moderately | 40 ≤ Er < 80 | Moderate contamination | 150 ≤ RI < 300 | Moderate |
| 3 ≤ CF ≤ 6 | Considerable | 80 ≤ Er < 160 | Considerable | 300 ≤ RI < 600 | Considerable |
| CF > 6 | Very high | 160 ≤ Er < 320 | High | RI ≥ 600 | Very high |
| - | - | Er ≥ 320 | Very high | - | - |
| Sediment Pollution Index (SPI) | Pollution Load Index (PLI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Values | Pollution Intensity | Values | Quality |
| 0 ≤ SPI < 2 | Healthy sediment | 0 | No pollution |
| 2 ≤ SPI < 5 | Slightly polluted sediment | 1 | Background pollution |
| 5 ≤ SPI < 10 | Moderately polluted sediment | >1 | Elevated pollution level |
| 10 ≤ SPI < 20 | Highly polluted sediment | - | |
| 20 ≤ SPI | Hazardous sediment | - | |
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Purpose/Use |
|---|---|---|
| Igeo | Geoaccumulation Index | Evaluates the level of heavy metal accumulation compared to natural background values. |
| EF | Enrichment Factor | Identifies the degree of anthropogenic influence on metal concentrations. |
| PLI | Pollution Load Index | Assesses the overall contamination status of a site using multiple metals. |
| PERI | Potential Ecological Risk Index | Estimates the ecological risk posed by heavy metals, considering their toxicity. |
| SPI | Sediment Pollution Index | Integrates metal concentration and toxicity into a composite pollution score. |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis | Identifies relationships between variables and potential sources of metal contamination. |
| HCA | Hierarchical Cluster Analysis | Groups sampling sites based on similarities in their contamination profiles. |
| Zn | Li | Co | Cu | Ni | Pb | V | Ba | Sr | Ce | Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF | |||||||||||
| Min | 1.24 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 1.02 | 2.29 | 1.03 | 0.28 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 1.74 |
| Max | 2.01 | 1.84 | 1.55 | 2.27 | 1.72 | 3.21 | 2.08 | 4.86 | 1.81 | 0.66 | 3.80 |
| Mean | 1.74 | 1.50 | 1.10 | 1.60 | 1.47 | 2.66 | 1.39 | 1.37 | 1.37 | 0.56 | 2.38 |
| SD | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 1.73 | 0.45 | 0.08 | 0.76 |
| EF | |||||||||||
| Min | 6.45 | 5.30 | 3.77 | 5.05 | 5.78 | 11.69 | 4.61 | 1.63 | 3.04 | 2.19 | 6.35 |
| Max | 20.41 | 14.52 | 15.99 | 23.42 | 17.73 | 26.06 | 21.39 | 38.38 | 18.67 | 5.10 | 39.16 |
| Mean | 11.03 | 9.38 | 7.22 | 10.51 | 9.39 | 16.40 | 9.20 | 10.10 | 8.98 | 3.40 | 16.37 |
| SD | 5.15 | 3.94 | 4.50 | 6.79 | 4.69 | 5.62 | 6.19 | 14.36 | 5.75 | 0.95 | 12.13 |
| Igeo | |||||||||||
| Min | −0.27 | −0.58 | −0.87 | −0.78 | −0.55 | 0.61 | −0.54 | −2.41 | −1.51 | −1.79 | 0.22 |
| Max | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.20 | 1.10 | 0.47 | 1.70 | 0.27 | −1.18 | 1.34 |
| Mean | 0.20 | −0.03 | −0.48 | 0.04 | −0.05 | 0.82 | −0.15 | −0.81 | −0.23 | −1.43 | 0.61 |
| SD | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 1.39 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.41 |
| Er | |||||||||||
| Min | 1.240 | - | 4.09 | 4.37 | 5.11 | 11.47 | 2.06 | 0.56 | - | - | 3.49 |
| Max | 2.010 | - | 7.76 | 11.36 | 8.60 | 16.03 | 4.15 | 9.72 | - | - | 7.60 |
| Mean | 1.740 | - | 5.50 | 8.01 | 7.37 | 13.31 | 2.77 | 2.73 | - | - | 4.75 |
| SD | 0.280 | - | 1.27 | 2.38 | 1.39 | 1.60 | 0.73 | 3.47 | - | - | 1.52 |
| mCd | RI | PLI | SPI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 1.13 | 35.96 | 1.26 | 6.17 |
| Max | 1.89 | 56.42 | 1.32 | 21.53 |
| Mean | 1.56 | 46.18 | 1.29 | 11.11 |
| SD | 0.30 | 7.63 | 0.02 | 5.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laaraj, M.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Mesnage, V.; Bensalem, F.; Lahmidi, I.; Mliyeh, M.M.; Fattasse, H.; Arari, K.; Benaabidate, L. Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments in the Inaouène Watershed (Morocco): Indices, Statistical Methods, and Contributions to Sustainable Environmental Management. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104668
Laaraj M, Ait Brahim Y, Mesnage V, Bensalem F, Lahmidi I, Mliyeh MM, Fattasse H, Arari K, Benaabidate L. Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments in the Inaouène Watershed (Morocco): Indices, Statistical Methods, and Contributions to Sustainable Environmental Management. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaaraj, Marouane, Yassine Ait Brahim, Valerie Mesnage, Fadwa Bensalem, Ikram Lahmidi, Mohammed Mouad Mliyeh, Hamid Fattasse, Khalid Arari, and Lahcen Benaabidate. 2025. "Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments in the Inaouène Watershed (Morocco): Indices, Statistical Methods, and Contributions to Sustainable Environmental Management" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104668
APA StyleLaaraj, M., Ait Brahim, Y., Mesnage, V., Bensalem, F., Lahmidi, I., Mliyeh, M. M., Fattasse, H., Arari, K., & Benaabidate, L. (2025). Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments in the Inaouène Watershed (Morocco): Indices, Statistical Methods, and Contributions to Sustainable Environmental Management. Sustainability, 17(10), 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104668








