The Application and Development of Historical Building Information Modeling in Chinese Architectural Heritage: Sustainability Assessment and Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What is the current development status of HBIM in China? What are the technical problems and trends?
- Has the cultural and technological sustainability of HBIM been emphasized and discussed/studied?
- Are there sustainable methods and paths for HBIM to carry out related work?
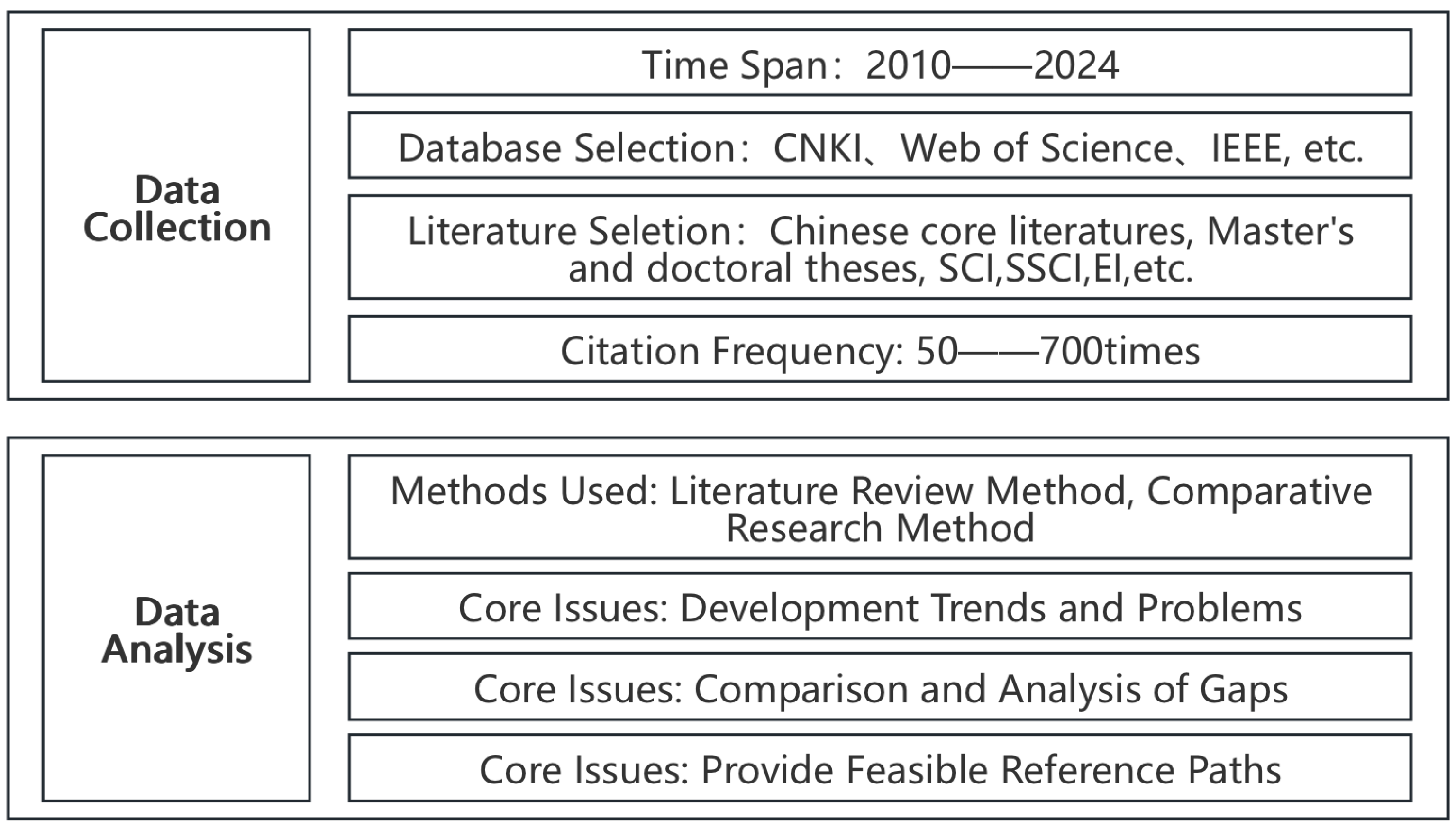
2. Research Methods and Framework
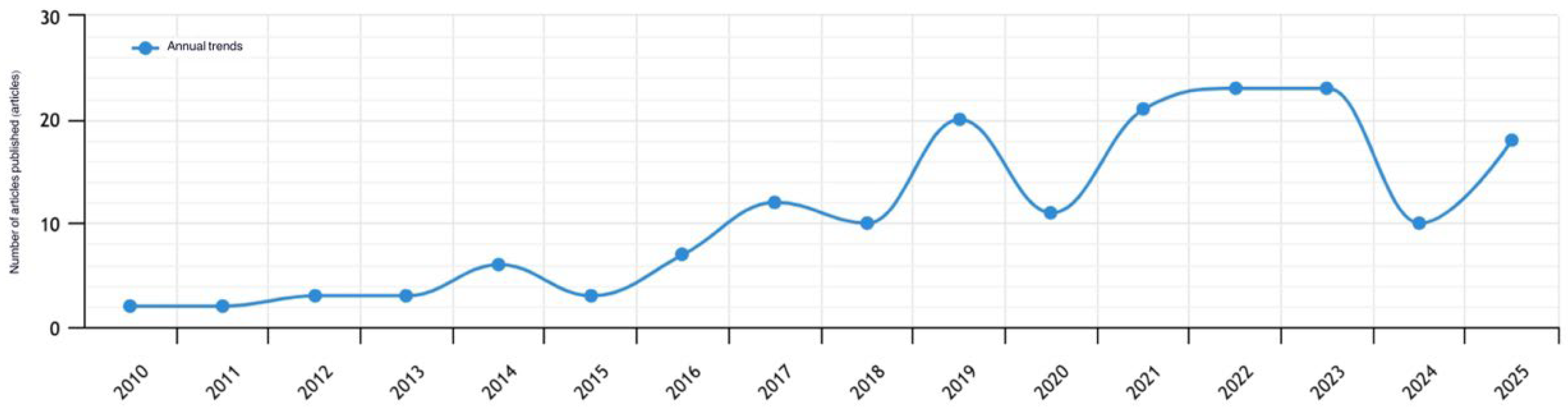
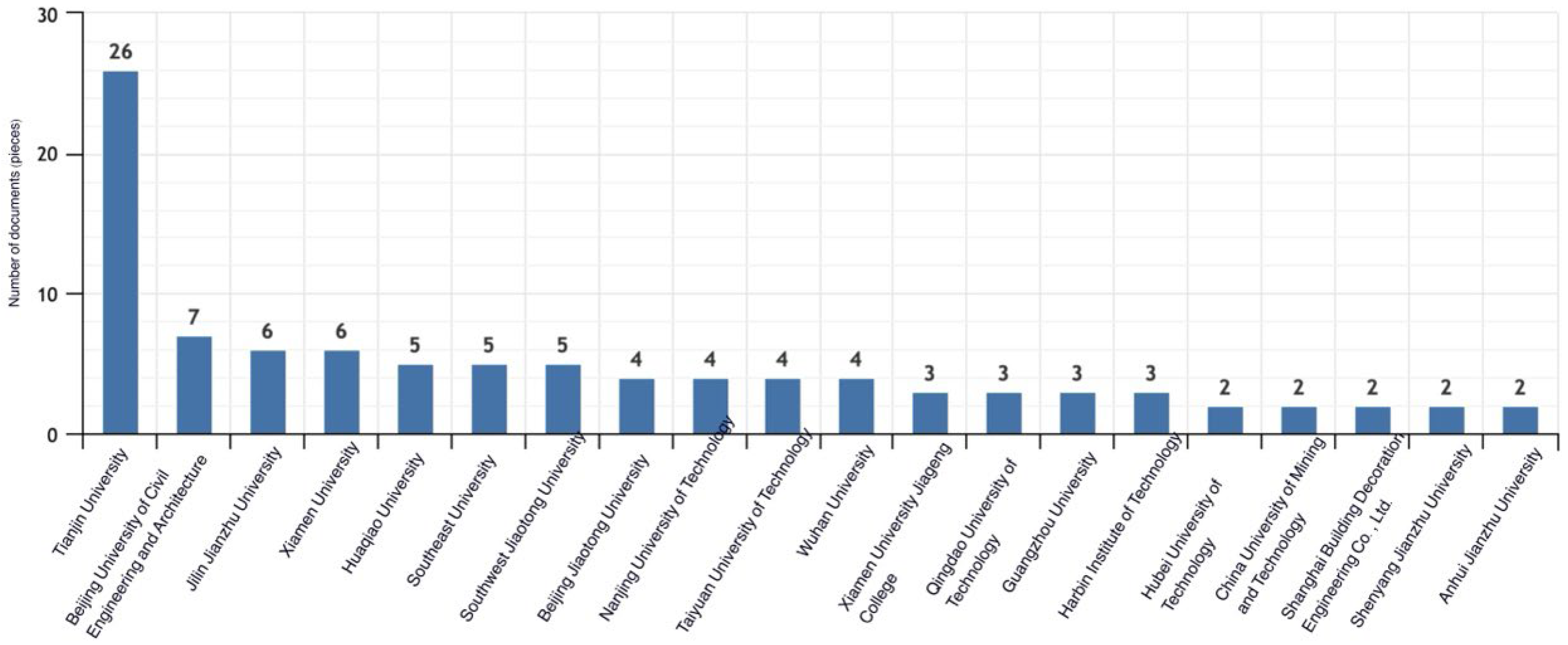
3. An Overview of the Application of HBIM in the Field of Chinese Architectural Heritage
3.1. Building Heritage Information Models and Visualization Display
3.2. Four Major Directions of HBIM Practice and Application
3.2.1. In the Aspect of Automatic Modeling Algorithms and Automated Routes
3.2.2. In the Aspect of Parametric and Procedural Modeling
3.2.3. In the Aspect of Multi-Dimensional Extended Applications
3.2.4. In the Aspect of Construction and Management of Collaborative Platforms
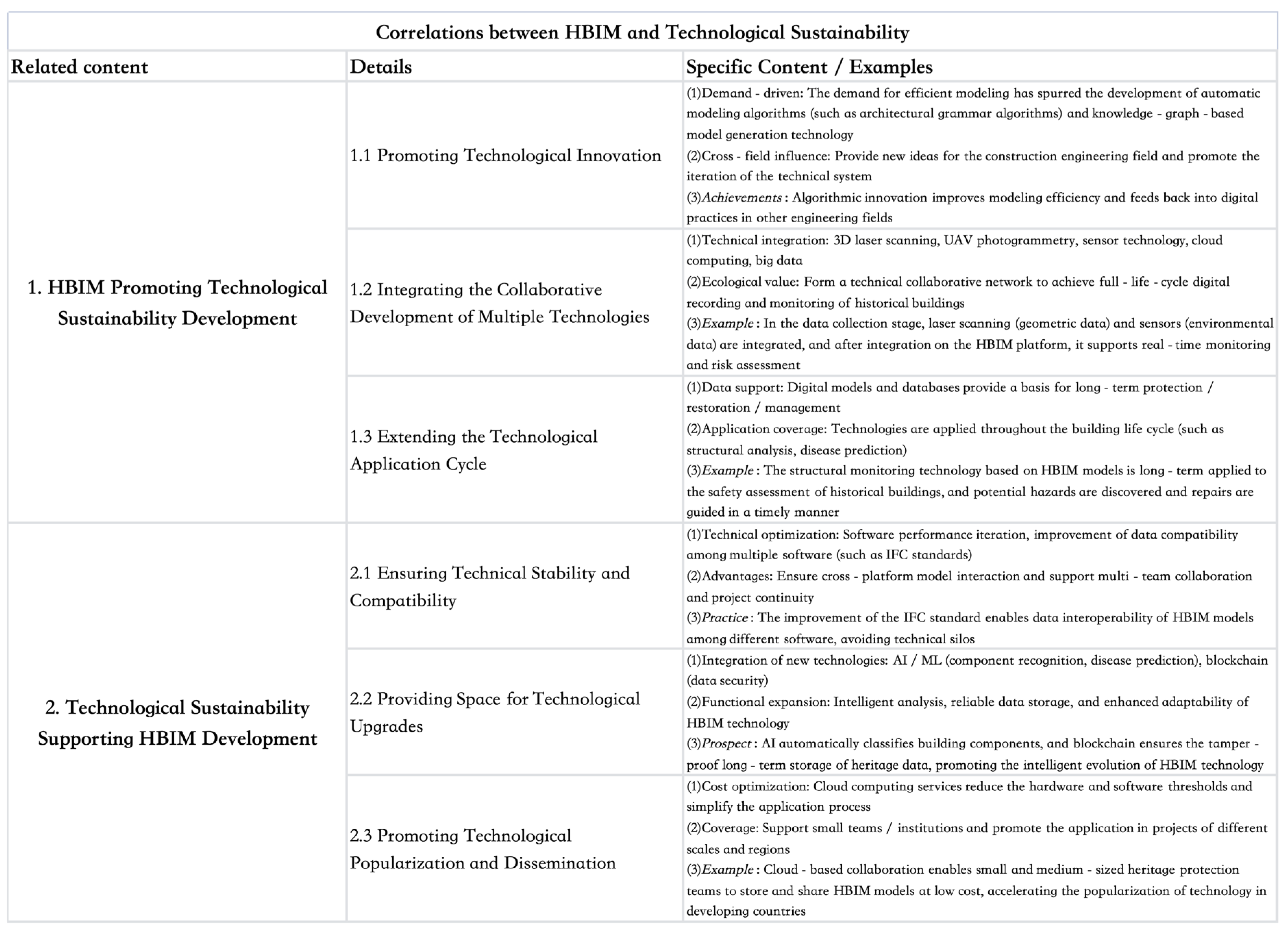
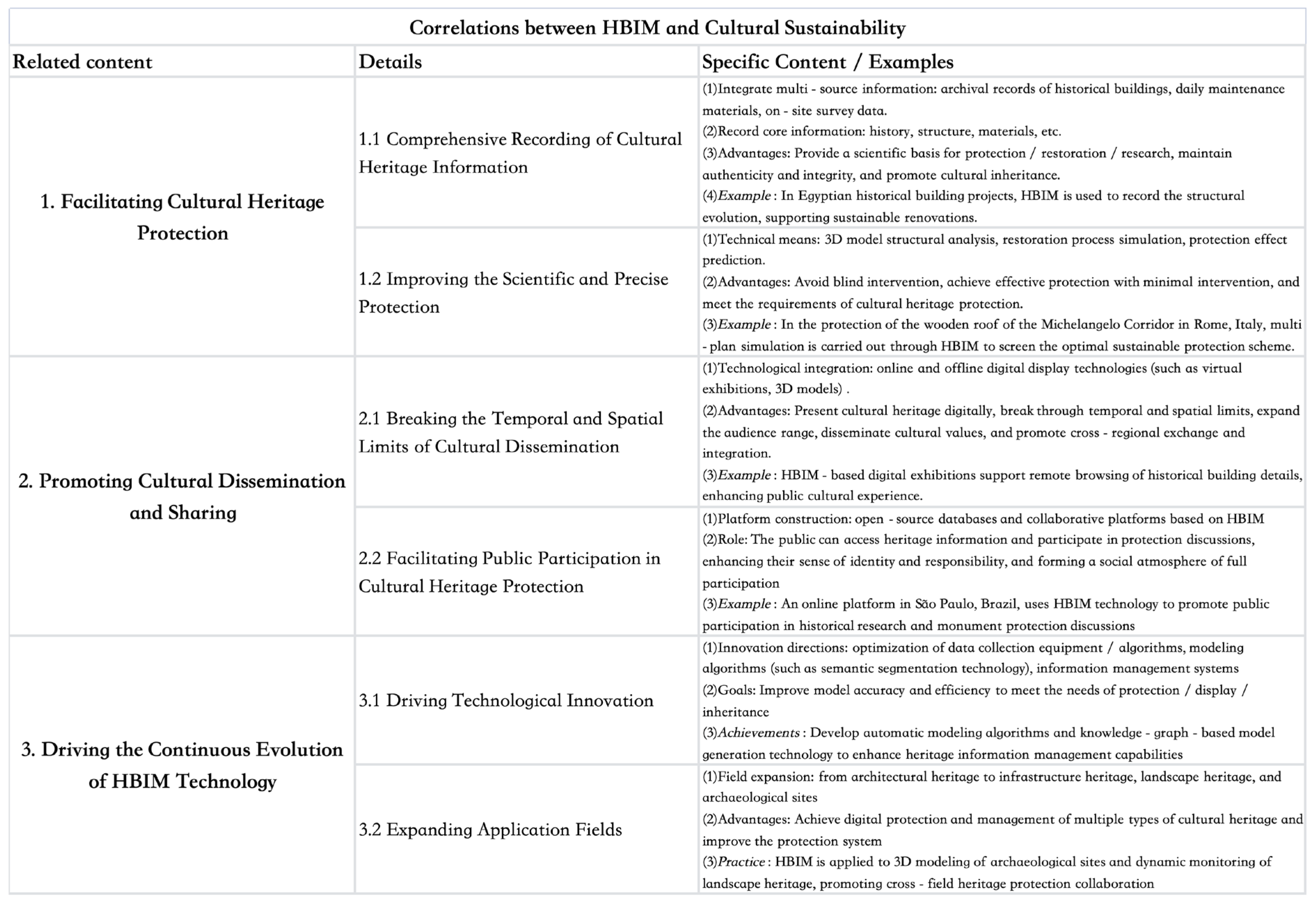
4. Problems of HBIM Technology in China in Terms of “Sustainability”
5. Evaluation and Suggestions on the Sustainability of HBIM Technology in China
- The first stage of the modeling phase. The team conducts model planning, data collection, and geometric measurement work internally. Different groups carry out scanning work on site with the help of point cloud scanning tools, generating formats such as .pts, .ptx, .pod, and .rcs. At the same time, set up the Revit and Dynamo modeling environment (insert the Python module and call the Revit API for programming at any time), and load the Open 3D module on the Python module to automatically filter the collected point cloud data (including open source codes for index filtering, statistical filtering, radius filtering, and voxel filtering), remove outliers, and generate more accurate point cloud data.
- The second stage of the modeling phase. Based on the filtered point cloud data, different groups load the new neural network PointNet++ module on Python (version 3.12.1, PSF, USA) to perform semantic segmentation on the point cloud data and import it into Dynamo. Through different steps such as point cloud display, simplification, slicing, projection, and solid modeling, the corresponding solid model is obtained. At the same time, with the help of the NAS server, exchange the Revit model information files and assemble the model in the “cloud” (premise: the PointNet++ model needs to be trained on the S3DIS dataset or the Shapenet dataset, which involves the spatial point clouds of different types of traditional Chinese architecture).
- The third stage of the modeling phase. Different groups input the sorted data of exploration, archaeology, interviews, monitoring, etc., into different blocks of the BIM model and finally complete the preliminary work of information modeling.
- The application phase: The team leader exports the final HBIM achievement in the IFC format (IFC4.3 add2) through Revit for data exchange. The file can be integrated with cloud-based collaboration platforms such as Autodesk BIM 360, Simplebim, NBS Platform, and BIMCC (China) to achieve the sustainability of HBIM protection, update, and management. The team and groups can continuously update the HBIM data across cycles according to customer needs, further realizing the sustainable management, sustainable interaction, and sustainable expansion of HBIM; they can also use functional analysis equipment to achieve the sustainable monitoring, sustainable display, and sustainable protection of heritage; and they can cooperate with institutions of higher education, use HBIM as an educational resource, open different permissions, and give play to the function of sustainable education.
6. Discussion
6.1. Restatement and Interpretation of Research Results
6.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
6.3. Limitations of the Research
6.4. Research Significance and Application Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. United Nations Conference on Environment and Development. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future [A/42/427]. 1992. Available online: http://www.un-documents.net/wced-ocf.htm (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- United Nations. United Nations General Assembly Resolution. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [A/RES/71/313]. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. The Fourth Session of the 13th National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China. Outline of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China and the Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Chen, W. Shanghai Drift: Roamers and Creators in the Urban Ruins; SDX Joint Publishing Company: Beijing, China, 2024; pp. 120–121. Available online: https://detail.tmall.com/item.htm?abbucket=8&detail_redpacket_pop=true&id=798798847608<k2=1747447938218jeugsjwv29gxpp83kuov0a&ns=1&priceTId=undefined&query=%E4%B8%8A%E6%B5%B7%E6%BC%82%E7%A7%BB%3A%E9%83%BD%E5%B8%82%E5%BA%9F%E5%A2%9F%E4%B8%AD%E7%9A%84%E6%BC%AB%E6%B8%B8%E8%80%85&spm=a21n57.1.hoverItem.1&utparam=%7B%22aplus_abtest%22%3A%22282a2eaedabe52e2b3842c9ebb4cf372%22%7D&xxc=taobaoSearch (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Research Institute of Architectural and Urban Space; Tongji University; Nihon Sekkei Inc. Experiences of Urban Regeneration in Tokyo: Case Studies of Major Urban Redevelopment Projects; Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 2019; Available online: http://book.ucdrs.superlib.net/views/specific/2929/bookDetail.jsp?dxNumber=000018620216&d=C85B48C3607B229D00884AC469EBA9C2&fenlei=1820150303 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Tallon, A. Urban Regeneration in the UK; Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 2017; Available online: http://book.ucdrs.superlib.net/views/specific/2929/bookDetail.jsp?dxNumber=000016527449&d=2136A6B0F34BE87657B51DA5FDCBE89D&fenlei=1820150305 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Chen, X. The Evolution of Architectural Heritage Protection Ideas; Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 2016; Available online: http://book.ucdrs.superlib.net/views/specific/2929/bookDetail.jsp?dxNumber=000016540296&d=72F1FA9A50393CEBE439037467ADC58C&fenlei=18200204 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Lin, Y. Basic Theories of Chinese Architectural Heritage Protection; China Architecture Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012; Available online: http://book.ucdrs.superlib.net/views/specific/2929/bookDetail.jsp?dxNumber=000008340439&d=0BB531423AB498EA9A74B0E9A6D3CD4F&fenlei=18200204 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Wu, C.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Bai, C. From Digitalization to Informatization: A Discussion on the Application of Information Technology in the Field of Architectural Heritage. Chin. Cult. Herit. 2016, 18–24. Available online: https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=668359294&from=Qikan_Search_Index (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Xu, J.; Ma, D.; Scaioni, M. Review of the Frontier Developments of Heritage Building Information Modeling (HBIM) for Foreign Built Heritage. Chin. Cult. Herit. 2024, 5–16. Available online: http://www.silkroads.org.cn/portal.php?mod=view&aid=84036 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Applied Practice of the Protection and Research of Liao Dynasty Brick Pagodas Based on Digital Technology. China Anc. City 2022, 36, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Information Preservation of Jiangnan Gardens Based on HBIM and Knowledge Ontology: A Case Study of Zhanyuan Garden in Nanjing; Nanjing University of Technology: Nanjing, China, 2024; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFDTEMP&filename=1024889989.nh (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Han, S.; Wu, C.; Li, D. Expression of Survey Information Results of Architectural Heritage Based on HBIM: A Case Study of the Survey Projects of Three Guardhouses in the Research–oriented Protection Project of Yangxin Hall in the Forbidden City. Tradit. Chin. Archit. Gard. 2022, 52–57. Available online: http://gjyl.ijournals.cn/gjyl/article/abstract/202216312?st=article_issue (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Han, S. Information Management and Expression of Survey and Design Based on HBIM: A Case Study of the Survey and Design of the Guardhouses Outside Yangxinmen in the Forbidden City; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Tian, X. Exploration of the Construction of an Information Database for Architectural Heritage Based on HBIM: A Case Study of the Xiangdian Hall in Qufu. Hous. Real Estate 2023, 74–76. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=vG2M3utQQCd0-ccYGVD7Ho5dDrWBvaHAM3HM_wGL75AoXaN7AxJVFzJtKs-qy-6yaro0K3ptIlw0OY7EUHoFSDsNGl7lTDzK8GJ36b99N3tN11ZoPB_tW2dNsU_w_puhg3SXU5hCipfNkWg59hRy8cClW_p2Oxk_mD-65y-KdYy58FPmtjPNtA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Guangshu, E. Research on HBIM Under the Concept of Preventive Conservation: A Case Study of the Architectural Heritage in Taipingjiao, Qingdao; Shandong Jianzhu University: Jinan, China, 2024; Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/Y4118605 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Fei, Y.; Zhuo, L. Research on the Informatization Display of Stone-structured Industrial Architectural Heritage in Southern Fujian: A Case Study of the Anxi Tea Factory in Quanzhou. Chin. Overseas Archit. 2024, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuo, L.; Fei, Y. Construction of Information Models for Modern Regional Historical Buildings in Southern Fujian: A Case Study of the Juren Di in Haicang, Xiamen. Ind. Constr. 2024, 54, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuo, L.; Fei, Y. Construction of the HBIM Information Management Model for Modern Regional Buildings in Southern Fujian: A Case Study of the Juren Di in Haicang, Xiamen. Industrial Construction. 2023. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=GYJZ20231012001 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Niu, P.; Tian, J. Exploration of the Application of 3D Laser Scanning and HBIM Technology in the Digital Archiving of Historical Buildings. Arch. Manag. 2022, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Research on Typical Diseases of Wooden Structures in Southern Hunan and Their Prevention and Control Strategies; Hunan University: Changsha, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Research on the Application of BIM Technology in the Protection and Renovation of Modern Historical and Cultural Buildings: A Case Study of the Former Residence of Duan Qirui in Tianjin; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.M.; Cao, Y.K.; Pan, W.Z. Application of HBIM in the Management of Survey Data of Architectural Heritage: A Case Study of the Shikumen Buildings in Zhangyuan, Shanghai. Archit. Cult. 2021, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Bai, M.; Wang, Q.; Feng, D. Research on the Data Standards and Family Construction Paths of Heritage Buildings Based on BIM. China Constr. Met. Struct. 2023, 22, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wang, C.E.; Li, J.F.; Hu, C.J. Research on the Digital Information of Architectural Heritage Based on BIM Technology: A Case Study of the Renovation of the Beamless Hall in Yongzuo Temple. Urban. Archit. 2023, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.R. Research on the Integrated Design of Digital Protection of Architectural Heritage; Guangzhou University: Guangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.H. Construction of an Ontology of Ancient Architecture Knowledge by Integrating HBIM and Humanistic Knowledge. Libr. Trib. 2024, 44, 90–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.Q. BIM Modeling and Application for the Timber Frame Units of Ancient Buildings: A Case Study of Traditional Buildings in the Hexi Corridor During the Ming and Qing Dynasties; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.L.; Li, Z.L.; Cheng, Z. Application of BIM Technology in the Whole Process of Ancient Building Restoration. Archit. Cult. 2024, 222–224. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=vG2M3utQQCdlpZRww4G9b58Cj6txZPUnBSzaypS-PzkhaULrht-Npy8ng0q7e8ORrGkygVi1zJrjxCeAa_gYK6Sz1ye5KAs38Y-xRI8usANBlJCgaoSxty0je4t5TPWDz3akrGZcbiGAhbdn-GFo3TTODgwzWWmPvkgn8ZF5BiU2D30tmWuAuQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Wang, L.C. Exploration of the Application of HBIM Technology in the Relocated Construction of Huizhou Traditional Dwellings: A Case Study of Guangqi Hall; Anhui Jianzhu University: Hefei, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, J.Z.; Ni, W.Q. Research on the Application of HBIM in Lifeng Architecture: A Case Study of the Design of the Door and Window Family Library for Building D-1 in Xian’anfang. In Proceedings of the 2020 National Academic Symposium on the Teaching and Research of Architectural Digital Technology in Architecture Departments, Changsha, China; 2020; pp. 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N. Research on the Strategies of Digital Protection and Reuse of Industrial Heritage Combined with BIM Technology; Qingdao University of Technology: Qingdao, China, 2013; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201402&filename=1013242438.nh (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Zhu, L. Practical Analysis of the Construction of Information Models (BIM) for Early Ancient Chinese Timber–Framed Buildings; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2013; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201301&filename=1013005171.nh (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Shi, Y. Application of BIM in Information Collection and Management of Industrial Heritage; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201701&filename=1016191849.nh (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Shi, R.M.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.Y.; Wei, Z.F. Research on the Establishment of an Information Model for the Ancient Buildings in Courtyard 36, Fuxue Hutong. J. Beijing Univ. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2014, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J. Information Collection and Expression of Architectural Heritage Based on BIM Technology Under the Background of Informatized Surveying and Mapping; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201701&filename=1016191974.nh (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Li, L.J. A Preliminary Exploration of the Informatization Development of the Expression of Architectural Heritage Surveying and Mapping Results [D/OL]; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2012; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD2012&filename=1012022337.nh (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Du, X. Surveying and Mapping of Industrial Architectural Heritage Based on BIM; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2015; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201501&filename=1015018386.nh (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Zhou, C.C.Q. Cloud Computing and Analysis of Architectural Heritage Sites; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2018; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201802&filename=1018013883.nh (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Xing, L. Research on the Application of BIM Technology in the Protection of Historical Buildings: A Case Study of the Protection of the Teaching Building of Changchun Institute of Geology; Jilin Jianzhu University: Changchun, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201702&filename=1017171846.nh (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Tong, Q.H.; Xu, P. Protection of Historical Buildings Based on BIM: A Case Study of Songqing Gymnasium of Wuhan University. Huazhong Archit. 2022, 40, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.H.; Yang, F.; Liu, T.H. Application of BIM Technology in the Protection of Historical Buildings: A Case Study of the Central China Hydraulic Laboratory of Wuhan University [J/OL]. Huazhong Archit. 2021, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.H.; Wei, W. Digital Protection Models for Architectural Heritage in Macau. New Archit. 2016, 39–43. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/xjz201606008 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Liu, Y.X. Research on the Application of Basic Information Models of Ancient Buildings in Protection Projects; Lanzhou Jiaotong University: Lanzhou, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201701&filename=1016279153.nh (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Guan, X. Application of BIM Technology in the Protection of Lingling Ancient City. Shanxi Archit. 2017, 43, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L. Research on the Implementation Technology of an Information Management Platform for Timber–Framed Architectural Heritage Based on BIM; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201701&filename=1016115842.nh (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Wang, Z.X. Research on the Information Protection Method of Tianjin’s Historic and Cultural Buildings Based on BIM Technology; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2019; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201901&filename=1019703731.nh (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Shi, L.W. Research on the Construction of Multilevel BIM Models for Typical Components of Song–Style Dougong Based on Point Clouds; Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Beijing, China, 2019; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201902&filename=1019095282.nh (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Meng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Exploration of the Digital Protection of Architectural and Cultural Heritage Based on the BIM+ Concept. Geospat. Inf. 2019, 17, 20–23, 26. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/343510324.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Xun, H.W. Research on the Protection and Optimization Strategies for the Existing Buildings in the East Campus of Hebei University of Technology Based on BIM; Hebei University of Technology: Tianjin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.K. Research on the Digital Information Recording, Display, and Protection of Industrial Architectural Heritage Based on Revit; Shandong University of Science and Technology: Qingdao, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y. Research on the 3D Visualization of Industrial Heritage Information Recording: A Case Study of the Shaanxi Laogangchang Building Complex; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zou, Y.Q. Research on the Protection and Regeneration of Modern Educational Buildings in Wuhan Based on BIM Technology. Archit. Cult. 2021, 196–197. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/jzywh202107074 (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Du, S.H. Research on the Protection of Traditional Dwellings Based on BIM Technology: A Case Study of the Western Six Courtyards on Shunhe North Street in Daokou Ancient Town; Zhengzhou University: Zhengzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ji, H. Protection of Heritage Buildings under Information Technology: A Case Study of Yangxizhai in Shenyang Imperial Palace. J. Shenyang Jianzhu Univ. 2022, 24, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y. Research on the Architectural Form and Protection Technology of the Dabei Hall in Chongshan Temple, Taiyuan; Taiyuan University of Technology: Taiyuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z. Research on the Protection and Renewal Design of the Gongzhuling Station Area of the Chinese Eastern Railway Based on Digital Technology; Jilin Jianzhu University: Changchun, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.H. Research on the Construction of Digital Archives of Ancient Bridges in Yunnan Based on BIM + 3D Laser Scanning Technology; Yunnan University: Kunming, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, S.F. Application of BIM Technology in the Information Expression of Architectural Heritage: A Case Study of the Damage Expression and Record of Wuying Hall; Hebei University of Engineering: Handan, China, 2017; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201702&filename=1017166436.nh (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Tao, Y. Construction of Information Models for Garden Heritage Based on Point Cloud Technology: A Case Study of the Digital Practice of Yipu Garden; Soochow University: Suzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Xu, P.C.; Zhang, D.B. Research on the BIM Automatic Modeling Algorithm for Historical Buildings Based on Dense 3D Point Clouds. Build. Technol. 2023, 54, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, P.P. Research on the Reconstruction of Roof Decoration Components of Ming and Qing Official-Style Buildings Based on the Template Library; Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.T. Knowledge Graph Assisted Automatic Construction of Historical Building Information Models. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2024, 49, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y. Procedural modeling of historic buildings’ timber frames for HBIM based on carpenters’ architectural rules. Autom. Constr. 2024, 168, 105862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Zhao, C.; Nie, F.D. Parametric and Computational HBIM Modeling Methods for the Timber Frames of Traditional Dwellings in Southern Fujian. J. Fuzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 52, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Que, R. Regularized rebuild workflow of hbim for built heritage documentation. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, VIII-M-1-2021, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Bai, C. Generating the regular axis from irregular column grids through genetic algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, Y.; Tian, M. The Synergy of Metadata and Metamodel through Algorithm Modeling—Case Study of the Roof Tiles in Yangxindian Palace (Beijing, China). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.Y. Research on the Application of BIM Technology in the Field of Modern Architectural Heritage; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Guo, Z.; Shi, J.; Bai, Z.H. Research on the Renovation of Industrial Heritage Based on the “BIM + VR” Technology: A Case Study of the Renovation Project of the Traditional Architecture Museum of Inner Mongolia University of Technology. Urban. Archit. 2023, 20, 174–178+186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.J.; Xu, B.C. Research on the Application of HBIM-MR Technology in the Evaluation and Management of Architectural Heritage from the Perspective of Ontology. Constr. Econ. 2021, 42, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.J.; Yuan, H.B. Visualization Research of HBIM Technology in Architectural Heritage Data under the “Internet +” Background: A Case Study of Huangxi Academy. J. Chang. Univ. 2021, 31, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.H.; Huang, J.X. A Preliminary Study on the Information Management of Architectural Heritage Based on BIM Technology: A Case Study of the Bagua Building on Gulangyu Island. Urban. Archit. 2020, 17, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.C. Research on the Timber Structure of Chinese Traditional Architecture Based on Parametric Modeling: A Case Study of the Corners of Song Dynasty Official-Style Architecture; Southeast University: Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Y. Application Strategies of the HBIM Concept in Architectural Heritage Conservation Projects under the Background of Multi-team Collaboration: A Case Study of the Bagua Building on Gulangyu Island. J. Eng. Manag. 2023, 37, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Research on the Construction of HBIM System for Ancient Building Structures; Beijing Jiaotong University: Beijing, China, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M. Research on the Monitoring System of Deshengmen Arrow Tower Based on the Theory of Preventive Conservation; Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cong, W.U. ‘Sustainable’ Recording and Preservation of Zangniang Stupa and Sangzhou Lamasery in Qinghai, China with Heritage Building Information Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 51301-2018; Building Information Modeling Design Delivery, 1st Edition. China Institute of Building Standard Design and Research Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 4.
- Centre for Digital Built Britain. A Report for the Government Construction Client Group- Building Information Modelling (BIM) Working Party Strategy Paper. 2011. Available online: https://www.thenbs.com/PublicationIndex/documents/details?Pub=BIS&DocId=299921 (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Moyano, J.; Musicco, A.; Nieto-Julián, J.E.; Domínguez-Morales, J.P. Geometric characterization and segmentation of historic buildings using classification algorithms and convolutional networks in HBIM. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, J.; Justo-Estebaranz, Á.; Nieto-Julián, J.E.; Ojeda Barrera, A.; Fernández-Alconchel, M. Evaluation of records using terrestrial laser scanner in architectural heritage for information modeling in HBIM construction: The case study of the La Anunciación church (Seville). J. Build. Eng. 2022, 62, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagati, C.; Papacharalambous, D.; Sanfilippo, G.; Bakirtzis, N.; Laurini, C.; Hermon, S. HBIM approach for the knowledge and documentation of the st. John the theologian cathedral in nicosia (cyprus). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 36, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, W.; El Antably, A. Knowledge-based HBIM for conservation: The case of yahya al-Shabih mausoleum. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2023, 30, e00278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrigila, C.; Giannetti, I.; Eramo, E.; Gabrielli, R.; Caruso, G. HBIM for conservation and valorization of structural heritage: The stylite tower at umm ar-Rasas, jordan. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 70, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelaru, B.; Onuțu, C.; Ungureanu, G.; Şerbanoiu, A.A. Integration of point cloud, historical records, and condition assessment data in HBIM. Autom. Constr. 2024, 161, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.; Cabaleiro, M.; Sousa, H.S.; Branco, J.M. HBIM for storing life-cycle data regarding decay and damage in existing timber structures. Autom. Constr. 2020, 117, 103262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Ashraf, F. HBIM platform & smart sensing as a tool for monitoring and visualizing energy performance of heritage buildings. Dev. Built Environ. 2021, 8, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskil-Leitan, R.; Reychav, I. A sustainable sociocultural combination of building information modeling with integrated project delivery in a social network perspective. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, B.F.; Sassi Boudemagh, S.; Kitouni, I.; Kamari, A. IPD and BIM-focussed methodology in renovation of heritage buildings. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2021, 40, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.Y.; Wang, X. The outlook of building information modeling for sustainable development. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Chang, L. Research on the Application System Integration of BIM Models for Chinese Timber-framed Architectural Heritage. Huazhong Archit. 2017, 35, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Driving Sustainable Cultural Heritage Tourism in China through Heritage Building Information Modeling. Buildings 2024, 14, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwijendra, N.K.A.; Winastri, K.D.A.K.; Krishna, K.D.N.M.B. Integration of Building Information Modelling (BIM) for Cultural Preservation in Infrastructure Development in Bali, Indonesia. In Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024; Volume 1416, p. 012040. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/1416/1/012040 (accessed on 5 May 2025).

| Building Information Modeling Design Delivery Standard | ||
|---|---|---|
| Grade | Code | Requirements |
| Level 1.0 model refinement | LOD1.0 | Project-level model unit (carrying project, sub-project, or local building information) |
| Level 2.0 model refinement | LOD2.0 | Function-level model unit (carrying module or space information of complete functions) |
| Level 3.0 model refinement | LOD3.0 | Component-level model unit (carrying single component or product information) |
| Level 4.0 model refinement | LOD4.0 | Part-level model unit (carries part information belonging to the assembly) |
| Level 1 geometric expression accuracy | G1 | Geometric expression accuracy that meets the needs of two-dimensional or symbolic recognition |
| Level 2 geometric expression accuracy | G2 | Geometric expression accuracy that meets the needs of rough recognition, such as space occupancy and main colors |
| Level 3 geometric expression accuracy | G3 | Geometric expression accuracy that meets the needs of fine recognition, such as construction and installation processes, procurement, etc. |
| Level 4 geometric expression accuracy | G4 | Geometric expression accuracy that meets the needs of high-precision recognition, such as high-precision rendering display, product management, manufacturing, and processing preparation |
| Level 1 information depth | N1 | It is advisable to include the model unit’s identity description, project information, organizational role, and other information |
| Level 2 information depth | N2 | It is advisable to include and supplement N1-level information; add entity system relationship, composition, and material performance; or attribute information |
| HBIM Modeling Software Classification | ||
|---|---|---|
| BIM Platform Name | Main Functions | Remark |
| Autodesk Revit Architecture (version 2025, Autodesk, Inc.) | Architectural modeling and parametric design | Dynamo (suitable for NAS file exchange) |
| Autodesk Revit Structure (version 2025, Autodesk, Inc.) | Structural modeling and parametric design | Dynamo (suitable for NAS file exchange) |
| Bentley Architecture (version 08.11.07.87, Bentley Systems, Inc.) | BIM modeling | (Suitable for NAS file exchange) |
| AccaSoftware Edificius (version 11.0.4, ACCA Software) | CADBuilding information modeling design and 3D CAD | Professionally developed software (suitable for NAS file exchange) |
| Vico Office (version 3.0, Vico Software) | Five-dimensional conceptual modeling | |
| Trelligence Affinity (version 9.0, Trelligence, Inc.) | Concept design modeling | Early design stage |
| Graphisoft ArchiCAD (version 27 build 3001, Graphisoft) | Architectural Concept Modeling | (Suitable for NAS file exchange) |
| Tekla Structures (version 2024 SP7, Tekla) | Architectural Concept Modeling | |
| Nemetschek Vectorworks Designer (version 2025, Vectorworks, Inc.) | Architectural Concept Modeling | |
| HBIM Functional Analysis Software | ||
|---|---|---|
| BIM Platform Name | Main Functions | Remark |
| Autodesk Robot (version 2025, Autodesk, USA) | Building structure analysis | Bidirectional link to Autodesk Revit Structure |
| Autodesk Ecotect (version 2011, Autodesk, USA) | Building energy analysis | Weather, energy, water, carbon emissions analysis |
| Autodesk Green Building Studio (Cloud platform, Autodesk, USA) | Building energy analysis | Measure energy use and carbon footprint |
| Bentley Systems Structural Analysis Design Detailing, Building Performance (version 08.11.07.87, Bentley Systems, Inc.) | Structural analysis, detailing, earthwork calculations, building performance | Measure, evaluate, and report building performance |
| Beck Technology DProfiler (version DProfiler11, Beck Technology, USA) | Cost estimate | With real-time cost-estimation function |
| Vico Office (version 5.5, Vico Software, USA) | Cost and schedule estimates | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Wu, C.; Tan, L.; Wan, D.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z. The Application and Development of Historical Building Information Modeling in Chinese Architectural Heritage: Sustainability Assessment and Prospects. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104667
Xu C, Wu C, Tan L, Wan D, Liu H, Chen Z. The Application and Development of Historical Building Information Modeling in Chinese Architectural Heritage: Sustainability Assessment and Prospects. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104667
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chaoran, Cong Wu, Lifeng Tan, Da Wan, Hanfang Liu, and Zequn Chen. 2025. "The Application and Development of Historical Building Information Modeling in Chinese Architectural Heritage: Sustainability Assessment and Prospects" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104667
APA StyleXu, C., Wu, C., Tan, L., Wan, D., Liu, H., & Chen, Z. (2025). The Application and Development of Historical Building Information Modeling in Chinese Architectural Heritage: Sustainability Assessment and Prospects. Sustainability, 17(10), 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104667








