Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Integrating Karst Seepage Field Characteristics with Water Inrush Prediction Models of the Qigan Mountain Tunnel
Abstract
1. Introduction
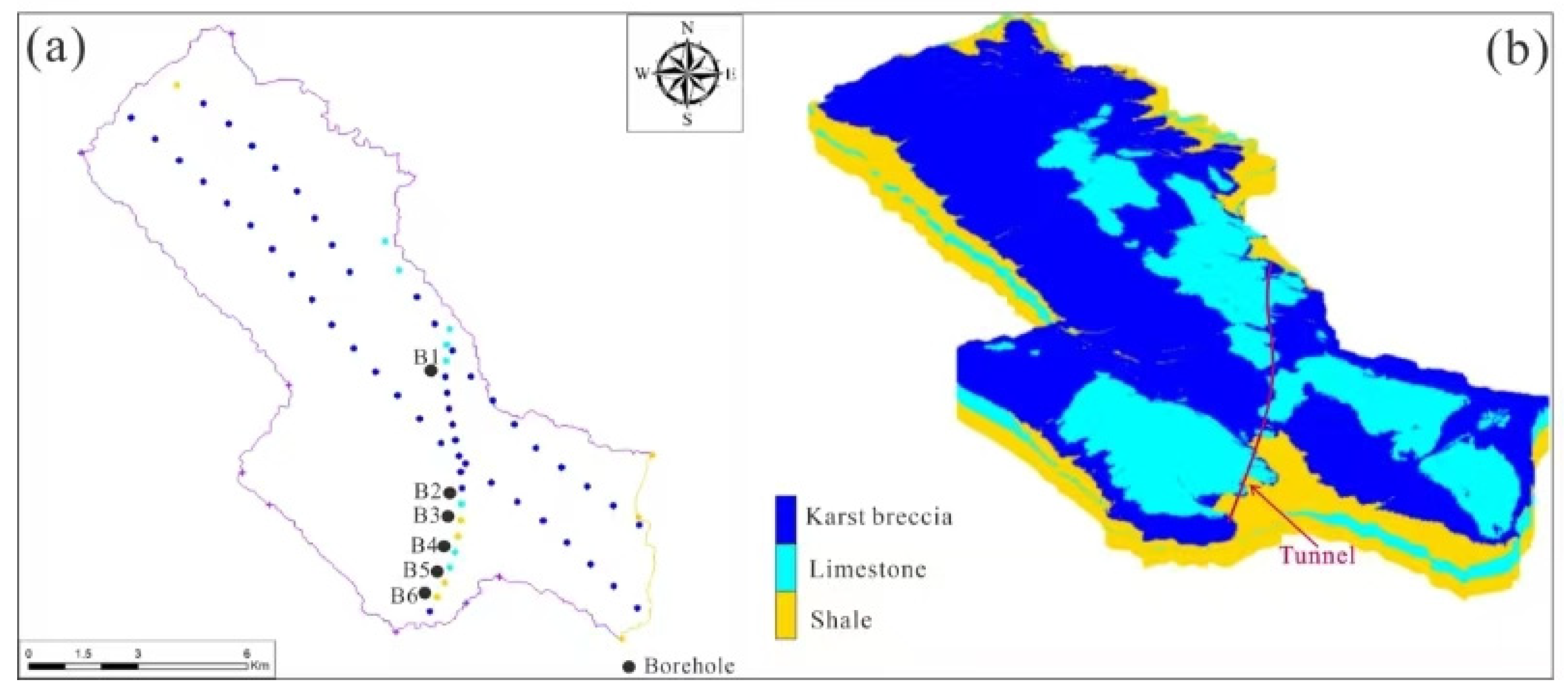
2. Geological Settings
3. Methodology
3.1. Water Chemistry Analysis in the Study Area
3.2. Establishment of Numerical Models
3.2.1. Mathematical Modeling of Groundwater
3.2.2. Model Scope and Boundary Condition Generalization
3.2.3. Construction of the Geological Model
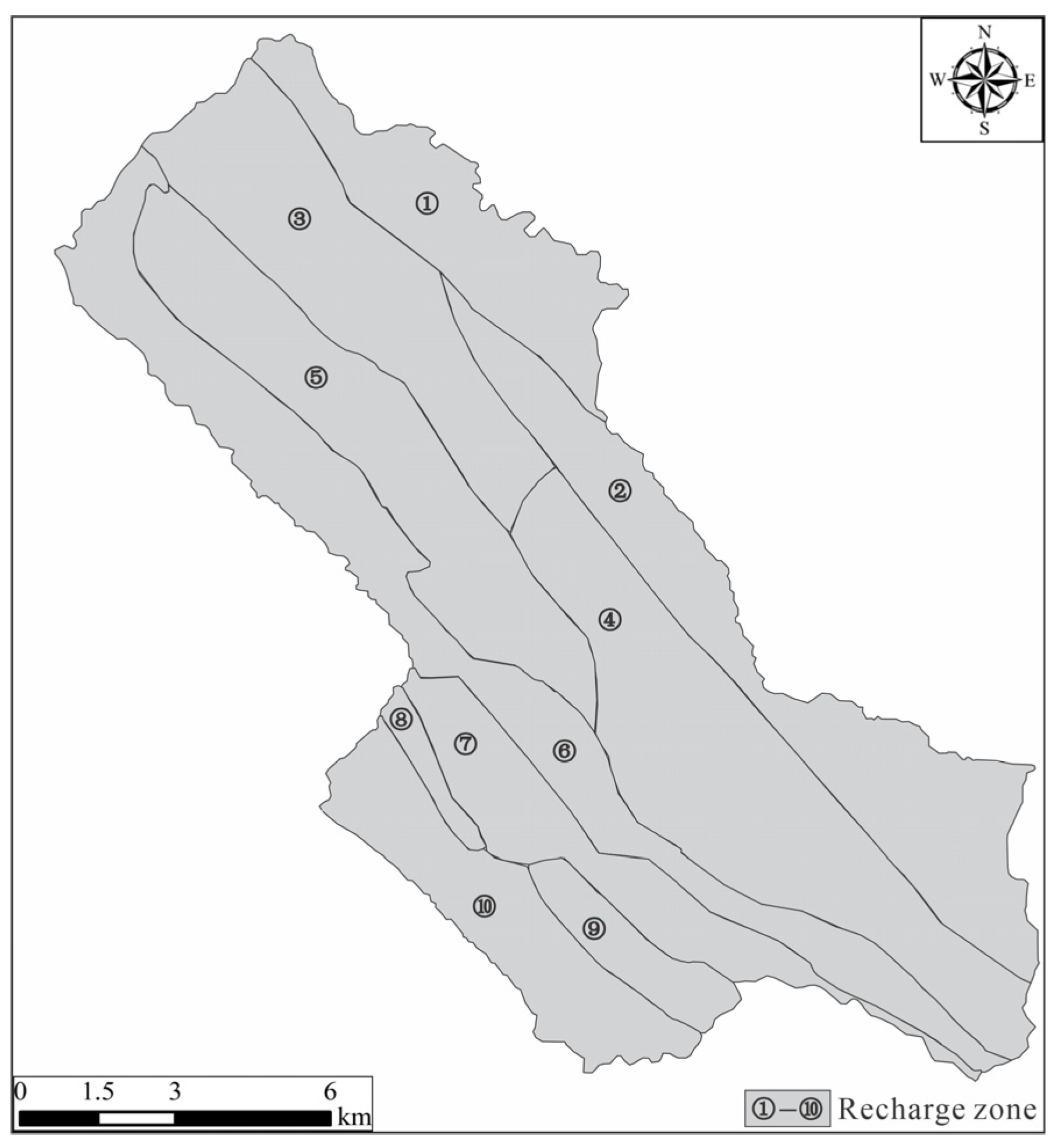
3.2.4. Rainfall Recharge Zone
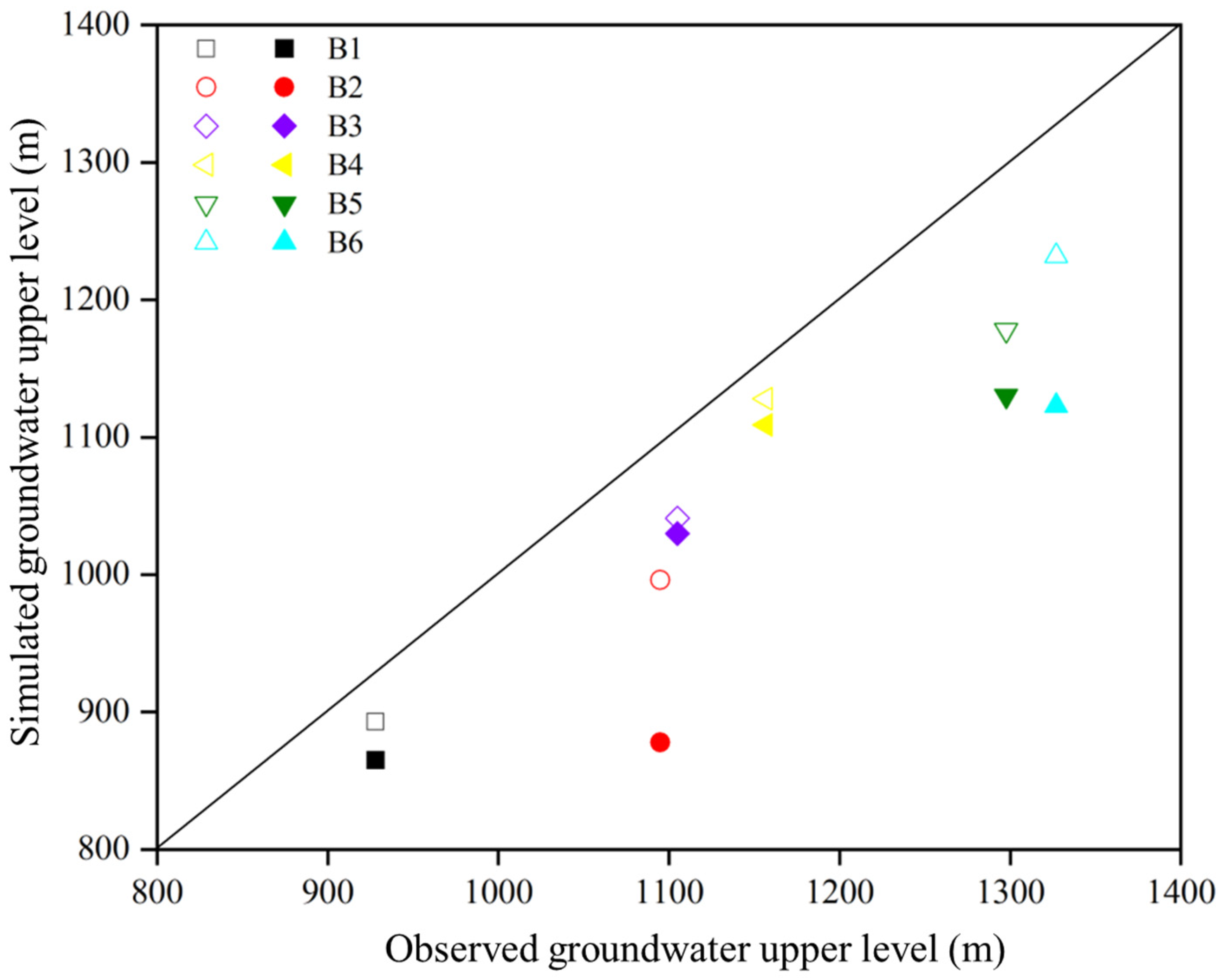
3.2.5. Observation Borehole Water Level Fitting
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Identification of Water Inrush Sources
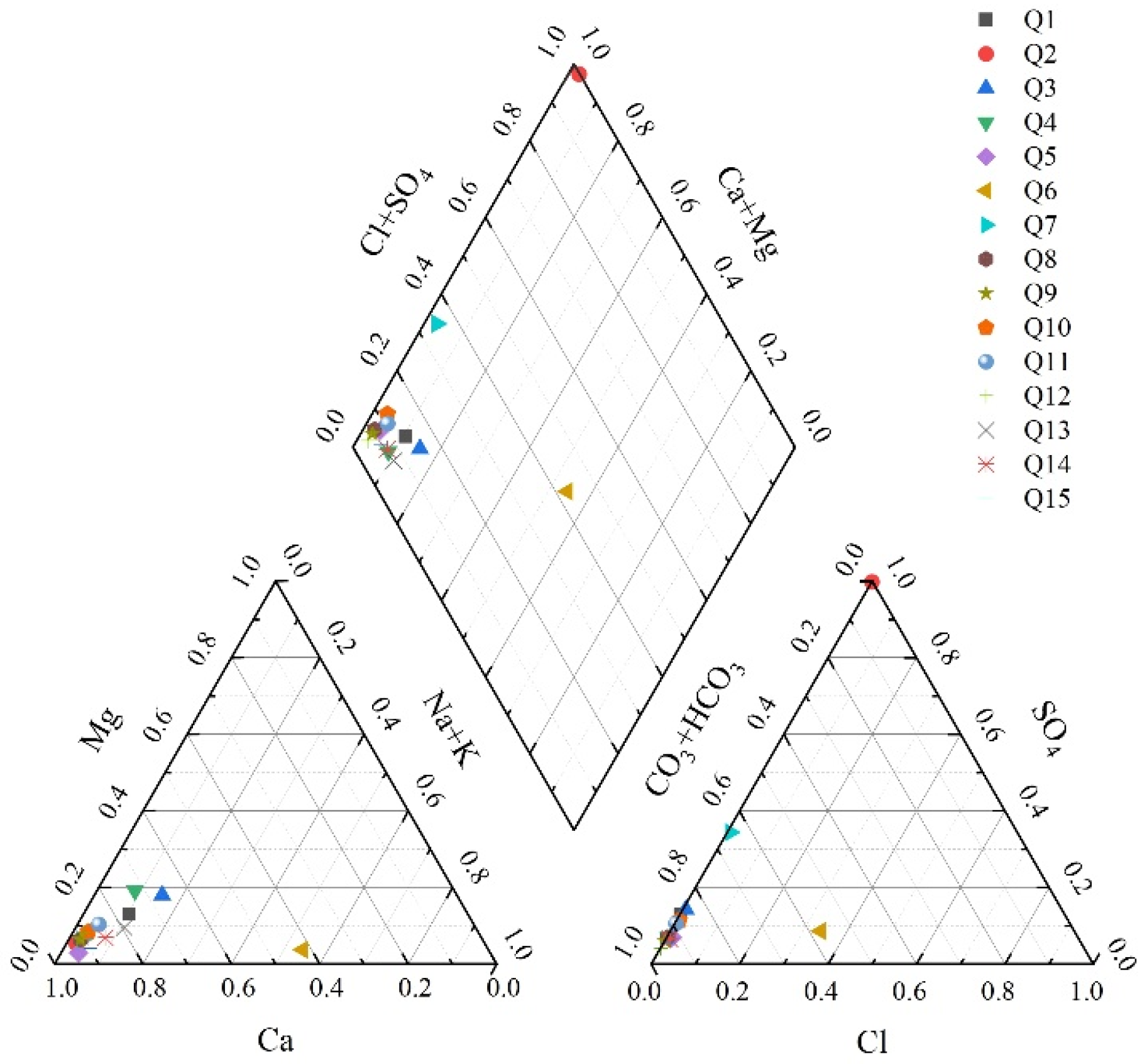
4.1.1. Water Chemistry Types and Distribution Patterns
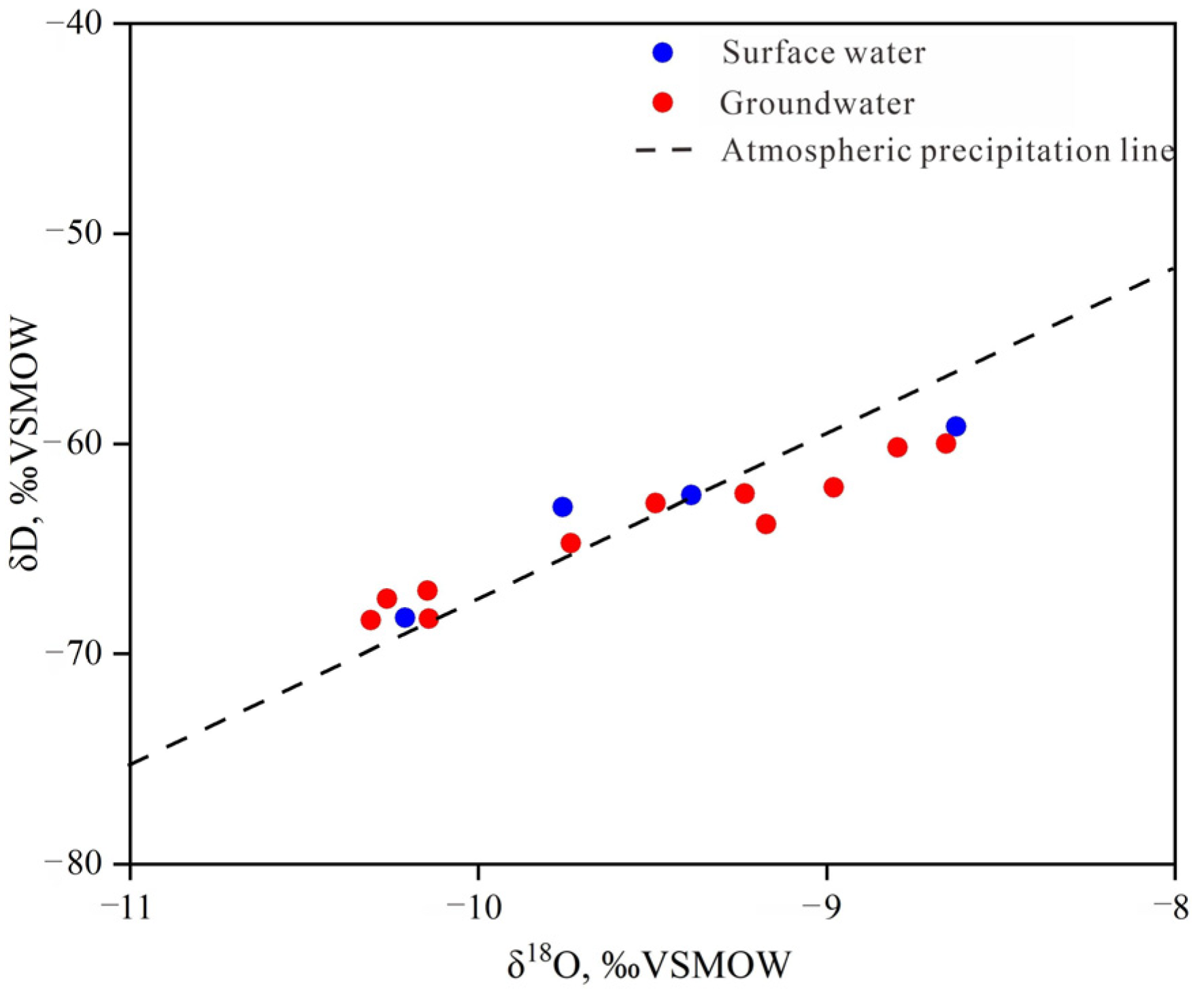
4.1.2. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics
4.2. Numerical Simulation Results
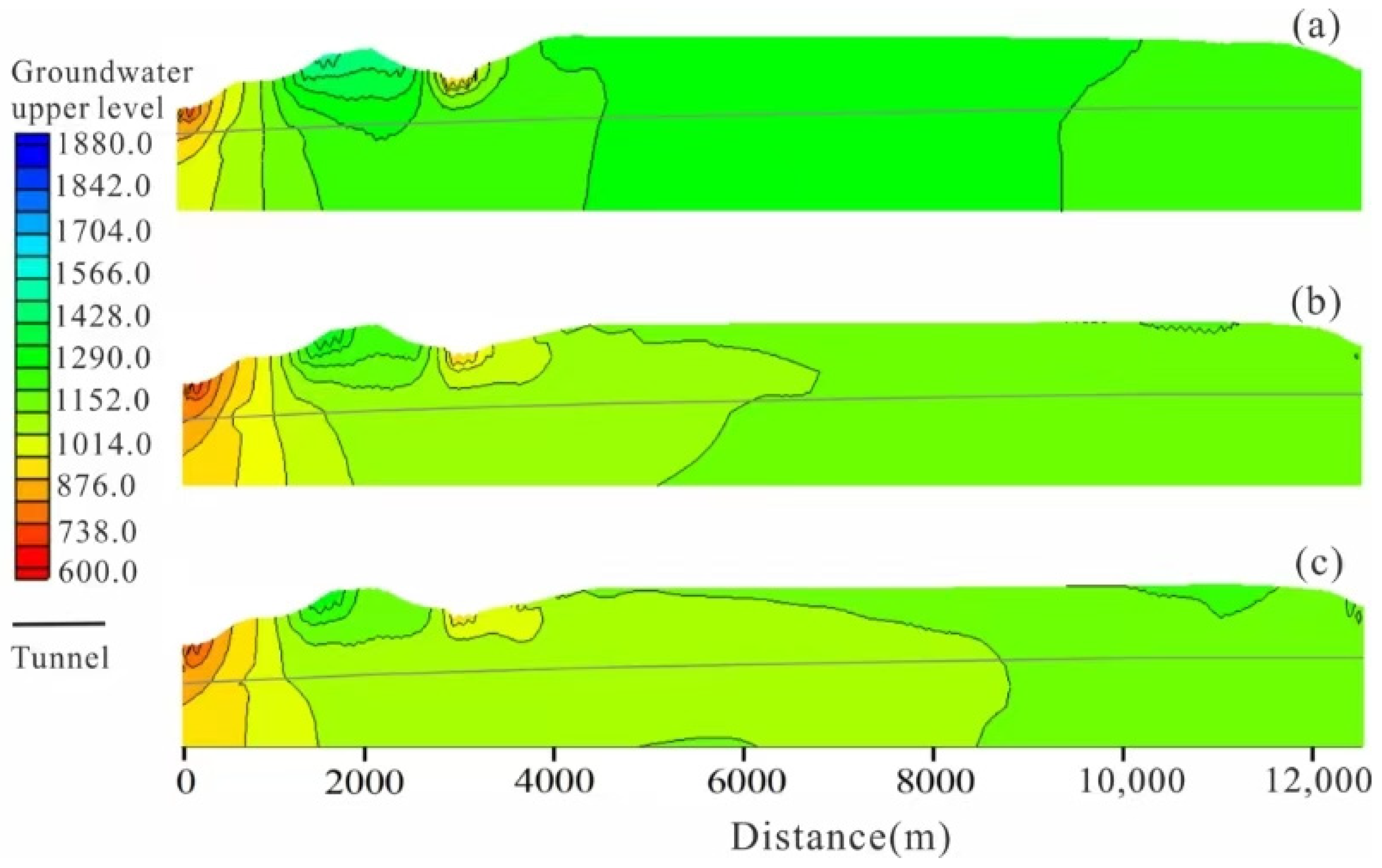
4.2.1. Regional Natural Seepage Field
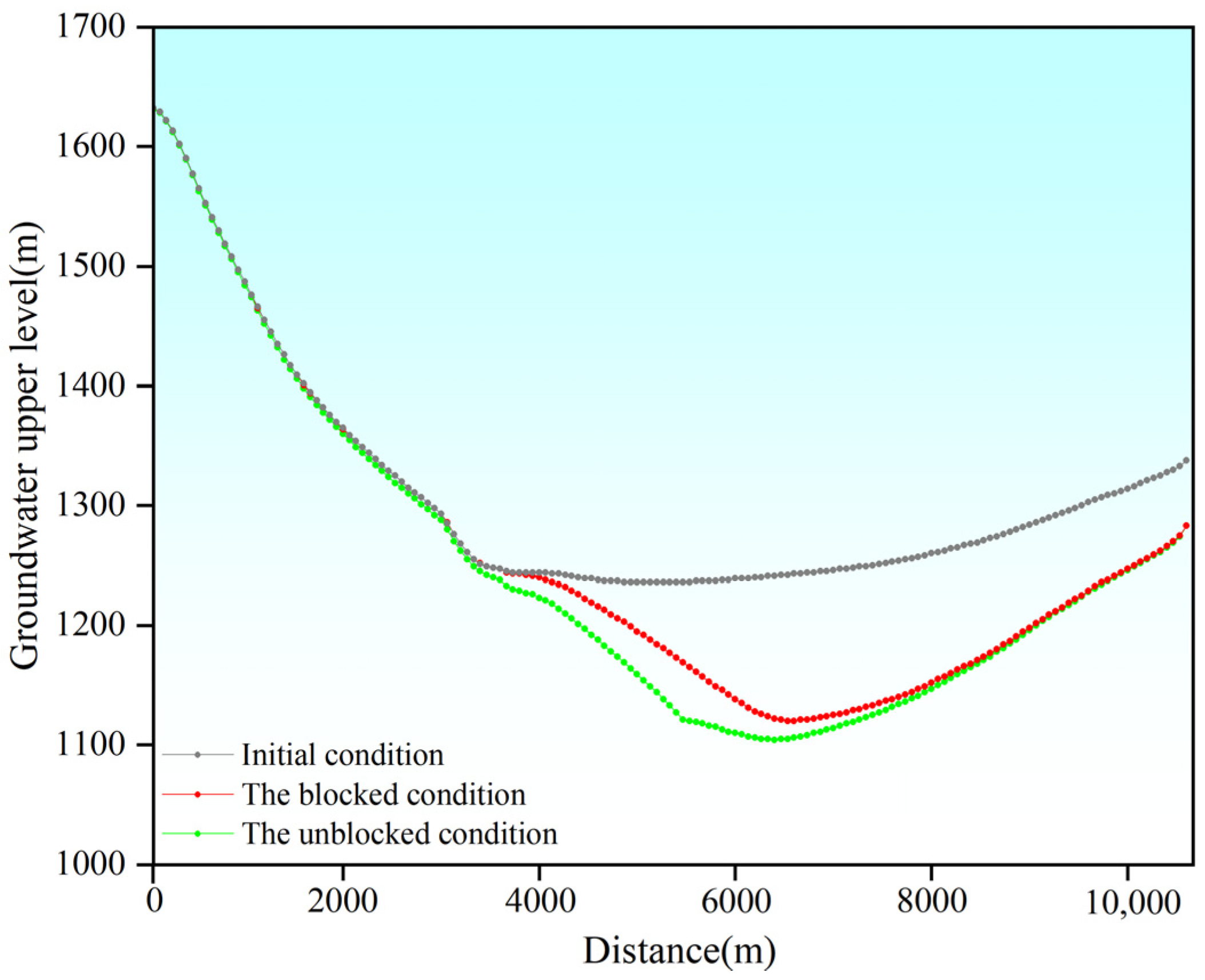
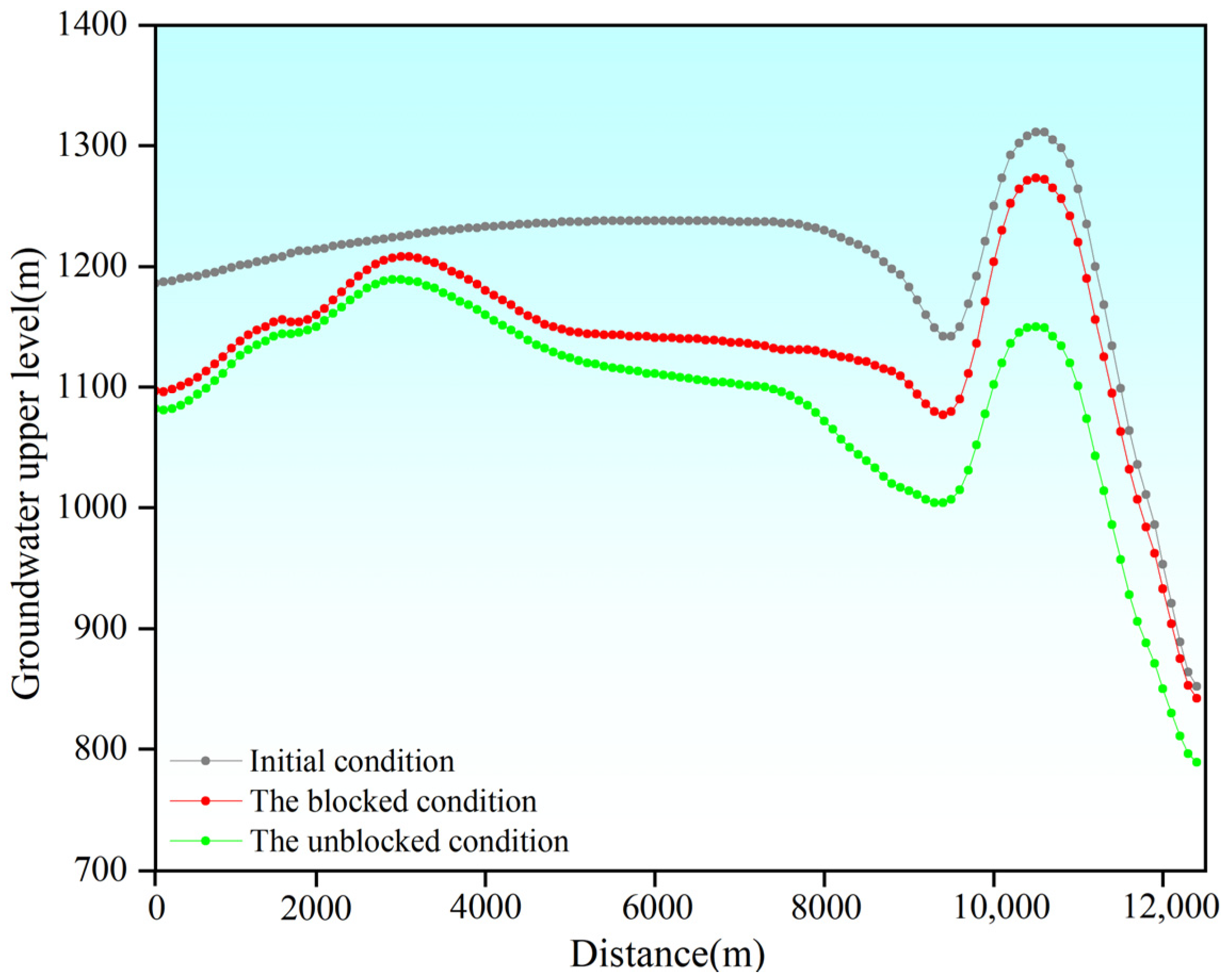
4.2.2. Analysis of Seepage Field Under Different Construction Conditions
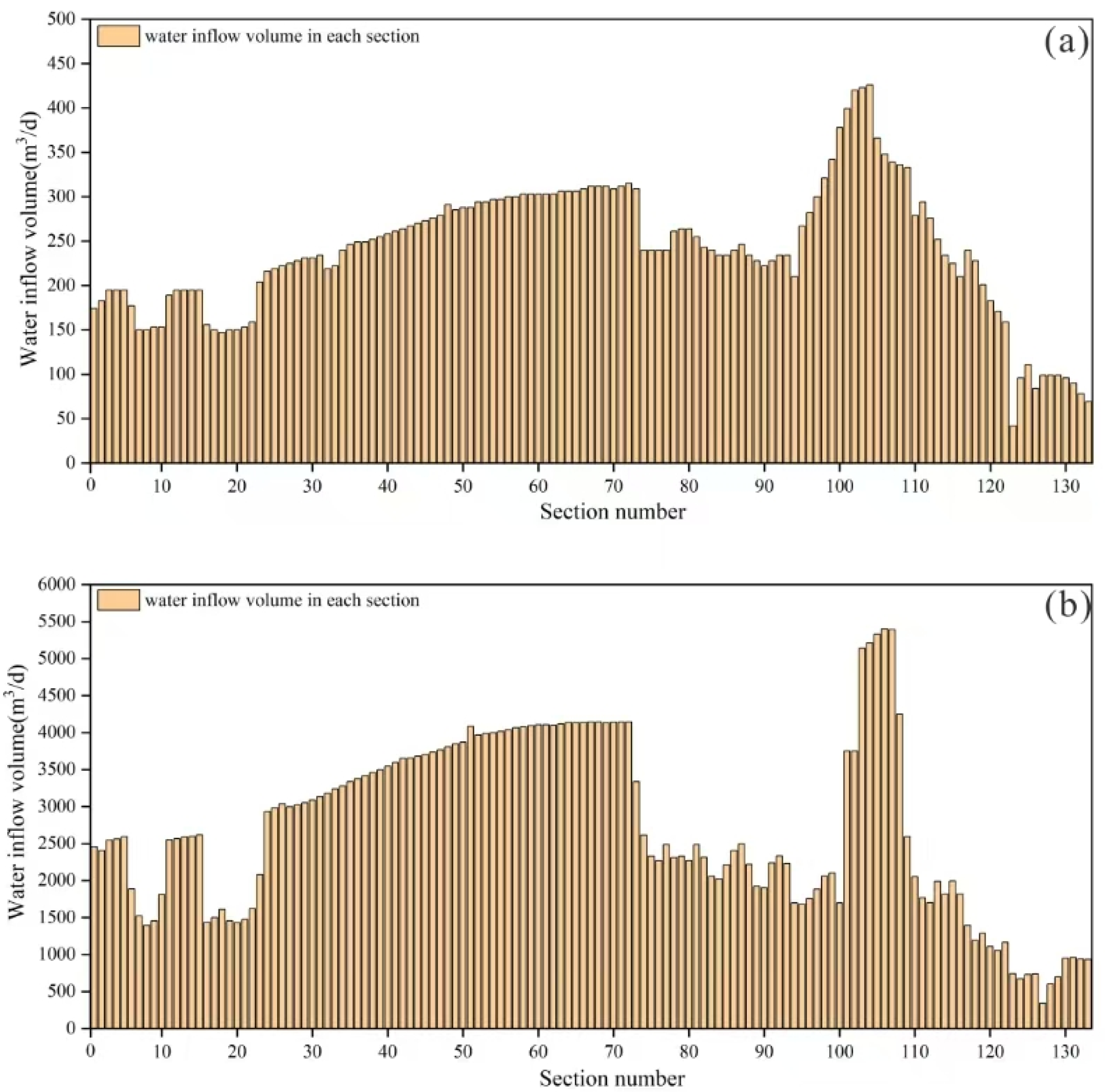
4.3. Inflow Prediction Under Different Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Hu, C.; Li, L.; Song, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, S. Bidirectional construction process mechanics for tunnels in dipping layered formation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 36, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Lin, M. Harnessing the catastrophic inrush of water into new Yungchuen tunnel in Taiwan. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2004, 19, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Pei, J.; Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Mei, G. Geological investigation and treatment measures against water inrush hazard in karst tunnels, A case study in Guiyang, southwest China. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2002, 124, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.; Bai, P.; Dong, Z. 3D multi-scale resistivity inversion method applied in the tunnel face to borehole observations for tunnel-ahead prospecting. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 196, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wu, F.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z. Disaster mechanism of tunnel face with large section in sandy dolomite stratum. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golian, M.; Abolghasemi, M.; Hosseini, A.; Abbasi, M. Restoring groundwater levels after tunneling: A numerical simulation approach to tunnel sealing decision-making. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 1161–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Cheng, K.; Ning, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, K. Detection method of karst features around tunnel construction by multi-resistivity data-fusion pseudo-3D-imaging based on the PCA approach. Eng. Geol. 2021, 288, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Sun, X.; Tang, C.; Yuan, F.; Wang, S.; Chen, T. Floor water inrush analysis based on mechanical failure characters and microseismic monitoring. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Kong, F.; Qiu, D.; Su, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K. The classifications of water and mud/rock inrush hazard: A review and update. B Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 1907–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.; Keim, S. Underground mine stream crossing assessment: A multi-disciplinary approach. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, K. Experimental investigation of the variations in hydraulic properties of a fault zone in Western Shandong, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Li, G.; Xie, X. A geological assessment method of floor water inrush risk and its application. Eng. Geol. 2012, 143–144, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Rezania, M.; Yu, H.; Bai, H. Variations of hydraulic properties of granular sandstones during water inrush: Effect of small particle migration. Eng. Geol. 2017, 217, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Protection against water or mud inrush in tunnels by grouting: A review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 2016, 8, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Peng, S. Sand-layer collapse treatment: An engineering example from Qingdao Metro subway tunnel. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, P.; Tian, S. Prevention and treatment technologies of railway tunnel water inrush and mud gushing in China. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 2013, 5, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liao, S. The analysis and control of inrush and mud gushing in the broken rock tunnel under high water pressure. Procedia Eng. 2016, 165, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Xie, X.; Bu, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z. Hazard-based evaluation model of water inrush disaster sources in karst tunnels and its engineering application. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Geng, F.; Yang, S.; Jing, H.; Meng, B. Numerical simulation of particle migration from crushed sandstones during groundwater inrush. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, G.T.; Yun, S.T.; Choi, B.Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Jo, H.Y.; Mayer, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y. Hydrochemistry of urban groundwater, Seoul, Korea: The impact of subway tunnels on groundwater quality. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2008, 101, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Sun, Q.; Qian, Z. Experimental research on water inrush in tunnel construction. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Rong, X.; Wang, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Z. Model test to investigate waterproof-resistant slab minimum safety thickness for water inrush geohazards. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 62, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Shi, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, C.; Tu, W.; Wang, M. Study on tunnel water inrush mechanism and simulation of seepage failure process. Rock Soil Mech. 2021, 41, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Y. Elaborate simulation and predication of the tunnel drainage effect on karst groundwater field and discharge based on Visual MODFLOW. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Feng, M.; Mao, X. Numerical analysis of water inrush from working-face floor during mining. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2008, 18, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, C.; Liang, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y. Numerical simulation on water inrush process due to activation of collapse columns in coal seam floor. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2009, 26, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.; Fernandez, G. Effect of excavation-induced groundwater level drawdown on tunnel inflow in a jointed rock mass. Eng. Geol. 2010, 110, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Capo, J.; Vazquez-Sune, E.; Carrea, J.; Marti, D.; Carbonell, R.; Perez-Estaun, A. Groundwater inflow prediction in urban tunneling with a tunnel boring machine (TBM). Eng. Geol. 2011, 121, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butscher, C. Steady-state groundwater inflow into a circular tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2012, 32, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongqing Geological Survey Institute. Regional Geology of China—Chongqing; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, B. The impact of formation heterogeneity on water discharge and groundwater depletion of an excavated tunnel. J. Hydrol. 2023, 627, 130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbaugh, A.W. MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model: The Ground-Water Flow Process; US Department of the Interior, USGS Reston: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.X. Origin of water in the Badain Jaran Desert, China: New insight from isotopes. Hydrol Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4419–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lou, K.; Tian, H.; Ma, C.; Jiang, B.; Gao, Z. Characterization and Health Risks of Groundwater Hydrochemistry in the Upper Weihe River Basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Qin, G.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Hu, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; et al. Exploring the Hydrochemical Characteristics and Controlling Processes of Groundwater in Agricultural Lower Reaches of a Typical Arid Watershed on Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, D.; Xu, J. How does the three gorges dam affect the spatial and temporal variation of water levels in the Poyang Lake? J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Railway Administration of PRC. Code for Hydrogeological Investigation of Railway Engineering; China Railway Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
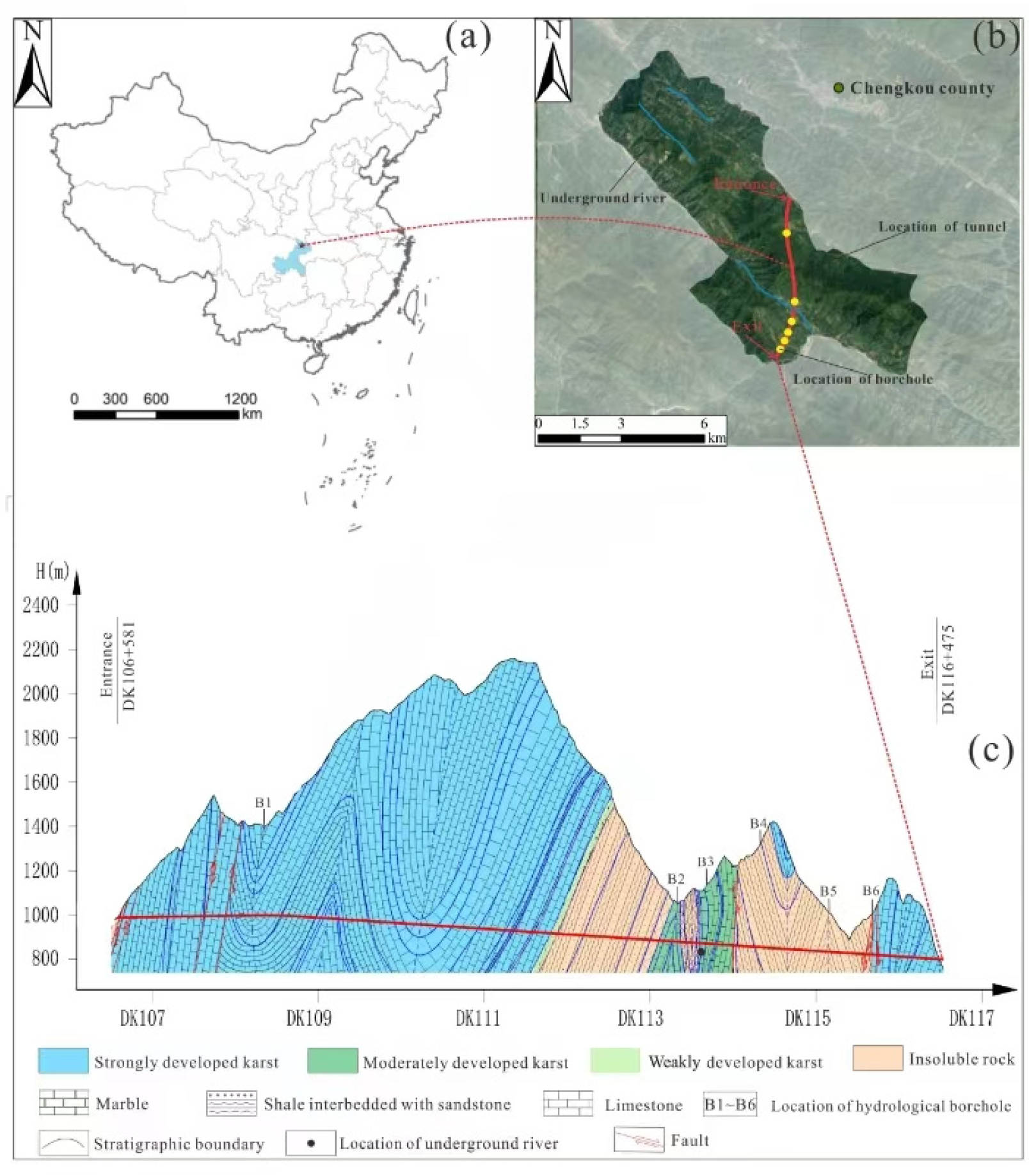
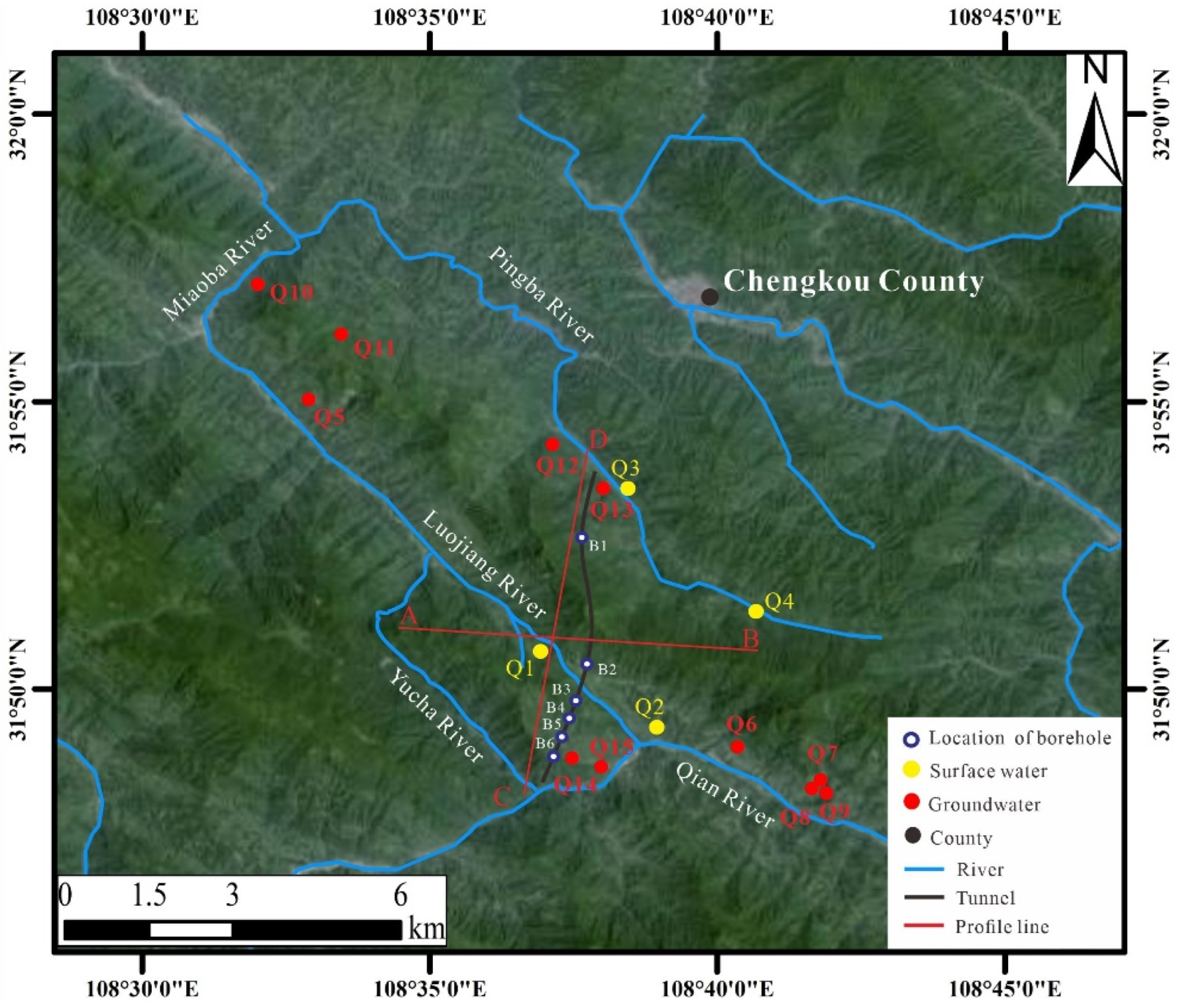
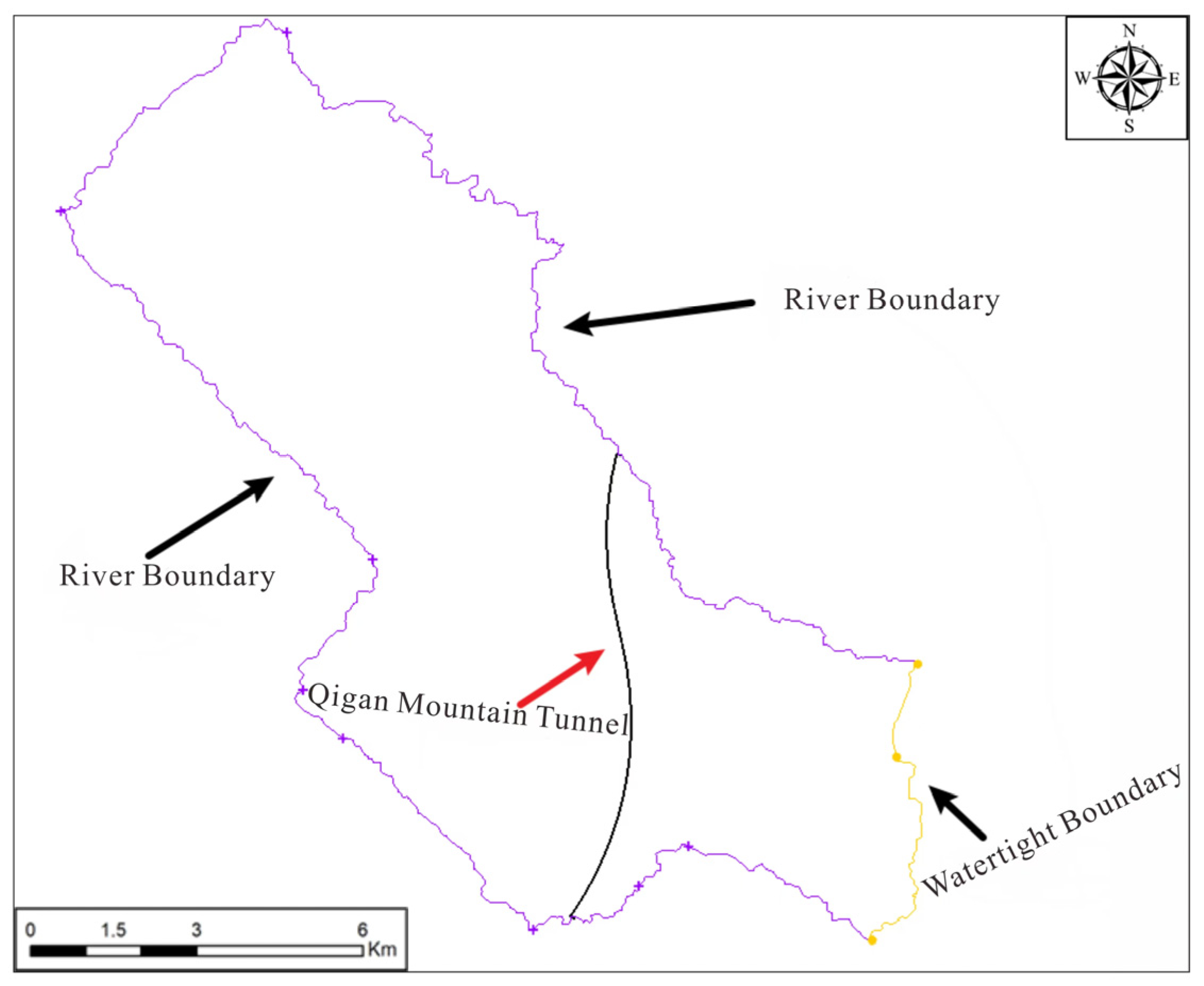
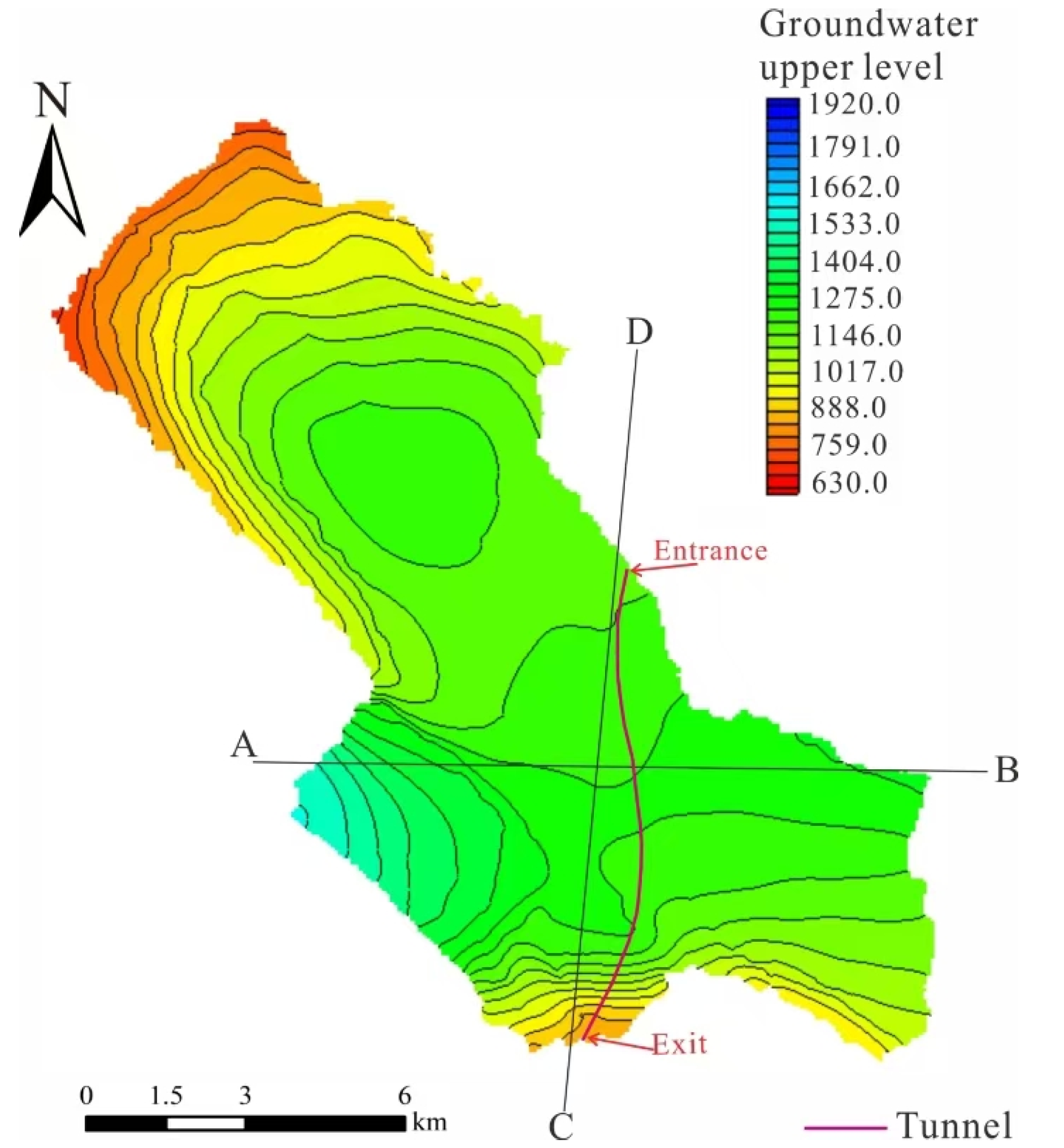
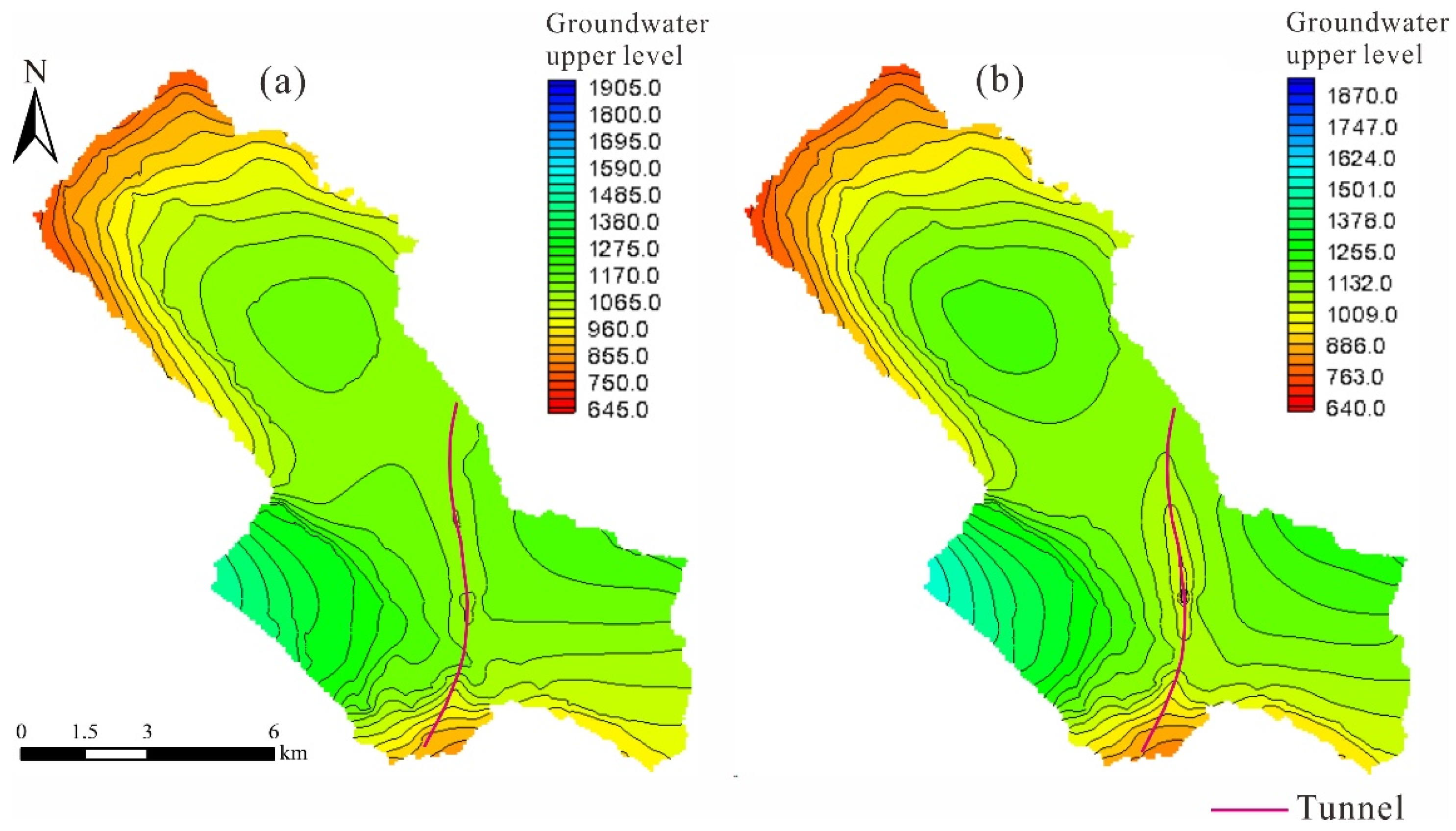
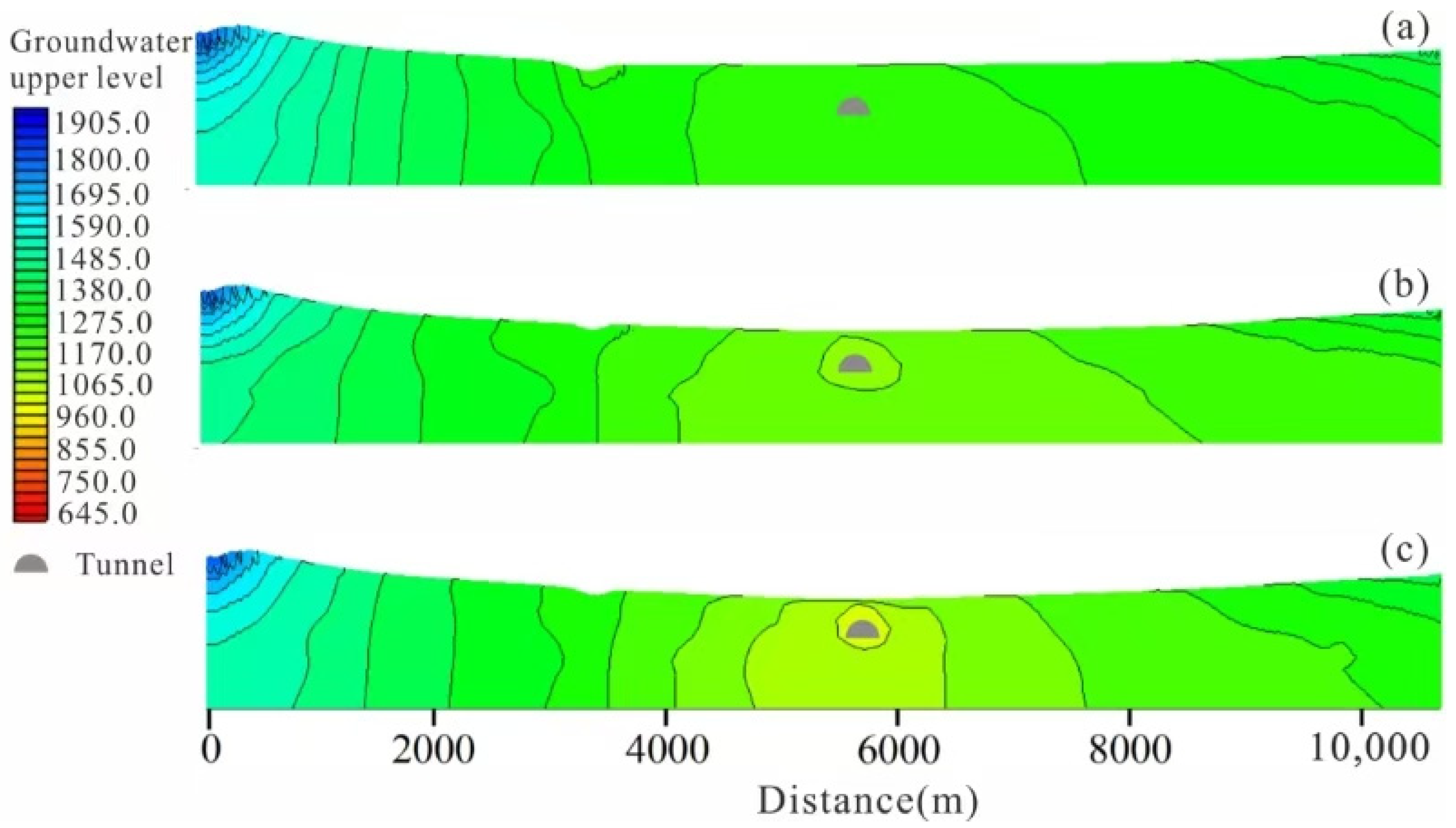
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infiltration Coefficient | 0.0005 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.0005 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.005 |
| Borehole Number | Measured Groundwater Upper Level (m) | Simulated Groundwater Upper Level (m) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 928.15 | 915.91 | 1.31 |
| 2 | 1094.88 | 1079.15 | 1.44 |
| 3 | 1326.97 | 1333.66 | −0.51 |
| 4 | 1297.62 | 1314.12 | −1.27 |
| 5 | 1105.01 | 1089.91 | 1.37 |
| 6 | 1156.52 | 1166.96 | −0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Que, B.; Liu, L.; Jiang, J.; Liao, X.; Xu, Z. Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Integrating Karst Seepage Field Characteristics with Water Inrush Prediction Models of the Qigan Mountain Tunnel. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104585
Zhang K, Que B, Liu L, Jiang J, Liao X, Xu Z. Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Integrating Karst Seepage Field Characteristics with Water Inrush Prediction Models of the Qigan Mountain Tunnel. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104585
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Binbin Que, Lizhao Liu, Junjie Jiang, Xin Liao, and Zhongyuan Xu. 2025. "Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Integrating Karst Seepage Field Characteristics with Water Inrush Prediction Models of the Qigan Mountain Tunnel" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104585
APA StyleZhang, K., Que, B., Liu, L., Jiang, J., Liao, X., & Xu, Z. (2025). Sustainable Infrastructure Development: Integrating Karst Seepage Field Characteristics with Water Inrush Prediction Models of the Qigan Mountain Tunnel. Sustainability, 17(10), 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104585






