Achieving Sustainable Construction Safety Management: The Shift from Compliance to Intelligence via BIM–AI Convergence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Risk Identification and Predictive Analytics
2.2. Real-Time Monitoring and Behavioral Governance
2.3. System Integration and Decision Optimization
3. Methodology
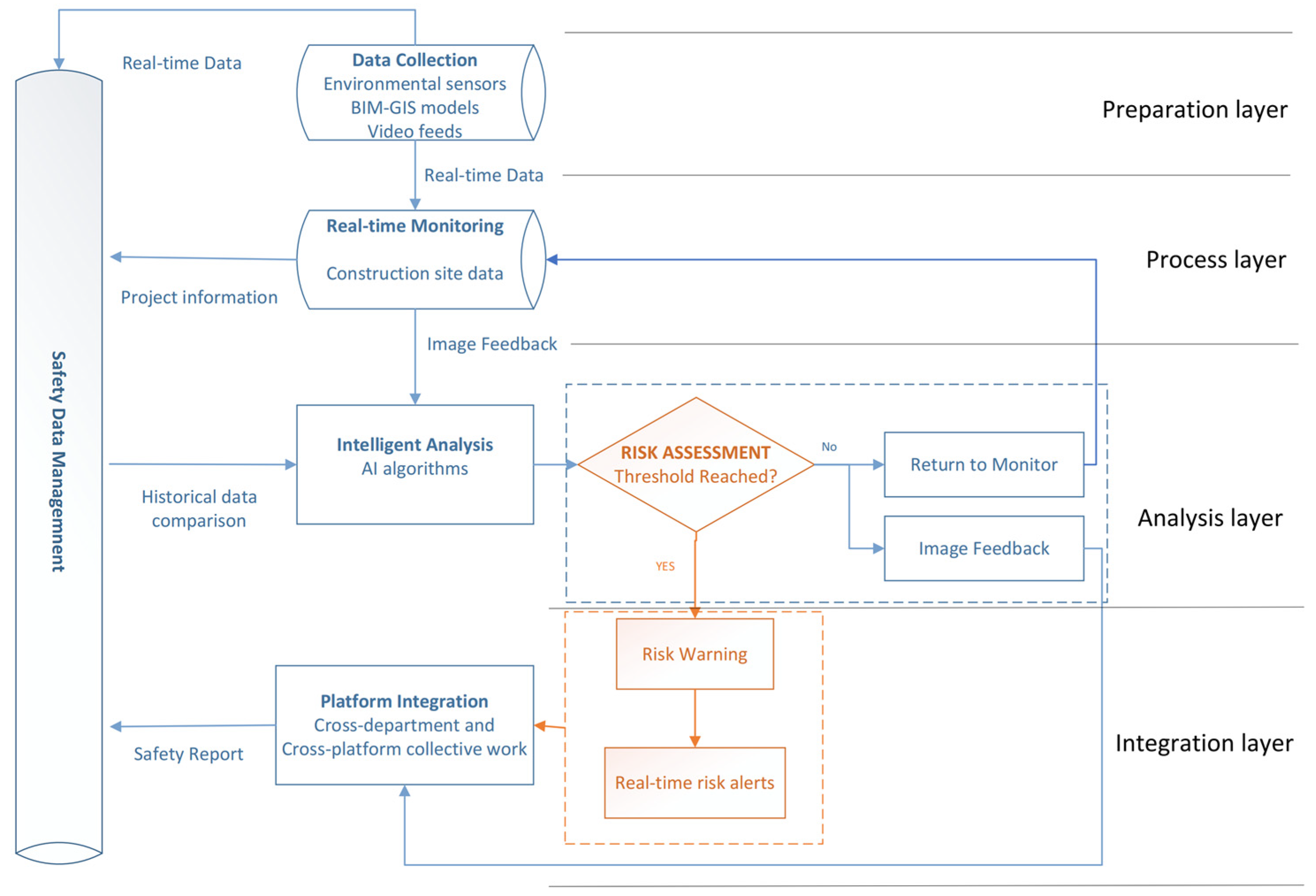
4. Framework Development and Design
4.1. Preparation Layer
4.2. Process Layer
4.3. Analysis Layer
- Structural Component (GNN): Graph Neural Networks process BIM-derived adjacency matrices (A) and node features (X) [43] through spectral graph convolution. The GAT architecture enables adaptive attention to critical structural relationships, quantifying material fatigue and connection vulnerabilities via message passing between BIM elements [44].
- Environmental Component (LSTM): Bidirectional LSTM networks [45,46] model sensor time series St through gated memory cells. The temporal attention mechanism dynamically weights meteorological, vibration, and acoustic inputs, capturing non-stationary environmental patterns preceding structural failures.
4.4. Integration Layer
4.4.1. Safety Data Management
4.4.2. Platform Integration
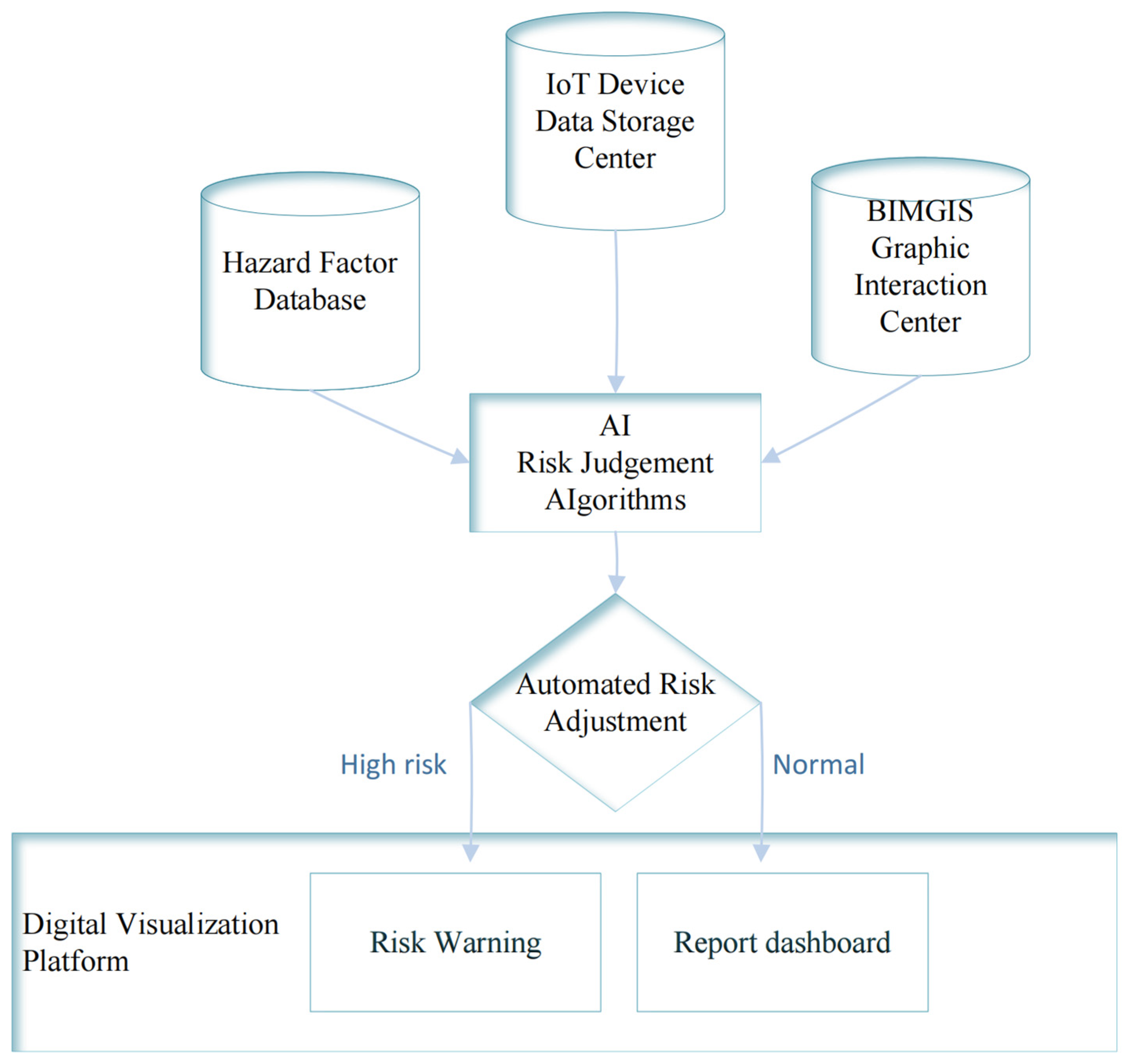
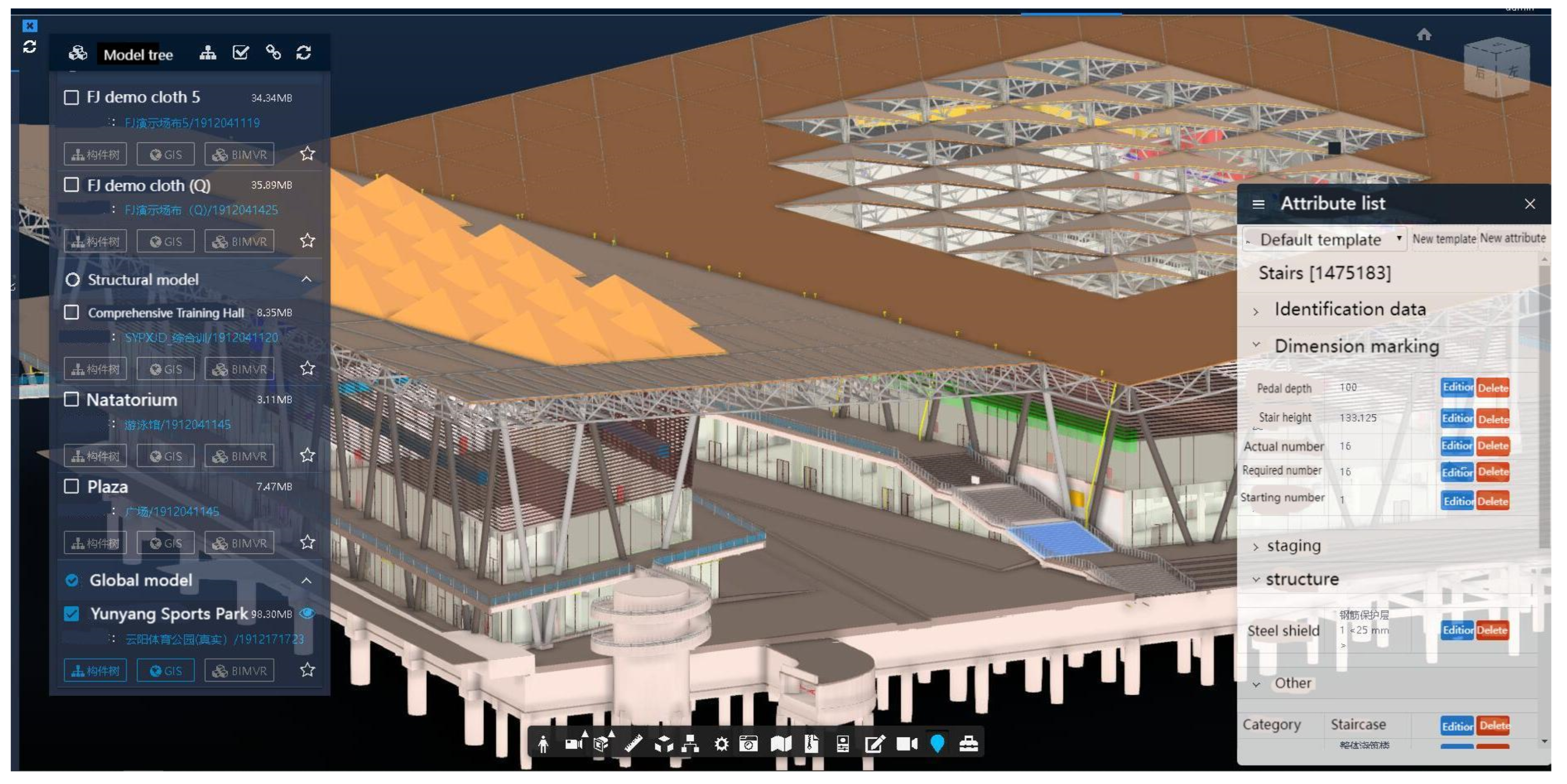
5. Prototype Testing and Evaluation
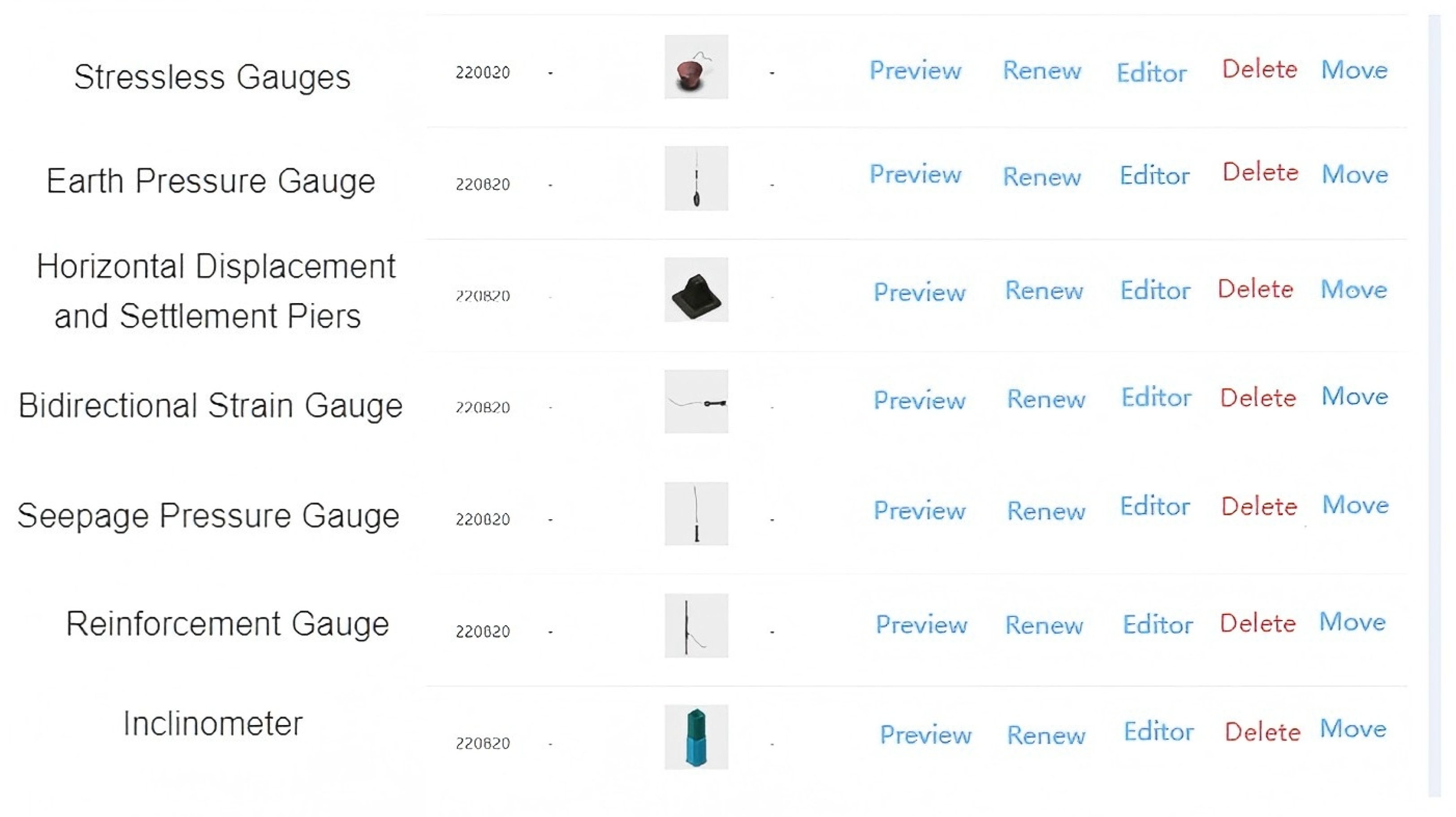
5.1. Data Sensing
5.2. Computing Process
5.3. Decision Output
5.4. Feedback from Users
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
8. Research Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Sulankivi, K.; Kiviniemi, M.; Romo, I.; Eastman, C.M.; Teizer, J. BIM-based fall hazard identification and prevention in construction safety planning. Saf. Sci. 2015, 72, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, J. Develop an Intelligent System of Construction Safety Management Using BIM and Multi-Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computer, Vision and Intelligent Technology, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, T.; Tran, S.V.-T.; Lee, D.; Park, C.; Lee, D. Automated Safety Risk Assessment Framework by Integrating Safety Regulation and 4D BIM-Based Rule Modeling. Buildings 2024, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for existing buildings—Literature review and future needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, H.L.; Jin, H.Y.; Liu, P. Methodologies of safety risk control for China’s metro construction based on BIM. Saf. Sci. 2018, 110, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.M. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Meng, J.; Zhong, X.J.; Tan, X. Intelligent early warning system for construction safety of excavations adjacent to existing metro tunnels. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8833473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Nielsen, R.O.; Johansen, K.W.; Teizer, J.; Larsen, P.G.; Schultz, C. Towards digital twins for knowledge-driven construction progress and predictive safety analysis on a construction site. In International Symposium on Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, C.; Bhatt, M.; Suchan, J.; Wałęga, P.A. Answer set programming modulo ‘Space-Time’. In Rules and Reasoning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- UK Government. International AI Safety Report: The International Scientific Report on the Safety of Advanced AI. 2025. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/679a0c48a77d250007d313ee/International_AI_Safety_Report_2025_accessible_f.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Integrating BIM and AI for smart construction management: Current status and future directions. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 1081–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshtaghian, F.; Noorzai, E. Integration of risk management within the building information modeling (BIM) framework. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 1951–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Bello, A.O.; Arqam, M.; Ullah, F. Integrating Building Information Modelling and Artificial Intelligence in Construction Projects: A Review of Challenges and Mitigation Strategies. Technologies 2024, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabin, A.; González, V.A.; Zou, Y.; Amor, R. Applications of machine learning to BIM: A systematic literature review. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 51, 101474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Hosseini, M.R.; Edwards, D.J.; Martek, I.; Shuchi, S. Comprehensive analysis of BIM adoption: From narrow focus to holistic understanding. Autom. Constr. 2024, 160, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Hancock, C.M.; Tang, L.; Wanatowski, D. BIM investment, returns, and risks in China’s AEC industries. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. A hybrid structured deep neural network with Word2Vec for construction accident causes classification. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 1120–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.; Hallowell, M.R.; Tixier, A.J.P. Automatically learning construction injury precursors from text. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zermane, A.; Mohd Tohir, M.Z.; Zermane, H.; Baharudin, M.R.; Mohamed Yusoff, H. Predicting fatal fall from heights accidents using random forest classification machine learning model. Saf. Sci. 2023, 159, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mohamed, E.; Jafari, P.; AbouRizk, S. Machine Learning–Based bayesian framework for interval estimate of unsafe-event prediction in construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Pan, X.; Love, P.E.D.; Ding, L.; Fang, W. Deep learning and network analysis: Classifying and visualizing accident narratives in construction. Autom. Constr. 2020, 113, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhong, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Identification of accident-injury type and bodypart factors from construction accident reports: A graph-based deep learning framework. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. Sound-Based Construction Activity Monitoring with Deep Learning. Buildings 2022, 12, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mneymneh, B.E.; Abbas, M.; Khoury, H. Vision-based framework for intelligent monitoring of hardhat wearing on construction sites. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 33, 4018066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Ding, L.; Zhong, B.; Love, P.E.D.; Luo, H. Automated detection of workers and heavy equipment on construction sites: A convolutional neural network approach. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 37, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Tran, D.Q.; Bak, J.; Park, S. Small and overlapping worker detection at construction sites. Autom. Constr. 2023, 151, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, I.; Asadi, K.; Ramshankar, H.; Han, K.; Albert, A. Real-time vision-based worker localization & hazard detection for construction. Autom. Constr. 2021, 121, 103448. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Transformer-based deep learning model and video dataset for unsafe action identification in construction projects. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.M.; Tian, J.; Chian, E.Y.T. Management of safe distancing on construction sites during COVID-19: A smart real-time monitoring system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 163, 107847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elelu, K.; Le, T.; Le, C. Collision Hazard detection for construction worker Safety using audio surveillance. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04022159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, M.; Wong, P.K.Y.; Cheng, J.C.P. Full body pose estimation of construction equipment using computer vision and deep learning techniques. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; El-Gohary, N. Deep learning-based relation extraction and knowledge graph-based representation of construction safety requirements. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Mostofi, F.; Ayözen, Y.E.; Tokdemir, O.B. Customized AutoML: An automated machine learning system for predicting severity of construction accidents. Buildings 2022, 12, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, K.; Ekmekcioğlu, Ö.; Gurgun, A.P. Developing a National Data-Driven Construction Safety Management Framework with interpretable fatal accident prediction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2023, 149, 04023010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, G.K.; Wu, S. Using context-guided data augmentation, lightweight CNN, and proximity detection techniques to improve site safety monitoring under occlusion conditions. Saf. Sci. 2023, 158, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondia, A.; Ezzeldin, M.; El-Dakhakhni, W. Machine learning-based decision support framework for construction injury severity prediction and risk mitigation. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2022, 8, 04022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevner, A.R. A three cycle view of design science research. Scand. J. Inf. Syst. 2007, 19, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Autodesk Inc. Autodesk Revit 2024. Autodesk Official Website. 2024. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/products/revit/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Python Software Foundation. Python 3.11: A High-Level Programming Language for General-Purpose Programming. Python Official Website. 2023. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- von Bertalanffy, L. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications; Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, D.D. Resilience Engineering: Concepts and Precepts; Hollnagel, E., Woods, D.D., Leveson, N., Eds.; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Farnham, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli, F.; Gori, M.; Tsoi, A.C.; Hagenbuchner, M.; Monfardini, G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 20, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Long short-term memory. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, R.M. Bayesian Learning for Neural Networks; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yarin, G.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Blundell, C.; Cornebise, J.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Wierstra, D. Weight uncertainty in neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
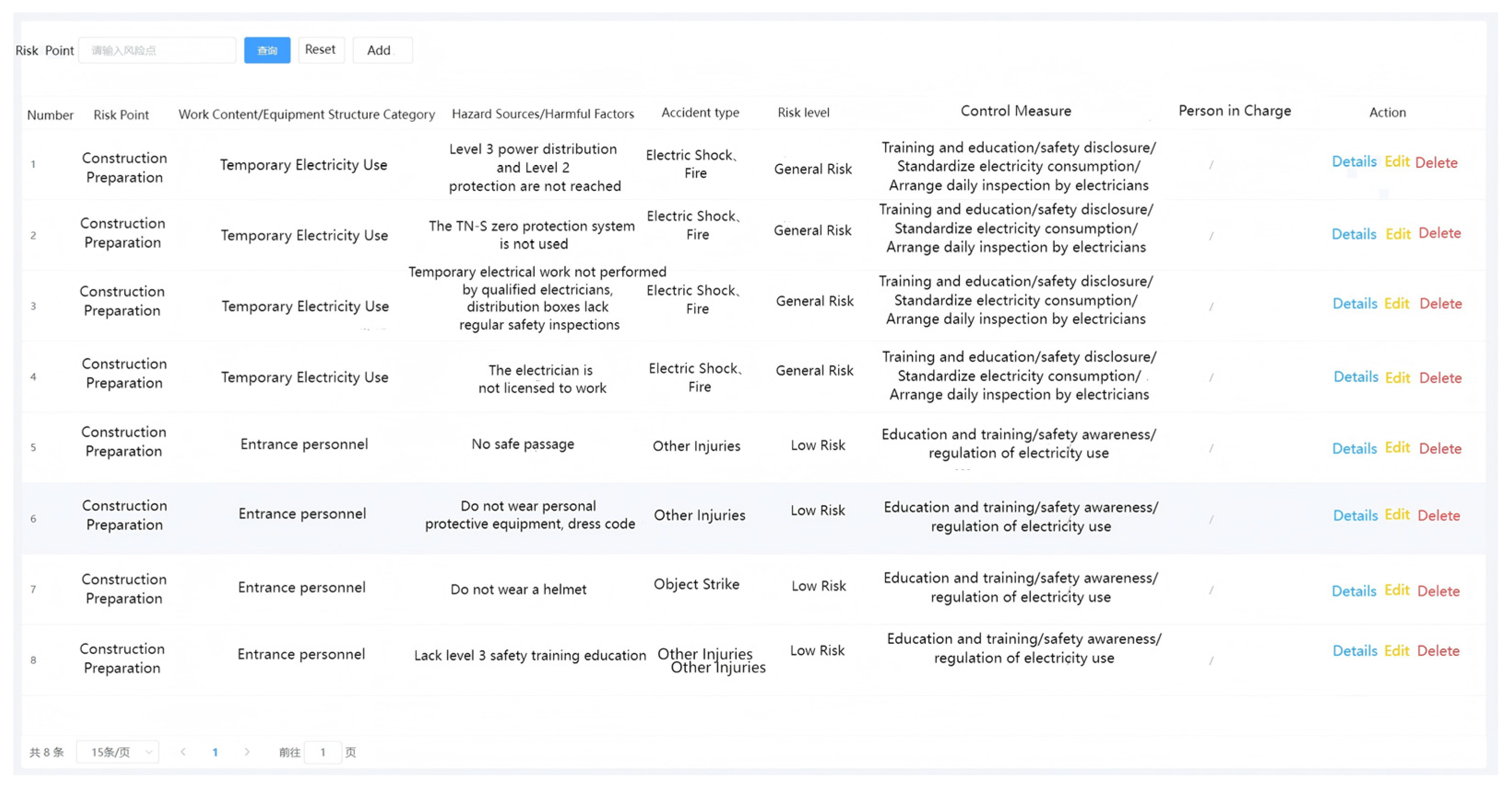
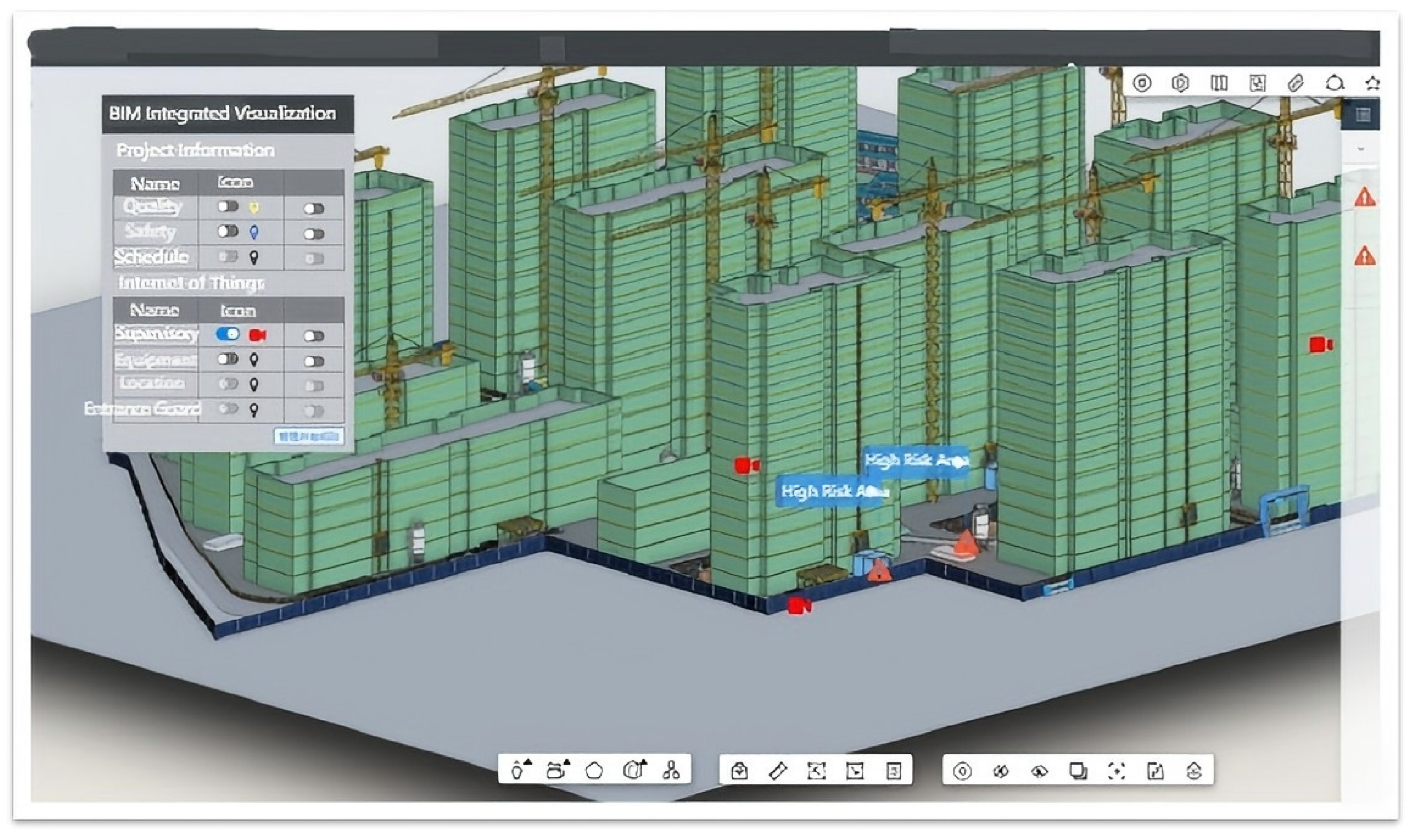
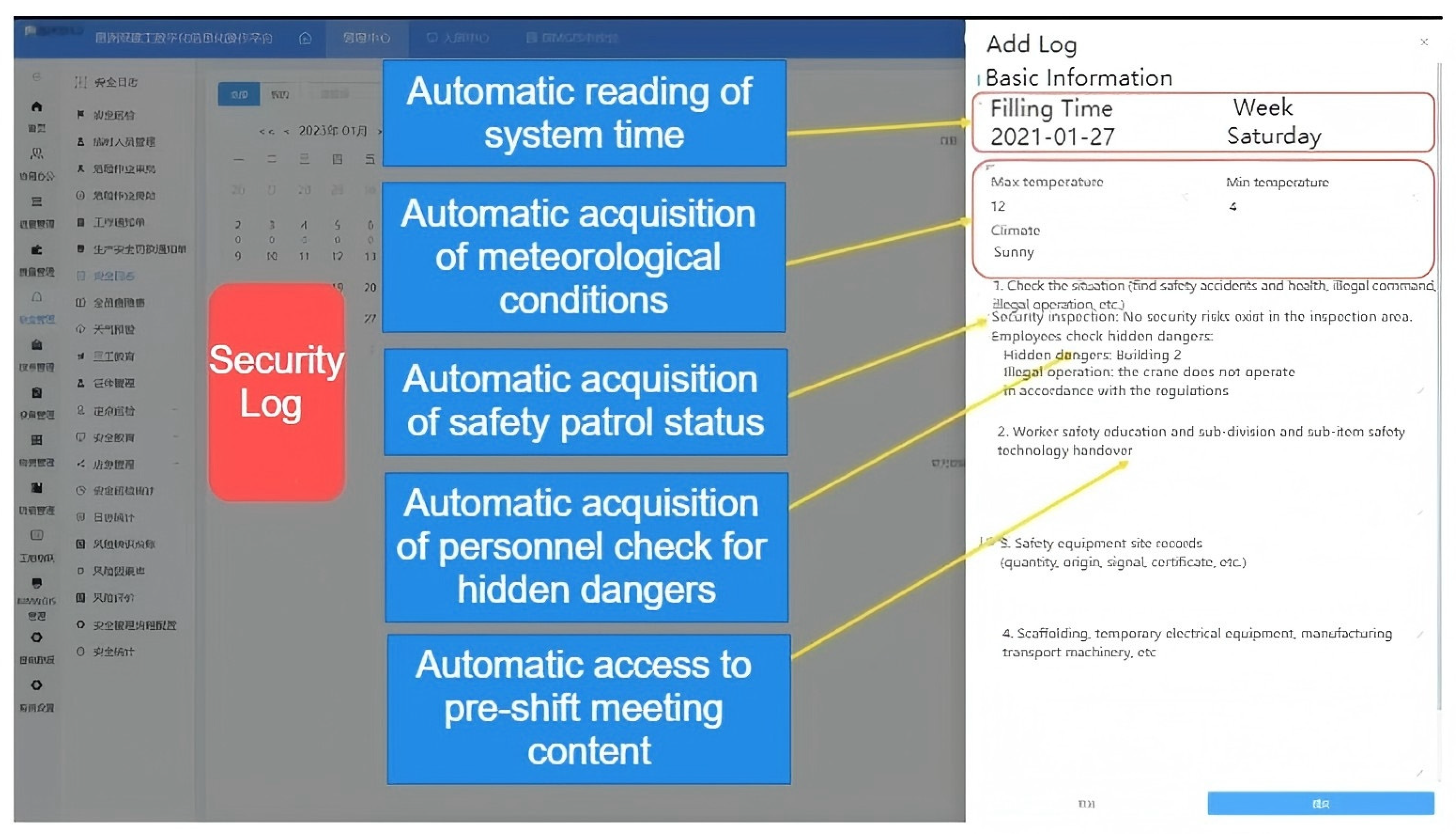
| Evaluation Variables | Mean | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Information input/output friendliness | 4.2 | Satisfied |
| Risk warning timeliness | 3.8 | Satisfied |
| Optimization of safety inspection tasks | 4.0 | Satisfied |
| Impact of improving the safety of construction projects | 4.1 | Satisfied |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chong, H.-Y.; Ma, Q.; Lai, J.; Liao, X. Achieving Sustainable Construction Safety Management: The Shift from Compliance to Intelligence via BIM–AI Convergence. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104454
Chong H-Y, Ma Q, Lai J, Liao X. Achieving Sustainable Construction Safety Management: The Shift from Compliance to Intelligence via BIM–AI Convergence. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104454
Chicago/Turabian StyleChong, Heap-Yih, Qinghua Ma, Jianying Lai, and Xiaofeng Liao. 2025. "Achieving Sustainable Construction Safety Management: The Shift from Compliance to Intelligence via BIM–AI Convergence" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104454
APA StyleChong, H.-Y., Ma, Q., Lai, J., & Liao, X. (2025). Achieving Sustainable Construction Safety Management: The Shift from Compliance to Intelligence via BIM–AI Convergence. Sustainability, 17(10), 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104454









