Abstract
Heavy metal soil pollution in urban areas is a critical environmental, public health, and sustainable living issue. The quantities of cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), and zinc (Zn) in urban soils in Larissa, Greece, are evaluated in this study along with their risks to human health. A total of 198 surface soil samples were collected from green areas over a three-year period (2021–2023) and analyzed using atomic absorption spectrometry. The results show that Zn has the highest mean concentration (99.80 mg/kg in the summer), followed by Cu (57.33 mg/kg), Pb (48.60 mg/kg), and Cd (0.10 mg/kg). Seasonal variations revealed increased metal levels in the summer due to reduced soil moisture and atmospheric deposition. For assessing the level of pollution in Larissa’s urban areas, thematic maps were created. Using the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) risk assessment framework, model estimates indicated that ingestion was the dominant exposure route, with children predicted to experience higher non-carcinogenic risks than adults due to the model default exposure assumptions. The hazard quotient (HQ) for Pb in children with soil-pica disorder reached 6.79, exceeding the safe threshold (HQ = 1), indicating significant adverse health risks. Although average metal concentrations were within EU safety limits, the cumulative health risk assessment highlights the need for continuous monitoring and pollution mitigation strategies in urban environments.
1. Introduction
Over the past few decades, heavy metal-induced soil contamination became a significant environmental issue that people are concerned about [1]. Heavy metals, also known as Potential Toxic Elements (PTEs), are metallic contaminants that may remain in the environment for a long time because they do not degrade but can be altered in their chemical status [2]. Their origin can be geochemical, i.e., they come from the minerals and rocks that contribute to the formation and geochemistry of soils [3]. However, several anthropogenic activities, such as the use of metal-containing formulations, metal plating processes, diverse industrial activities, and fossil fuel combustion for house heating and vehicle power, are important sources of heavy metals that end up in the soil. Long-term pollution in the environment is recorded in the reservoir known as soil and therefore the importance of the continuous control and permanent monitoring of its quality, pollution, and sustainable health is particularly important [4]. In addition to their physical and chemical properties, soils are divided into a number of groups. There is a significant contrast between agricultural and urban soil based on the activities that are carried out on the soil [5].
Heavy metal pollution is unfortunately a common threat in both rural and urban soil environments. There are numerous agricultural practices that contribute to heavy metal contamination of cultivated soils. For example, the use of copper-based formulations as well as the indiscriminate use of superphosphate fertilizers have resulted in an accumulation of toxic metals in rural areas, away from cities and industries. On the other hand, numerous studies are focusing on the problems of soil contamination by hazardous metals in urban environments. Wei and Yang [6] in a review of studies from various Chinese cities over the past decade reveal that concentrations of metals, such as Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd, frequently exceed background values and regulatory thresholds in urban soils. These findings highlight the pervasive influence of anthropogenic activities—including traffic emissions, industrial processes, and agricultural practices—on soil quality and environmental health. Pecina and his colleagues [7] assessed urban soil contamination across 101 cities in China using data from over 17,000 samples. The findings reveal that 11% of the cities were heavily polluted, with Cd, Hg, Cr, and As posing the greatest health and ecological risks—particularly to infants and urban green spaces (UGSs). Industry, rather than urban population size, was identified as the primary driver of pollution, underscoring the need for targeted environmental management in industrial urban centers. Binner and her colleagues [8] in a systematic analysis of heavy metal contamination in European urban soils revealed significant data heterogeneity, with common contaminants—Pb, Zn, and Cu—frequently exceeding the national safety thresholds, largely due to anthropogenic activities, such as traffic and industry, although geogenic enrichment was also evident in several regions. Singh et al. [9], investigating topsoil samples from the city of Nagpur, India, revealed that the metals Cd, Pb, Co, and Zn exhibited high mobility and availability rates. Furthermore, performing an ecological risk assessment, they also proved that Cd, Cu, Ni, and Pb posed higher risks, especially in industrial and residential areas. Adewumi and Ogundele [10], in their research evaluating data from published articles for the years 2010–2022 on land pollution in 174 cities worldwide, concluded that urban sprawl and exhaust gases are the main causes of high pollution levels.
In Greece, urban soil pollution has been extensively studied in megacities, such as Athens, which is located close to the largest industries in Greece, having the highest population and therefore the heaviest traffic and heating needs [11,12], but also in Greek island towns [13], where strong anthropogenic enrichment was revealed. In order to determine the level of hazardous metal pollution in urban soils, geochemistry in green areas, such as parks or playgrounds, has also been examined [3,14]. Coastal cities that have ports with commercial activity and a railway station, such as Thessaloniki [15,16], also highlight and indicate important sources of heavy metals in soil. So why is the study of soil pollution so important? Obviously, soil is the connecting link for transporting pollution, both in the underground aquifer and via plant production to animals and humans [1]. Several hazardous diseases, primarily of a neurological nature, as well as cancer and the death of living organisms, are caused by the presence of toxic elements when their concentration exceeds a concentration threshold. Metals move through the human body in a wide variety of ways. Ingestion of soil and skin contact are the two main pathways that metals enter the human body [17,18]. Health risk assessment models, including hazard index (HI) and Cancer Risk (CR) calculations, are commonly used to evaluate non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks, particularly for children, who are more susceptible due to behavioral factors, such as frequent hand-to-mouth activity, while other exposure pathways, such as potential dermal contact, may contribute to children’s overall vulnerability. Health risk depends on a number of parameters, such as age, body weight, duration of exposure to pollution, underlying diseases of people exposed to contaminated soils, etc. Previous studies identified significant health risks in urban agglomerations with Pb and Cr often exceeding safe thresholds, posing neurotoxic and carcinogenic risks [15,19,20,21,22].
Larissa is a major urban and agricultural center in central Greece, known for its intensive farming activities and growing population. Environmental challenges, such as pesticide use and flood events, have raised concerns about public health impacts in the region. A hospital-based case–control study conducted in the agricultural region of Larissa indicated that pesticide exposure was significantly associated with an increased risk of LHC (lymphohematopoietic cancer), including myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia [23]. Moreover, a recent study utilized wastewater-based surveillance and reported a strong correlation between increased RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) concentrations in wastewater and higher rates of influenza-like illness (ILI) in children under 14 years old [24]. These studies underscore the potential risk posed by environmental contaminants and the value of monitoring environmental indicators to assess public health risks. The current research aims a. to evaluate the levels of heavy metals in the urban soils of Larissa, b. to assess the possible risk for human health, both for adults and children, and c. to create thematic maps in order to capture the levels of burden and risk in Larissa city.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Definition—Soil Sampling
During the years 2021–2023 a total of 198 surface (0–20 cm) samples (66 each year) were collected from green areas of the city of Larissa (Figure 1). Soil samples were repeatedly collected from the same locations and from a 20 cm surface layer, since no changes were detected over the research period. Larissa is the largest city of the Thessaly region in the middle of Greece. According to the 2021 census, Larissa has approximately 170,000 residents in the city proper, making it the fifth-most populated city in Greece. Larissa is surrounded by mountains (such as Mount Olympus and Kissavos), is built at an altitude of 70 m (230 ft), and the river Pinios runs through the city. Within the urban area of Larissa, the soil is subjected to significant pressure from the traffic of vehicles, buses, and trucks as the city is an important urban center. There is also a permanent railway station within the city with significant train traffic. Even though there are no large industrial units, there are nevertheless large military units with constant heavy vehicle traffic and many small industries. Intensive industrial activity is found in the peri-urban area of Larissa. Larissa experiences cold, semi-arid weather with certain Mediterranean traits, such as drier summers and somewhat wetter winters. There may be some snowfall during the coldest times of the year, although it is rarely substantial. Summers are especially hot, with temperatures close to or above 40 °C (104 °F). Larissa has an average yearly temperature of 15.4 °C (59.7 °F) and receives around 413 mm (16 in) of rain annually. The downtown city core, which occupies 2.18 km2, is the focus of this research [25]. The samples were distributed over five parks in the center of Larissa city, namely Post-Office Square, Central Square, Triangular Square, Jewish Square, and Mother’s Square, and some at key points of the city, such as the Ancient City Theatre and a roundabout at a road junction.
Figure 1.
The city of Larissa in Thessaly and the sampling area.
Each year sampling was carried out in two periods, i.e., one in March, after the wet season (mentioned as winter hereafter) and in September, after the dry season with the high summer temperatures and before the autumn rain started (mentioned as summer hereafter), in order to study the spatio-temporal variability of metal contaminants in soils. Selected areas have been chosen where there is increased human traffic throughout the year, as they are close to cafés, restaurants, and small playgrounds. The sampling was carried out using a special wooden sampler, without any metallic parts, to avoid metal contamination in the soil samples.
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Analyses
A composite soil sample consisting of 4 subsamples was taken from each sampling point with a diameter in the range of 50–100 cm depending on the case. A total of 1 kg of soil was taken from each sampling point in order to carry out the analyses. After collection, the soil samples were taken to the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki’s Laboratory of Soil Science, where they were allowed to air dry for three to four days before being passed through a sieve with a 2 mm hole diameter to perform the physicochemical analyses outlined by Page [26]. In particular, the soil reaction value was determined by using an electronic pH meter and the electrical conductivity (EC) value was determined by using an electronic conductivity meter, in an aqueous suspension with a soil-to-water ratio of 1:2.5 [27]. The textural characterization of the soil samples was conducted by determining the percentages of sand, silt, and clay following the Bouyoukos method after the chemical dispersion of clay using sodium hexametaphosphate [28]. To calculate the proportion of organic matter, the Walkey Black method was followed, after oxidation by potassium dichromate solution in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, and a subsequent volumetric measurement with an iron sulphate solution [26]. To calculate the percentage of calcium carbonate, a Bernard calorimeter was used, using a sulfuric acid solution, and measuring the resulting release of carbon dioxide [29].
The concentration of four (4) heavy metals—Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb—which are among the most frequently found contaminants in urban environments and are known to be highly toxic or can become toxic at elevated concentrations—was determined using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Europe-AA-6300, Duisburg, Germany). Their selection allowed for a direct comparison with the international standards (EU soil quality guidelines) and other regional studies supporting more robust risk assessments. This was followed by extraction using specific heated, closed-type equipment using a 3:1 combination of powerful hydrochloric and nitric acids. The extracts of the soils were diluted to the required dilutions and determined after the construction of the corresponding standard curve for each metal. For the verification of the accuracy of the analyses, a certified reference material (CRM) (No 141R, calcareous loam soil) from the Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) was analyzed with the soil samples, and it was shown that the recovery of the method ranged from 97.4 to 102.3%.
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
Health risk assessment is a typical technique for calculating the hazards, both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic, arising from ingestion, inhalation, and dermal exposure. In this research, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) guidelines on exposure factors were applied to assess human risks [30] via ingestion and dermal contact. Average daily doses (ADDs) (mg/kg/day) for heavy metals in soils were calculated as follows [31]:
where ADDing and ADDderm are the daily doses of exposure to metals in soils through ingestion and dermal contact, respectively. In this study, we focused on ingestion and dermal contact as the primary exposure pathways for heavy metals from urban soils as these routes are generally recognized as the most critical for the population, especially children [17,18]. To understand the different types of human exposure to soil in the study area, two distinct scenarios were evaluated: Scenario 1 included all residents (adults and children) living in the area, while Scenario 2 focused specifically on children with pica disorder, i.e., a persistent compulsion to consume soil in large amounts (20,000 mg/d) on a daily basis over an extended period, which is likely prevalent in children [32]. While comprehensive data on the prevalence of pica in Greece are scarce, the existing studies and clinical observations indicate its presence, particularly among specific populations, such as children with development disorders and pregnant women [33,34,35]. The parameters that vary in these scenarios were adapted directly from the EPA guidelines [36] and the values are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Exposure parameters for different health risk scenarios.
The non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risks of the analyzed metals were assessed through the hazard quotient (HQ), the hazard index (HI), and the carcinogenic risk index (CR) [37]. Non-carcinogenic risks through ingestion (HQing) and dermal contact (HQderm) are the ratio of the average daily dose (ADD) of the analyzed heavy metal for each exposure pathway to the corresponding reference dose (RfD) for the same exposure pathway, according to the formulas [38]:
where RfDing is the reference dose from the oral path (mg/kg/day) and RfDderm is the reference dose for dermal contact (mg/kg/day) representing the highest daily oral and dermal dosage that is permitted, respectively, of a metal that is neither harmful nor has detrimental consequences on humans during their lifetime. Values of HQs above the safe level (=1) mean adverse health effects [16,30,31].
The carcinogenic risk (CR) is defined as the possibility of an individual developing any type of cancer over their lifetime owing to exposure to carcinogenic risks [39], and calculated using the following formula:
where i defines the different paths of exposure, i.e., ingestion and dermal contact, and SFi is the slope factor (mg/kg/day) for each pathway. If the carcinogenic risk (CR) is below 10−6, the carcinogenic health risk from soil is considered insignificant. Conversely, a CR above 10−4 shows a possibly increased risk of cancer in people. A CR value ranging from 10−6 to 10−4 is generally considered an acceptable or tolerable risk to public and human health [40]. The values of reference doses (RfDs) and slope factors (SFs) for each element are provided in the screening level (RSL) tables by the USEPA [41] and are listed in Table 5.
2.4. Statistical—Geostatistical Analyses
SPSS-29 software was used to conduct a one-way ANOVA on 3-year data from 33 sample locations with a p-value of <0.05. The results reveal no statistically significant changes in the mean three-year values; however, an increasing tendency is found from year to year. Moreover, analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) was applied in order to determine whether there are statistically significant differences among the sampling periods (winter and summer). The mean values were utilized to create thematic maps. Based on the concentration distribution, a geographic interpolation procedure was carried out in QGIS Desktop 3.42.0 [25] using the ordinary kriging technique, data logarithmic transformation, and a grid with a spatial resolution of 10 m. Table 4 displays the geographical statistics. For every element, the ordinary kriging procedure produced raster pictures of contamination. Using QGIS 3.42.0 and the web map service OpenStreetMap as the base layer, these rasters were combined with the sample point vector information and local points of interest (POIs) on the thematic maps (Figure 2).
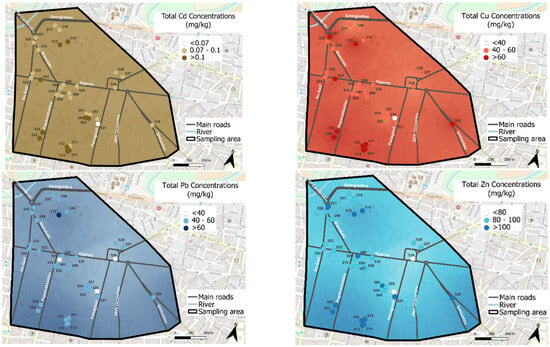
Figure 2.
Thematic maps of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn based on total soil concentrations in Larissa (mean values of the three years of the September sampling period).
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Parameters—Levels of Heavy Metals
The physicochemical properties of soil samples are presented in Table 2. The results reveal a pH range from 6.6 to 8.9 indicating near-neutral to slightly alkaline conditions. Specifically, 88% of the sampled soils were alkaline, whereas 12% had a slightly acidic soil reaction (<7). Electrical conductivity values varied between 105.6 and 355.9 μS/cm, suggesting low-to-moderate salinity levels. On the other hand, organic matter (OM) content exhibited a mean of 2.8%, reflecting moderate soil fertility, while the obtained sand (mean 52%) and clay (mean 19%) contents suggested loamy-to-sandy textures.

Table 2.
Physicochemical parameters of the soil samples from Larissa city (mean values of the three-year study, n = 99).
Soil pH ranges from slightly acidic to strongly alkaline values. The proportion of acidic soils is significantly lower than alkaline soils within urban soil environments, as documented by Golia et al. [4], where urban and peri-urban soils worldwide, contaminated mainly with heavy metals, were studied. Electrical conductivity values suggest that no strong fertilizer additions to green areas by the municipal services were observed during sampling [42]. The addition of inorganic and organic fertilizers is known to contribute to the accumulation of salt in soils, altering soil electrical conductivity values [43]. Soil organic matter values are relatively low compared to those found in agricultural soils. However, as suggested by Guo et al. [44], it seems that the presence of organic carbon in urban soils relates directly to the climate crisis and the multiple changes it brings to the environment.
Regarding the heavy metals contents, Table 3 shows the overall results for metal concentrations in the examined urban soils from Larissa city.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics of heavy metal concentrations in urban soils from Larissa city.
Among the studied heavy metals, Zn exhibited the highest contents, followed by Cu, Pb, and Cd. Variations were revealed among the sampling periods, with the studied heavy metals exhibiting significantly (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.05) higher contents during summer. Specifically, the concentrations of Cd ranged from 0.06 to 0.11 mg/kg, with a mean of 0.09 mg/kg (±0.01) in the winter, while a slightly higher mean of 0.10 mg/kg (±0.01) was recorded during summer. Although this difference is statistically significant (p < 0.05), the magnitude of the change is small and may have limited practical or environmental relevance. For Cu, concentrations varied between 32.20 and 56.00 mg/kg, with a mean of 46.31 mg/kg (±5.44) during winter, while in the summer concentrations ranged from 39.60 to 68.40 mg/kg, with an increased mean of 57.33 mg/kg. Similarly, Pb levels increased slightly during summer, ranging from 34.43 to 62.55 mg/kg, with a mean of 48.60 mg/kg (±5.82) compared to the obtained values (mean of 42.62 mg/kg) in winter. Likewise, Zn contents increased to a range from 71.50 to 121.00 mg/kg (mean of 99.80 mg/kg) in summer, compared to a mean of 85.12 mg/kg (±11.75) recorded during winter. Temperature fluctuations in areas located in the Thessalian plain, such as the study area (Larissa city), are subject to extreme temperature variations, which inevitably lead to changes in moisture content. These changes were intensified by the climate crisis, so that an increase in the concentration of heavy metals in the soil during summer was expected. Moreover, weather conditions in summer do not allow for soil resuspension, resulting in the buildup of heavy metals [16]. The obtained heavy metal contents during summer are in agreement with the previous studies. Roy et al. [45], studying the seasonal variations in the pseudo-total concentrations for metals like our work, observed that both in-road dust and urban surface soils have the highest concentrations, and, consequently, the highest ecological risk indicators occurred in the summer months. In their study of twenty-one metals in India, the researchers Thakkar et al. [46] also observed significant seasonal variations in metal levels during the period of higher temperatures as well as the period of higher and more frequent rainfall. The study of Abdullahi et al. [47] on the seasonal variation in toxic elements in maize soils indicated that Zn presence is higher in both dry and wet seasons. A change in the metal level pattern was also seen, with higher levels of the majority of metals appearing to present pollution hazards during the summer months.
The CV values indicate low variability, suggesting sources relatively stable and consistent over time and space, and the absence of localized pollution sources and differences in soil composition across sampling sites. Overall, the concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn were within the safe limits prescribed by the EU.
3.2. GIS Tools—Geostatistical Analyses
Geostatistical analyses and Geographic Information Systems (GISs) serve a fundamental role in assessing and visualizing environmental contamination, particularly in urban soil studies [14]. In this study, GIS-based geostatistical analyses were applied to evaluate the spatial variability of heavy metal contamination in the urban soils of Larissa. The spatial distribution of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn was assessed using the ordinary kriging method, allowing for the generation of thematic maps that illustrate the extent of soil contamination. These maps are presented in Figure 2. Τhematic maps were created based on heavy metal concentrations after a dry period (summer), where higher levels were recorded. Additionally, statistical parameters, such as nugget, sill, and range, were determined and are presented in Table 4. These analyses offer valuable insights into the factors affecting pollution spread and emphasize areas of potential risk for human exposure.

Table 4.
Geostatistical parameters for heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) are utilized to create and validate thematic maps.
The distribution of heavy metals across the sampling area (Figure 2) shows distinct yet overlapping patterns, indicating common contamination sources. Cd concentrations reveal a relatively uniform distribution with most sampling points exhibiting low levels (<0.1 mg/kg). A few locations show slightly elevated values above 0.1 mg/kg, but there are no significant hot spots. Given that Cd is often associated with industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, and atmospheric deposition, its relatively uniform distribution suggests minor contamination sources in this area. On the contrary, Cu concentrations reveal a more varied distribution. Several sampling points, in particular green areas near main roads and intersections (i.e., Triagular Square), show high Cu levels exceeding 60 mg/kg. This pattern suggests that traffic-related activities, such as brake and tire wear, vehicle emissions, and possibly construction activities, contribute to enhanced Cu levels. Areas with moderate concentrations (40–60 mg/kg) are more widespread, indicating diffuse contamination. Pb contents display a somewhat similar pattern to Cu but with no extreme hot spots. Values above 60 mg/kg were revealed only in the Ancient City Theatre, which could be linked to high traffic or even paint residues. Most of the area has Pb levels in the range of 40–60 mg/kg, suggesting widespread but moderate contamination. Zinc distribution follows a similar pattern to Cu and Pb, reinforcing the role of traffic-related pollution.
The spatial distribution of the heavy metals studied suggests that mainly vehicle, bus, and truck traffic, and other anthropogenic activities contribute significantly to soil contamination. Cu, Pb, and Zn showed elevated concentrations in green areas near main roads, emphasizing the impact of transportation emissions and infrastructure on soil quality. Cadmium, being more uniformly distributed, may originate from atmospheric deposition or minor industrial sources. These findings underscore the effectiveness of thematic mapping to urban planning, soil remediation strategies, and public health assessments, as heavy metal contamination can pose risks to human health and the environment.
Thematic maps are a crucial tool for visualizing and assessing heavy metal contamination in urban soils. A comprehensive study conducted in Volos, Greece, between 2018 and 2020, included thematic maps and highlighted higher contamination near heavy traffic roads, the railway station, bus stations, and the commercial port, indicating significant anthropogenic influences on soil quality [48]. Similarly, in Athens, a geochemical mapping project on surface soil samples from playgrounds, schools, and urban parks produced thematic maps within a GIS framework aiding in the identification of potential sources and areas of environmental concern [3]. In Hong Kong, Li et al. [49] produced geochemical maps using GIS technology and revealed significant spatial relationships among certain metals, suggesting common sources of contamination, particularly near road junctions, main roads, and industrial buildings. Such information seems to be reflected in the present study, leading to potential sources of heavy metal pollution in the study area.
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
The health hazards of metal exposure in soil were assessed for each studied soil, considering adults, children, and a soil-pica scenario for children. The resulting HQs and CRs are presented in Table 5. The cumulative HQs during summer sampling, where higher risks were observed, and the average HQs are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively.

Table 5.
Non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks of each element and exposure pathway for urban soils from Larissa city, Greece. Bold: the values above the safe level (=1); underlined: the values close to the safe level (=1).
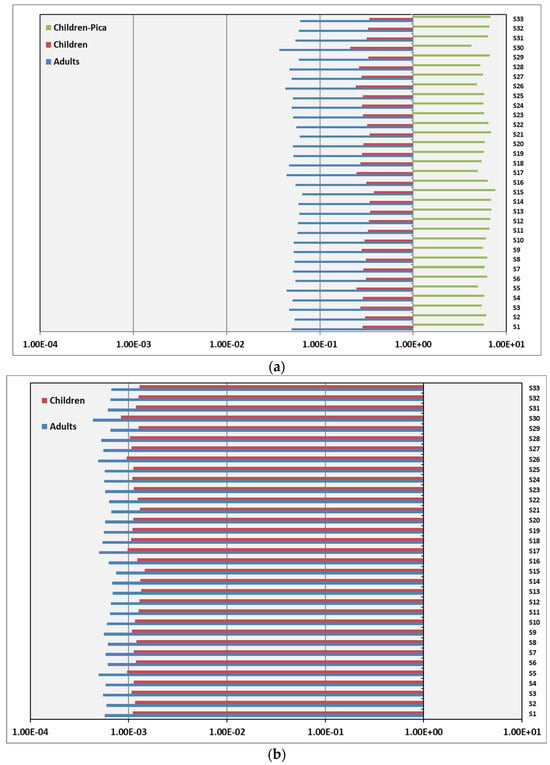
Figure 3.
Cumulative hazard quotient (HQ) of exposure via ingestion (a) and dermal contact (b) to heavy metals during dry-season sampling of urban soils from the city of Larissa.
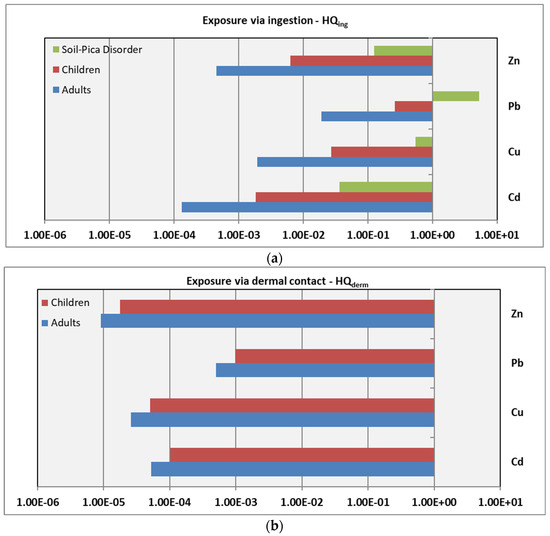
Figure 4.
Average non-carcinogenic health risks (HQs) of exposure via ingestion (a) and dermal contact (b) to heavy metals in urban soils from the city of Larissa.
As expected, based on the EPA model structure, the calculated HQs for both adults and children followed the order: ingestion > dermal contact, reflecting the model’s underlying assumptions that prioritize ingestion as the primary exposure pathway for all the heavy metals studied. Furthermore, the estimated HQs for children were consistently higher than those for adults, which is an expected outcome based on the default exposure parameters of the EPA model (e.g., body weight and intake rates), and is also consistent with the trends reported in previous studies [16,50]. The non-carcinogenic average HQ values exhibited a descending order of Pb > Cu > Zn > Cd for ingestion and Pb > Cd > Cu > Zn for dermal contact for both adults and children. Among the studied heavy metals, Pb exhibited higher non-carcinogenic risks with HQing ranging from 1.35 × 10−2 to 2.45 × 10−2 for adults and from 1.87 × 10−1 to 3.39 × 10−1 for children, while HQderm showed a range from 3.58 × 10−4 to 6.51 × 10−4 for adults and 6.98 × 10−4 to 1.27 × 10−3 for children. In Thessaloniki, Golia et al. [15], who also calculated the risks via ingestion and dermal contact, reported lower HQ values than the corresponding ones in the present research. Nevertheless, the calculated HQs were close or below the safe level (=1), however their proximity to this limit suggests a potential for risk under prolonged or repeated exposure to contaminated urban soils, warranting precautionary attention.
The model estimated non-carcinogenic risks for children exhibiting pica disorder, i.e., an intentional soil ingestion behavior, were significantly higher than the corresponding ones of unintentional ingestion, due to significantly higher ingestion rates used in the risk calculations. Specifically, mean HQs for Cu and Zn were 0.126 and 0.545, respectively, well below the threshold of 1, indicating that continued exposure of children with soil-pica disorder may still cause concern over time, especially when considering the cumulative effects of multiple metals, though not related to cancer. Conversely, HQ values for Pb ranged from 3.74 to 6.79, well above the safe level (=1), suggesting Pb as the dominant health risk contaminant for children diagnosed with a soil-pica disorder. Pb contributed the most (88%) to the cumulative HQ. Our findings are consistent with the findings from urban areas worldwide [51,52]. Pan et al. [21] conducted a large-scale review of heavy metal contamination in Chinese cities and found HI values often exceeding 1 (safe limit) for Pb with children being the most vulnerable population. Similarly, Ghanavati et al. [19] analyzed urban soils in Ahvaz, Iran, and reported HI values of 0.111 and 0.698 for adults and children, respectively, exposed to Pb, suggesting a potential risk of chronic diseases. Pavlović and his colleagues [22] assessed the risk exposure to PTEs via soil for adults and children in some European cities, and though they reported lower HQ values, they also identified Pb as the primary contributor to non-carcinogenic risks. Lead is a toxic, cumulative metal that disrupts the development of the nervous system, making it especially harmful to children. Exposure to Pb can lead to long-lasting learning and behavioral disorders [53]. Therefore, the risk of Pb exposure through intentional or unintentional ingestion must not be underestimated. For carcinogenic risk, the CRs obtained for Cd and Pb were within the acceptable safety limits (10−6 to 10−4).
It is important to acknowledge the limitations associated with the use of EPA risk assessment models in this study. These models are based on standardized exposure parameters and reference doses, many of which are derived from generalized population data and may not fully capture site-specific or population-specific variability. Moreover, the model assumes additive effects for individual metals and does not account for potential synergistic or antagonistic interactions between multiple contaminants. Finally, by using the pseudo-total heavy metal concentrations for conducting risk assessments, we usually overestimate the actual health risks [16].
4. Conclusions
Studying and recording the levels of heavy metals in urban soil environments is of particular importance as knowledge and control of their changes as well as the risks to adults’ and children’s health is necessary. The study area constitutes a special city in the center of Greece since it is located in the center of the Thessaly plain, yet it has a highly urbanized environment, a large number of citizens, and rich peri-urban industrial activity. To this end, a three-year study was conducted in a city in central Greece, and the levels of four metals (Cu, Cd, Pb, and Zn) were studied in two periods each year, one following the summer hot season and the other after the winter cold and rainy season. A thorough study of heavy metal pollution levels in green spaces in the area, as well as the seasonal variation in metal concentrations, is being carried out for the first time. Alongside, health risk levels were calculated for adults, children, and children with pica disorder, considering two scenarios: dermal contact and ingestion. During the summer months, metal accumulation was observed to be higher. Focusing on the calculated non-carcinogenic HQs, the model projected higher health risks for children compared to adults—an outcome influenced by the default exposure assumptions and primarily driven by the contribution of Pb concentrations in the soil. While the measured concentrations are within the acceptable EU guideline values, modeled risk estimates based on specific urban exposure assumptions suggest that long-term vigilance remains important, particularly in areas with vulnerable populations or cumulative exposure concerns. Finally, the thematic maps constructed using Geostatistical Analysis tools, and the database created, are expected to provide a useful guide and a valuable legacy for future research. The data can be updated by ongoing seasonal and spatial analyses, while the mathematical models used can update the depiction of pollution or even predict pollution levels for sustainable and healthy living in the study area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.E.G. and A.B.; methodology, E.E.G., A.B. and H.D.S.; software, S.G.P. and H.D.S.; validation, E.E.G. and A.B.; formal analysis, E.E.G., S.G.P. and V.-S.G.; investigation, E.E.G. and V.-S.G.; resources, E.E.G., A.B. and V.-S.G.; data curation, E.E.G., A.B. and S.G.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B., S.G.P. and V.-S.G.; writing—review and editing, E.E.G. and A.B.; visualization, S.G.P., H.D.S. and V.-S.G.; supervision, E.E.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the Postgraduate Program of the University of Thessaly, entitled: Applied Public Health and Environmental Hygiene. Part of the results come from the post-graduate dissertation of student Violeta-Stefania Gkoltsou.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xu, W.; Jin, Y.; Zeng, G. Introduction of Heavy Metals Contamination in the Water and Soil: A Review on Source, Toxicity and Remediation Methods. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2024, 17, 2404235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, G.; Soktoev, B.; Farkhutdinov, I.; Matveenko, I. Heavy Metals in Urban Soil: Contamination Levels, Spatial Distribution and Human Health Risk Assessment (the Case of Ufa City, Russia). Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyraki, A.; Kelepertzis, E. Urban Soil Geochemistry in Athens, Greece: The Importance of Local Geology in Controlling the Distribution of Potentially Harmful Trace Elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.E.; Bethanis, J.; Xagoraris, C.; Tziourrou, P. Potentially Toxic Elements in Urban and Peri-Urban Soils—A Critical Meta-Analysis of Their Sources, Availability, Interactions, and Spatial Distribution. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazaryan, K.; Agrawal, S.; Margaryan, G.; Harutyunyan, A.; Rajput, P.; Movsesyan, H.; Rajput, V.D.; Singh, R.K.; Minkina, T.; Elshikh, M.S.; et al. Soil Pollution: An Agricultural and Environmental Problem with Nanotechnological Remediation Opportunities and Challenges. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A Review of Heavy Metal Contaminations in Urban Soils, Urban Road Dusts and Agricultural Soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecina, V.; Brtnický, M.; Baltazár, T.; Juřička, D.; Kynický, J.; Vašinová Galiová, M. Human Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Urban Soils of 101 Cities in China: A Meta-Analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binner, H.; Sullivan, T.; Jansen, M.A.K.; McNamara, M.E. Metals in Urban Soils of Europe: A Systematic Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Jadhao, P.S.; Kumar, A.R. Occurrence, Fractionation, and Human Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals in Urban Soils of Different Land Use Types. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.J.; Ogundele, O.D. Hidden Hazards in Urban Soils: A Meta-Analysis Review of Global Heavy Metal Contamination (2010–2022), Sources and Its Ecological and Health Consequences. Sustain. Environ. 2024, 10, 2293239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Ehaliotis, C.; Kalivas, D.; Panagopoulou, G. Concentrations and Availability Indicators of Soil Heavy Metals; the Case of Children’s Playgrounds in the City of Athens (Greece). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyraki, A.; Kelepertzis, E.; Botsou, F.; Paraskevopoulou, V.; Katsikis, I.; Trigoni, M. Environmental Availability of Trace Elements (Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu) in Soil from Urban, Suburban, Rural and Mining Areas of Attica, Hellas. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 187, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Ehaliotis, C.; Gerontidis, S.; Sarris, E. Elevated Heavy Metal Concentrations in Top Soils of an Aegean Island Town (Greece): Total and Available Forms, Origin and Distribution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Gamvroula, D.E. Land Suitability Mapping Using Geochemical and Spatial Analysis Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.E.; Emmanouil, C.; Charizani, A.; Koropouli, A.; Kungolos, A. Assessment of Cu and Zn Contamination and Associated Human Health Risks in Urban Soils from Public Green Spaces in the City of Thessaloniki, Northern Greece. EuroMediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2023, 8, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliva, A.; Kantiranis, N.; Papadopoulou, L.; Aidona, E.; Christophoridis, C.; Kollias, P.; Evgenakis, M.; Fytianos, K. Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Magnetic Susceptibility and Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Road Dusts of Thessaloniki City, Greece: A One-Year Monitoring Period. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P.C. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil-Vegetable System: A Multi-Medium Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, H.B.; Yu, S. Incorporating Bioaccessibility into Human Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Urban Park Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanavati, N.; Nazarpour, A.; De Vivo, B. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Metals in Street Dusts and Surface Soils in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Investigating the Sources and Potential Health Risks of Environmental Contaminants in the Soils and Drinking Waters from the Rural Clusters in Thiva Area (Greece). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A Review of Heavy Metal Pollution Levels and Health Risk Assessment of Urban Soils in Chinese Cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlović, P.; Sawidis, T.; Breuste, J.; Kostić, O.; Čakmak, D.; Đorđević, D.; Pavlović, D.; Pavlović, M.; Perović, V.; Mitrović, M. Fractionation of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Urban Soils from Salzburg, Thessaloniki and Belgrade: An Insight into Source Identification and Human Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koureas, M.; Mellou, K.; Vontas, A.; Kyritsi, M.; Panagoulias, I.; Koutsolioutsou, A.; Mouchtouri, V.A.; Speletas, M.; Paraskevis, D.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Wastewater Levels of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Associated with Influenza-like Illness Rates in Children—A Case Study in Larissa, Greece (October 2022–January 2023). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokouva, M.; Bitsolas, N.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Rachiotis, G.; Papadoulis, N.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Pesticide Exposure and Lymphohaematopoietic Cancers: A Case-Control Study in an Agricultural Region (Larissa, Thessaly, Greece). BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Development Team QGIS Geographic Information System; QGIS: Berne, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.L. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 1st ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390:2005; Soil Quality, Determination of PH. International Standards Organization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2005.
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.E.; Moodie, C.D. Carbonate. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1379–1396. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Child-Specific Exposure Factors Handbook; EPA-600-P-00-002B; National Center for Environmental Assessment; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Super Fund. In Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bierkens, J.; Van Holderbeke, M.; Cornelis, C.; Torfs, R. Exposure Through Soil and Dust Ingestion. In Dealing with Contaminated Sites; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 261–286. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzimavroudis, G.; Christopoulos, P.; Atmatzidis, S.; Papadakis, G.; Nalbanti, P.; Papaziogas, B.; Koutelidakis, I.; Atmatzidis, K. Pica: An Uncommon Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain in Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2011, 78, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotoulaki, M.; Panagopoulou, P.; Efstratiou, I.; Nousia-Arvanitakis, S. Pitfalls in the Approach to Pica. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerontidis, A.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Tzimos, C.; Gkiouras, K.; Taousani, E.; Athanasiadis, L.; Goulis, D.G. Effectors of Pregorexia and Emesis among Pregnant Women: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. OSWER Directive 9200.1-120 and FAQ. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Chabukdhara, M.; Nema, A.K. Heavy Metals Assessment in Urban Soil around Industrial Clusters in Ghaziabad, India: Probabilistic Health Risk Approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Guidance for Evaluating the Oral Bioavailability of Metals in Soils for Use in Human Health Risk Assessment; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Li, R.; Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, W.; Cheng, H.; Lin, C. Contents and Chemical Forms of Heavy Metals in School and Roadside Topsoils and Road-Surface Dust of Beijing. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Yang, G.; Wan, H.; Wu, L. Levels and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Urban Soils in Dongguan, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)—Generic Tables; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ji, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, N. Effect of Different Fertilization on Soil Fertility, Biological Activity, and Maize Yield in the Albic Soil Area of China. Plants 2025, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xie, W.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Li, W. Effect of Different Fertilization Measures on Soil Salinity and Nutrients in Salt-Affected Soils. Water 2023, 15, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Han, J.; Bao, H.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Smith, P.; Abdalla, M. A Systematic Analysis and Review of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Urban Greenspaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Kumari, M.; Kumar, A. Exploring Heavy Metal Dynamics and Risks from Dust and Soil in Urban Cities of Jharkhand, India. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, D.; Valand, M.; Vachhrajani, K. Assessment of Seasonal Variations in Soil Heavy Metal Concentrations and Potential Health Risks in Gujarat, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, N.; Dandago, M.A.; Gambo, M.S.; Abubakar, S.S.; Tsoho, A.U.; Idah, P.G. Heavy Metals Seasonal Variation and Uptake Pattern in Rice Grown in Kano State, Nigeria. J. Agric. Environ. 2024, 20, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanidis, P.-S.C.; Golia, E.E. Urban Sustainability at Risk Due to Soil Pollution by Heavy Metals—Case Study: Volos, Greece. Land 2022, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lee, S.; Wong, S.; Shi, W.; Thornton, I. The Study of Metal Contamination in Urban Soils of Hong Kong Using a GIS-Based Approach. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Shen, Z. Pollution Characteristics, Risk Assessment, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Road Dust in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N. Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and Potential Health Risks Assessment: A Case Study from Semi-Arid Region of South India. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Belyaeva, O.; Maghakyan, N.; Saghatelyan, A. Human Health Risk Assessment and Riskiest Heavy Metal Origin Identification in Urban Soils of Yerevan, Armenia. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, B. Heavy Metals in the Environment; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780824744755. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).