Topographical Discrepancy in Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment from Cornfields in the Licheng District, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Collection
2.2. pH and Organic Matter Analysis
2.3. HMs Analysis
2.4. Pollution and Risk Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
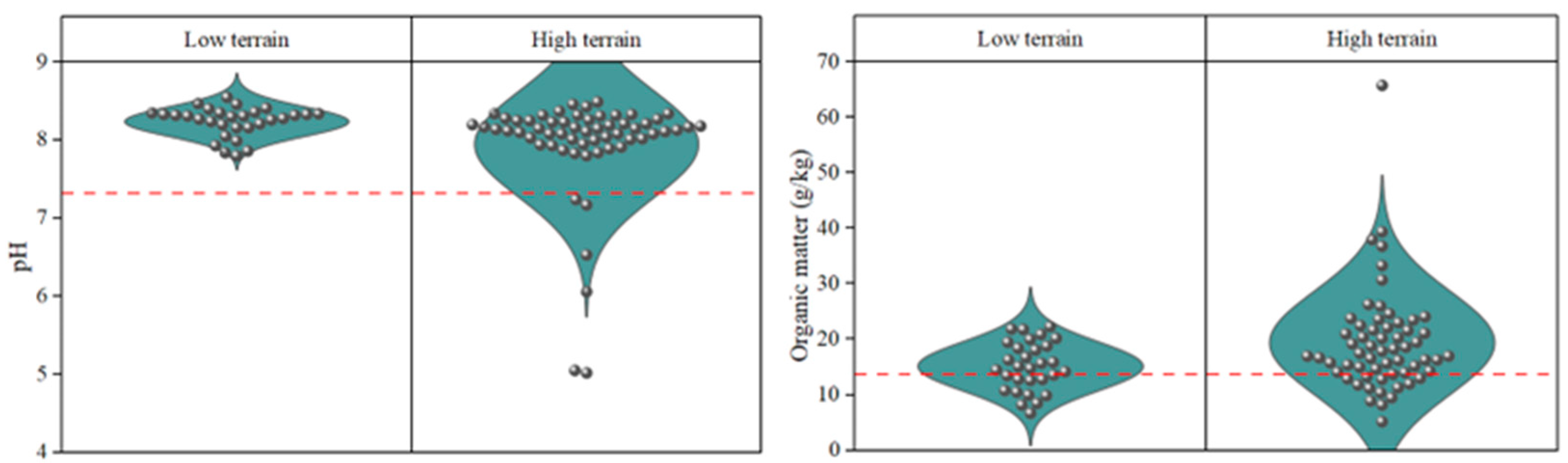
3.1. pH Spatial Distributions
3.2. Organic Matter Spatial Distributions
3.3. HM Spatial Distributions
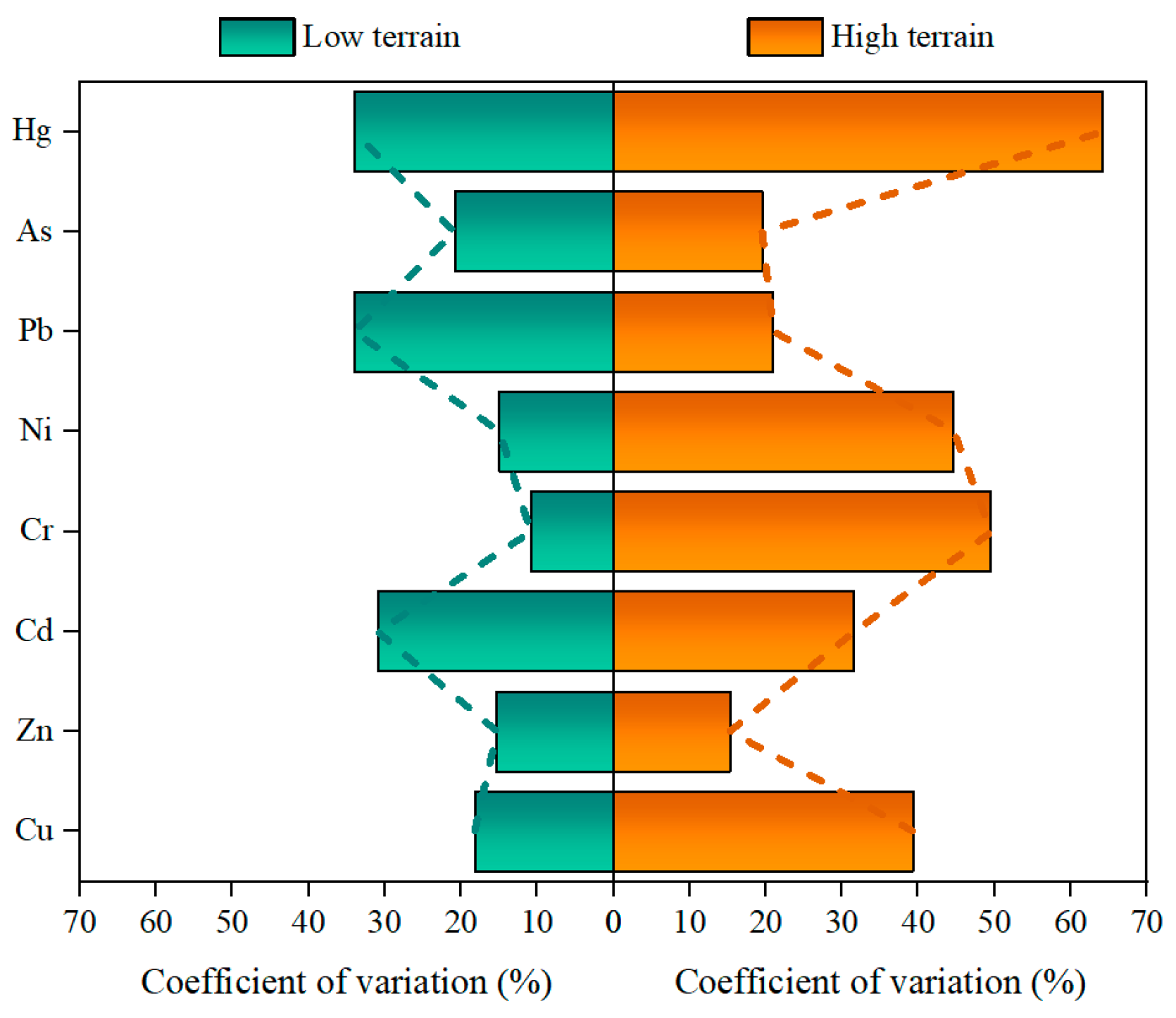
3.4. Soil Physicochemical and Anthropogenic Influences on HM Contamination
4. Discussion
4.1. Source Apportionment of HM Contamination
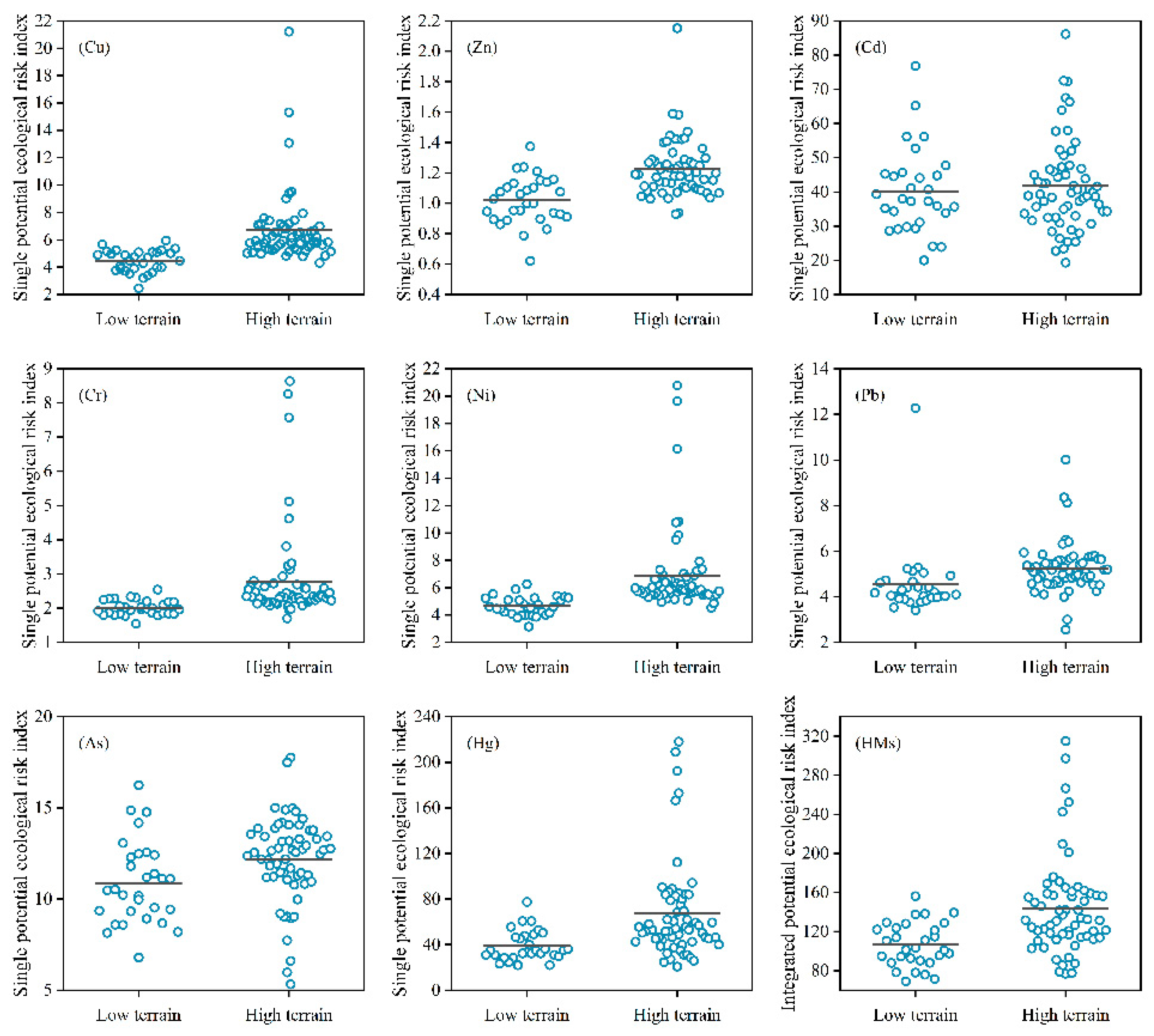
4.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Bai, R. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation: Case Study of Xicheng Lead-Zinc Mining Area. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Sun, J.; Shaghaleh, H.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhai, S.; Hamoud, Y.A. Environmental assessment of soils and crops based on heavy metal risk analysis in Southeastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Ren, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W. Assessment of potentially toxic elements pollution and human health risks in polluted farmland soils around distinct mining areas in China—A case study of Chengchao and Tonglushan. Toxics 2023, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, P.; Dash, S.; Khwairakpam, M.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Ecological and health risk assessment associated with translocation of heavy metals in Lycopersicum esculentum from farmland soil treated with different composts. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Ran, G.; Liu, X. Effects of multi-heavy metal composite pollution on microorganisms around a lead-zinc mine in typical karst areas, southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2023, 262, 115190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, A.; Chen, H. Evaluation of the heavy metal pollution ecological risk in topsoil: A case study from Nanjing, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridas, M.; Kannan, K.; Venugopal, D.; Arumugam, V.; Arumugam, M. Geospatial assessment of variations in the heavy metals and pesticides concentration in the agricultural environment of Kasaragod District, Kerala, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, M.; Darvishiyan, M.; Momeni, M.; Eslami, H.; Fallahzadeh, R.A.; Zarei, A. Ecological risk assessment of trace elements (TEs) pollution and human health risk exposure in agricultural soils used for saffron cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J. Heavy-metal speciation distribution and adsorption characteristics of Cr (VI) in the soil within sewage Irrigation Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Shi, C.; Wang, J. A study of the differences in heavy metal distributions in different types of farmland in a mining area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Perales, N.S.; Escobedo-Pacheco, E.; Maus, D.; Neimaier, A.; Pumi, G. Dataset of metals and metalloids in food crops and soils sampled across the mining region of Moquegua in Peru. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of amendments derived from vermicompost combined with modified shell powder on Cd immobilization in Cd-contaminated soil by multiscale experiments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Xue, W.; Shi, H. Linkage between human population and trace elements in soils of the Pearl River Delta: Implications for source identification and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q. Straw removal or non-removal affects cadmium (Cd) accumulation in soil-rice (Oryza sativa L.) system at different ambient air Cd levels. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, P.; Yang, W. Characteristics, health risk assessment, and transfer model of heavy metals in the soil—Food Chain in cultivated land in Karst. Foods 2022, 11, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatemi-Usman, S.; Akindele, O.; Ayanlade, A.; Perez, M.; Attahiru, I.; Norton, G.; Feldmann, J.; Krupp, E. Trace elements concentrations in soil contaminate corn in the vicinity of a cement-manufacturing plant: Potential health implications. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2003, 33, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ge, S.; Liu, J.; Iqbal, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, R.; Ruan, X.; Wang, Y. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal(oid)s contamination in topsoil around a lead and zinc smelter in Henan Province, Central China. Toxics 2023, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Lin, M.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Gui, H. Environmental geochemical baseline determination and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of typical coal-based cities: A case study of Suzhou City in Anhui Province, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, W. Does land certification increase farmers’ use of organic fertilizer? Evidence from China. J. Land Use Sci. 2023, 18, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W.; Xiang, P.; Ma, L.Q. Heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soil from main grain production regions of China: Bioaccessibility and health risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, N.; Gedik, K.; Wang, J.J. Tea-based biochar-mediated changes in cation diffusion homeostasis in rice grown in heavy metal(loid) contaminated mining soil. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H. Soil heavy metal(loid) pollution and health risk assessment of farmlands developed on two different terrains on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, S.; Ng, J.; Gao, Y.; Peng, C.; He, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z. Pollution characteristics and chronic health risk assessment of metals and metalloids in ambient PM2.5 in Licheng District, Jinan, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Ru, X.; Gu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Han, J. Pollution characteristics, spatial distribution, and evaluation of heavy metal(loid)s in farmland soils in a typical mountainous hilly area in China. Foods 2023, 12, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Xu, S.; Yang, B.; Zeng, G.; Qian, L.; Huang, H.; Ren, S. Contamination, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils surrounding a typical copper tailings pond. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Hu, W.; Zu, Y.; Zhan, F. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmlands and vegetables surrounding a lead-zinc mine in Yunnan Province, China. Soil. Sediment. Contam. 2022, 31, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Meng, W.; Liu, L.; Feng, K.; Yin, C. Spatial distribution and associated risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil surrounding the Ganhe Industrial Park in Qinghai Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zang, K.; He, L.; Wan, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z. Potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in cultivated land based on soil geochemical zoning: Yishui County, North China case study. Water 2021, 13, 3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaiduli, H.; Abliz, A.; Abulizi, A.; Sun, X.; Ye, P. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution and health risks in different functional areas on the northern slope of the eastern Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang, NW China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yang, M. Risk assessment of heavy metal in farmlands and crops near Pb-Zn Mine Tailing Ponds in Niujiaotang, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholley, M.S.; George, L.Y.; Wang, G.; Ullah, S.; Qiao, Z.; Ling, S.; Wu, J.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W. Risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metalloids from typical farmlands provinces in China. Process Saf. Environ. 2023, 171, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Xie, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liang, R. Ecological responses of soil microbial communities to heavy metal stress in a coal-based industrial region in China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, K.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y. Accumulation pattern and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in permafrost-affected agricultural soils in Northeast China. Toxics 2023, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Background values of soil geochemistry in Shandong Province. Shandong Land. Resour. 2018, 34, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Pei, J.; Li, S.; An, T.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.; Xu, P. Temporal and spatial dynamics of soil organic matter and pH in cultivated land of Liaoning province during the past 30 years. Chin. J. Soil. Sci. 2016, 47, 636–644. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wen, L.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Sun, X. Influencing factors of soil organic matter in cultivated land of Daxing District in recent 40 years. Chin. J. Soil. Sci. 2020, 51, 40–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, X. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of old industrial areas—A case study of Shanghai, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, C.; Gao, N. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils at the Northern foot of the Qinling mountains, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.; Yang, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, T.; Dong, N. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, B. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bruun, H.H.C.; He, Y.; Holm, P.E. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yu, R.; Li, N.; Zheng, J.; Yu, Y. Soil quality assessment in farmland of a rapidly industrializing area in the Yangtze Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhi, Y.; Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Zeng, L.; Wu, L. Positive matrix factorization as source apportionment of soil lead and cadmium around a battery plant (Changxing County, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7698–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, C.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.; Qin, M.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Dick, R.P. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Ju, X.; Dinis, F.; Yu, E.; Yu, Z. Source identification and superposition effect of heavy metals (HMs) in agricultural soils at a high geological background area of Karst: A case study in a typical watershed. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Zuo, L.; Fan, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, H.; Qin, Q. Risk and sources of heavy metals and metalloids in dust from university campuses: A case study of Xi’an, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syso, A.I. Distribution Patterns of Chemical Elements in Parent Rocks and Soils of Western Siberia; Izd. SO RAN: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2007; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Huo, A.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nover, D. Heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Fenghe River Basin, China: Assessment and source analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3072–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Li, T. Geographic distribution, source analysis, and ecological risk assessment of PTEs in the topsoil of different land uses around the antimony tailings tank: A case study of Longwangchi tailings pond, Hunan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mao, J.; Tan, J.; Zhong, K.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Gu, X.; Zhang, C. Heavy metal contamination, accumulation, and risk assessment in a paddy field near Pb-Zn mine, in Guangxi Province, China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, F.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, H. Distribution, source investigation, and risk assessment of topsoil heavy metals in areas with intensive anthropogenic activities using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model coupled with self-organizing map (SOM). Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6353–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lan, X.; Yu, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Du, L. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop system based on PMF and evolutionary game theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhai, S. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland in the south of Zhangbei County, Hebei Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, F.N.; Ahmed, M.M.S.; Kabir, M.H.; Shammi, R.S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Sarker, M.E.; Hasan, K.M.M.; Ahammed, M.S.; Bakar, S.M.A.; et al. Enrichment, sources, and distributions of toxic elements in the farming land’s topsoil near a heavily industrialized area of central Bangladesh, and associated risks assessment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Zeng, T. Source apportionment and source-specific risk evaluation of potential toxic elements in oasis agricultural soils of Tarim River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, Z.; He, L. Source identification and health risk assessment of heavy metals with mineralogy: The case of soils from a Chinese industrial and mining city. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 7255–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Deng, L.; Guo, Y.; Guo, G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Huan, Y.; Liang, T. The spatial analysis, risk assessment and source identification for mercury in a typical area with multiple pollution sources in southern China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4057–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ren, L.; Bao, L. Cumulative risk assessment of soil-crop potentially toxic elements accumulation under two distinct pollution systems. Minerals 2022, 12, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandari, A.; Abbasnejad, B. Environmental pollution status and health risk assessment of selective heavy metal(oid)s in Iran’s agricultural soils: A review. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 256, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, W.; Fan, K.; Pei, W.; Liu, S. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the farmland of Tangwang Village, Huainan City, China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, K.; Tuo, X.; Zang, F. Pollution characteristics and probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils across the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Single-Factor Pollution Index a | Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index b | Potential Ecological Risk Index c | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | Pollution Grade | PN | Pollution Grade | Ei | Risk Grade | RI | Risk Grade |
| ≤1 | Clean | ≤0.7 | Clean | <40 | Low risk | <150 | Low risk |
| 1–2 | Potential pollution | 0.7–1 | Warning limit | 40–80 | Moderate risk | 150–300 | Moderate risk |
| 2–3 | Mild pollution | 1–2 | Slight pollution | 80–160 | Considerable risk | 300–600 | High potential risk |
| 3–5 | Moderate pollution | 2–3 | Moderate pollution | 160–320 | High risk | ≥600 | Significantly high risk |
| >5 | Heavy pollution | >3 | Heavy pollution | ≥320 | Serious risk | - | - |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HMs | Cu | Zn | Cd | Cr | Ni | Pb | As | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| contents | 11.09–95.88 | 39.30–136.24 | 0.09–0.38 | 47.93–267.70 | 17.06–112.59 | 12.08–57.93 | 4.58–15.27 | 0.02–0.17 | |
| Low terrain | Mean value | 20.17 | 64.51 | 0.18 | 62.36 | 25.23 | 21.42 | 9.36 | 0.03 |
| Standard deviation | 3.66 | 9.90 | 0.05 | 6.75 | 3.77 | 7.28 | 1.94 | 0.01 | |
| CF | 0.89 | 1.02 | 1.34 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 1.09 | 0.97 | |
| High terrain | Mean value | 30.27 | 77.51 | 0.18 | 85.87 | 37.33 | 24.79 | 10.45 | 0.05 |
| Standard deviation | 11.90 | 11.84 | 0.06 | 42.52 | 16.66 | 5.20 | 2.05 | 0.03 | |
| CF | 1.34 | 1.22 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.05 | 1.21 | 1.68 | |
| t value | 8.40 | 23.78 | 6.81 | 4.92 | 5.14 | 9.47 | 10.73 | 0.30 | |
| HMs | Low Terrain | High Terrain | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| Cu | 0.502 | 0.765 | 0.928 | 0.068 |
| Zn | 0.346 | 0.897 | 0.703 | 0.572 |
| Cd | −0.054 | 0.880 | −0.008 | 0.796 |
| Cr | 0.635 | 0.562 | 0.949 | −0.192 |
| Ni | 0.760 | 0.536 | 0.936 | −0.164 |
| Pb | 0.656 | 0.084 | −0.290 | 0.754 |
| As | 0.762 | 0.441 | −0.620 | 0.428 |
| Hg | 0.849 | 0.036 | −0.011 | 0.543 |
| Variance/% | 39 | 37 | 45 | 26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C. Topographical Discrepancy in Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment from Cornfields in the Licheng District, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104420
Jiang H, Sun W, Liu L, Cao Y, Zhu W, Zhang C. Topographical Discrepancy in Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment from Cornfields in the Licheng District, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104420
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Haiyang, Wenxian Sun, Lian Liu, Yanling Cao, Wenfeng Zhu, and Chao Zhang. 2025. "Topographical Discrepancy in Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment from Cornfields in the Licheng District, China" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104420
APA StyleJiang, H., Sun, W., Liu, L., Cao, Y., Zhu, W., & Zhang, C. (2025). Topographical Discrepancy in Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment from Cornfields in the Licheng District, China. Sustainability, 17(10), 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104420






