Performance Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Gaussian Plume Models: Their Application in the Prairie Grass Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Simulation Setup
2.3. Gaussian Plume Model (GPM)
2.4. ALOHA
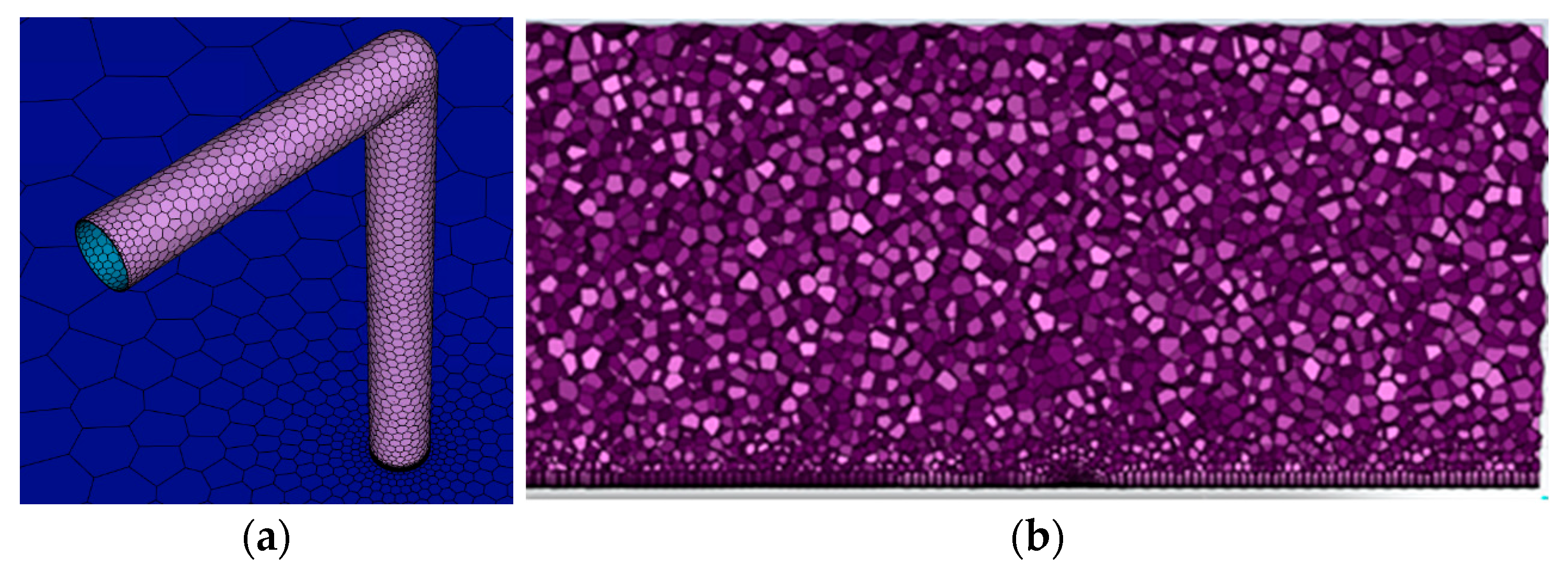
2.5. Gas Dispersion Case in the Presence of Obstacles
3. Results and Discussion
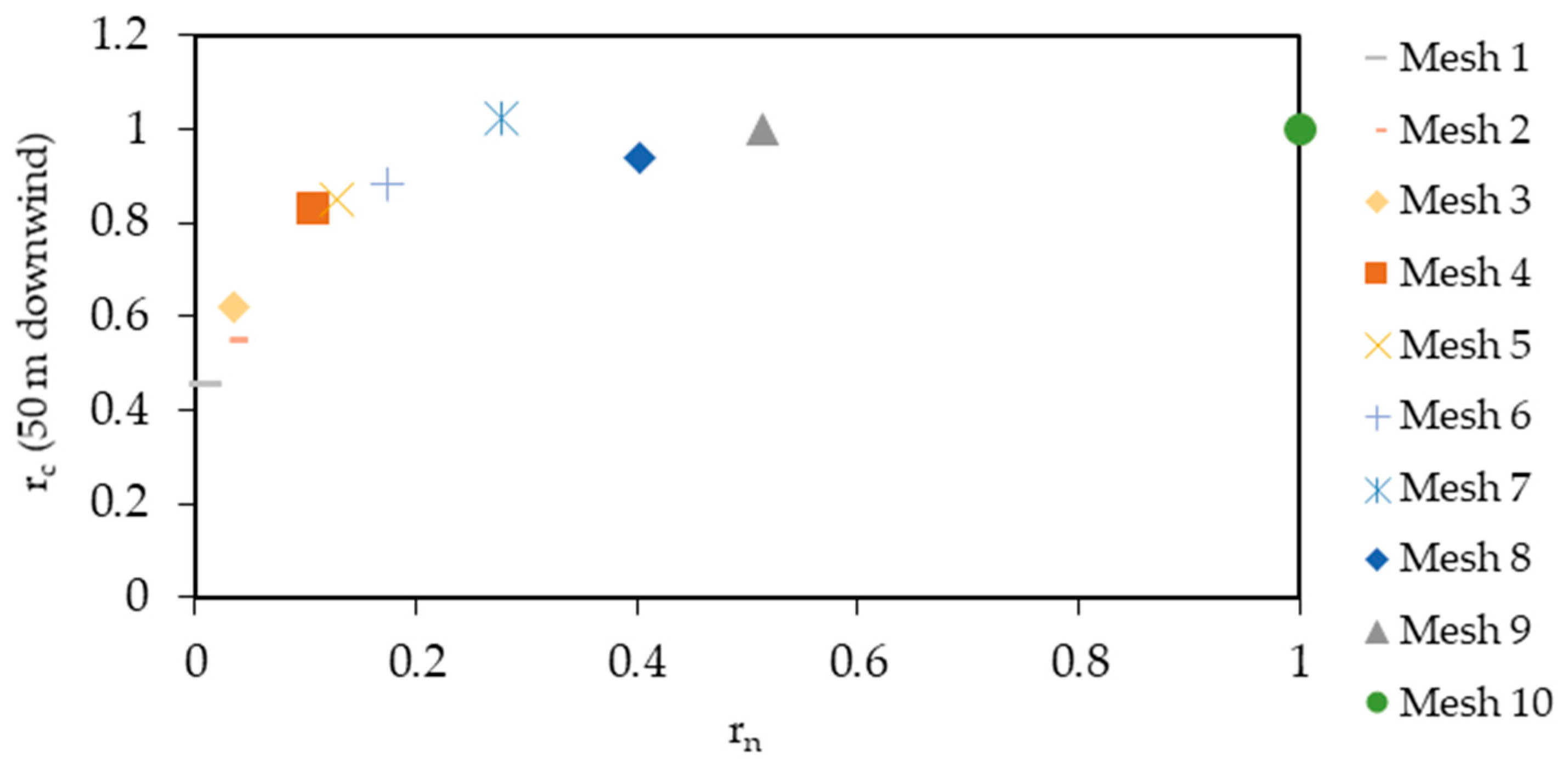
3.1. Mesh Independency
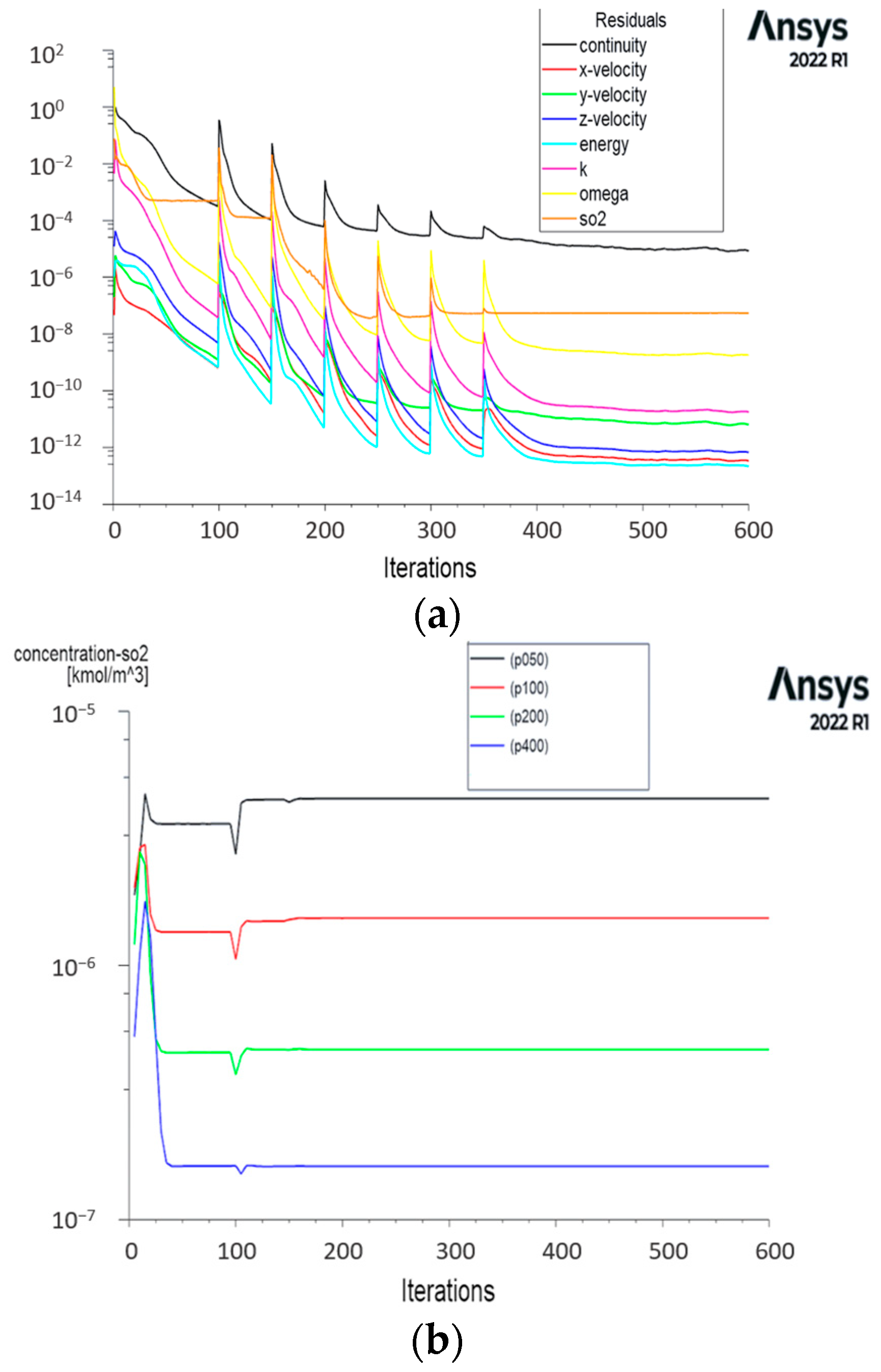
3.2. Convergence Analysis
3.3. Comparison Against Experimental Data
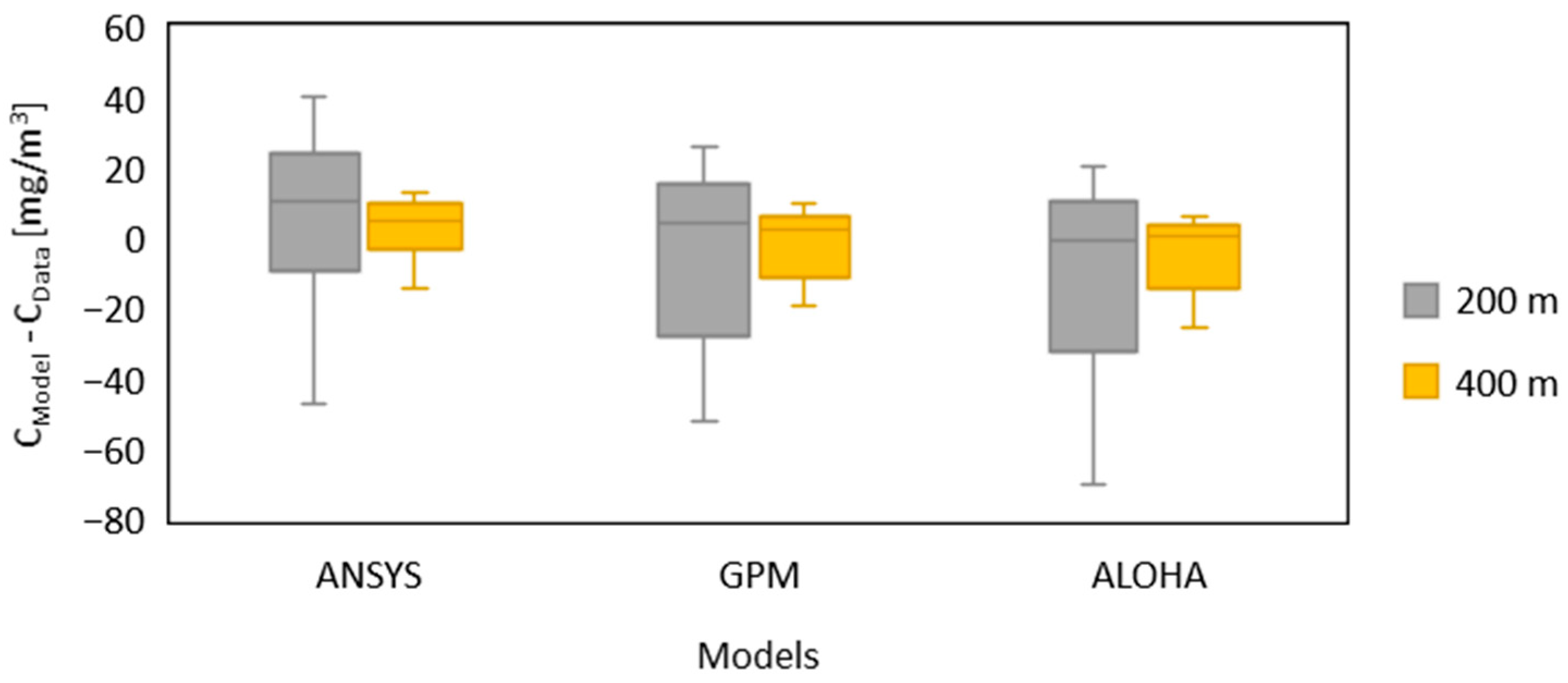
3.4. Model Comparison
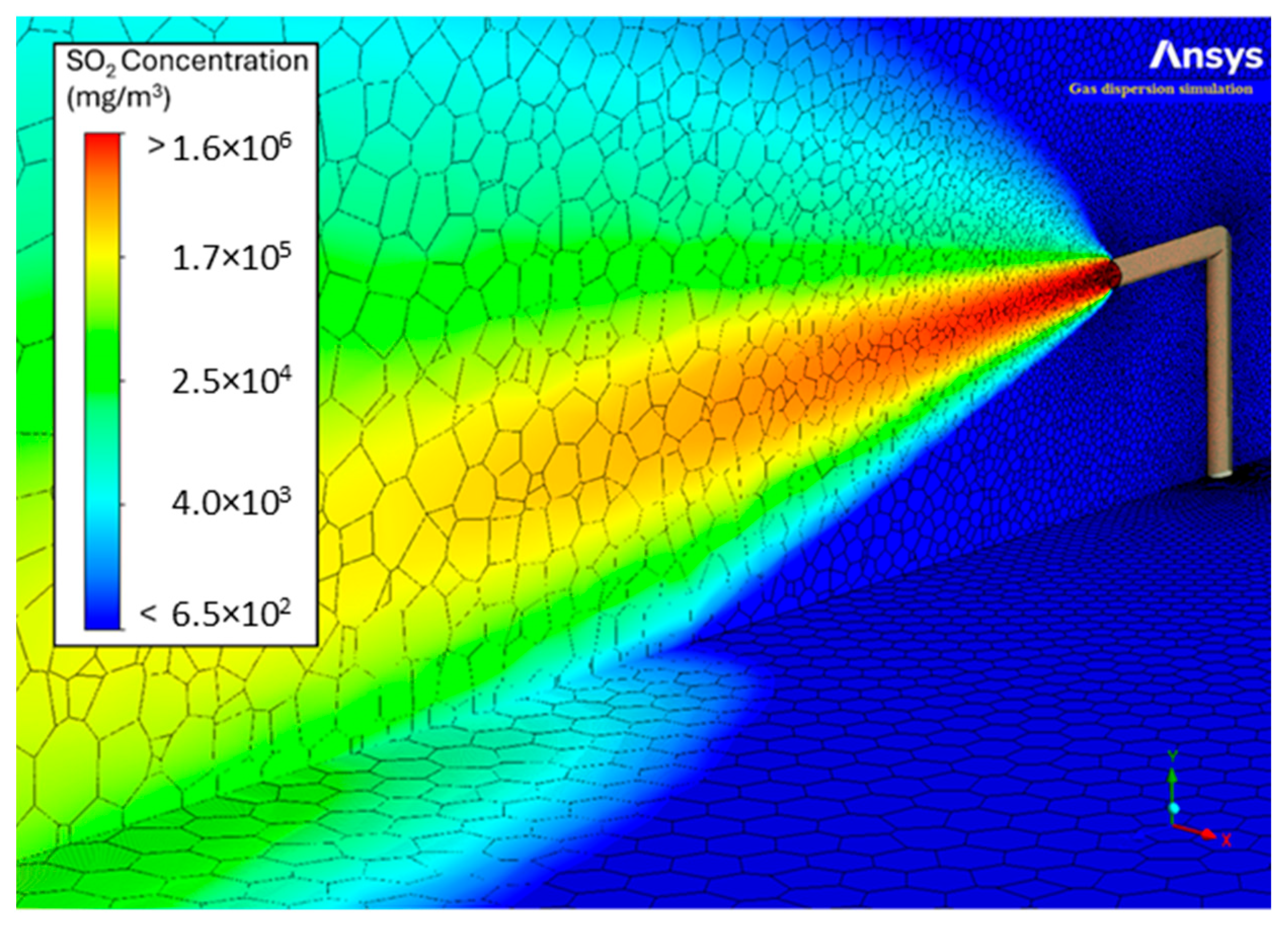
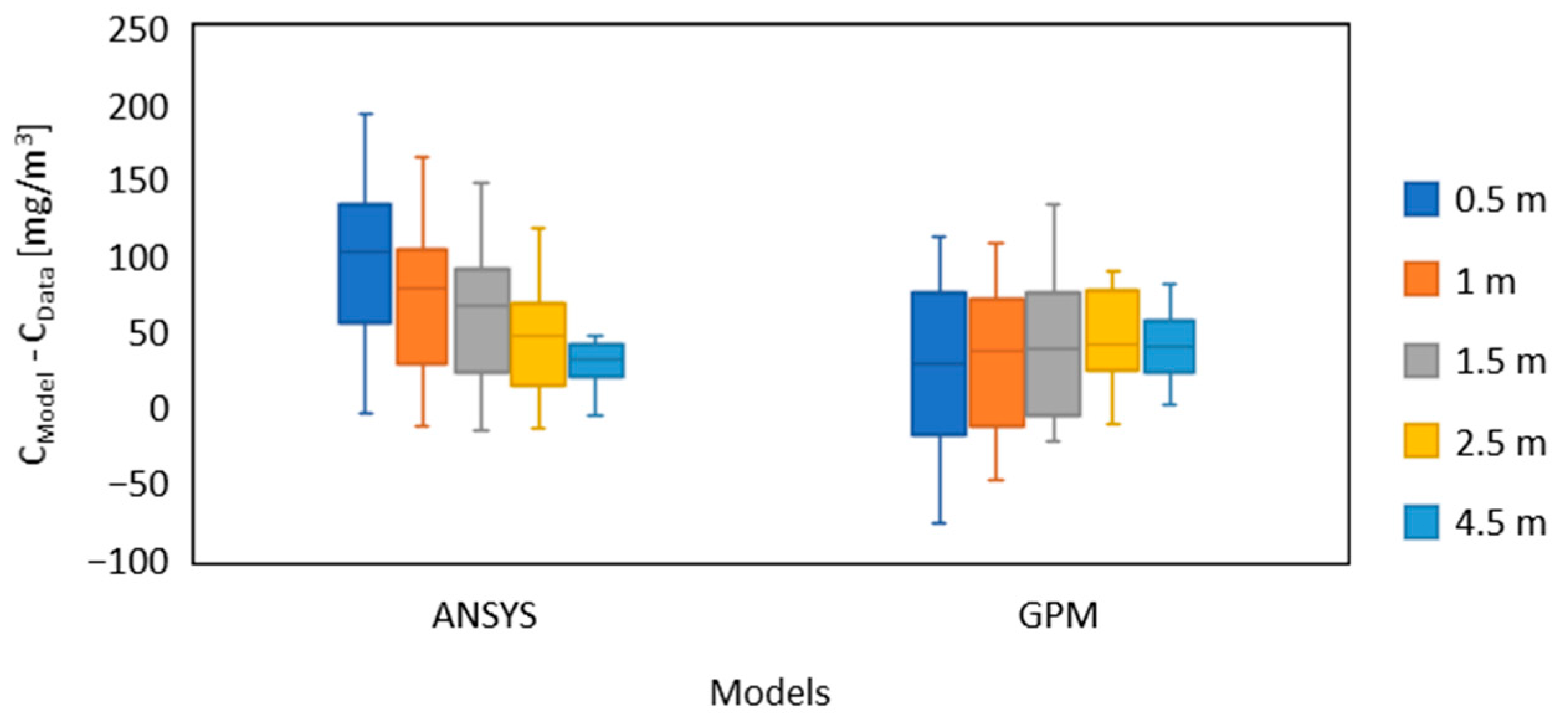
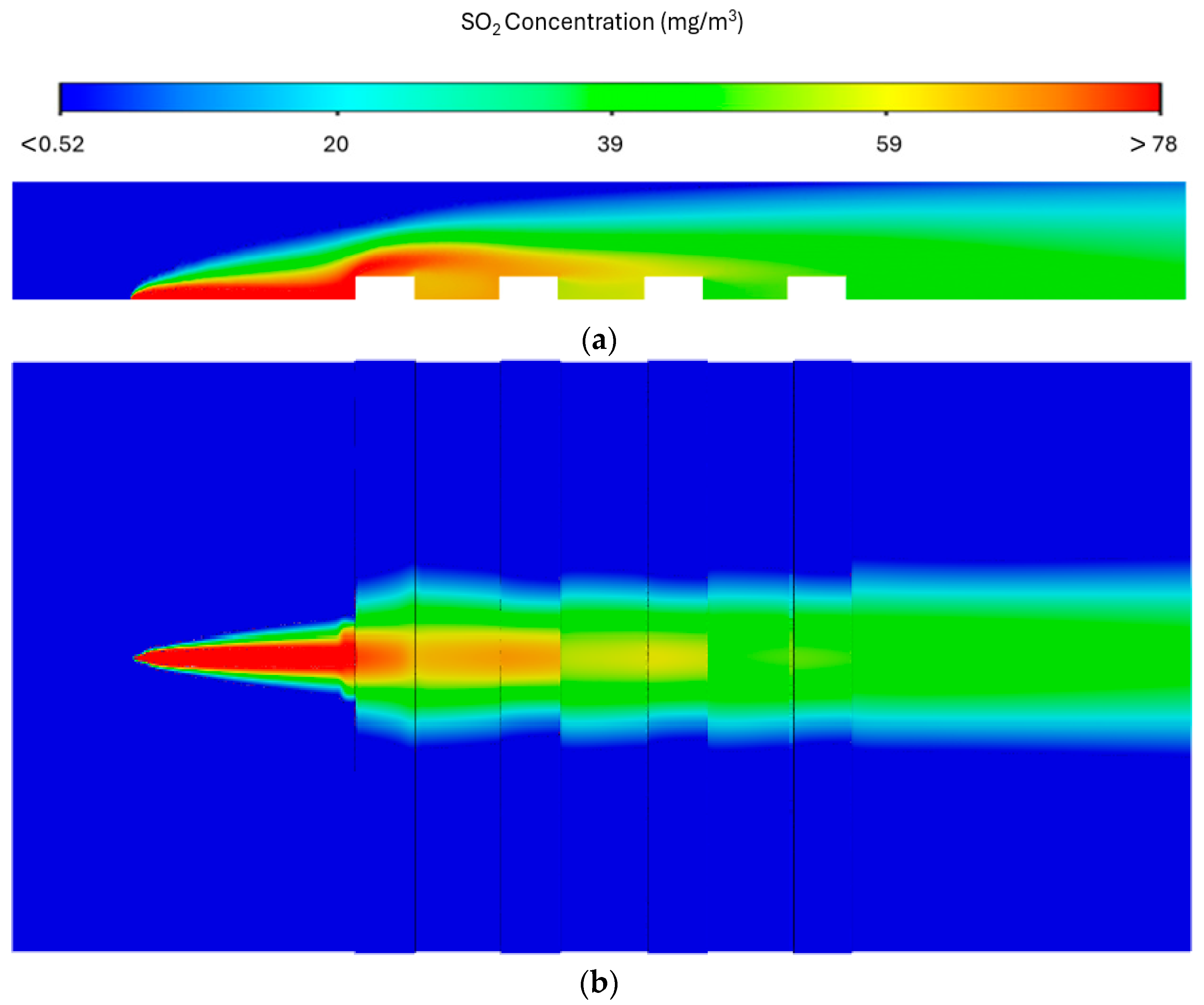
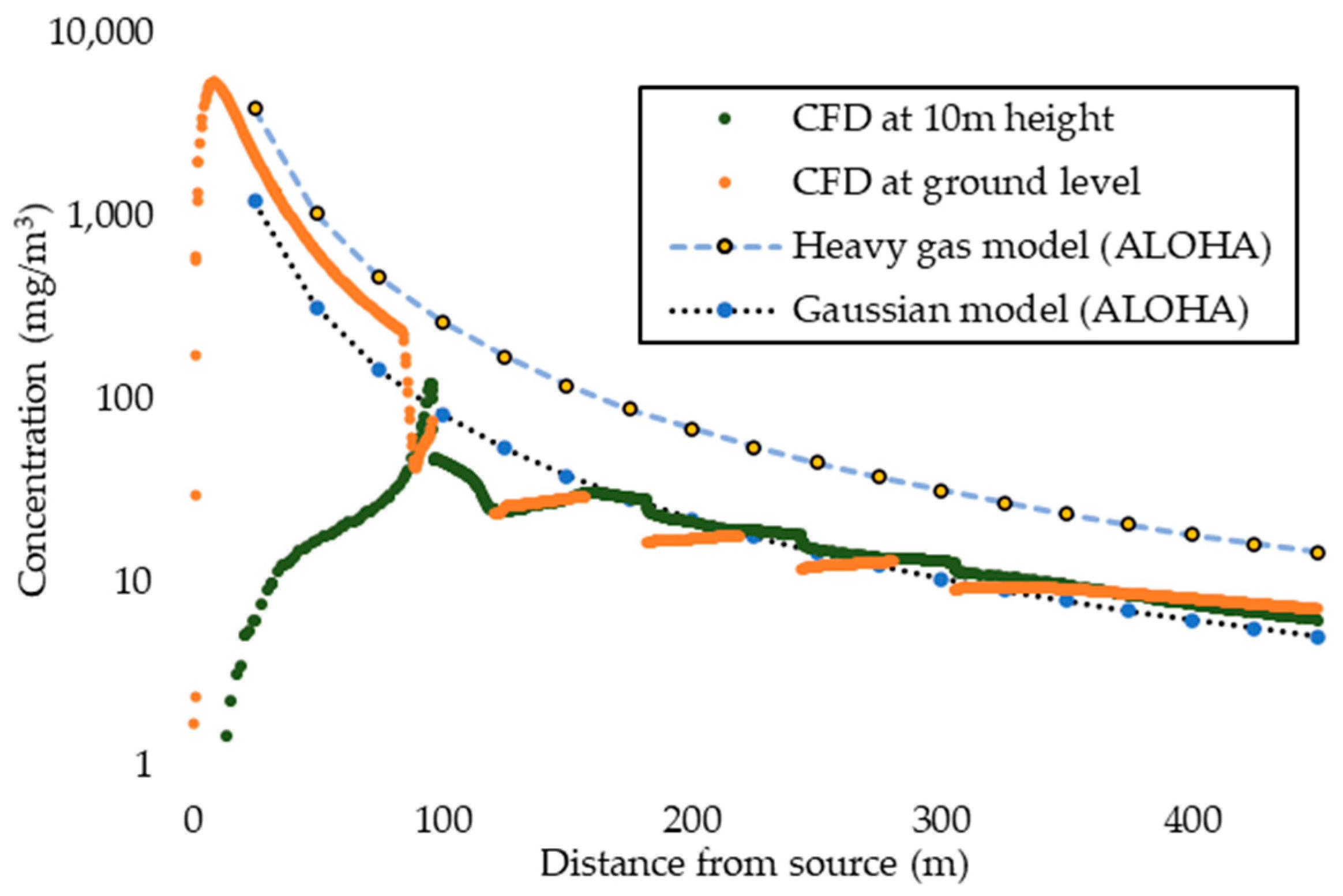
3.5. Results of Gas Dispersion in the Presence of Obstacles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALOHA | Areal Location of Hazardous Atmosphere |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| CRL | Cell Refine Level |
| FAC2 | Fraction of the Prediction Within a Factor of 2 of the Observations |
| GPM | Gaussian Plume Model |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| FB | Fractional Bias |
| NMSE | Normalized Mean Square Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SO2 | Sulphur Dioxide |
| SST | Shear Stress Transport |
References
- EEA. How Air Pollution Affects Our Health; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2024; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/topics/in-depth/air-pollution/eow-it-affects-our-health (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- WHO. Air Pollution: The Invisible Health Threat; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/air-pollution--the-invisible-health-threat (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Newby, D.E.; Manucci, P.M.; Grethe, S.T.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Brook, R.D.; Donaldson, K.; Forastiere, F.; Franchini, M.; Franco, O.H.; Graham, I.; et al. Expert Position Paper on Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J. New Directions: The Growing Urban Heat and Pollution Island Effect-Impact on Chemistry and Climate. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.; Arasa, R.; Codina, B. Aeolian Dust Forecast in Arid and Semiarid Regions of Peru and Chile and Their Contribution over Particulate Matter Concentration. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive-EU-2024/2881-EN-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2024/2881/oj (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Lacome, J.-M.; Leroy, G.; Joubert, L.; Truchot, B. Harmonisation in Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling Approaches to Assess Toxic Consequences in the Neighbourhood of Industrial Facilities. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, G.; Mao, Z. Leak Detection and Localization in Multi-Grid Space Using Improved Gaussian Plume Model. Sensors 2023, 23, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelőssy, Á.; Molnár, F.; Izsák, F.; Havasi, Á.; Lagzi, I.; Mészáros, R. Dispersion Modeling of Air Pollutants in the Atmosphere: A Review. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2014, 6, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.C.; Hanna, S.R. Modelers’ Data Archive. A Collection of Atmospgeric Transport and Dispersion Data Sets. In Proceedings of the 16th AMS Conference on Air Pollution Meteorology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- George Mason University. Field Data Sets. Available online: http://camp.cos.gmu.edu/FieldDatasetInventory.htm (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Irwin, J.S. Project Prairie Grass—Atmospheric Transport and Diffusion Data Archive. Available online: https://www.harmo.org/jsirwin/PrairieGrassDiscussion.html (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Lu, J.; Huang, M.; Wu, W.; Wei, Y.; Liu, C. Application and Improvement of the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm in Source-Term Estimations for Hazardous Release. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatram, A.; Thé, J. Introduction to Gaussian Plume Models. In Air Quality Modeling—Theories, Methodologies, Computational Techniques, and Available Databases and Software; Zannetti, P., Ed.; The EnviroComp Institute and the Air & Waste Management Association: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.K.; Kabir, G.; Khan, M.S.A. Development of a Consequence-Based Decision-Making Framework for Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2022, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, J.; Miao, H. An Integrated Solution for Nuclear Power Plant On-Site Optimal Evacuation Path Planning Based on Atmospheric Dispersion and Dose Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). ALOHA® (Areal Locations of Hazardous Atmospheres) 5.4.4: Technical Documentation; NOAA: Seattle, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Terzioglu, L.; Iskender, H. Modeling the Consequences of Gas Leakage and Explosion Fire in Liquefied Petroleum Gas Storage Tank in Istanbul Technical University, Maslak Campus. Process Saf. Prog. 2021, 40, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Micallef, C. The Gaussian Plume Model Equation for Atmospheric Dispersion Corrected for Multiple Reflections at Parallel Boundaries: A Mathematical Rewriting of the Model and Some Numerical Testing. Sci 2024, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boikos, C.; Rapkos, N.; Ioannidis, G.; Oppo, S.; Armengaud, A.; Siamidis, P.; Tsegas, G.; Ntziachristos, L. Factors affecting pedestrian-level ship pollution in port areas: CFD in the service of policy-making. Build. Environ. 2024, 258, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakchotanon, P.; Veawab, A.; Aroonwilas, A.; Sema, T. Atmospheric Dispersion of Gaseous Amine Emitted from Absorption-Based Carbon Capture Plants in Saskatchewan, Canada. Energies 2022, 15, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D.; Hoch, S.W.; Horel, J.D.; Charland, A. Relationship between Particulate Air Pollution and Meteorological Variables in Utah’s Salt Lake Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuval; Tritscher, T.; Raz, R.; Levi, Y.; Levy, I.; Broday, D.M. Emissions vs. Turbulence and Atmospheric Stability: A Study of Their Relative Importance in Determining Air Pollutant Concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udina, M.; Rosa Soler, M.; Arasa, R. Effects of Nocturnal Thermal Circulation and Boundary Layer Structure on Pollutant Dispersion in Complex Terrain Areas: A Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 48, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.R.; Arasa, R.; Merino, M.; Olid, M.; Ortega, S. Modelling Local Sea-Breeze Flow and Associated Dispersion Patterns Over a Coastal Area in North-East Spain: A Case Study. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 140, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemel, C.; Burns, P. Pollutant Dispersion in a Developing Valley Cold-Air Pool. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, H. Risk Assessment for an Acetone Storage Tank in a Chemical Plant in Istanbul, Turkey: Simulation of Dangerous Scenarios. Process Saf. Prog. 2021, 40, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Rashid, Z.A.; El-Harbawi, M.; Al-Awadi, A.S. High-Pressure Methanol Synthesis Case Study: Safety and Environmental Impact Assessment Using Consequence Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 8555–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, J.F.; García-Ros, G.; Castro, E. Simultaneous Determination of the Position, Release Time and Mass Release Rate of an Unknown Gas Emission Source in Short-Term Emissions by Inverse Problem. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee Barjoee, S.; Elmi, M.R.; Talebi Varaoon, V.; Keykhosravi, S.S.; Karimi, F. Hazards of Toluene Storage Tanks in a Petrochemical Plant: Modeling Effects, Consequence Analysis, and Comparison of Two Modeling Programs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4587–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouilleau, Y.; Champassith, A. CFD Simulations of Atmospheric Gas Dispersion Using the Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS). J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2009, 22, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węsierski, T.; Piec, R.; Majder-łopatka, M.; Król, B.; Gawroński, W.; Kwiatkowski, M. Hazards Generated by an LNG Road Tanker Leak: Field Investigation of Vapour Propagation Under Class B Conditions of Atmospheric Stability. Energies 2021, 14, 8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, W.; Long, J.; Wang, S.; Tan, D.; Yin, Z. Performance and Emission Evaluation of a Marine Diesel Engine Fueled with Natural Gas Ignited by Biodiesel-Diesel Blended Fuel. Energy 2022, 256, 124662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Zealand. Ministry for the Environment. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (N.Z.); Aurora Pacific (Firm); Earth Tech (Firm) Good Practice Guide for Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling; Ministry for the Environment: Wellington, New Zealand, 2004; ISBN 0478189419. [Google Scholar]
- Gant, S.E.; Tucker, H. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modelling of Atmospheric Dispersion for Land-Use Planning around Major Hazards Sites in Great Britain. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2018, 54, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bao, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Du, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, B. A CFD Model Based on Wet Deposition of Large-Scale Natural Draft Cooling Tower. Rev. Int. De Contam. Ambient. 2019, 35, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys. Engineering Simulation Software. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/ (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Gianfelice, M.; Aboshosha, H.; Ghazal, T. Real-Time Wind Predictions for Safe Drone Flights in Toronto. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Arasa, R.; Pérez-Foguet, A.; Ángeles González, M. Simulating Large Emitters Using CMAQ and a Local Scale Finite Element Model. Analysis of the Surroundings of Barcelona. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 62, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, M.; Pilla, F.; McNabola, A. Enhancing ventilation in street canyons using adjustable roof-level wind flow de-flectors. Energy Built Environ. 2025, 6, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, L. A Study on Street Tree Planting Strategy in Pingtan Island Based on Road Wind Environment Simulation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Lang, J.; Li, M.; Mao, S.; Hu, F.; Xuan, B. Impact of Inlet Boundary Number and Locations on Gas Diffusion and Flow in a Typical Chemical Industrial Park near Uneven Terrain. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleder, A.M.; Martins, M.R. Experimental Data and CFD Performance for CO2 Cloud Dispersion Analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 43, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarti-Guillem, M.S.; Hoyas, S.; García-Raffi, L.M. Rocket Plume URANS Simulation Using OpenFOAM. Results Eng. 2019, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synylo, K.; Krupko, A.; Zaporozhets, O.; Makarenko, R. CFD Simulation of Exhaust Gases Jet from Aircraft Engine. Energy 2020, 213, 118610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José, R.; Pérez, J.L.; Pérez, L.; Gonzalez Barras, R.M. Effects of Climate Change on the Health of Citizens Modelling Urban Weather and Air Pollution. Energy 2018, 165, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjalić, K.; Kenjereš, S. Dynamic Simulation of Pollutant Dispersion Over Complex Urban Terrains: A Tool for Sustainable Development, Control and Management. Energy 2005, 30, 1481–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójtowicz-Wróbel, A.; Kania, O.; Kocewiak, K.; Wójtowicz, R.; Dzierwa, P.; Trojan, M. Thermal-Flow Calculations for a Thermal Waste Treatment Plant and CFD Modelling of the Spread of Gases in the Context of Urban Structures. Energy 2023, 263, 125952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, B.; Dang, W.; Yan, X.; Yu, J.; Bai, Y. Dispersion Characteristics and Hazard Area Prediction of Mixed Natural Gas Based on Wind Tunnel Experiments and Risk Theory. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 152, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; Panin, M.P. Use of Computational Fluid Dynamics Tools to Calculate the Dispersion of Gas and Aerosol Emissions in Conditions of a Complex Terrain. Nucl. Energy Technol. 2021, 7, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.N.; Ali, M.E.; Rahman, M.M.; Hossain, M.N.; Molla, M.M. Simulation of Air Pollution Dispersion in Dhaka City Street Canyon. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 065022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.; Coburn, M.; Cox, S.J.; Bulot, F.M.J.; Xie, Z.-T.; Vanderwel, C. Comparing Large-Eddy Simulation and Gaussian Plume Model to Sensor Measurements of an Urban Smoke Plume. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.T.; Costa Reis, N., Jr.; Meri Santos, J.; Valentim Goulart, E.; Engel de Alvarez, C. The Impact of Urban Block Typology on Pollutant Dispersion. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 210, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.T.; Reis, N.C.; Santos, J.M.; Goulart, E.V.; de Alvarez, C.E. Influence of Urban Form on Air Quality: The Combined Effect of Block Typology and Urban Planning Indices on City Breathability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Vaidya, U.; Ganapathysubramanian, B. Contaminant Source Identification from Finite Sensor Data: Perron–Frobenius Operator and Bayesian Inference. Energies 2021, 14, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, D. Simulation Study on Gas Leakage Law and Early Warning in a Utility Tunnel. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scire, J.S.; Strimaitis, D.G.; Yamartino, R.J. A User’s Guide for the CALPUFF Dispersion Model; Earth Technology Inc.: Cedar City, UT, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jittra, N.; Pinthong, N.; Thepanondh, S. Performance Evaluation of AERMOD and CALPUFF Air Dispersion Models in Industrial Complex Area. Air Soil Water Res. 2015, 8, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L. Barad Project Prairie Grass; Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories: Bedford, UK, 1958; Volume I and II. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, G.M. Quantitative Risk Analysis of Toxic Gas Release Caused Poisoning—A CFD and Dose-Response Model Combined Approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; You, R. Evaluating different categories of turbulence models for calculating air pollutant dispersion in street canyons with generic and real urban layouts. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2024, 255, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Fluent Theory Guide; ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2022.
- Guevara Luna, F.A.; Guevara Luna, M.A.; Belalcázar Cerón, L.C. CFD modeling and validation of tracer gas dispersion to evaluate self-pollution in School Buses. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenFOAM: User Guide: AtmBoundaryLayer. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/latest/doc/guide-bcs-inlet-atm-atmBoundaryLayer.html (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Martin, D.O. Comment On “The Change of Concentration Standard Deviations with Distance”. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1976, 26, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Resources Laboratory. READY Tools—Pasquill Stability Classes. Available online: https://www.ready.noaa.gov/READYpgclass.php (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- ALOHA. Office of Environment, Health, Safety & Security. Department of Energy. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/ehss/aloha (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. ALOHA (Areal Locations of Hazardous Atmospheres). Available online: https://www.oit.va.gov/Services/TRM/ToolPage.aspx?tid=9015 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Ermak, D.L. User’s Manual for SLAB: An Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Denser-Than-Air-Releases; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL): Livermore, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation, 6th ed.; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H.; Gersten, K. Boundary-Layer Theory, 8th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, H.R.; Berkowicz, R.; Løfstrøm, P. Evaluation of OML and AERMOD. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Cambridge, UK, 2–5 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, A.; Schalau, B.; Schmidt, D. Comparing Tools of Varying Complexity for Calculating the Gas Dispersion. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.). Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals. Volume 8. 9-Sulfur Dioxide; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; ISBN 0309145163. [Google Scholar]
- INSST. Documentación Toxicológica Para El Establecimiento Del Límite de Exposición Profesional Del Dióxido de Azufre; INSST: Madrid, Spain, 2014. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]




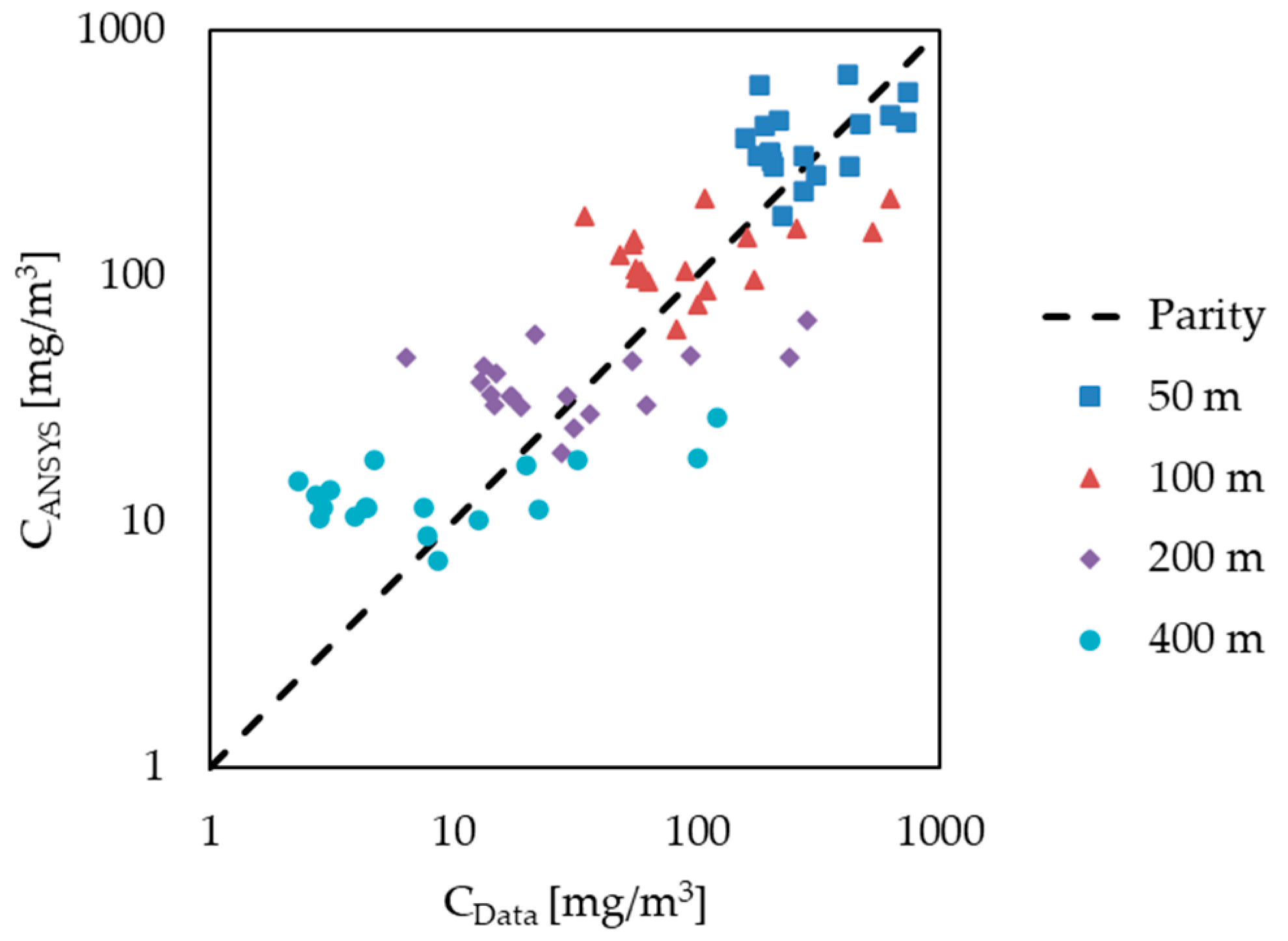
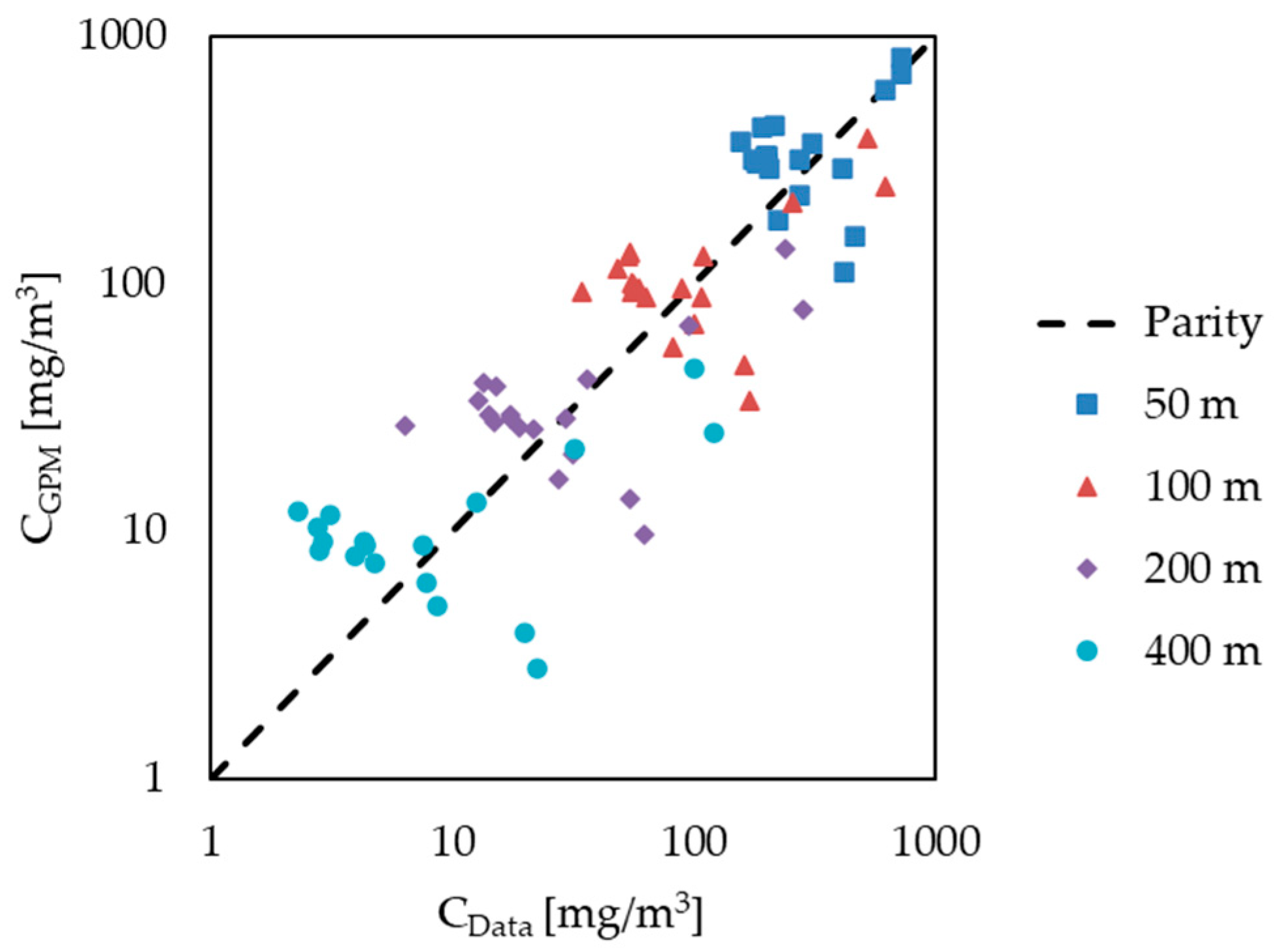
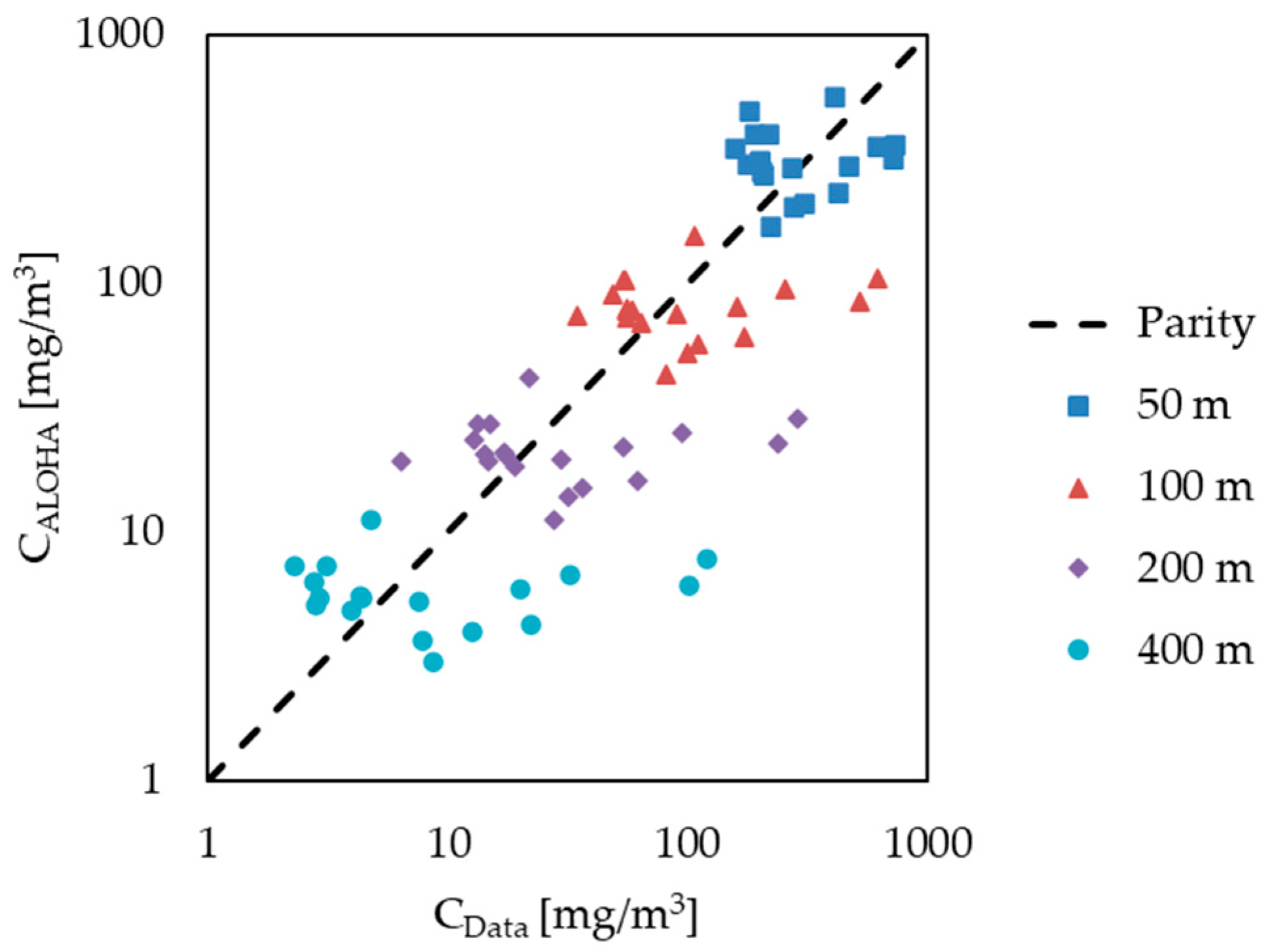


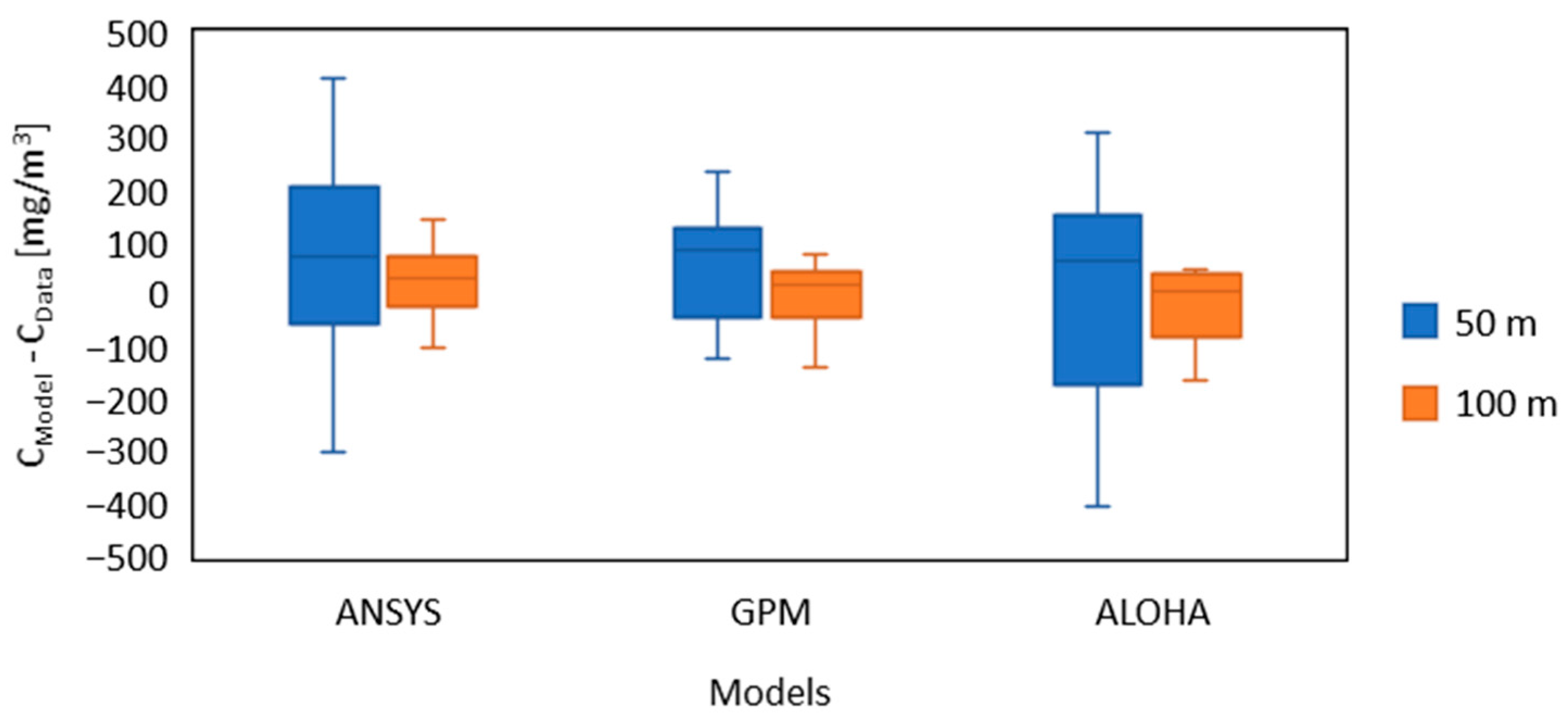

| Parameter | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Length | 500 | m |
| Width | 250 | m | |
| Height | 50 | m | |
| Prairie Grass emission pipe [59] | Height | 0.46 | m |
| Diameter | 0.0508 | m |
| Mesh Name | Max Sizing [m] | Ground Surface Sizing [m] | Inflation Layers | Refinement Criteria | Nodes (106) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh 1 | 5 | 5 | - | - | 1.1 |
| Mesh 2 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 4.3 |
| Mesh 3 | 3 | 3 | - | 10−6 | 4.6 |
| Mesh 4 | 2.56 | 1 | 5 | - | 13.7 |
| Mesh 5 | 2.56 | 1 | 10 | - | 16.5 |
| Mesh 6 | 2.56 | 1 | 20 | - | 22.3 |
| Mesh 7 * | 2.56 | 1 | 10 | 10−7 | 35.6 |
| Mesh 8 | 2.56 | 0.5 | 10 | - | 51.7 |
| Mesh 9 | 2.56 | 0.5 | 10 | 10−6 | 66.0 |
| Mesh 10 | 2.56 | 0.5 | 10 | 10−7 | 128.7 |
| Method | MAE (mg/m3) | RMSE (mg/m3) | FB | FAC2 | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSYS CFD | 61 | 99 | 0.16 | 0.64 | 0.58 |
| GPM | 54 | 87 | 0.088 | 0.60 | 0.49 |
| ALOHA | 63 | 107 | −0.051 | 0.61 | 0.85 |
| Method | 50 m | 100 m | 200 m | 400 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSYS CFD | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.41 |
| GPM | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.41 |
| ALOHA | 0.74 | 0.82 | 0.56 | 0.35 |
| Method | MAE (mg/m3) | RMSE (mg/m3) | FB | FAC2 | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANSYS CFD | 63 | 115 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 2.74 |
| GPM | 43 | 95 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 2.05 |
| Measurement Height | ANSYS CFD | GPM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | NMSE | FB | NMSE | |
| 0.5 m | 0.16 | 1.8 | −0.086 | 1.6 |
| 1 m | 0.11 | 1.8 | 0.009 | 1.3 |
| 1.5 m | 0.10 | 1.5 | 0.081 | 0.9 |
| 2.5 m | 0.31 | 0.9 | 0.41 | 0.5 |
| 4.5 m | 0.72 | 0.8 | 0.80 | 1.0 |
| 7.5 m | 1.02 | 1.7 | 0.91 | 1.4 |
| 10.5 m | 1.07 | 1.8 | 0.60 | 1.0 |
| 13.5 m | 1.03 | 1.5 | 0.077 | 0.68 |
| 17.5 m | 0.93 | 1.3 | −0.70 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabello, R.; Troyano Ferré, C.; Plesu Popescu, A.E.; Bonet, J.; Llorens, J.; Arasa Agudo, R. Performance Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Gaussian Plume Models: Their Application in the Prairie Grass Project. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104403
Cabello R, Troyano Ferré C, Plesu Popescu AE, Bonet J, Llorens J, Arasa Agudo R. Performance Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Gaussian Plume Models: Their Application in the Prairie Grass Project. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104403
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabello, Ruben, Carles Troyano Ferré, Alexandra Elena Plesu Popescu, Jordi Bonet, Joan Llorens, and Raúl Arasa Agudo. 2025. "Performance Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Gaussian Plume Models: Their Application in the Prairie Grass Project" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104403
APA StyleCabello, R., Troyano Ferré, C., Plesu Popescu, A. E., Bonet, J., Llorens, J., & Arasa Agudo, R. (2025). Performance Evaluation of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Gaussian Plume Models: Their Application in the Prairie Grass Project. Sustainability, 17(10), 4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104403








