Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
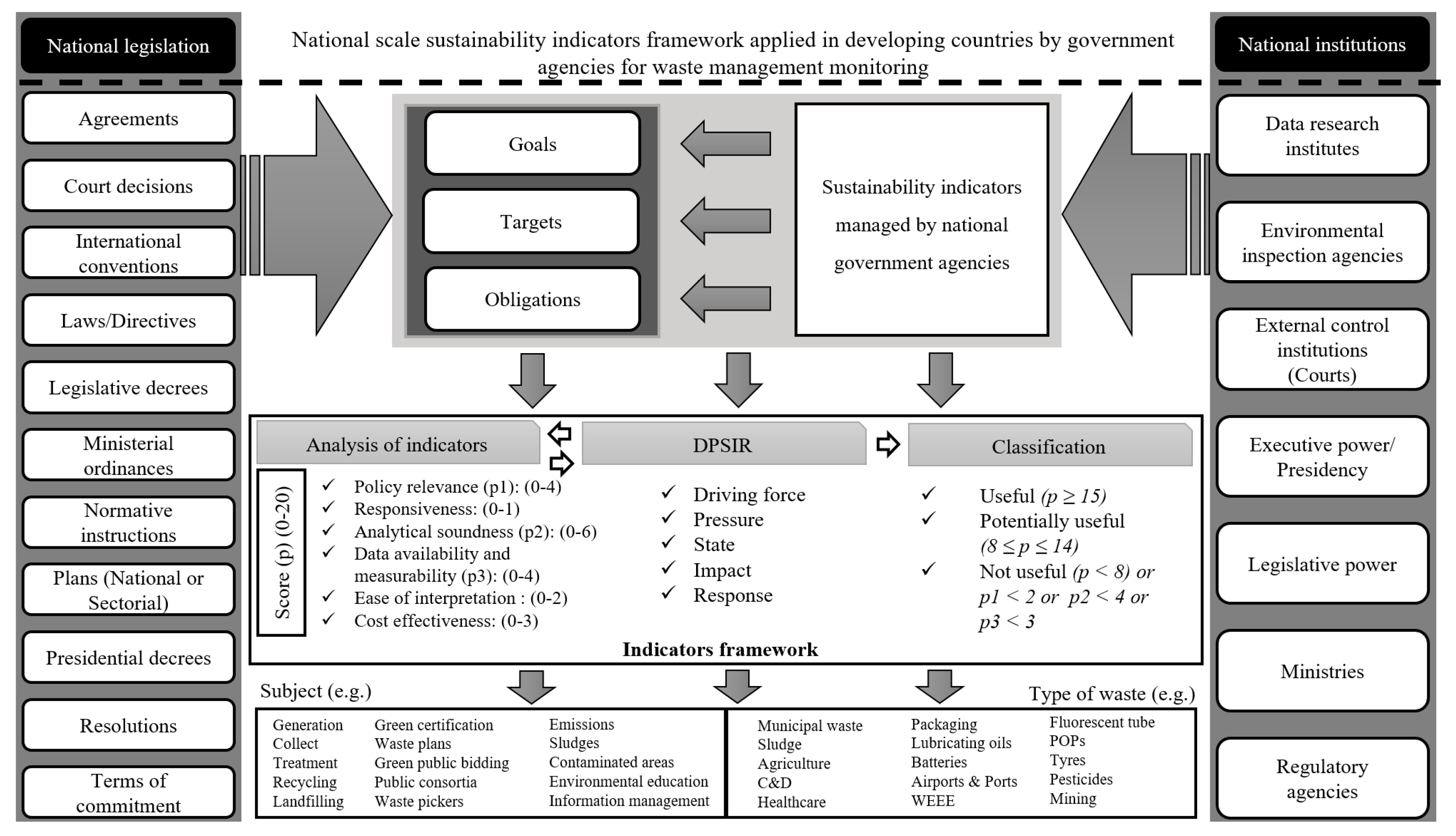
2.1. Evaluation Framework
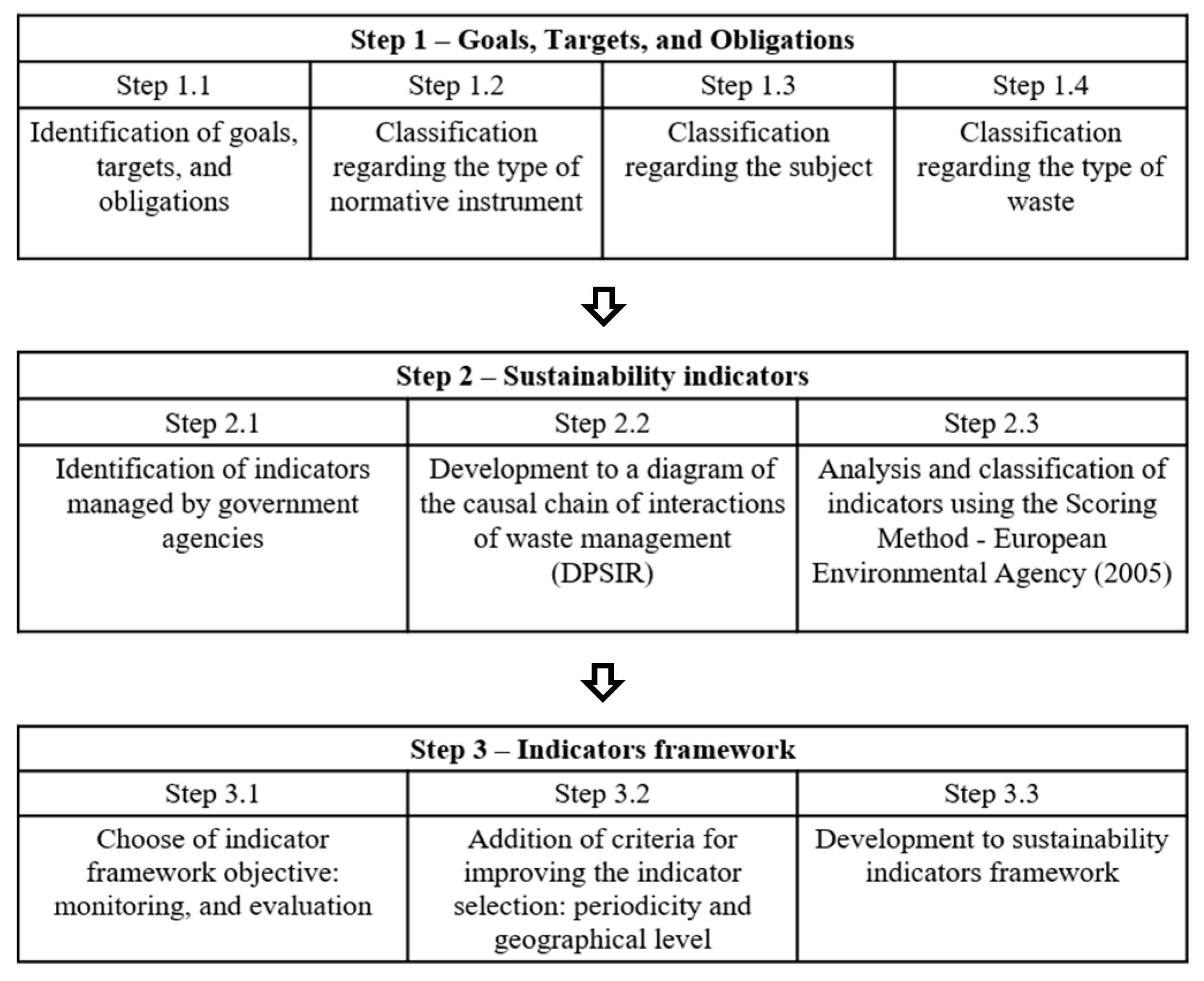
2.2. Selection of Sustainability Indicators
2.2.1. Step 1: Goals, Targets, and Obligations
2.2.2. Step 2: Sustainability Indicators in Waste Management
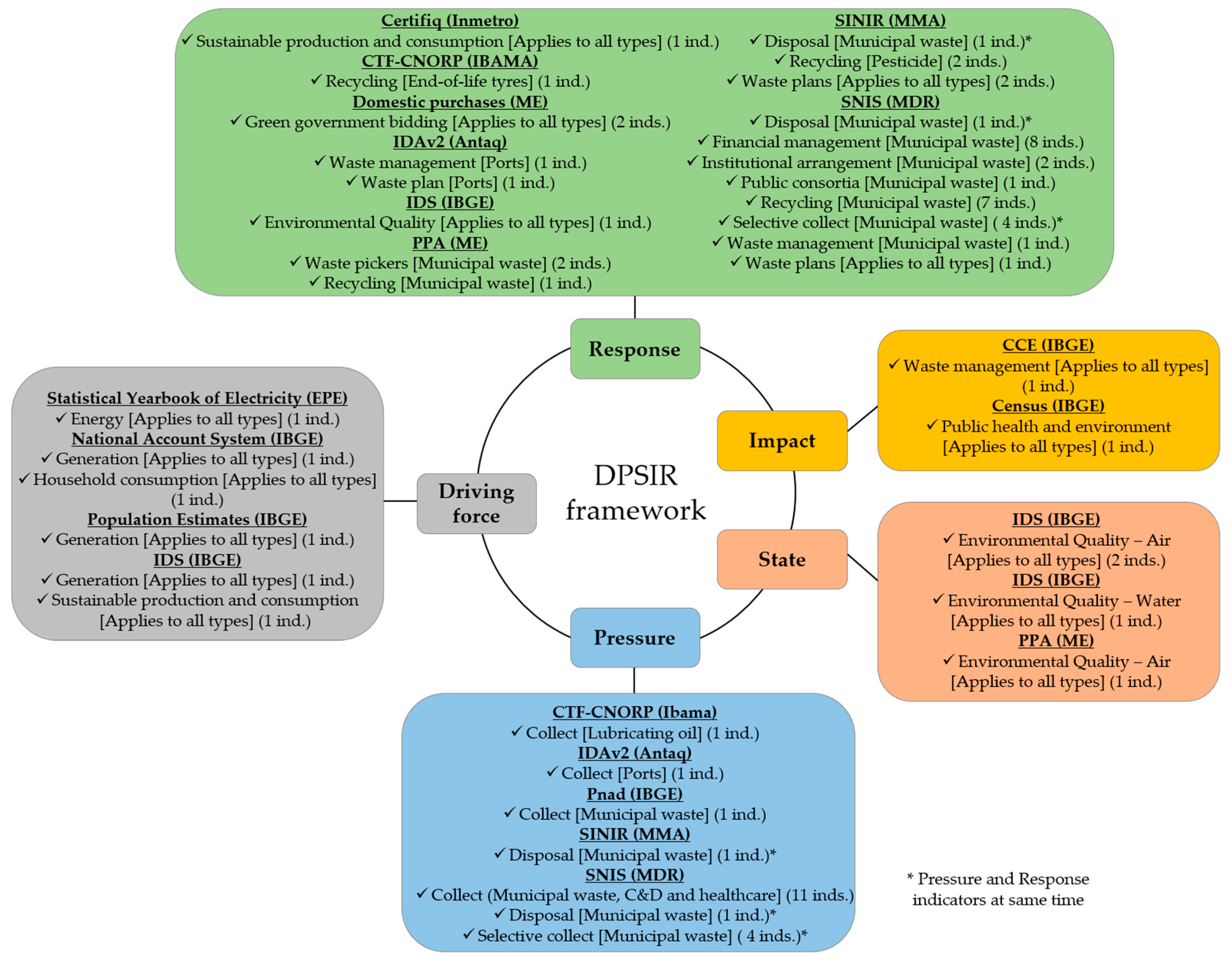
2.2.3. Step 3: Indicators Framework
3. Results and Discussion
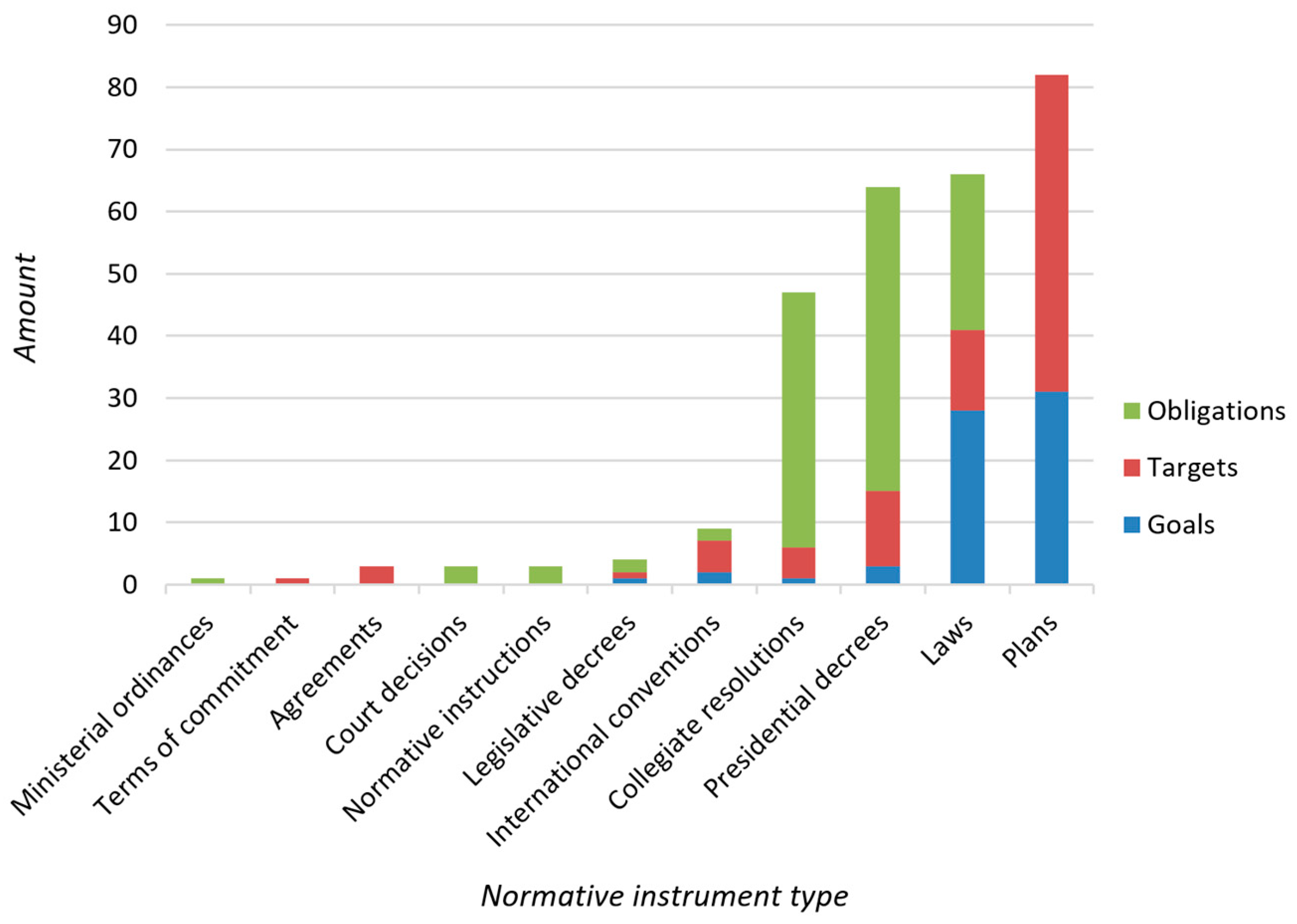
3.1. Goals, Targets, and Obligations
3.1.1. Identification of Goals, Targets, and Obligations
3.1.2. Goals, Targets, and Obligations Regarding the Type of Normative Instrument
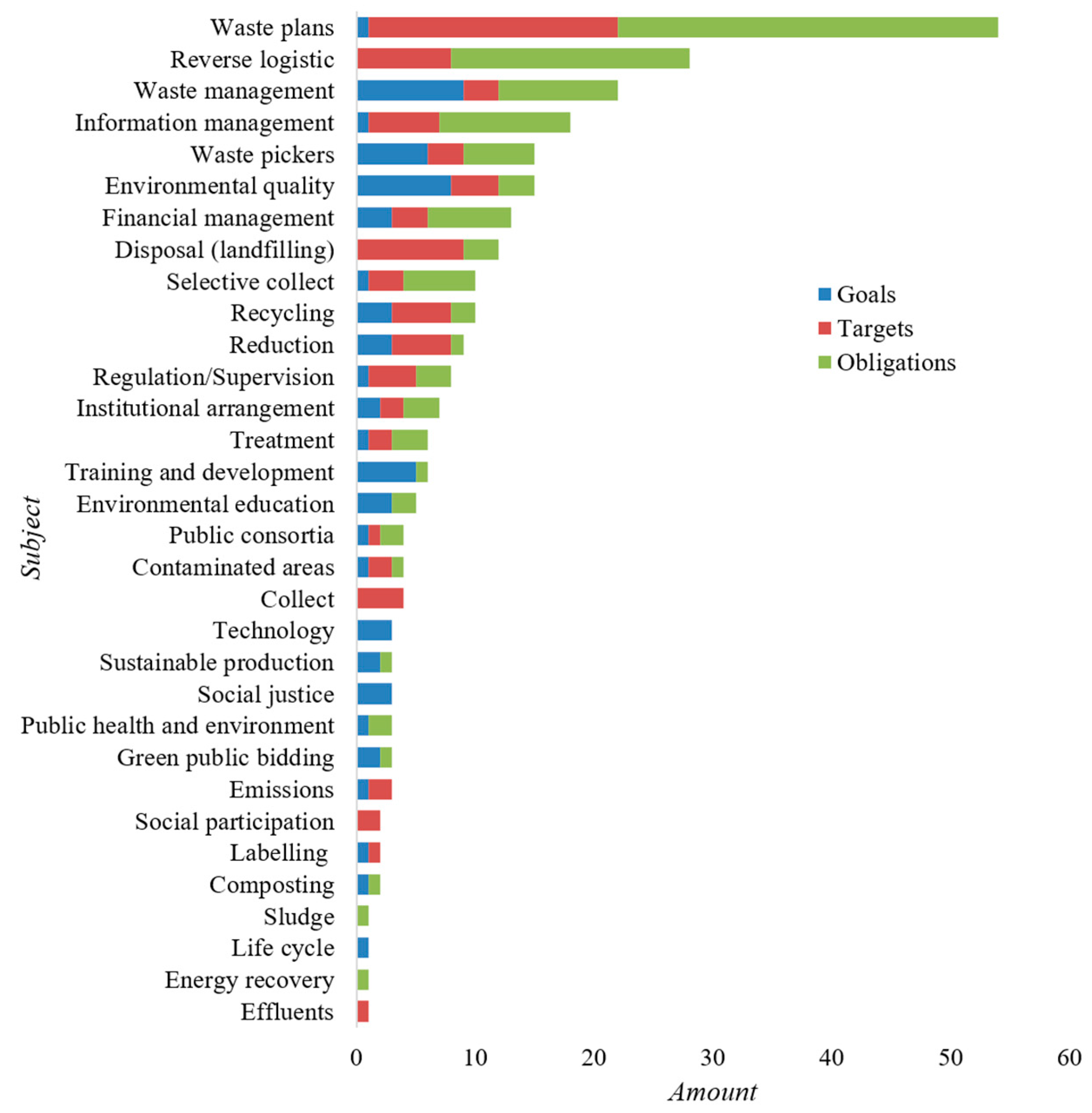
3.1.3. Goals, Targets, and Obligations Regarding the Subject
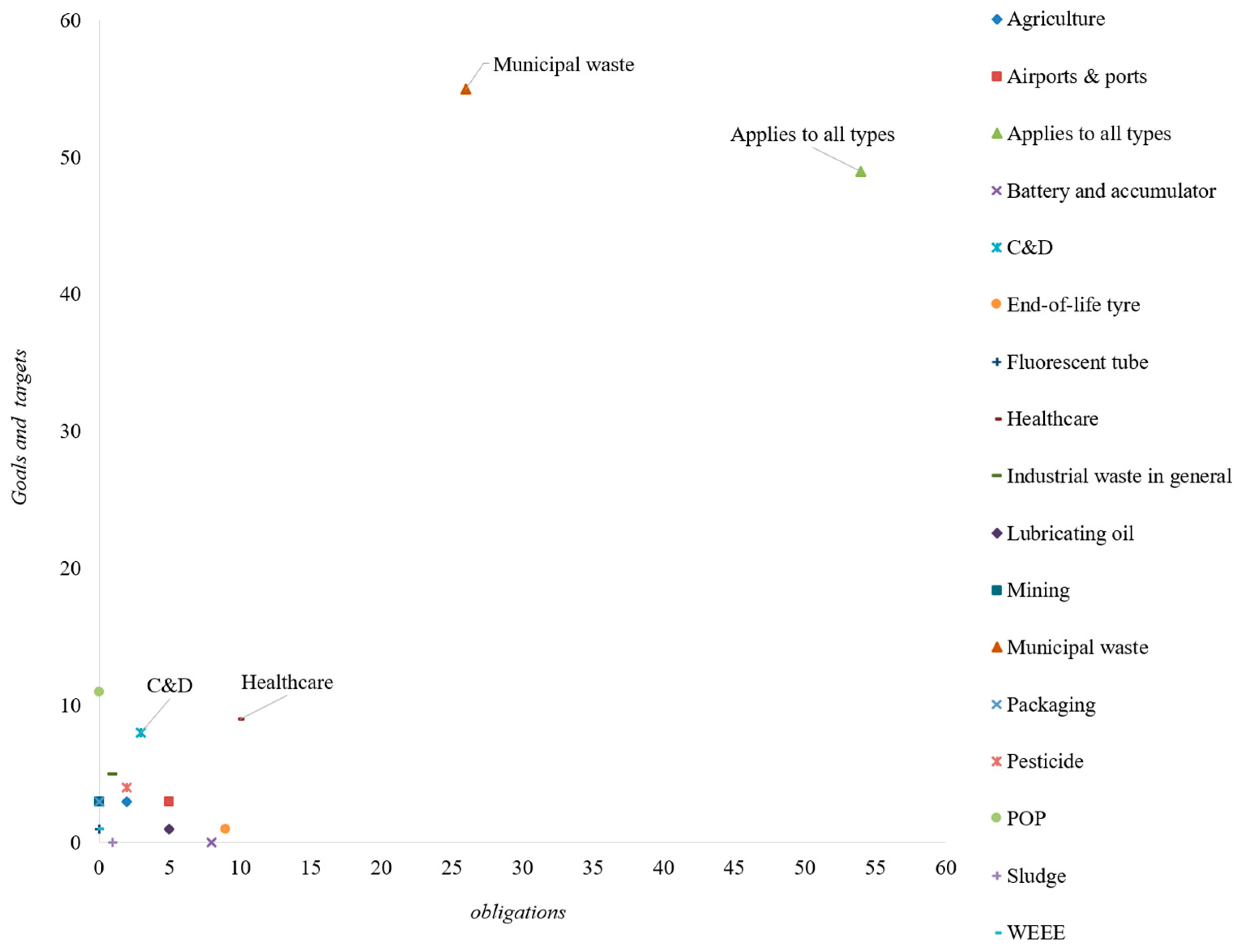
3.1.4. Goals, Targets, and Obligations Regarding the Type of Waste
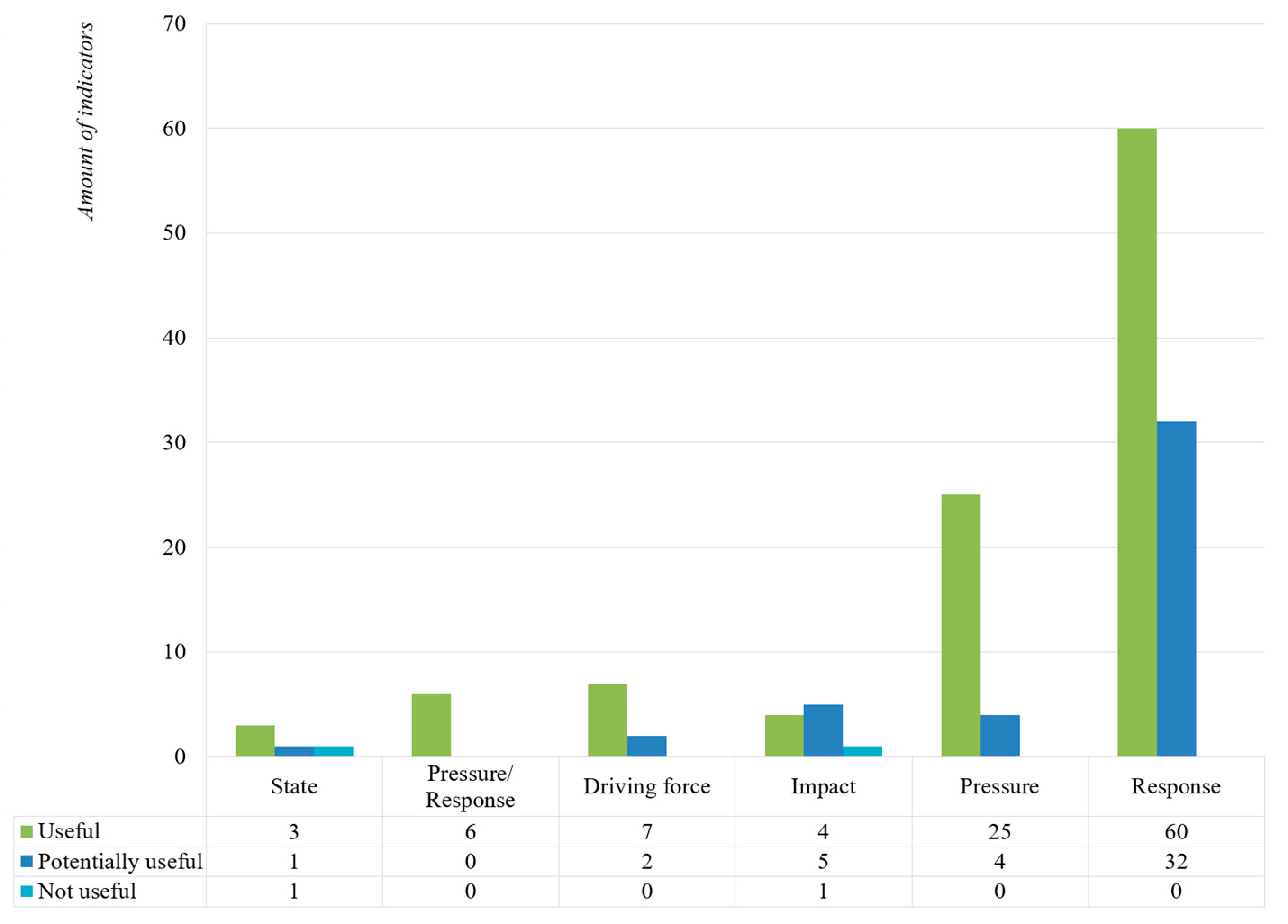
3.2. Sustainability Indicators in Waste Management
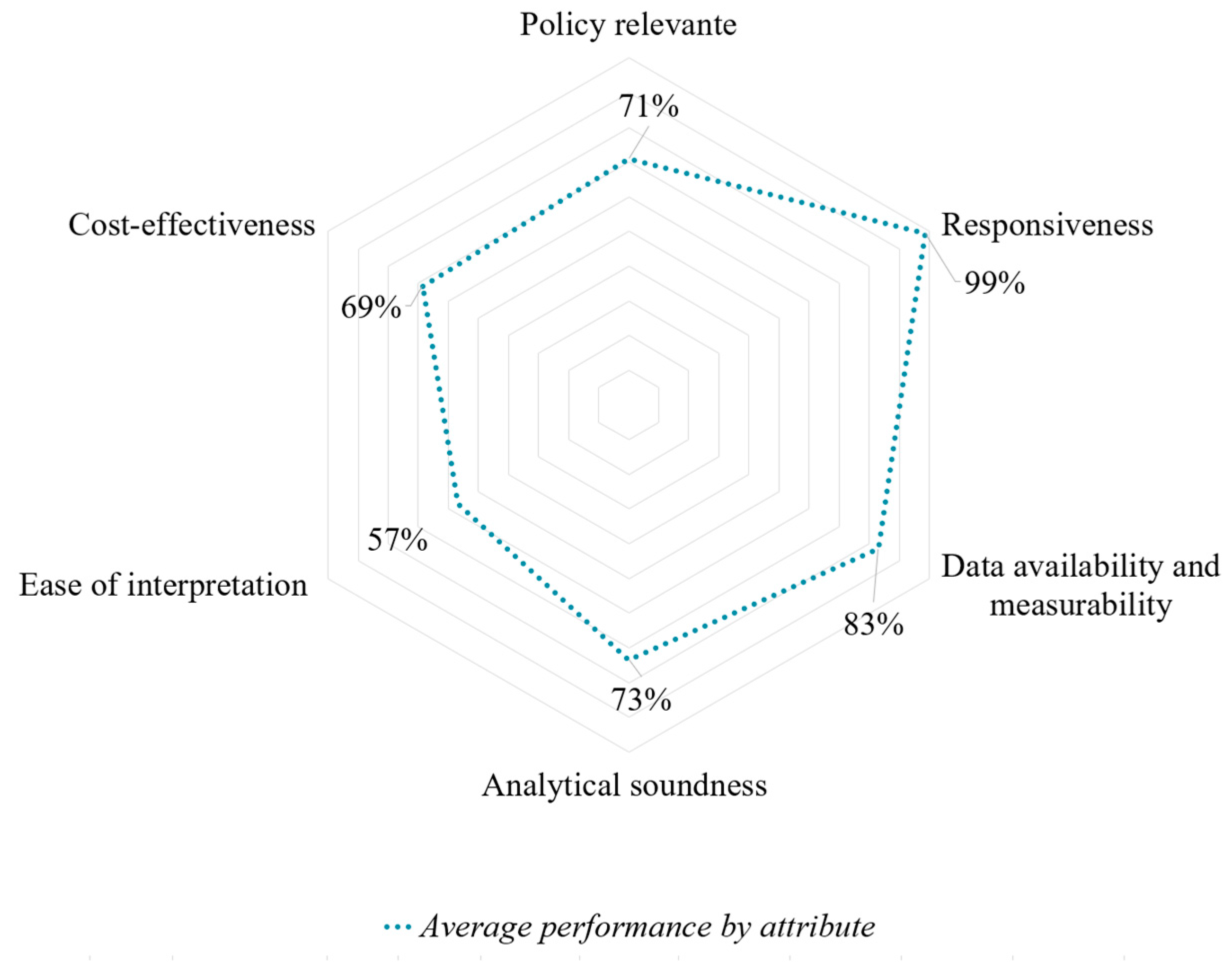
3.3. Indicators Framework
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meadows, D. Indicators and Information Systems for Sustainable Development; The Sustainability Institute: Hartland Four Corners, VT, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmandoust, A.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Rahmani, B.; Azizi, A. Government intervention in municipal waste collection with a sustainable approach: A robust bi-level problem. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 3323–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, A.; Ceylan, F.; Daoud, M.; Kahuthu, A. A systemic approach to tackling ocean plastic debris. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2022, 42, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA—European Environment Agency. Digest of EEA Indicators; Technical Report Nº 8; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Torkayesh, A.; Rajaeifar, M.; Rostom, M.; Malmir, B.; Yazdani, M.; Suh, S.; Heidrich, O. Integrating life cycle assessment and multi criteria decision making for sustainable waste management: Key issues and recommendations for future studies. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 168, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, A.; Adriaanse, A.; Rodenburg, E.; Bryant, D.; Woodward, R. Environmental Indicators; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Agamuthu, P.; Hotta, Y. Indicators as a tool to evaluate waste management efficiency. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circular Econ. 2014, 32, 1147–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Dijkstra, G.; Scholten, P.; Sucozhañay, D. The effectiveness of inter-municipal cooperation for integrated sustainable waste management: A case study in Ecuador. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Huang, N.; Yang, G.; Ma, S. Assessing the sustainability of municipal solid waste management in China 1980–2019. Sust. Horizons 2022, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D. Development drivers for waste management. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.; Martinho, G.; Chang, N.-B. Solid waste management in European countries: A review of systems analysis techniques. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, L.; Maas, G.; Hogland, W. Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, D.; Martínez, A.; Hernández, M.; Cortázar, A. Using indicators as a tool to evaluate municipal solid waste management: A critical review. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondh, S.; Upadhyay, D.; Patel, S.; Patel, R. A strategic review on Municipal Solid Waste (living solid waste) management system focusing on policies, selection criteria and techniques for waste-to-value. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 356, 131908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T. Solid Waste Technology and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste mismanagement in developing countries: A review of global issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaia, R.; Costa, A.; Campos, J. Municipal solid waste in Brazil: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIGS-Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. 2022 Population Census; BIGS: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2024.
- IMF—International Monetary Fund. World Economic Outlook 2019; IMF: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- BIGS—Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Estimates of Resident Population; BIGS: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019.
- Costa, I.; Dias, M.; Robaina, M. Evaluation of the efficiency of urban solid waste management in Brazil by data envelopment analysis and possible variables of influence. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, F.; Ismail, K.; Castañeda-Ayarza, J. Municipal solid waste treatment in Brazil: A comprehensive review. Energy Nexus 2023, 11, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABRELPE—Associação Brasileira de Empresas de Limpeza Pública e Resíduos Especiais. Panorama Do Resíduos Sólidos No Brasil 2022; ABRELPE: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, V.; Silva, V.; Cardoso, J.; Brito, P.; Tuna, C.; Silveira, J. A review of waste management in Brazil and Portugal: Waste-to-energy as pathway for sustainable development. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 802–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, M.; Puppim de Oliveira, J.; Mancini, S.; Rieradevall, J. Waste management intervention to boost circular economy and mitigate climate change in cities of developing countries: The case of Brazil. Habitat Int. 2024, 143, 102990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebehy, P.; Salgado Junior, A.; Ometto, A.; Espinoza, D.; Rossi, E.; Novi, J. Municipal solid waste management (MSWM) in Brazil: Drivers and best practices towards to circular economy based on European Union and BSI. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Contreras, F.; Bortoleto, A. Life-cycle assessment of municipal solid waste management options: A case study of refuse derived fuel production in the city of Brasilia, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucá, J.; Barbosa, K.; Sobral, M. Sustainability indicators for municipal solid waste management: A case study of the Recife Metropolitan Region, Brazil. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, M.; Barros, R.; Poganietz, R. Designing a framework for municipal solid waste management towards sustainability in emerging economy countries-An application to a case study in Belo Horizonte (Brazil). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, I.; Fidelis, R.; Fidelis, D.; Pilatti, L.; Picinin, C. The integration of recycling cooperatives in the formal management of municipal solid waste as a strategy for the circular economy—The case of Londrina, Brazil. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, L.; Silva, F.; Lagarinhos, C.; Tenório, J.; Espinosa, D. E-waste management and sustainability: A case study in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25221–25232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.; Monteiro, M.; Silva, M.; Miranda, R.; Santos, S. Household practices regarding e-waste management: A case study from Brazil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Oliveira, E.; Fonseca, A. Strategies to promote circular economy in the management of construction and demolition waste at the regional level: A case study in Manaus, Brazil. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, I.; Galvão, N.; Bassin, I.; Bassin, J. Waste characterization in Brazil. In Waste Management and Resource Recycling in the Developing World; Singh, P., Verma, P., Singh, R., Ahamad, A., Batalhão, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, I.; Gomes, F.; Castro, S. Reflections on COVID-19 pandemic and waste management in developing countries: A case study in São Paulo city, Brazil. Waste Manag. Res. 2024, 42, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Pedro, F.; Sousa, M.; Patil-Dake, J.; Arenhardt, V. The case of Brazil’s municipal solid waste management: Residents’ perceptions. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, R.M.; Battistelle, R.; Silva, G. Solid waste in Brazil: Context, gaps and trends. Eng. Sanitária Ambient. 2015, 20, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Godfrey, L. Facilitating the improved management of waste in South Africa through a national waste information system. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifrián, E.; Andres, A.; Viguri, J. Developing a regional environmental information system based on macro-level waste indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Forés, V.; Bovea, M.; Coutinho-Nóbrega, C.; Medeiros, H. Assessing the social performance of municipal solid waste management systems in developing countries: Proposal of indicators and a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, I. Municipal solid waste management in developing countries: Future challenges and possible opportunities. In Integrated Waste Management; Kumar, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; Volume II, pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, Y.; Visvanathan, C.; Kojima, M.; Pariatamby, A. Developing 3R policy indicators for Asia and the Pacific region: Experience from Regional 3R Forum in Asia and the Pacific. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduro-Appiah, K.; Afful, A. Sustainable pathway for closing solid waste data gaps: Implications for modernization strategies and resilient cities in developing countries. In Strategies of Sustainable Solid Waste Management; Saleh, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume I, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olay-Romero, E.; Turcott-Cervantes, D.; Hernández-Berriel, M.; Cortázar, A.; Cuartas-Hernández, M.; Rosa-Gómez, I. Technical indicators to improve municipal solid waste management in developing countries: A case in Mexico. Waste Manag. 2020, 107, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, B.; Kaneko, H.; Hirayama, K.; Katayama-Hirayama, K. Municipal solid waste management in Phnom Penh, capital city of Cambodia. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbrügg, C. Assessment Methods for Waste Management Decision-Support in Developing Countries. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Brescia, Brescia, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maiello, A.; Britto, A.; Valle, T. Implementation of the Brazilian national policy for waste management. Rev. Adm. Pública 2018, 52, 24–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Prietto, P.; Korf, E. Sustainability indicators for urban solid waste management in large and medium-sized worldwide cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.; Farahbakhsh, K. Systems approaches to integrated solid waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A.; Pinas, C.; Osobajo, O. Designing effective waste management practices in developing economies: The case of Suriname. Clean. Wast Syst. 2022, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunhara, J.; Macedo, K.; Tapas, D.; Innocentini, M. A Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) tool to help waste pickers’ cooperatives self-evaluate their environmental and economic performance. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2023, 6, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP—United Nations Environment Programme. Africa Waste Management Outlook; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kazuva, E.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z.; Si, A.; Na, L. The DPSIR model for environmental risk assessment of municipal solid waste in Dar es Salaam city, Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Lv, T.; Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Liu, F.; Lam, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X. Evaluation of urban public transport sustainability in China based on the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) framework: A case study of 36 major cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD—Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Core Set of Indicators for Environmental Performance Reviews; OECD: Paris, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- EEA—European Environment Agency. Europe’s Environment: The Dobris Assessment; State of Environment Report Nº 1; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1995.
- USEPA—US Environmental Protection Agency. Beyond the Horizon: Using Foresight to Protect the Environmental Future; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 39.
- EC—European Commission. Commission Notice on Technical Guidance on the Classification of Waste (2018/C 124/01). 2018. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52018XC0409(01) (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- EEA—European Environment Agency. Agriculture and Environment in EU-15: The IRENA Indicator Report; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005.
- Chun, Y.; Rainey, H. Consequences of goal ambiguity in public organizations. In Public Service Performance: Perspectives on Measurement and Management; Boyne, G., Meier, K., O’Toole, J., Walker, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume I, pp. 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, L. Análise de Conteúdo; Edições 70: Lisboa, Portugal, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, E.; Weterings, R. Environmental Indicators: Typology and Overview; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999.
- Sauvenier, X.; Valckz, J.; Van Cauwenbergh, N.; Wauters, E.; Bachev, H.; Biala, K.; Bielders, C.; Brouckaert, V.; Garcia-Cidad, V.; Goyens, S.; et al. Framework for Assessing Sustainability Levels in Belgian Agricultural Systems-SAFE; Final Report-SPSD II CP 28; Belgian Science Policy: Brussels, Brussels, 2006.
- BME—Brazilian Ministry of Environment. National Plan to Combat Marine Litter; BME: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019.
- BRP—Brazilian Republic Presidency. National Sanitation Policy; Brazilian Law No 5.318; BRP: São Paulo, Brazil, 1967.
- BATS—Brazilian Association of Technical Standards. Transport and Storage of Waste; Series 7500; BATS: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdve, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Wendin, M.; Bengtsson, C.; Wiktorsson, M. Waste flow mapping to improve sustainability of waste management: A case study approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 98, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patón-Romero, D.; Baldassarre, M.; Rodriguez, M.; Piattini, M. Application of ISO 14000 to information technology governance and management. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2019, 65, 180–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Matos, E.; Fisciletti, R. Solid residual yesterday and today: Historical evolution of solid residuals in Brazilian environmental legislation. Amaz. Res. Environ. Law 2017, 5, 126–142. [Google Scholar]
- BRP—Brazilian Republic Presidency. National Solid Waste Policy; Brazilian Law No 12.305; BRP: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010.
- Vallero, D. Risk Assessment, Management, and Accountability. In Waste: A Handbook for Management; Letcher, T., Vallero, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; Volume I, pp. 503–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIERNR—Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources. Brazilian Waste List; BIERNR: Brasília, Brazil, 2012; Volume Normative Instruction No 13.
- Faria, M. A política de resíduos sólidos na União Europeia e no Brasil: Estudo comparativo e análise quanto à efetividade. Rev. Programa Direito União Eur. 2014, 3, 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Cifrian, E. Development of an Environmental Information System to Apply in Cantabria Region: Waste Area Indicators. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cantabria, Santander, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilian, B.; Wang, B.; Lewis, K.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C.; Behdad, S. The future of waste management in smart and sustainable cities: A review and concept paper. Waste Manag. 2018, 81, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNGA—United Nations General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; UNGA: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Braat, L. The predictive meaning of sustainability indicators. In In Search of Indicators of Sustainable Development; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wu, T. Sustainability indicators and indices: An overview. In Handbook of Sustainability Management; Kuei, C.N.M.A.C., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 65–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cetrulo, T.; Marques, R.; Cetrulo, N.; Pinto, F.; Moreira, R.; Mendizábal-Cortés, A.; Malheiros, T. Effectiveness of solid waste policies in developing countries: A case study in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupin, P.; Brumatti, L.; Borges, A. Análise dos dados sobre resíduos sólidos nas bases da PNSB e do SNIS. Rev. Nac. Gerenciamento Cid. 2015, 3, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
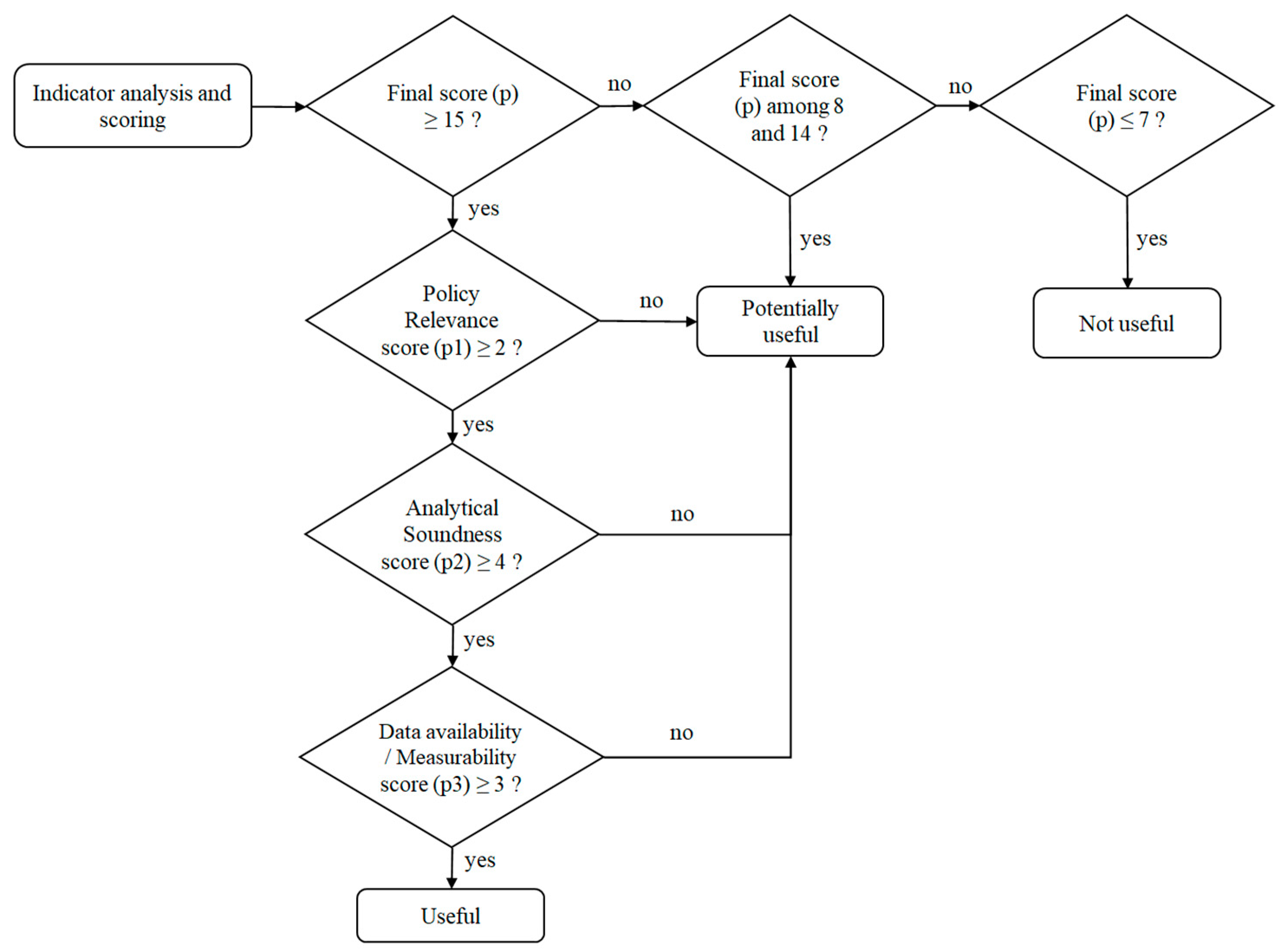
| Indicator’s Attributes | Description | Scoring |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical soundness | Is the indicator derived from direct or does it rely on indirect, or modeled waste data? | Indirect (0) Modeled (1) Direct (2) |
| Is the indicator based on well-founded technical and scientific waste statistics or data? | Low-quality data (0) Medium quality data (1) High-quality data (2) | |
| What are the causal links with other indicators within the DPSIR framework? | Weak or no link (0) Qualitative link (1) Quantitative link (2) | |
| Cost-effectiveness | Is the indicator based on existing waste statistics and data sets? | No (0) Yes (1) |
| Are the waste statistics or data needed for compilation easily accessible? | No (0) Yes, but requires lengthy processing (1) Yes (2) | |
| Data availability and measurability | Does the indicator have good geographical coverage? | Only case studies (0) National (1) National and regional (2) |
| Are waste data available in regular time series? | No (0) Occasional data source (1) Regular data source with at least 10 years (2) | |
| Ease of interpretation | Are the key messages easy to seize, clear, simple and unambiguous? | Not clear (0) Fairly clear (1) Very clear (2) |
| Policy relevance | Is the indicator linked to national waste policy goals, targets, or obligations? | No (0) Yes, indirectly (1) Yes, directly (2) |
| Could the indicator provide waste-related information valuable for policy actions or decisions? | Not useful (0) Fairly useful (1) Very useful (2) | |
| Responsiveness | Is the indicator sensitive to changes in the field of waste management? | Slow, delayed response (0) Fast, immediate response (1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, E.; Fonseca, F.; Santiago, A.; Rodrigues, D. Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052192
Santos E, Fonseca F, Santiago A, Rodrigues D. Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework. Sustainability. 2024; 16(5):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052192
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Eduardo, Fernando Fonseca, Aníbal Santiago, and Daniel Rodrigues. 2024. "Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework" Sustainability 16, no. 5: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052192
APA StyleSantos, E., Fonseca, F., Santiago, A., & Rodrigues, D. (2024). Sustainability Indicators Model Applied to Waste Management in Brazil Using the DPSIR Framework. Sustainability, 16(5), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052192








