Determining Cost and Causes of Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Current Research Trends in Cost Overruns of Infrastructure Projects
2.2. Five Independent Variables for Cost Overruns
- Type of projects. Cost overruns have been influenced by the different transport infrastructure projects, roadways, railways, bridges, and tunnels [10,25,34]. It can be concluded from Table 1 that cost overruns are influenced by the different types of infrastructure, railways, roadways, tunnels, ports, electrical power projects, and others. The first variable is the project type.
- Location of projects. Table 1 highlights the importance of project location on cost overrun rates. The different regions and countries have experienced different values of cost overruns. Within this research, geographical location is selected as the second variable that influences cost overruns.
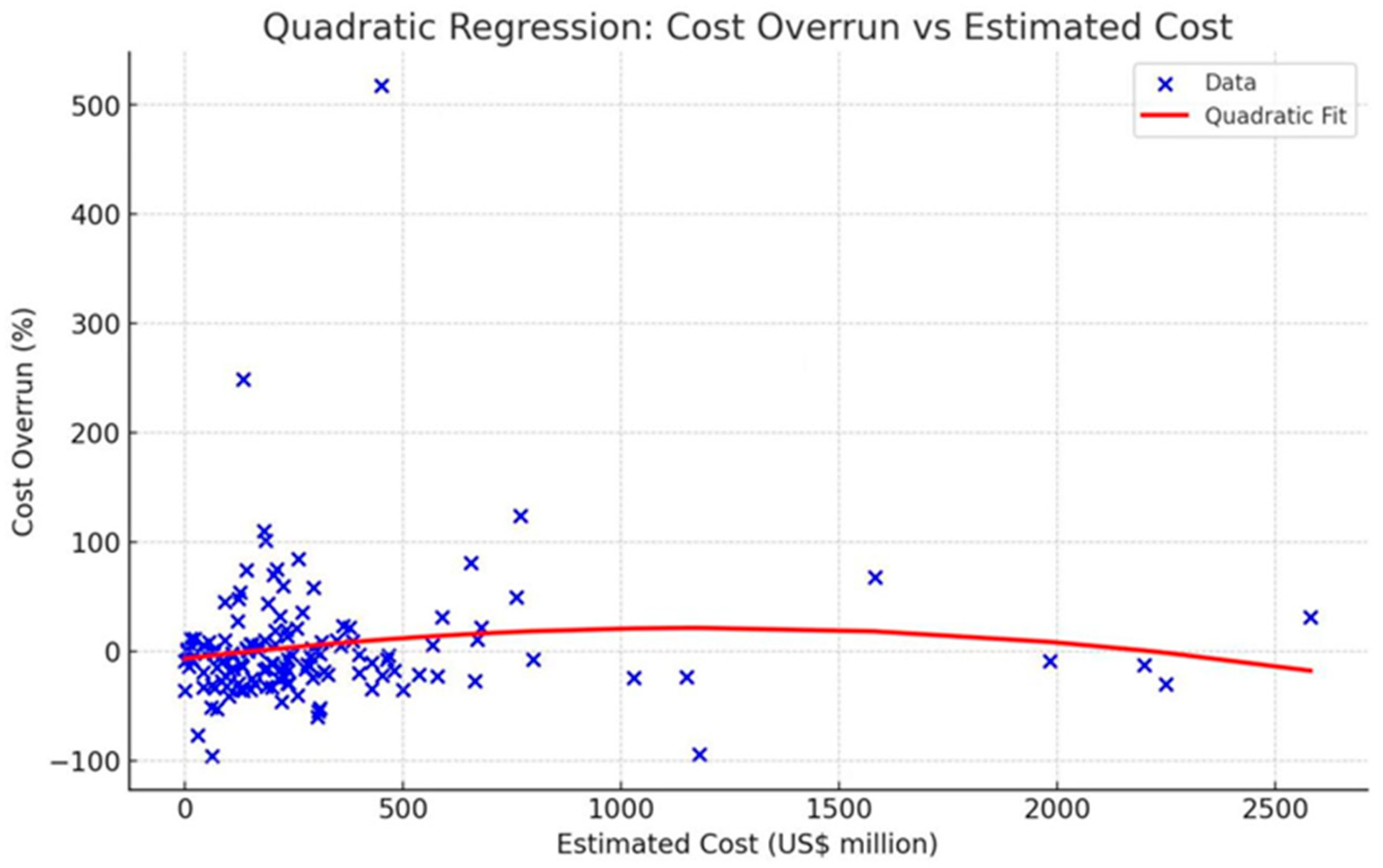
- Project size. The project size represents the estimated value of the project at the time of the decision to be built. Cost overruns are correlated with the project size according to a large body of research. For example, there is a statistical correlation between the estimated cost and the actual amount of infrastructure projects [35,50,53]. Also, Verweij et al. [54] have concluded that smaller projects tend to have higher cost overruns and larger projects tend to have lower cost overruns. Hence, it is assumed that cost overruns will vary due to project size.
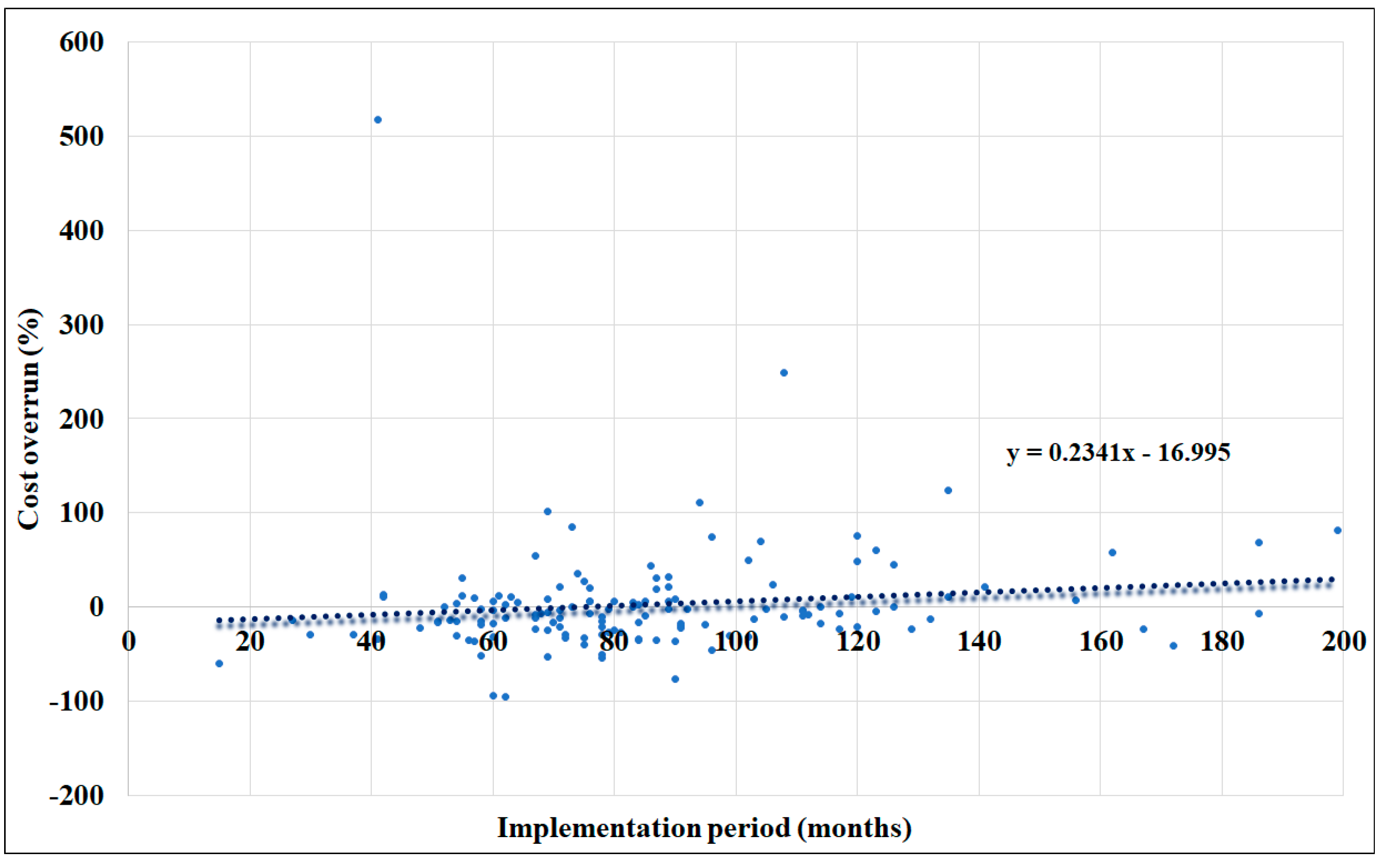
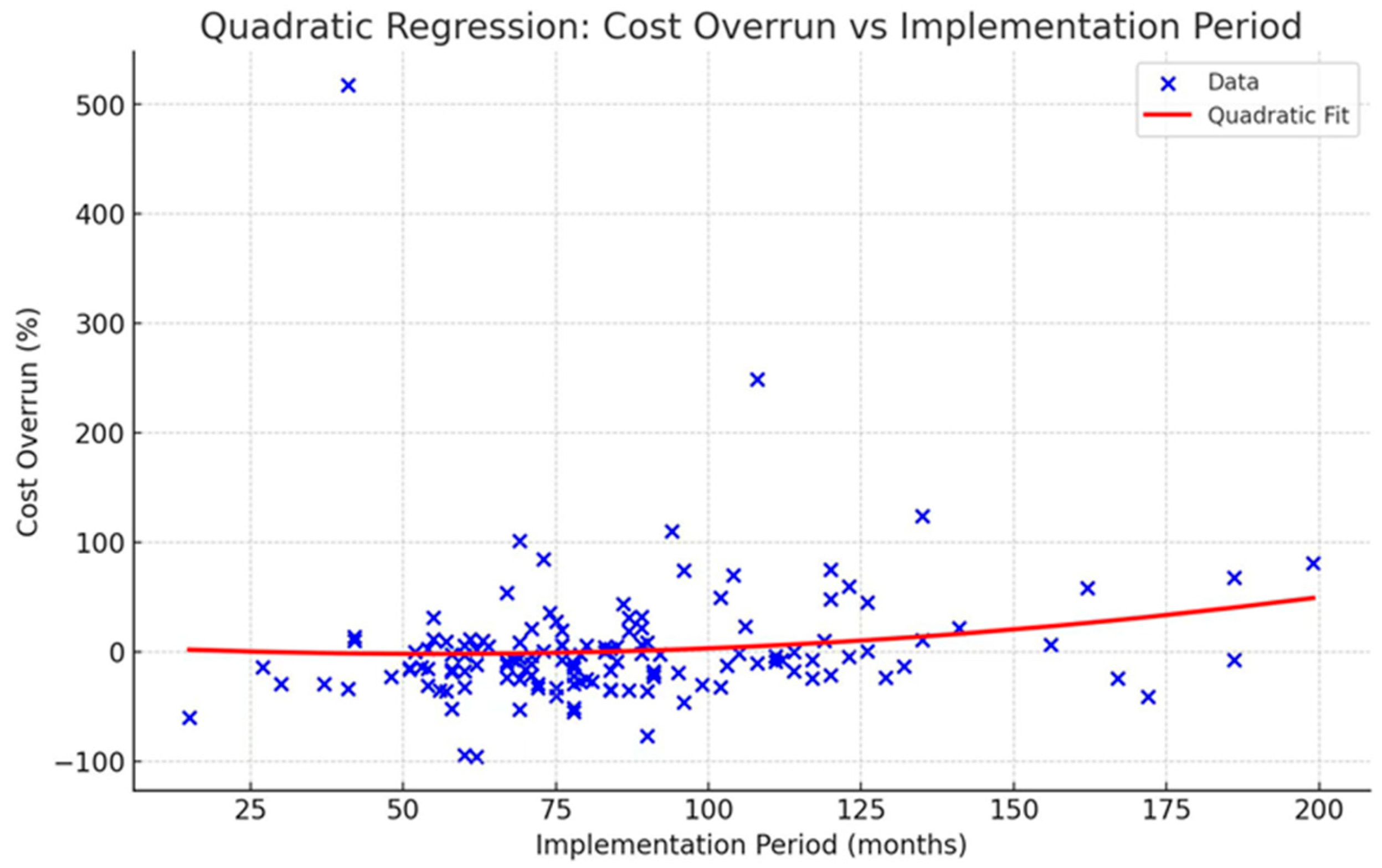
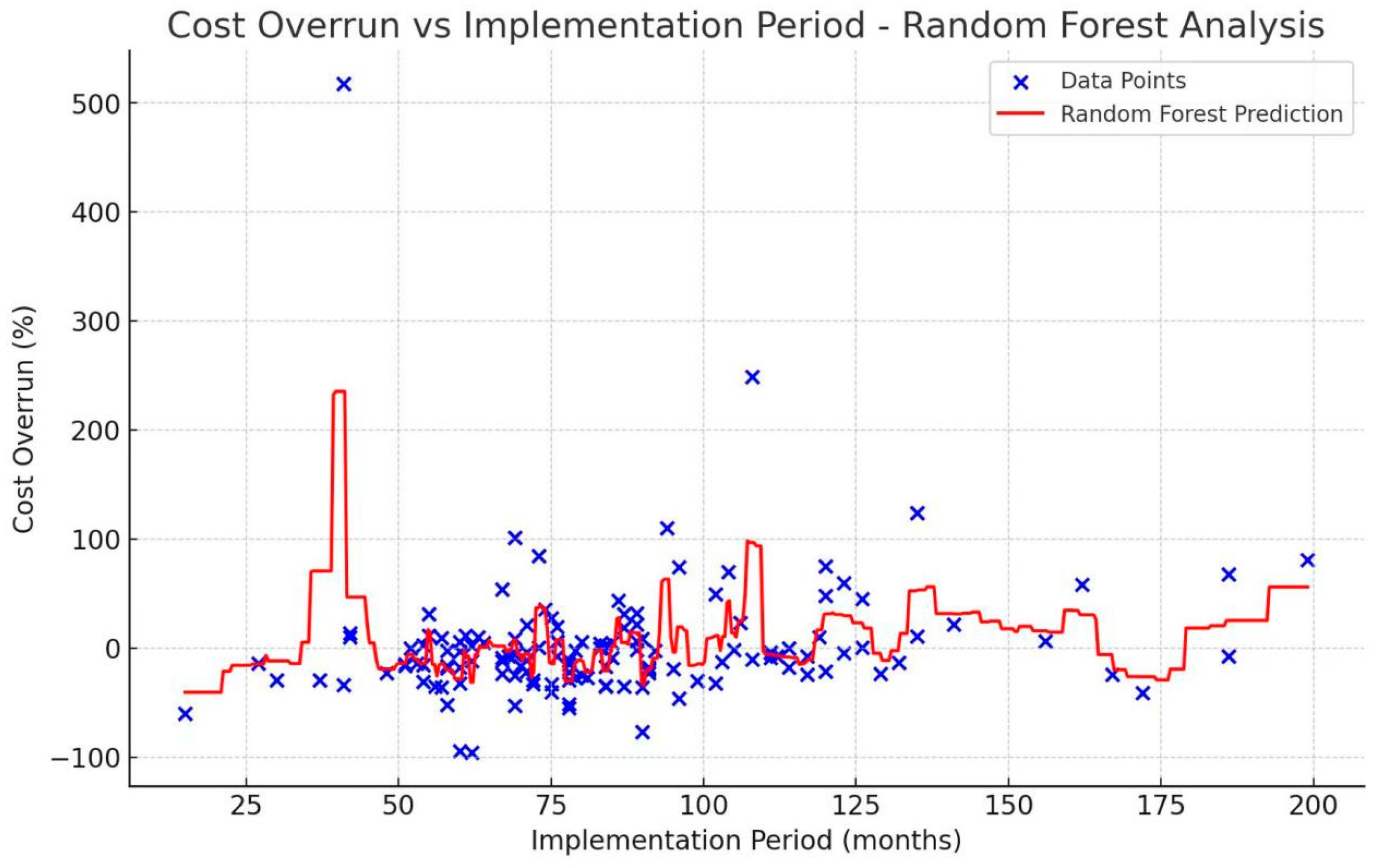
- Implementation period of projects. The implementation period signifies the duration of the project from the initiation of construction to the ultimate completion. The duration of the project is measured in months. The study conducted by Park and Papadopoulou [55] identified a statistically significant correlation between the duration of construction and cost overruns. In this context, it is assumed that cost overruns are influenced by the duration of the implementation phase.
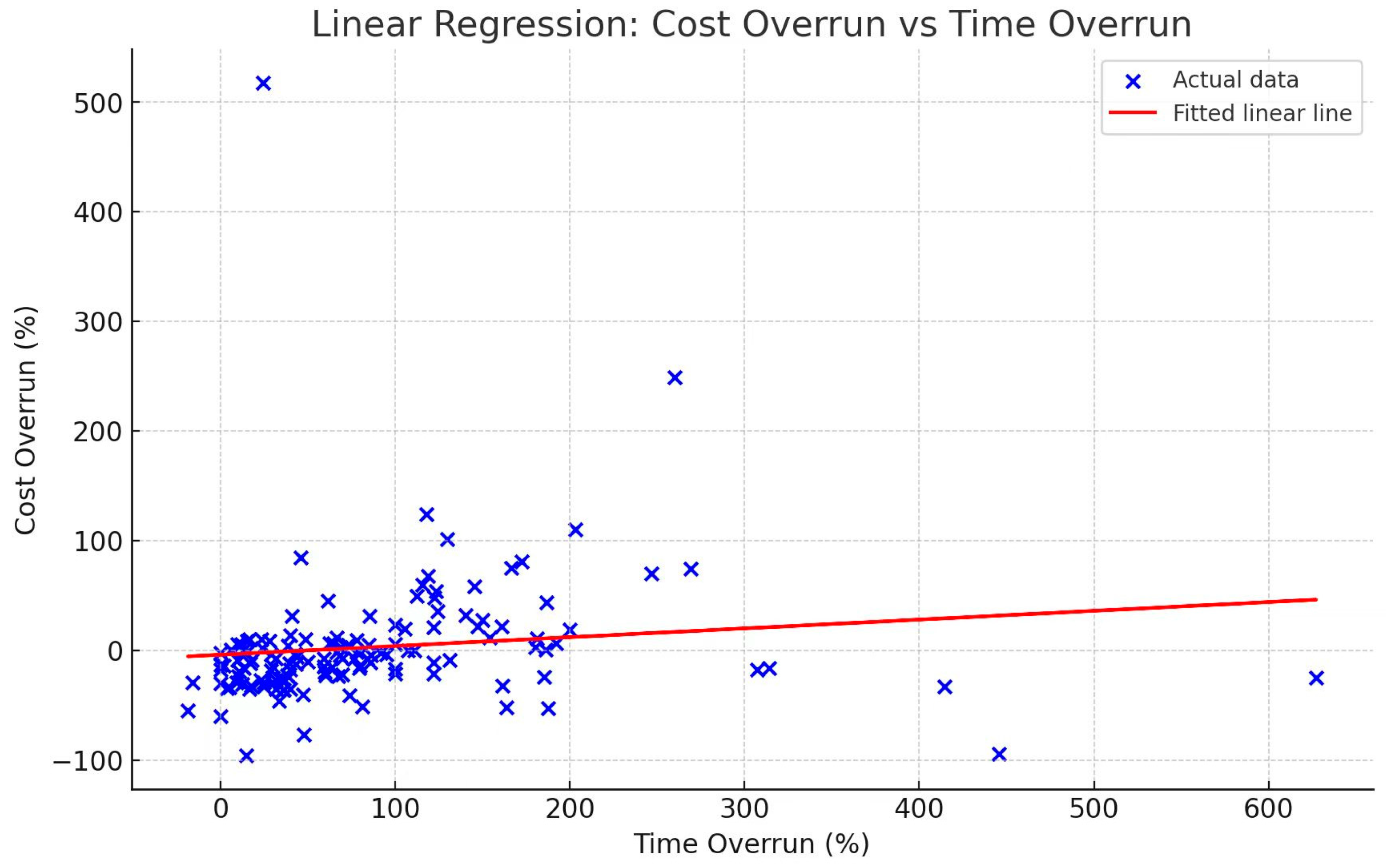
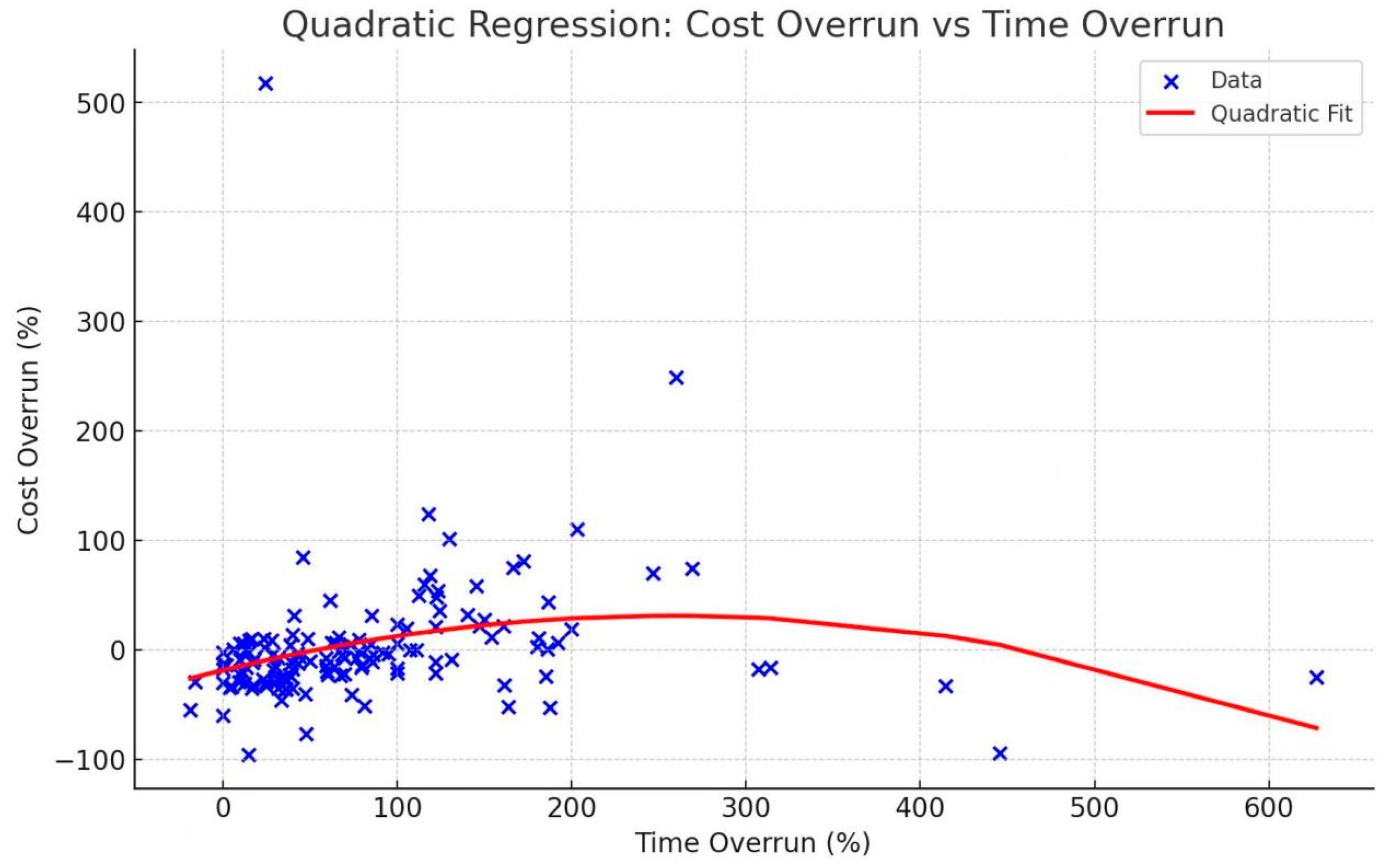
- Time overruns of projects. There is minor research on the dependency between cost and time overruns. However, there is no evidence that any scholars studying the impact of time overruns as a variable on cost overruns.
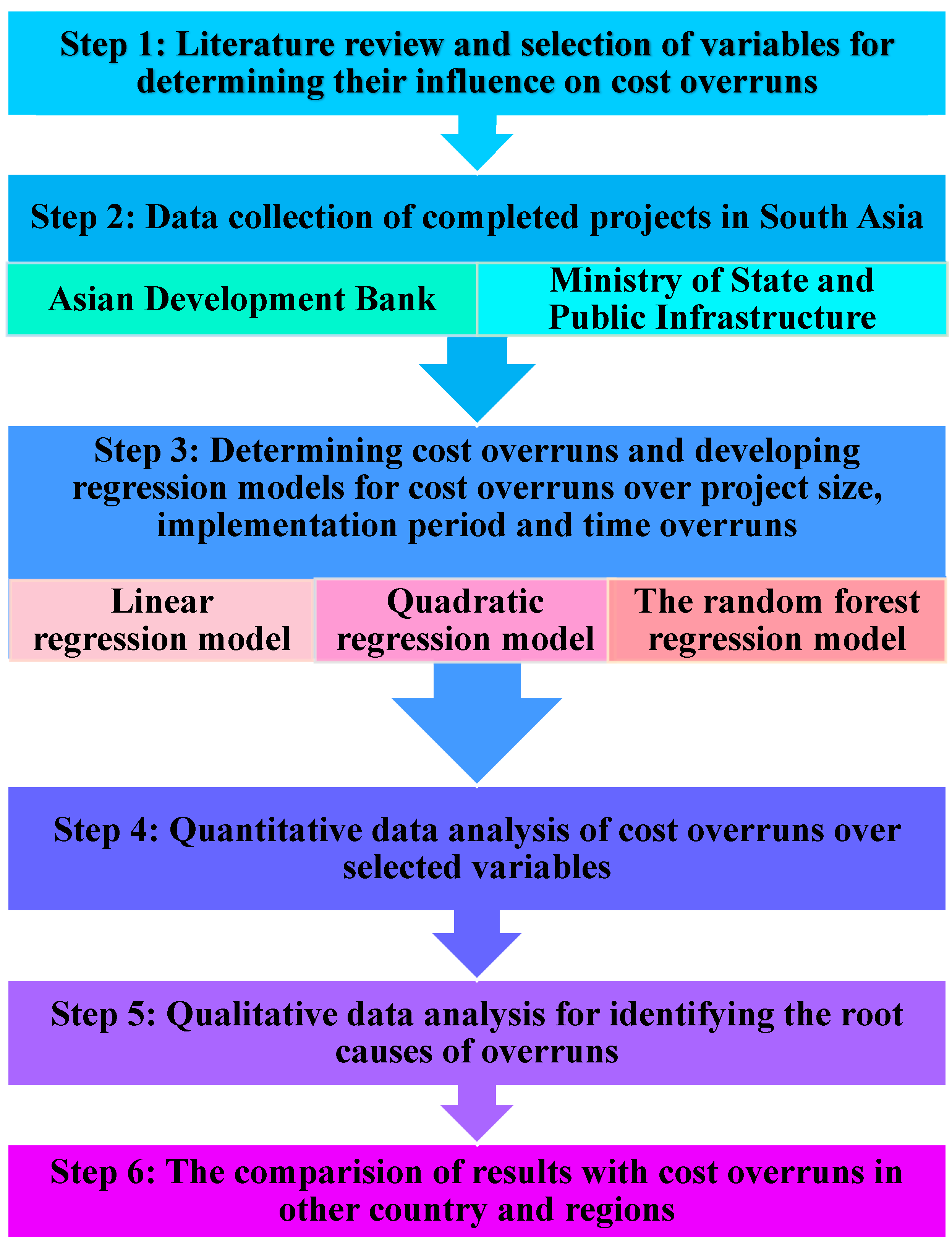
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Methods for Data Analysis
4. Data Analysis of Cost Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia
4.1. The Characteristics of Cost Performance
- Cost overruns in infrastructure projects in South Asia range from −95.79% to 517.40%;
- The mean value of cost overruns is 3% (SD = 60.65);
- In total, 36.96% of projects were affected by cost overruns; while 59.42% of projects were underrun and 3.62% of projects were completed within a budget;
- The mean value of cost overrun is 46.38% (SD = 80.05) with projects affected by over-runs, while the mean value of cost underruns is −23.80% (SD = 18.79) with projects affected by underruns.

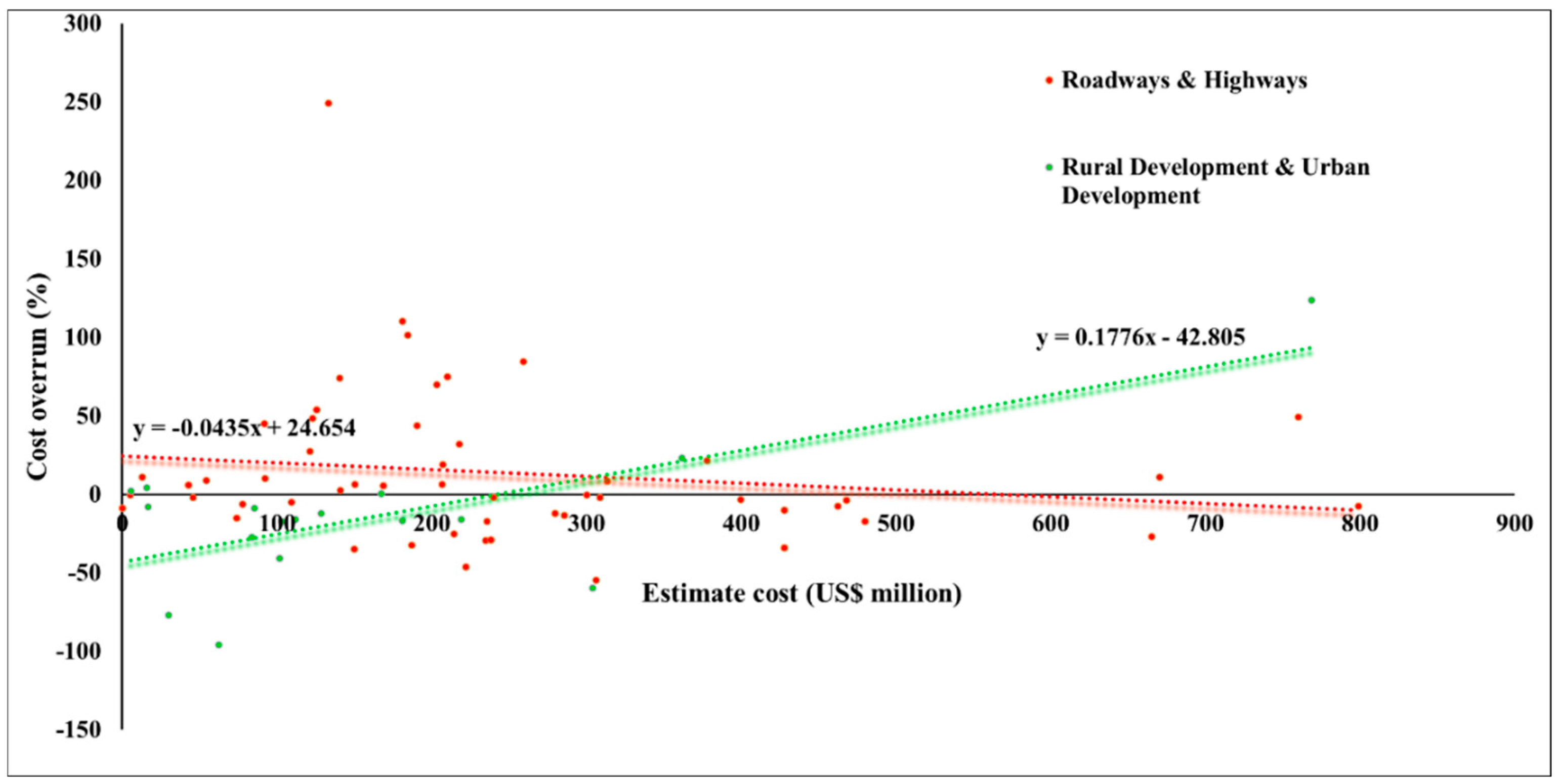
4.2. Cost Overrun over Project Type
- Infrastructure projects with a cost overrun are as common as projects with cost underrun for energy sector projects (Binominal test, p = 0.0141), for roadways and highways projects (Binominal test, p = 0.5), for rural and urban development projects (Binominal test, p = 0.0728).
- When it comes to projects that experience cost underruns, the average cost underrun is the lowest for rural and urban sector projects (One-way ANOVA, F = 2.78611, p = 0.068228).
4.3. Cost Overrun over Project Location
- There is a significant difference in cost underruns for projects in Pakistan since the average cost underrun is the lowest compared to other countries (One-way ANOVA, F = 3.87546, p = 0.012673).
- The majority of projects were completed at lower costs than estimated.
- There are only two projects in Pakistan that have experienced cost overruns.
| Location of Projects | Number of Overrun | Mean Value | SD | Number of Underrun | Mean Value | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 6 | 23.11 | 21.78 | 6 | −25.26 | 5.76 |
| India | 35 | 59.87 | 93.29 | 48 | −20.83 | 14.87 |
| Pakistan | 2 | 3.29 | 4.45 | 14 | −38.27 | 29.77 |
| Sri Lanka | 4 | 18.36 | 20.17 | 7 | −15.49 | 10.71 |
| Total: | 47 | 75 |
4.4. Cost Overrun over Project Size
4.5. Cost Overrun over Project Implementation Period
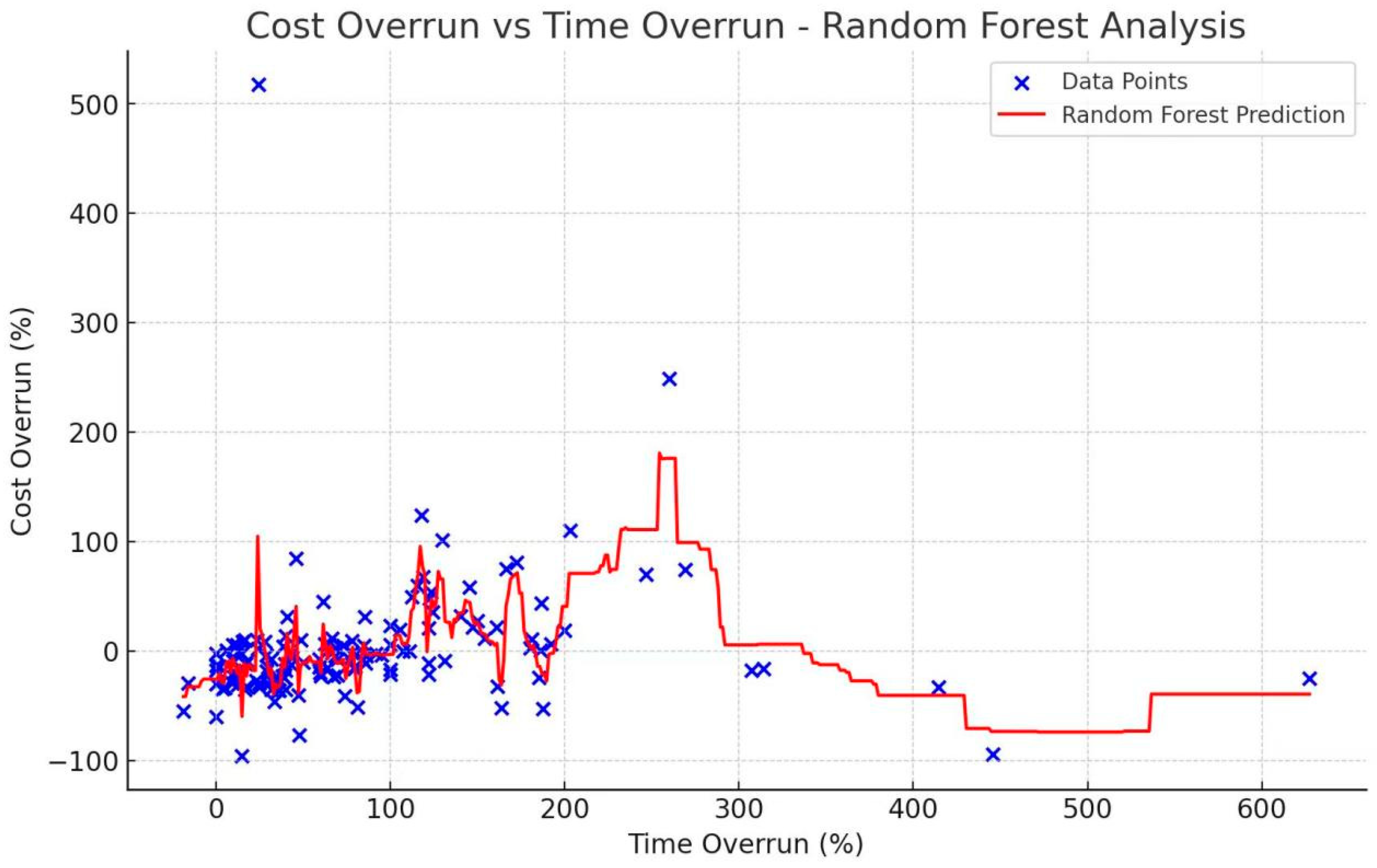
4.6. Cost Overrun over Time Overrun
4.7. Summary of Results
5. The Causes of Cost Overruns
6. Discussions, Limitations, and Comparison of Results in South Asia with Worldwide
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNECE. The Transformative Impact of Infrastructure for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://unece.org/economic-cooperation-and-integration/news/transformative-impact-infrastructure-sustainable (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Thacker, S.; Adshead, D.; Fay, M.; Hallegatte, S.; Harvey, M.; Meller, H.; O’Regan, N.; Rozenberg, J.; Watkins, G.; Hall, J.W. Infrastructure for sustainable development. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.; De Gooyert, V.; Veeneman, W. Sustainable development goals as accountability mechanism? A case study of Dutch infrastructure agencies. J. Responsible Technol. 2023, 14, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarelli, C.C.; Flyvbjerg, B.; Buhl, S.L. Geographical variation in project cost performance: The Netherlands versus worldwide. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 24, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.; Sing, C.P.; Wang, X.; Irani, Z.; Thwala, D.W. Overruns in transportation infrastructure projects. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 10, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, G.; Invernizzi, D.C.; Brookes, N.J. Project characteristics and performance in Europe: An empirical analysis for large transport infrastructure projects. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 98, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Anastasopoulos, P.C.; Labi, S.; Sinha, K.C.; Mannering, F.L. Three-stage least-squares analysis of time and cost overruns in construction contracts. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 136, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Touran, A. Cost overruns and formal risk assessment program in US rail transit projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 05020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantata, N.A.; Touran, A.; Schneck, D.C. Trends in US Rail Transit Project Cost Overrun; Transport Research Board (TRB): Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cantarelli, C.C.; Molin, E.J.; van Wee, B.; Flyvbjerg, B. Characteristics of cost overruns for Dutch transport infrastructure projects and the importance of the decision to build and project phases. Transp. Policy 2012, 22, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.; Zhou, J.; Edwards, D.J.; Irani, Z.; Sing, C.P. Off the rails: The cost performance of infrastructure rail projects. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 99, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, M.; Emslie, O.; Moran, G. The Rise of Megaprojects; Geattan Institute: Carlton, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Love, P.E.; Ahiaga-Dagbui, D.D.; Irani, Z. Cost overruns in transportation infrastructure projects: Sowing the seeds for a probabilistic theory of causation. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 92, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, G.; Anzinger, N. Large infrastructure projects in Germany: A cross-sectoral analysis. In Large Infrastructure Projects in Germany: Between Ambition and Realities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Steininger, B.I.; Groth, M.; Weber, B.L. Cost overruns and delays in infrastructure projects: The case of Stuttgart 21. J. Prop. Invest. Financ. 2021, 39, 256–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, M.; Cristaudo, R.; Guccio, C. On the magnitude of cost overruns throughout the project life-cycle: An assessment for the Italian transport infrastructure projects. Transp. Policy 2019, 79, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marella, G.; Antoniucci, V. Time Overrun in Public Works—Evidence from North-East Italy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, L.; Haezendonck, E.; Mabillard, V. Cost overruns of Belgian transport infrastructure projects: Analyzing variations over three land transport modes and two project phases. Transp. Policy 2023, 134, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Luu, T.V.; Kim, S.Y.; Vien, D.T. Assessing the impact of cost overrun causes in transmission lines construction projects. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinradewo, O.; Aigbavboa, C.; Oke, A.; Coffie, H.; Ogunbayo, B. Unearthing Causative Factors of Cost Overrun on Ghanaian Road Projects. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2022, 17, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.T.; Ogunlana, S.O.; Hong, W.T. Understanding the dynamics of cost overrun triggers in highway infrastructure projects in Nigeria: A system thinking modelling approach. J. Financ. Manag. Prop. Constr. 2022, 27, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, C.; Szklo, A.; Schaeffer, R. Cost overruns and delays in energy megaprojects: How big is big enough? Energy Policy 2018, 114, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrinčević, M.; Vukomanović, M.; Perić, R. Influence of Technical Reasons on Cost Overruns of Infrastructural Projects: A Sustainable Development Perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Skamris Holm, M.K.; Buhl, S.L. What causes cost overrun in transport infrastructure projects? Transp. Rev. 2004, 24, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Ren, H.; Cai, W.; Shen, G.Q.; Liu, B.; Zhu, M.; Wu, H. Measurement and dependence analysis of cost overruns in megatransport infrastructure projects: Case study in Hong Kong. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 05018001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trading Economics, South Asia—Population, Total. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/south-asia/population-total-wb-data.html (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- MoSPI—Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Project Implementation Status Report of Central Sector Projects Costing Rs. 150 Crore and Above, Infrastructure and Project Monitoring Division, July–September 2017, Sardar Patel Bhavan, Sansad Marg, New Delhi; Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2017.
- Iyer, K.C.; Jha, K.N. Critical factors affecting schedule performance: Evidence from Indian construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2006, 132, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, W.; Johansen, B.G. Regional repercussions of new transport infrastructure investments: An SCGE model analysis of wider economic impacts. Res. Transp. Econ. 2017, 63, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.U.; Islam, M.M.; Miao, Q.; Metwally AS, M. Does transport infrastructure make South Asian economies growth more inclusive? An application of a new transportation infrastructure index. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2023, 49, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang AH, S.; Tang, W.H. Probability Concepts in Engineering: Emphasis on Applications in Civil and Environmental Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Lu, J. A quick look at NVivo. J. Electron. Resour. Librariansh. 2018, 30, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Skamris Holm, M.K.; Buhl, S.L. How common and how large are cost overruns in transport infrastructure projects? Transp. Rev. 2003, 23, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeck, J. Cost overruns in road construction—What are their sizes and determinants? Transp. Policy 2004, 11, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, H.P.; Teixeira, J.C. Dealing with Cost and time in the Portuguese Construction Industry; International Council for Research &Innovation in Building & Construction: Queensland, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, M.; Jenpanitsub, A.; Pyddoke, R. Cost Overruns in Swedish Transport Projects; Centre for Transport Studies: Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Makovšek, D.; Tominc, P.; Logožar, K. A cost performance analysis of transport infrastructure construction in Slovenia. Transportation 2012, 39, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Gilbert, A.; Nugent, D. An international comparative assessment of construction cost overruns for electricity infrastructure. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalão, F.P.; Cruz, C.O.; Sarmento, J.M. Determinants of cost deviations and overruns in UK transport projects. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Transp. 2021, 176, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalão, F.P.; Cruz, C.O.; Sarmento, J.M. The determinants of cost deviations and overruns in transport projects, an endogenous models approach. Transp. Policy 2019, 74, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Narbaev, T. Factors of schedule and cost performance of tunnel construction megaprojects. Open Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 15, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berechman, J.; Wu, Q. Cost Overruns Risk Analysis in Transportation Infrastructure Investments; Phelps Centre for the Study of Government and Business, Sauder School of Business, University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Love, P.E.; Ahiaga-Dagbui, D.; Welde, M.; Odeck, J. Light rail transit cost performance: Opportunities for future-proofing. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 100, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Touran, A. Cost overruns in US Rail Transit Projects: A statistical analysis. In Construction Research Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K. Cost overrun and cause in Korean social overhead capital projects: Roads, rails, airports, and ports. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2008, 134, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Delays and cost overruns in infrastructure projects: Extent, causes and remedies. Econ. Political Wkly. 2010, 45, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Senouci, A.; Ismail, A.; Eldin, N. Time delay and cost overrun in Qatari public construction projects. Procedia Eng. 2016, 164, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazim, N.; Salem, Z.A.; Ahmad, H. Delay and cost overrun in infrastructure projects in Jordan. Procedia Eng. 2017, 182, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, J.M.; Mahamadu, A.M.; Wang, J.; Zou, P.X.; Zhong, R. The cost performance and causes of overruns in infrastructure development projects in Asia. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2019, 25, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, W.; Kostka, G.; Habich-Sobiegalla, S. Socio-economic development and infrastructure cost performance in China: Comparing transport and energy sectors. J. Curr. Chin. Aff. 2020, 49, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku Belay, S.; Tilahun, S.; Yehualaw, M.; Matos, J.; Sousa, H.; Workneh, E.T. Analysis of cost overrun and schedule delays of infrastructure projects in low-income economies: Case studies in Ethiopia. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 4991204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Kure, A.M.; Palaniappan, S. Study on time and cost overruns in mega infrastructure projects in India. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. A 2019, 100, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, S.; van Meerkerk, I.; Korthagen, I.A. Reasons for contract changes in implementing Dutch transportation infrastructure projects: An empirical exploration. Transp. Policy 2015, 37, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.I.; Papadopoulou, T.C. Causes of cost overruns in transport infrastructure projects in Asia: Their significance and relationship with project size. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2012, 2, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Holm, M.S.; Buhl, S. Underestimating costs in public works projects: Error or lie? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2002, 68, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, P.E.; Sing, M.C.; Ika, L.A.; Newton, S. The cost performance of transportation projects: The fallacy of the Planning Fallacy account. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 122, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarelli, C.C.; Van Wee, B.; Molin, E.J.; Flyvbjerg, B. Different cost performance: Different determinants? The case of cost overruns in Dutch transport infrastructure projects. Transp. Policy 2012, 22, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skitmore, R.M.; Ng, S.T. Forecast models for actual construction time and cost. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghayedi, A.; Windapo, A. Modelling the uncertainty of cost and time in highway projects. Infrastruct. Asset Manag. 2022, 9, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Development Bank. Available online: https://www.adb.org/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- MoSPI—Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Project Implementation Status Report of Central Sector Projects, Infrastructure and Project Monitoring Division, Sardar Patel Bhavan, Sansad Marg, New Delhi. 2018. Available online: http://www.cspm.gov.in (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Thrane, C. Applied Regression Analysis: Doing, Interpreting and Reporting; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- García-García, J.I.; Coronado, F.N.A.; Arredondo, E.H.; Rivera, I.A. The binomial distribution: Historical origin and evolution of its problem situations. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, T.M. Linear regression. In Machine learning; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Stanimirović, I. Correlation and Regression Analysis: Applications for Industrial Organizations; Arcler Press: Oakville, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.; Müller, H.G. Functional quadratic regression. Biometrika 2010, 97, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, N.; Ye, C.; Ma, J.; Zheng, T. Cost prediction for water reuse equipment using interpretable machine learning models. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavuma, A.; Ock, J.; Jang, H. Factors influencing time and cost overruns on freeform construction projects. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Ansar, A.; Budzier, A.; Buhl, S.; Cantarelli, C.; Garbuio, M.; Van Wee, B. Five things you should know about cost overrun. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 118, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsop, D.B.; Chelladurai, J.M.; Kimball, E.R.; Marks, L.D.; Hendricks, J.J. Qualitative methods with Nvivo software: A practical guide for analyzing qualitative data. Psych 2022, 4, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Salfi, N.A.; Dogar, A.H. Usage of NVivo software for qualitative data analysis. Acad. Res. Int. 2012, 2, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Adu, P. A Step-by-Step Guide to Qualitative Data Coding; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]



| Authors | Sample Size | Region/Country | Project Type | Mean Cost Overrun |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flyvbjerg et al. [34] | 258 | Europe and North America | Railways, roadways, and fixed links | 28% |
| Odeck [35] | 620 | Norway | Roadways | 7.88% |
| Moura and Teixeira [36] | 26 | Portugal | Roadways | 39% |
| Lundberg et al. [37] | 167 | Sweden | Railways and roadways | 15% |
| Makovšek et al. [38] | 20 | Slovenia | Roadways | 19% |
| Cantarelli et al. [10] | 78 | Netherlands | Railways, roadways, and fixed links | 16.5% |
| Sovacool et al. [39] | 113 | Europe | Electrical power projects | 26.5% |
| Cavalieri et al. [16] | 1083 | Italy | Roadways | 26.35% |
| Kostka and Anzinger [14] | 50 | Germany | Transportation projects | 32% |
| Catalão et al. [40] | 175 | UK | Transport projects | 60% |
| Catalão et al. [41] | 1091 | Portugal | Transport projects | 17.8% |
| Molinari et al. [18] | 35 | Belgium | Railways, roadways, and inland waterways | 10.26% |
| De Marco and Narbaev [42] | 39 | Worldwide | Tunnels | 27% |
| Berechman and Wu [43] | 127 | Vancouver | Roadways | 5.9% |
| Love et al. [44] | 32 | USA | Light rails transit | 42% |
| Sovacool et al. [39] | 155 | North America | Electrical power projects | 115.2% |
| Gao and Touran [45] | 83 | USA | Railways | 32.4% |
| Callegari et al. [22] | 401 | Brazil | Energy sector | 64.65% |
| Love et al. [11] | 16 | Australia | Railways | 23% |
| Lee [46] | 161 | South Korea | Railways, roadways, ports and airports | 11% |
| Singh [47] | 107 | India | Power sector | 51.94% |
| Singh [47] | 122 | India | Railways | 94.84% |
| Singh [47] | 157 | India | Roadways and highways | 15.84% |
| Singh [47] | 61 | India | Shipping and ports | −1.35% |
| Sovacool et al. [39] | 96 | Asia-Pacific | Electrical power projects | 48.1% |
| Senouci et al. [48] | 122 | Qatar | Roads, drainage, public buildings | 54% |
| Al-Hazim et al. [49] | 40 | Jordan | Infrastructure projects | 214% |
| Huo et al. [25] | 57 | Hong Kong | Railways, roadways, and fixed links | 39.18% |
| Andrić et al. [50] | 120 | Asia | Roadways, railways, and energy sector projects | 26.24% |
| Rabe et al. [51] | 153 | China | Roadways, railways, and energy sector projects | 22% |
| Melaku et al. [52] | 26 | Ethiopia | Roadways | 18% |
| Types of Projects | Number of Overrun | Mean Value | SD | Number of Underrun | Mean Value | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Sector | 21 | 49.01 | 112.56 | 39 | −25.13 | 16.89 |
| Roadways and Highways | 26 | 45.55 | 51.49 | 27 | −17.75 | 14.45 |
| Rural and Urban Development | 5 | 38.53 | 50.06 | 12 | −32.86 | 28.05 |
| Total: | 52 | 78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrić, J.M.; Lin, S.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, B. Determining Cost and Causes of Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411159
Andrić JM, Lin S, Cheng Y, Sun B. Determining Cost and Causes of Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia. Sustainability. 2024; 16(24):11159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411159
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrić, Jelena M., Shuangyu Lin, Yuan Cheng, and Bin Sun. 2024. "Determining Cost and Causes of Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia" Sustainability 16, no. 24: 11159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411159
APA StyleAndrić, J. M., Lin, S., Cheng, Y., & Sun, B. (2024). Determining Cost and Causes of Overruns in Infrastructure Projects in South Asia. Sustainability, 16(24), 11159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411159






