Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
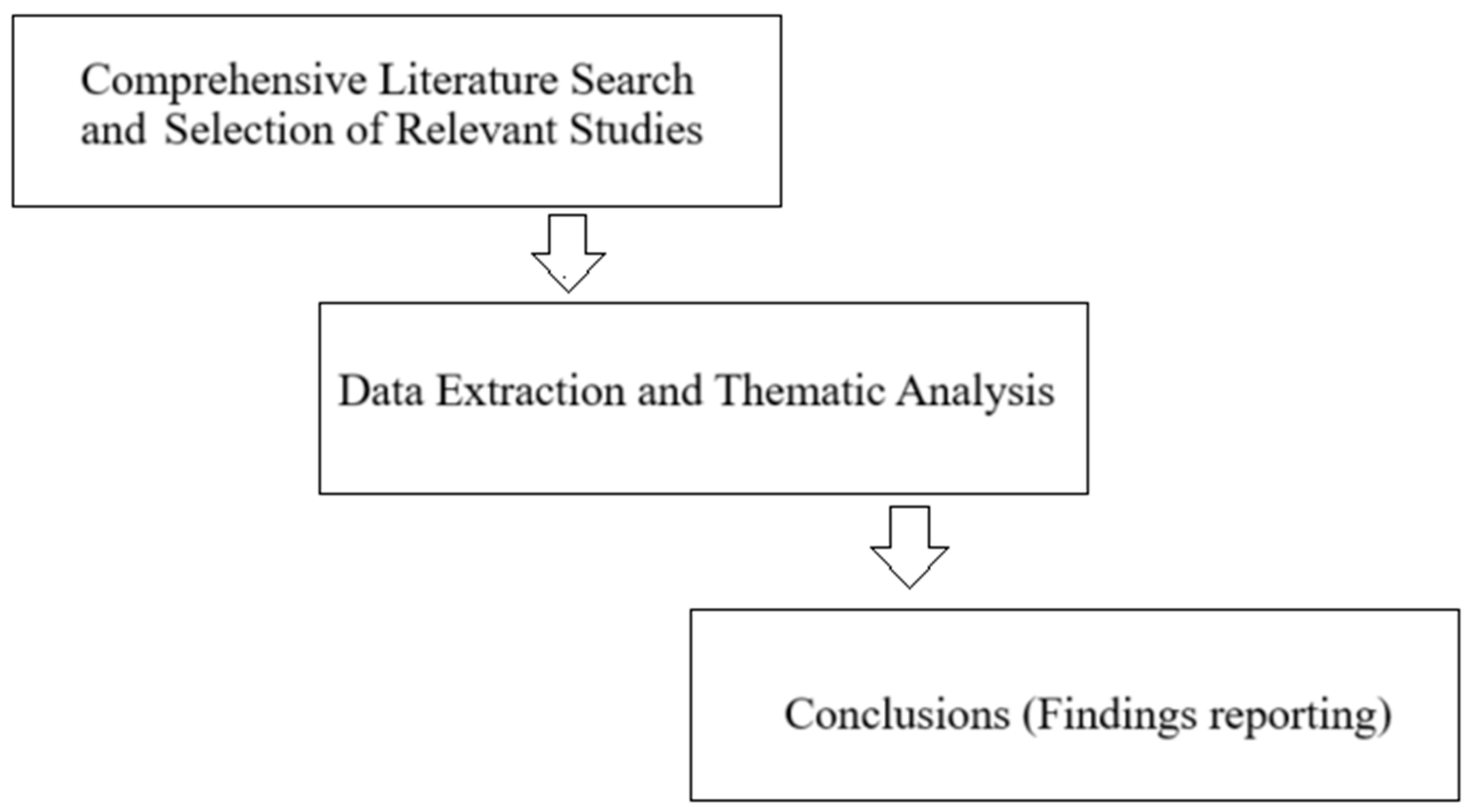
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- How does AI impact the efficiency and sustainability of digital marketing practices? This sub-question aims to assess the effects of AI on the efficiency and sustainability of digital marketing applications.
- (2)
- In what ways does AI contribute to the development of more sustainable digital marketing strategies? This sub-question focuses on exploring AI’s role in creating innovative and sustainable marketing strategies.
- (3)
- What are the advantages of using AI in digital marketing to achieve sustainability goals compared to traditional marketing practices? This sub-question aims to identify the benefits of using AI to achieve sustainability goals.
3. Findings and Discussion
3.1. Transition from Traditional to Digital Marketing
3.2. Sustainable Digital Marketing
3.3. The Role of AI in Enhancing Sustainable Business Practices
- -
- Consumer Trust and Loyalty: Consumers’ trust in AI-driven sustainable marketing strategies significantly impacts brand engagement and loyalty. Trust enhances customer commitment in both online and offline transactions;
- -
- Sustainability Expectations: The growing environmental and social awareness among consumers compels brands to adopt more responsible production processes and sustainable marketing strategies. This serves as a crucial motivation for brands to better meet consumer demands;
- -
- Targeted Marketing Opportunities: AI accurately segments consumers based on demographics, interests, and online behaviors, enabling the creation of more targeted marketing campaigns. This, in turn, helps brands improve their return on investment (ROI).
3.4. Case Studies on AI for Sustainable Marketing
3.5. Discussion
- -
- How does AI impact the efficiency and sustainability of digital marketing practices? The findings indicated that AI enhances the efficiency of digital marketing by enabling precise targeting and personalization, which reduces resource waste. By leveraging data analytics, companies can optimize their campaigns in real-time, ensuring that marketing efforts are not only more effective but also more aligned with sustainability goals. This leads to a marked improvement in overall campaign performance while lessening the environmental footprint;
- -
- In what ways does AI contribute to the development of more sustainable digital marketing strategies? AI facilitates the creation of innovative marketing strategies that prioritize sustainability. For instance, AI-driven insights help businesses identify consumer preferences for eco-friendly products, allowing them to tailor their campaigns accordingly. This strategic alignment not only drives engagement but also positions brands as leaders in sustainability, thereby contributing to long-term business success;
- -
- What are the advantages of using AI in digital marketing to achieve sustainability goals compared to traditional marketing practices? The advantages of using AI in this context are substantial. Compared to traditional marketing, AI offers enhanced precision, reduced waste, and improved resource allocation. By adopting AI technologies, businesses can achieve sustainability goals more efficiently, creating campaigns that resonate with environmentally conscious consumers. The ability to analyze vast amounts of data in real time enables companies to make informed decisions, further enhancing their sustainability efforts. As AI continues to advance, its potential to drive more effective and sustainable marketing strategies becomes increasingly apparent. Sustainability is a key priority for technology companies, but little is known about how they can effectively use AI to accelerate sustainability through the development and implementation of targeted strategies [57].
4. Conclusions
- -
- Precision and Efficiency: AI enhances the precision of marketing efforts by enabling real-time data analysis and targeted campaign optimization. This results in a more effective use of resources, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional marketing methods that often generate substantial waste;
- -
- Personalization and Engagement: AI-driven tools facilitate the creation of personalized customer experiences, fostering deeper engagement and loyalty. By aligning marketing strategies with individual preferences, businesses can move away from broad, ineffective campaigns, enhancing customer satisfaction while minimizing resource consumption;
- -
- Sustainability Integration: The use of AI in digital marketing aligns closely with sustainability goals. By enabling brands to communicate their eco-friendly practices and social responsibilities effectively, AI helps businesses resonate with the growing number of consumers prioritizing sustainability in their purchasing decisions;
- -
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: While AI presents many advantages, it also raises challenges related to data privacy and ethics. Companies must ensure that their sustainability claims are authentic and transparent to avoid pitfalls like “greenwashing”;
- -
- Continuous Adaptation: The rapid evolution of digital technologies necessitates that businesses remain adaptable in their marketing strategies. By staying attuned to emerging trends and technologies, companies can optimize their marketing practices while addressing sustainability challenges.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotler, P.; Keller, K.L. Marketing Management, 12th ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, L.E. Contemporary Marketing; Cengage Learning Canada Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Deiss, R.; Henneberry, R. Digital Marketing for Dummies; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.M. The New Rules of Marketing and PR: How to Use Social Media, Blogs, News Releases, Online Video, and Viral Marketing to Reach Buyers Directly; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Esch, P.; Stewart Black, J. Artificial intelligence (AI): Revolutionizing digital marketing. Australas. Mark. J. 2021, 29, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precedence Research. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Market Size. 2023. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/artificial-intelligence-market (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Brundtland, G.H. World commission on environment and development. Environ. Policy Law 1985, 14, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishant, R.; Kennedy, M.; Corbett, J. Artificial intelligence for sustainability: Challenges, opportunities, and a research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hult, G.T.M. Market-focused sustainability: Market orientation plus! J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2011, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, W.P.; Kusumojanto, D.D.; Martha, J.A.; Ningsih, G.; Hapsari, N.T. The Role of Digital Marketing, Innovation, Self-Efficacy in Business Sustainability At the Rengginang Industrial Centre in the New Normal. Int. J. Bus. Econ. Law 2021, 24, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, I.C.; Branco, M.C.; Curto, J.D.; Eugénio, T. How does the market value corporate sustainability performance? J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 108, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lenne, O.; Vandenbosch, L. Media and sustainable apparel buying intention. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 2017, 21, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, C.E.; Alevizou, P.J.; Tan, J.; Huang, Q.; Ryding, D. Consumption strategies and motivations of Chinese consumers: The case of UK sustainable luxury fashion. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 2017, 21, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, A.; Sherry, J.F., Jr.; Venkatesh, A.; Wang, J.; Chan, R. Fast fashion, sustainability, and the ethical appeal of luxury brands. Fash. Theory 2012, 16, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, E. Leveraging artificial intelligence in marketing for social good—An ethical perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 179, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.M.; Schouten, J.W. Consumption-driven market emergence. J. Consum. Res. 2014, 40, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, V.L.; Crittenden, W.F.; Ferrell, L.K.; Ferrell, O.C.; Pinney, C.C. Market-oriented sustainability: A conceptual framework and propositions. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2011, 39, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, R.T. The future of marketing. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2020, 37, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.; Adam, S.; Denize, S.; Kotler, P. Principles of Marketing; Pearson Australia: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, V.; Vidyapeeth, B. Digital marketing: A review. Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev. 2019, 5, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschen, J.; Wilson, M.; Ferreira, J.J. Collaborative intelligence: How human and artificial intel-ligence create value along the B2B sales funnel. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce Stuart, H. An identity-based approach to the sustainable corporate brand. Corp. Commun. Int. J. 2011, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LePla, F.J. Integrated Branding: Becoming Brand-Driven Through Companywide Action; Quorum Books: Westport, CT, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Obermiller, C.; Burke, C.; Atwood, A. Sustainable business as marketing strategy. Innov. Mark. 2008, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, J.A.; Ballantine, P.W. What do we mean by sustainability marketing? J. Mark. Manag. 2019, 35, 277–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, P.; Lee, N. Best of breed: When it comes to gaining a market edge while supporting a social cause, “corporate social marketing” leads the pack. Soc. Mark. Q. 2005, 11, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belz, F.M.; Schmidt-Riediger, B. Marketing strategies in the age of sustainable development: Evidence from the food industry. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2010, 19, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meise, J.N.; Rudolph, T.; Kenning, P.; Phillips, D.M. Feed them facts: Value perceptions and consumer use of sustainability-related product information. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2014, 21, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubor, A.; Milovanov, O. Brand strategies in the era of sustainability. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. INDECS 2017, 15, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Watson, I.V. GF Marketing ecosystem: An outside-in view for sustainable advantage. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 88, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Guha, A.; Grewal, D.; Bressgott, T. How artificial intelligence will change the future of marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaz, V.; Centeno, M.A.; Callahan, P.W.; Causevic, A.; Patterson, T.; Brass, I.; Levy, K. Artificial intelligence, systemic risks, and sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Martin, F.; Blanco-Gonzalez, A.; Prado-Roman, C. Research challenges in digital marketing: Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipola, J.; Saunila, M.; Ukko, J. Adopting artificial intelligence in sustainable business. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucan, B.; Uzar, C. Managing sustainability risks and opportunities in finance and marketing. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Stud. 2014, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, A.K.; Choudhary, S.K.; Singh, V.K. How can artificial intelligence impact sustainability: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Gou, Z. Regional differences in household water technology adoption: A longitudinal study of Building Sustainability Index-certified dwelling units in New South Wales, Australia. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Reinartz, W. Creating enduring customer value. J. Mark. 2016, 80, 36–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Xie, C. Paradoxes of artificial intelligence in consumer markets: Ethical challenges and opportunities. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 129, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.A.; Rabiul, M.K. The relationships of corporate sustainability, customer loyalty, and word of mouth: The mediating role of corporate image and customer satisfaction. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2024, 25, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenitzerová, M.; Gaňa, J. Customer satisfaction and loyalty as a part of customer-based corporate sustainability in the sector of mobile communications services. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryl, M.D.; Verma, S.; Srivastava, V. How does AI drive branding? Towards an integrated theoretical framework for AI-driven branding. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Prentice, C.; Weaven, S.; Hisao, A. The influence of customer trust and artificial intelligence on customer engagement and loyalty–The case of the home-sharing industry. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 912339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, B. AI and the Future of Ethical Fashion Marketing: A Comprehensive Analysis of Sustainable Methods and Consumer Engagement. Eduzone Int. Peer Rev./Ref. Multidiscip. J. 2016, 5, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegle, L. To Die for: Is Fashion Wearing Out the World? Fourth Estate: London, UK, 2011; 352p, ISBN 9780007432530. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, C.M.; Niinimäki, K.; Kujala, S.; Karell, E.; Lang, C. Sustainable product-service systems for clothing: Exploring consumer perceptions of consumption alternatives in Finland. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, S.K.; Gill, A.Y.; Hussain, H.K. Green Innovations: Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Materials in Production. BULLET J. Multidisiplin Ilmu 2024, 3, 492–507. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, H. Sustainability of Artificial Intelligence in Marketing. Indian Institute of Foreign Trade. 2022. Available online: https://campus360.iift.ac.in/secured/DProject/5815/Interim6107530157566.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Aim Research. How Unilever is Leveraging AI to Drive Innovation and Sustainability. Aim Research. 2023. Available online: https://aimresearch.co/market-industry/how-unilever-is-leveraging-ai-to-drive-innovation-and-sustainability (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Marken, G.; Frick, V.; Schmelzle, F.; Meyer, A. The (Un-) Sustainability of Artificial Intelligence in Online Marketing; Institute for Ecological Economy Research (IÖW): Berlin, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dauvergne, P. Is artificial intelligence greening global supply chains? Exposing the political economy of environmental costs. Rev. Int. Political Econ. 2022, 29, 696–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, N.; Maher, M. How Shell Fueled Digital Transformation by Establishing DIY Software Development. MIS Q. Exec. 2023, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, B. How Shell is using web3 and blockchain for sustainability and energy transition. Forbes. 15 July 2022. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2022/07/15/how-shell-is-using-web3-and-blockchain-for-sustainability-and-energy-transition/ (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Kindylidi, I.; Cabral, T.S. Sustainability of AI: The case of provision of information to consumers. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechiel, F.; Blaurock, M.; Weber, E.; Büttgen, M.; Coussement, K. How tech companies advance sustainability through artificial intelligence: Developing and evaluating an AI x Sustainability strategy framework. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2024, 119, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Marketing Approach | Traditional Marketing | Digital Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Model | One-way communication (advertising, press releases, traditional media) | Two-way communication (social media, blogs, online video) |
| Audience Reach | Broad campaigns and media buys targeting large audiences | Targeted and personalized campaigns |
| Market Research | General, non-personalized data; lengthy and costly processes | Data analytics and segmentation for more targeted and faster market research |
| Pricing | Focus on product or service pricing, price-based competition | Content-driven strategy, value creation, and customer engagement |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Results: Digital marketing provides the capability to view results in real time. | Internet Dependence: Digital marketing can be ineffective in areas with no internet access or weak connectivity. |
| Global Reach and Interaction: Digital marketing allows for global reach and interaction with potential customers. | Competition and Clutter: The high volume of advertisements online can make it difficult for ads to stand out and for brands to be noticed. |
| Personalized Promotion: Digital marketing enables personalized and targeted advertising. | Trust Issues: Many online advertisements may be perceived as fraudulent, impacting customer trust. |
| Targeting Capabilities: Digital marketing offers better targeting of audiences and precise reach. | Negative Perception: Individuals or small groups can damage the image of well-known brands. |
| Sales Conversion Challenges: Digital marketing often focuses on disseminating information, which may not always translate into sales due to the lack of purchasing authority among many potential customers. |
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Customer Orientation and Value Proposition | Understanding what customers value from sustainable products is crucial, as it allows researchers to develop metrics that assess sustainability perceptions and enhance consumer experiences through targeted digital strategies, such as mobile augmented reality apps. |
| 2. Digital Consumer Behavior | Sustainability significantly influences consumer commitment, prompting inquiries into which digital marketing actions can encourage green purchasing behaviors and how consumers’ environmental values correlate with their online buying habits. |
| 3. Digital Green Marketing | Exploring how green marketing tools operate in digital environments is vital, particularly in sectors with high pollution levels, as it can reveal the impact of eco-labels and social campaigns on consumers’ purchase intentions and loyalty. |
| 4. Competitive Advantage | Sustainability has emerged as a competitive advantage, raising questions about how digital marketing strategies can leverage this aspect to build trust and foster strong stakeholder relationships while promoting sustainable business models. |
| 5. Supply Chain | Digital marketing plays a crucial role in supply chain management to achieve sustainability goals, and researchers can explore how it contributes to reducing consumption and enhancing the sustainability of industries and households. |
| 6. Capabilities | Investigating how digital marketing capabilities foster sustainable attitudes within organizations is essential, as it can reveal which skills and innovations are most effective in driving environmental commitment. |
| Theoretical Implications | Summary |
|---|---|
| AI Adoption | 68% of 25 enterprises used AI by 2020; this figure increased to 80% by 2021 (indicating a 12% rise). |
| Holistic View | AI helps manage diverse business sectors (supply chains, production, marketing) for sustainability. |
| Beyond Ecological Focus | AI initiatives enhance employee safety and governance by optimizing heating and identifying training needs. |
| Ecological Sustainability | AI manages large data sets to enhance ecological performance, optimizing raw materials and energy use. |
| Ethical AI Development | The need for auditing and standards in AI systems to ensure data quality and holistic supply chain assessments. |
| Enhanced Image and Social Impact | AI enables social impact analysis, optimizing logistics and materials for better sustainability outcomes. |
| Company | Industry | AI-Driven Sustainability Initiatives | AI Application and Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adidas (Herzogenaurach, Germany) | Sportswear | 100% recyclable running shoe made from a single material (TPU) | Adidas used machine learning techniques to predict the performance of TPU and other sustainable materials, creating high-performance running shoes made from recyclable materials. |
| Tesla (Palo Alto, CA, USA) | Electric Vehicles | Use of recycled materials in battery production | Tesla applied AI algorithms to optimize recycling processes and forecast the performance of recycled materials in new batteries, increasing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. |
| Unilever (London, UK) | Consumer Goods | Use of recycled plastics, biodegradable materials, and paper-based substitutes | Unilever uses AI across its business to drive innovation and increase efficiency, promoting sustainability and meeting customer expectations while paving the way for a sustainable future. |
| IKEA (Älmhult, Sweden) | Furniture | Recycled wood fibers and agricultural byproducts | IKEA used AI to model and simulate the properties of new sustainable materials, leading to the development of environmentally friendly furniture with lower energy use and waste. |
| Technology | AI Application | AI Application and Results |
|---|---|---|
| IBM Watson & Salesforce | Marketing Automation | Teamed to automate decision-making processes by applying AI to shopping habits, weather forecasts, and customer preferences. Result: Automated, personalized emails to potential shoppers. |
| Amazon | Predictive AI System | Developed an AI system to predict customer desires and deliver products before they even know it. Result: Cost-effective distribution, increased sales, and predictive modeling. |
| Slice | Email Automation | AI system that examines customer inboxes and provides real-time information on shipments and default actions. Result: Enhanced customer experience with timely delivery information. |
| Resonance | Consumer Preference AI | Recognizes and interprets user preferences across devices and applications. Result: Compiles data to create a holistic view of consumer habits and automates connected goods actions. |
| Hutoma | AI Chatbot Platform | Centralized marketplace and network for AI chatbots. Result: Developers can focus on use cases and consumer experiences, while Hutoma provides the neural networks that power chatbots. |
| Neurence | AI Cloud Engine | Developed a cloud-based AI engine that understands unstructured human environments. Result: Computers can intuitively understand and interact with complex, real-world settings. |
| Etsy | Product Discovery AI | Improves product discovery by understanding customer preferences and needs. Result: Better product recommendations and customer satisfaction. |
| Msg.AI | Conversational AI | Delivers a conversational AI platform for business connections. Result: Enables firms to communicate with customers via text, a preferred method over email or phone calls. |
| Twiggle | E-Commerce AI | Uses machine learning, natural language processing, and data mining to provide automated solutions for e-commerce challenges. Result: More accurate search and better user experience. |
| Afiniti | AI-Driven Routing | Combines AI and big data to replace traditional time-based routing in call centers, connecting consumers and agents based on behavior. Result: More efficient and personalized customer-agent interactions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gündüzyeli, B. Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310511
Gündüzyeli B. Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management. Sustainability. 2024; 16(23):10511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310511
Chicago/Turabian StyleGündüzyeli, Bora. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management" Sustainability 16, no. 23: 10511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310511
APA StyleGündüzyeli, B. (2024). Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management. Sustainability, 16(23), 10511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310511


_Li.png)






