Holistic Analysis of the Impact of Power Generation Plants in Mexico during Their Life Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Power Generation in Mexico
3. Materials and Methods
4. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods
4.1. Analytical Hierarchy Process
- Structured Framework: simplifies complex decisions by organizing them hierarchically;
- Multiple criteria: considers both qualitative and quantitative factors;
- Group decision-making: facilitates consensus among groups;
- Consistency check: ensures logical and reliable judgments;
- Flexibility: adaptable to various fields and scenarios;
- Prioritization: focuses on the most critical factors;
- Transparency: provides a clear audit trail;
- Quantification: converts subjective assessments into quantitative data;
- Comprehensive analysis: offers a holistic view of the decision problem.
AHP Methodology
5. Criteria for the Evaluation of Generation Plants
Weighting of Criteria
6. Life-Cycle Assessment
- Comprehensive evaluation: assesses environmental impacts throughout the entire life cycle;
- Informed decision-making: guides strategies for improvement and sustainability;
- Comparison of alternatives: helps choose the most sustainable option;
- Identification of trade-offs: balances various sustainability goals;
- Regulatory compliance: supports adherence to environmental regulations;
- Market differentiation: enhances reputation and competitive advantage;
- Resource efficiency: identifies inefficiencies and reduces costs and environmental burdens;
- Transparency and credibility: ensures reliable and credible results through standardized methodologies;
- Stakeholder engagement: provides clear data to communicate sustainability efforts.
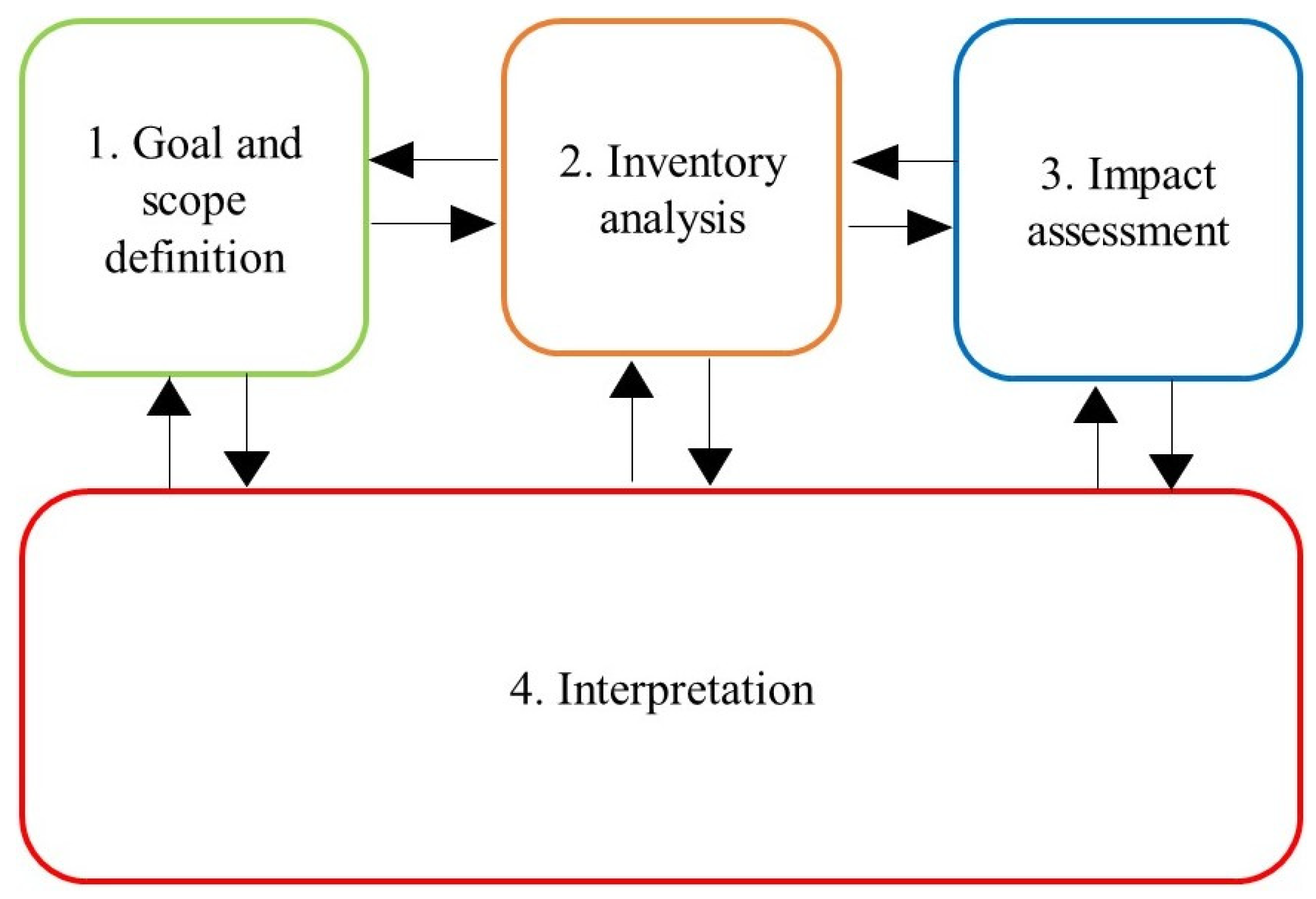
6.1. LCA Methodology
6.1.1. Definition of Objectives and Scope
6.1.2. Inventory Analysis
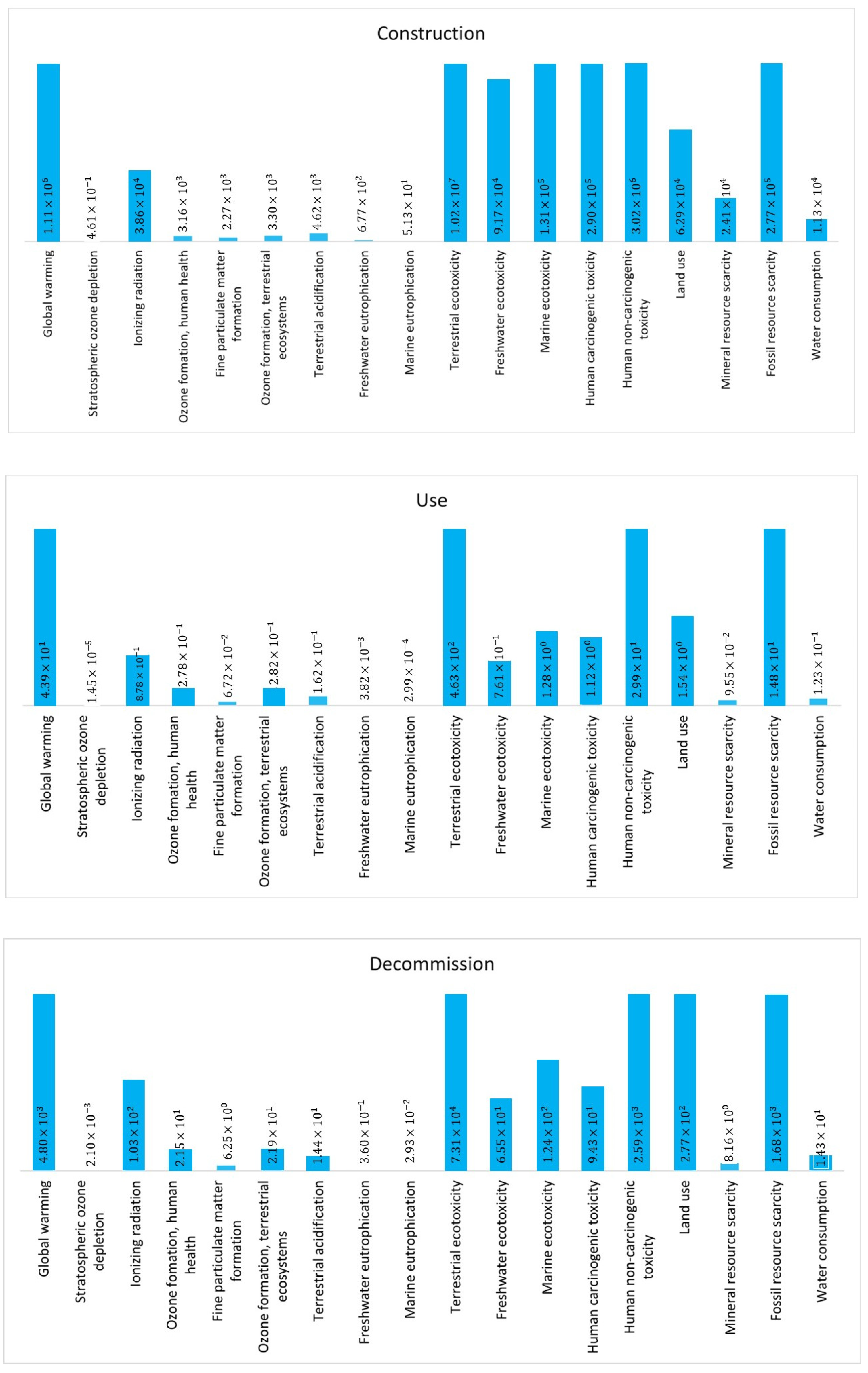
6.1.3. Impact Evaluation
- Global warming;
- Ionizing radiation;
- Ozone formation and human health;
- Ozone formation and terrestrial ecosystems;
- Stratospheric ozone depletion;
- Fine particulate matter formation;
- Freshwater eutrophication;
- Freshwater ecotoxicity;
- Water consumption;
- Marine eutrophication;
- Marine ecotoxicity;
- Human non-carcinogenic toxicity;
- Human carcinogenic toxicity;
- Terrestrial acidification;
- Terrestrial ecotoxicity;
- Land use;
- Mineral resource scarcity;
- Fossil resource scarcity.
6.1.4. Interpretation
7. AHP Simulations and Results
7.1. Results by Categories
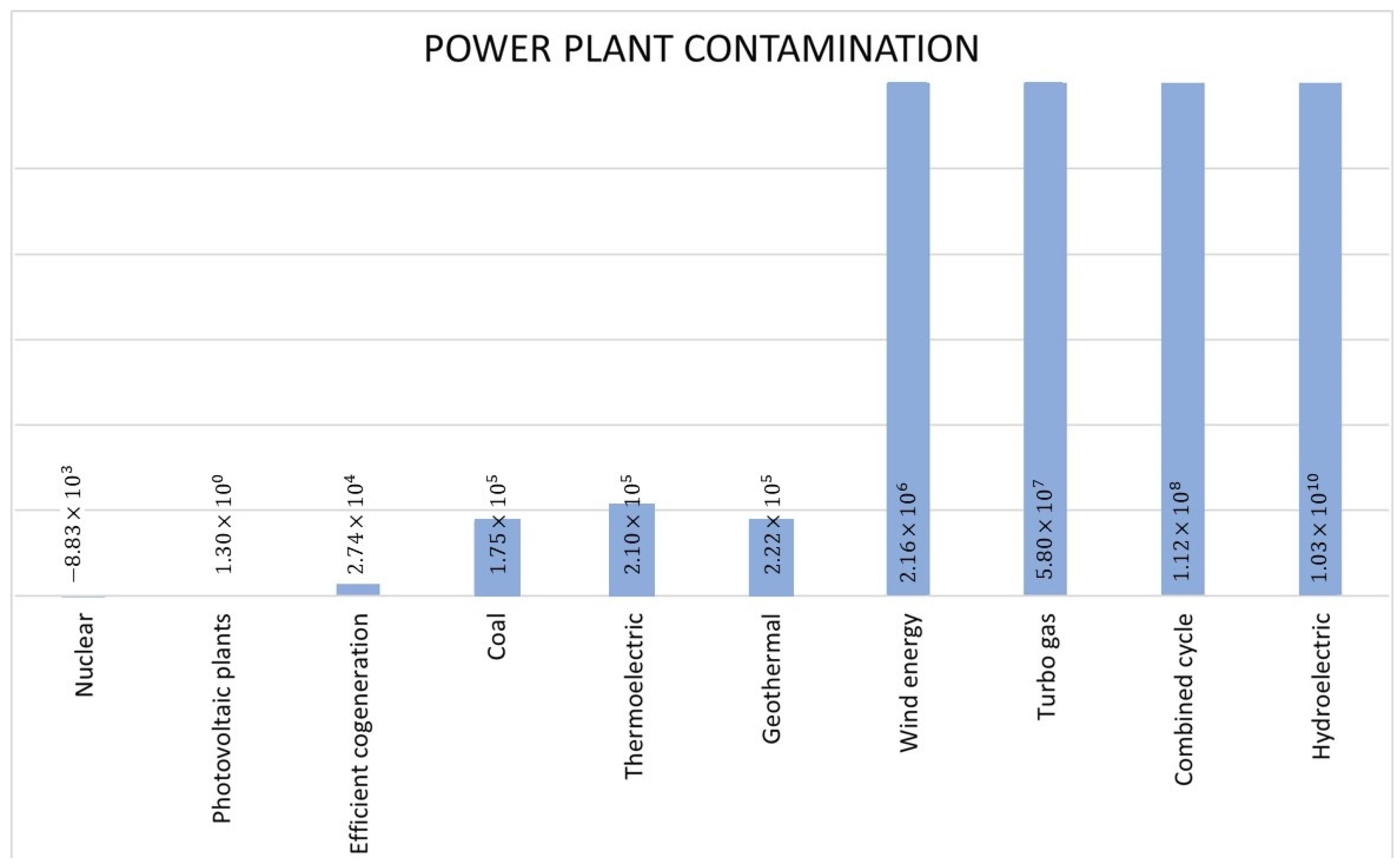
7.1.1. Ranking of Power Plants: Environmental Category
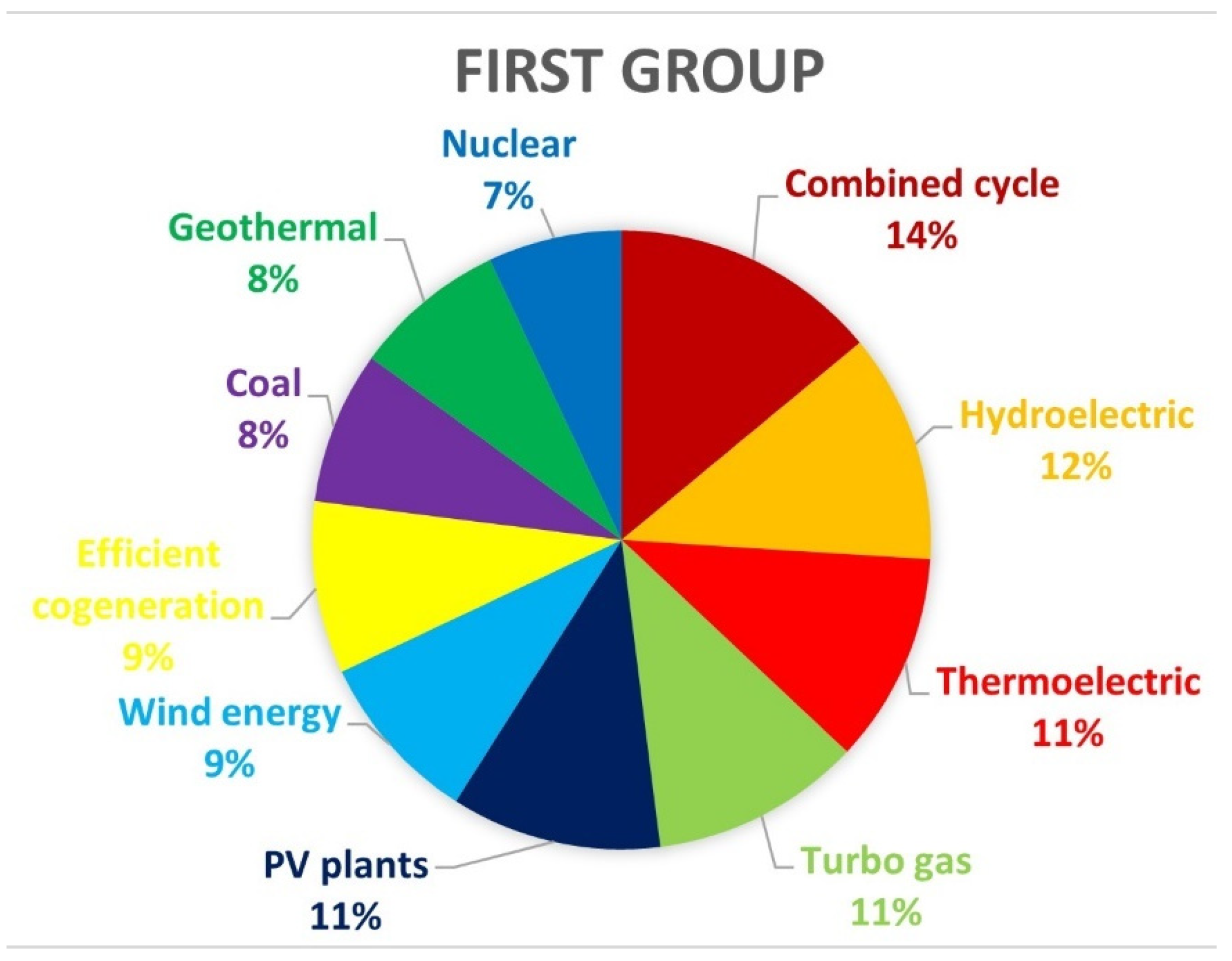
7.1.2. Results According to the First Group of People Surveyed
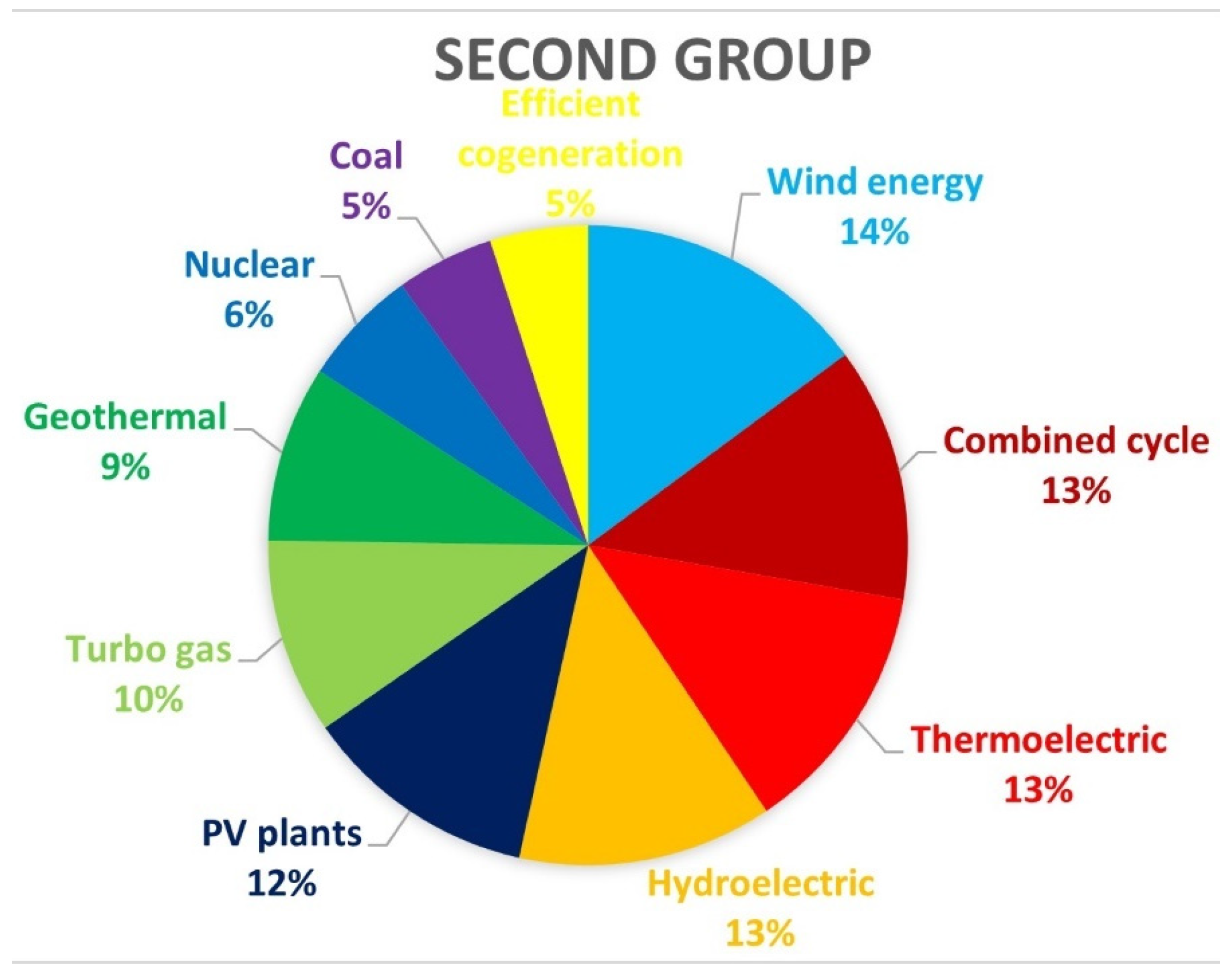
7.1.3. Results According to the Second Group of People Surveyed
7.2. Overall Results
7.2.1. Global Ranking According to the First Group of People
7.2.2. Global Ranking According to the Second Group of People
8. Discussion of the Results
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordaan, S.M.; Combs, C.; Guenther, E. Life cycle assessment of electricity generation: A systematic review of spatiotemporal methods. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 3, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2022. International Energy Agency (IEA). Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2022/executive-summary?language=es (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Barragán, E. Factores que influyen en la selección de energías renovables en la ciudad. EURE 2019, 45, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SENER. Reporte de Avance de Energías Limpias: Primer Semestre 2018. Secretaría de Energía (SENER), México. 2018. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/418391/RAEL_Primer_Semestre_2018.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Turconi, R.; Boldrin, A.; Astrup, R. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of electricity generation technologies: Overview, comparability, and limitations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, L.; Bélanger, C.; Uchiyama, Y. Life-cycle assessment of electricity generation options: The status of research in year 2001. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilgan, B.; Azapagic, A. Renewable electricity in Turkey: Life cycle environmental impacts. Renew. Energy 2016, 89, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez-Mahmud, M.A.; Huda, N.; Hisan-Farjana, S.; Lang, C. Life-cycle impact assessment of renewable electricity generation systems in the United States. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 1028–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez-Mahmud, M.A.; Hisan-Farjana, S. Comparative life cycle environmental impact assessment of renewable electricity generation systems: A practical approach towards Europe, North America and Oceania. Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle-Flores, D.L.; Peña-Gallardo, R.; Palacios-Hernández, E.R. The current state of power generation plants in Mexico from the life cycle assessment point of view. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Autumn Meeting on Power, Electronics and Computing (ROPEC), Ixtapa, Mexico, 9–11 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, A.; Jiménez, R.; López, E.; Monteagudo, J. Multicriterium Decision Methods in Renewable Energy Planning; Universidad de Cienfuegos: Cienfuegos, Cuba, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sah, B.; Singh, A.R.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Kumar, P.; Bansal, R.C. A review of multi criteria decision making (MCDM) towards sustainable renewable energy development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ospino-Castro, A.; Robles-Algarín, C.; Mangones-Cordero, A.; Romero-Navas, S. An Analytic Hierarchy Process Based Approach for Evaluating Feasibility of Offshore Wind Farm on the Colombian Caribbean Coast. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy (IJEEP) 2023, 64–73. Available online: https://www.zbw.eu/econis-archiv/bitstream/11159/631309/1/1871296358_0.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.; Romana, M. Aplicación de Métodos de Decisión Multicriterio Discretos al Análisis de Alternativas en Estudios Informativos de Infraestructuras de Transporte. Investigación 2016, 6, 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira-Pires, A.; Da, R.; Ribeiro, S. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of a gas turbine power plant. In Proceedings of the 17th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering, São Paulo, Brazil, 10–14 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- GOB. Reforma Energética. Gobierno de la República (GOB). 2013. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/164370/Resumen_de_la_explicacion_de_la_Reforma_Energetica11_1_.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- PRODESEN. Informe 2022-2036. Secretaría de Energía (SENER). Programa para el Desarrollo del Sistema Eléctrico Nacional (PRODESEN), SENER. 2022. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cenace/documentos/programa-para-el-desarrollo-del-sistema-electrico-nacional-2022-2036 (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Mannan, S. Lees’ Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 2507–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Infante, A. Técnicas multicriterio hibridas para la selección de proyectos renovables eólicos. Polo Conoc. 2021, 6, 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Mayor, J.; Botero, S.; González-Ruiz, J. Modelo de decisión multicriterio difuso para la selección de contratistas en proyectos de infraestructura: Caso Colombia. Obras Proy. 2016, 20, 56–74. Available online: https://www.scielo.cl/pdf/oyp/n20/art05.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rebitzer, G.; Ekvall, T.; Frischknecht, R.; Hunkeler, D.; Norris, G.; Rydberg, T.; Schmidt, W.P.; Suh, S.; Weidema, B.P.; Pennington, D.W. Life cycle assessment: Part 1: Framework, goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, and applications. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, D.; Goglio, P.; Williams, A.; Manning, D.A.C.; de Azevedo, A.C.; Bergmann, M.; Meersmans, J.; Smith, P. Assessing the potential of soil carbonation and enhanced weathering through Life Cycle Assessment: A case study for Sao Paulo State, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Cruz, R. Analysis of the Life Cycle Applied to Conventional and Combined Cycle Thermoelectric Plants. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico, 2014. Available online: http://132.248.9.195/ptd2014/junio/0714732/0714732.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Wibawa, B.S.; Iswara, A.P.; Boedisantoso, R. Impact assessment of coal power plant using life cycle assessment (LCA). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 506, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.; Sirenia, P. Life Cycle Analysis of Electric Power from Fossil Fuels. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California, Tijuana, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Relaño, L. Analysis of the Life Cycle of Wind and Hydraulic Technologies in Spain; Proyecto de Fin de Grado, Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros de Minas y Energía: Madrid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Calderón, V. Análisis del Ciclo de Vida de Sistemas Solares Fotovoltaicos Policristalinos Centralizados en Instalaciones de Generación Distribuida para Autoconsumo. Proyecto Final de Graduación para optar por el grado de Licenciatura en Ingeniería Ambiental, Instituto Tecnológico de Costa Rica, Cartago, Costa Rica. 2019. Available online: https://repositoriotec.tec.ac.cr/bitstream/handle/2238/11228/analisis_ciclo_vida_sistemas_solares.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Thomas, L.K.; Tinjum, J.M.; Holcomb, F.H. Environmental life cycle assessment of a deep direct-use geothermal system in Champaign, Illinois. In Proceedings of the 45th Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford, CA, USA, 10–12 February 2020; Available online: https://pangea.stanford.edu/ERE/db/GeoConf/papers/SGW/2020/Thomas.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Zaky, A.S.; Carter, C.E.; Meng, F.; Frech, C.E. A preliminary life cycle analysis of bioethanol production using seawater in a coastal biorefinery setting. Processes 2021, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usubharatana, P.; Phungrassami, H. Life cycle assessment for enhanced efficiency of small power plants by reducing air input temperature. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1781–1793. Available online: https://www.pjoes.com/pdf-78433-24605?filename=Life%20Cycle%20Assessment%20for.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- CCHEN. Study for the Identification and Evaluation of Possible Effects and Environmental Impacts Produced by the Generation of Nuclear Power in Chile. IDOM; Chilean Nuclear Energy Commission (CCHEN): Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, F. Analysis of the Life Cycle, Comparative of An Organic and Non-Organic Orange Marmalade. Bachelor’s Thesis, Proyecto fin de carrera, Escuela de ingenierías industriales, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Yang, H.; Heo, G.; Zubair, M.; Khalil Ur, R. Study on Nuclear Accident Precursors Using AHP and BBN. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2014, 2014, 206258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanakas, J.A.; Van der Heide, A.; Radavičius, T.; Denafas, J.; Lemaire, E.; Wang, K.; Poortmans, J.; Voroshazi, E. Towards a circular supply chain for PV modules: Review of today’s challenges in PV recycling, refurbishment and re-certification. Prog. Photovolt. 2020, 28, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Conventional | Clean | Other |
|---|---|---|
| Combined cycle Thermoelectric Coal Turbo gas Internal combustion Fluidized bed | Wind energy Hydroelectric PV plants Bioenergy Geothermal Solar thermal | Efficient cogeneration Nuclear Regenerative brakes |
| Value | Definition |
|---|---|
| 9 | Extremely more important. |
| 7 | Strongly more important. |
| 5 | Much more important. |
| 3 | Slightly more important. |
| 1 | Equally important. |
| 1/3 | Slightly less important. |
| 1/5 | Much less important. |
| 1/7 | Strongly less important. |
| 1/9 | Extremely less important. |
| n | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Random index | 0.525 | 0.882 | 1.115 | 1.252 | 1.341 | 1.404 | 1.452 | 1.484 | 1.513 | 1.535 |
| n | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| Random index | 1.555 | 1.570 | 1.583 | 1.595 | 1.6075 | 1.620 | 1.6325 | 1.645 | 1.6575 | 1.670 |
| Category | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Greenhouse gas emission (C1). |
| Acidification (C2). | |
| Eutrophication (C3). | |
| Area availability and urban obstacles (C4). | |
| Visual impact (C5). | |
| Noise (C6). | |
| Waste production (C7). | |
| Technical | Efficiency (C8). |
| Technical maturity and ability (C9). | |
| Supply quantity (C10). | |
| Useful life (C11). | |
| Spare parts and maintenance (C12). | |
| Network integration problems (C13). | |
| Availability of the primary source (C14). | |
| Economic | Investment and installation cost (C15). |
| Operation and maintenance cost (C16). | |
| Investment recovery period (C17). | |
| Energy cost (C18). | |
| Social | Job creation (C19). |
| Social acceptance (C20). | |
| Compatibility with international, regional, or local policies (C21). | |
| Home and social benefits (C22). |
| Criteria | Totals | Allocated Weight |
|---|---|---|
| C8 | 2034 | 9 |
| C15 | 2017 | 9 |
| C11 | 2010 | 7 |
| C9 | 2004 | 7 |
| C18 | 1993 | 7 |
| C10 | 1980 | 5 |
| C17 | 1972 | 5 |
| C12 | 1971 | 5 |
| C16 | 1962 | 3 |
| C14 | 1916 | 3 |
| C19 | 1899 | 3 |
| C13 | 1887 | 1 |
| C21 | 1883 | 1/3 |
| C7 | 1849 | 1/3 |
| C22 | 1820 | 1/3 |
| C4 | 1765 | 1/5 |
| C1 | 1746 | 1/5 |
| C20 | 1714 | 1/5 |
| C2 | 1657 | 1/7 |
| C3 | 1587 | 1/7 |
| C6 | 1582 | 1/9 |
| C5 | 1462 | 1/9 |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | C19 | C20 | C21 | C22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 3 | 1/3 | 1/3 |
| C2 | 1/5 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/3 |
| C3 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/3 | 5 | 3 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/5 |
| C4 | 1 | 1/3 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 5 | 1/3 | 1/3 |
| C5 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/5 |
| C6 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 3 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 5 | 1/3 | 3 |
| C7 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 5 | 1/3 | 3 |
| C8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 7 | 7 |
| C9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 7 | 1/5 | 5 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 |
| C10 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 1/3 | 3 | 1 | 1/7 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 1/7 | 3 | 3 | 1/3 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| C11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1/3 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 1/3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| C12 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1/5 | 3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1/7 | 3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| C13 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| C14 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 1/5 | 5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 3 | 1 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| C15 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 7 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| C16 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1/5 | 5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 3 | 3 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| C17 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1/5 | 3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 1/3 | 3 | 1 | 1/3 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
| C18 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 1/3 | 3 | 3 | 1/3 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 1/3 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 |
| C19 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1/5 | 5 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| C20 | 1/3 | 3 | 3 | 1/5 | 3 | 3 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/3 |
| C21 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1/7 | 5 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 5 | 1 | 3 |
| C22 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 1/3 | 1/7 | 7 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 3 | 1/3 | 1 |
| No. | Construction | Use | Decommission |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nuclear | Nuclear | Nuclear |
| 2. | Coal | Hydroelectric | Hydroelectric |
| 3. | Thermoelectric | PV plants | PV plants |
| 4. | PV plants | Wind energy | Efficient cogeneration |
| 5. | Combined cycle | Turbo gas | Turbo gas |
| 6. | Efficient cogeneration | Efficient cogeneration | Coal |
| 7. | Geothermal | Coal | Geothermal |
| 8. | Wind energy | Geothermal | Thermoelectric |
| 9. | Turbo gas | Thermoelectric | Wind energy |
| 10. | Hydroelectric | Combined cycle | Combined cycle |
| No. | Economic | Technical | Social |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | PV plants | Combined cycle | Efficient cogeneration |
| 2. | Turbo gas | Thermoelectric | Combined cycle |
| 3. | Coal | Hydroelectric | Hydroelectric |
| 4. | Wind energy | Efficient cogeneration | Thermoelectric |
| 5. | Geothermal | Turbo gas | Geothermal |
| 6. | Hydroelectric | Geothermal | Wind energy |
| 7. | Nuclear | Wind energy | PV plants |
| 8. | Efficient cogeneration | Nuclear | Nuclear |
| 9. | Combined cycle | PV plants | Turbo gas |
| 10. | Thermoelectric | Coal | Coal |
| No. | Economic | Technical | Social |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wind energy | Thermoelectric | Turbo gas |
| 2. | Nuclear | Geothermal | Thermoelectric |
| 3. | Hydroelectric | Combined cycle | Combined cycle |
| 4. | Coal | Coal | Hydroelectric |
| 5. | Combined cycle | Turbo gas | Geothermal |
| 6. | Efficient cogeneration | Hydroelectric | PV plants |
| 7. | PV plants | PV plants | Coal |
| 8. | Thermoelectric | Wind energy | Efficient cogeneration |
| 9. | Geothermal | Nuclear | Wind energy |
| 10. | Turbo gas | Efficient cogeneration | Nuclear |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ovalle Flores, D.L.; Peña Gallardo, R.; Palacios Hernández, E.R.; Soubervielle Montalvo, C.; Ospino Castro, A. Holistic Analysis of the Impact of Power Generation Plants in Mexico during Their Life Cycle. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167041
Ovalle Flores DL, Peña Gallardo R, Palacios Hernández ER, Soubervielle Montalvo C, Ospino Castro A. Holistic Analysis of the Impact of Power Generation Plants in Mexico during Their Life Cycle. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167041
Chicago/Turabian StyleOvalle Flores, Diana L., Rafael Peña Gallardo, Elvia R. Palacios Hernández, Carlos Soubervielle Montalvo, and Adalberto Ospino Castro. 2024. "Holistic Analysis of the Impact of Power Generation Plants in Mexico during Their Life Cycle" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167041
APA StyleOvalle Flores, D. L., Peña Gallardo, R., Palacios Hernández, E. R., Soubervielle Montalvo, C., & Ospino Castro, A. (2024). Holistic Analysis of the Impact of Power Generation Plants in Mexico during Their Life Cycle. Sustainability, 16(16), 7041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167041






