Analysis of Surface Runoff Characteristics in Zhengzhou City under Extreme Rainfall Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Overview and Research Methods
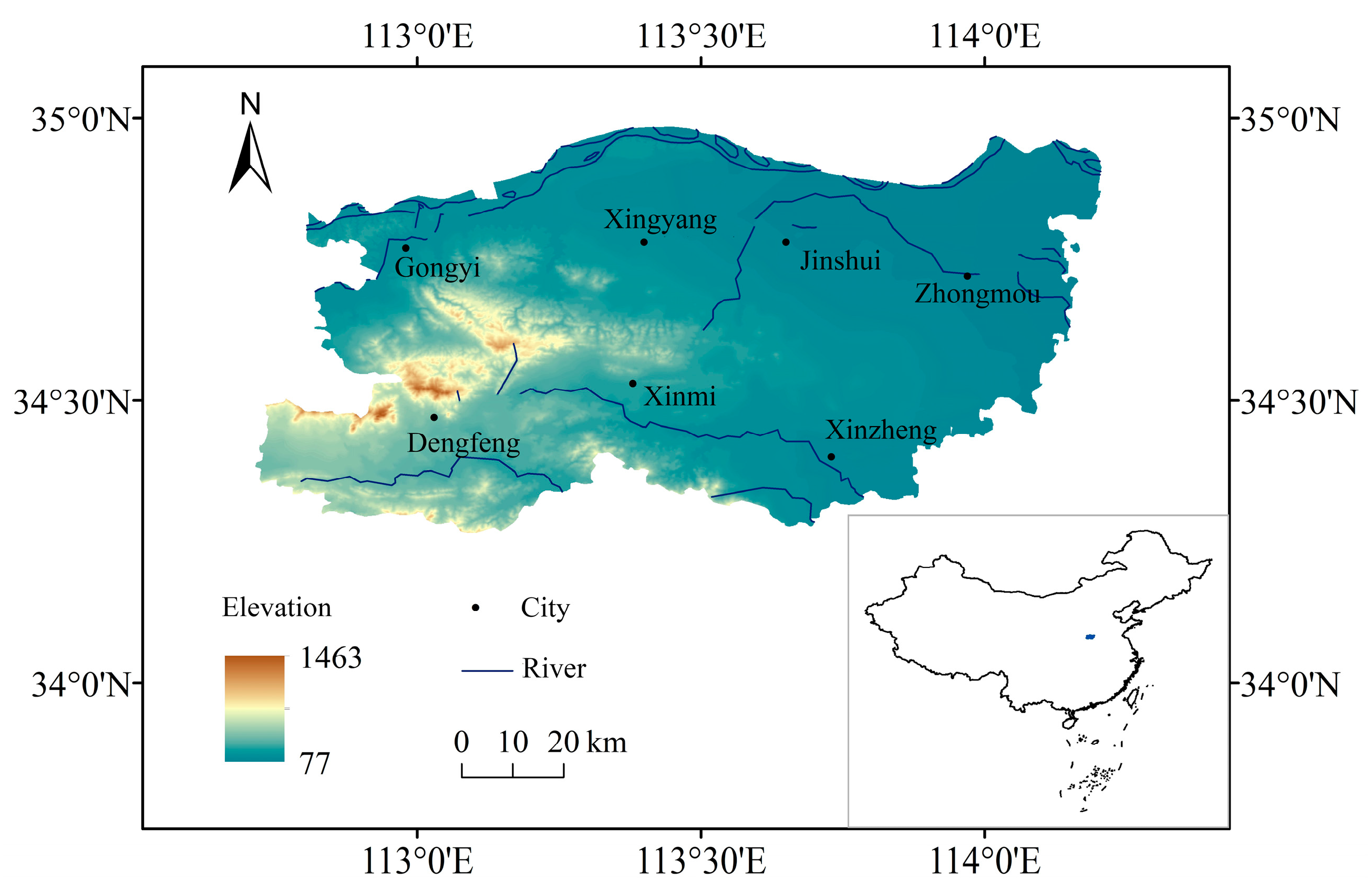
2.1. Regional Overview
2.2. Research Methods
3. Results
3.1. Extreme Rainfall and Surface Runoff in the Study Area from 2005 to 2020
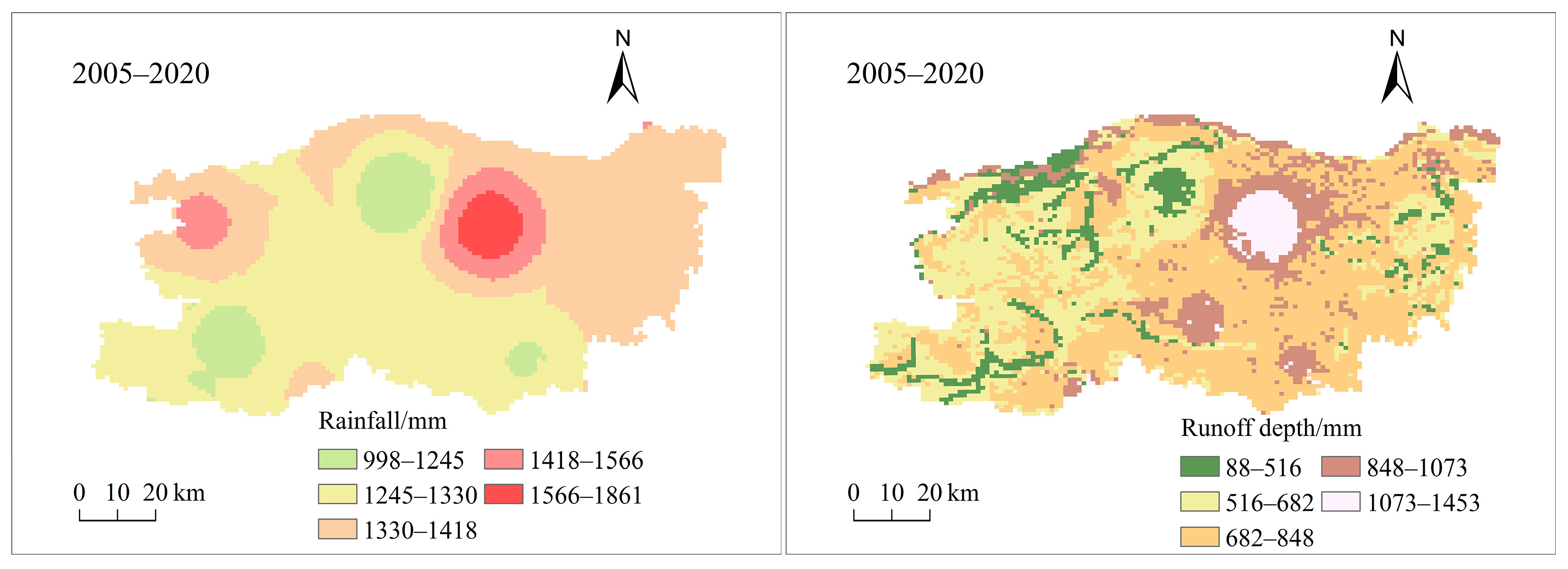
3.1.1. Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall and Surface Runoff in the Study Area from 2005 to 2020
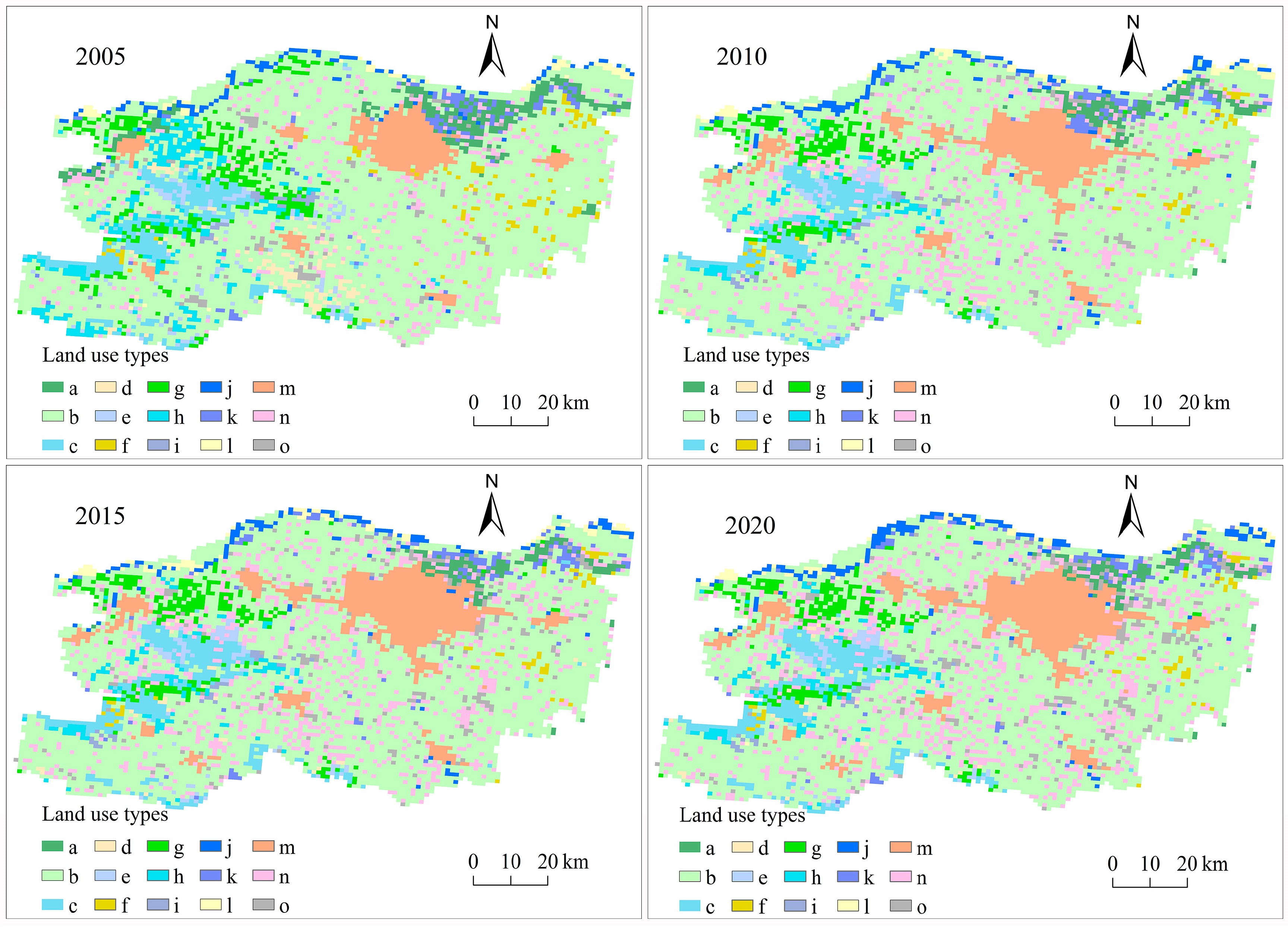
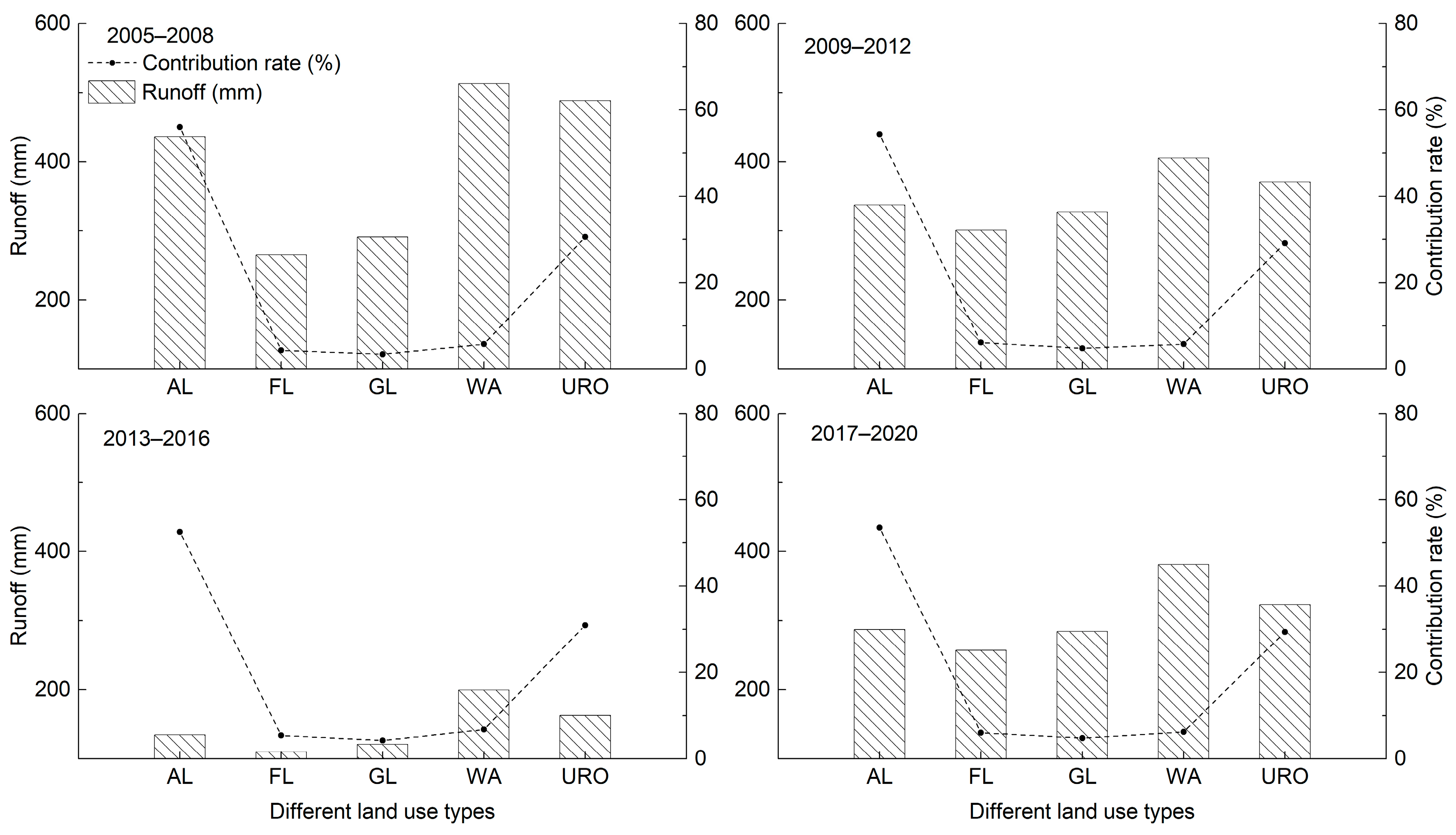
3.1.2. The Contribution of Different Land Use Types to Surface Runoff in the Study Area from 2005 to 2020
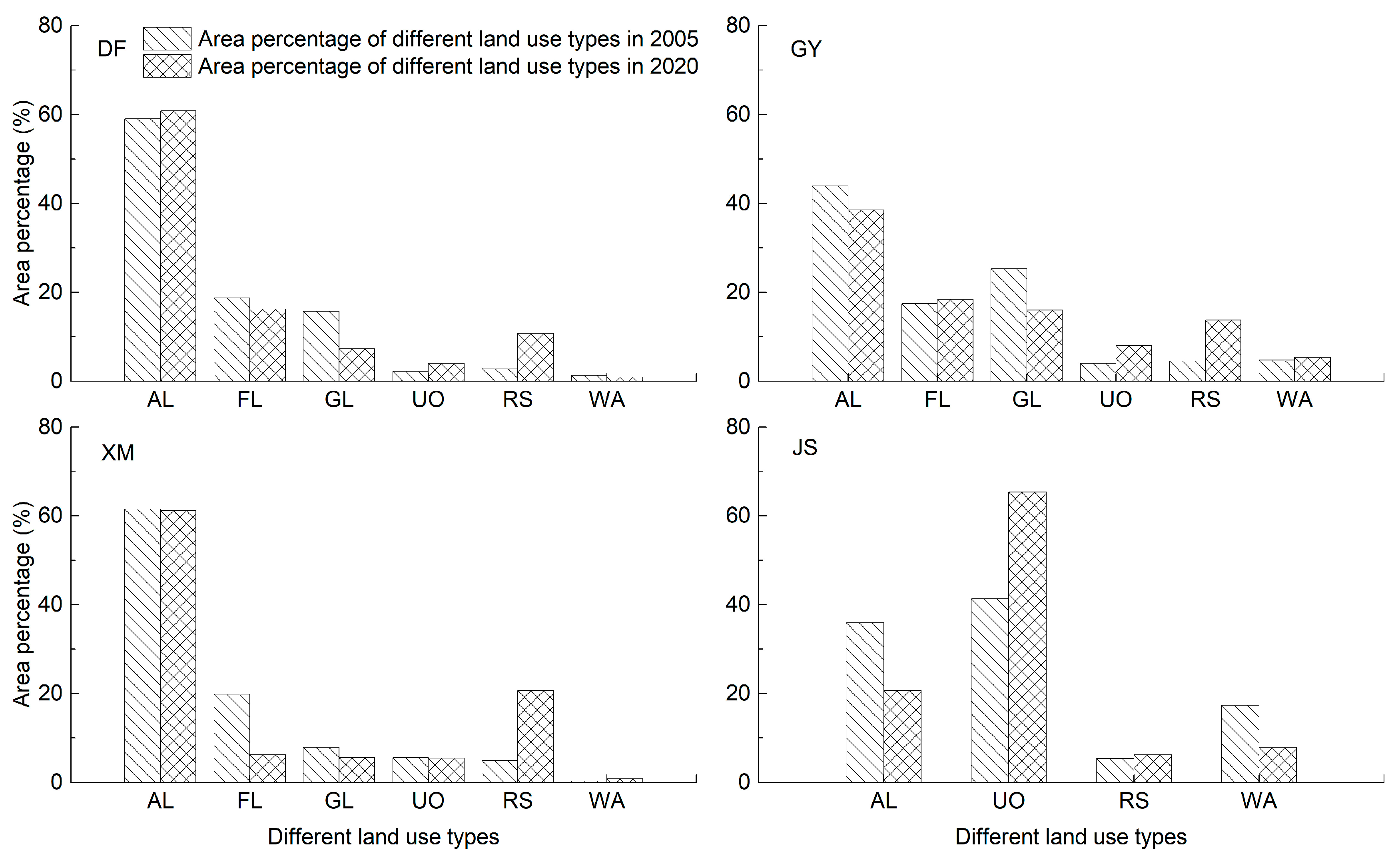
3.2. The Influence of Different Land Use Types on Surface Runoff
3.3. Surface Runoff under Extreme Rainfall Events
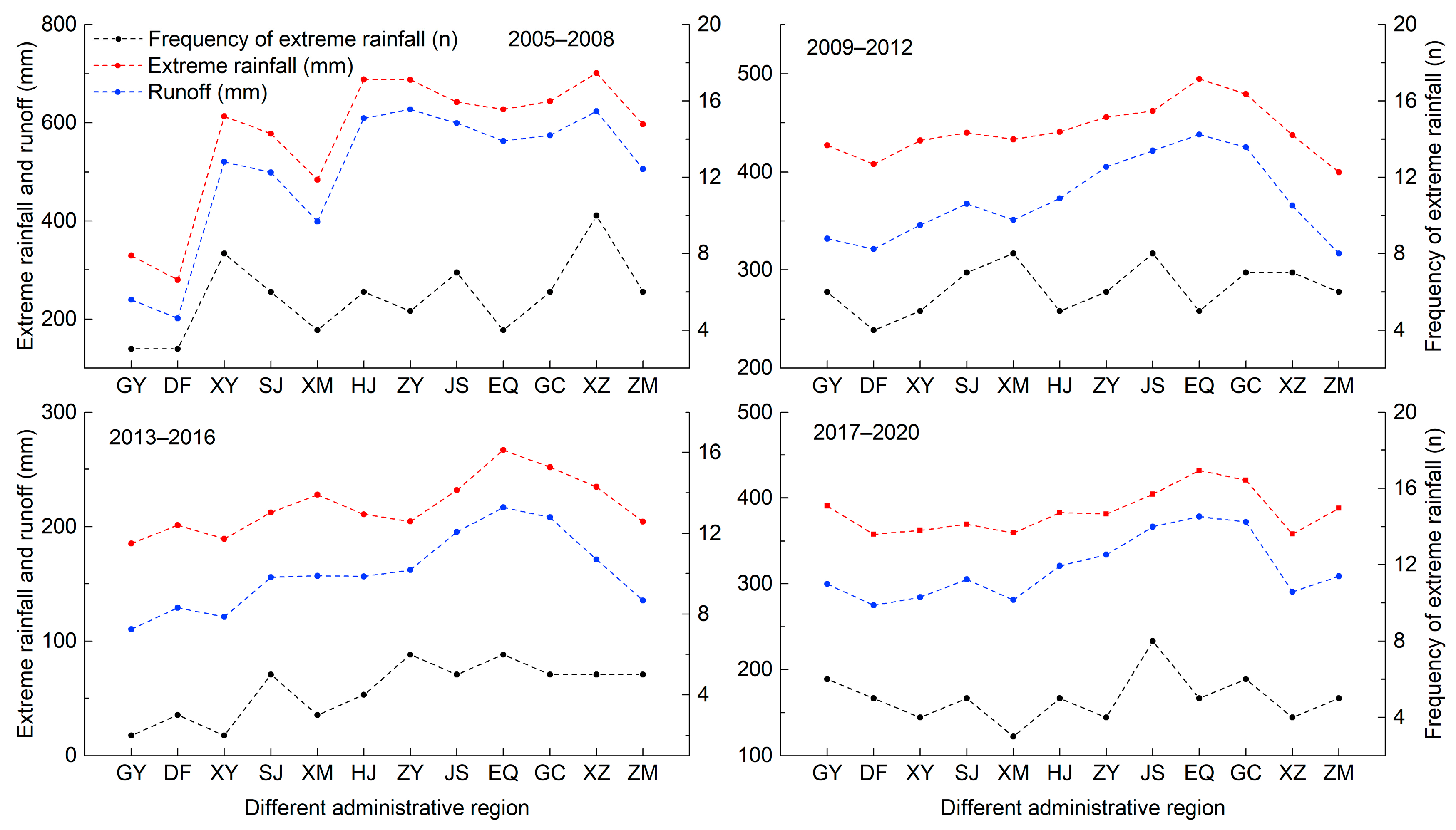
3.3.1. Surface Runoff from Different Administrative Areas under Extreme Rainfall Events
3.3.2. Surface Runoff of Different Slopes under Extreme Rainfall Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Influencing Factors of Surface Runoff
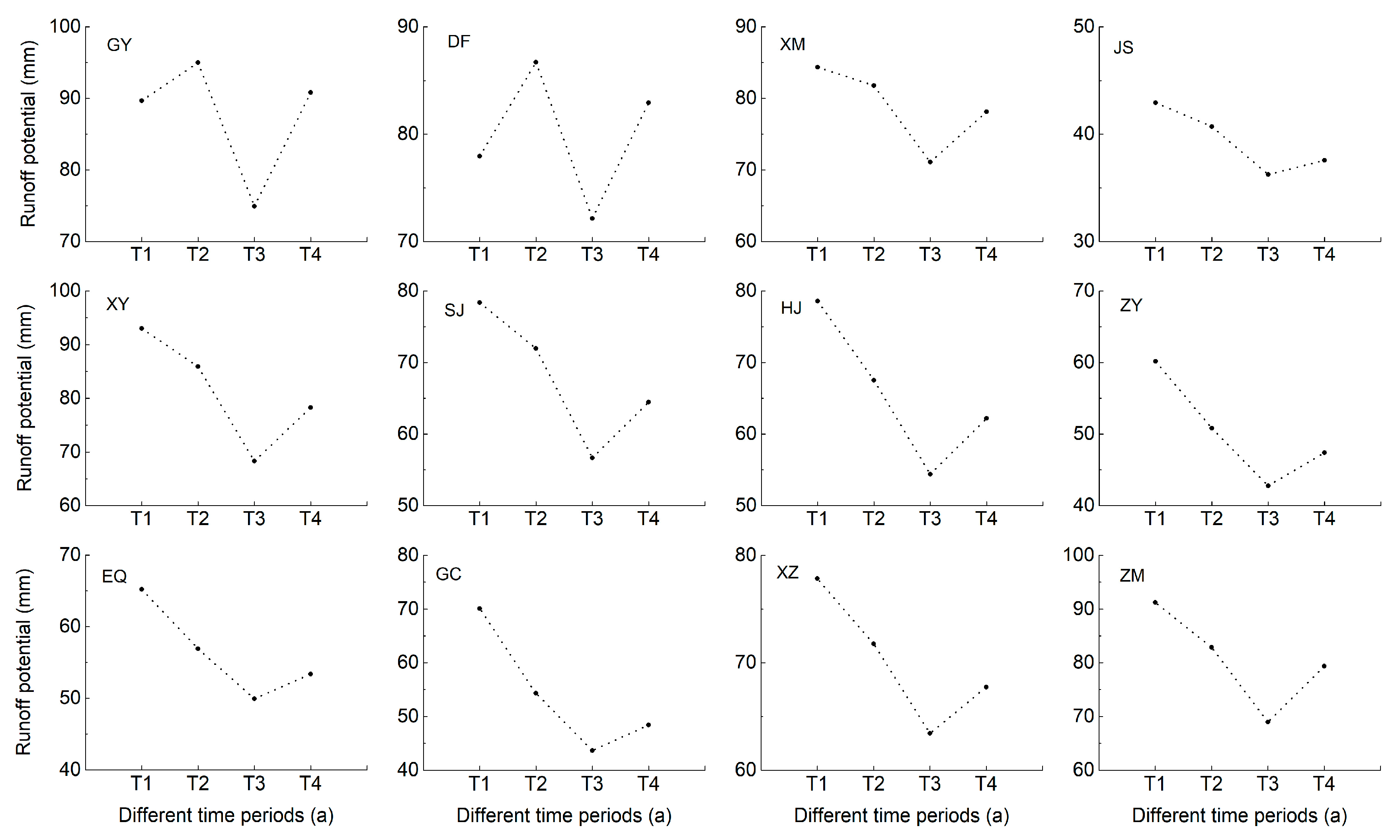
4.2. The Change in Surface Runoff Potential in Different Regions of the Study Area
4.3. Enlightenment of Land Use Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, G.P.; Andrew, R.M.; Boden, T.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P.; Le Quéré, C.; Marland, G.; Raupach, M.R.; Wilson, C. The challenge to keep global warming below 2 °C. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, M.G.; Lowry, A.L.; Alexander, L.V.; O’gorman, P.A.; Maher, N. More extreme precipitation in the world’s dry and wet regions. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Xie, P. The roles of short-lived climate forcers in a changing climate. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 17, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, I.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Trends in seasonal precipitation extremes—An indicator of ‘climate’ change in Kerala, India. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Van Meijgaard, E. Increase in hourly precipitation extremes beyond expectations from temperature changes. Nature Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camorani, G.; Castellarin, A.; Brath, A. Effects of land-use changes on the hydrologic response of reclamation systems. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2005, 30, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, S.; Band, L.E. Simulating runoff behavior in an urbanizing watershed. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2000, 24, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeiren, B.; Van De Voorde, T.; Canters, F.; Binard, M.; Cornet, Y.; Batelaan, O. Assessing urbanisation effects on rainfallrunoff using a remote sensing supported modelling strategy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Fahy, B.; Brenneman, E.; Chang, H.; Shandas, V. Spatial analysis of urban flooding and extreme heat hazard potential in Portland, OR. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 39, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Bao, J.; Liu, X. Assessment Method and Empirical Study on the Population Affected by Urban Waterlogging Disaster: Daoli District of Harbin as an Example. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 40, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, J. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Short-Duration Rainstorm Pattern and Its Influence on Urban Waterlogging in Tianjin. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2021, 37, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengtao, Z.; Chao, G.; Qing, L. Risk Assessment on Storm Flood Disasters of Different Return Periods in Huaihe River Basin. Geography Study 2014, 33, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, M.J.; Schubert, J.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Sanders, B.F. Testing the impact of at-source stormwater management on urban flooding through a coupling of network and overland flow models. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesner, L.A.; Nichandros, H.M.; Shubinski, R.P.; Feldman, A.D.; Abbott, J.W. A model for evaluating runoff-quality in metropolitan master planning. Hydrol. Eng. Cent. Tech. Pap. 1974, 234–312. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, D. Urban Interface Area model—Linking stormwater management and planning controls. Aust. Plan. 2009, 46, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobio, J.A.S.; Maniquiz-Redillas, M.C.; Kim, L.H. Optimization of the design of an urban runoff treatment system using stormwater management model (SWMM). Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce V, M.; Hawkins R, H. Runoff curve number: Has it reached maturity? J. Hydrol. Eng. 1996, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Singh, P.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, V.; Singh, A. Activation soil moisture accounting (ASMA) for runoff estimation using soil conservation service curve number (SCS-CN) method. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, W.C. A review of the USDA SCS curve number method. Soil Res. 1989, 27, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.B.; Gallichand, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Goulet, M. A modification to the soil conservation service curve number method for steep slopes in the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Yuan, A. Method of Determining CN Value in the SCS-CN Model. Arid Land Geogr. 2012, 35, 415–421. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Guo, X.; Rong, Y. Study on the Water Conservation Function Based on Budyko Hypothesis and SCS-CN Method in the Headstream Area of the Qinhe Basin. Res. Soil Water Conversat. 2018, 25, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Gao, Z.; Ma, H.; Feng, B.; Ma, L. Effects of Gully Land Consolidation Project on CN in Catchments with Different Vegetation Coverage. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.C. Characteristics of pollutant dynamics under rainfall-runoff events in the Chaohe River Watershed. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3316–3327. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, S.; Peters, N.E. Effects of Urbanization on Streamflow in the Atlanta area (Georgia, USA): Acomparative Hydrological Approach. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutu, G.W.; Vega, C. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Runoff Generation in the East Branch of the Brandywine Creek Watershed Using a GIS-based Hydrologic Model. Middle States Geogr. 2007, 40, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Gao, X.; Li, W.; Han, L.; Mao, J. Effects of land use change on surface runoff in Beijing-Tianjin-Heibei urban agglomeration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Schleuss, U.; Wu, Q.; Blume H, P. Variability of Soils in Urban and Periurban Areas in Northern Germany. Catena 1998, 33, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, S.; Roger, A. Land use and climate change. Science 2005, 310, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatzk, Y.A. The effect of trees on the urban climate. In Trees in the 21st Century; Academic Publishes: Berkhamster, UK, 1983; pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, G.; Xue, K.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C. Evaluation of rainwater runoff storage by urban green spaces in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsi, H.K. Simulation of green roof test bed runoff. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 250–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. The capacity of greening roof to reduce stormwater runoff and pollution. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 144, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Bi, B.X.; Chang, Y.F.; Hai, X. Runoff reduction effect of sunken lawn under different designed rainstorm intensity in Beijing area. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Peng, C. Assessing the effectiveness of green infrastructures on urban flooding reduction: A community scale study. Ecol. Model. 2014, 291, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Type | Hydrological Combination Type | Soil Type | Hydrological Combination Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brown soil | C | Meadow aeolian soil | A |
| Cinnamon soil | C | Skeletol soil | C |
| Calcareous cinnamon soil | C | Fluvo-aquic soil | C |
| Leached cinnamon soil | C | De-fluvo-aquic soil | C |
| Developed cinnamon soil | D | Alkaline fluvo-aquic soil | C |
| Cultivated loessial soil | B | Irrigated fluvo-aquic soil | C |
| Alluvial soil | A | Residential area | D |
| Land Use Type | A | B | C | D | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNI | CNII | CNIII | CNI | CNII | CNIII | CNI | CNII | CNIII | CNI | CNII | CNIII | |
| Paddy field | 43 | 64 | 80 | 56 | 75 | 87 | 66 | 82 | 91 | 70 | 85 | 93 |
| Dry land | 41 | 62 | 79 | 51 | 71 | 85 | 60 | 78 | 89 | 64 | 81 | 91 |
| Forest land | 15 | 30 | 50 | 34 | 55 | 74 | 49 | 70 | 84 | 58 | 77 | 89 |
| Shrub land | 19 | 36 | 56 | 39 | 60 | 78 | 53 | 73 | 86 | 61 | 79 | 90 |
| Open forest land | 26 | 45 | 65 | 45 | 66 | 82 | 58 | 77 | 89 | 67 | 83 | 92 |
| Other forest land | 24 | 43 | 63 | 44 | 65 | 81 | 57 | 76 | 88 | 66 | 82 | 91 |
| Grassland | 29 | 49 | 69 | 48 | 69 | 84 | 61 | 79 | 90 | 69 | 84 | 92 |
| River-canal | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Reservoir and pond | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Beach land | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Urban land | 58 | 77 | 89 | 70 | 85 | 93 | 79 | 90 | 95 | 83 | 92 | 96 |
| Rural residential area | 30 | 51 | 71 | 47 | 68 | 83 | 61 | 79 | 90 | 69 | 84 | 92 |
| Other construction land | 64 | 81 | 91 | 75 | 88 | 94 | 81 | 91 | 96 | 85 | 93 | 97 |
| Location | X/° | Y/° | Location | X/° | Y/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gongyi | 112.97 | 34.73 | Yuanyang | 113.95 | 35.05 |
| Xingyang | 113.43 | 34.80 | Mengjin | 112.43 | 34.83 |
| Dengfeng | 113.03 | 34.45 | Mengzhou | 112.78 | 34.92 |
| Zhengzhou | 113.65 | 34.72 | Yichuan | 112.42 | 34.42 |
| Xinmi | 113.22 | 34.33 | Ruzhou | 112.83 | 34.18 |
| Xinzheng | 113.73 | 34.40 | Wenxian | 113.10 | 34.95 |
| Zhongmou | 114.02 | 34.72 | Yuzhou | 113.50 | 34.15 |
| Fengqiu | 114.42 | 35.03 | Weisi | 114.20 | 34.40 |
| Wuling | 113.40 | 35.10 |
| Land Use Type | Runoff (mm) | Land Use Type | Runoff (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy field | 62 | Low coverage grassland | 58 |
| Dry land | 50 | River-canal | 110 |
| Forest land | 41 | Reservoir and pond | 110 |
| Shrub land | 37 | Beach land | 110 |
| Open forest land | 45 | Urban land | 81 |
| Other forest land | 33 | Rural residential area | 50 |
| High-coverage grassland | 46 | Other construction land | 81 |
| Medium-coverage grassland | 54 |
| Slope | 20 July 2021 Runoff (mm) | 28–30 September 2023 Runoff (mm) | Area Percentage of Dryland, Forest Land, and Grassland (%) | Area Percentage of Urban Land and Other Construction Land (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <5° | 271.1 | 69.2 | 62 | 16 |
| 5°–8° | 257.5 | 66.3 | 84 | 4 |
| 8°–15° | 251.2 | 62.1 | 87 | 3 |
| 15°–25° | 237.4 | 60.2 | 93 | 1 |
| 25°–35° | 190.2 | 53.4 | 98 | 0 |
| >35° | 159.4 | 45.6 | 100 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Ren, J.; Liu, P.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, M. Analysis of Surface Runoff Characteristics in Zhengzhou City under Extreme Rainfall Conditions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6980. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166980
Wang Y, Li S, Hu C, Ren J, Liu P, Zhao C, Zhu M. Analysis of Surface Runoff Characteristics in Zhengzhou City under Extreme Rainfall Conditions. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6980. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166980
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yong, Shuangquan Li, Chanjuan Hu, Jie Ren, Peng Liu, Chang Zhao, and Mengke Zhu. 2024. "Analysis of Surface Runoff Characteristics in Zhengzhou City under Extreme Rainfall Conditions" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6980. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166980
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, S., Hu, C., Ren, J., Liu, P., Zhao, C., & Zhu, M. (2024). Analysis of Surface Runoff Characteristics in Zhengzhou City under Extreme Rainfall Conditions. Sustainability, 16(16), 6980. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166980





