Investigation of Thermoregulation Effect of Stabilized Phase Change Gypsum Board with Different Structures in Buildings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Board and Experimental Setup
2.1. Preparation of Phase Change Gypsum Board
2.2. Phase Change Gypsum Board
2.2.1. Test of Strength
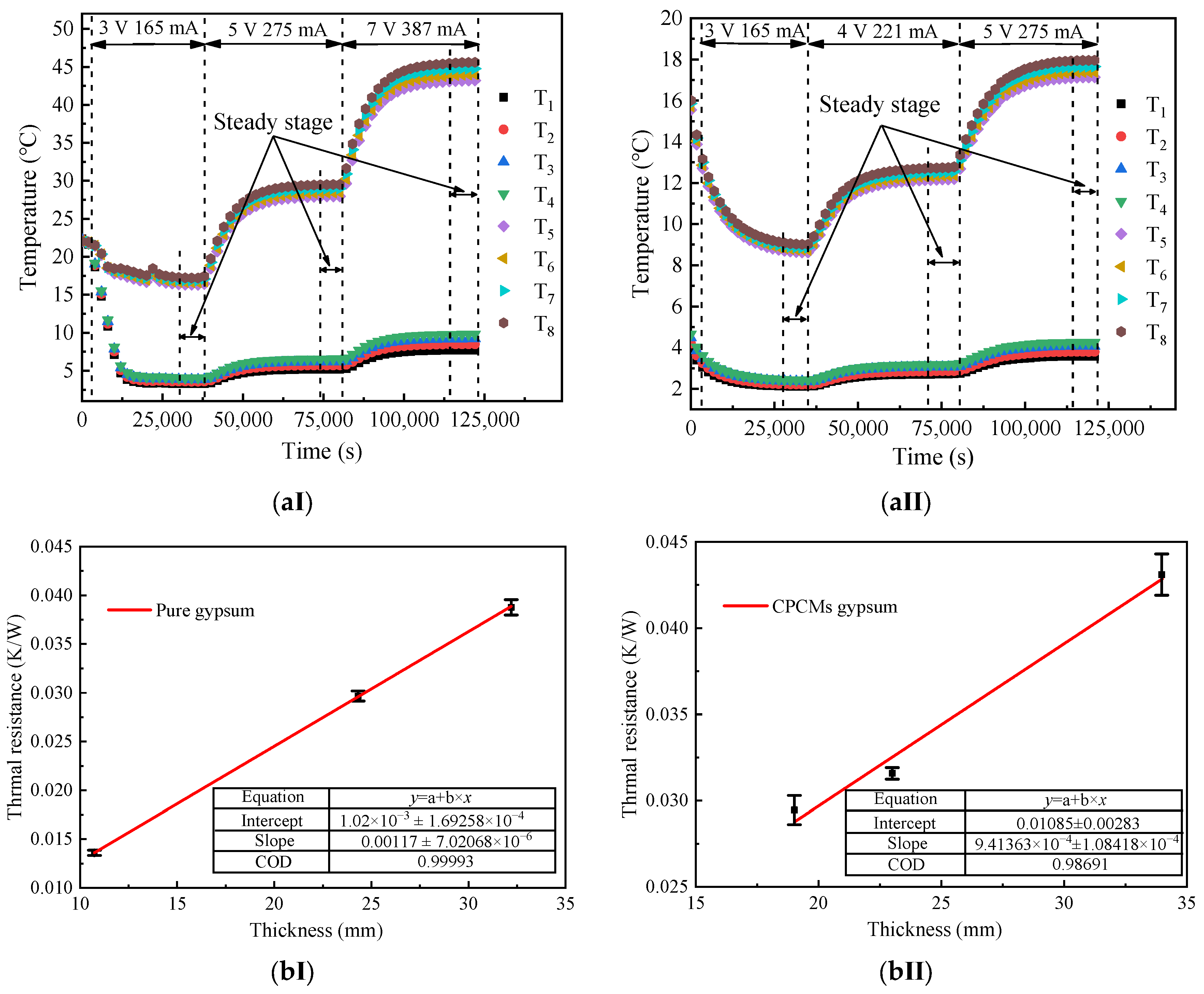
2.2.2. Properties of Phase Change Gypsum Board
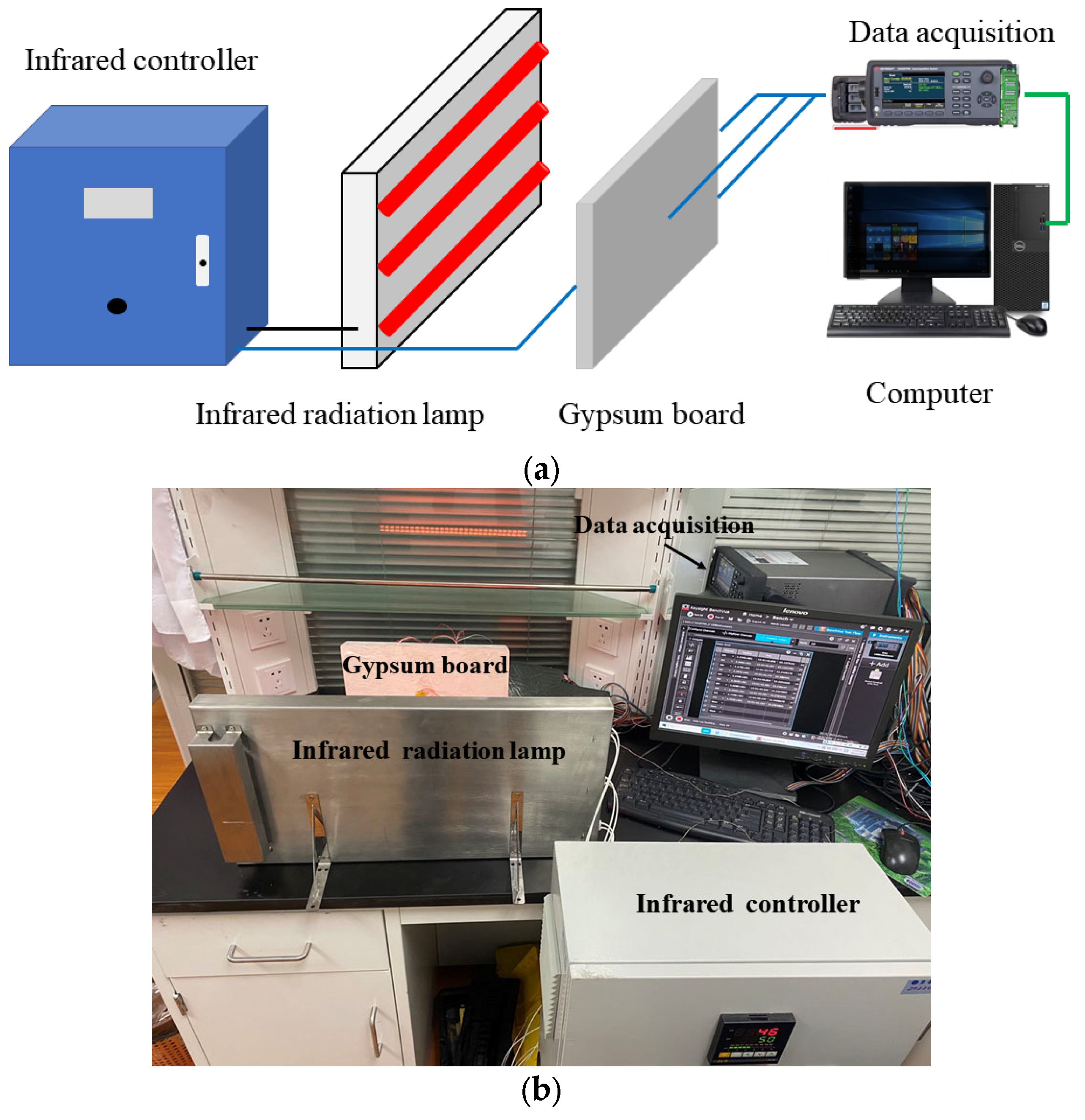
2.3. Radiant Thermal Response Apparatus
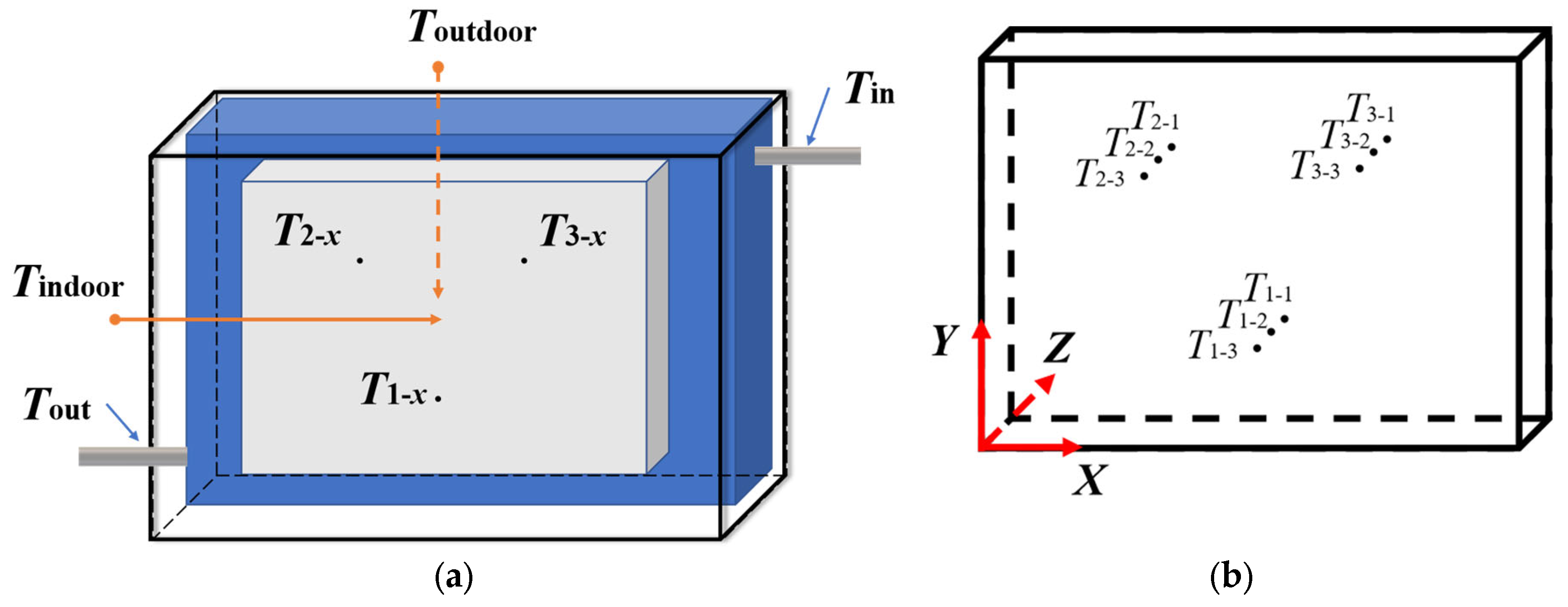
2.4. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
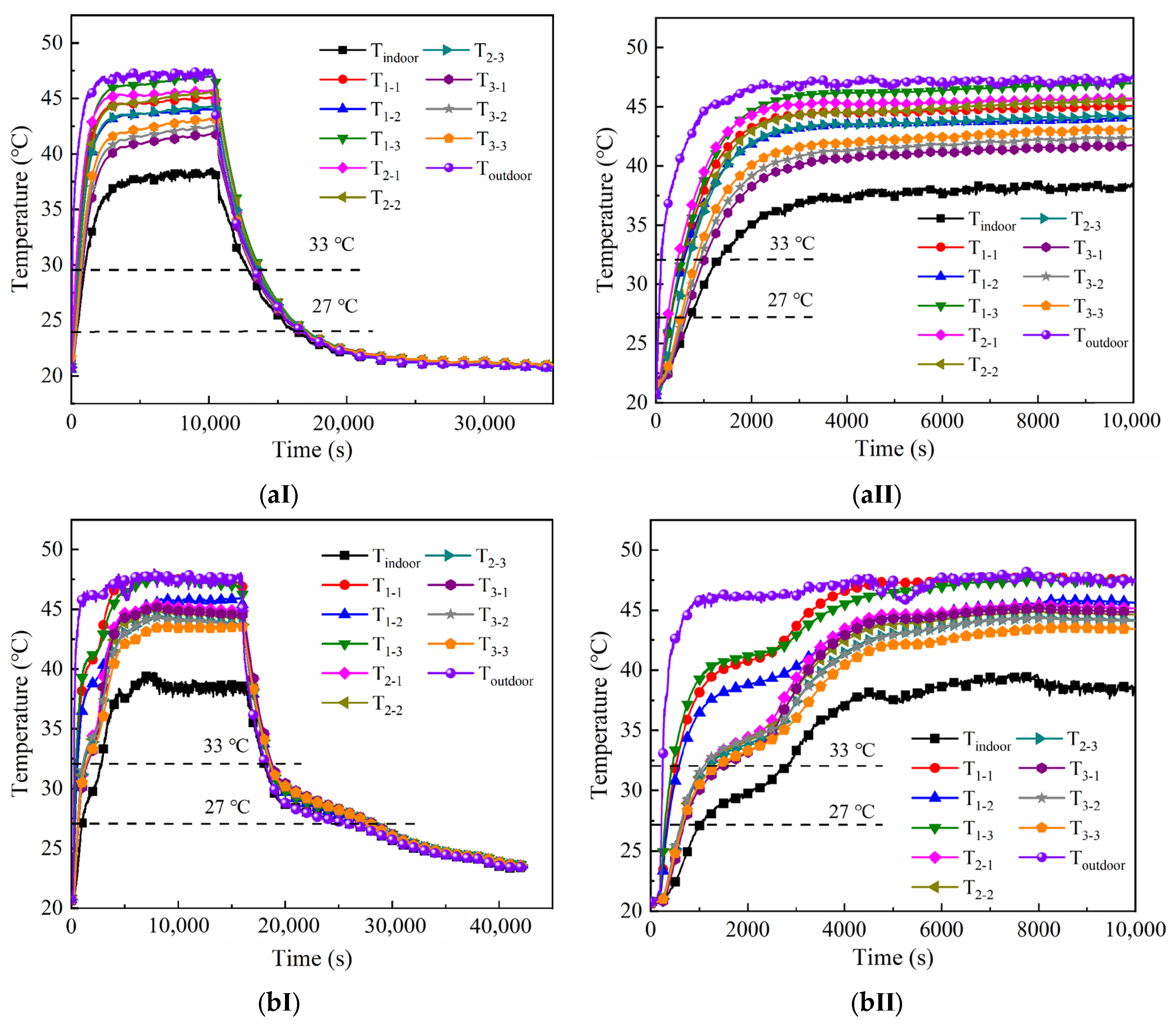
3.1. Thermal Response with Different Gypsum Boards
3.2. Comparisons of Different Positions of Layers
3.3. Comparisons of Different Temperatures
3.4. Economic and Practice Analysis
4. Conclusions
- Pure gypsum board was found to have a strength larger than 9 MPa, and the strengths of sandwich phase change gypsum boards slightly decreased, with a maximum pressure of 5 MPa, which could match with strength requirements in buildings.
- Experimental investigations indicated that sandwich phase change gypsum board at different positions shows good thermal performance, e.g., the indoor heating rate is slowed down and the environmental temperature fluctuation is within a smaller range, because of the latent heat of the phase change gypsum board.
- Comparing the phase change gypsum boards at different interlayer positions, we found that the phase change gypsum board with the interlayer in the indoor side shows better thermal performance and relatively longer time durations of thermal comfort; e.g., when the setting temperatures are 37 °C, 40 °C, 45 °C and 50 °C, respectively, the relative time durations of thermal comfort with the sandwich phase change gypsum boards are 4825 s, 3160 s, 1980 s and 1710 s.
- Various climate zones require different structures of phase change gypsum boards; the present research could provide information and guidance on the advantages and potential of phase change gypsum board when applied to the building envelope.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amini Toosi, H.; Lavagna, M.; Leonforte, F.; Del Pero, C.; Aste, N. Building decarbonization: Assessing the potential of building-integrated photovoltaics and thermal energy storage systems. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.-S.; Mudgal, V.; Mallick, T.-K. Review of latent heat thermal energy storage for improved material stability and effective load management. J. Energy Storage 2018, 15, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, S.R.L.; de Aguiar, J.L.B. Phase change materials and energy efficiency of buildings: A review of knowledge. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souayfane, F.; Fardoun, F.; Biwole, P.-H. Phase change materials (PCM) for cooling applications in buildings: A review. Energy Build. 2016, 129, 396–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.-V.; Parameshwaran, R.; Ram, V.-V. PCM-mortar based construction materials for energy efficient buildings: A review on research trends. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematpour, K.-A.; Sheikholeslami, M. Nanoparticle enhanced PCM applications for intensification of thermal performance in building: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, M.; Nadir, Y. Geopolymer mortar integrated with phase change materials for improvement of thermal efficiency in buildings: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.-K.-S.; Shukla, S.-K. Enhanced thermophysical properties of organic PCM through shape stabilization for thermal energy storage in buildings: A state of the art review. Energy Build. 2021, 236, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, G.-J.; Jafarian, M.; Dally, B.B.; Saw, W.-L.; Ashman, P.-J.; Hu, E.; Steinfeld, A. Solar thermal hybrids for combustion power plant: A growing opportunity. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 64, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Gracia, A.; Colclough, S.; Browne, M.; McCormack, S.-J.; Griffiths, P.; Cabeza, L.-F. Thermal energy storage in building integrated thermal systems: A review. Part 1. active storage systems. Renew. Energy 2016, 88, 526–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-T.; Nord, N.; Xiao, Q.-Q.; Tereshchenko, T. Building heating applications with phase change material: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage 2020, 31, 101634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, S.-B.; Amamou, A.; Khalifa, R.-B.; Saïd, N.M.; Younsi, Z.; Jemni, A. A review on thermal energy storage using phase change materials in passive building applications. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borri, E.; Zsembinszki, G.; Cabeza, L.-F. Recent developments of thermal energy storage applications in the built environment: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 189, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaeian, A.; Bahrami, L.; Pourfayaz, F.; Khodabandeh, E.; Yan, W.-M. Experimental studies on the applications of PCMs and nano-PCMs in buildings: A critical review. Energy Build. 2017, 154, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Hu, Q.; Jiao, H.-S.; Wang, Y.F.; Badiei, A. Simulation and machine learning investigation on thermoregulation performance of phase change wall. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.-L.; Zhang, X.-G.; Huang, Z.-H.; Fang, M.-H.; Liu, Y.-A.; Wu, X.-W.; Min, X.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.-F. Preparation and thermal properties of fatty acid/diatomite form-stable composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 178, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-C.; Wang, M.-F.; Xie, B.-S.; Ma, H.; Chen, J. Enhanced properties of diatomite-based composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-L.; Wang, Q.-H.; Ye, R.-D.; Fang, X.-M.; Zhang, Z.-G. A calcium chloride hexahydrate/expanded perlite composite with good heat storage and insulation properties for building energy conservation. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, Y.-S. Incorporation of phase change material and carbon nanofibers into lightweight aggregate concrete for thermal energy regulation in buildings. Energy 2020, 197, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, S.; Mahdaoui, M.; Kousksou, T.; El Afou, Y.; Ait Msaad, A.; Arid, A.; Ahachad, A. Thermal behaviour of wallboard incorporating a binary mixture as a phase change material. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 25, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagou, A.; Kylili, A.; Šadauskiene, J.; Fokaides, P.-A. Numerical investigation of phase change materials (PCM) optimal melting properties and position in building elements under diverse conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Wu, W.-D.; Fu, S.-Y.; Zhang, H. Study of a novel ceramsite-based shape-stabilized composite phase change material (PCM) for energy conservation in buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattan, H.-A.; Madhkhan, M.; Marani, A. Thermal and mechanical properties of building external walls plastered with cement mortar incorporating shape-stabilized phase change materials (SSPCMs). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-W.; Chang, S.-J.; Wi, S.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, S.-M. Energy performance evaluation of heat-storage gypsum board with hybrid SSPCM composite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasaraonaik, B.; Singh, L.-P.; Sinha, S.; Tyagi, I.; Rawat, A. Studies on the mechanical properties and thermal behavior of microencapsulated eutectic mixture in gypsum composite board for thermal regulation in the buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abden, M.-J.; Tao, Z.; Pan, Z.; George, L.; Wuhrer, R. Inclusion of methyl stearate/diatomite composite in gypsum board ceiling for building energy conservation. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-G.; Wi, S.; Chang, S.-J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. An experimental study on applying organic PCMs to gypsum-cement board for improving thermal performance of buildings in different climates. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghari, O.; Hassani, F.-Z.-S.-A.; Mekhzoum, M.-E.-M.; Zari, N.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.-K. Elaboration of a composite material based on plaster reinforced with phase change material/Oakum Fiber: Physical, thermal and mechanical properties. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, M.; Azenha, M.; Aguiar, J.; Castro-Gomes, J. Experimental and numerical studies of hybrid PCM embedded in plastering mortar for enhanced thermal behaviour of buildings. Energy 2016, 94, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesuriya, S.; Brandt, M.; Tabares-Velasco, P.-C. Parametric analysis of a residential building with phase change material (PCM)-enhanced drywall, precooling, and variable electric rates in a hot and dry climate. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, N.-B. Preparation and characterization of fatty acid stabilized composite phase change materials based on diatomite for construction. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 50, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Xiao, X. Thermal conductivity measurement of flexible composite phase-change materials based on the steady-state method. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthaichotirat, P.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Jitsangiam, P.; Suksiripattanapong, C.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Thermal and sound properties of concrete mixed with high porous aggregates from manufacturing waste impregnated with phase change material. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 29, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-N.; He, F.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, H.-T.; Gao, W.-J. Thermal behavior analysis of hollow bricks filled with phase-change material (PCM). J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| PCMs | Melting Temperature (℃) | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Latent Heat (kJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LA-MA-SA | 29.74 | 0.56 | 151.64 |
| EG block [32] | - | 160.2 | - |
| DE | - | 0.05 | - |
| LA-MA-SA/10 wt.% EG/10 wt.% DE | 29.67 | 4.51 | 117.06 |
| Types of Board | Mass (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gypsum Powder | Composite PCM | Water | |
| Pure gypsum board | 3000 | 0 | 1160 |
| Phase change layer in the exterior/interior side | 2800 | 558 | 1120 |
| Phase change layer in the middle side | 2800 | 559 | 1120 |
| Types of Gypsum Board | Temperature (℃) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37 | 40 | 45 | 50 | |
| Pure gypsum board | 2995 | 1160 | 815 | 560 |
| Interlayer in the exterior side | 4630 | 1845 | 1195 | 1085 |
| Interlayer in the middle side | 5065 | 3015 | 1785 | 1510 |
| Interlayer in the interior side | 4825 | 3160 | 1980 | 1710 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Xiao, X.; Shu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Investigation of Thermoregulation Effect of Stabilized Phase Change Gypsum Board with Different Structures in Buildings. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166929
Gao F, Xiao X, Shu Z, Zhong K, Wang Y, Li M. Investigation of Thermoregulation Effect of Stabilized Phase Change Gypsum Board with Different Structures in Buildings. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166929
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Feng, Xin Xiao, Zhao Shu, Ke Zhong, Yunfeng Wang, and Ming Li. 2024. "Investigation of Thermoregulation Effect of Stabilized Phase Change Gypsum Board with Different Structures in Buildings" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166929
APA StyleGao, F., Xiao, X., Shu, Z., Zhong, K., Wang, Y., & Li, M. (2024). Investigation of Thermoregulation Effect of Stabilized Phase Change Gypsum Board with Different Structures in Buildings. Sustainability, 16(16), 6929. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166929








