An Approach for Future Droughts in Northwest Türkiye: SPI and LSTM Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Standardized Precipitation Index
2.2.2. Long Short-Term Memories
2.2.3. Adaptive Moment Estimation Optimizer
2.2.4. Inverse Distance Weighting
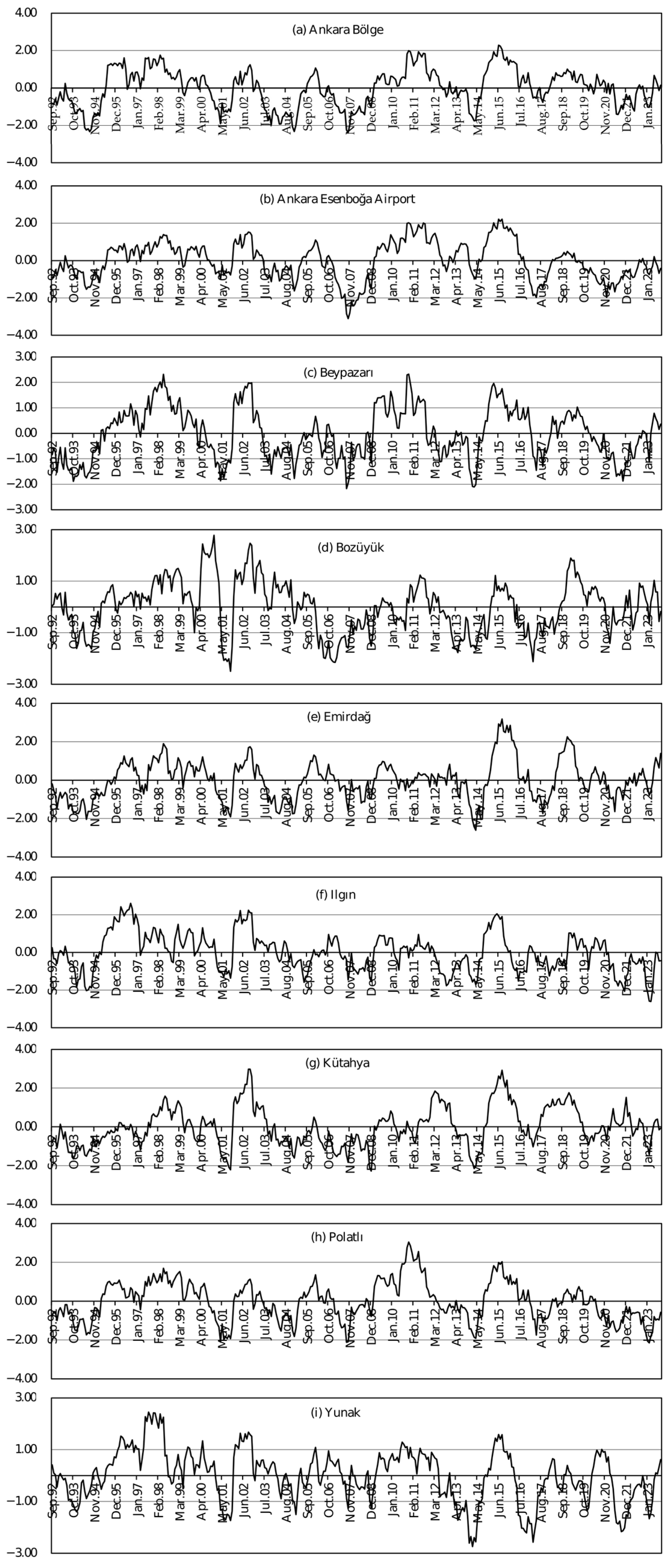
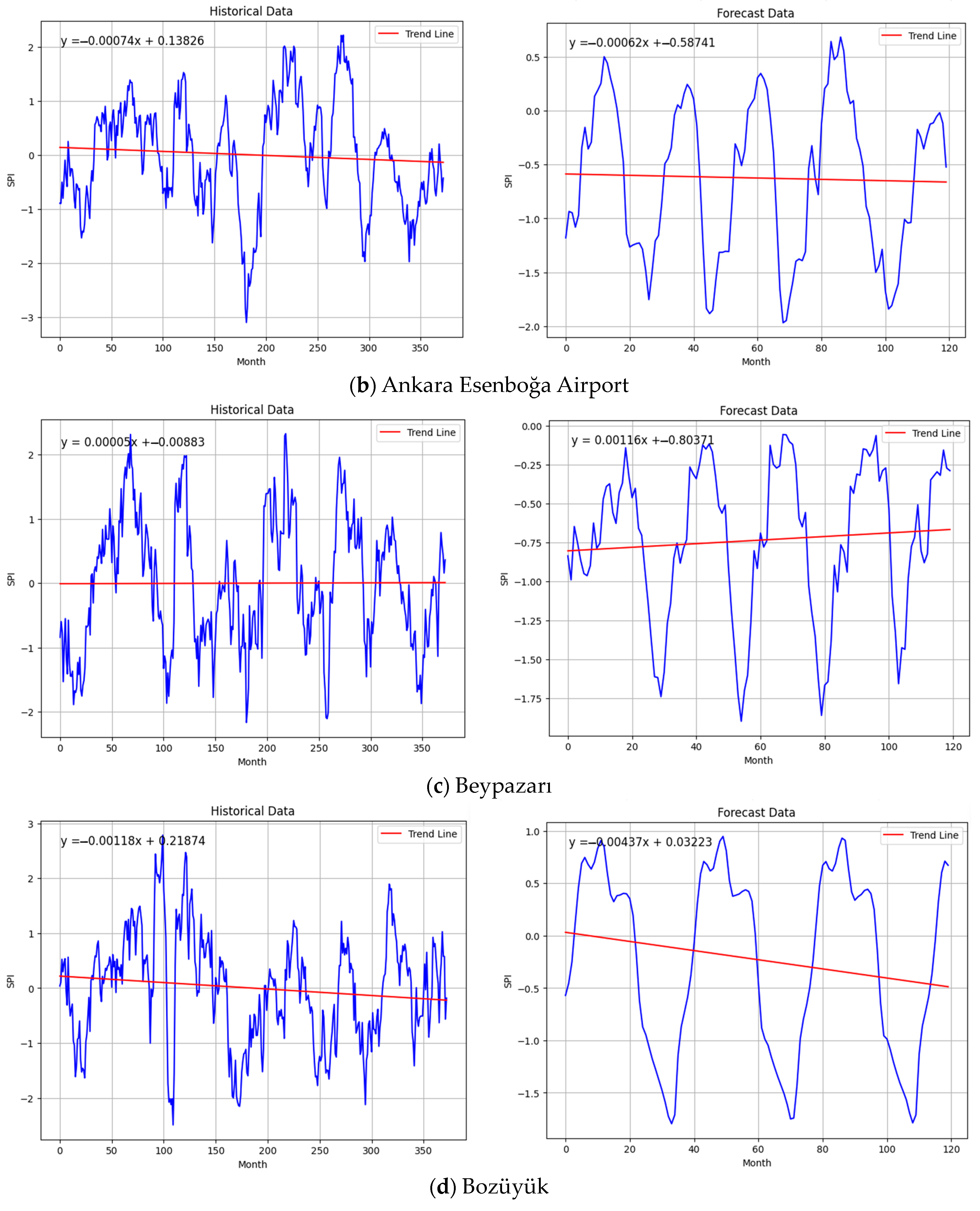
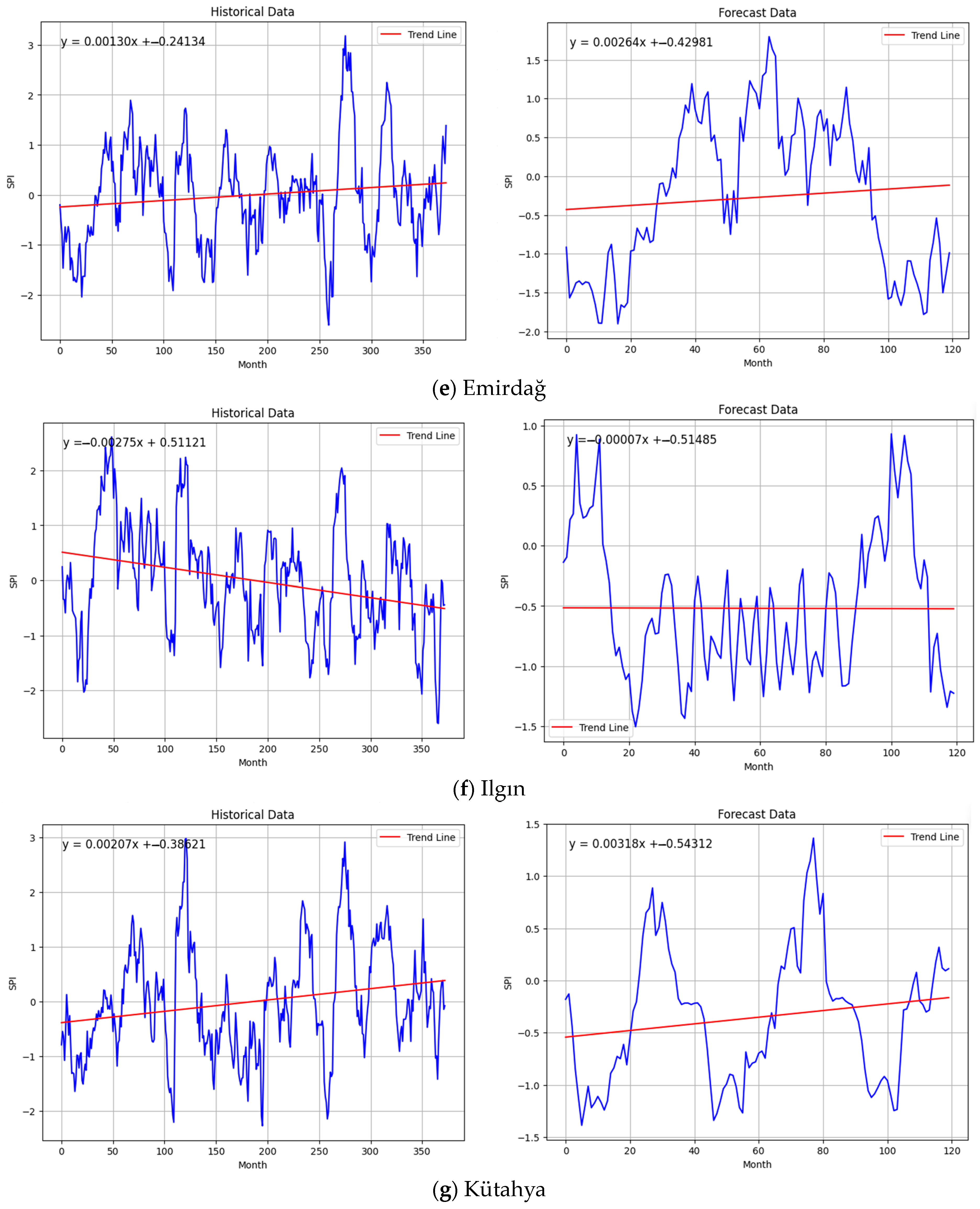
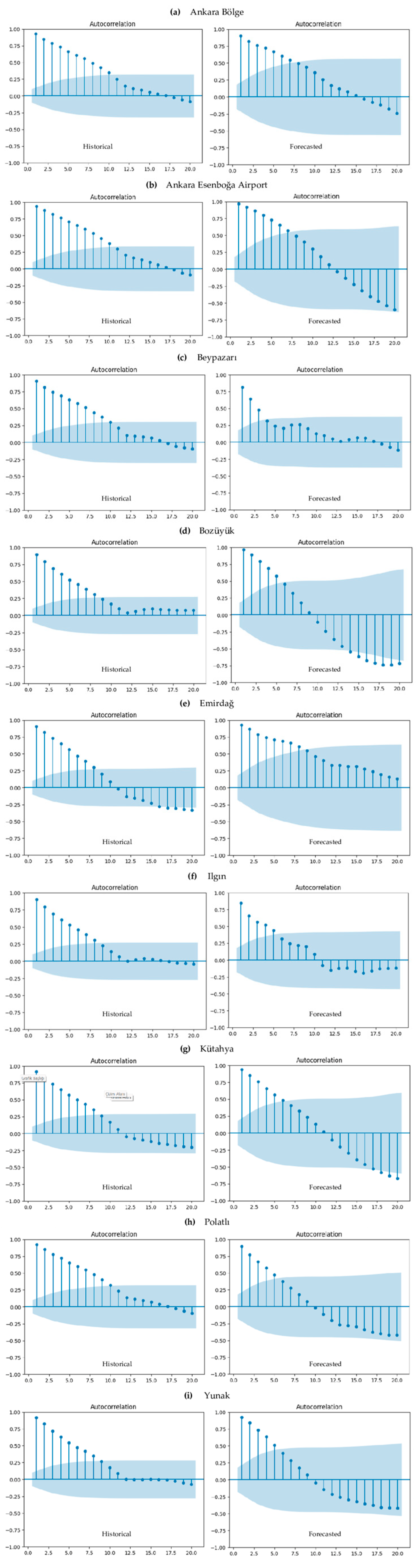
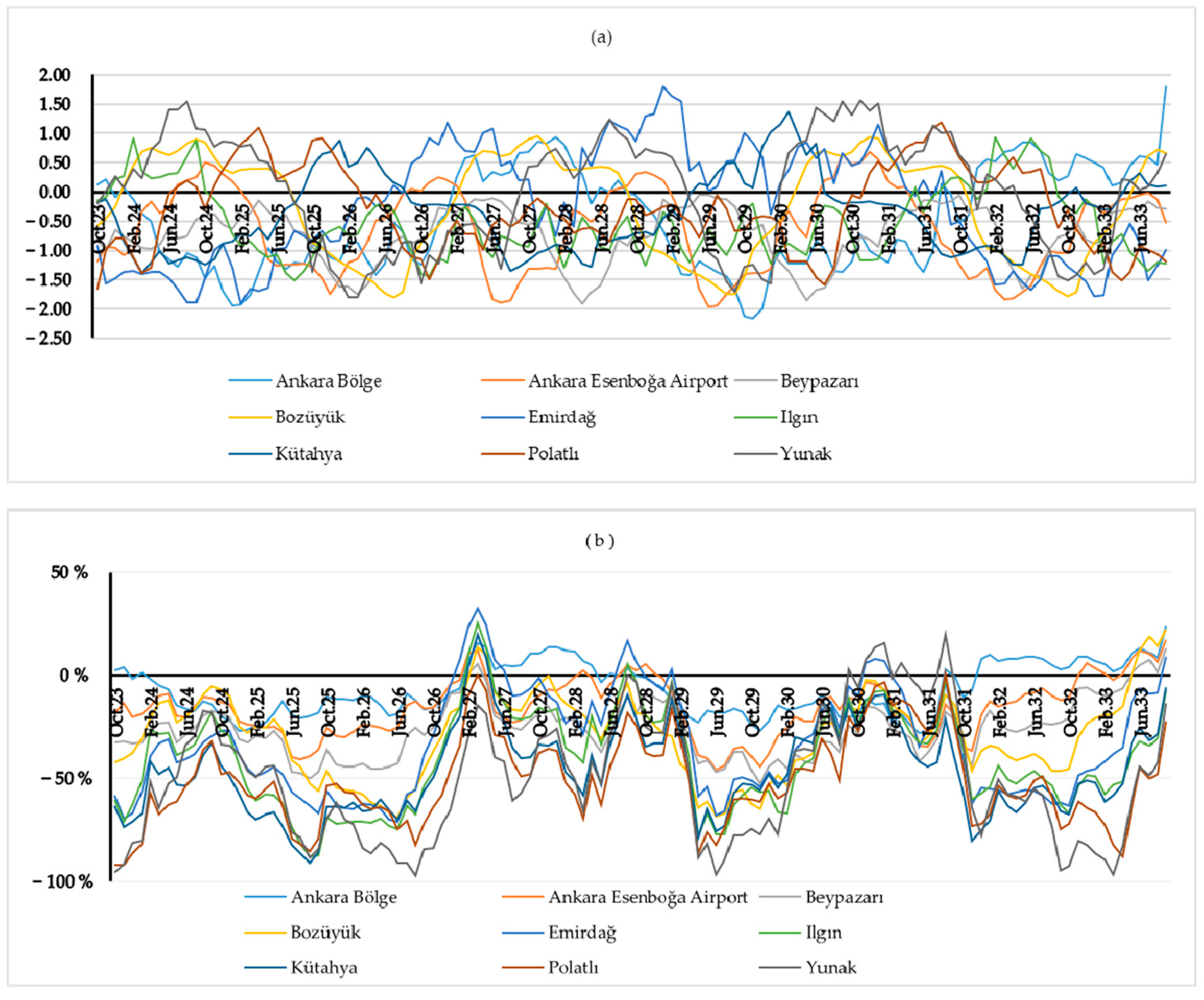
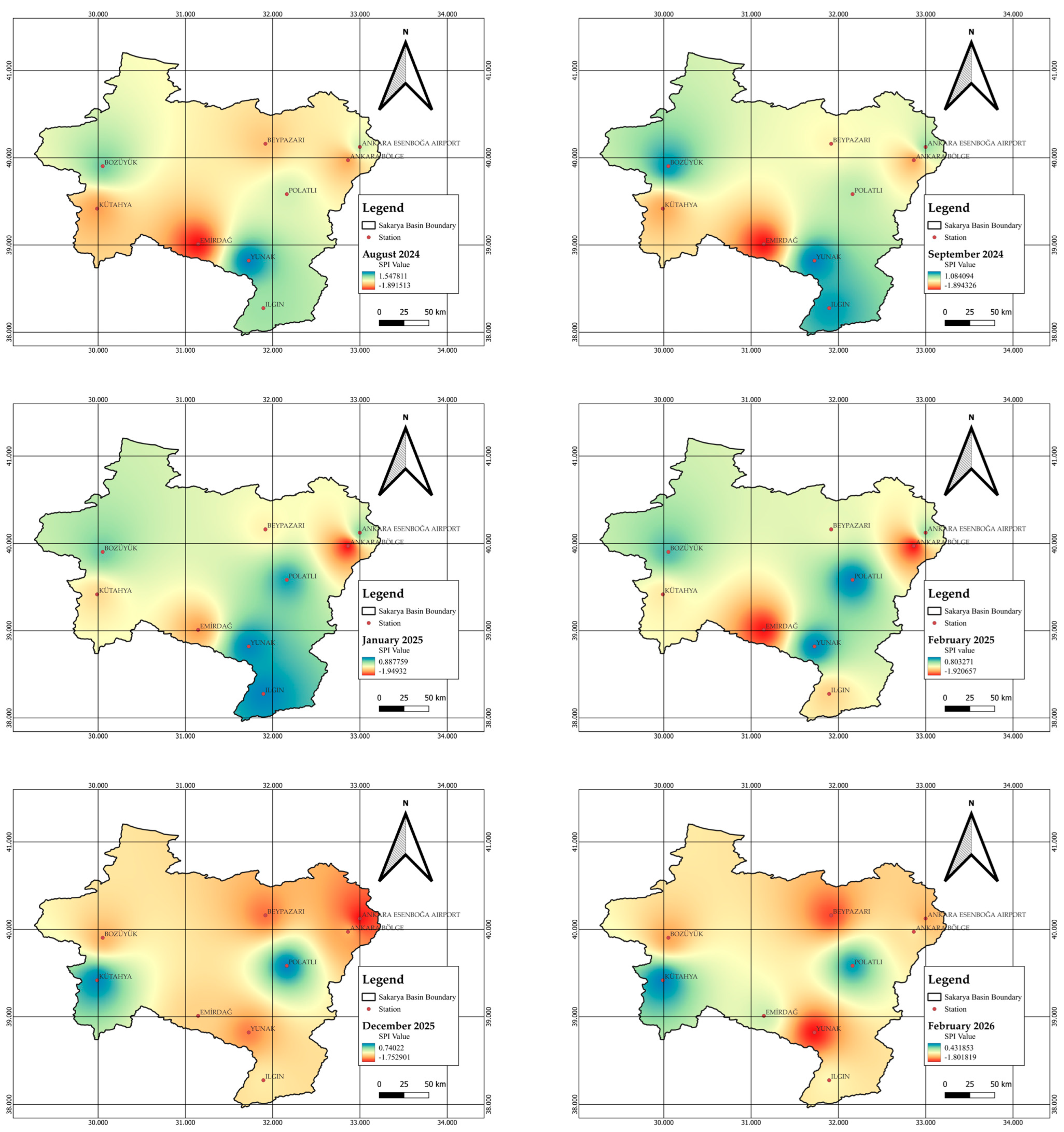
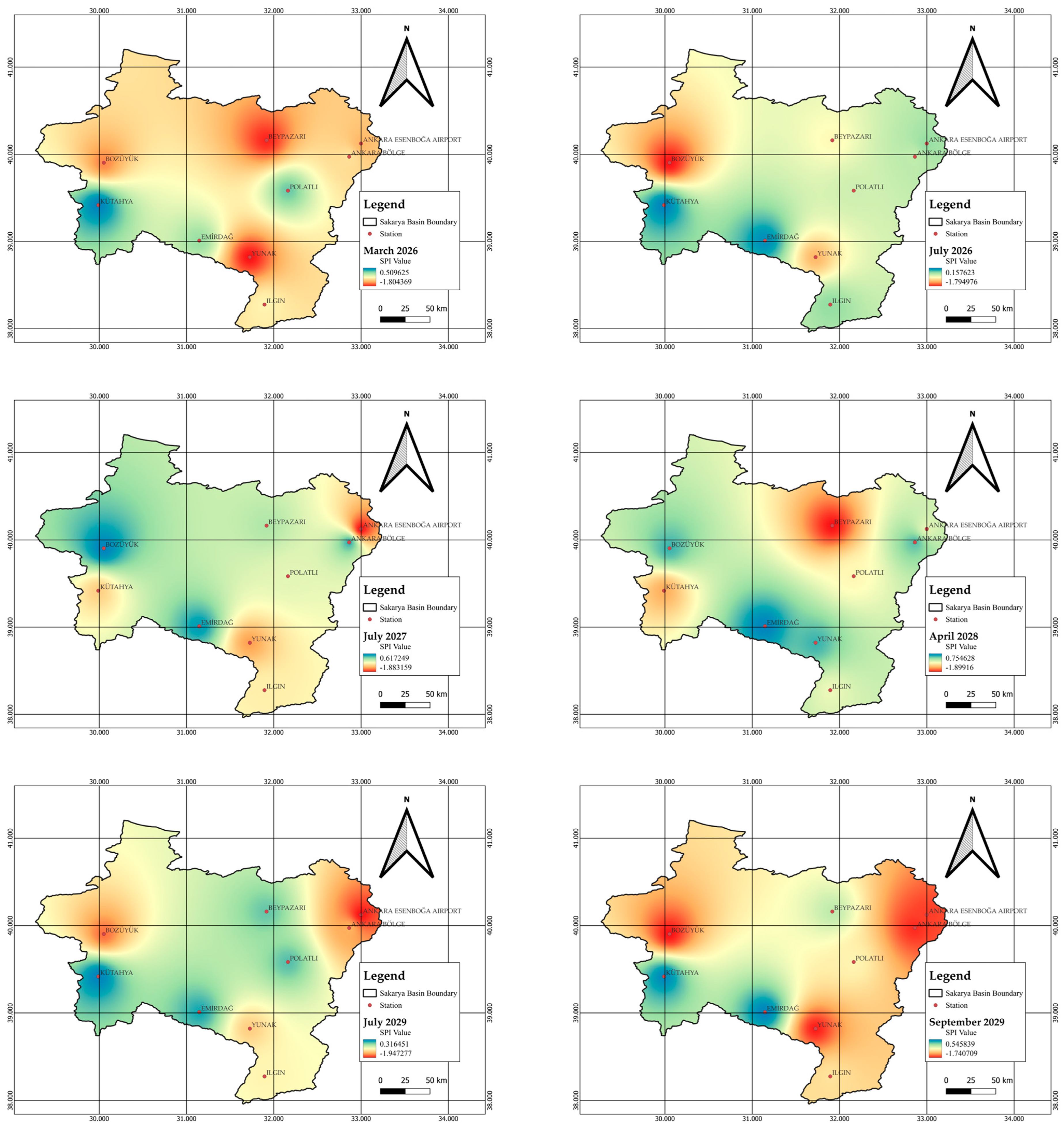
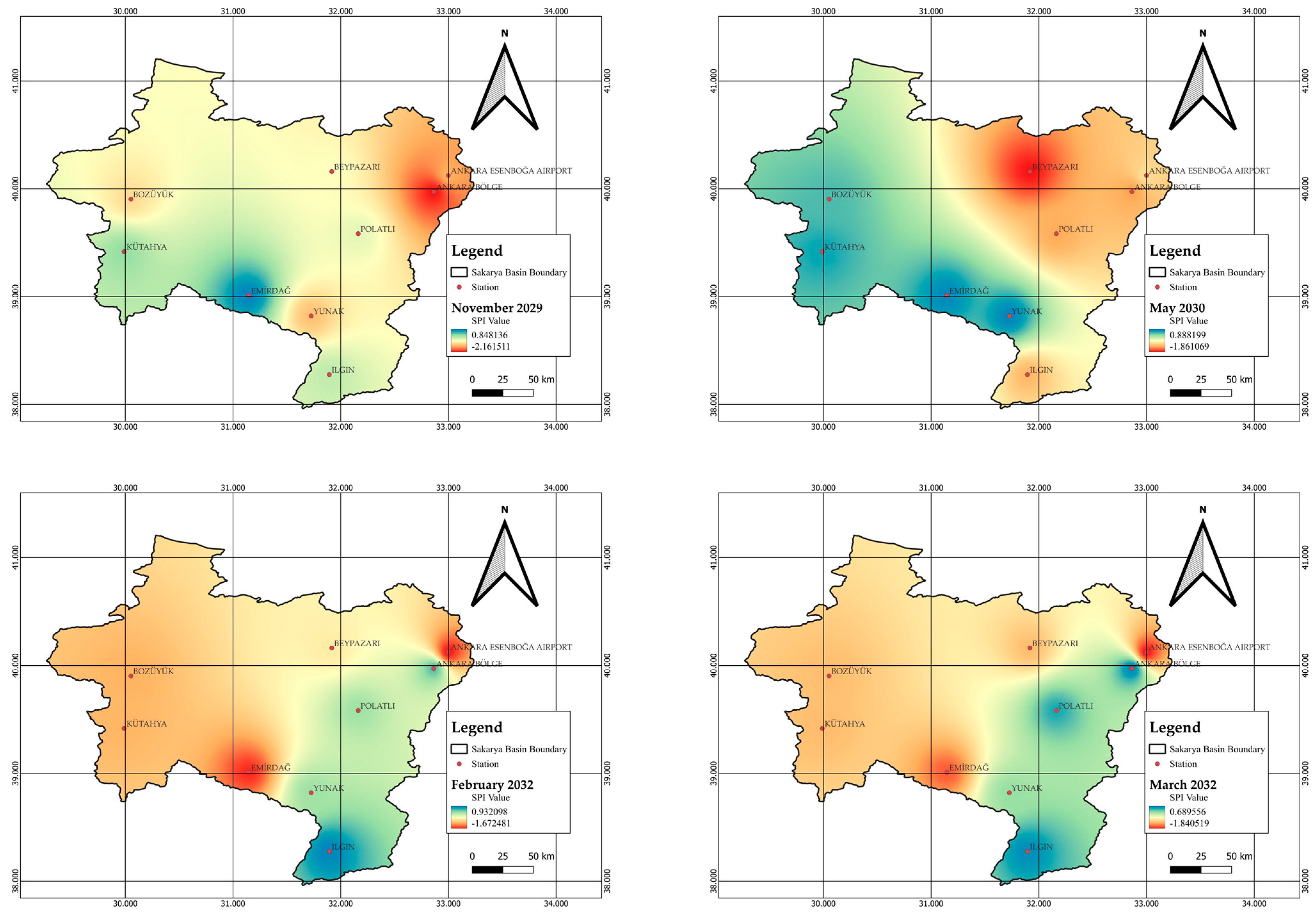
3. Results
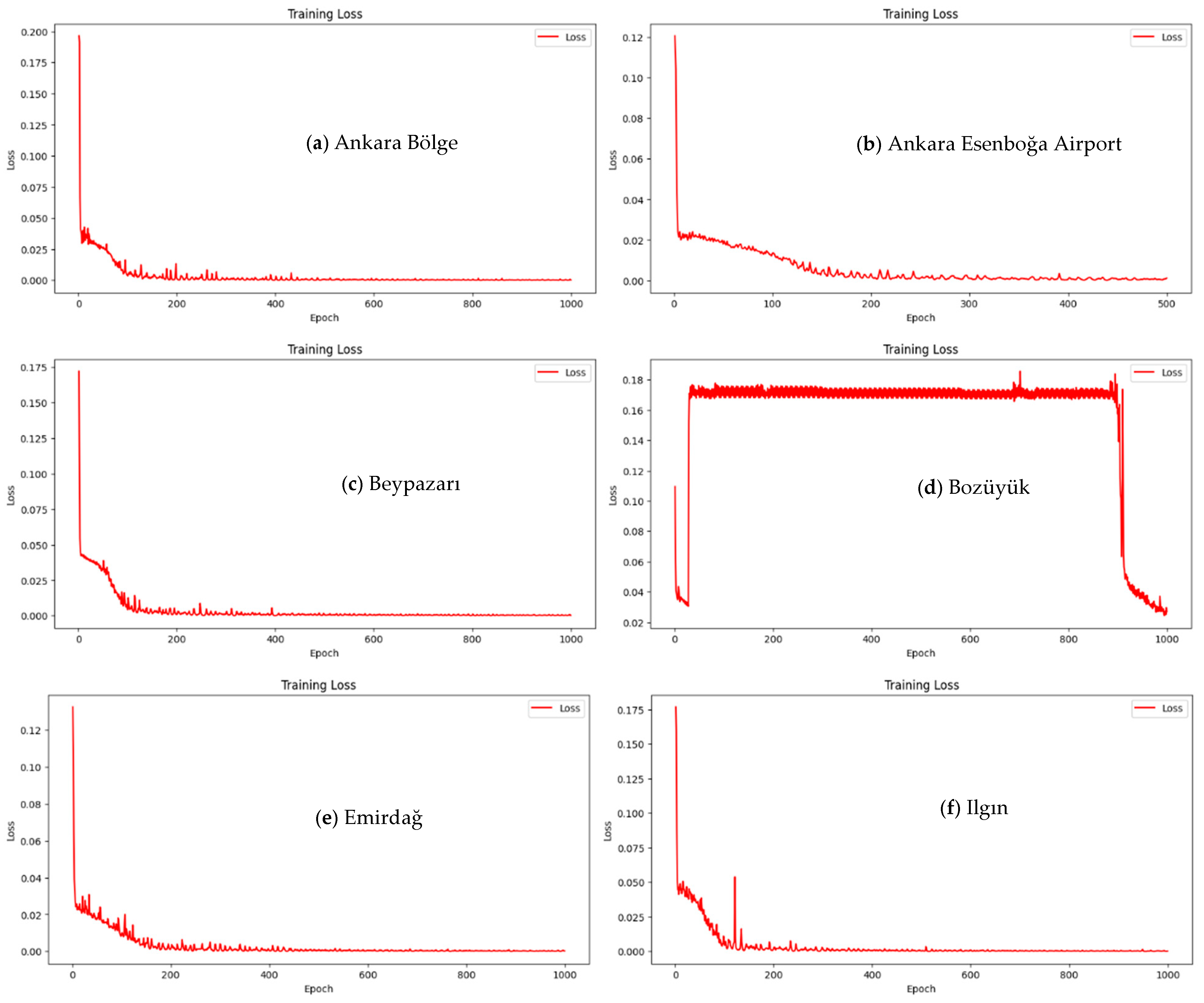
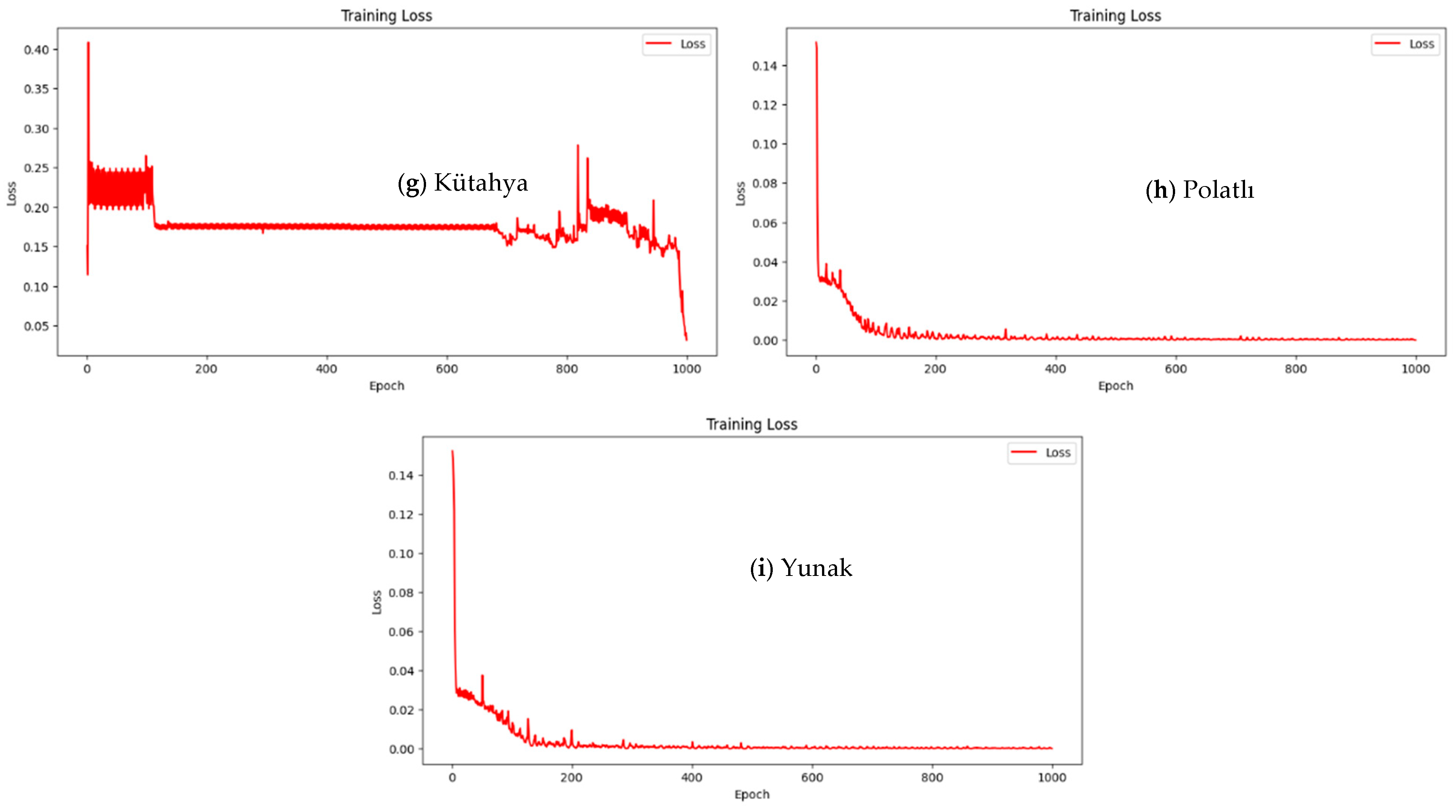
- Learning Rate: It was set to 0.001 in all models.
- Epoch Range: Models were trained for 500 to 1000 epochs to minimize MSE towards zero.
- Hidden Layer Sizes: Considered sizes were 32, 64, 128, 256, and 512.
- Number of Hidden Layers (Nodes): Models were tested with 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 hidden layers.
- Optimizer: The Adam optimizer was utilized in all cases.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Türkeş, M. A Detailed Analysis of the Drought, Desertification and the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification. Marmara J. Eur. Stud. 2012, 20, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, C.; Yilmaz, M.U.; Benli, K. Assessing drought in Turkish basins through satellite observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 3613–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkendiz, H.; Tatli, H.; Kılıç, A.; Çetin, M.; Sungur, A. Analysis of drought intensity, frequency and trends using the spei in Turkey. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.; Kuriqi, A. Regional Climate Change and Drought Dynamics in Tunceli, Turkey: Insights from Drought Indices. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2024, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, E.S. Turkey’s Drought Status Associated with Climate Change. J. Nat. Hazards Environ. 2018, 4, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballar, Z. Stormwater Management in Cities as a Climate Change Adaptation Strategy: Case of Halkapınar District (Izmir, Turkey). Master’s Thesis, Izmir Institute of Technology, Urla, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kadıoğlu, M.; Ünal, Y.; İlhan, A.; Yürük, C. Climate Change and Sustainability in Agriculture in Turkey. Federation of Turkish Food and Beverage Industry Associations. 2017. Available online: https://www.tgdf.org.tr/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/iklim-degisikligi-rapor-elma.compressed.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Türkeş, M.; Sümer, U.M. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Trends and Variability in Diurnal Temperature Ranges of Turkey. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 77, 195–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkeş, M. Observed and Projected Climate Change, Drought and Desertification in Turkey. Ankara Univ. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, G.; Sökün, H. Drought Analysis with Dynamic Mode Decomposition for the Aegean Region. Int. J. 3D Print. Technol. Digit. Ind. 2022, 6, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Shi, H.; Peng, J. The response of agricultural drought to meteorological drought modulated by air temperature. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; He, B. Temporal and spatial propagation characteristics of meteorological drought to hydrological drought and influencing factors. Atmos. Res. 2024, 299, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arra, A.A.; Alashan, S.; Şişman, E. Trends of meteorological and hydrological droughts and associated parameters using innovative approaches. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The Relationship of Drought Frequency and Duration to Time Scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Oluwatobi, A.; Gbenga, O.; Oluwafunbi, F. An Artificial Intelligence Based Drought Predictions in Part of the Tropics. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ibrahimi, A.; Baali, A. Application of Several Artificial Intelligence Models for Forecasting Meteorological Drought Using the Standardized Precipitation Index in the Saïss Plain (Northern Morocco). Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2018, 11, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Rai, P.; Kuriqi, A. Prediction of Multi-Scalar Standardized Precipitation Index by Using Artificial Intelligence and Regression Models. Climate 2021, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, E.E.; Paulo, A.A.; Pereira, L.S.; Mexia, J.T. Analysis of SPI Drought Class Transitions Using Loglinear Models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebenik, U.; Brilly, M.; Šraj, M. Drought Analysis Using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Acta Geogr. Slov. 2017, 57, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, P.; Das, P.; Maiti, R. Meteorological Drought Study through SPI in Three Drought Prone Districts of West Bengal, India. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, S.; Steinschneider, S. On the need for physical constraints in deep learning rainfall–runoff projections under climate change: A sensitivity analysis to warming and shifts in potential evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, J. Artificial intelligence to predict climate and weather change. JMST Adv. 2024, 6, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swagatika, S.; Paul, J.C.; Sahoo, B.B.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, P.K. Improving the forecasting accuracy of monthly runoff time series of the Brahmani River in India using a hybrid deep learning model. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria-Mena, J.B.; Plaza, D.; Giraldo, E. Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting. Information 2024, 15, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xu, X. TRNN: An efficient time-series recurrent neural network for stock price prediction. Inf. Sci. 2024, 657, 119951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.M. Long Lead Time Drought Forecasting Using Lagged Climate Variables and a Stacked Long Short-Term Memory Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Rikhtehgar Ghiasi, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Sorman, A.U.; Abualigah, L. A Novel Intelligent Deep Learning Predictive Model for Meteorological Drought Forecasting. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 14, 10441–10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.A.; Bui, M.D.; Rutschmann, P. Long Short Term Memory for Monthly Rainfall Prediction in Camau, Vietnam. Res. Gate 2018. in preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Poornima, S.; Pushpalatha, M. Drought Prediction Based on SPI and SPEI with Varying Timescales Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 8399–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Gautam, V.; Jain, P.; Sarkar, K. An Approach for Rainfall Prediction Using Long Short Term Memory Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 30–31 October 2020; pp. 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, D. Application of a Hybrid ARIMA-LSTM Model Based on the SPEI for Drought Forecasting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4128–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, D.T.; Thanh, D.V.; Le, H.M.; Sy, B.T.; Tanim, A.H.; Pham, Q.B.; Thanh, D.D.; Son, T.M.; Dang, N.M. Effect of Gradient Descent Optimizers and Dropout Technique on Deep Learning LSTM Performance in Rainfall-Runoff Modeling. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solgi, R.; Loaiciga, H.A.; Kram, M. Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM-NN) for Aquifer Level Time Series Forecasting Using In-Situ Piezometric Observations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orieschnig, C.; Cavus, Y. Spatial characterization of drought through CHIRPS and a station-based dataset in the Eastern Mediterranean. Proc. IAHS 2024, 385, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workneh, H.T.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Bayable, E.; Dash, A. Comparison of IDW, Kriging and orographic based linear interpolations of rainfall in six rainfall regimes of Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Neilson, R.P.; Phillips, D.L. A Statistical-Topographic Model for Mapping Climatological Precipitation over Mountainous Terrain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1994, 33, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.G.; Younes, K.; Esmaeil, A.; Fatemeh, T. Assessment of Geostatistical Methods for Spatial Analysis of SPI and EDI Drought Indices. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 15, 474–482. [Google Scholar]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical Approaches for Incorporating Elevation into the Spatial Interpolation of Rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Lateh, H. Meteorological Drought in Bangladesh: Assessing, Analysing and Hazard Mapping Using SPI, GIS and Monthly Rainfall Data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, D.R.; Dodamani, B.M. Spatial and Temporal Drought Analysis in the Krishna River Basin of Maharashtra, India. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1185926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustani, A.; Ülke, A. Investigation of Meteorological Drought Indices for Environmental Assessment of Yesilirmak Region. J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 2020, 8, 374–381. [Google Scholar]
- Coşkun, Ö.; Citakoglu, H. Prediction of the Standardized Precipitation Index Based on the Long Short-Term Memory and Empirical Mode Decomposition-Extreme Learning Machine Models: The Case of Sakarya, Türkiye. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 131, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvan, A.; Aktürk, G.; Yıldız, O. Effect of Climate Change on Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Meteorological Drought in Sakarya Basin, Turkey. J. Eng. Sci. Res. 2021, 3, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, T.; Atesoglu, A.; Ozel, H.B.; Cetin, M. Copula-based multivariate standardized drought index (MSDI) and length, severity, and frequency of hydrological drought in the Upper Sakarya Basin, Turkey. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 3669–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, V.; Emiroglu, M.E. Hydrological Drought and Trend Analysis in Kızılırmak, Yeşilırmak and Sakarya Basins. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2024, 181, 1919–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TUBITAK. Watershed Protection Action Plan for Sakarya Basin, Final Report; TUBITAK: İstanbul, Turkey, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yaykiran, S. Structuring the High Resolution Hydrological Model of Sakarya Basin. Master’s Thesis, Istanbul Technical University, İstanbul, Turkey, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvin, S.; Vinayakumar, R.; Gopalakrishnan, E.A.; Menon, V.K.; Soman, K.P. Stock Price Prediction Using LSTM, RNN and CNN-Sliding Window Model. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Udupi, India, 13–16 September 2017; pp. 1643–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Xie, K.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, H.; Xing, F. The Development of a Hybrid Wavelet-ARIMA-LSTM Model for Precipitation Amounts and Drought Analysis. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagheer, A.; Kotb, M. Time Series Forecasting of Petroleum Production Using Deep LSTM Recurrent Networks. Neurocomputing 2019, 323, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chandriah, K.K.; Naraganahalli, R.V. RNN/LSTM with Modified Adam Optimizer in Deep Learning Approach for Automobile Spare Parts Demand Forecasting. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 26145–26159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.P.; Priya, G.S.; Dileep, M.; Raju, B.E.; Shaik, A.R.; Sarman, K.V.S.H.G. Image Deconvolution Using Deep Learning-Based Adam Optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology, Coimbatore, India, 1–3 December 2022; pp. 901–904. [Google Scholar]
- Şen, S.Y.; Özkurt, N. Convolutional Neural Network Hyperparameter Tuning with Adam Optimizer for ECG Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU), Istanbul, Turkey, 15–17 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, H.M.; Yılmaz, D.S.; Kılıç, O.M. Mapping and Interpreting Some Soil Surface Properties of Central Kelkit Basin by Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Method. Gaziosmanpaşa J. Sci. Res. 2013, 6, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, C.D. Local Models for Spatial Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Fan, L.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.B. Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Soil Moisture and Its Application for Monitoring Drought. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpanyaro, Z.; Kalumba, A.M.; Zhou, L.; Afuye, G.A. Mapping and Assessing Riparian Vegetation Response to Drought along the Buffalo River Catchment in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Climate 2024, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, A. Global Solar Irradiance Time Series Prediction Using Long Short-Term Memory Network. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. Part C Des. Technol. 2019, 7, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Yu, H.; Dehghani, A.; Galavi, H.; Shokri, V.; Mohsenzadeh Karimi, S.; Sookhak, M. A novel stacked long short-term memory approach of deep learning for streamflow simulation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
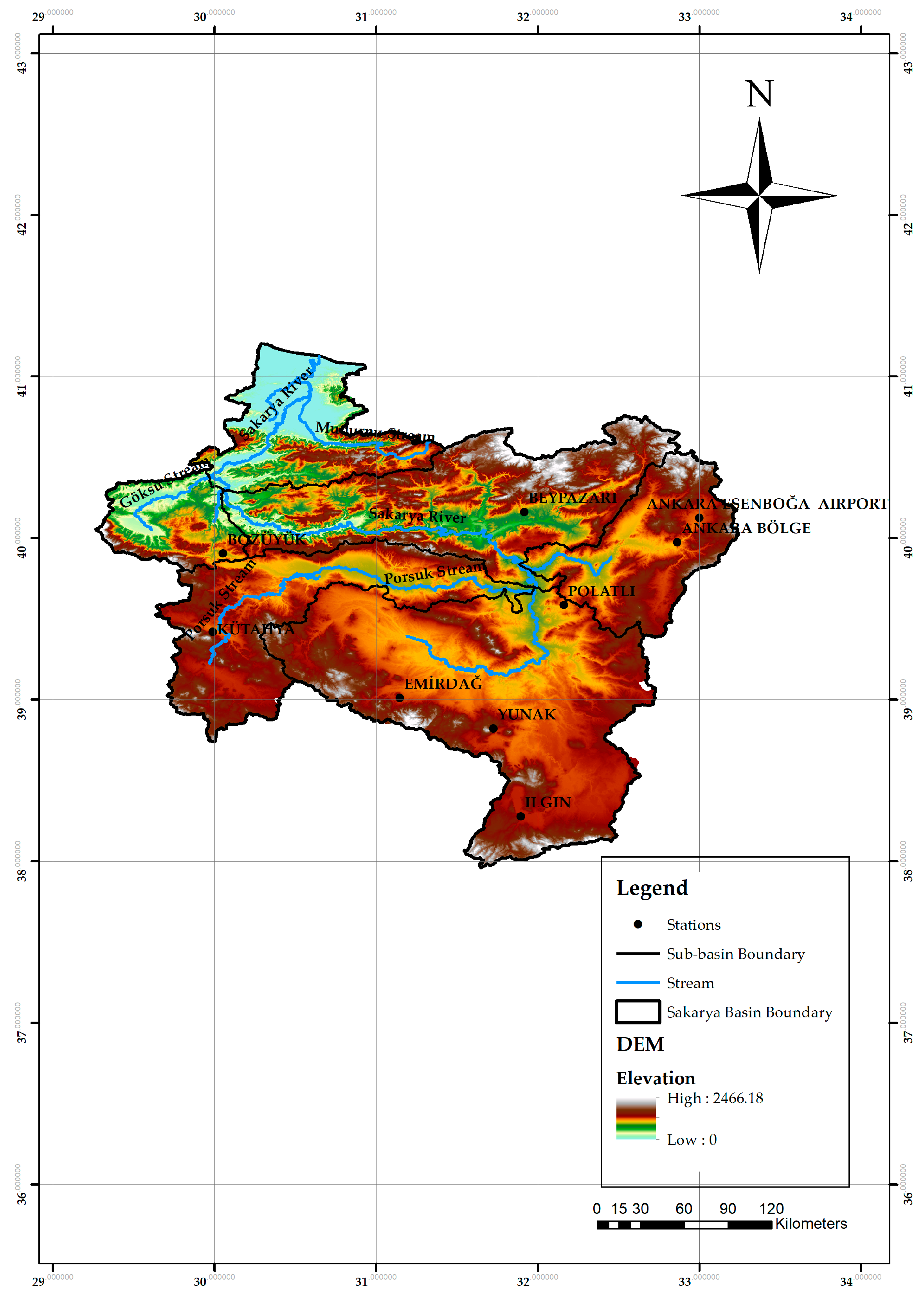



| Station | Station Number | Latitude | Longitude | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankara Bölge | 17130 | 39.9727 | 32.8637 | 412.36 |
| Ankara Esenboğa Airport | 17128 | 40.1240 | 32.9992 | 400.14 |
| Beypazarı | 17680 | 40.1608 | 31.9172 | 406.33 |
| Bozüyük | 17702 | 39.9039 | 30.0525 | 497.03 |
| Emirdağ | 17752 | 39.0098 | 31.1463 | 429.52 |
| Ilgın | 17832 | 38.2763 | 31.8940 | 435.32 |
| Kütahya | 17155 | 39.4171 | 29.9891 | 555.30 |
| Polatlı | 17728 | 39.5834 | 32.1624 | 362.12 |
| Yunak | 17798 | 38.8205 | 31.7258 | 441.05 |
| SPI | Drought Categories |
|---|---|
| 0 to −0.99 | Mild drought |
| −1.0 to −1.49 | Moderate drought |
| −1.5 to −1.99 | Severe drought |
| −2.0 | Extreme drought |
| Station | ADF Statistics | p-Value | Critical Value (1%) | Critical Value (5%) | Critical Value (10%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankara Bölge | −3.681 | 0.0240 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Ankara Esenboğa Airport | −3.490 | 0.0400 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Beypazarı | −3.593 | 0.0300 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Bozüyük | −3.651 | 0.0260 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Emirdağ | −4.866 | 0.0003 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Ilgın | −4.311 | 0.0030 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Kütahya | −4.390 | 0.0023 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Polatlı | −3.420 | 0.0488 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Yunak | −4.432 | 0.0019 | −3.984 | −3.423 | −3.134 |
| Station | Hidden Layer Size | Number of Hidden Layers |
|---|---|---|
| Emirdağ | 128 | 3 |
| Yunak | 128 | 3 |
| Ankara Region | 256 | 3 |
| Ankara Esenboğa Airport | 256 | 2 |
| Beypazarı | 256 | 2 |
| Kütahya | 256 | 5 |
| Polatlı | 256 | 3 |
| Bozüyük | 512 | 3 |
| Ilgın | 512 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylan, E.D. An Approach for Future Droughts in Northwest Türkiye: SPI and LSTM Methods. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166905
Taylan ED. An Approach for Future Droughts in Northwest Türkiye: SPI and LSTM Methods. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166905
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylan, Emine Dilek. 2024. "An Approach for Future Droughts in Northwest Türkiye: SPI and LSTM Methods" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166905
APA StyleTaylan, E. D. (2024). An Approach for Future Droughts in Northwest Türkiye: SPI and LSTM Methods. Sustainability, 16(16), 6905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166905






