1. Introduction
Management innovation capacity, which is an important component of sustainable development capacity, plays an important role in the development of sustainable development strategy support systems. By incorporating new concepts, methods, and tools, management innovation can effectively improve the operational efficiency and management level of an organization, reduce resource consumption, lower operating costs, improve product and service quality and ultimately achieve coordinated development of the organization, resources, and environment.
In recent years, the implementation of management innovation to promote economic and social development has shifted from relying primarily on the consumption of material resources to relying on scientific and technological progress and improving worker literacy. The implementation of innovation-driven growth has become an important initiative for building new development patterns in China. “Made in China 2025” proposes to “take talents as the foundation of building a strong manufacturing country, establish and improve the scientific mechanism for selecting, employing and educating talents, and accelerate the cultivation of professional and technical talents, business management talents and skilled talents urgently needed for the development of the manufacturing industry”. It also proposes “supporting enterprises to implement green management” as an important content of “actively building a green manufacturing system”. In the Outline of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China and Vision 2035, “promoting the modernization of the management system” is regarded as an important means of adhering to innovation-driven development and comprehensively shaping new advantages. Environmental deterioration and resource scarcity have prompted green management to become a social consensus. Realizing cost reduction and efficiency enhancement through management innovation and building a sustainable development pattern have become major challenges for enterprise management [
1,
2,
3].
Green management is a type of management innovation practice that uses a variety of means to manage human, financial, and material resources in an organization in an integrated way, promote the sustainable development of the organization, and achieve organic unity of economic, social, ecological, and environmental benefits. To systematically pursue green management, enterprises not only need to master the green management concept, model, and technology but also apply green management in procurement, production, marketing, finance, and customer maintenance. In addition, they must establish an evaluation system to monitor green management effectiveness, as shown in
Figure 1 [
4,
5]. Presently, green management is an important means of promoting energy conservation, consumption reduction, and sustainable economic and social development. An important feature of green management is that it adheres to the concept of sustainable development, highlights the characteristics of green science and technology management and green humanistic management, and jointly serves the construction of a resource-saving and environmentally friendly society [
6,
7]. Employees play a key role in promoting green management and the cultivation of green employee behavior is directly related to the sustainable development of an organization [
8]. Therefore, in enterprise green management practices, green management system construction and employee green behavior training are important.
The mastery and application of green management knowledge in the field of human resource management has become an important driving factor in promoting green management development and employee green behavior training. To meet the demand for innovative management personnel in the context of green management, many domestic universities and colleges have established human resource management majors and many other majors have offered courses on human resource management. The cultivation goal of the human resource management major is to equip students with modern management theory through professional knowledge; master the basic knowledge of organizational change and work design; master the basic theories and operational applications of recruitment and allocation, training and development, performance appraisal, compensation design, and labor relations management, among others; and promote the ability of students to analyze and integrate the design of human resource management work and enhance the effectiveness of organizational management. In modern enterprise management, human resource management is regarded as the “strategic partner of the enterprise”. Thus, appropriate enterprise development strategies must be developed based on a full study of changes in the internal and external environment [
9]. Therefore, the knowledge level and ability characteristics of human resource management practitioners have a key impact on the long-term healthy development of enterprises. Enhancing the green management literacy of enterprise human resource management practitioners is crucial for enterprises to better practice the concept of sustainable development.
However, in the teaching process, teachers often focus only on teaching basic knowledge of human resource management, paying less attention to the latest research progress of green management and the challenges faced by the integration of green management into human resource management. There is also little integration of green management into the teaching of human resource management courses, resulting in students being unable to incorporate advanced green management concepts and green management modes in human resource management work. As a result, green management can hardly be effectively integrated into the teaching, research, and practice of human resource management and the theoretical knowledge mastered by students cannot fully play its role in promoting the innovative practice of human resource management. Therefore, to promote management innovation and solve sustainable development problems, green management must be integrated into the teaching and practice of human resource management.
To highlight the cost-saving and consumption-reducing features of modern management and enhance the sustainable development capability of organizations, the concepts of green management and green management skills must be integrated into the knowledge-teaching and skill-cultivation of human resource management in the talent cultivation process of human resource management majors in colleges and universities. This study analyzes the current research status and application progress of green human resource management, discusses the problems and challenges faced by green human resource management, and analyzes how to integrate green management into the talent cultivation process of human resource management majors at the three levels of teaching, scientific research, and management practice. The section on management practice shows the process of green management integrated into the practical teaching of human resource management courses in the form of case studies, emphasizing the application of green management in human resource management majors. The research presented in this article helps clarify the application of green management in various modules of human resource management and supports the realization of the goal of training innovative management talent.
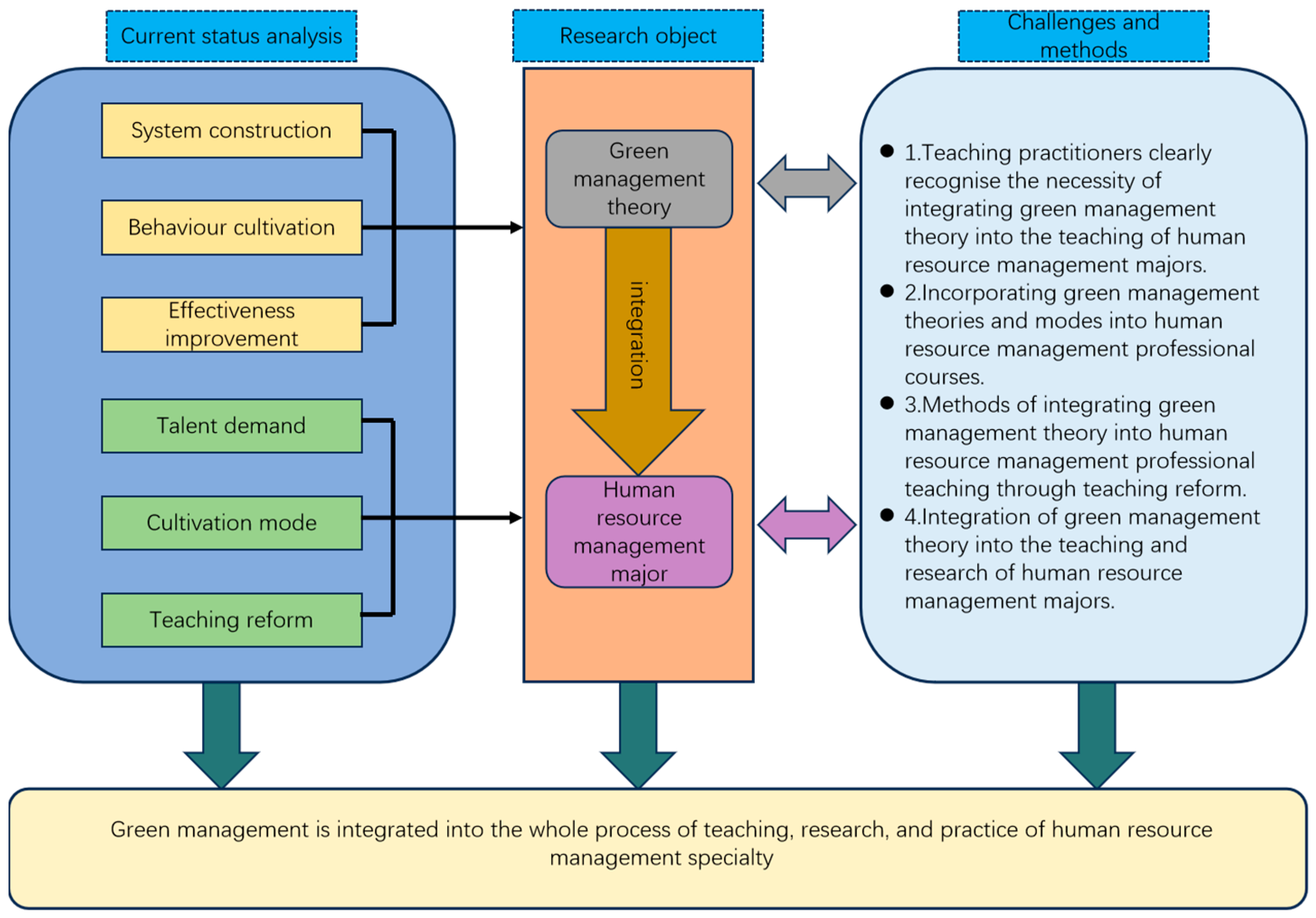
2. Research Purpose and Framework
Against the background of rapid socioeconomic development, the standardization level of China’s enterprise management has been continuously upgraded and management innovation has entered a high-speed development stage. However, under the influence of the social environment, institutional norms, and other factors, China’s enterprise management faces many practical difficulties in transitioning to green management. Green human resource management—a new management mode that integrates the concept of green management into the field of human resource management—is at the core of leading management innovation. Therefore, the implementation of green human resource management is indispensable to promote green management and achieve cost savings and efficiency gains. Accelerating the promotion of green human resource management can not only better integrate the various modules of human resource management and care more about the needs, growth, and development of employees but also bring more economic, social, and ecological benefits to the enterprise. In this context, the integration of green management into human resource management teaching, research, and practice can meet the needs of enterprises for green human resource management talents, help improve the career development ability of employees and the sustainable operational ability of enterprises, and promote enterprises to achieve comprehensive benefits.
Based on this, this study starts from the latest research progress of green management, analyzes the challenges of integrating green management theory into the teaching and research of human resource management, describes the main research progress in the field of green management, puts forward the methods of integrating green management into the teaching and research of human resource management, and demonstrates the concrete effects of integrating green management into the teaching and research of human resource management through the case of practical teaching reform. It also gives human resource management practitioners have a deeper understanding of the great benefits of such a teaching reform and thus provides scientific methodological guidance for the cultivation of green human resource management talents. The specific research framework is shown in
Figure 2.
In order to achieve the above research objectives, this article clarifies the main research results in the field of green management from the aspects of green management system construction, green behavior cultivation, and green management effectiveness improvement. Combined with the talent demand, training methods, and teaching reform of human resource management majors in colleges and universities, it puts forward the integration of green management into the classroom teaching process. In view of the current status and progress of research in the field of green management, it analyzes the problems and challenges of green management from the perspective of teachers’ teaching and research. Finally, from the perspective of integration of management practice, teaching, and research, it elaborates on how to integrate green management into university teaching and research, cultivate compound talents with innovative spirit and green management consciousness, and encourage enterprises to pursue green sustainable development and social and ecological benefits more actively.
The theoretical significance of this study is to provide a basis for the integration of green management into the teaching and research of human resource management and to provide methodological support for the cultivation of innovative human resource managers with the concept of sustainable development and green management capability. The practical significance of this study is to provide a scientific method for the integration of green management theory into the teaching and research of human resource management, to provide talent training ideas for promoting the innovation of green management system, and to provide new ideas for cultivating human resource management personnel training objectives oriented to the needs of social development and enterprise change. At the same time, it also provides new scientific research perspectives and a research methodology reference for the majority of university teachers.
3. Current Status of Green Management Research
In recent years, the level of integration of green management with various enterprise modules, such as procurement, production, sales, finance, human resource affairs, and research and development, has increased. Emphasis is placed on avoiding harm to society and ecology by meeting the needs of economic development and moving forward toward achieving the coordinated development of society, economy, and ecology. Meanwhile, the cost reduction and efficiency enhancement function of green management has received attention from scholars at home and abroad, and extensive research has been conducted on the cost saving, consumption reduction, and efficiency enhancement of green management in terms of the green management system construction, green behavior cultivation, and green management efficiency improvement.
Green management is widely used in the field of human resource management but the integration of green management theory into the teaching and research of human resource management majors faces many challenges. Firstly, the integration of green management theory into human resource management activities such as recruitment, training, assessment, and so on is affected by the business environment and business objectives, and the differences in the production and management objectives of enterprises at different stages of development will affect the degree of adoption of green management theory. Secondly, the construction of a green management system as a systematic project is also affected by different departments of the enterprise and the understanding and implementation of the green management system by different departments may also be biased. Furthermore, evaluating the performance of green management in human resource management poses difficulties. Management work involves planning, organizing, coordinating, controlling, and motivating, among other matters, and a management activity may deviate from its initial goal after passing through many links. In addition, as a basic activity of enterprise management, the effectiveness of human resource management is mostly reflected in improvements in the performance of other departments. Determining the effectiveness of green human resource management on enterprise management performance is a more difficult task. Therefore, in the construction of a green management system, the development of a scientific and reasonable performance evaluation system is the basis for improving the effectiveness of green human resource management. Studying the green effect evaluation indices of specific activities, such as recruitment and allocation, training and development, performance management, and compensation management, can help evaluate and enhance the effectiveness of green human resource management. Many scholars have focused on green management evaluation index systems and proposed green human resource management effectiveness evaluation indicators [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. Many indicators have been applied to green human resource management.
In terms of green management system construction, Mustapha et al. proposed that different information and resources can be collected, monitored, analyzed, and managed through a green management system, which ultimately achieves the goals of saving resources, improving profitability, and operational efficiency [
17]. Liu proposed optimization suggestions for green financial personnel training and green management system design [
18]. Through a study of Japan’s waste classification experience, Li et al. [
19] concluded that the construction of discipline and coordination mechanisms should be regarded as important elements of green management work. To enhance green management efficiency, Zhao et al. proposed the construction of a proactive green management mechanism by building a green management system based on regulatory mechanisms and ecological awareness cultivation [
20]. Li et al. proposed that green management mechanism construction should be consolidated by perfecting legal regulations and enhancing customer awareness of green consumption [
21].
Wang et al. proposed four types of green management behavior: internal environmental control, green cooperation, green design, and green recycling, which are considered to strengthen employees’ green behavior cultivation and promote cleaner production [
22]. Tabrizi et al. proposed encouraging employees’ green vocal behaviors, demonstrating that organizations practice their commitment to environmental sustainability and reward green behaviors, and organizing green activities can promote the generation of green behaviors among employees [
23]. Masud et al. [
24] stated that in green human resource management, social responsibility awareness plays a positive role in promoting organizational environmental performance improvement. Organizational culture plays an important role in guiding members’ values and behavioral orientations. Aggarwal et al. showed that green organizational culture can play a significant role in green human resource management practices and organizational environmental performance enhancement and can drive organizational members to generate green actions and enhance green performance [
25]. Amel et al. suggested that conscious attention is an important means of cultivating sustainable habits. Conversely, conscious action and self-reporting reinforce sustainable behaviors [
26].
In terms of promoting green management effectiveness, Rahman et al. and Li et al. argue that it is necessary to strengthen education and training guidance, implement tax incentives and subsidies, and optimize the equity strategy to motivate corporate stakeholders to take more active green management measures and promote the sustainable development of enterprises [
27,
28]. Liu found that improving the education level of top management could promote the green management level of an organization [
29]. Qin suggested that strengthening supervision and establishing reward and punishment mechanisms can promote the formation of a corporate green management environment and enhance green management effectiveness [
30]. Ansari et al. and Huo et al. suggested that attention should be paid to the construction of organizations’ green commitment and the cultivation of employees’ proenvironmental behaviors through green commitment to enhancing green management effectiveness [
31,
32]. Alfred et al. argued that enterprises can enhance green management effectiveness by designing green behavioral standards and green institutional norms [
33]. Lee [
34] believes that the promotion of organizational structural innovation can encourage organizations to be more proactive in the implementation of management innovation and achieve the goal of improving green management effectiveness. Migdadi believes that improving the effectiveness of corporate green management requires adopting appropriate incentives, specifically from the optimization of internal processes, improving the quality of green management, implementing green procurement, and adopting green customer relationship management, among other aspects of practice [
35].
The above results state the latest research progress in the field of green management. Some of the more mature green management concepts and green management modes have been applied to enterprise production and operation and the rest of the research results provide a research basis and direction for teaching and research workers. However, in the teaching process of human resource management courses, the results are rarely integrated into classroom teaching and thus cannot meet the demand for talent in the field of green human resource management. Therefore, it is necessary to explore how green management can be integrated into the teaching, research, and practice of human resource management.
4. Methods of Integrating Green Management into the Teaching and Research of a Human Resource Management Major
To further cultivate practitioners in the field of human resource management who practice the concept of green management, it is necessary to do the following: (1) deeply integrate the theory of green management with the teaching and research of the human resource management profession; (2) form a solid disciplinary team and stable research direction; and (3) actively declare teaching and scientific research projects in teaching and research. Gradually, a way to drive discipline construction, talent training, and result transformation through project research will be formed.
4.1. Integrating Green Management Theory into the Theoretical and Practical Teaching of Human Resource Management Majors
In the theoretical teaching of human resource management professional courses, it is first necessary to clarify the ideological connotations and value embodiment of green management so that students can grasp the core features of green management at the theoretical level. Second, green management theory must be mastered in the main modules of the human resource management course where design points are taught, including green recruitment, green training and development, green performance appraisal, green compensation, and welfare. Finally, students need to understand the application of green management modes, such as the design of flexible employee management systems, flexible working hours, job expansion, and job enrichment, to improve green human resource management through innovative job design.
In addition to the integration of green management theory into the teaching of the curriculum, the practice of the curriculum is also an important means to promote in-depth understanding and mastery of green human resource management skills by teachers and students. Therefore, in the practice teaching of human resource management, we can add green management practice projects in the core courses of human resource management or integrate green management into the existing practice projects so that students can consolidate the theoretical knowledge of the courses. However, teachers should integrate research results in the field of green human resource management into the teaching of the program to create a situation where teaching and learning are mutually reinforcing. In addition, students need to be encouraged to take the initiative to innovate in courses and enterprise practices, integrate green management theories into enterprise production and operations management, and solve the problems faced by enterprises in sustainable development.
4.2. Building a Platform for School-Enterprise Cooperation, Realizing Curriculum Docking, and Forming a Talent Cultivation Model for School-Enterprise Cooperation
The effective integration of educational resources of colleges and universities and industrial resources of enterprises should be promoted and the sharing level between colleges, universities, and enterprises in the fields of information, resources, and talent should be enhanced. In the process of teaching, schools can arrange green management practice classrooms for enterprises or enterprise personnel to provide students with green management practice skills guidance so that they can understand the enterprise’s green management mode and operation process. Enterprises can recruit students through interns, management trainees, and by other means. In addition to unified management and assessment, there needs to be training for the development of high-quality applied green management personnel suitable for the needs of the enterprise. Colleges and universities need to jointly cultivate high-quality and innovative talent. Enterprises, colleges, and universities can also build a platform for school–enterprise cooperation, construct school–enterprise codevelopment courses, adopt a common teaching mode for teachers and enterprise personnel, and fully absorb the practical cases of enterprise green management in teaching to establish an education mode of green management talents that suits the needs of different enterprises.
4.3. Promoting Teaching through Research
Incorporating scientific research results from the field of green management into the teaching content of courses, professional apprenticeships, graduation internships, and graduation theses of human resource management majors can enrich the teaching content of courses and practical projects. Grassroots teaching organizations should set up different course groups (course teaching teams) and project groups (academic teams) in accordance with the core curriculum of human resource management and the positioning of talent training objectives, organize teachers to actively declare relevant projects in the field of green human resource management, support teachers in absorbing students to participate in project research, enhance the students’ understanding of green human resource management, and enrich the research achievements in the field of green human resource management in a sustained manner.
4.4. Development of Teaching Staff
Teachers of core courses in human resource management must uphold the concept of continuous learning, closely track the latest research results in the field of green management, master practical cases of green management, integrate green management into the teaching and research work of human resource management, and continue to achieve new teaching and research results. Universities should support teaching and research conditions and invite experts and scholars in the field of green management to conduct seminars and exchanges to provide solid support for the continuous improvement of teachers’ teaching and research abilities.
4.5. Promoting Learning through Competition
In the course of teaching and professional practice, it is necessary to establish the concept of promoting learning through competition, relying on the curriculum to set up green management innovation competitions, actively organizing students to participate in various management innovation competitions, continuously improving the knowledge level and practical operational ability of students in the area of green management, and strengthening the students’ concept of green human resource management and operation skills.
5. Case Studies and Results
5.1. Cases of Practical Teaching Reform
5.1.1. Description of Practical Teaching Methods
To better integrate green management theory into the teaching and research of human resource management and to cultivate students’ innovation ability in the green management mode and the concept of sustainable development, the team reformed the practical teaching of human resource management. It applies green management theory to the human resource management practice course and designs the practice content of green human resource management systems according to the concept and management means of green management.
Human resource management is based on the strategic needs of organizational development through the recruitment of employees, selection, training, assessment, motivation, adjustment, and other activities; mobilizing the enthusiasm of employees; stimulating their potential to meet the current and future development needs of the organization; and ultimately achieving the organizational development goals of management activities. In the traditional management model, although enterprises regard employees as important resources and strive to achieve the unity of employee growth and enterprise development, in practice, more is carried out to serve the enterprise development strategy and pursue higher economic benefits. Green human resource management is achieved through the adoption of management measures in line with the concept of green management to achieve the common development of employees and enterprises and the organic unity of economic, social, and ecological benefits.
Although human resource management work consists of recruitment, training, assessment, compensation and benefits management, labor relations management, employee career management, and other activities, recruitment, training, and assessment are core duties [
36]. Compensation and welfare management, labor relations management, and employee career management mainly serve recruitment, training, and assessment activities. Therefore, during the practical teaching reform, three important activities—recruitment, training, and assessment—were selected for the practical study of green human resource management. The practical task is to compare the differences between the enterprise human resource management system under the traditional management concept and the enterprise human resource management system under the green management concept and to analyze the value embodiment dimension of green human resource management and the value support level shown by different green human resource management activities.
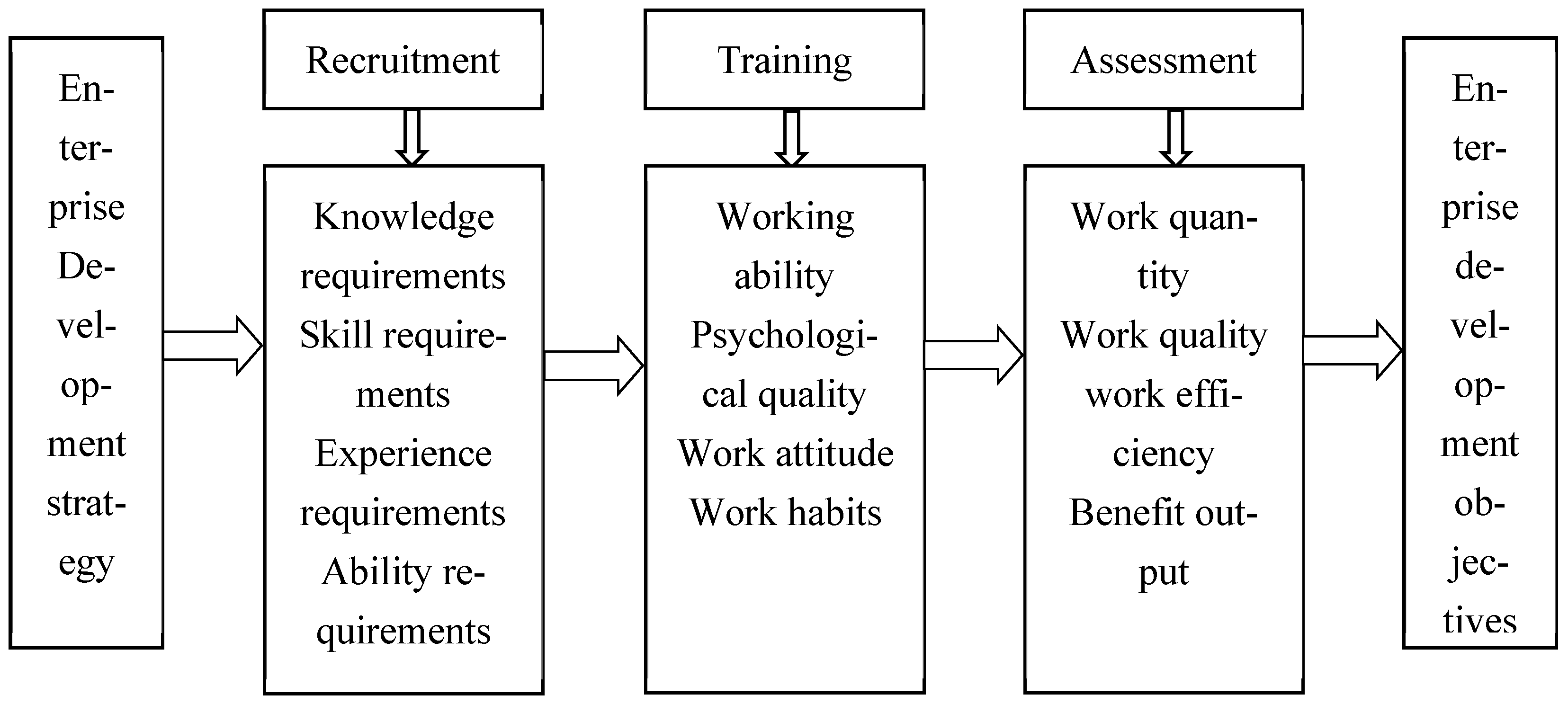
First, the teacher guides students in designing the enterprise’s human resource management system based on the traditional objective of maximizing economic benefits (
Figure 3).
At the same time, based on green management theory, teachers and students jointly design the green human resource management system, which includes three activities: recruitment, training, and assessment (
Figure 4).
5.1.2. Practical Results and Analysis
After completing the design of the human resource management system with the goal of maximizing economic benefits and the human resource management system under the concept of green management, the two management systems are compared in terms of the four dimensions of philosophy, degree of concern for employees and society, improvement of employee quality, and output target (
Table 1) to prompt students to deepen their understanding of the differences between the two types of human resource management systems. Through comparative analysis, it can be seen that at the conceptual level, the traditional human resource management system embodies a “thing”-centered approach, treats employees as costs, focuses on the use and control, and aims to achieve economic benefits. The green human resource management system upholds “people” as the core, focuses on reflecting the value of employees, pays attention to the connection between employees, enterprises, and society, and aims to achieve comprehensive benefits.
To further demonstrate the specific value of green human resource management in terms of saving costs and promoting sustainable development, the concerns and value-embodied dimensions of green recruitment, training, and assessment implemented by enterprises were analyzed (
Figure 5).
Finally, the specific roles of different human resource management activities in realizing green management values were analyzed. In this way, the extent to which different green human resource management activities support value realization was demonstrated. In practice, although green recruitment alone can recruit environmentally aware and energy-saving employees and inject new forces into green management, its effectiveness is relatively limited and its sustainability is low. Considering the differences in production and operation characteristics and the company culture of each enterprise, the role of green management for newly recruited employees is limited. After the implementation of green training, recruits will be better integrated into the team and will continue to enhance their sense of belonging and responsibility. Not only will they be able to implement green behavior on their own initiative but they will also be able to work with the rest of the company to reduce operating costs and promote sustainable development. Incorporating green management indicators into the performance appraisal of the enterprise will convey a clear guidance function, encouraging all employees to take the initiative to implement green management training and green behaviors, which will not only enhance the green management knowledge and skills of employees but also promote the enterprise to move toward the three-dimensional benefit goal of unifying economic, social, and ecological benefits. In this way, it will better demonstrate the positive social image of an enterprise and enhance its level of sustainable development. With the application of green management in recruitment, training, assessment, and other modules, its effect will be shown in a wider range and at a deeper level.
On the basis of theoretical analysis and organizational discussions, the team demonstrated the role of “green recruitment”, “green training”, “green assessment”, “green recruitment and green training”, “green training and green assessment”, “green recruitment, green training, and green assessment” in “improving green literacy”, “Promoting green behaviors”, “Reducing operating costs”, “Promoting sustainable development”, and “Achieving comprehensive benefits” (
Table 2). In order to ensure the objectivity and fairness of the analysis results, the team invited the teachers who undertook the main courses of the human resource management profession to participate in the process based on the positioning of human resource management professional talent cultivation objectives and the course content and learning requirements and organized several rounds of voting on the basis of full communication before finally obtaining the results of the role evaluation. Corresponding scores were assigned after full research and discussion. When characterizing the magnitude of the effect, “△” is used to indicate that the activity item has a high impact on the realization of the function, which is scored as 3 points; “○” is used to indicate that the activity item has a medium impact on the realization of the function, which is scored as 2 points; and “▽” is used to indicate that the activity item has a low impact on the realization of the function, which is scored as 1 point. Because it is difficult to measure specific effect sizes using particularly precise numerical values, the scores assigned here can be viewed as referencing the Likert scale to assign the appropriate level. In other words, a score of 1 represents a low level of impact, a score of 2 represents a medium level of impact, and a score of 3 represents a high level of impact. This will make the case analysis more scientific.
The results of the analysis showed that the scores of green recruitment, green training, and green assessment alone were 5, 6, and 10, respectively; the score of green recruitment and green training was 7; the score of green training and green assessment was 12; and the score of green recruitment, green training, and green assessment was 15. Thus, it can be concluded that the adoption of green recruitment and training alone produces a relatively weak effect. The effect of adopting green appraisal alone was higher and exceeded the score of adopting both green recruitment and green training activities in terms of the numerical value of the score. The simultaneous integration of green management in recruitment, training, and appraisal had the highest effect, exceeding the score for the simultaneous adoption of green training and appraisal.
5.2. Exploration of Practical Teaching Reform
In summary, it can be found that the enterprise that adopts green management will pay attention to the staff’s competence and the cultivation of the green concept and green behavior of the staff and better practice the concept of “people-orientation” in management, unify the enterprise operation and staff development, and bring more social and ecological benefits on the basis of generating economic benefits. In addition to generating economic benefits, it also brings more social and ecological benefits that are conducive to promoting energy conservation, emissions reduction, and sustainable development. It is relatively ineffective for enterprises to adopt green recruitment and green training alone or to implement green recruitment and green training together. The implementation of green assessment can encourage employees to actively acquire green management knowledge and practice green behaviors, thus generating greater benefits. The simultaneous implementation of green recruitment, green training, and green assessment will enrich employees’ knowledge of green management in a wider and deeper scope and promote employees’ green behaviors on their own initiative, which will lead to more significant results. This also indicates that in the teaching of human resource management, it is necessary to strengthen the teaching of green management theory in recruitment, training, assessment, and other core modules and to strengthen the research on the integration of green management theory into the teaching of human resource management, so as to promote the green management theories, modes, and technologies throughout the teaching of human resource management, thereby contributing to the construction of a green human resource management talent system.
The analysis showed that the integration of green management into the teaching and research of human resource management could enhance green management effectiveness in enterprises, promote the practice of green and sustainable development, and promote the pursuit of a higher level of comprehensive benefits for enterprises. These findings are consistent with the results of previous research on training employees’ green awareness to build a green management system [
20,
21]. At the same time, this study systematically proposes a feasible path to promote the enhancement of corporate green management effectiveness, which provides a more effective implementation plan for the effective implementation of the initiatives proposed by scholars, such as optimizing green management system design [
18], ecological awareness cultivation [
20], green behavior motivation [
23], the construction of organizations’ green commitment [
31,
32], and the implementation of management innovation [
34].
The above practical projects are based on the team’s scientific research activities on green management, during which teachers and students work together to apply green management theories to human resource management activities and compare the green human resource management system with the traditional human resource management system in terms of the concepts, the degree of concern for employees and society, the staff quality improvement, and output target. This prompts the students to have a comprehensive and objective understanding of the green human resource management system and enhances the students’ application skills in realizing energy conservation, emission reduction, and the promotion of sustainable development through the adoption of green human resource management activities.
The above practical courses not only enable students to keep up with the development of green management and master the core concepts and functions of green management but also have the following impact: (1) providing a more profound understanding of the traditional human resource management system and the green human resource management system; (2) clarifying where the value of the green human resource management system lies, as well as the functions and specific effects of different green human resource management activities; (3) providing theoretical learning guidance and practical basis for the development of green human resource management; and (4) laying the foundation for students to engage in future management practice innovation and scientific research. Of course, the data used in the study were mainly derived, analyzed, and applied by our team and the teachers of the main courses of human resource management majors in combination with their years of teaching and research experience, with no data collected from the student level. In future research, the team will also strengthen contact with the graduates of the human resource management major and strive to obtain the support of the graduated students’ work units to obtain data on the performance effect at the level of green human resource management in enterprises.
6. Discussion and Conclusions
To integrate the concept of green management into the talent cultivation process of human resource management, this study discussed the application of green management in human resource management teaching, research, and practice. First, it clarifies the main research results in the field of green management from the aspects of green management system construction, green behavior cultivation, and green management efficiency improvement, as well as the problems and challenges faced by the integration of green management into the teaching and research of human resource management majors. Combined with talent demand, cultivation methods, and teaching reforms for human resource management majors in universities, we propose a method for integrating green management theory into teaching and research on human resource management majors. Finally, the case study is based on the author’s teaching team’s research results on current green human resource management, and the practical teaching of the green human resource management system and its functional embodiment are designed to enable students to master the theoretical knowledge of green human resource management and its application skills in the process of practical teaching. The integration of green management into the teaching and research of human resource management not only enriches the curriculum system of human resource management but also provides direction and methodological support for teachers to engage in teaching and scientific research in the field of green management and provides a new way of thinking for the cultivation of innovative management talents with the awareness of energy saving, emission reduction, and green management.
The wide application of green management in enterprises is an important means to achieve the enhancement of enterprise management effectiveness, promote the fulfillment of corporate social responsibility and promote enterprises to embark on sustainable development, provide management support for enterprises to change their management mode, promote energy saving and emission reduction and industrial transformation and upgrading, and is an important way for enterprises to achieve green development. To better achieve this goal, first, it is necessary to keep abreast of the latest scientific research progress in green management and ensure that the results of green management can meet the needs of the current development of enterprises and society. Second, it is necessary for human resource management practitioners to master the latest theories of green management and green management mode and to be able to apply them to management practice. Thus, colleges and universities must continuously integrate green management knowledge into the curriculum and practical teaching of human resource management so that future business managers can apply green management. Finally, to adapt to the green development needs of enterprises and society, enterprises, especially their human resource management departments, need to carry out corresponding reforms and actively apply advanced green management theories and modes to production and operation practices. Therefore, in the training of human resource management professionals, whether in theoretical teaching or management practice, colleges and universities should integrate green management into students’ theoretical learning and practical skills training.