Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Properties of Residual Sewage Sludge
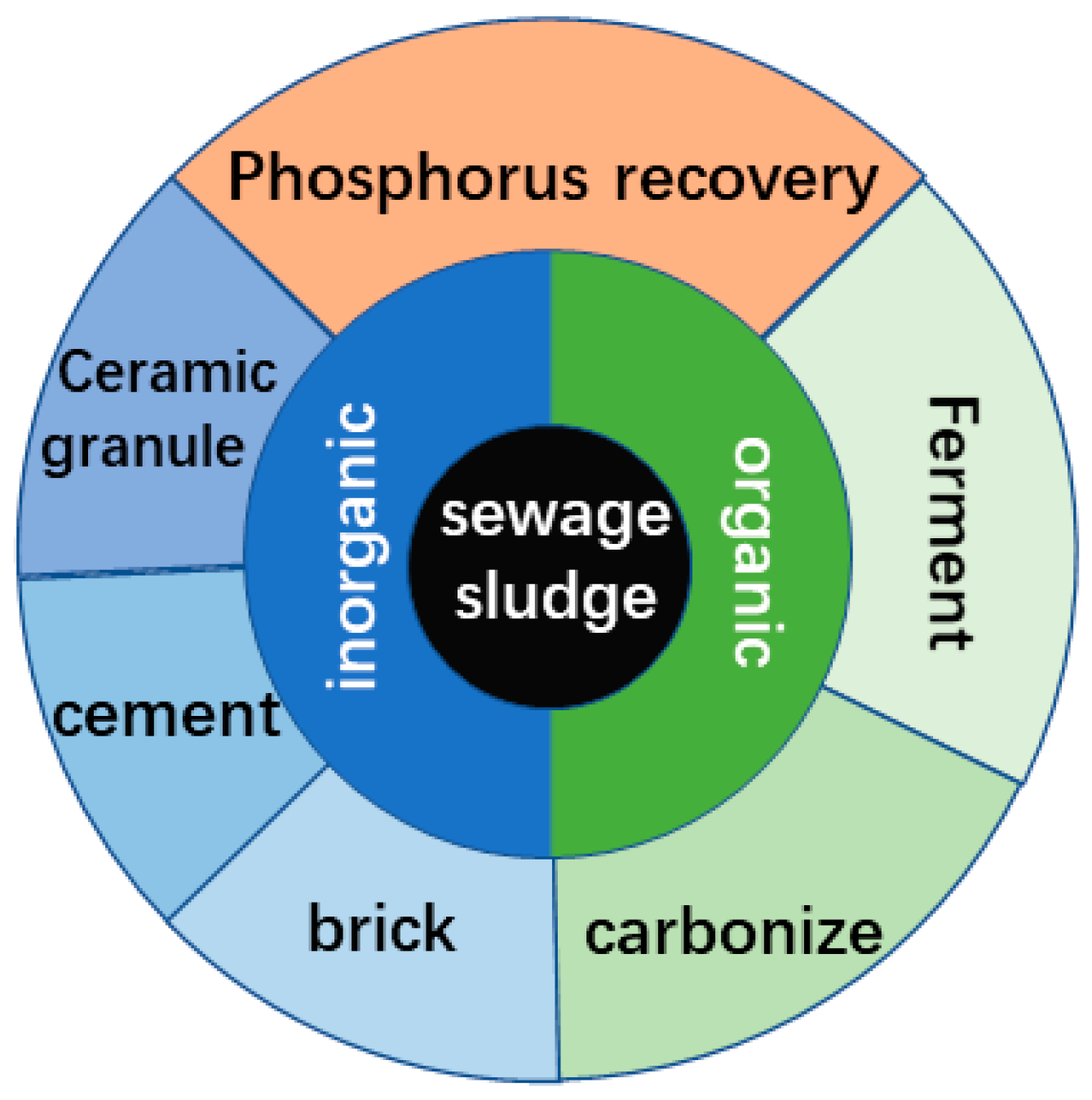
3. Resource Utilization Technologies for Residual Sewage Sludge Disposal
3.1. Residual Sewage Sludge for Building Material Utilization
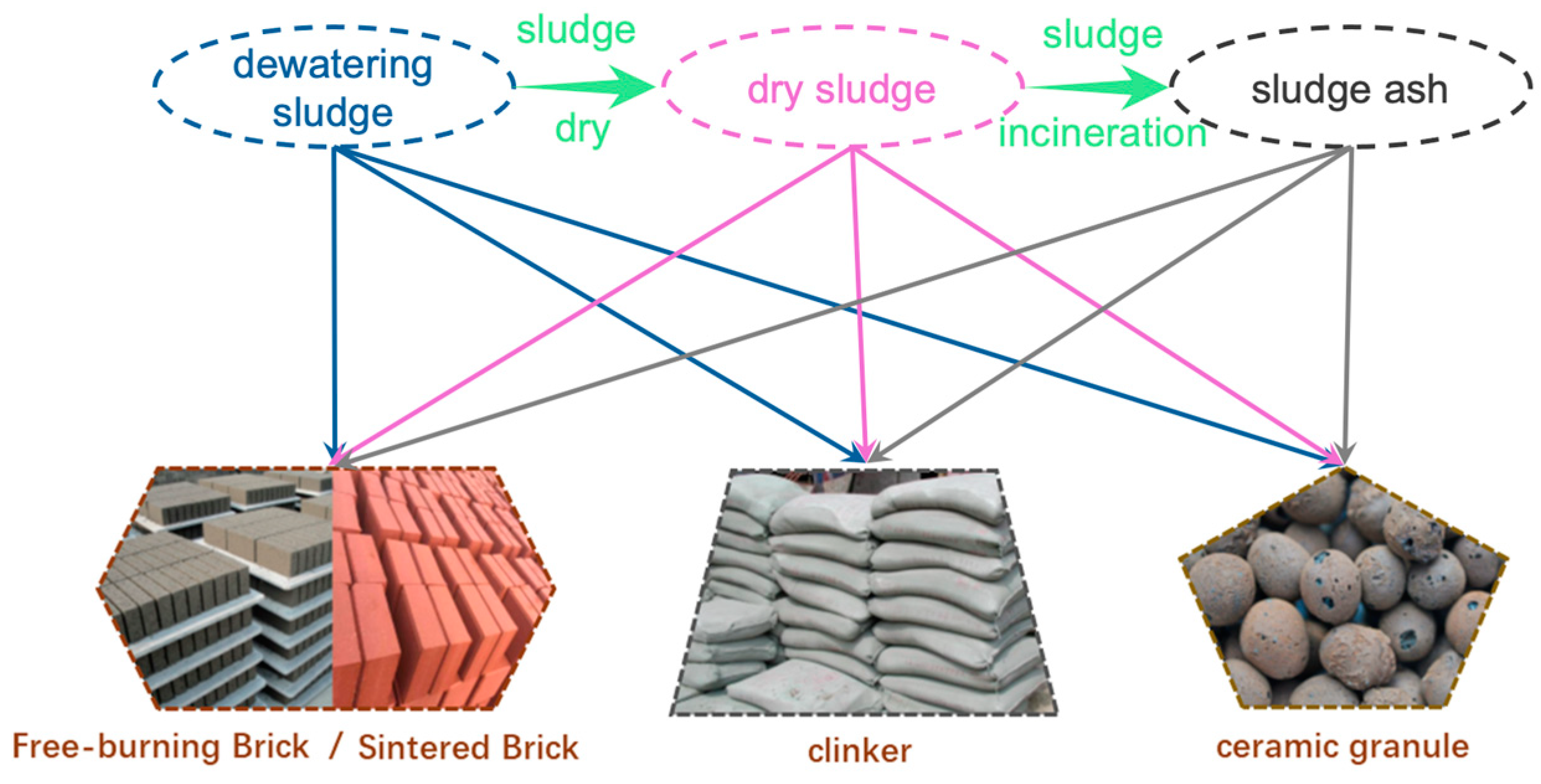
3.1.1. Sludge Brick-Making
3.1.2. Cement Produced from Sludge
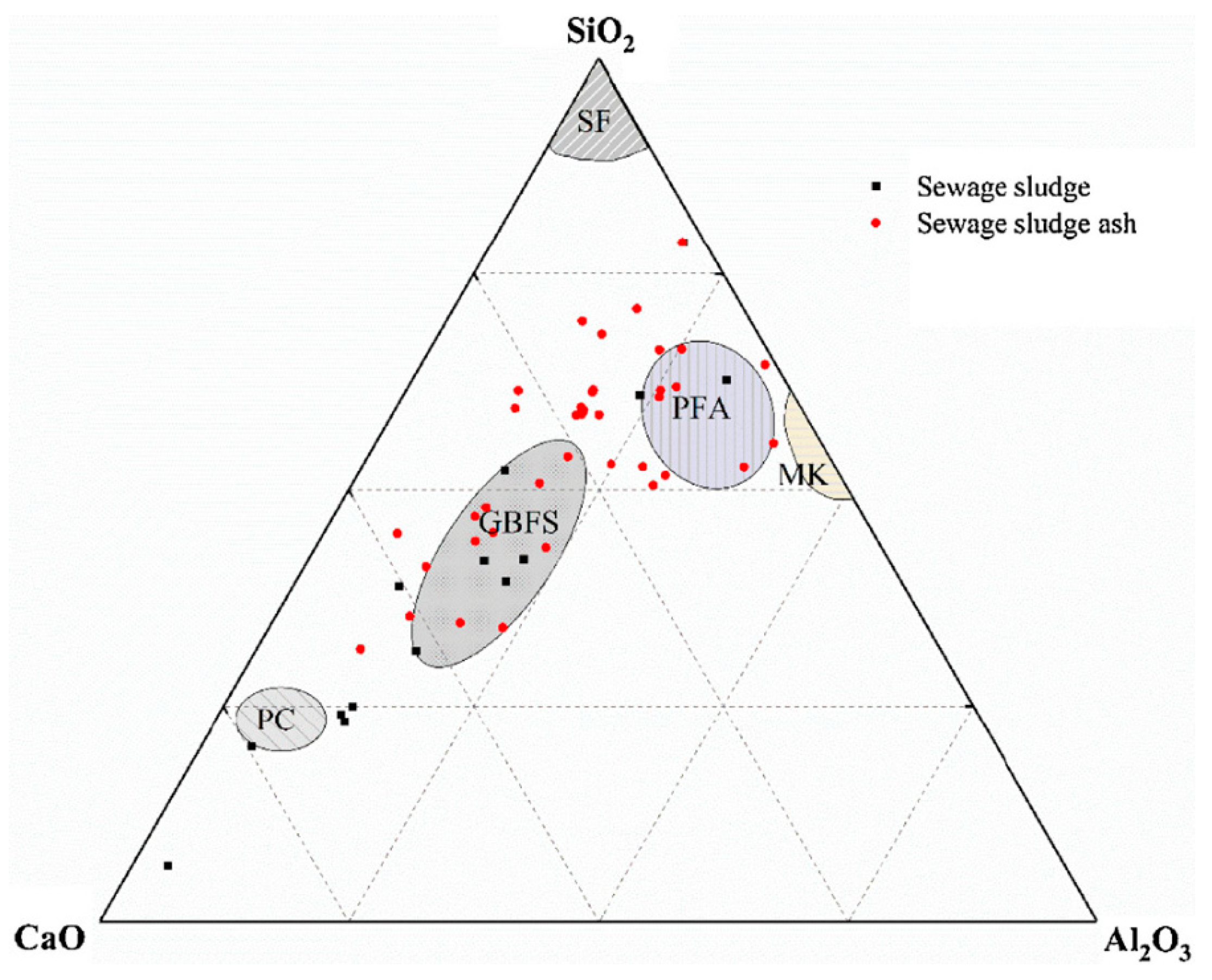
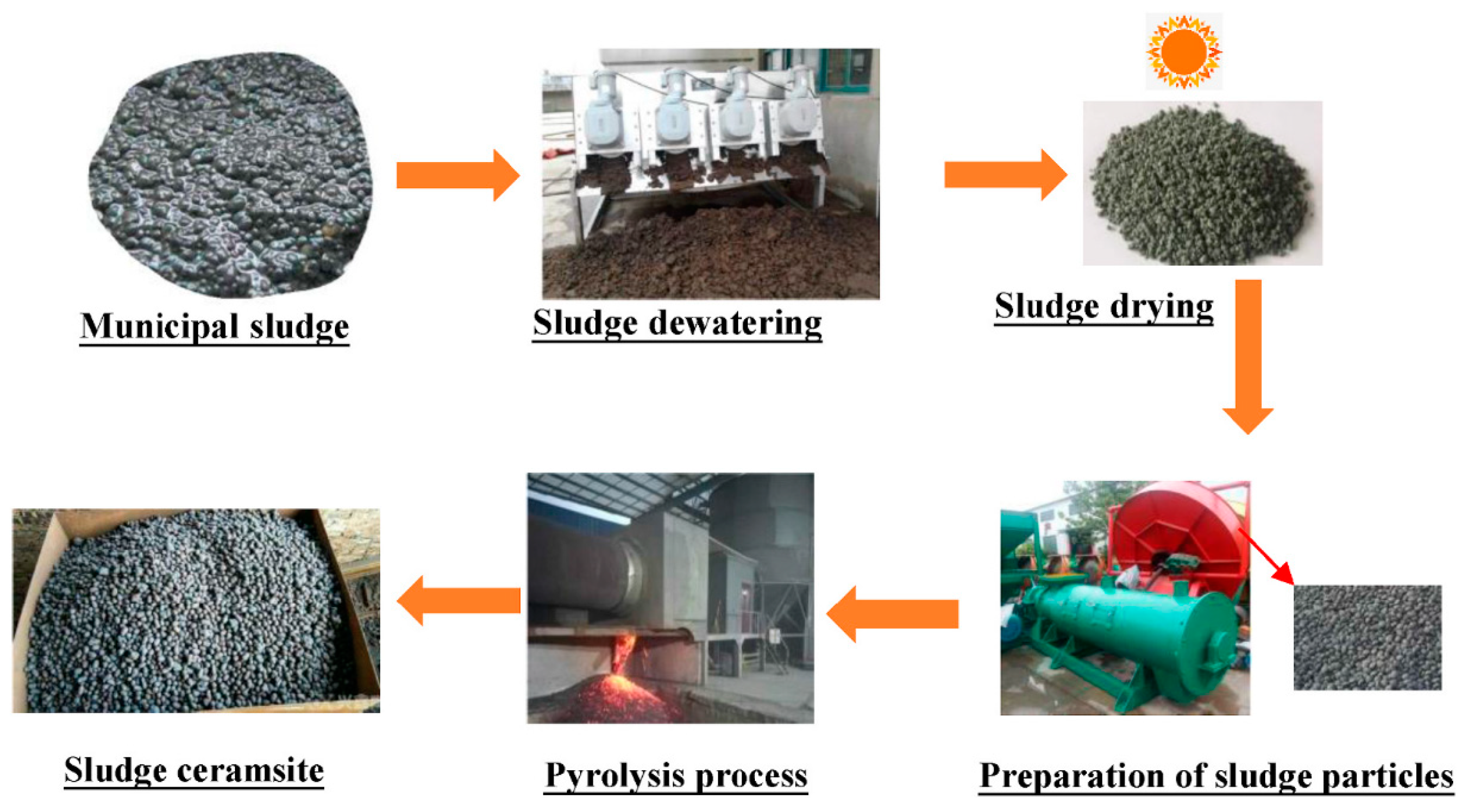
3.1.3. Sludge Ceramsite Production
3.2. Residual Sewage Sludge Utilization for Energy
3.2.1. Sludge Anaerobic Fermentation
3.2.2. Sludge Co-Incineration
3.2.3. Residual Sewage Sludge Carbonization
3.3. Phosphorus Recovery from Residual Sewage Sludge
4. The Comparison of Resource Utilization Technologies for Residual Sewage Sludge
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abidli, A.; Huang, Y.; Ben Rejeb, Z.; Zaoui, A.; Park, C.B. Sustainable and Efficient Technologies for Removal and Recovery of Toxic and Valuable Metals from Wastewater: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Callegari, A. Energy and Resources Recovery from Excess Sewage Sludge: A Holistic Analysis of Opportunities and Strategies. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2023, 19, 200184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.C.; Li, Z.H.; Long, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Huo, W.Z.; Luo, Z.R.; Lu, W.J. Direct Humification of Biowaste with Hydrothermal Technology: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Kumar, R.; Nana Amaniampong, P.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Z.-T. Synergetic Effects in the Co-pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass and Plastic Waste for Renewable Fuels and Chemicals. Fuel 2023, 353, 129210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Luo, L.; Li, D.; Johnravindar, D.; Varjani, S.; Wong, J.W.C.; Zhao, J. Hydrochar Prepared from Digestate Improves Anaerobic Co-digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge: Performance, Mechanisms, and Implication. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, K.; Alam, M. Sustainable Management of Water Treatment Sludge through 3‘R’ Concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaker, A.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Q. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 187, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimersson, S.; Svanström, M.; Laera, G.; Peters, G. Life Cycle Inventory Practices for Major Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Carbon Flows in Wastewater and Sludge Management Systems. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1197–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; He, J. Opportunities and Challenges in Sustainable Treatment and Resource Reuse of Sewage Sludge: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 616–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.P.; Zeng, G.M. Influence of Salinity on Microorganisms in Activated Sludge Processes: A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L.; Wei, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chang, C.C. Activated Sludge and Other Aerobic Suspended Culture Processes. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.-W.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Shao, Z.; Iris, Ç.; Pan, B.; Li, X.; et al. A Review of China’s Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) and Comparison with International Regions: Management and Technologies in Treatment and Resource Utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmas, N.; Manfe, N.; Zerva, I.; Melidis, P.; Raga, R.; Ntougias, S. A Critical Review on the Microbial Ecology of Landfill Leachate Treatment Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, L. Investigation and Analysis on the Treatment and Disposal Methods of Typical Sewage Treatment Plant Sludge in China’s Key River Basins. China Water Wastewater 2022, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Analysis on Urban Sludge Nutrition Element and Heavy Metal Content in China. China Environ. Prot. Ind. 2015, 04, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, E.; Yeneneh, A.M.; Sen, T.K.; Ang, H.M.; Kayaalp, A. A comprehensive review on rheological studies of sludge from various sections of municipal wastewater treatment plants for enhancement of process performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 257, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukkaram, S.; Kumar, A.A. Characteristics of Sewage Sludge and Its Potential Applications in the Construction Industry: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2021, 28, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, C.J.; Dhir, R.K.; Ghataora, G.S.; West, R.P. Sewage Sludge Ash Characteristics and Potential for Use in Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieszczad, A.; Popardowski, E.; Lubinska, W.; Gliniak, M.; Nawalany, G.; Sokolowski, P. Possibility of Using Waste Materials as Substitutes for Gravel or Water in Concrete Mix. Materials 2023, 16, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gainey, L.; Mackinnon, I.D.R.; Allen, C.; Gu, Y.; Xi, Y. Thermal Behaviors of Clay Minerals as Key Components and Additives for Fired Brick Properties: A Review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.Y.; Long, G.C.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of Sewage Sludge in the Fabrication of Construction and Building Materials: A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.H. Bricks Manufactured from Sludge. J. Environ. Eng.-ASCE 1987, 113, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.H.; Lin, D.F.; Chiang, P.C. Utilization of Sludge as Brick Materials. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, N.; Takahashi, S. Full Scale Application of Manufacturing Bricks from Sewage. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Experimental Study on No-roasting Bricks Made from Sludge and Building Rubbish. Non-Met. Mines 2011, 34, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy, V.; Kannan, R.; Muralidharan, G.; Sidharthan, R.K.; Veerasamy, G.; Venkatesh, S.; Amirtharajan, R. A Comprehensive Review on Advanced Process Control of Cement Kiln Process with the Focus on MPC Tuning Strategies. J. Process Control 2023, 121, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ma, S.H.; Li, W.F.; Yang, H.; Shen, X.D. Research Progress on the Hydration of Portland Cement with Calcined Clay and Limestone. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2021, 1036, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haustein, E.; Kurylowicz-Cudowska, A.; Luczkiewicz, A.; Fudala-Ksiazek, S.; Cieslik, B.M. Influence of Cement Replacement with Sewage Sludge Ash (SSA) on the Heat of Hydration of Cement Mortar. Materials 2022, 15, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.B.; Li, J.S.; Xing, X.D.; Sun, P.C. Recycling Hazardous Textile Effluent Sludge in Cement-Based Construction Materials: Physicochemical Interactions between Sludge and Cement. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 30760-2014; Technical Specification for Coprocessing of Solid Waste in Cement Kiln. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ba, M.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, S. Effect of Heavy Metal Sludge Ground Powder on Properties of Portland Cement-Based Materials. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 41, 450–460. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Wang, G. Is Ceramsite the Last Straw for Sewage Sludge Disposal: A Review of Sewage Sludge Disposal by Producing Ceramsite in China. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, L. Preparation of Ceramsite from Municipal Sludge and Its Application in Water Treatment: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zou, J.; Li, G. Ceramsite Made with Water and Wastewater Sludge and Its Characteristics Affected by SiO2 and Al2O3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7417–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Wang, J. Research Progress on Preparation Technology and Application of Municipal Sludge Ceramsite. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2022, 54, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, Z. Preparation of CFB Fly Ash/Sewage Sludge Ceramsite and the Morphological Transformation and Release Properties of Sulfur. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.L.; Xu, G.R.; Li, G.B. Ceramsite Obtained from Water and Wastewater Sludge and Its Characteristics Affected by Fe2O3, CaO, and MgO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.R.; Zou, J.L.; Li, G.B. Ceramsite Obtained from Water and Wastewater Sludge and Its Characteristics Affected by (Fe2O3+CaO+MgO)/(SiO2+Al2O3). Water Res. 2009, 43, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, S.; Poon, C.S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Novel Recycling of Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash (ISSA) and Waste Bentonite as Ceramsite for Pb-Containing Wastewater Treatment: Performance and Mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.R.; Zou, J.L.; Li, G.B. Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Characteristics of Sludge Ceramsite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Lin, S.; Liu, G. Study on the Preparation of Biochar Ceramsite Based on Sewage Sludge and the Characterization of Its Properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Duan, D.; Huang, D.; Chen, Q.; Tu, M.; Wu, K.; Wang, D. Lightweight Ceramsite Made of Recycled Waste Coal Gangue & Municipal Sludge: Particular Heavy Metals, Physical Performance and Human Health. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, X.; He, S.; Li, F.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, L. Performance of a New Low-Cost Zn/Fe-Layered Double Hydroxide-Modified Ceramsite for the Removal of P from Agricultural Runoff. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 159, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Huang, H.; Diao, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Z. Advanced Treatment of Dye Wastewater Using a Novel Integrative Fenton-like/MnO2-Filled Upward Flow Biological Filter Bed System Equipped with Modified Ceramsite. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Long, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Lu, M.; Huang, L.-Z. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater by Ceramsite: Adsorption Mechanism, Plant Cultivation and Sustainability Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, W.L.; Chong, S.; Lim, J.-W.; Chan, Y.; Chong, M.; Tiong, J.; Chin, J.; Pan, G.-T. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Wastewater Sludge: A Review of Potential Co-Substrates and Operating Factors for Improved Methane Yield. Processes 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Qin, Z.H.; Mou, J.H.; Sun, J.; Huang, S.Y.; Chaves, A.V.; Gao, L.; et al. Bioproduction and Applications of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Secondary Sludge Anaerobic Fermentation: A Critical Review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2023, 183, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lyu, Q.; Che, D. Investigation on Co-Combustion Characteristics and NOx Emissions of Coal and Municipal Sludge in a Tangentially Fired Boiler. Fuel 2023, 340, 127608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.M.; Dutta, A.; Corscadden, K.; Havard, P.; Dickie, L. Review of Biosolids Management Options and Co-Incineration of a Biosolid-Derived Fuel. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2228–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Strazzera, G.; Valentino, F.; Gottardo, M.; Villano, M.; Matos, M.; Silva, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Astals, S.; et al. New Insights in Food Waste, Sewage Sludge and Green Waste Anaerobic Fermentation for Short-Chain Volatile Fatty Acids Production: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, L.; Jiang, B. Microbial Characteristics in Anaerobic Digestion Process of Food Waste for Methane Production–A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh Nguyen, V.; Kumar Chaudhary, D.; Hari Dahal, R.; Hoang Trinh, N.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.W.; Hong, Y.; Duc La, D.; Nguyen, X.C.; Hao Ngo, H.; et al. Review on Pretreatment Techniques to Improve Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge. Fuel 2021, 285, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Bao, M.; Huo, W.; Ye, R.; Ajmal, M.; Lu, W. From Biomass to Humic Acid: Is There an Accelerated Way to Go? Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Bao, M.; Huo, W.; Ye, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W. Production of Artificial Humic Acid from Biomass Residues by a Non-Catalytic Hydrothermal Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Geng, Y.; Li, Z.; Long, Y.; Ajmal, M.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J. Unlocking the Potential of Humic Acid Production through Oxygen-Assisted Hydrothermal Humification of Hydrochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 145098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huo, W.; Ye, R.; Liu, Y.; Ajmal, M.; Lu, W. Hydrothermal Humification of Lignocellulosic Components: Who Is Doing What? Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, P.; Haddad, M.; Carrère, H. Thermal Hydrolysis of Municipal Sludge: Finding the Temperature Sweet Spot: A Review. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Mirsoleimani Azizi, S.; Dastyar, W.; Meshref, M.N.A.; Maal-Bared, R.; Ranjan Dhar, B. Low-Temperature Thermal Hydrolysis for Anaerobic Digestion Facility in Wastewater Treatment Plant with Primary Sludge Fermentation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.; Park, K.Y. Enhancement of Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge by Hydrothermal Pre-Treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 101, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chang, S. Impact of Temperatures on Microbial Community Structures of Sewage Sludge Biological Hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.U.; Kim, Y.M.; Choi, Y.-N.; Kim, H.G.; Park, J.M. Influence of Temperature on Volatile Fatty Acid Production and Microbial Community Structure during Anaerobic Fermentation of Microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, N.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. Pyrosequencing Reveals the Key Microorganisms Involved in Sludge Alkaline Fermentation for Efficient Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4262–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.J.; Pan, J.G.; Zhang, A.A.; Jiang, H.M.; Ji, X.; Cai, L. Optimize the Effects of C/N Ratio and pH on Sludge Anaerobic Fermentation Gas Production Utilizing CCD. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2016, 55, 1422–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Zuo, J. Production of Medium Chain Fatty Acids through Co-Fermentation of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge without External Electron Donors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J. Co-Fermentation of Sewage Sludge and Lignocellulosic Biomass for Production of Medium-Chain Fatty Acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, N. Progress in Inhibition Mechanisms and Process Control of Intermediates and By-Products in Sewage Sludge Anaerobic Digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.M.; Xu, C.Q.; Hong, J.L.; Tan, X.F.; Chen, W. Life Cycle Assessment of Sewage Sludge Co-Incineration in a Coal-Based Power Station. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, P.; Ma, L.; Xia, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, G. Co-Firing Sludge in a Pulverized Coal-Fired Utility Boiler: Combustion Characteristics and Economic Impacts. Energy 2017, 119, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, T.Y.; Yin, L.B.; Fang, Q.Y.; Zhan, Z.G.; Xu, Q.S.; Cheng, G. Field Test and Numerical Simulation for Co-combustion of Sludge in a 100 MW Coal Fired Boiler. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2015, 21, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Long, J. Co-Combustion Characteristics of Municipal Sewage Sludge and Coal in a Lab-Scale Fluidized Bed Furnace. Energies 2023, 16, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraman, O.Y.; Topal, H.; Bayat, O.; Atimtay, A.T. Emission Characteristics of Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge with Olive Cake and Lignite Coal in a Circulating Fluidized Bed. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2004, 39, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, G.; Duan, Y.; Duan, L. Co-combustion characteristic of sewage sludge and coal in 0.3MWth circulating fluidized bed. Clean Coal Technol. 2022, 28, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathekga, H.I.; Oboirien, B.O.; North, B.C. A review of oxy-fuel combustion in fluidized bed reactors. Int. J. Energy Res. 2016, 40, 878–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Alam, N.; Ahommed, M.S.; He, Z.B.; Ni, Y.H. Emerging Applications of Sludge Biochar-Based Catalysts for Environmental Remediation and Energy Storage: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Chang, Y.Z.; Li, A.M. Hydrothermal Carbonization for Energy-Efficient Processing of Sewage Sludge: A Review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 108, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, D.L.; Antal, M.J. Study of the Kinetics of Sewage Sludge Pyrolysis Using DSC and TGA. Fuel 1982, 61, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L.; Harris, E.; Robinson, B.; Sizmur, T. A Review of Biochars’ Potential Role in. the Remediation, Revegetation and Restoration of Contaminated Soils. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3269–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thengane, S.K.; Kung, K.S.; Gomez-Barea, A.; Ghoniem, A.F. Advances in Biomass Torrefaction: Parameters, Models, Reactors, Applications, Deployment, and Market. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 93, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Production of Char from Sewage Sludge Employing Hydrothermal Carbonization: Char Properties, Combustion Behavior and Thermal Characteristics. Fuel 2016, 176, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Giannis, A.; Wang, J.-Y. Conversion of Sewage Sludge to Clean Solid Fuel Using Hydrothermal Carbonization: Hydrochar Fuel Characteristics and Combustion Behavior. Appl. Energy 2013, 111, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P. Regimes of Hydrochar Yield from Hydrothermal Degradation of Various Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, K.; Jin, M.; Xiao, H.; Yao, H. Combustion and Pyrolysis Characteristics of Hydrochar Prepared by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Typical Food Waste: Influence of Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, K.; Liu, X.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Yao, H. Correlations between the Physicochemical Properties of Hydrochar and Specific Components of Waste Lettuce: Influence of Moisture, Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Rui, Z.; Yang, R.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, J. Sludge Char-to-Fuel Approaches Based on the Hydrothermal Fueling IV: Fermentation. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Shen, Y.; Ge, S.; Yoshikawa, K. Energy Recycling from Sewage Sludge by Producing Solid Biofuel with Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.F.; Pan, X.W.; Tan, J.Y.; Yang, S.S.; Wu, J.T.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Ren, N.Q. Sewage Sludge Derived Biochar for Environmental Improvement: Advances, Challenges, and Solutions. Water Res. X 2023, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Van, H.T.; Chu, T.H.H.; Nguyen, T.H.V.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hoang, L.P.; Hoang, V.H. Paper Waste Sludge-Derived Hydrochar Modified by Iron (III) Chloride for Enhancement of Ammonium Adsorption: An Adsorption Mechanism Study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Xue, L.; Singh, B.P.; Yu, S.; Müller, K.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Pan, G.; Zheng, X.; Yang, L. Sewage Sludge-Derived Hydrochar That Inhibits Ammonia Volatilization, Improves Soil Nitrogen Retention and Rice Nitrogen Utilization. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Lian, F.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Sun, H. Unraveling the Critical Role of Iron-Enriched Sludge Hydrochar in Mediating the Fenton-like Oxidation of Triclosan. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, C.; Duan, Y.; Wong, J.W.-C. Impact of Pyrochar and Hydrochar Derived from Digestate on the Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Swine Manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangredi, A.; Barca, C.; Ferrasse, J.-H.; Boutin, O. Effect of Process Parameters on Phosphorus Conversion Pathways During. Hydrothermal Treatment of Sewage Sludge: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hušek, M.; Moško, J.; Pohořelý, M. Sewage SludgeTreatment Methods and P-recovery Possibilities: Current State-of-the-art. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belevi, H.; Moench, H. Factors Determining the Element Behavior in Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators. 1. Field Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2501–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Teng, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, R.; Yang, T. Potential Recovery of Phosphorus during the Fluidized Bed Incineration of Sewage Sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzel, H.; Krüger, O.; Hermann, L.; Adam, C. Sewage Sludge Ash—A Promising Secondary Phosphorus Source for Fertilizer Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyckx, L.; Van Caneghem, J. Recovery of Phosphorus from Sewage Sludge Ash: Influence of Incineration Temperature on Ash Mineralogy and Related Phosphorus and Heavy Metal Extraction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerci, N.; Ahadi, S.; Coşgun, S. Comparison of Dried Sludge and Sludge Ash for Phosphorus Recovery with Acidic and Alkaline Leaching. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, R.; Yang, T.; Zhai, Z.; Li, R. Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Different Size Fly Ash from a Sewage Sludge Circulating Fluidized Bed Incinerator. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 2044–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kato, S.; Shima, H.; Sarai, E.; Ichioka, T.; Hatyakawa, S.; Miyajiri, H. Technology for Recovering Phosphorus from Incinerated Wastewater Treatment Sludge. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, F.; Fang, Y.; Qian, G. Transformation of Phosphorus by MgCl2 and CaCl2 during Sewage Sludge Incineration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60268–60275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplinski, B.; Adam, C.; Michaelis, M.; Kley, G.; Emmerling, F.; Simon, F. Reaction Sequences in the Thermo-Chemical Treatment of Sewage Sludge Ashes Revealed by X-ray Powder Diffraction—A Contribution to the European Project SUSAN. Z. Krist. 2009, 30, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
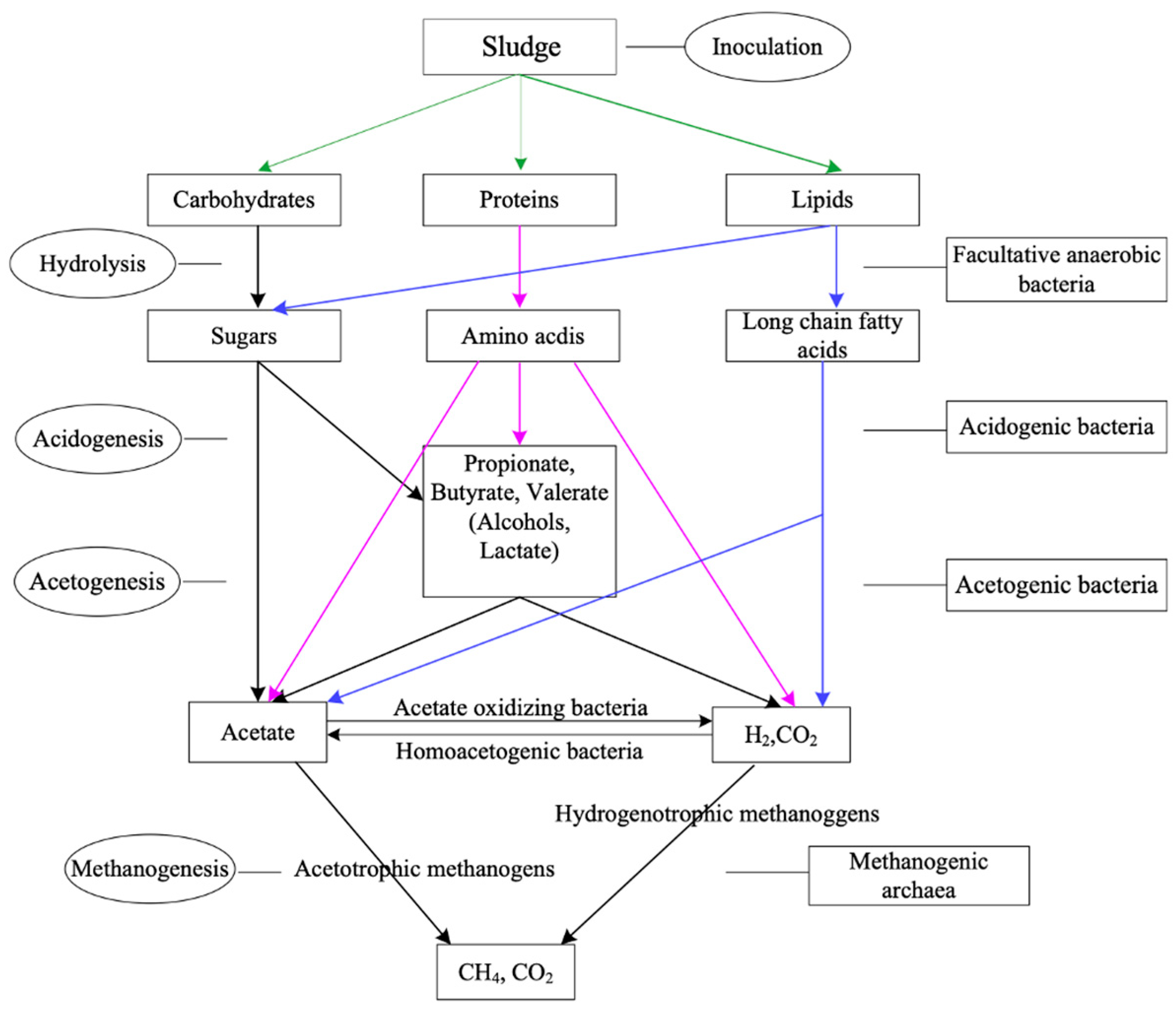
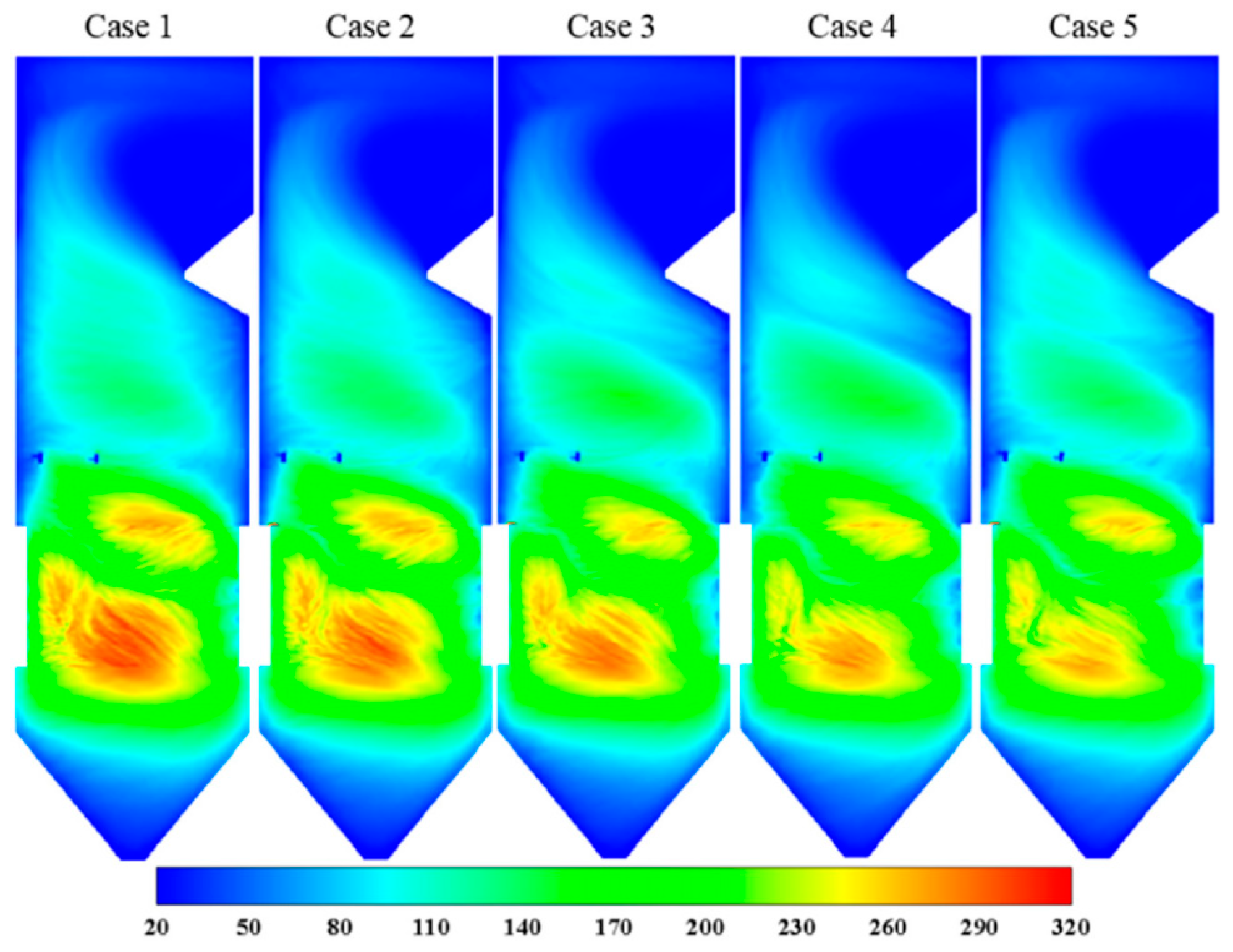
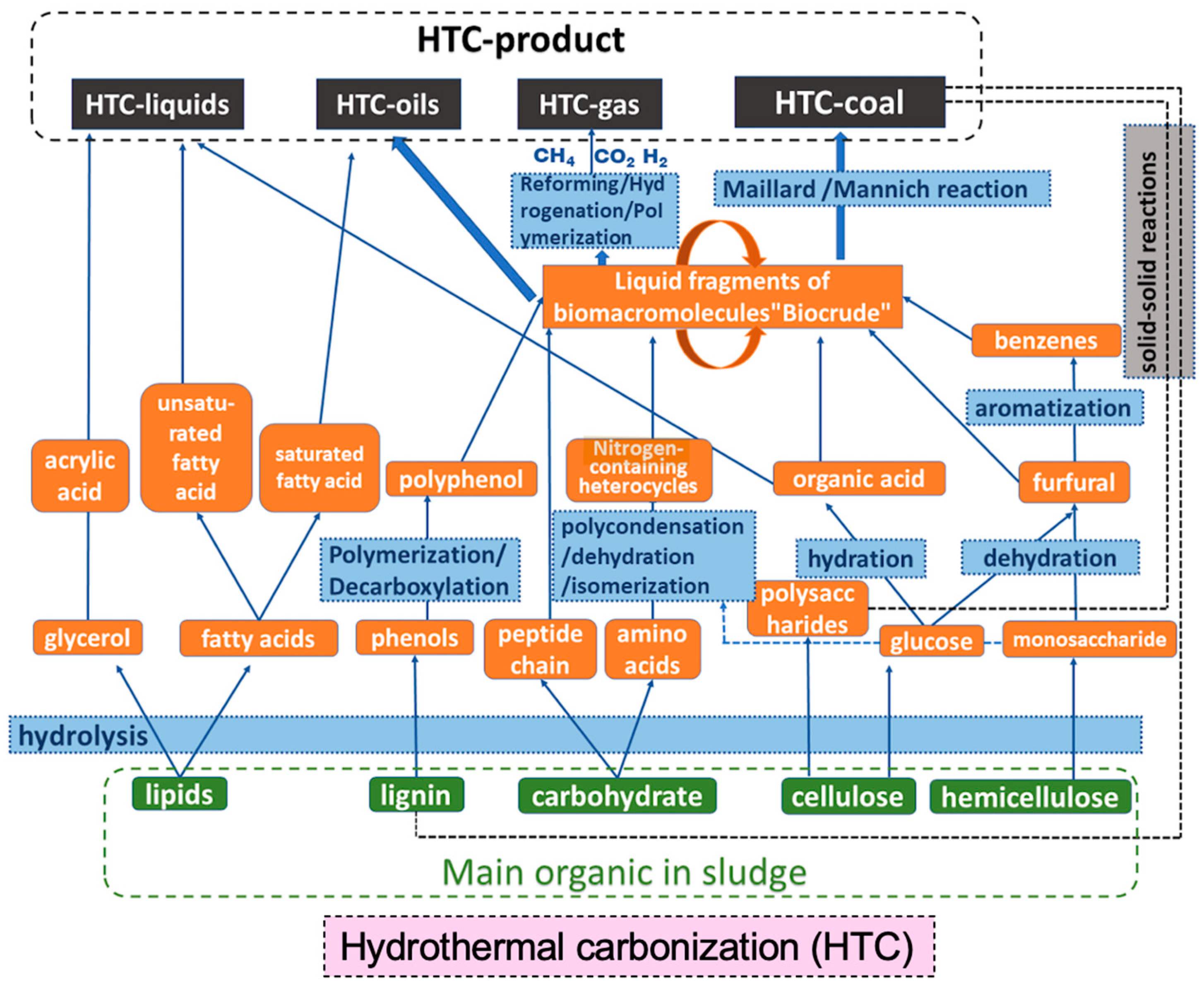

| Indicator | Average Value | Maximum Value | Minimum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic matter (%) | 51.4 | 77.0 | 13.4 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 3.6 | 7.2 | 0.3 |
| Total phosphorus (%) | 2.3 | 14.7 | 0.0 |
| Total potassium (%) | 1.4 | 7.4 | 0.1 |
| Cd (mg/kg) | 2.8 | 49.6 | / |
| Hg (mg/kg) | 5.7 | 13.6 | 0.0 |
| Pb (mg/kg) | 93.0 | 729.0 | 2.7 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 266.7 | 2960.0 | 9.6 |
| As (mg/kg) | 29.0 | 301.0 | 0.0 |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 120.2 | 615.4 | 2.7 |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 1794.7 | 14,285.0 | 15.9 |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 493.3 | 10,531.1 | 16.9 |
| B (mg/kg) | 41.7 | 98.6 | / |
| Composition (wt%) | Primary Sludge | Digested Sludge | Residual Sludge | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Typical Value | Range | Typical Value | Range | |
| Total solids | 5.0~9.0 | 6.0 | 2~5 | 4.0 | 0.8~1.2 |
| Volatile solids | 60~80 | 65 | 30~60 | 40 | 59~88 |
| Oils and fats | 6.0~30 | / | 5~20 | 18 | / |
| Protein | 20~30 | 25 | 15~20 | 18 | 32~41 |
| Cellulose | 8.0~15 | 10 | 8.0~15 | 10 | / |
| Nitrogen | 1.5~4.0 | 2.5 | 1.6~3.0 | 3.0 | 2.4~5.0 |
| Phosphorus | 0.8~2.8 | 1.6 | 1.5~4.0 | 2.5 | 2.8~11 |
| Potassium | 0~1.0 | 0.4 | 0~3.0 | 1.0 | 0.5~0.7 |
| Characteristics | Low-Temperature Carbonization | Medium-Temperature Carbonization | High-Temperature Carbonization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonization temperature (°F) | ≤600 | 800~1000 | 1200~1800 |
| Additional pressure | / | / | 6~8 Mpa |
| Pretreatment requirement | No drying | Drying to reduce the sludge moisture content (<90%) | Drying to reduce the sludge moisture content (<30%) |
| Operating odor | Micro-odor | Odorless | Odorless |
| Biochar calorific value (Kcal/kg) | 3600~4900 | 2600~4300 | 2000~3000 |
| Application | Wide | Less | Seldom |
| RSS Utilization Methods | Advantages | Restrictions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building material utilization | Brick-making |
|
|
| Cement production |
|
| |
| Ceramsite production |
|
| |
| Utilization for energy | Anaerobic fermentation |
|
|
| Co-incineration |
|
| |
| Pyrolytic carbonization |
|
| |
| Hydrothermal carbonization |
|
| |
| Phosphorus recovery (from ash fraction of RSS incineration) | Wet chemical methods |
|
|
| Thermal chemical methods |
|
| |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Shao, Y.; Qin, S.; Wang, Z. Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166710
Zheng W, Shao Y, Qin S, Wang Z. Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166710
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Weicheng, Yuchao Shao, Shulin Qin, and Zhongquan Wang. 2024. "Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166710
APA StyleZheng, W., Shao, Y., Qin, S., & Wang, Z. (2024). Future Directions of Sustainable Resource Utilization of Residual Sewage Sludge: A Review. Sustainability, 16(16), 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166710







