Assessing the Effects of Whey Hydrogel on Nutrient Stability in Soil and Yield of Leucosinapis alba and Hordeum vulgare
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling of Soil and Analysis
2.2. Adjustment of Hydrogel and Analysis
2.3. Pot Trial
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrogel and Soil Characterization
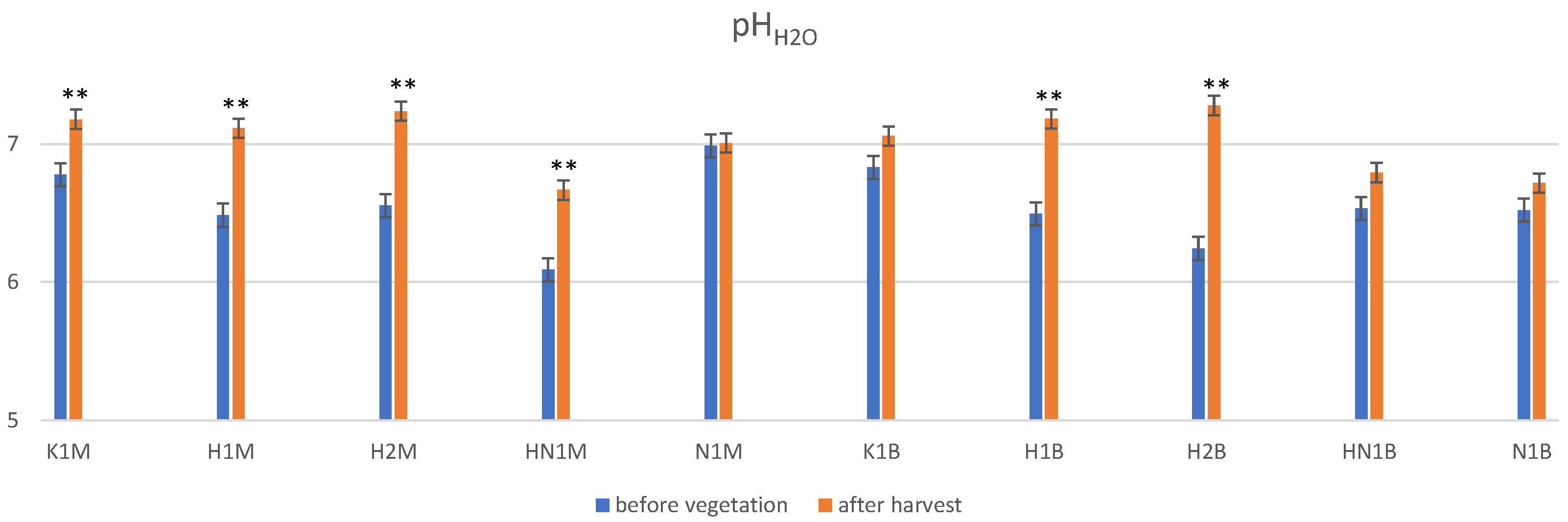
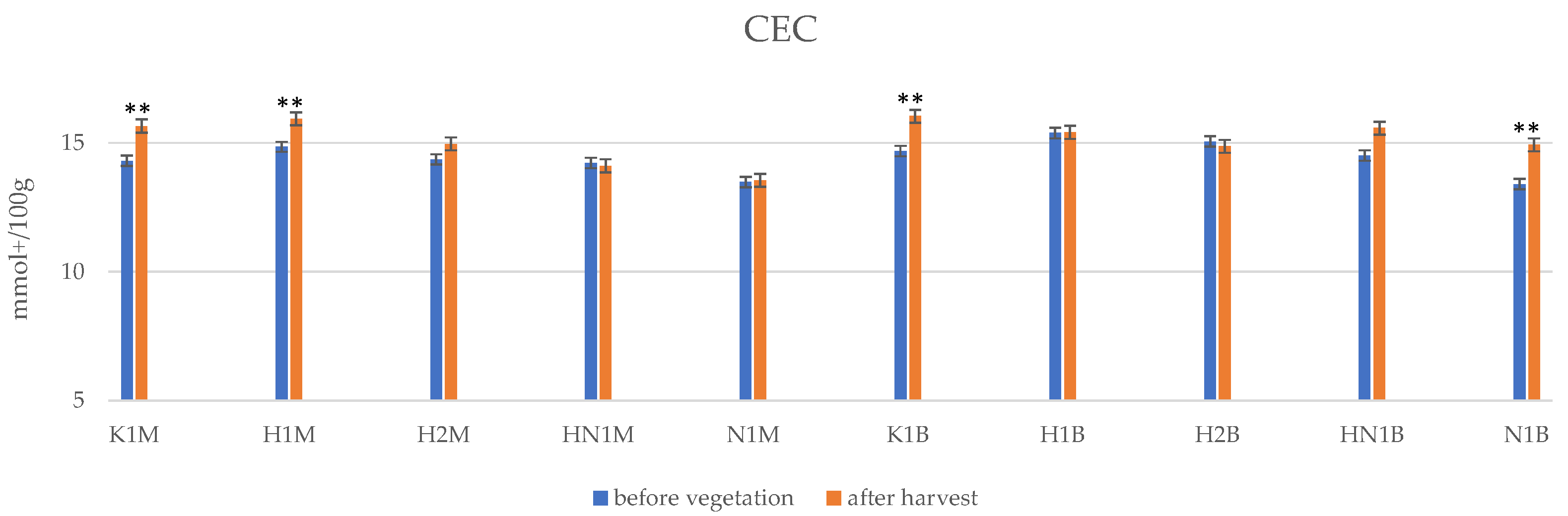
3.2. Soil Quality after Whey Hydrogel and NPK Addition
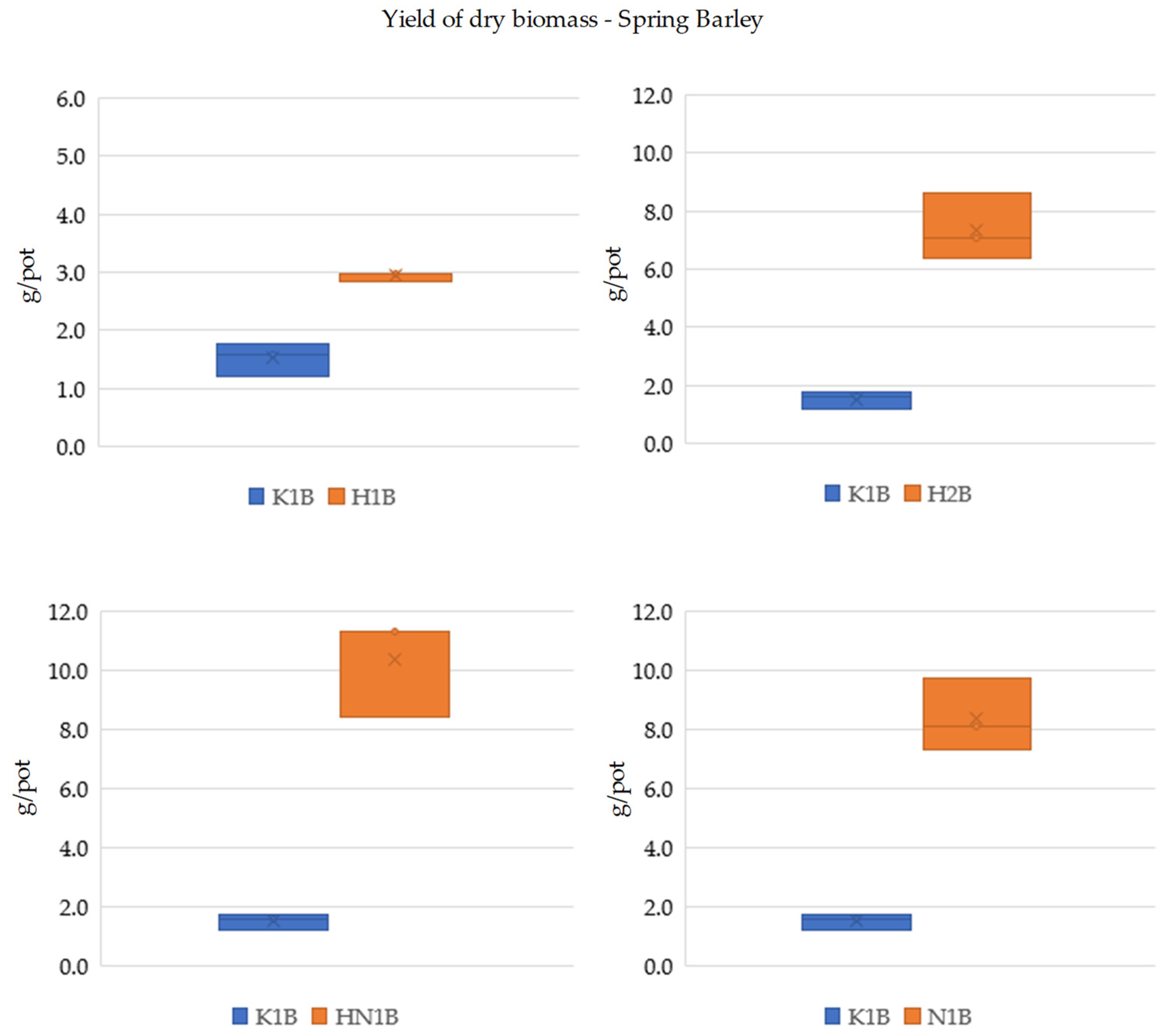
3.3. Yield of Dry Biomass
3.4. Soil Quality after the Harvest
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Penuelas, J.; Coello, F.; Sardans, J. A better use of fertilizers is needed for global food security and environmental sustainability. Agric. Food Secur. 2023, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lü, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Ning, P.; Liu, M. Environmentally friendly fertilizers: A review of materials used and their effects on the environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 613–614, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröster, M.F.; Sauer, J. IoFarm in Field Test: Does a Cost-Optimal Choice of Fertilization Influence Yield, Protein Content, and Market Performance in Crop Production? Agriculture 2021, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomášková, I.; Svatoš, M.; Macků, J.; Vanická, H.; Resnerová, K.; Čepl, J.; Holuša, J.; Hosseini, S.M.; Dohrenbusch, A. Effect of Different Soil Treatments with Hydrogel on the Performance of Drought-Sensitive and Tolerant Tree Species in a Semi-Arid Region. Forests 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmakçi, R.; Salik, M.A.; Çakmakçi, S. Assessment and Principles of Environmentally Sustainable Food and Agriculture Systems. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, N. The concept of agricultural sustainability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 46, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Manevski, K.; Lærke, P.E.; Jørgensen, U. Biomass yield, yield stability and soil carbon and nitrogen content under cropping systems destined for biorefineries. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miricescu, A.; Byrne, T.; Doorly, C.M.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Barth, S.; Graciet, E. Experimental comparison of two methods to study barley responses to partial submergence. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.; Veríssimo, A.M.; Brites, P.; Baptista, F.M.; Góis, J.C.; Quina, M.J. Greenhouse Assays with Lactuca sativa for Testing Sewage Sludge-Based Soil Amendments. Agronomy 2022, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, F.F.; Parente, A.; Santamaria, P.; Sannino, A.; Serio, F. Biodegradable Superabsorbent Hydrogel Increases Water Retention Properties of Growing Media and Plant Growth. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, D. Superabsorbent polymers used for agricultural water retention. Polym. Test. 2021, 94, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Ansar, A.A.; Anwar, F.; Ullah, I.; Rashid, U. Improvement in the Water Retention Characteristics of Sandy Loam Soil Using a Newly Synthesized Poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic Acid)/AlZnFe2O4 Superabsorbent Hydrogel Nanocomposite Material. Molecules 2012, 17, 9397–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannazza, G.; Cataldo, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A. Experimental Assessment of the Use of a Novel Superabsorbent polymer (SAP) for the Optimization of Water Consumption in Agricultural Irrigation Process. Water 2014, 6, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I. Applications of Absorbent Polymers for Sustainable Plant Protection and Crop Yield. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.K.; Poddar, R.; Brestic, M.; Acharjee, P.U.; Bhattacharya, P.; Sengupta, S.; Pal, P.; Bam, N.; Biswas, B.; Barek, V.; et al. Prospects of Hydrogels in Agriculture for Enhancing Crop and Water Productivity under Water Deficit Condition. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 2022, 4914836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilske, B.; Bai, M.; Lindenstruth, B.; Bach, M.; Rezaie, Z.; Frede, H.-G.; Breuer, L. Biodegradability of a polyacrylate superabsorbent in agricultural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9453–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, R.; Wandzik, I. A Mini-Review on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels with Potential for Sustainable Agricultural Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadini, R.C.; Martins, V.C.A.; Pawlicka, A. Synthesis and characterization of gellan gum: Chitosan biohydrogels for soil humidity control and fertilizer release. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Song, S.; Du, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, P. Nutrient controlled release performance of bio-based coated fertilizer enhanced by synergistic effects of liquefied starch and siloxane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Abd-Eladl, M.; Abou-Baker, N.H. Lignocellulosic biomass for the preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel and its use for optimizing water resources in agriculture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demitri, C.; Scalera, F.; Madaghiele, M.; Sannino, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Potential of Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels as Water Reservoir in Agriculture. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 435073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Liang, H.; Sun, R.; Peng, P.; Jiang, Y.; She, D. Hydrogel synthesis based on lignin/sodium alginate and application in agriculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodkouieh, S.M.; Kalantari, M. Synthesis of a New Hydrogel Based on Ethylene Glycol Crosslinked Tragacanth Gum with Emphasis on Its Agricultural Potential. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushbu; Warkar, S.G.; Kumar, A. Synthesis and assessment of carboxymethyl tamarind kernel gum based novel superabsorbent hydrogels for agricultural applications. Polymer 2019, 182, 121823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, M.R.; Aouada, F.A.; Fajardo, A.R.; Martins, A.F.; Paulino, A.T.; Davi, M.F.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Superabsorbent hydrogels based on polysaccharides for application in agriculture as soil conditioner and nutrient carrier: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kruif, C.; Anema, S.G.; Zhu, C.; Havea, P.; Coker, C. Water holding capacity and swelling of casein hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, D. Environmentally friendly hydrogel: A review of classification, preparation and application in agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aziz, G.H.A.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Fahmy, A.H. Using Environmentally Friendly Hydrogels to Alleviate the Negative Impact of Drought on Plant. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, R.A. Slow release fertilizer hydrogels: A review. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6073–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, W.E.; Dave, A.M.; Vaishnav, U.H.; Kumbar, S.G.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Hydrogels as controlled release devices in agriculture. Des. Monomers Polym. 2002, 5, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Yang, S. Water retention and fertilizer slow release integrated superabsorbent synthesized from millet straw and applied in agriculture. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 160, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Ghosh, G.K. Hydrogel-biochar composite for agricultural applications and controlled release fertilizer: A step towards pollution free environment. Energy 2022, 242, 122977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.G.; Cesco, C.T.; de Lima, G.F.; Artifon, S.E.; Rosa, D.d.S.; Paulino, A.T. Arabic gum-based composite hydrogels reinforced with eucalyptus and pinus residues for controlled phosphorus release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. A pH-responsive/sustained release nitrogen fertilizer hydrogel based on aminated cellulose nanofiber/cationic copolymer for application in irrigated neutral soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppakundilograt, S.; Pheatcharat, N.; Kiatkamjornwong, S. Multilayer-coated NPK compound fertilizer hydrogel with controlled nutrient release and water absorbency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, A.C.; Rodrigues, J.S.; de Freitas, A.S.M.; Machado, G.T.; Botaro, V.R. Renewable Source Hydrogel as a Substrate of Controlled Release of NPK Fertilizers for Sustainable Management of Eucalyptus urograndis: Field Study. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonatto, F.; Muniz, E.C.; Tambourgi, E.B.; Paulino, A.T. Adsorption and controlled release of potassium, phosphate and ammonia from modified Arabic gum-based hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Kosmerl, E.; Krentz, A.; Zhang, L.; Badiger, S.; Miyagusuku-Cruzado, G.; Mayta-Apaza, A.; Giusti, M.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; García-Cano, I. Invited review: Acid whey trends and health benefits. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrsch, G.A.; Robbins, C.W. Cheese Whey as an Amendment to Disturbed Lands: Effects on Soil Hydraulic Properties; USDI Bureau of Mines Special Publication No. SP06C-94; NTIS: Springfield, VA, USA, 1994; pp. 330–336.
- Robbins, C.W.; Lehrsch, G.L. Cottage cheese whey effects on sodic soils. Arid Soil Res. Rehab. 1992, 6, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, L.; Fernandez, B.; Grigoras, C.G.; Patriciu, O.I.; Grig-Alexa, I.C.; Nicuta, D.; Ciobanu, D.; Gavrila, L.; Finaru, A.L. Valorization of whey from diary industry for agricultural use as fertilizer: Effects on plant germination and growth. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2012, 11, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.; Sert, D. The effects of whey application on the soil biological properties and plant growth. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. (EJSS) 2020, 9, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotta, T.; Solieri, L.; Iacumin, L.; Picozzi, C.; Gullo, M. Valorization of cheese whey using microbial fermentations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2749–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Photis, P.; Kotsaki, P. Technological Utilization of Whey towards Sustainable Exploitation. J. Adv. Dairy Res. 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar]
- echmánková, J.; Skála, J.; Sedlařík, V.; Duřpeková, S.; Drbohlav, J.; Šalaková, A.; Vácha, R. The Synergic Effect of Whey-Based Hydrogel Amendment on Soil Water Holding Capacity and Availability of Nutrients for More Efficient Valorization of Dairy By-Products. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durpekova, S.; Filatova, K.; Cisar, J.; Ronzova, A.; Kutalkova, E.; Sedlarik, V. A Novel Hydrogel Based on Renewable Materials for Agricultural Application. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 2020, 8363418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390:2005; Soil Quality—Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- ISO 14235:1998; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic Carbon by Sulfochromic Oxidation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- ISO 11261:1995; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Modified Kjeldahl Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 13536:1995; Soil Quality—Determination of the Potential Cation Exchange Capacity and Exchangeable Cations Using Barium Chloride Solution Buffered at pH = 8,1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Berry, R.A. The production, composition and utilisation of whey. J. Agric. Sci. 1923, 13, 192–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharratt, W.J.; Peterson, A.E.; Calbert, H.E. Effect of Whey on Soil and Plant Growth. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emad, A.; Elsayed, A.; Ibrahem, G. Effects of Cheese Whey on Some Chemical and Physical Properties of Calcareous and Clay Soils. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2018, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sanatawy, A.M.; Ash-Shormillesy, S.M.A.I.; El-Yazied, A.A.; El-Gawad, H.G.A.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Sitohy, M.; Osman, A. Enhancing Grain Yield and Nitrogen Accumulation in Wheat Plants Grown under a Mediterranean Arid Environment by Foliar Spray with Papain-Released Whey Peptides. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, A.; Labdelli, F.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Djerbaoui, M.; Kucher, D.E.; Hadjout, S.; Ouaret, W.; Zakharova, O.A.; Latati, M. Investigating the Potassium Fertilization Effect on Morphological and Agrophysiological Indicators of Durum Wheat under Mediterranean Rain-Fed Conditions. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwaziri, E.; Ismail, H.; El-Khair, E.-S.A.; Al-Qahtani, S.M.; Al-Harbi, N.A.; El-Gawad, H.G.A.; Omar, W.A.; Abdelaal, K.; Osman, A. Biostimulant application of whey protein hydrolysates and potassium fertilization enhances the productivity and tuber quality of sweet potato. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2023, 51, 13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, H.; Basri, M.I.; Rembon, F.S.; Ramadhan, L.O.A.N.; Nurdin, M. High performance of chitosan-co-polyacrylamide-TiO2 crosslinked glutaraldehyde hydrogel as soil conditioner for soybean plant (Glycine max). Soil Sci. Ann. 2020, 71, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, E.; Safari, M.; Salimi, M. Improvement of tomato yield and quality using slow release NPK fertilizers prepared by carnauba wax emulsion, starch-based latex and hydrogel nanocomposite combination. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, H.A.; Sorour, M.H.; Aboulnour, A.G. Development of a multi-component fertilizing hydrogel with relevant techno-economic indicators. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2008, 3, 764–770. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, D.F.B.A.; Wasli, M.E.; Tan, C.S.Y.; Musa, Z.; Chin, S.-F. Eco-friendly cellulose-based hydrogels derived from wastepapers as a controlled-release fertilizer. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Kossińska, N.; Widera, B.; Warchoł, J.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Biodegradable hydrogel materials for water storage in agriculture—Review of recent research. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 194, 324–332. [Google Scholar]





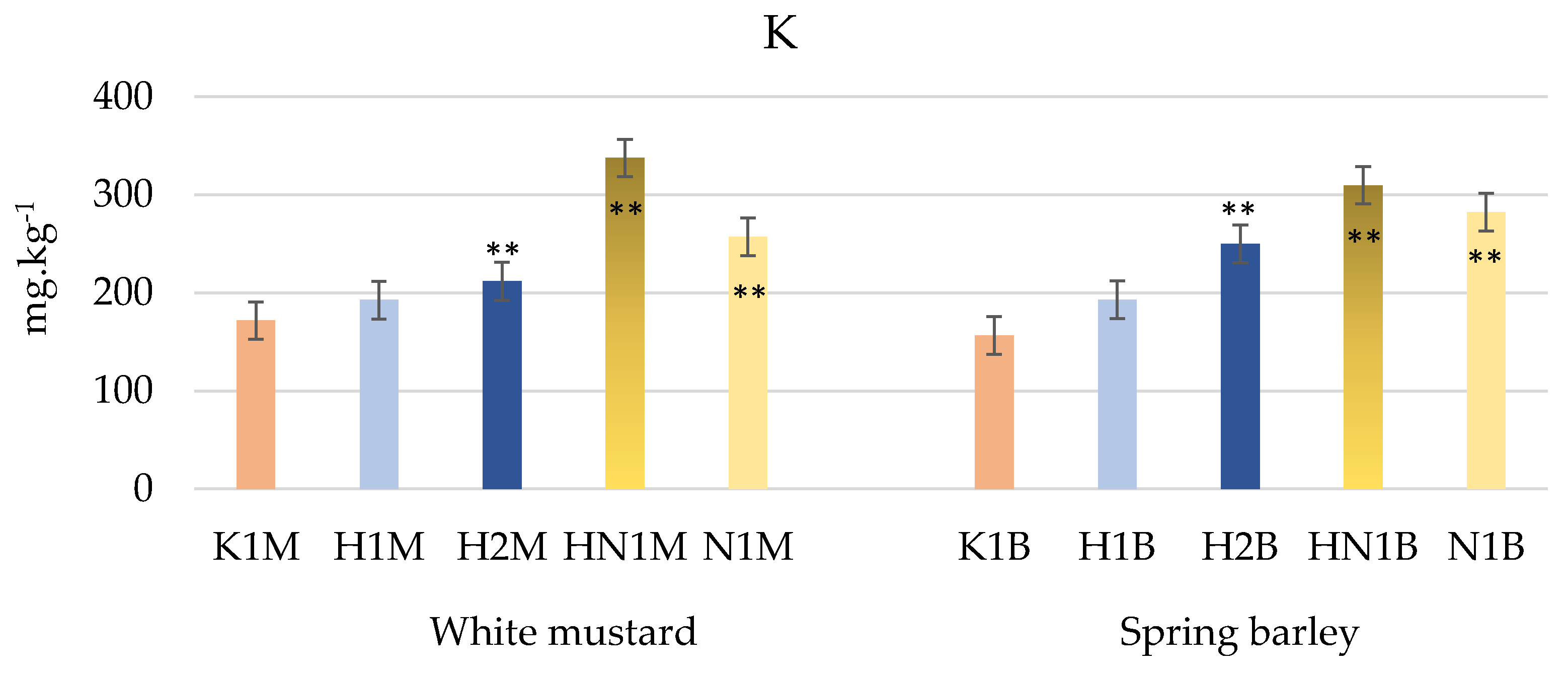





| Method | Reference | Accuracy (% rel.) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | determination of pH | ISO 10390 [49] | 4–5 |
| C | oxidimetric method | ISO 14235 [50] | 10–15 |
| N | modified Kjeldahl method | ISO 11261 [51] | 15–20 |
| P | Mehlich III solution | Mehlich (1984) [52] | 20 |
| K | Mehlich III solution | Mehlich (1984) [52] | 20 |
| Ca | Mehlich III solution | Mehlich (1984) [52] | 20 |
| Mg | Mehlich III solution | Mehlich (1984) [52] | 20 |
| CEC | barium chloride solution | ISO 13536 [53] | 20 |
| Properties | Hydrogel Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| pHH2O | 4.17 | |
| C | % | 40.1 |
| N | % | 1.26 |
| P | mg·kg−1 | 6683 |
| K | mg·kg−1 | 13.059 |
| Ca | mg·kg−1 | 6093 |
| Mg | mg·kg−1 | 806 |
| CEC | mmol·100 g−1 | 82.2 |
| Soil Properties | Haplic Cambisol Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| pHH2O | 6.80 | |
| C | % | 0.66 |
| N | % | 0.10 |
| P | mg·kg−1 | 113 |
| K | mg·kg−1 | 164 |
| Ca | mg·kg−1 | 2370 |
| Mg | mg·kg−1 | 204 |
| CEC | mmol·100 g−1 | 14.8 |
| Variant | White Mustard | Spring Barley |
|---|---|---|
| control | 3.19 | 1.52 |
| 1% whey hydrogel | 3.96 ** | 2.93 ** |
| 2% whey hydrogel | 5.80 ** | 7.34 ** |
| 1% whey hydrogel+ NPK | 8.35 ** | 10.3 ** |
| NPK | 6.74 ** | 8.36 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čechmánková, J.; Sedlařík, V.; Duřpeková, S.; Drbohlav, J.; Šalaková, A.; Vácha, R. Assessing the Effects of Whey Hydrogel on Nutrient Stability in Soil and Yield of Leucosinapis alba and Hordeum vulgare. Sustainability 2024, 16, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010045
Čechmánková J, Sedlařík V, Duřpeková S, Drbohlav J, Šalaková A, Vácha R. Assessing the Effects of Whey Hydrogel on Nutrient Stability in Soil and Yield of Leucosinapis alba and Hordeum vulgare. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleČechmánková, Jarmila, Vladimír Sedlařík, Silvie Duřpeková, Jan Drbohlav, Alexandra Šalaková, and Radim Vácha. 2024. "Assessing the Effects of Whey Hydrogel on Nutrient Stability in Soil and Yield of Leucosinapis alba and Hordeum vulgare" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010045
APA StyleČechmánková, J., Sedlařík, V., Duřpeková, S., Drbohlav, J., Šalaková, A., & Vácha, R. (2024). Assessing the Effects of Whey Hydrogel on Nutrient Stability in Soil and Yield of Leucosinapis alba and Hordeum vulgare. Sustainability, 16(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010045






