A Battery of Simple Bioassays for Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Konya, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Samples
2.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of the Wastewater Samples
2.3. Bioassays
2.3.1. Lepidium sativum
2.3.2. Vibrio fischeri Toxicity Test
2.3.3. Fish Bioassay (TDF) Toxicity Test
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Analysis Results
3.2. Toxicity Classification of the Samples
3.3. Results of the Lepidium sativum Toxicity Test
3.4. Results for the Vibrio fischeri Toxicity Test
3.5. Results for the Fish Bioassay (TDF) Toxicity Test
3.6. Evaluation of the Toxicity Tests by Toxic Unit Classes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mustafa, E.; Valente, M.J.; Vinggaard, A.M. Complex chemical mixtures: Approaches for assessing adverse human health effects. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2023, 34, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyad, M.T.; Kumar, M.; Malik, A. Mutagenicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by pesticide industry wastewater using bacterial and plant bioassays. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Välitalo, P.; Massei, R.; Heiskanen, I.; Behnisch, P.; Brack, W.; Tindall, A.J.; Du Pasquier, D.; Küster, E.; Mikola, A.; Schulze, T.; et al. Effect-based assessment of toxicity removal during wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2017, 126, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Cui, H.; Gao, J.; Cao, J.; Klobučar, G.; Li, M. Using a Battery of Bioassays to Assess the Toxicity of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents in Industrial Parks. Toxics 2023, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zuo, Y.-T.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.-X.; Chen, M.; Tang, F.; Lu, W.-Q.; Liu, A.-L. Investigating the performance of three modified activated sludge processes treating municipal wastewater in organic pollutants removal and toxicity reduction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.S.; Souiad, F.; Fernandes, A.; Baía, A.; Pacheco, M.J.; Ciríaco, L.; Bendaoud-Boulahlib, Y.; Lopes, A. Treatment of fruit processing wastewater by electrochemical and activated persulfate processes: Toxicological and energetic evaluation. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponza, D.T. Application of toxicity tests into discharges of the pulp-paper industry in Turkey. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2003, 54, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.F.R.; Kaur, N.; Hassan, F.E. Ornamental Date Palm and Sidr Trees: Fruit Elements Composition and Concerns Regarding Consumption. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 22, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.E.; Aydin, S.; Tongur, S.; Kara, G.; Kolb, M.; Bahadir, M. Application of simple and low-cost toxicity tests for ecotoxicological assessment of industrial wastewaters. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgórska, A.; Arendarczyk, A.; Grabińska-Sota, E. Toxicity assessment of hospital wastewater by the use of a biotest battery. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2011, 37, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Persoone, G.; Janssen, C.R. Freshwater Invertebrate Toxicity Tests. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponza, D.T.; Oztekin, R. Removals of PAHs and acute toxicity via sonication in a petrochemical industry wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusek, A.J.; Samec, D.; Salic, A. Modern Techniques for Flavonoid Extraction-To Optimize or Not to Optimize? Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS 5676; WPCR Sampling and Analysis Methods Communiqué Annex-1. Volume Annex-1, Turkish Standards Institute, 1998. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/Standard/Standard/Standard.aspx (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Dogan, N.; Yazıcı, Z.; Sisman, T.; Askin, H. Acute toxic effects of fenpyroximate acaricide on Guppy (Poecilia reticulata Peters, 1859). Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 29, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, H. Determination of Toxicological. Effects of Konya Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant and Organized Industrial Zone Wastewater; Konya Technical University: Konya, Türkiye, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cēbere, B.; Faltiņa, E.; Zelčāns, N.; Kalniņa, D. Toxicity Tests for Ensuring Succesful Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant Operation. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2010, 3, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Zuo, J.; Li, R.; Gan, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F. A combined evaluation of the characteristics and acute toxicity of antibiotic wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbe, M.C.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Vicari, T.; Cestari, M.M. Toxicity evaluation of water samples collected near a hospital waste landfill through bioassays of genotoxicity piscine micronucleus test and comet assay in fish Astyanax and ecotoxicity Vibrio fischeri and Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Etxebarria, J.; de las Fuentes, L. Evaluation of wastewater toxicity: Comparative study between Microtox® and activated sludge oxygen uptake inhibition. Water Res. 2002, 36, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Venkataraman, C.; Mukherji, S. A review on advantages of implementing luminescence inhibition test (Vibrio fischeri) for acute toxicity prediction of chemicals. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponza, D.T. Toxicity studies in a chemical dye production industry in Turkey. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponza, D.T. Incorporation of Toxicity Tests into the Turkish Industrial Discharge Monitoring Systems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues de Souza, I.; de Oliveira, J.B.V.; Sivek, T.W.; de Albuquerque Vita, N.; Canavez, A.D.P.M.; Schuck, D.C.; Cestari, M.M.; Lorencini, M.; Leme, D.M. Prediction of acute fish toxicity (AFT) and fish embryo toxicity (FET) tests by cytotoxicity assays using liver and embryo zebrafish cell lines (ZFL and ZEM2S). Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Chen, Z.; Qin, Z. Zebrafish larvae acute toxicity test: A promising alternative to the fish acute toxicity test. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 246, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wen, Q. Investigation on degradation behavior of dissolved effluent organic matter, organic micro-pollutants and bio-toxicity reduction from secondary effluent treated by ozonation. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaider, L.A.; Rodgers, K.M.; Rudel, R.A. Review of Organic Wastewater Compound Concentrations and Removal in Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7304–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Z.; Huo, Y.; Yang, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring of 943 organic micropollutants in wastewater from municipal wastewater treatment plants with secondary and advanced treatment processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Süheyla Tongur, S.Y. Toxicological evaluation of carbamazepine active pharmaceutical ingredient with Lepidium sativum, Daphnia magna and Vibrio fischeri toxicity test methods. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 201, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Blum, K.; Jernstedt, H.; Renman, G.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Haglund, P.; Andersson, P.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Screening and prioritization of micropollutants in wastewaters from on-site sewage treatment facilities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 328, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M.A.K.; Escher, B.I.; Krauss, M.; Teodorovic, I.; Brack, W. Effect-directed analysis (EDA) of Danube River water sample receiving untreated municipal wastewater from Novi Sad, Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G. Monitoring wastewater for assessing community health: Sewage Chemical-Information Mining (SCIM). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama Adam, W.A. In vitro Antimicrobial Assessment of Lepidium sativum L. Seeds Extracts. Asian J. Med. Sci. 2011, 3, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Arienzo, M.; Christen, E.W.; Quayle, W.C. Phytotoxicity testing of winery wastewater for constructed wetland treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, D.-P. 18—Ecotoxicological monitoring of wastewater. In Bioassays; Häder, D.-P., Erzinger, G.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccotelli, M.; Crippa, S.; Colombo, A. Bioindicators for toxicity assesment of effluents from a wastewater treatment plant. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Benites, S.M.; Rojas-Flores, S.; Otiniano, N.M.; Sabogal Vargas, A.M.; Alfaro, R.; Cabanillas-Chirinos, L.; Rojas-Villacorta, W.; Nazario-Naveda, R.; Delfín-Narciso, D. Use of Wastewater and Electrogenic Bacteria to Generate Eco-Friendly Electricity through Microbial Fuel Cells. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H. Antidepressants in wastewater treatment plants: Occurrence, transformation and acute toxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, J.; Masunaga, S.; Ma, F. Reduction in toxicity of wastewater from three wastewater treatment plants to alga (Scenedesmus obliquus) in northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



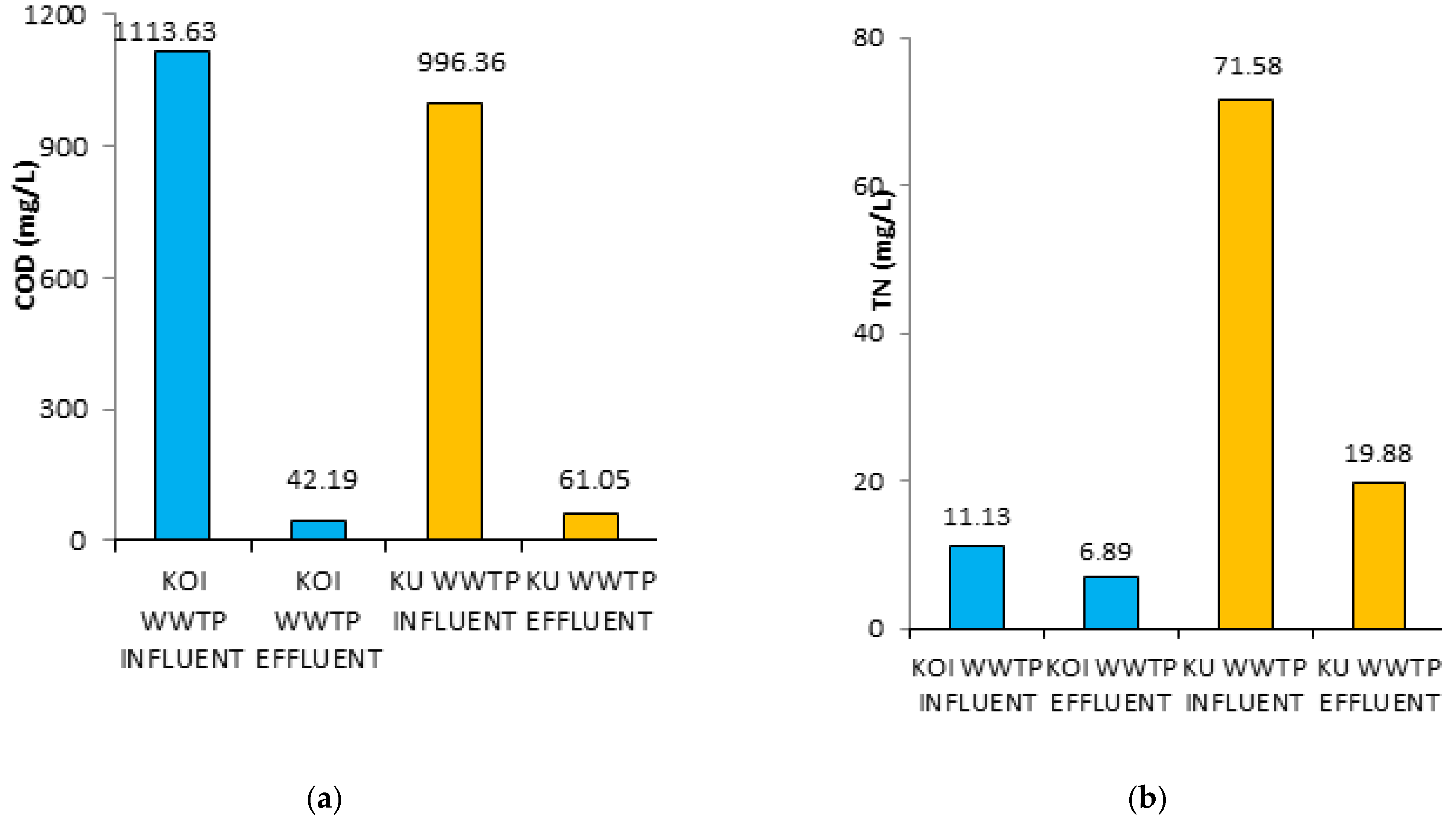
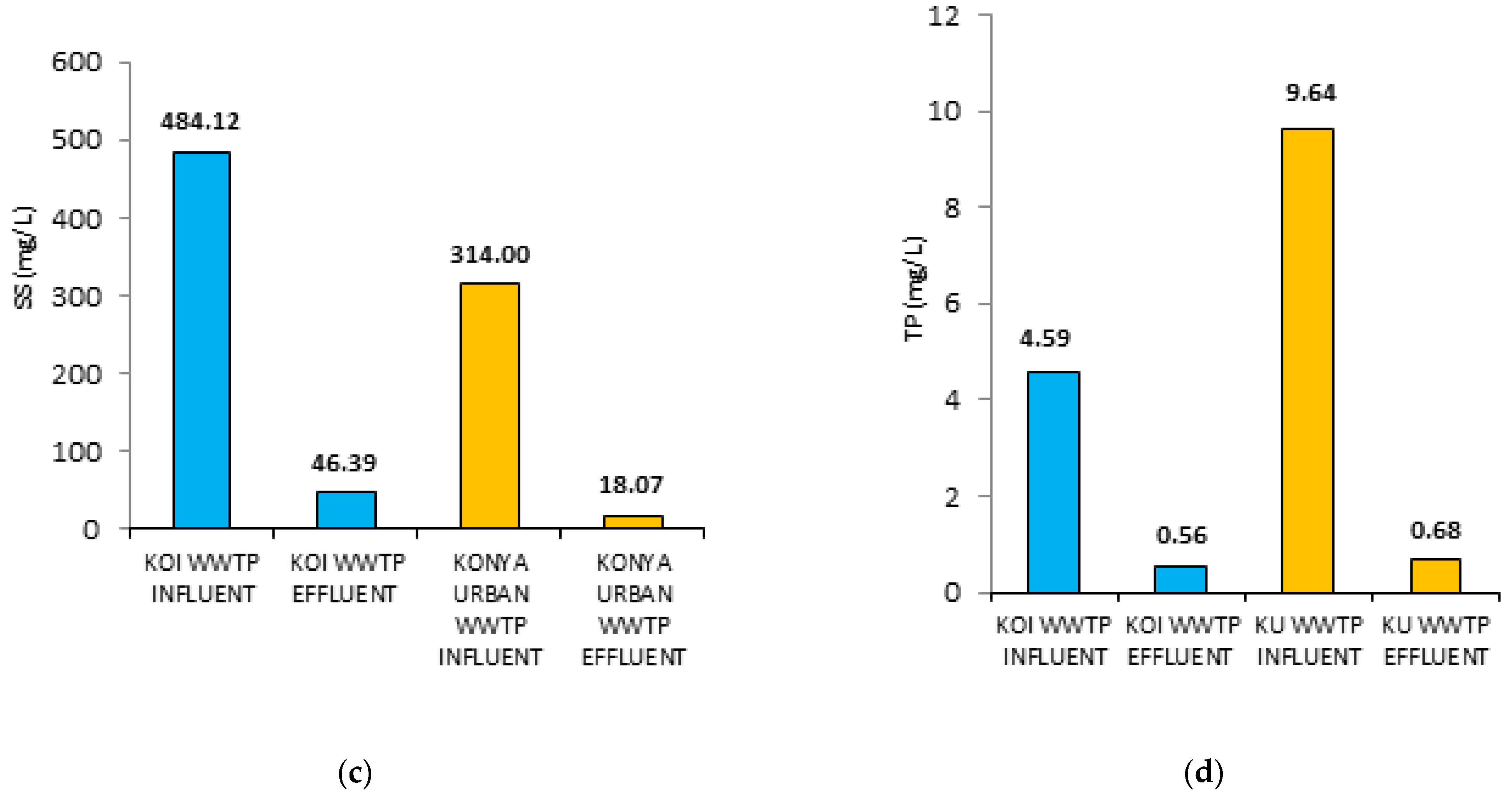
| Wastewater Type | pH | COD (mg/L) | SS (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KOI WWTP influent | 7.11 ± 0.3 | 1113.63 ± 100 | 484.12 ± 50 | 11.13 ± 2 | 4.59 ± 2 |
| KOI WWTP effluent | 7.58 ± 0.5 | 42.19 ± 10 | 46.39 ± 10 | 6.89 ± 0.5 | 0.56 ± 0.2 |
| KU WWTP influent | 7.47 ± 0.4 | 996.36 ± 100 | 314.00 ± 60 | 71.58 ± 5 | 9.64 ± 3 |
| KU WWTP effluent | 7.67 ± 0.5 | 61.05 ± 15 | 18.07 ± 7 | 19.88 ± 2 | 0.68 ± 0.3 |
| Parameter | Influent Values | Effluent Values | Unit | WPCR Table 19. (2-h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromium (Cr+6) | 0.48 ± 0.4 | 0.14 ± 0.4 | mg/L | 0.5 |
| Lead (Pb) | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 0.57 ± 0.1 | mg/L | 2 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.45 ± 0.1 | 0.34 ± 0.1 | mg/L | 0.1 |
| Iron (Fe) | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 2 ± 0.3 | mg/L | 10 |
| Fluoride (F−) | 13.4 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | mg/L | 15 |
| Copper (Cu) | 2.86 ± 0.2 | 0.42 ± 0.2 | mg/L | 3 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 1.99 ± 0.4 | 3.61 ± 0.4 | mg/L | 5 |
| Sulfate (SO4) | 1000 ± 300 | 1000 ± 300 | mg/L | 1500 |
| Color | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | (Pt-Co) | 280 |
| Acute Toxicity Classes | Toxic Unit | Toxicity Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | No toxic effect | Non-toxic |
| Class 2 | <1 | Slightly acute toxicity |
| Class 3 | 1–10 | Acute toxicity |
| Class 4 | 10–100 | Highly acute toxicity |
| Class 5 | >100 | Extremely acute toxicity |
| Acute Toxicity Classes | Inhibition Rates (%) | Toxicity Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 0–10% | Non-Toxic |
| Class 2 | 11–49% | Slightly Acute Toxicity |
| Class 3 | 50–100% | Acute Toxicity |
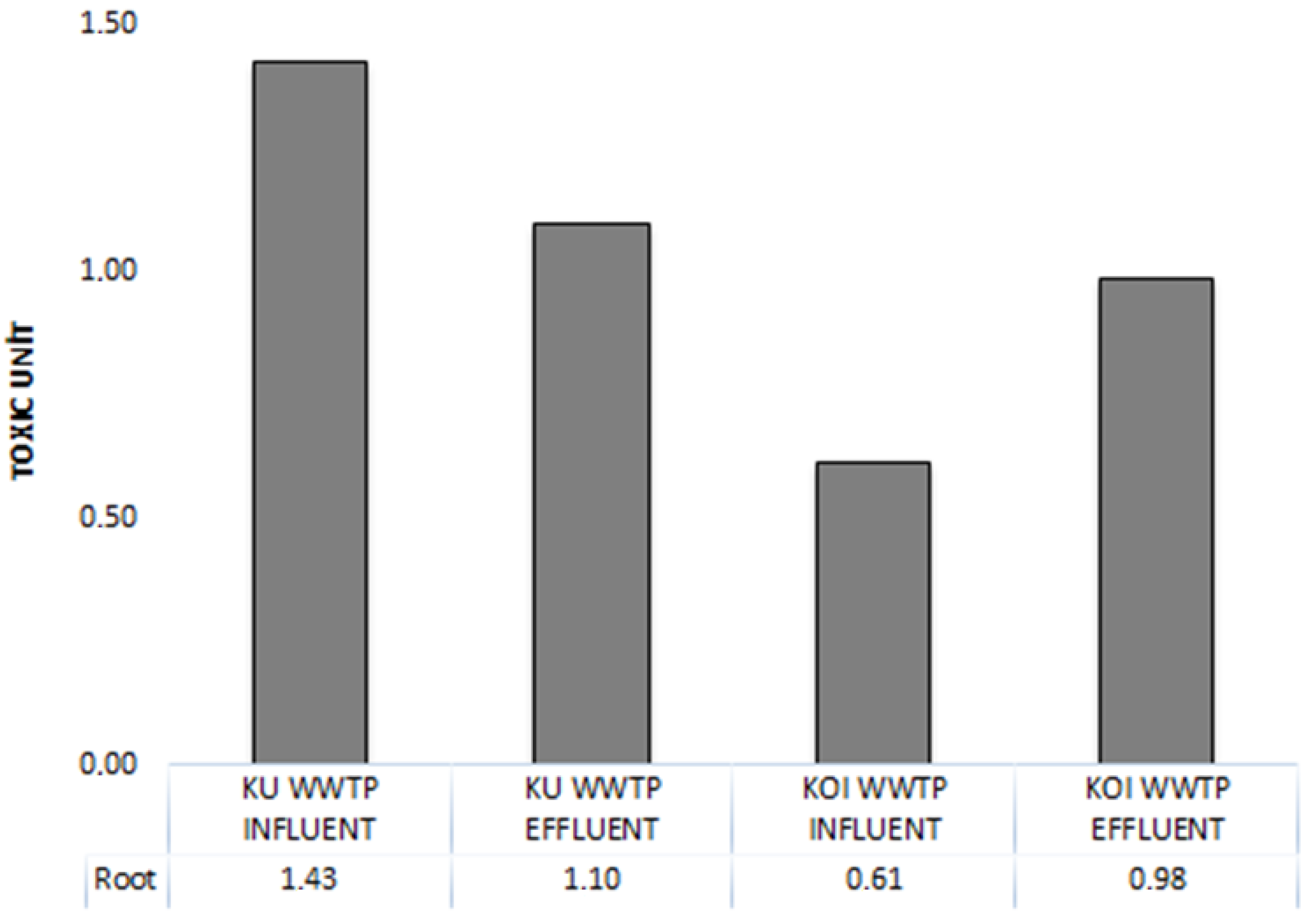
| Wastewater Types | EC50 (%) | Toxic Unit | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| KU WWTP influent | 70.17 ± 30 | 1.43 ± 0.3 | Toxic |
| KU WWTP effluent | 91.05 ± 50 | 1.10 ± 0.5 | Toxic |
| KOI WWTP influent | 163.47 ± 30 | 0.61 ± 0.3 | Slightly Toxic |
| KOI WWTP effluent | 101.55 ± 10 | 0.98 ± 0.1 | Slightly Toxic |
| Wastewater Type | Test Period | Inhibition Rate (%) | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| KU WWTP influent | For 30 min | 79–100% | Toxic |
| KU WWTP effluent | For 30 min | 6–9% | Non-toxic |
| KOI WWTP influent | For 30 min | 70–100% | Toxic |
| KOI WWTP effluent | For 30 min | 30–48% | Slightly Toxic |
| Wastewater Type | Analysis Result for Fish Bioassay (TDF) | WPCR (Discharge Standards of Mixed Industrial Wastewaters to the Receiving Environment, Small and Large Organized Industrial Zones and Other Industries of Undefined Sectors) | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composite Sample 2-h | |||
| Influent Wastewater | 13 | 10 | Toxic |
| Effluent Wastewater | 4 | Non-toxic |
| Wastewater Type | Lepidium sativum | Vibrio fischeri | Fish Bioassay |
|---|---|---|---|
| KU WWTP influent | Class 3 | Class 3 | * |
| KU WWTP effluent | Class 3 | Class 1 | * |
| KOI WWTP influent | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 3 |
| KOI WWTP effluent | Class 2 | Class 2 | Class 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tongur, S.; Atmaca, H. A Battery of Simple Bioassays for Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Konya, Turkey. Sustainability 2024, 16, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010316
Tongur S, Atmaca H. A Battery of Simple Bioassays for Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Konya, Turkey. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010316
Chicago/Turabian StyleTongur, Süheyla, and Hande Atmaca. 2024. "A Battery of Simple Bioassays for Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Konya, Turkey" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010316
APA StyleTongur, S., & Atmaca, H. (2024). A Battery of Simple Bioassays for Domestic and Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants in Konya, Turkey. Sustainability, 16(1), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010316







