Abstract
The remote sensing inversion of the water quality parameters of a complex river network in the absence of historical ground data is a difficult problem in the field of remote sensing. In this paper, a sub-regional inversion method for typical water quality parameters is presented for a complex river network using Gaofen-1 satellite data. Qidong’s rivers were selected as the survey region, and different band combination models and datasets on different river sub-regions were used to perform the remote sensing inversion, which realized the inversion of the permanganate index (CODMn), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), total phosphorus (TP), and total nitrogen (TN) in the rivers. The results show that all the coefficients of determination (R^2) of the inversion models are larger than 0.5, indicating an increase of about 0.4 when compared with the inversion method of the whole region, indicating good relevance. Water quality data and satellite data collected at different times were used for validation, which showed good results. On the basis of the water quality inversion, the key polluted areas were extracted in combination with on-site surveys to find the pollution source in order to verify the results of the inversion. The sub-region inversion method proposed in this paper can be used for the remote sensing inversion of the water quality parameters of complex river networks in the absence of historical ground data.
1. Introduction
As an important part of surface water monitoring, the quality monitoring of water in rivers can provide data and information for water environment management and can form the basis for evaluating the water quality of rivers [1,2]. Thus, it is of important practical significance to conduct studies on water quality monitoring. Complex river networks are an important part of rivers in plain areas. Water quality monitoring and pollution tracing of complex river networks have always been one of the most important aspects in water environment monitoring [3,4].
Traditional artificial monitoring methods are laborious and cannot reflect the overall situation of a region’s water environment. Remote sensing technology is advantageous in terms of its synchronous large-area monitoring, multi-temporal nature, comprehensiveness, comparability, and economic benefits, which can offset the shortcomings of the traditional monitoring methods [5,6,7,8].
The optical characteristics of river networks are complex and are not only affected by phytoplankton but also inanimate suspended matter and yellow materials [9]. For shallow waters, the influence of underwater materials on the water’s optical characteristics should also be taken into account [10]. Field detection, analysis, and measurement are required to obtain the physical and chemical parameters of a water body, which are tedious and difficult to keep synchronized with the satellite data’s time. Additionally, there is the possibility of large differences in the optical characteristics between different rivers.
There is some research on satellite data with different spatial resolutions: (1) Low spatial resolution satellite data such as Landsat and Modis are commonly used for the inversion of oceans, lakes, and wide rivers. For example, a remote sensing method was used to obtain the optical attenuation distribution characteristics of Lake Daye [11]. Based on Landsat 8 images, remote sensing inversion models for total suspended matter (TSM) and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in West Lake were compared, and the best ones were determined using exponential functions and green/red band ratios [12]. Hyperspectral data from EO-1 were used to monitor chlorophyll a (chl-a) and suspended sediment (ss) over Lake Taihu in East China [13]. Using Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM) data, water quality retrieval models were established in Guanting Reservoir and analyzed for eight common water quality variables, including algae content, turbidity, and concentrations of chemical oxygen demand, total nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, total phosphorus, and dissolved phosphorus [14]. In China, remote sensing technologies have been applied to monitor the Pearl River, Lake Taihu, the Yangtze River, Hangzhou Bay, and the Yellow River Estuary [15,16,17,18,19], and the water surface types in these study areas were uniform. (2) When remote sensing inversion is performed on a river network with a narrow width (less than 20 m), satellite data with a low spatial resolution cannot be used and only satellite data with a high spatial resolution of 10 m or less (Gaofen-1, Gaofen-2, Sentinel-2, etc.) can be used. When using high spatial resolution satellite data for the inversion of a river network, optical parameters (such as suspended particulate matter concentration, chlorophyll a, colored dissolved organic matter, total dissolved solids, etc.) and black and odorous water bodies are usually analyzed [20,21,22,23], and the chemical parameters of water quality (such as the permanganate index, ammonia nitrogen, total phosphorus, and total nitrogen) are rarely analyzed. One of the reasons is that the surface water quality monitoring data of complex river networks are seriously insufficient, and it is difficult to complete the remote sensing inversion of the water quality chemical indexes of complex river networks only through remote sensing data.
In fitting models for the remote sensing inversion of water quality, existing studies have mainly conducted the evaluation and classification based on the physical and chemical parameters of water bodies, i.e., from the perspective of water quality [24]. The commonly used model-building methods include empirical models, semi-empirical models, and biological optical models [25,26], and some papers use satellite data from multiple time periods for analysis [27]. Empirical and semi-empirical models are built via statistical analysis of sample data. They are easy to operate but tend to overfit. Machine learning and deep learning are usually used to obtain higher accuracy and adaptability. However, for a new research area, there may be a lack of sufficient ground samples to support machine learning and deep learning. There is little research on applying remote sensing technologies to analyze and monitor the chemical parameters of water quality for complex river networks in the absence of historical ground data. Therefore, the study of the inversion of Qidong’s complex river network in this paper is meaningful.
This paper takes Qidong’s rivers as the survey region and adopts the sub-region remote sensing inversion method, which creates multiple sub-regions according to the waterway orientation and applies different inversion models to carry out the inversion of the water quality parameters from Gaofen-1 satellite data for the major rivers in the area. The parameters include the permanganate index (CODMn), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), total phosphorus (TP), and total nitrogen (TN). Compared with other water pollution parameters such as dissolved oxygen, the concentrations of heavy metals, the degree of salinity, and conductivity, the data on the four parameters selected in this paper are easier to obtain in China with reference to the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (EQSSW) [28,29] and can better reflect the overall pollution level of the region. The validation data include water quality data from automatic water quality monitoring stations and satellite data from Qidong. Additionally, the obvious abnormalities in the inversion results were verified on site. Through field verification, it was found that the inversion method in this paper is effective at identifying pollution sources.
2. Survey Region and Data Acquisition
The survey region is located at 121°39′27″ east longitude and 31°48′29″ north latitude in Qidong city, Jiangsu Province, China. Qidong is a coastal city that is peninsula-shaped. The city has high-density, crisscrossing inland water systems. The region is part of a plain river network, and all the rivers are connected to each other. The water system is developed, and there are multiple rivers. Most of these rivers are between 15 m and 30 m wide (approximately 2–4 pixels in the Gaofen-1 satellite data) and are deep and turbid enough for the satellite sensor not to see the bottom. Most of these rivers are not located in urban areas and are free of buildings’ shadows. In recent years, the water quality in this region has become worse. The survey region is shown in Figure 1.
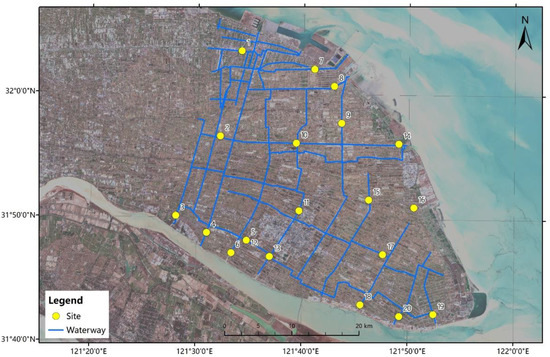
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the water quality monitoring scope in Qidong.
The remote sensing data are from the Gaofen-1 satellite. This satellite is equipped with panchromatic multispectral spectroradiometer (PMS) sensors and includes four multi-spectral channels of blue, green, red, and near-infrared, as well as one panchromatic channel [30]. The spatial resolution of its multi-spectral data is 8 m, with one scene covering 60 km × 60 km [31]. The Gaofen-1 satellite’s revisiting period is 4 days. However, it does not acquire data on every visit due to its limited storage capacity. All satellite data used in this paper for inversion were obtained from the Gaofen-1 satellite on 26 August 2021.
Meanwhile, ground observation data were collected at the same time as the Gaofen-1 data. In total, 20 locations are selected to cover the main rivers within the territory of Qidong (including Lianxing Port, Gaiyao River, Zhongyang River, Touxing Port, Tongqi Canal, Nanyin River, Sanhe Port, Daoan River, etc.). The samples were taken at 0.5 m underwater according to the technical specification requirements for the monitoring of surface water and wastewater within 2 h of the Gaofen-1 satellite data capture time. The assay parameters include CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN. The assay results of the water quality parameters from various sites are shown in Table 1 and were used for inversion. These water quality data are the result of a single measurement, and there may be a maximum random error of 5% in the measurement according to China’s water quality standards.

Table 1.
Ground observation data.
The validation data include water quality data from 12 automatic water quality monitoring stations in Qidong and satellite data of Qidong from the Gaofen-1 satellite on 17 June 2022.
3. Methods
The methodology in this paper mainly includes data pre-processing, modeling, and validation (see Figure 2). Firstly, the radiation correction and geometric rectification of the original PMS data are carried out to obtain multi-spectral reflectivity data. Then, the multi-spectral reflectivity data and water quality parameters were divided into three sub-regions according to the river connectivity, and the data for each sub-region were modeled separately. The spectral data corresponding to the ground sampling sites were extracted in combination with the laboratory numerical assay result to build the water quality parameter inversion models of CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN by means of an empirical statistical method so as to obtain the water quality parameter distribution map of each sub-region. Finally, water quality data and satellite data collected at different times and a comparison with the inversion of the whole region were used for validation.
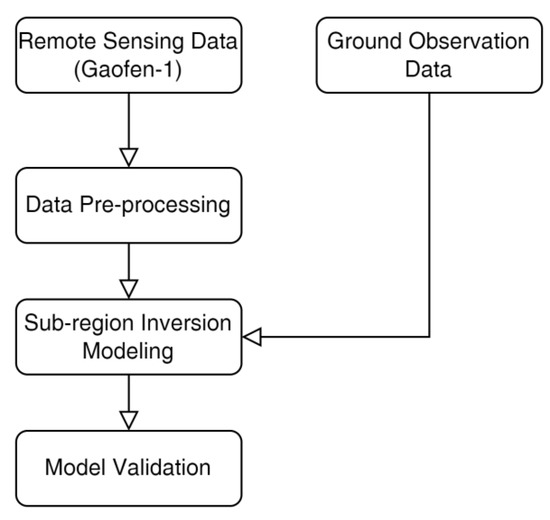
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the sub-region inversion method based on Gaofen-1 satellite data.
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
The data pre-processing of the satellite data includes radiation correction, geometric rectification, and panchromatic and multi-spectral image fusion.
Radiation correction includes radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction. Radiometric calibration is the process of converting the image digital number (DN) value to the atmosphere’s outer surface reflectivity L (also referred to as the radiance value). The calculation formula is L = gain ∗ DN + Bias, where gain and bias are the radiometric calibration parameters and are usually saved in the metadata file.
The atmospheric correction method adopted in the paper is based on the 6S atmospheric radiation transferring model [32], and the model inputs include geometric condition parameters such as the solar altitude, solar azimuth, satellite elevation, satellite observation angle, and image acquisition date (month and day), as well as the sensor spectral response function. These parameters are obtained from the metadata file. The model output is a raster file indicating the actual ground surface reflectivity.
Geometric rectification is used to correct the geometric distortions caused by systematic and non-systematic factors, including geometric coarse correction and geometric fine correction [33].
Geometric rectification is conducted in the Environment for Visualizing Images (ENVI) software (from Exelis Visual Information Solutions), where the raster images containing the rational polynomial coefficients (RPC) metadata information are input to perform the terrain correction for every pixel in an image through standard procedures and to output the images conforming to the requirements of the orthographic projection.
3.2. Building of the Sub-Region Water Quality Parameter Inversion Model
Qidong’s rivers are crisscrossed. Through a field investigation of the rivers in Qidong, we found that the rivers are mainly north–south oriented and are connected by a few east–west rivers. The different rivers in different sub-regions are polluted due to different reasons and show different optical characteristics. The relation between the water quality parameters (CODMn, NH3-N, TP, TN) and the spectral reflectivity is affected by the water environment. Before model building, it is necessary to divide different datasets according to the waterway orientation, assay values, and spectral values. As is shown in Figure 3, these rivers are divided into three classes. The sites in the figure indicate the water quality sampling site, and different colors indicate different sub-regions: west, middle, and east, corresponding to three datasets (see Figure 3), where dataset 1 (No. 1–6) represents the western sub-region, dataset 2 (No. 7–13) represents the middle sub-region, and dataset 3 (No. 14–20) represents the eastern sub-region.
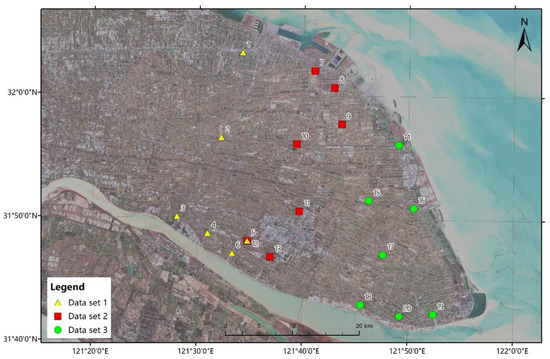
Figure 3.
Different datasets corresponding to the water quality sampling site.
Several studies have confirmed that multispectral data can improve the estimation of water’s inherent optical properties (IOP) [34,35,36,37]. For a specific small watershed over a certain period of time, due to the relatively fixed type of pollution source, there is a specific correlation between IOP and water quality parameters such as CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN. The literature shows that spectral bands, their differences, and their logarithms can be used for water quality inversion in a pixel-by-pixel manner. For each dataset, the single band or two bands are combined into different forms, including single band (1), two-band subtraction (2), two-band division (3), the ratio of two-band reflectivity difference to two-band reflectivity sum (4), and the ratio of the logarithm of one band to another band (5):
C = X,
C = X − Y,
C = X/Y,
C = (X − Y)/(X + Y),
C = ln(X)/Y,
X and Y are different bands and may be blue bands (B), green bands (G), red bands (R), or near infrared bands (NIR). C is the band combination.
We calculated the correlation between various band combinations and water quality parameters and selected the optimal band combination with the highest correlation for each dataset.
In this paper, the correlation between the band combination and the manual assay result is used to evaluate the results of the water quality parameter inversion. The optimal band combination is incorporated into different models, including a first-order equation, a second-order equation, an exponential model, and a logarithmic model, to build a regression statistics equation using the water quality parameters. Finally, the coefficients and average relative error are determined after comprehensive consideration to confirm the final models of each dataset.
The correlation between the band combination and water quality parameters is calculated for three datasets, and then the band combination with the optimal correlation is selected.
First, the most relevant band combination is selected for each water quality parameter in each dataset.
Then, they are fitted with different fitting types such as polynomial fitting (6), second order polynomial fitting (7), exponential fitting (8), or power fitting (9).
y = a·x + b,
y = a·x2 + b·x + c,
y = a·eb·x,
y = a·xb,
The correlation results include R^2, root mean square error (RMSE), relative root mean square error (RRMSE) [38], and mean relative error (MRE).
3.3. Validation of the Sub-Region Water Quality Parameter Inversion Model
The validation method involved performing the remote sensing inversion at different times using the model established in this paper and using the inversion results and water quality monitoring data to calculate the relative error (10) and the Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient (NSE) (11).
r = |I − M|/M,
r is the relative error, I is the inversion result, and M is the water quality monitoring data.
is the observed value, is the simulated value, is the value at time t, and is the total average of the observed values.
In addition, the inversion model of the whole region was built, and the results are compared with the results of the sub-region inversion in this paper.
For the inversion model of the whole region, all rivers in Qidong are taken as a whole dataset. By virtue of the optimal band combination and fitted equation described above, the inversion model for Qidong’s rivers was built for the whole dataset, and the corresponding parameters were used to invert the region’s water quality.
4. Results
4.1. Model Results for Different Datasets
The correlation of band combinations for each dataset is shown in Figure A1, Figure A2 and Figure A3, Appendix A and these show that rivers in different sub-regions have different optical characteristics. The fitted equations and correlation results of CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Results of the fitting models with different fitting types for the CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN.
The fitted equations with the highest R^2 and the lowest error for each dataset in Table 2 are selected as the optimal model. The results of the optimal model for all parameters of all datasets are shown in Table 3, which corresponds to the second-order polynomial fitting results in Table 2.

Table 3.
Results of the optimal model for datasets.
It can be seen that the optimal model for each sub-region is second-order polynomial fitting, which has the highest R^2, the lowest RMSE, RRMSE, and MRE, and the results obtained from the sub-region inversion all show R^2 values higher than 0.5 and RRMSE values lower than 40%, indicating good correlation. The results of polynomial fitting, exponential fitting, and power fitting are poor, which indicates that the water quality inversion of CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN in Qidong is suitable for second-order polynomial fitting.
Compared to the R^2 values of the fitted equation in datasets 2 and 3, the R^2 values of the fitted equation in dataset 1 are lower, which may be due to the different optical characteristics between the rivers in the corresponding sub-region.
4.2. Inversion Results for Qidong’s Rivers Based on an Optimal Inversion Model
The inversion results for Qidong’s rivers are shown in Figure 4. The overall water quality of all-region rivers in Qidong is relatively good. The inversion results show that the parameters CODMn, NH3-N, and TP show strong correlations and that the main pollution area for these parameters is in the middle of the southern part of Qidong City, including Touxing Port, Zhongyang River, etc. On the other hand, the correlation between TN and the other three parameters is poor, and the main pollution area of TN is in the northeast of Qidong City, where the water quality reaches Class VI (the standard requirement is Class III or lower, and the corresponding pollution level exceeds the standard) according to the EQSSW.
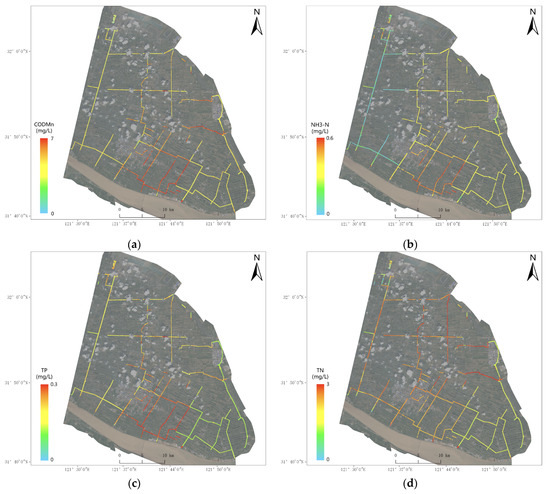
Figure 4.
Inversion results in the survey region: (a) CODMn; (b) NH3-N; (c) TP; (d) TN.
4.3. Model Validation
4.3.1. Validation of the Sub-Region Water Quality Parameter Inversion Model at Different Times
Water quality data from automatic water quality monitoring stations and satellite data of Qidong were selected to verify the effect of the optimization model.
The relative errors of the validation data are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Relative error of the validation data.
It can be seen from Figure A1 that most of the temporal data have good accuracy, while the inversion results of a few water quality sites are quite different from the water quality values. The NSE of CODMn and TN is not so good. There is still room for further optimization of the model.
4.3.2. Comparison with the Inversion Method for the Whole Region
The results of the optimal model of the inversion method for the whole region are shown in Table 5. The band combination with the best correlation with the water quality data changes as the regional range increases. Due to the different pollution and optical characteristics of each region of the river network, it is difficult to form a unified inversion model, and the results are poor, with R^2 values being between 0.1 and 0.6.

Table 5.
Results of the optimal model for the inversion method of the whole region.
Compared with the results of the inversion method for the whole region in Table 5, the results of the sub-region inversion method in this paper are better, with the R^2 values being increased by about 0.4.
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance of the Sub-Region Water Quality Parameter Inversion Model
The chemical parameters of water quality (CODMn, NH3-N, TP, TN) have no spectral characteristics, but for a fixed area in a fixed period, the source of sewage is relatively fixed, so it may show specific spectral characteristics. Therefore, the models established in the same area of Qidong show good accuracy at different times, with the exception of a few individual sites.
Compared with other papers [39,40,41,42,43], the RRMSE in this paper is a little high and the R^2 is a little low, except for the TN parameter. This is because the region selected in this paper lacks ground historical data, and it is not possible to use multi-period Gaofen-1 satellite data to achieve remote sensing inversion. Additionally, the rivers are relatively narrow and only suitable for high-spatial-resolution satellites (multispectral data from four bands). Compared to hyperspectral data with low spatial resolution, the retrieval accuracy will also decrease. This paper hopes to achieve a preliminary assessment of regional water quality in regions that also lack ground historical data.
5.2. Field Investigation of the Key Polluted Regions
From the inversion results of various parameters, the regions suffering relatively heavy pollution are selected as the key polluted regions. The field investigation method was applied to perform an adequate investigation into regions to find the surrounding ground object sources influencing water quality, which proves the accuracy of the inversion of water quality parameters from Gaofen-1 satellite data.
The pollution mainly appears in the middle and southern regions. The main pollution parameters are TP and TN. The TP of some rivers in the middle and southern regions exceeds the standard limit of 0.2 mg/L, according to the EQSSW [29], which indicates that the water quality in this region has deteriorated significantly.
According to our inversion results, the main parameters influencing water quality in Qidong are TP, TN, and CODMn. Thus, the regions showing high pollution parameters were selected (the red color of the river means a higher pollution level). As shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, the regions include the Daoan River, Touxing Port, Zhongyang River, Sanhe Port, etc.
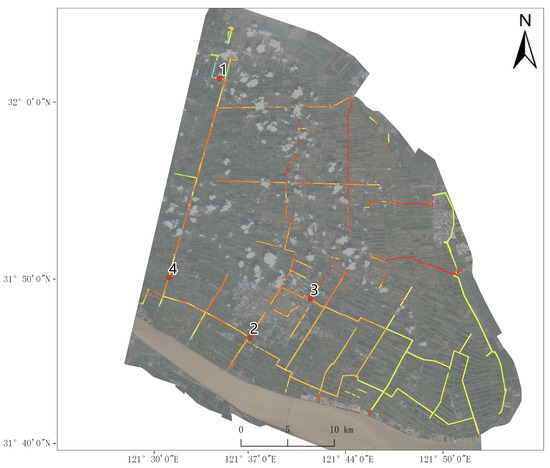
Figure 5.
Diagram of key polluted regions: (1) Daoan River; (2) Touxing Port; (3) Zhongyang River; (4) Sanhe Port.
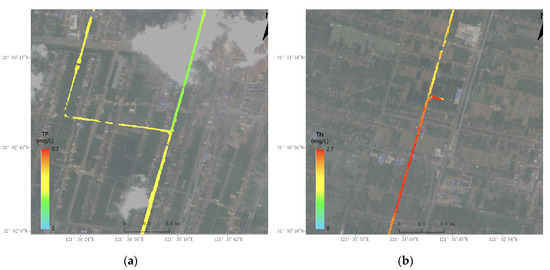
Figure 6.
Key polluted regions: (a) Daoan River; (b) Sanhe Port.
The field survey method was adopted to conduct an adequate investigation into the key regions and find the surrounding pollution sources. Figure 7 shows the main pollution sources found during the investigation.

Figure 7.
Result of the field verification: (a) Daoan River; (b) Zhongyang River; (c) and (d) Sanhe Port.
The inversion results show that the values of CODMn, NH3-N, and TN in the Daoan River are all relatively high and have some influence on the water quality in the downstream main streams. The field investigation shows that there are dwellings and drains near the river, causing the problem of sanitary sewage.
The inversion results reveal that Touxing Port is a region of high CODMn and TP. The field investigation found that the water in Xingtou Port is relatively turbid and that the water quality there is poor (results not shown).
The inversion results reveal that the Zhongyang River has CODMn with an obvious and abrupt change, where it is suspected that there is a pollution afflux. The field investigation found that there are construction sites, dwellings, farmland, pre-cast concrete plants, and some vegetable fields along the Zhongyang River, and there is possible pollution afflux here.
The satellite inversion results reveal that Sanhe Port has multiple locations suffering from abnormally high TN. The field investigation found that there are yards and sand/broken concrete pilings on the bankside of Sanhe Port, as well as ships. There is a PVC sewage drainage outlet from a food processing plant and yards near the river, which means that traces of lime water flow into the river. There are fish ponds, dwellings, poultry yards, and yellow sand yards near the riverbank, which cause heavy pollution to the water body.
By means of a field investigation into the polluted regions we found from the inversion result, this paper traces multiple pollution sources influencing the water quality and verifies the relation between the inversion of water quality parameters from the Gaofen-1 satellite data and the actual water quality, which proves the feasibility of the method.
Remote sensing water quality inversion has high requirements in terms of the ground monitoring water sampling time. Due to the large collection area in this inversion, there was a time interval of as much as 6 h between the water sampling time and the satellite data taking time, and some water samples were collected at times inconsistent with the satellite data measuring time, thus influencing the analytical precision. Moreover, the methods of artificial inspection and taking photos were mainly used in the field verification, and only a qualitative analysis can be performed between these findings and the spectrum result of the satellite remote sensing. No quantitative calculation can be performed to identify correlations.
6. Conclusions
This paper establishes a sub-region remote sensing water quality spectrum inversion method for a flat river network that can be used for the remotely sensed water quality inversion of complex river networks in the absence of historical ground data. In this study, the sub-region inversion models of the river network for four indexes, including CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN, were built based on Gaofen-1 satellite data. The inversion of the water quality parameters from Gaofen-1 satellite data on Qidong’s rivers was realized with a RRMSE value lower than 40%, and all the R^2 values were higher than 0.5, exhibiting an increase of about 0.4 compared with the inversion method involving the whole region, which indicates a good inversion result correlation.
The experimental results implied that the sub-region inversion model built in this paper can be applied to other complex river networks in China. In the future, we plan to investigate other water quality inversion parameters, such as chlorophyll a, dissolved oxygen, etc. Additionally, we plan to use devices such as ground object spectrometers and multi-spectral UAVs to enhance on-site ground spectrum verification.
Author Contributions
X.Z. and Y.W. conceived of and designed the experiments; X.Z. analyzed the data; X.Z. and X.L. prepared the draft of the manuscript; S.Z. and F.Y. guided and supervised the improvement of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61627804).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank the people who investigated the rivers in Qidong by collecting water samples and checking pollution sources, including H. Ben, Yongxiao Liu, and Jian Li. We also thank the anonymous reviewers and assistant editors, for their constructive comments that helped improve the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
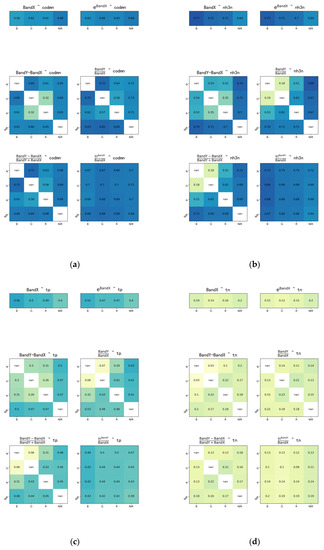
Figure A1.
The correlation of band combinations for dataset 1: (a) CODMn; (b) NH3-N; (c) TP; (d) TN.
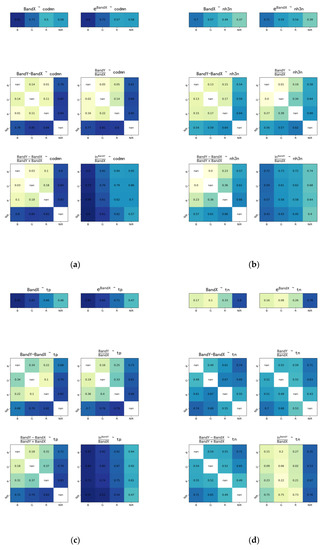
Figure A2.
The correlation of band combinations for dataset 2: (a) CODMn; (b) NH3-N; (c) TP; (d) TN.
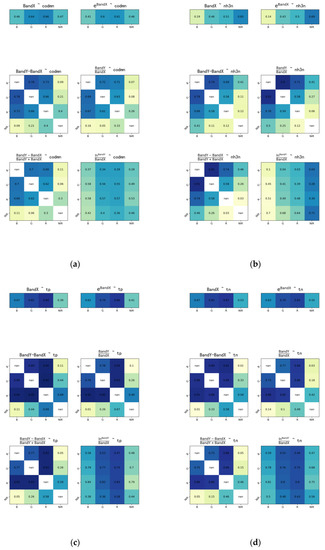
Figure A3.
The correlation of band combinations for dataset 3: (a) CODMn; (b) NH3-N; (c) TP; (d) TN.
References
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A.; Sofoniou, M.; Kouimtzis, T. Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4119–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate Statistical Techniques of the Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Water Quality of Gomti River (India)—A Case Study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Ni, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Assessment of Water Quality Improvement Schemes for a Complex River Network: A Case Study of Wenling. Clean-Soil Air Water 2018, 47, 1800008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.S. Using multivariate statistical methods for the assessment of the surface water quality for a river: A case study. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 588–597. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Ahn, M.H. Introduction of the in-orbit test and its performance for the first meteorological imager of the Communication, Ocean, and Meteorological Satellite. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xie, H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Quantitative monitoring of inland water using remote sensing of the upper reaches of the Huangpu River, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2471–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.K.; Kellndorfer, J.; Lehner, B.; Tobler, M. Remote sensing of floodplain geomorphology as a surrogate for biodiversity in a tropical river system (Madre de Dios, Peru). Geomorphology 2007, 89, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, P.K.; Pandey, A.C.; Gautam, S.K. Integrated Assessment of Groundwater Influenced by a Confluence River System: Concurrence with Remote Sensing and Geochemical Modelling. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4291–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wu, X.; Nie, H.; Xiao, C.; Ge, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, L. Optical attenuation characteristics of Lake Daye, Hubei Province based on remote sensing inversion of Landsat 8 OLI. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 791–803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, L.; Sun, N.; Chen, J.; Pang, S. Landsat 8-observed water quality and its coupled environmental factors for urban scenery lakes: A case study of West Lake. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yan, F.; Yi, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Y. Water quality monitoring using hyperspectral remote sensing data in Taihu Lake China. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2005. IGARSS ’05, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–29 July 2005; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, S. Water quality monitoring in a slightly-polluted inland water body through remote sensing—Case study of the Guanting Reservoir in Beijing, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Doerffer, R. An inverse technique for remote detection of suspended matter, phytoplankton and yellow substance from CZCS measurements. Adv. Space Res. 1987, 7, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L. Influence of different linear polarized light on the measurement of water absorption coefficient: A case study in Qujiang Lake, China. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wu, G.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Wang, Y. A MODIS-Based Retrieval Model of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration for the Two Largest Freshwater Lakes in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Bing, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Study on Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Based on Landsat OLI Imagery in the Haihe River, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wen, Z.; Jacinthe, P.-A.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. Remote estimates of CDOM using Sentinel-2 remote sensing data in reservoirs with different trophic states across China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ou, M.; Jia, S.; Li, Y. Remote Sensing Retrieval and Evaluation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in East Dongting Lake, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 668, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, G.; Ferrati, R.; Marinelli, C.; Dukatz, F. Artificial neural networks and remote sensing in the analysis of the highly variable Pampean shallow lakes. Math. Biosci. Eng. Mbe 2017, 5, 691–711. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.J.; Li, S.M.; Li, H.; Sun, D.; Zhou, L. Spectral Characteristics Analysis and Remote Sensing Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Han Shiqiao Wetland. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2010, 30, 757–761. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Retrieval of Inherent Optical Properties for Turbid Inland Waters from Remote-Sensing Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3761–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valjarević, A.; Popovici, C.; Štilić, A.; Radojković, M. Cloudiness and water from cloud seeding in connection with plants distribution in the Republic of Moldova. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.; Li, X. Urban growth management in the Pearl River delta: An integrated remote sensing and GIS approach. ITC J. 1996, 1, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Seasonal–spatial variation and remote sensing of phytoplankton absorption in Lake Taihu, a large eutrophic and shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hua, H.L.; Zhou, C. Study on lake surface area change in the mid-lower reaches of the Yangtze River based on the remote sensing technique. J. East China Norm. Univ. 2008, 23, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, D.; Zeng, A.; Zhao, X. Research on the Change of Coastline on the South Coast of Hangzhou Bay Based on Multi-temporal Remote Sensing Images. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 022024–022030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q. Dynamic Monitoring of Coastline in the Yellow River Delta by Remote Sensing. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2004, 6, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, N.; Ni, Y.; Yi, J.; Wilson, J.P.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, C.; et al. China’s improving inland surface water quality since 2003. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaau3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GHZB-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Li, Y.; Shu, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. Atmospheric Correction and Image Quality Assessment of WFV Camera in GaoFen-1 Satellite. Acta Opt. Sin. 2020, 40, 2001004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Q. Three-dimensional information extraction from GaoFen-1 satellite images for landslide monitoring. Geomorphology 2018, 309, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M. Second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum, 6s: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L. Processing Camera-Captured Document Images: Geometric Rectification, Mosaicing, and Layout Structure Recognition; University of Maryland at College Park: College Park, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammenberg, P.; Flink, P.; Lindell, T.; Pierson, D.; Strombeck, N. Bio-optical modelling combined with remote sensing to assess water quality. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1621–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Cherukuru, N.; Lavender, S.J. Apparent and inherent optical properties of turbid estuarine waters: Measurements, empirical quantification relationships, and modeling. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, R.; Bechini, L. A preliminary evaluation of the simulation model CropSyst for alfalfa. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Tedesco, L.; Hall, B.; Li, L. Hyperspectral remote sensing of total phosphorus (TP) in three central Indiana water supply reservoirs. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 1481–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Lou, L.; Chen, Y. Empirical estimation of total phosphorus concentration in the mainstream of the Qiantang River in China using Landsat TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparslan, E.; Coskun, H.G.; Alganci, U. Water quality determination of Küçükçekmece Lake, Turkey by using multispectral satellite data. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Tang, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhan, H.; Larson, M.; Jönsson, L. Remotely sensed assessment of water quality levels in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whistler, J. A phenological approach to land cover characterization using Landsat MSS data for analysis of nonpoint source pollution. KARS Rep. 1996, 96, 1–59. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).