Habitat Modification Alters Food Web Interactions with Focus on Biological Control of Aphids in Apple Orchards
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Unconnected Patches
2.1.1. Study Site
2.1.2. Population Dynamic
2.2. Connected Patches: Intercropping Experiment
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Food Web
2.3.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Unconnected Patches
3.1.1. Population Dynamic
3.1.2. Species Interactions
3.2. Connected Patches: Intercropping Experiment
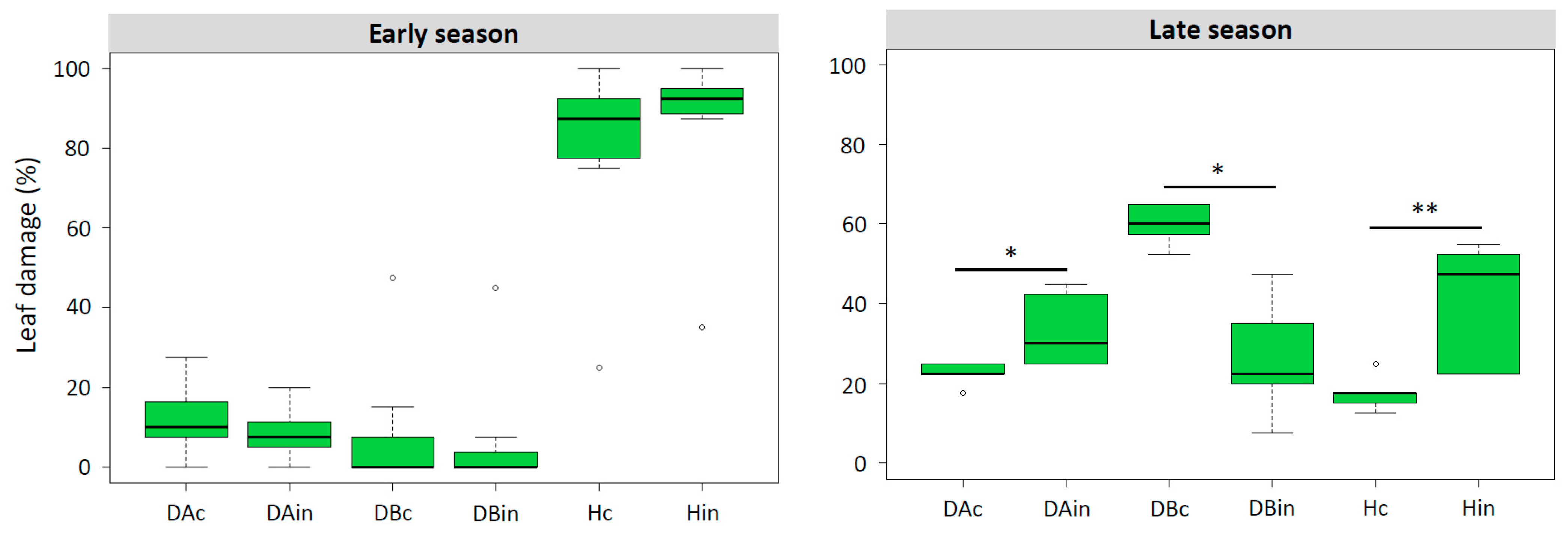
3.2.1. Population Dynamic
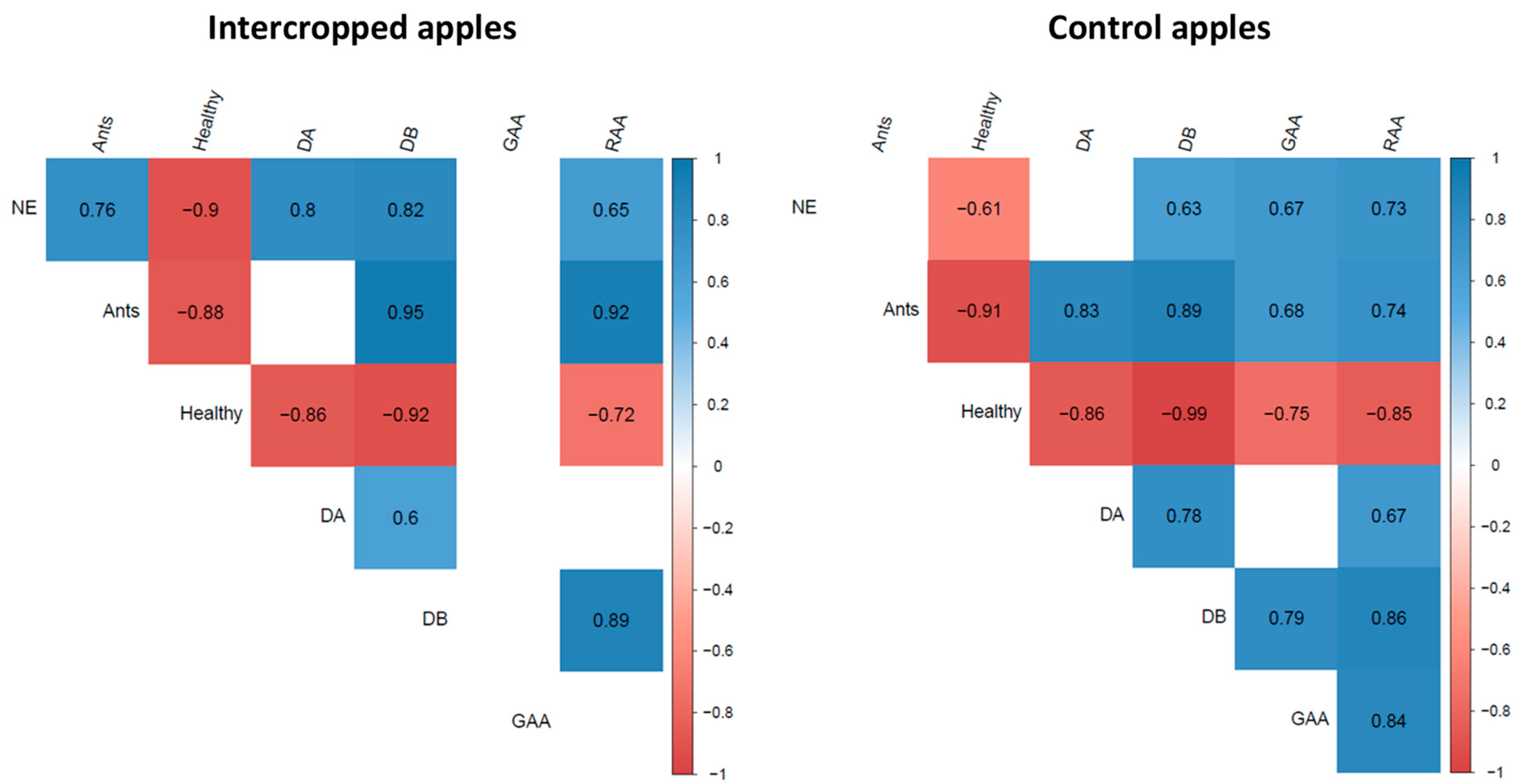
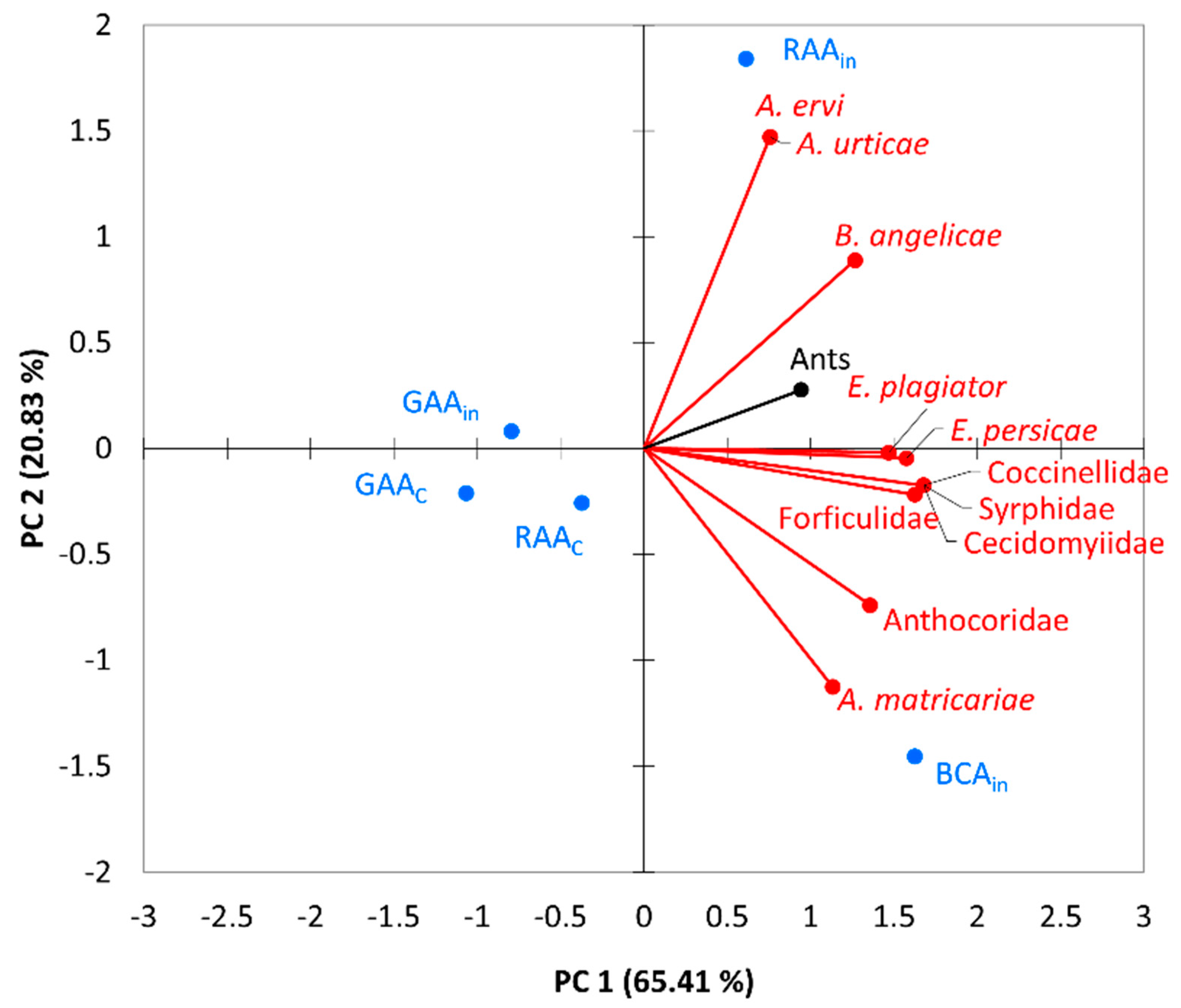
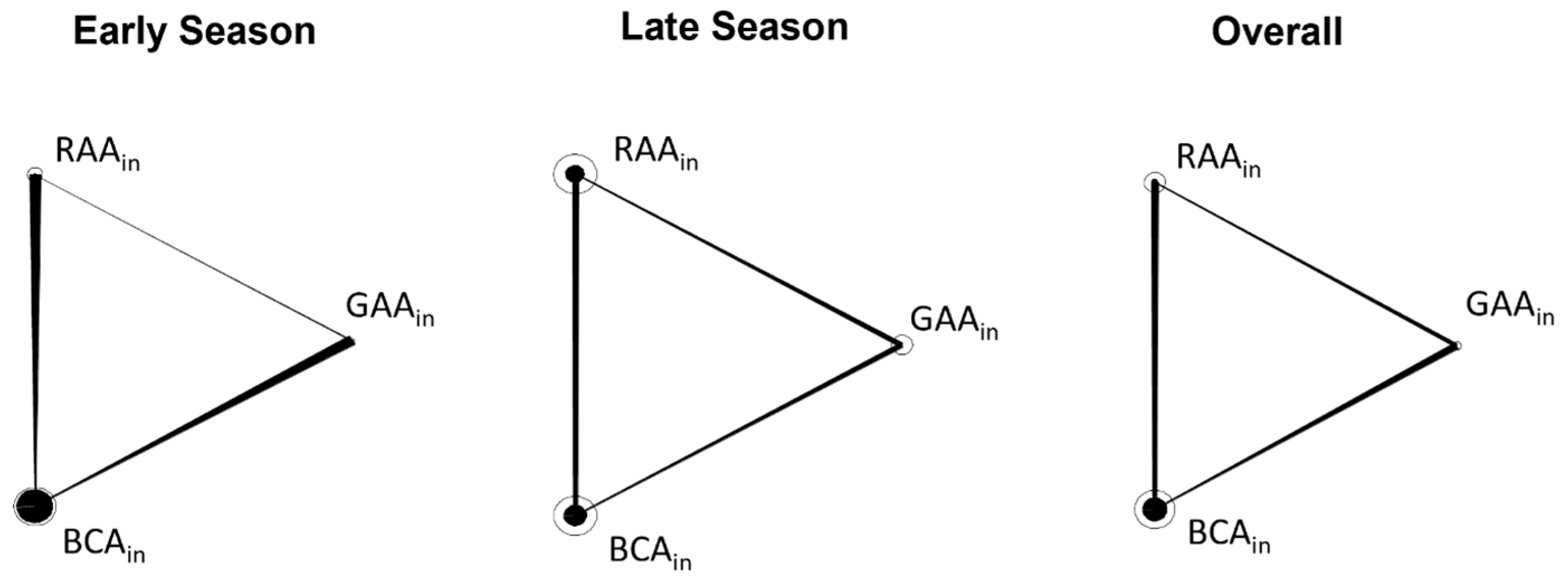
3.2.2. Species Interactions
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, C.B.; Godfray, H.C.J. Apparent Competition between Two Aphid Species. J. Anim. Ecol. 1997, 66, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.J.; Lewis, O.T.; Godfray, H.C.J. Experimental Evidence for Apparent Competition in a Tropical Forest Food Web. Nature 2004, 428, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.M.; Woodward, G.; Emmerson, M.C.; Solé, R.V. Press Perturbations and Indirect Effects in Real Food Webs. Ecology 2009, 90, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhmedi, A.; Haubruge, E.; D’Hoedt, S.; Francis, F. Quantitative Food Webs of Herbivore and Related Beneficial Community in Non-Crop and Crop Habitats. Biol. Control 2011, 58, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, C.M.; Peralta, G.; Rand, T.A.; Didham, R.K.; Varsani, A.; Tylianakis, J.M. Apparent Competition Drives Community-Wide Parasitism Rates and Changes in Host Abundance across Ecosystem Boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastolla, U.; Fortuna, M.A.; Pascual-García, A.; Ferrera, A.; Luque, B.; Bascompte, J. The Architecture of Mutualistic Networks Minimizes Competition and Increases Biodiversity. Nature 2009, 458, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, K. The Ecological Effects of the Ant–Hemipteran Mutualism: A Meta-Analysis. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2012, 13, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, N.M.; Parker, B.J. Mechanisms of Symbiont-Conferred Protection against Natural Enemies: An Ecological and Evolutionary Framework. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 4, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, C.; Cross, J.V.; Markó, V. Can Artificial Nectaries Outcompete Aphids in Ant-Aphid Mutualism? Applying Artificial Sugar Sources for Ants to Support Better Biological Control of Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea Passerini in Apple Orchards. Crop Prot. 2015, 77, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, B.; Dixon, A.F.G. Ecology and Evolution of Aphid-Ant Interactions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2005, 36, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Jones, A.; Pope, T.W.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Poppy, G.M. The Effect of Ant Attendance on the Success of Rosy Apple Aphid Populations, Natural Enemy Abundance and Apple Damage in Orchards. Agric. Forest Entomol. 2008, 10, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.B.; Adriaanse, I.C.T.; Belshaw, R.; Godfray, H.C.J. The Structure of an Aphid-Parasitoid Community. J. Anim. Ecol. 1999, 68, 346–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, A.S.; Godfray, H.C.J. The Structure of a Leafminer-Parasitoid Community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, O.T.; Memmott, J.; Lasalle, J.; Lyal, C.H.C.; Whitefoord, C.; Godfray, H.C.J. Structure of a Diverse Tropical Forest Insect–Parasitoid Community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2002, 71, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, T.; Murakami, M. Quantitative Food Webs of Lepidopteran Leafminers and Their Parasitoids in a Japanese Deciduous Forest. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.D.; Lawton, J.H. The Ecological Consequences of Shared Natural Enemies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1994, 25, 495–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.D.; Barfield, M. Impacts of Temporal Variation on Apparent Competition and Coexistence in Open Ecosystems. Oikos 2003, 101, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailleux, A.; Mohl, E.K.; Teixeira Alves, M.; Messelink, G.J.; Desneux, N. Natural Enemy-Mediated Indirect Interactions among Prey Species: Potential for Enhancing Biocontrol Services in Agroecosystems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisser, E.L.; Bolnick, D.I.; Benard, M.F. Scared to Death? The Effects of Intimidation and Consumption in Predator–Prey Interactions. Ecology 2005, 86, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.E.; Urban, M.C.; Tewksbury, J.; Gilchrist, G.W.; Holt, R.D. A Framework for Community Interactions under Climate Change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Gray, V.; Díaz-Castelazo, C.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Guimarães, P.R.; Nathaniel Holland, J. Abiotic Factors Shape Temporal Variation in the Structure of an Ant–Plant Network. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2012, 6, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.R. The Evolutionary Consequences of Indirect Effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñarro, M.; Hemptinne, J.-L.; Dapena, E. Colonization of Apple Orchards by Predators of Dysaphis plantaginea: Sequential Arrival, Response to Prey Abundance and Consequences for Biological Control. Biocontrol 2005, 50, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, S.; Entling, M.H. Effects of the Landscape Context on Aphid-Ant-Predator Interactions on Cherry Trees. Biol. Control 2011, 57, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, H.; Sauphanor, B.; Capowiez, Y. Effect of Management Strategies on Arthropod Communities in the Colonies of Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis Plantaginea Passerini (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in South-Eastern France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhmedi, A.; Raymaekers, S.; Tomanović, Ž.; Bylemans, D.; Beliën, T. Food Web Structure of Aphids and Their Parasitoids in Belgian Fruit Agroecosystems: Food Webs of Aphids and Parasitoids. Entomol. Sci. 2018, 21, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retallack, M.; Thomson, L.; Keller, M. Native Insectary Plants Support Populations of Predatory Arthropods for Australian Vineyards. BIO Web. Conf. 2019, 15, 01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhmedi, A.; Haubruge, E.; Francis, F. Effect of Stinging Nettle Habitats on Aphidophagous Predators and Parasitoids in Wheat and Green Pea Fields with Special Attention to the Invader Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Entomol. Sci. 2009, 12, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolin, P.; Bresch, C.; Poncet, C.; Desneux, N. Functional Characteristics of Secondary Plants for Increased Pest Management. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2012, 58, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bribosia, E.; Bylemans, D.; Migon, M.; Impe, G.V. In-Field Production of Parasitoids of Dysaphis plantaginea by Using the Rowan Aphid Dysaphis sorbi as Substitute Host. Biocontrol 2005, 50, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.V.; Cubison, S.; Harris, A.; Harrington, R. Autumn Control of Rosy Apple Aphid, Dysaphis plantaginea (Passerini), with Aphicides. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhmedi, A.; Bylemans, D.; Bangels, E.; Beliën, T. Cultivar-Mediated Effects on Apple—Dysaphis plantaginea Interaction. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blommers, L.H.M.; Helsen, H.H.M.; Vaal, F.W.N.M. Life History Data of the Rosy Apple Aphid Dysaphis plantaginea (Pass.) (Homopt., Aphididae) on Plantain and as Migrant to Apple. J. Pest Sci. 2004, 77, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qubbaj, T.; Reineke, A.; Zebitz, C.P.W. Molecular Interactions between Rosy Apple Aphids, Dysaphis plantaginea, and Resistant and Susceptible Cultivars of Its Primary Host Malus domestica. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2005, 115, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Enkegaard, A.; Osborne, L.S.; Ramakers, P.M.J.; Messelink, G.J.; Pijnakker, J.; Murphy, G. The Banker Plant Method in Biological Control. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Landis, D.A.; You, M. Habitat Management to Suppress Pest Populations: Progress and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavallieratos, N.G.; Tomanović, Ž.; Petrović, A.; Janković, M.; Starý, P.; Yovkova, M.; Athanassiou, C.G. Review and Key for the Identification of Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) of Aphids Infesting Herbaceous and Shrubby Ornamental Plants in Southeastern Europe. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2013, 106, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavallieratos, N.G.; Tomanović, Ž.; Starý, P.; Žikić, V.; Petrović-Obradović, O. Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) Attacking Aphids Feeding on Solanaceae and Cucurbitaceae Crops in Southeastern Europe: Aphidiine-Aphid-Plant Associations and Key. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2010, 103, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshani, E.; Kazemzadeh, S.; Starý, P.; Barahoei, H.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Ćetković, A.; Popović, A.; Bodlah, l.; Tomanović, Ž. Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) of Northeastern Iran: Aphidiine-Aphid-Plant Associations, Key and Description of a New Species. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanović, Ž.; Starý, P.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Gagić, V.; Plećas, M.; Janković, M.; Rakhshani, E.; Ćetković, A.; Petrović, A. Aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) in wetland habitats in western Palaearctic: Key and associated aphid parasitoid guilds. Ann. Société Entomol. Fr. 2012, 48, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Research, Inc. Mathematica, Version 5.0; Wolfram Research, Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Development Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zabel, J.; Tscharntke, T. Does Fragmentation of Urtica Habitats Affect Phytophagous and Predatory Insects Differentially? Oecologia 1998, 116, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branson, D.H. Relationships between Plant Diversity and Grasshopper Diversity and Abundance in the Little Missouri National Grassland. Psyche J. Entomol. 2011, 2011, 748635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M. The Dynamics of Colonizing Arthropod Communities at the Interface of Abandoned, Organic and Commercial Apple Orchards and Adjacent Woodland Habitats. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1986, 16, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, L.J.; Hoffmann, A.A. Spatial Scale of Benefits from Adjacent Woody Vegetation on Natural Enemies within Vineyards. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, A.; Rosenheim, J.A. Impact of a Natural Enemy Overwintering Refuge and Its Interaction with the Surrounding Landscape. Ecol. Entomol. 1996, 21, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, D.; Malchev, S. Preliminary Assessment of Selected Sweet Cherry Hybrids Regarding Their Resistance to Black Cherry Aphid (Myzus cerasi Fabr.) in Bulgaria. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 12, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackauer, M.; Völkl, W. Regulation of Aphid Populations by Aphidiid Wasps: Does Parasitoid Foraging Behaviour or Hyperparasitism Limit Impact? Oecologia 1993, 94, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimpel, G.E.; Rosenheim, J.A.; Mangel, M. Predation on Adult Aphytis Parasitoids in the Field. Oecologia 1997, 110, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colfer, R.G.; Rosenheim, J.A. Predation on Immature Parasitoids and Its Impact on Aphid Suppression. Oecologia 2001, 126, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, W.E.; Ives, A.R. Generalist Predators Disrupt Biological Control by a Specialist Parasitoid. Ecology 2001, 82, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailleux, A.-C.; Deneubourg, J.-L.; Detrain, C. Regulation of Ants’ Foraging to Resource Productivity. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devigne, C.; Detrain, C. Foraging Responses of the Aphid Tending Ant Lasius niger to Spatio-Temporal Changes in Aphid Colonies Cinara Cedri. Acta Zool. Sin. 2005, 51, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, J.P.; Andow, D.A. Behavioral Mechanisms Underlying Ants’ Density-Dependent Deterrence of Aphid-Eating Predators. Oikos 2007, 116, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.E.; Polaszek, A.; Evans, D.M. A Dearth of Data: Fitting Parasitoids into Ecological Networks. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.W.; England, S. Indirect Interactions in Biological Control of Insects: Pests and Natural Enemies in Alfalfa. Ecol. Appl. 1996, 6, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

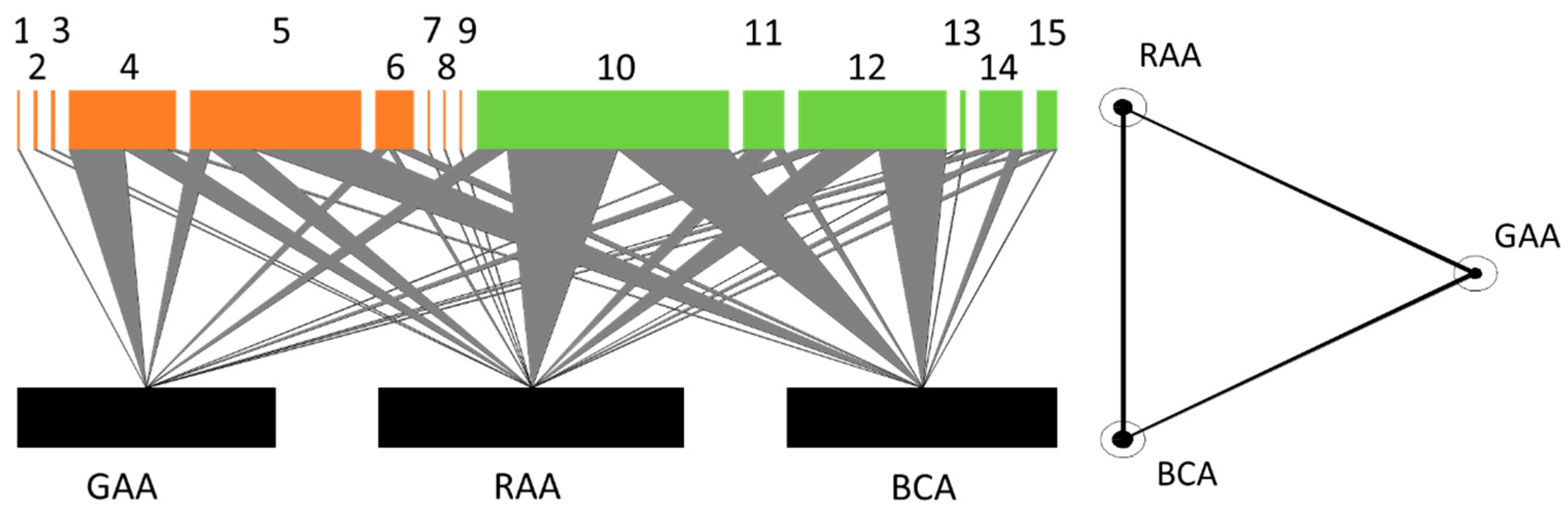
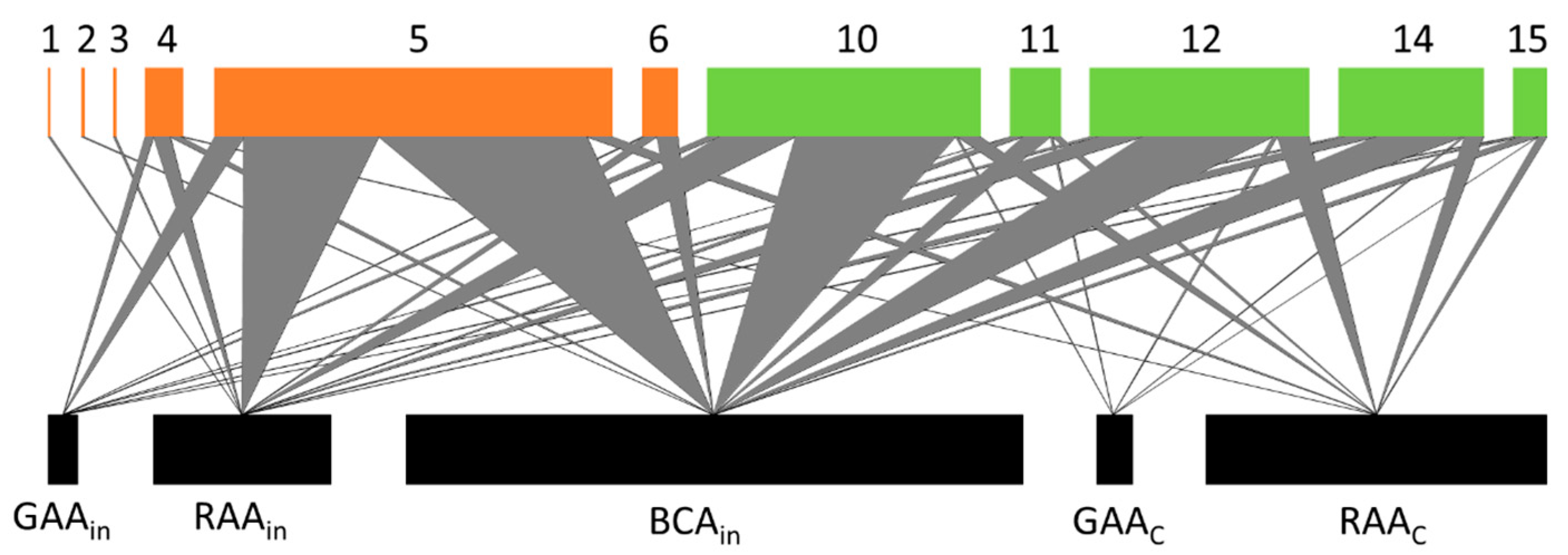
| Natural Enemies (Code) | |
|---|---|
| Parasitoids Aphidius ervi (1), A. matricariae (2), A. urticae (3), Binodoxys angelicae (4), Ephedrus persicae (5), E. plagiator (6), Lipolexis gracilis (7), Praon abjectum (8), Toxares deltiger (9). | Predators Cecidomyiidae (10), Forficulidae (11), Syrphidae (12), Chrysopidae (13), Coccinellidae (14), Anthocoridae (15). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhmedi, A.; Belien, T.; Bylemans, D. Habitat Modification Alters Food Web Interactions with Focus on Biological Control of Aphids in Apple Orchards. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075978
Alhmedi A, Belien T, Bylemans D. Habitat Modification Alters Food Web Interactions with Focus on Biological Control of Aphids in Apple Orchards. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075978
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhmedi, Ammar, Tim Belien, and Dany Bylemans. 2023. "Habitat Modification Alters Food Web Interactions with Focus on Biological Control of Aphids in Apple Orchards" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075978
APA StyleAlhmedi, A., Belien, T., & Bylemans, D. (2023). Habitat Modification Alters Food Web Interactions with Focus on Biological Control of Aphids in Apple Orchards. Sustainability, 15(7), 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075978






