Social Support and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Internal Locus of Control and Adolescents’ Physical Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. Measure for Physical Activity
2.2.2. Measure for Internal Health Locus of Control
2.2.3. Measure for Social Support
2.2.4. Measure for Self-Efficacy
2.3. Techniques for Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Regression Analysis
3.2. Basic Analysis
3.3. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Locus of Control, Social Support, and Self-Efficacy on PA
4.2. Mediation of Social Support
4.3. Mediation of Self-Efficacy
5. Research Implications
6. Strengths, Limitations and Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonini Philippe, R.; Schwab, L.; Biasutti, M. Effects of physical activity and mindfulness on resilience and depression during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 700742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habe, K.; Biasutti, M.; Kajtna, T. Wellbeing and flow in sports and music students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Think. Ski. Creat. 2021, 100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini Philippe, R.; Biasutti, M.; van der Schyff, D.; Schiavio, A. Challenges and understandings of creative practice in professional sport training. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, S.; Kiyani, T.; Kayani, S.; Morris, T.; Biasutti, M.; Wang, J. Physical Activity and Anxiety of Chinese University Students: Mediation of Self-System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, S.; Wang, J.; Kayani, S.; Kiyani, T.; Qiao, Z.; Zou, X.; Imran, M. Self-system mediates the effect of Physical Activity on Students’ Anxiety: A study from Canada. Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 2020, 30, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, S.; Wang, J.; Biasutti, M.; Zagalaz Sánchez, M.L.; Kiyani, T.; Kayani, S. Mechanism between Physical Activity and Academic Anxiety: Evidence from Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Gao, S.; Tang, G. The influence of exercise on the mental health of middle school students: Intermediary effect of self-efficacy. China Sport Sci. Technol. 2016, 5, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hallal, P.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Bull, F.C.; Guthold, R.; Haskell, W.; Ekelund, U.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Global physical activity levels: Surveillance progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Lancet 2012, 380, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchley, J.; Currie, D.; Jewell, J.; Breda, J.; Barnekow, V. Adolescent Obesity and Related Behaviours; World Health Organisation, Regional Office for Europe: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Abdeta, C.; Abi Nader, P.; Adeniyi, A.F.; Aguilar-Farias, N.; Tenesaca, D.S.A.; Bhawra, J.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Cardon, G. Global matrix 3.0 physical activity report card grades for children and youth: Results and analysis from 49 countries. J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15 (Suppl. S2), S251–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vancampfort, D.; Van Damme, T.; Firth, J.; Smith, L.; Stubbs, B.; Rosenbaum, S.; Koyanagi, A. Correlates of physical activity among 142, 118 adolescents aged 12–15 years from 48 low-and middle-income countries. Prev. Med. 2019, 127, 105819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China CDC. The Report of 2010 Behavioral Risk Factors Surveillance of PRC. 2011. Available online: http://www.chinacdc.cn/zxdt/201109/t20110906_52141.htm (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Lu, C.; Stolk, R.P.; Sauer, P.J.; Sijtsma, A.; Wiersma, R.; Huang, G.; Corpeleijn, E. Factors of physical activity among Chinese children and adolescents: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.W.; Popkin, B.M. Time use and physical activity: A shift away from movement across the globe. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 659–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiyani, T.; Kayani, S.; Kayani, S.; Batool, I.; Qi, S.; Biasutti, M. Individual, Interpersonal, and Organizational Factors Affecting Physical Activity of School Adolescents in Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyani, T.; Kayani, S.; Kayani, S.; Qi, S.; Biasutti, M. A School-Based Multilevel Intervention to Increase Physical Activity of Adolescents in Pakistan: From a Social-Ecological Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, M.R.; Crawford, K.L.; Jackson, B. Social cognitive theory and physical activity: Mechanisms of behavior change, critique, and legacy. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2019, 42, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, R.E.; McEwan, D.; Rebar, A.L. Theories of physical activity behaviour change: A history and synthesis of approaches. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2019, 42, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavayuth, D.; Poyago-Theotoky, J.; Zikos, V. Locus of control, health and healthcare utilization. Econ. Model. 2020, 86, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, J.; Wilcox, S. Self-efficacy and social support mediate the relationship between internal health locus of control and health behaviors in college students. Am. J. Health Educ. 2015, 46, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallston, K.A.; Strudler Wallston, B.; DeVellis, R. Development of the multidimensional health locus of control (MHLC) scales. Health Educ. Monogr. 1978, 6, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouserie, R. Sources and levels of stress in relation to locus of control and self esteem in university students. Educ. Psychol. 1994, 14, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, M. On the Concept of Health Capital and the Demand for Health. In Determinants of Health; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6–41. [Google Scholar]
- San Román-Mata, S.; Puertas-Molero, P.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G. Benefits of physical activity and its associations with resilience, emotional intelligence, and psychological distress in university students from southern Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaini, F.A.; Sharifi, N.; Dowlatkhah, H.R. Compare health promoting behaviors and health locus of control in medical and non-medical students in 2017. Pars. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 16, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghaffar, E.-A.; Siham, B. Perspectives of adolescents, parents, and teachers on barriers and facilitators of physical activity among school-age adolescents: A qualitative analysis. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haidar, A.; Ranjit, N.; Archer, N.; Hoelscher, D.M. Parental and peer social support is associated with healthier physical activity behaviors in adolescents: A cross-sectional analysis of Texas School Physical Activity and Nutrition (TX SPAN) data. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Conway, T.L.; Cain, K.L.; Frank, L.D.; Saelens, B.E.; Geremia, C.; Kerr, J.; Glanz, K.; Carlson, J.A.; Sallis, J.F. Interactions of psychosocial factors with built environments in explaining adolescents’ active transportation. Prev. Med. 2017, 100, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavior change. Pshchological Rev. 1983, 84, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenfeld, S.A.; O’Leary, A.; Bandura, A.; Brown, S.; Levine, S.; Raska, K. Impact of perceived self-efficacy in coping with stressors on components of the immune system. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1990, 59, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Health promotion by social cognitive means. Health Educ. Behav. 2004, 31, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, K.; Warner, L.M.; Schwarzer, R. The role of self-efficacy and friend support on adolescent vigorous physical activity. Health Educ. Behav. 2017, 44, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.A.; Williams, D.M.; Frayeh, A.; Marcus, B.H. Self-efficacy versus perceived enjoyment as predictors of physical activity behaviour. Psychol. Health 2016, 31, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qalawa, S.A.A. Health locus of control related daily living activities during COVID 19 pandemic as an indicator of Bronchial Asthma. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2022, 13, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, D.A.; Ditto, B.; Lavoie, K.L.; Campbell, T.; Arsenault, A.; Bacon, S.L. Health locus of control is associated with physical activity and other health behaviors in cardiac patients. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2018, 38, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egoshi, S.; Hayashi, S.; Horie, J.; Shiranita, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kawaura, F.; Takahashi, K.; Asami, T.; Sueoka-Aragane, N. Effect of health locus of control on physical activity in stable patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2021, 33, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Pakistan-Global School-Based Student Health Survey 2009. 2019. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/ncdsmicrodata/index.php/catalog/203 (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Xu, G.; Sun, N.; Li, L.; Qi, W.; Li, C.; Zhou, M.; Han, L. Physical behaviors of 12–15 year-old adolescents in 54 low-and middle-income countries: Results from the Global School-based Student Health Survey. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 010423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F. Age-related decline in physical activity: A synthesis of human and animal studies. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2000, 32, 1598–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Taylor, W.C.; Dowda, M.; Freedson, P.S.; Pate, R.R. Correlates of vigorous physical activity for children in grades 1 through 12: Comparing parent-reported and objectively measured physical activity. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2002, 14, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dishman, R.K.; Hales, D.P.; Sallis, J.F.; Saunders, R.; Dunn, A.L.; Bedimo-Rung, A.L.; Ring, K.B. Validity of social-cognitive measures for physical activity in middle-school girls. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2010, 35, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eather, N.; Morgan, P.J.; Lubans, D.R. Social support from teachers mediates physical activity behavior change in children participating in the Fit-4-Fun intervention. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Z.; Hu, L.; Yu, J.J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Zou, L. The Influence of Social Support on Physical Activity in Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Exercise Self-Efficacy. Children 2020, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Ji, B. Correlation between perceived social support and loneliness among Chinese adolescents: Mediating effects of psychological capital. Psychiatr. Danub. 2019, 31, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, B.H.; Selby, V.C.; Niaura, R.S.; Rossi, J.S. Self-efficacy and the stages of exercise behavior change. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1992, 63, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Celis-Morales, C.A.; Salas, C.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Martínez-López, E. Parental support for physical activity in schoolchildren and its influence on nutritional status and fitness. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2018, 89, 732–740. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.; Centeio, E.; Garn, A.; Martin, J.; Kulik, N.; Somers, C.; McCaughtry, N. Parental social support, perceived competence and enjoyment in school physical activity. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesler, R.; Kolobov, T.; Ng, K.W.; Shapiro, E.; Walsh, S.D.; Shuval, K.; Harel-Fisch, Y. Ethnic disparities in physical activity among adolescents in Israel. Am. J. Health Behav. 2019, 43, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hager, E.R.; Magder, L.S.; Arbaiza, R.; Wilkes, S.; Black, M.M. A dyadic analysis on source discrepancy and a mediation analysis via self-efficacy in the parental support and physical activity relationship among black girls. Child. Obes. 2019, 15, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Unstandardized Effect | Standard Error | Standardized Effect | t-Value | p-Value | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 1.63 | 0.105 | ||
| LOC | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 5.56 | 0.000 | ||
| SS | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 6.43 | 0.000 | 75.74 | 0.35 |
| SE | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.40 | 11.20 | 0.000 |
| Variable (n = 569) | Mean | Std. Deviation | Locus of Control | Social Support | Self-Efficacy | Physical Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC | 17.60 | 4.49 | 1 | 0.147 ** | 0.179 ** | 0.307 ** |
| SS | 9.38 | 2.29 | 1 | 0.262 ** | 0.369 ** | |
| SE | 14.69 | 4.12 | 1 | 0.497 ** | ||
| PA | 11.63 | 2.36 | 1 |
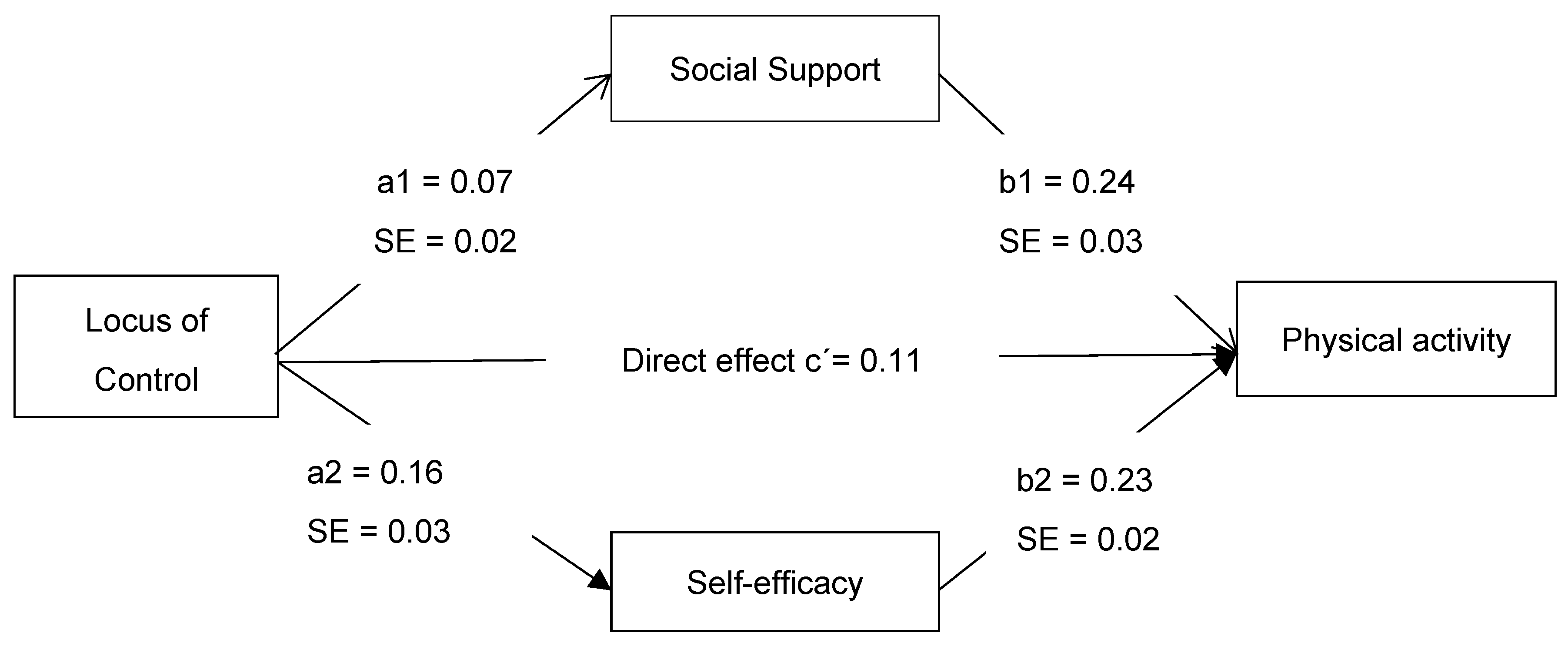
| Path | Beta | Boot-LLCI | Boot-ULCI | SE | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c = (a1b1 + a2b2 + c’) | 0.1616 | 0.1203 | 0.2029 | 0.0210 | 7.6869 | 0.0000 |
| c’ | 0.1059 | 0.0699 | 0.1418 | 0.0183 | 5.7891 | 0.0000 |
| IV-M1 (a1) | 0.0751 | 0.0335 | 0.1166 | 0.0212 | 3.5463 | 0.0004 |
| IV-M2 (a2) | 0.1641 | 0.0897 | 0.2385 | 0.0379 | 4.3311 | 0.0000 |
| M1-DV (b1) | 0.2420 | 0.1702 | 0.3139 | 0.0366 | 6.6157 | 0.0000 |
| M2-DV (b2) | 0.2289 | 0.1887 | 0.2690 | 0.0204 | 11.2000 | 0.0000 |
| (a1b1 + a2b2) | 0.1060 | 0.0625 | 0.1499 | 0.0225 | - | - |
| IV-M1-DV(a1b1) | 0.0345 | 0.0131 | 0.0595 | 0.0118 | - | - |
| IV-M2-DV(a2b2) | 0.0714 | 0.0369 | 0.1064 | 0.0176 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yiming, Y.; Shi, B.; Alghamdi, A.A.; Kayani, S.; Biasutti, M. Social Support and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Internal Locus of Control and Adolescents’ Physical Activity. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075662
Yiming Y, Shi B, Alghamdi AA, Kayani S, Biasutti M. Social Support and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Internal Locus of Control and Adolescents’ Physical Activity. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075662
Chicago/Turabian StyleYiming, Yikeranmu, Bing Shi, Abdulelah A. Alghamdi, Sumaira Kayani, and Michele Biasutti. 2023. "Social Support and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Internal Locus of Control and Adolescents’ Physical Activity" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075662
APA StyleYiming, Y., Shi, B., Alghamdi, A. A., Kayani, S., & Biasutti, M. (2023). Social Support and Self-Efficacy as Mediators between Internal Locus of Control and Adolescents’ Physical Activity. Sustainability, 15(7), 5662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075662








