Network Construction for Overall Protection and Utilization of Cultural Heritage Space in Dunhuang City, China
Abstract
1. Network for the Conservation and Utilization of Heritage Space
2. Research Area and Research Methods
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods and Technical Process
2.3.1. Quantitative Methods and Process of Indexes
2.3.2. Index System for the Suitability Evaluation
3. Refinement and Suitability Evaluation of Historical Information of Conservation and Utilization Factors of the Cultural Heritage Space
3.1. Refinement of the Historical Information of Various Factors in Different Periods
3.2. Suitability Evaluation of Conservation and Utilization of Various Factors
4. Network Construction of Conservation and Utilization of the Cultural Heritage Space
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- State Administration of Cultural Heritage of the People’s Republic of China. The “Fourteenth Five Year Plan” for the Protection and Utilization of Major Sites; State Administration of Cultural Heritage of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
- Shao, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhao, J. Integrated conservation and utilization of historic and cultural resources from the Regional Perspective—The case of southern Anhui. Urban Plan. Forum 2016, 229, 98–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. The protection and sustainable development model of Han Chang’an City based on the theory of Garden City. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 47, 283–288. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Liu, A.; Yang, L. Exploration of Canal Heritage Protection Planning Based on Heritage Corridor Construction: A Case Study of Suzhou Ancient City Section of Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. Landsc. Archit. Acad. J. 2022, 39, 39–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Zhou, Q. The research on the modes of regional protection and utilization of the military fortresses along the great wall in the Ming dynasty in Shanxi province. Urban Dev. Stud. 2016, 23, 32–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Historic Urban and Rural Settlements: A New Category towards Regional and Integral Conservation of Cultural Heritage. Urban Plan. Forum 2015, 226, 5–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The Athens Charter on the Restoration of Historic Monuments (Also Known as the Restoration Charter). In Proceedings of the First International Conference of Architects and Technicians of Historical Monuments, Athens, Greece; 1931.
- Suggestions on the Protection of Historic Areas and Their Contemporary Role (Nairobi Recommendations). In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Session of the General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Nairobi, Kenya, 16 November 1972.
- Lima Conference. Charter of Machu Picchu; International Building Association: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- The eighth plenary meeting of the International Council of Monuments and Sites. In International Charter for the Protection of Historic Towns and Areas (Charter of Washington); International Council of Monuments and Sites(ICOMS): Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- Beijing Charte. In Proceedings of the 20th World Congress of Architects of International Construction Association, Beijing, China, 23 June 1999.
- Zhang, S. An Introduction to Integrated Conservation: A Way for the Protection of Cultural Heritage and Historic Environment Protection, 3rd ed.; Tongji University Press: Shanghai, China, 2022; p. 1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- International Council on Monuments and Sites, CllC. ICOMOS Cultural Line Charter; International Council on Monuments and Sites, CllC: Quebec, QC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, R.A. Cultural Routes between East and West: A Network for Cooperation between Mediterranean Cities. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 223, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocariu, S. The Development of Cultural Routes: A Valuable asset for Romania. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 32, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomopoulou, E.; Delegou, E.T.; Sayas, J.; Moropoulou, A. An innovative approach to the protection of cultural heritage: The case of cultural routes in Chios Island, Greece. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 14, 742–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C. Between “protection” and “utilization” of cultural heritage—Comment on the 2018 revision of Japan’s cultural heritage protection law. Cult. Herit. 2020, 1, 16–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Su, C. Protection and activation utilization of industrial heritage in Adelaide Port, Australia. Ind. Constr. 2019, 49, 41–45+52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F. Study on Structure Evolution of Linear Cultural Heritage: On the Role of Tourism. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 35, 133–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Rui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S. Research on Construction of Spatial Network for Integrated Protection of Community-Type Cultural Heritage: Take the Emperor Mausoleum Group of Western Han and Tang Dynasty in Shaanxi for Example. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 37, 98–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, G. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Tourism Flows and Network Analysis of Traditional Villages in Western Hunan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C. Research on the Construction of Ecological—Cultural Complex Heritage Corridor Network Based on Suitability Analysis: Taking Pu’er City, Yunnan Province as an Example. Landsc. Archit. Acad. J. 2022, 39, 19–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Hou, W. Research on regional historical heritage network from the perspective of cultural landscape: Take the Jinzhong basin as an example. Urban Dev. Stud. 2020, 27, 101–108. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dunhuang Urban and Rural Planning Bureau. Protection Planning of the Famous Historical and Cultural City of Dunhuang; Beijing Tsinghua Tongheng Planning and Design Institute Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 8–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B. Historical Geography of Dunhuang; Gansu Education Press: Lanzhou, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R. Investigation and Study of the Hexi Fortress in Han Dynasty; Cultural Relics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Qi, J.; Zhang, K. Spatial Identification and Pattern Evolution of Cultural Memory in Gansu Province. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 74–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B. The Model Analysis and Trend Study of Spatial Evolution in Shizuishan Urban Region; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y. The Study on Sustainable Development Strategy of Chinese Cultural Landscape Heritage Community: Take the West Lake as an Example; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Spennemann, D.H.R. The Shifting Baseline Syndrome and Generational Amnesia in Heritage Studies. Heritage 2022, 5, 2007–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, J. Interpretation of the cultural values of the imperial maritime customs house in shamien, Guangzhou (previous shamian customs house). Archit. J. 2013, 2013 (Suppl. S1), 76–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- International Council on Monuments and Sites. The Burra Charter: The Australia ICOMOS Charter for Places of Cultural Significance; International Council on Monuments and Sites: Burwood, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. the Value Attribute and Management Mode of Cultural Heritage. Acad. Exch. 2016, 272, 132–137. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Qiu, Y. Conservation of Disappeared Historic heritages through Value Recognition, Discrimination and revalorization: The case of Wuhan. Urban Plan. Forum 2018, 242, 106–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Jin, C. Research on the Application of GIS Based Historic and Cultural City Protection System; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Study on Urban Design in the Regeneration of Historical Environment; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.; Chen, X. Desertification Monitoring of Dunhuang City Based on GIS and RS. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 125–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. The Composition of the Cultural Space System and the Whole Analysis of its Historical Environment in Han-Dynasty Dunhuang County. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 201–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dunhuang Academy. Gansu Provincial Plan for the Construction and Protection of the Great Wall National Cultural Park (Draft); 2020; Dunhuang Academy: Lanzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]







| Conservation Representation | Conservation Index | Interpretation of Connotation | Utilization Representation | Utilization Index | Interpretation of Connotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservation value | Scientific and technological value (P1) | It embodies people’s capability and aesthetic concept of understanding nature and transforming the natural environment, as well as the advanced nature of manufacturing technology. | Utilization value | Humanistic value (U1) | It is beneficial for the facilitation of cultural conservation and spatial memory, enhancing local cultural self-confidence, excavating local culture and national spirit, and promoting cultural communication and interaction. |
| Artistic value (P2) | It embodies the social system, social production, and social living environment of all ages and nationalities in history. | Social value (U2) | It is beneficial for the facilitation of people’s communication and health, enhancing production and the living environment, promoting dialogue between history and reality, and optimizing the regional labor force. | ||
| Historical value (P3) | The environment influenced by human beings may be in possession of the value of arts and crafts in numerous aspects, such as shape, decoration, and color. | Economic value (U3) | It is beneficial for the imporevement of the local economic structure, facilitating the development of cultural tourism, advancing the revitalization of rural culture, and achieving the integration of the three industries. | ||
| Ecological value (P4) | It can help maintain ecological security and stability, improve the landscape, promote ecological and organic restoration, and encourage the construction of ecological civilization. | ||||
| Conservation foundation | Conservation integrity (P5) | It is complete in the overall pattern, and comprehensive in the physical composition. | Utilization foundation | Location conditions (U4) | It enjoys a good comparative advantage of natural and human resources, and is closely linked with other spaces of utilization factors. |
| Conservation coordination (P6) | It is mutually associated in terms of system composition, and orderly in the relationship between heritage and the environment. | Facility conditions (U5) | It lays a supporting foundation for public facilities and infrastructure, offering certain conditions for utilization. | ||
| Conservation strength (P7) | The conservation and research work is in depth, and stability restoration work achieves fruitful results. | Utilization expectation (U6) | It arouses more attention and attraction, and the public has high expectations for its utilization. |
| Factors of Cultural Heritage Space | Conservation Evaluation | Utilization Evaluation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Method | Assignment (1~0) | Weight | Analytical Method | Assignment (1~0) | Weight | |
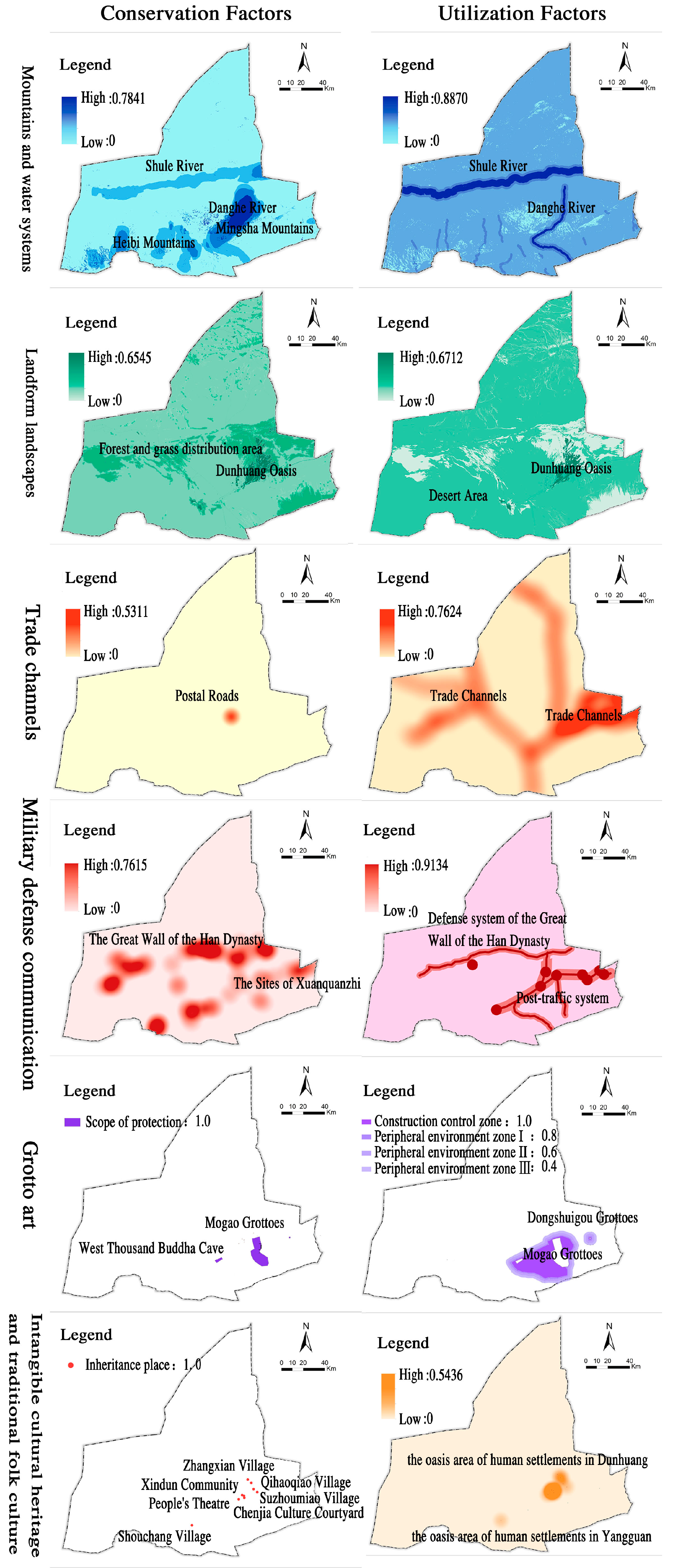
| Mountains and water | Kernel density analysis | The protection value and foundation of the front area of Qilian Mountains and the middle reaches of Danghe River scored high | 0.0991 | Kernel density analysis | The utilization value and foundation scores of Danghe River and Shule River are high | 0.0898 |
| Landform landscapes | Neighborhood analysis | The score of protection value in oasis area is high | 0.1213 | Neighborhood analysis | The score of basic utilization in oasis area is higher, followed by Gobi area | 0.2243 |
| Trade channels | Buffer analysis | The protection value score of the existing ancient road remains is high | 0.1634 | Buffer analysis | The utilization value and basic scores along the historic road are high | 0.1767 |
| Military defense | Kernel density analysis | The protection value and foundation score of the Great Wall site is good | 0.3105 | Buffer analysis | The utilization value and basic score of the Great Wall National Cultural Park and the post road are good | 0.2565 |
| Grotto art | Neighborhood analysis | The core protection area of the grottoes has a high score of protection value | 0.1945 | Buffer analysis | Grotto construction control zone and surrounding utilization base score is good | 0.1652 |
| Intangible cultural heritage and traditional folk culture | Point element analysis | The protection and inheritance value and foundation score of the institute is high | 0.1112 | Buffer analysis | The value of cultural inheritance and development in the residential oasis is great | 0.0875 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, B.; Ma, Y. Network Construction for Overall Protection and Utilization of Cultural Heritage Space in Dunhuang City, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054579
Feng B, Ma Y. Network Construction for Overall Protection and Utilization of Cultural Heritage Space in Dunhuang City, China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(5):4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054579
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Bin, and Yongchi Ma. 2023. "Network Construction for Overall Protection and Utilization of Cultural Heritage Space in Dunhuang City, China" Sustainability 15, no. 5: 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054579
APA StyleFeng, B., & Ma, Y. (2023). Network Construction for Overall Protection and Utilization of Cultural Heritage Space in Dunhuang City, China. Sustainability, 15(5), 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054579





