Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
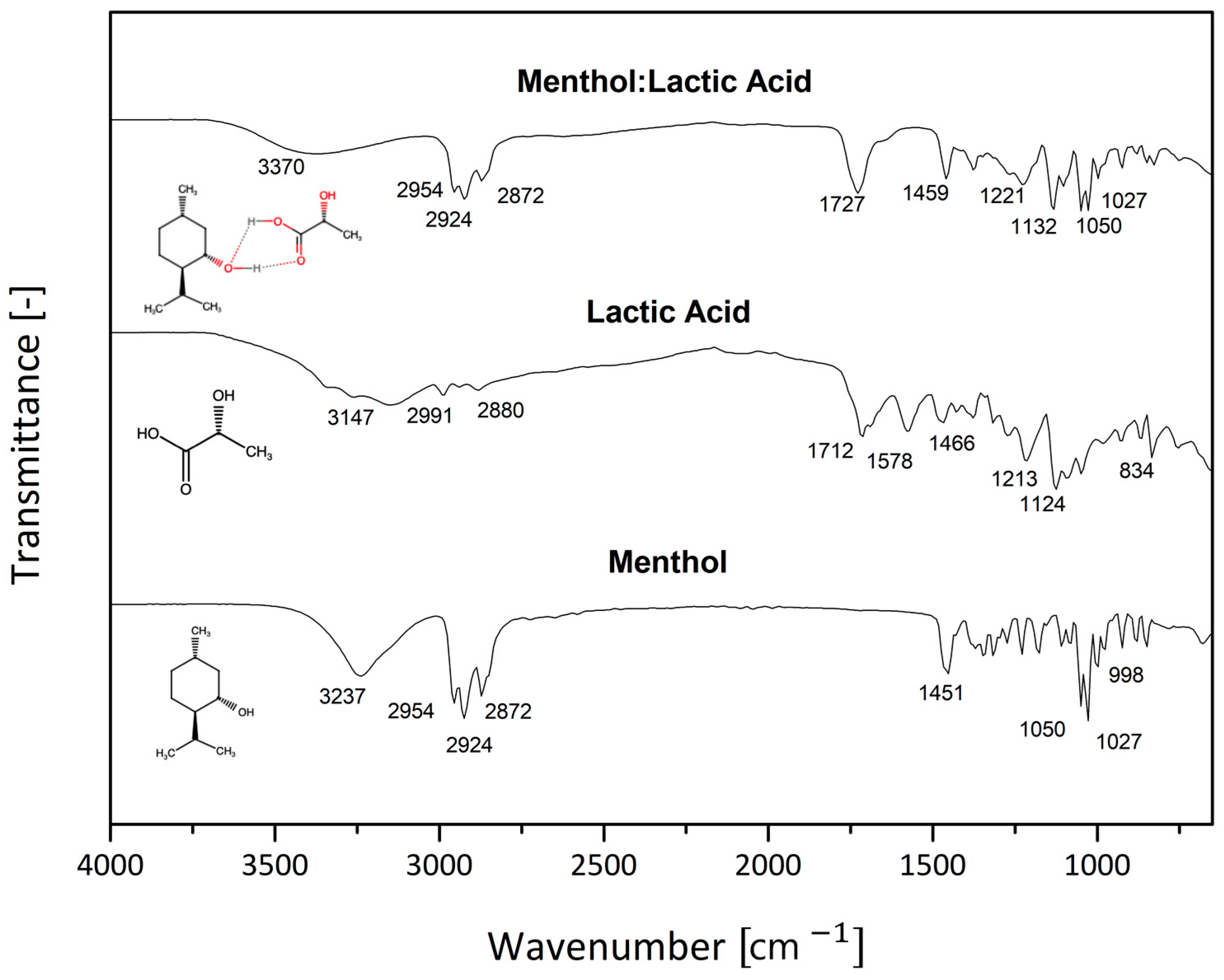
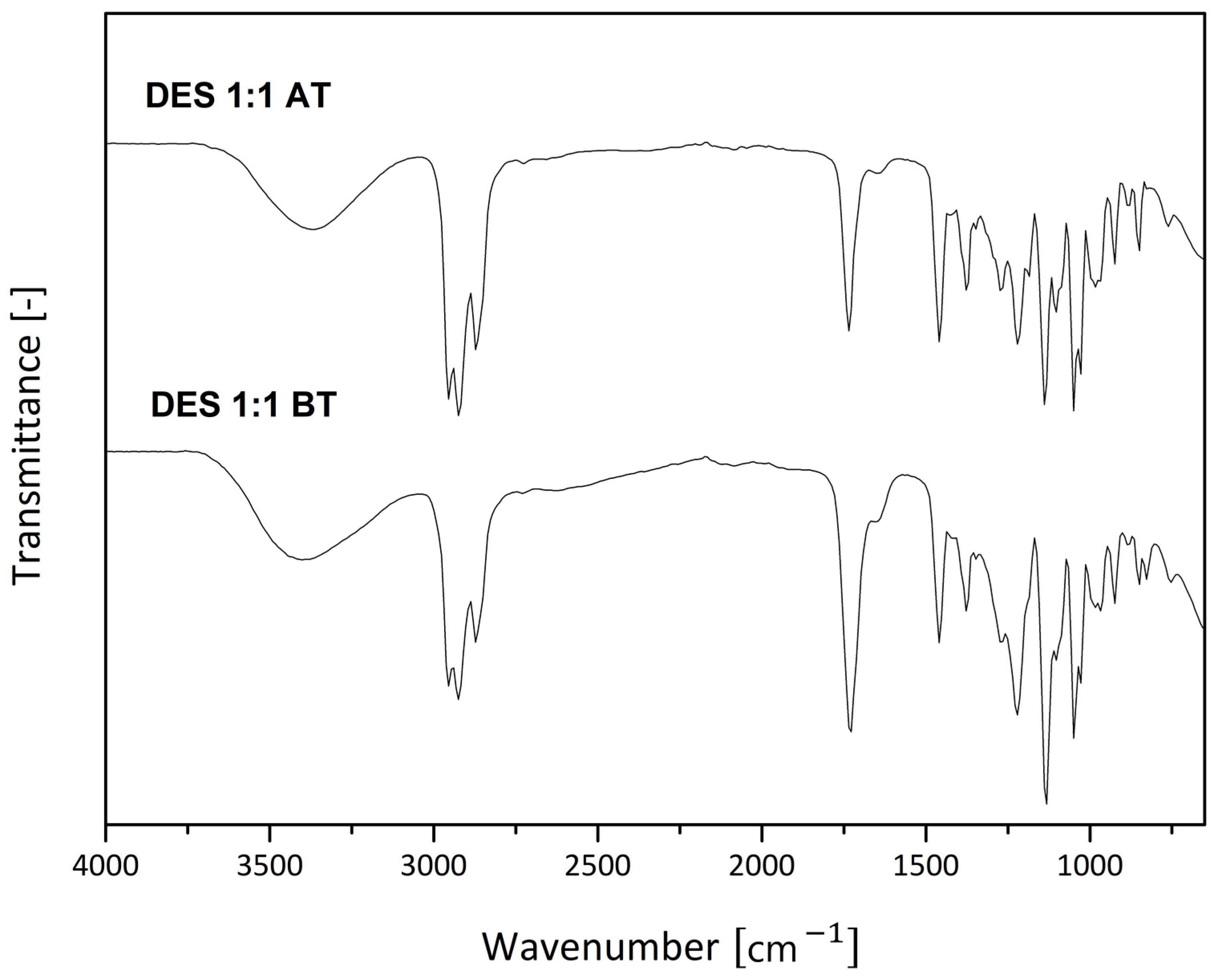
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jameel, A.T.; Muyubi, S.A.; Karim, M.I.A.; Alam, M.Z. Removal of Oil and Grease as Emerging Pollutants of Concern (EPC) in Wastewater Stream. IIUM Eng. J. 2011, 12, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefelahiyeh, R.; Dominic, C.C.S.; Ducoste, J. Modeling fats, oil and grease deposit formation and accumulation in sewer collection systems. J. Hydroinform. 2017, 19, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Din, M.F.M.; Rezania, S.; Khademi, T.; Kumar, A. Palm Oil Mill Effluent as an Environmental Pollutant. In Palm Oil; Waisundara, V., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljaiek-Urzola, M.; Romero-Sierra, N.; Segrera-Cabarcas, L.; Valdelamar-Martínez, D.; Quiñones-Bolaños, É. Oil and grease as a water quality index parameter for the conservation of marine biota. Water 2019, 11, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor Adejumoke, A.; Adebesin Babatunde, O.; Oluyori Abimbola, P.; Adelani-Akande Tabitha, A.; Dada Adewumi, O.; Oreofe Toyin, A. Water Pollution: Effects, Prevention, and Climatic Impact. In Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Scholz, M. Climate change, water quality and water-related challenges: A review with focus on Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed Between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Li, J.; Hua, C. Research Progresses of Deep Eutectic Solvents and its Application in Separation and Catalysis. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 921, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivabalan, V.; Sahith, J.K.; Lal, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents as the New Norm for Oil and Gas Industry: A Mini Review; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś-Chełstowska, P.; Słupek, E.; Małachowska, A. Superhydrophobic sponges based on green deep eutectic solvents for spill oil removal from water. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 425, 127972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe Drinking Water Foundation. Oil Spills. Available online: https://www.safewater.org/fact-sheets-1/2017/1/23/oil-spills (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; De la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep eutectic solvents vs. ionic liquids: Similarities and differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, M.; González, A.S.; de Dios, S.L.G.; Weggemans, W.; Kroon, M.C. Comparison of a low transition temperature mixture (LTTM) formed by lactic acid and choline chloride with choline lactate ionic liquid and the choline chloride salt: Physical properties and vapour-liquid equilibria of mixtures containing water and ethanol. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 23553–23561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonsky, M.; Šima, J. Is it correct to name DESs deep eutectic solvents? Bioresources 2022, 17, 3880–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottaras, P.; Koulianos, M.; Makris, D.P. Low-transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs) made of bioorganic molecules: Enhanced extraction of antioxidant phenolics from industrial cereal solid wastes. Recycling 2017, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Q.; Luo, H. Menthol-based eutectic mixtures: Novel potential temporary consolidants for archaeological excavation applications. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A. Novel Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Application in the Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Aromatic Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Row, K.H. Evaluation of Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Bisphenol A from Environment Water. Anal. Lett. 2021, 54, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMarullo, S.; Meli, A.; Dintcheva, N.T.; Infurna, G.; Rizzo, C.; D’Anna, F. Environmentally friendly eutectogels comprising l-amino acids and deep eutectic solvents: Efficient materials for wastewater treatment. ChemPlusChem 2020, 85, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Monteiro, N.V.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for purification of water contaminated with Bisphenol-A. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Jordão, N.; Branco, L.C. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as low-cost and green electrolytes for electrochromic devices. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škulcová, A.; Jablonský, M. Properties and thermal behavior of deep eutectic solvents based lactic acid. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2018, 25, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Abuhasel, K.; Kchaou, M.; Alquraish, M.; Munusamy, Y.; Jeng, Y.T. Oilywastewater treatment: Overview of conventional and modern methods, challenges, and future opportunities. Water 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, J. Characterization of Composition of the Fat-Rich Residues from Grease Separators; Linaeus University: Växjö, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Páez-Flor, N. (Universidad de las Fuerzas Armadas, Quito, Ecuador). Personal communication, 2022.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagos, A.S.; Landázuri, A.C. Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054176
Lagos AS, Landázuri AC. Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods. Sustainability. 2023; 15(5):4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054176
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagos, Andrés S., and Andrea C. Landázuri. 2023. "Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods" Sustainability 15, no. 5: 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054176
APA StyleLagos, A. S., & Landázuri, A. C. (2023). Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods. Sustainability, 15(5), 4176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054176









