PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Using GRA-GRU Network in Air Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Technical Proposal
3.1. Correlation Analysis of PM2.5 Concentration and Meteorological Elements
3.2. Data Correlation
3.3. Spatial Weight Matrix Based on Grey Correlation Analysis
4. PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Based on GRA-GRU Network
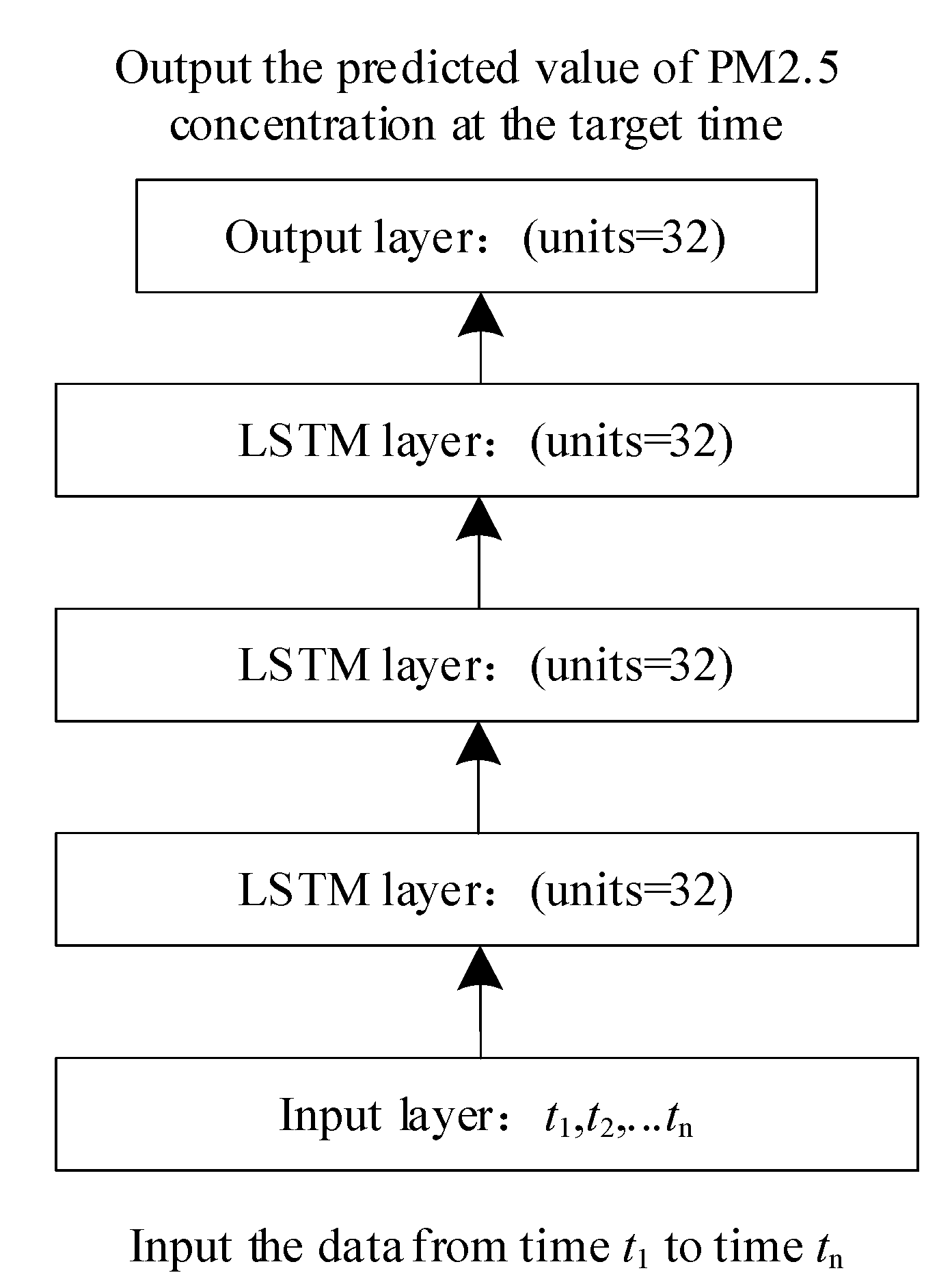
4.1. Network Structure
4.2. LSTM and GRU
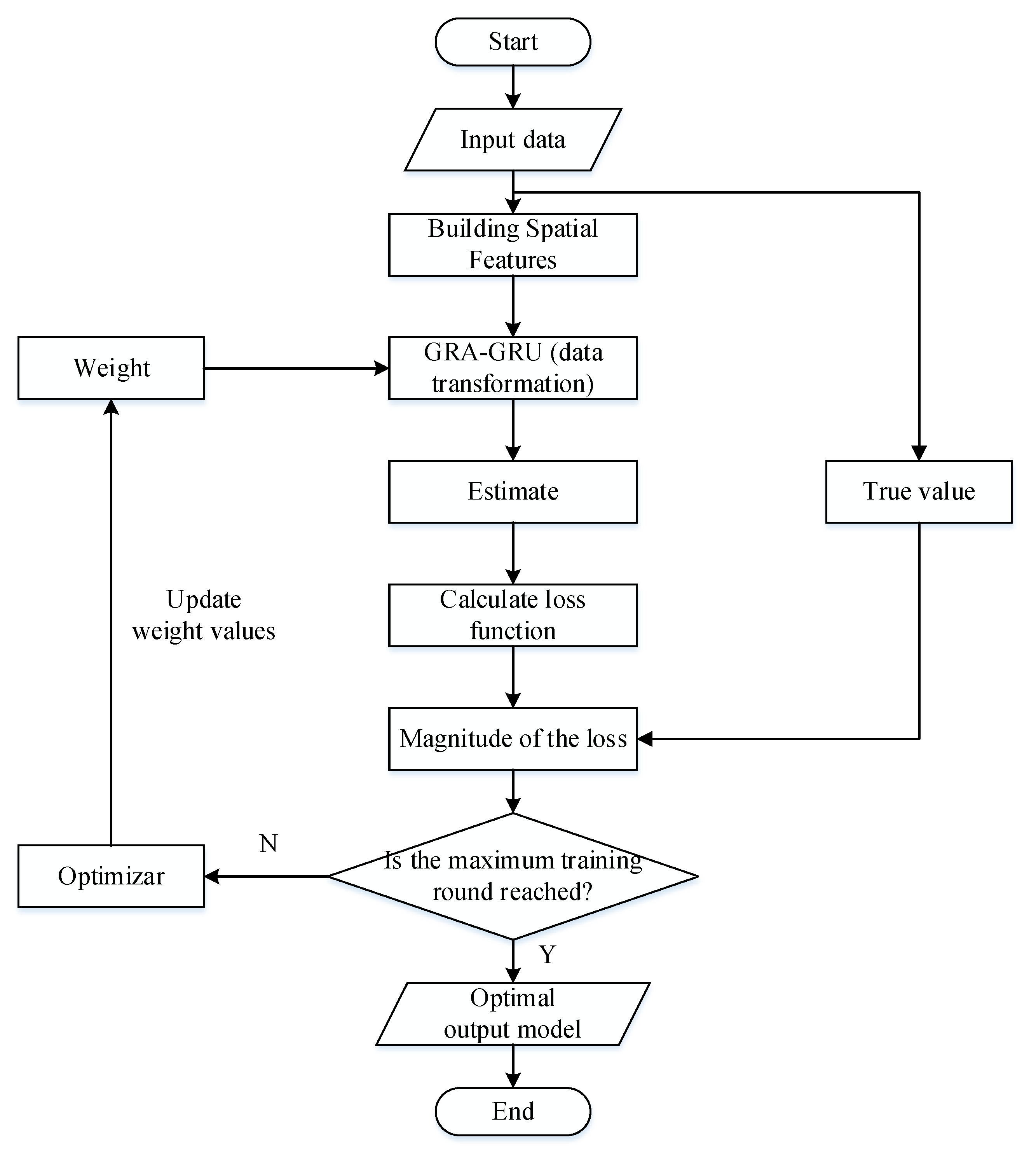
4.3. Prediction of PM2.5 Concentration Based on GRA-GRU Model
5. Experiment and Analysis
5.1. Simulation Parameters and Environment
5.2. Loss Function and Precision Evaluation Index
5.3. Super Parameter Selection of GRU Model
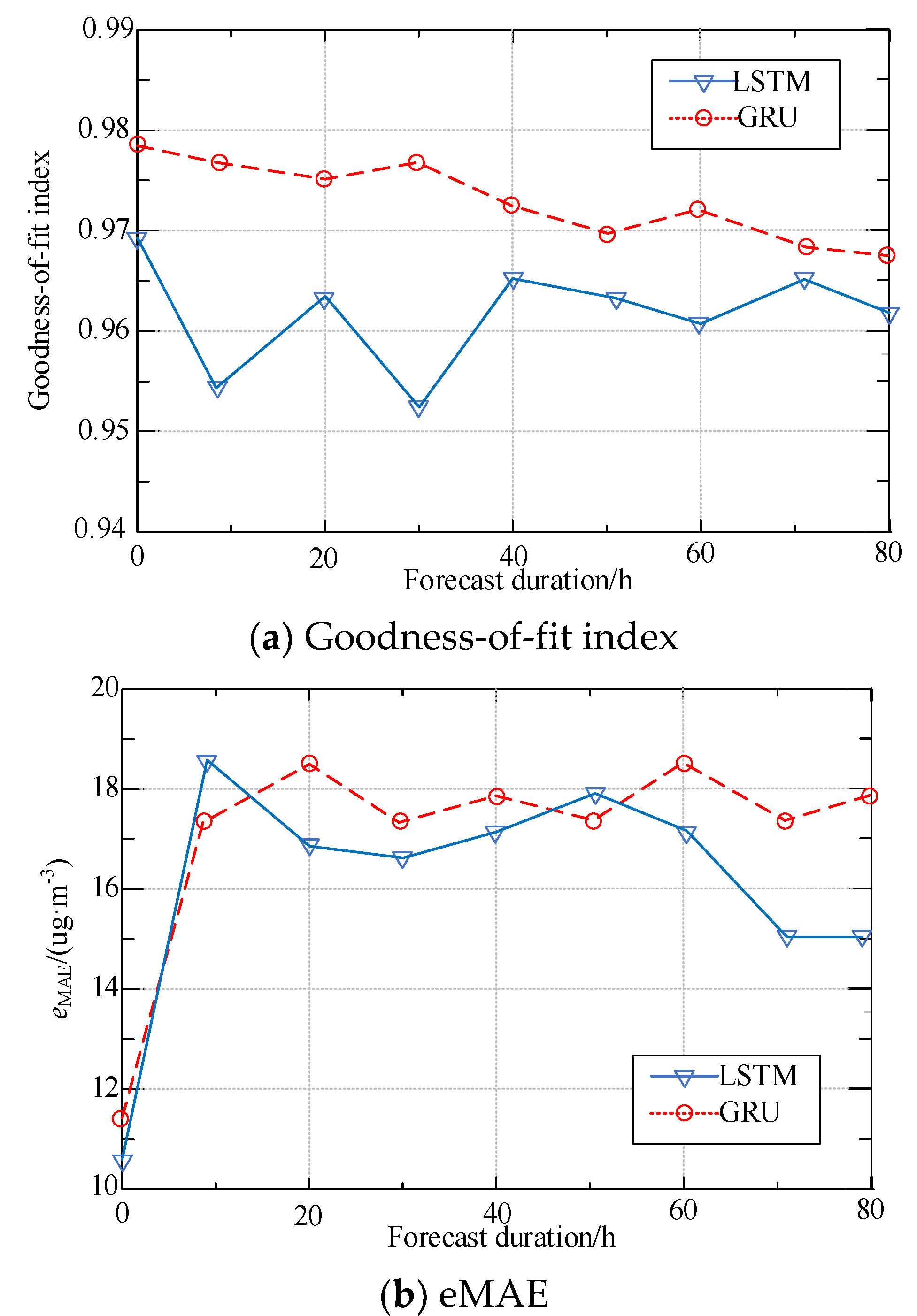
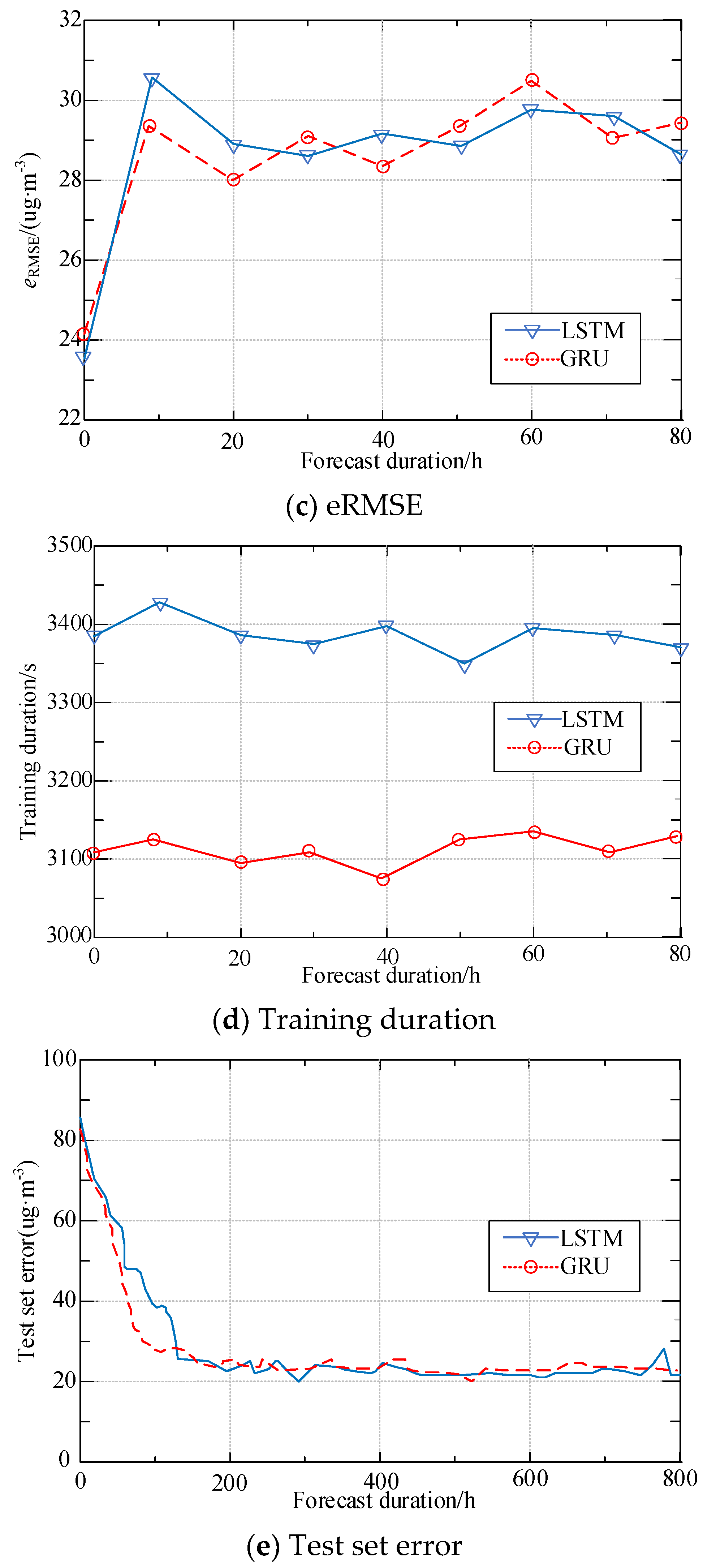
5.4. Comparison of Regional PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Models Based on LSTM and GRU
5.5. Performance Comparison with Other Methods
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Q.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Ye, K.; Wang, C.Y.; Huo, X. Air pollution and body burden of persistent organic pollutants at an electronic waste recycling area of China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.W. Adsorption ability of air pollutants by indigenous tree species in ta-pieh mountains. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 2908–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Celiktas, V.; Otu, H.; Duzenli, S.; Alharby, H.; Bamagoos, A.; Islam, M.S.; Hossain, A.; Sabagh, A.E. Traffic-induced air pollution effects on physio-biochemical activities of the plant eucalyptus camuldensis. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 9373–9378. [Google Scholar]
- Tolis, E.I.; Panaras, G.; Douklias, E.; Ouranos, N.; Bartzis, J.G. Air quality measurements in a medium scale athletic hall: Diurnal and I/O ratio analysis. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 658–665. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Enrique, J.; Turias, I.J.; Jesus Ruiz-Aguilar, J.; Antonio Moscoso-Lopez, J.; Jerez-Aragones, J.; Franco, L. Estimation of NO2 concentration values in a monitoring sensor network using a fusion approach. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Afridi, S.G.; Islam, N.; Shams, D.F.; Shams, S.; Khan, A.; Shah, M.; Khan, W.; Shah, M.; Islam, M.; Iqbal, A. Assessment of air pollution tolerance of selected trees and crop species using biochemical and physiological analyses. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 4805–4810. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, C.; Lei, M. Dynamic forecasting model of short-term PM2.5 concentration based on machine learning. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 37, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Karadirek, I.E.; Aktas, K.; Topkaya, B. Environmental pollution of the mediterranean sea: Evaluation of research activities in the mediterranean sea countries. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 867–872. [Google Scholar]
- Duzenli, T.; Alpak, E.M.; Yilmaz, S. Children’s imaginations about environment and their perceptions on environmental problems. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 9798–9808. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Azam, M.; Islam, T.; Zaman, K. Environment and air pollution like gun and bullet for low income countries: War for better health and wealth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 3641–3657. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.H.; Yang, W.X. Evaluating China’s air pollution control policy with extended AQI indicator system: Example of the Beijing-tianjin-hebei region. Sustainability 2019, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Fang, J.; Mittleman, M.A.; Kapral, M.K.; Wellenius, G.A. Fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5) and the risk of acute ischemic stroke. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolim, C.M.; Weissmann, L.; Ferreira, C.K.d.O.; Zordão, O.P.; Dornellas, A.P.S.; Castro, G.D.; Zanotto, T.M.; Boico, V.F.; Quaresma, P.G.F.; Lima, R.P.A.; et al. Short-term exposure to air pollution (PM2.5) induces hypothalamic inflammation, and long-term leads to leptin resistance and obesity via Tlr4/Ikbke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, K.C.; Bell, M.L. Do fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5) exposure and its attributable premature mortality differ for immigrants compared to those born in the United States? Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.R.; Brandley, D.C. Exercise in thermal inversions: PM2.5 air pollution effects on pulmonary function and aerobic performance. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2020, 31, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, M.; Upadhya, A.; Savio, E.; Sreekanth, V.; Asundi, J.; Apte, J.; Marshall, J. Mobile-monitoring of Black Carbon and PM2.5 air pollution data only approach from Bangalore, India. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 200–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, J.; Pokorna, P.; Rychlik, S.; Skachova, H.; Vlcek, O.; Smolik, J.; Zdimal, V.; Hunova, I. Assessment of air pollution origin based on year-long parallel measurement of PM2.5 and PM10 at two suburban sites in Prague, Czech Republic. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Hua, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Communicating air pollution-related health risks to the public: An application of the Air Quality Health Index in Shanghai, China. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Avise, J.C.; DaMassa, J.A.; Kleeman, M.J.; Kaduwela, A.P. Seasonal modeling of PM2.5 in California’s San Joaquin Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Z.; Xu, W.S.; Shi, A.J.; Li, Y.T.; Zhao, X.J.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, J.X.; Wang, L.N. Air quality forecast of PM10 in Beijing with Community Multi-scale Air Quality Modeling (CMAQ) system: Emission and improvement. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2014, 7, 2243–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, F.; Deng, J.; Shen, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D. Urban air quality and regional haze weather forecast for Yangtze River Delta region. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.C.; Deng, F.; Cai, Y.Y.; Chen, J. Long short-term memory—Fully connected (LSTM-FC) neural network for PM2.5 concentration prediction. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidushi, C.; Anand, D.; Vijayanand, K. Time series based LSTM model to predict air pollutant’s concentration for prominent cities in India. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Utility-Driven Mining, London, UK, 20 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thaweephol, K.; Wiwatwattana, N. Long short-term memory deep neural network model for PM2.5 forecasting in the Bangkok urban area. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on ICT and Knowledge Engineering (ICT&KE), Bangkok, Thailand, 20–22 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.B.; Yu, E.P.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, H.L.; Cheng, D.P.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Manomaiphiboon, K.; Li, L. A novel hybrid machine learning method (OR-ELM-AR) used in forecast of PM2.5 concentrations and its forecast performance evaluation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-R.; Hsu, Y.-K.; Chen, H.-Y.; Jau, H.-J. Air pollution prediction based on factory-aware attentional LSTM neural network. Computing 2020, 103, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, P.-W.; Chang, J.-W.; Huang, J.-W. Adaptive deep learning-based air quality prediction model using the most relevant spatial-temporal relations. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38186–38199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Kuo, P.-H. A deep CNN-LSTM model for particulate matter (PM2.5) forecasting in smart cities. Sensors 2018, 18, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-W.; Chang, C.-L.; Li, L.-T.; Liao, S.-W. Reinforcement Learning for Improving the Accuracy of PM2.5 Pollution Forecast Under the Neural Network Framework. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 9864–9874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Yu, J.; Jeong, S.; Yeom, J. Hourly Ground-Level PM2.5 Estimation Using Geostationary Satellite and Reanalysis Data via Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satria, H.; Soekirno, S. Design of PM2.5 and PM10 measuring instruments for analysis of air pollution distribution patterns in the dramaga area based on internet of things. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1816, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Field Name | Describe |
|---|---|
| ID | Station No |
| PM2.5 | PM2.5 concentration |
| PM10 | PM10 concentration |
| SO2 | sulfur dioxide concentration |
| O3 | ozone concentration |
| vis | visibility |
| tem | visibility |
| win | wind speed |
| rh | relative humidity |
| prs | Average air pressure |
| Structure | Number of Layers | Hide Node | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRU-1 | 1 | 64 | 9.93 | 17.66 |
| GRU-1 | 1 | 128 | 12.34 | 18.92 |
| GRU-2 | 2 | 128 | 9.81 | 15.74 |
| GRU-3 | 3 | 384 | 9.93 | 50.84 |
| GRU-4 | 4 | 512 | 20.68 | 54.25 |
| Algorithm | ||
|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 23.77 | 17.83 |
| FAA- LSTM | 20.16 | 15.25 |
| CNN-LSTM | 19.78 | 14.15 |
| GRA-GRU | 18.32 | 13.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qing, L. PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Using GRA-GRU Network in Air Monitoring. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031973
Qing L. PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Using GRA-GRU Network in Air Monitoring. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031973
Chicago/Turabian StyleQing, Ling. 2023. "PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Using GRA-GRU Network in Air Monitoring" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031973
APA StyleQing, L. (2023). PM2.5 Concentration Prediction Using GRA-GRU Network in Air Monitoring. Sustainability, 15(3), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031973






