Irrigation Technology Interventions as Potential Options to Improve Water Security in India and Africa: A Comparative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.1.1. India
2.1.2. Africa
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Micro-Irrigation Technologies
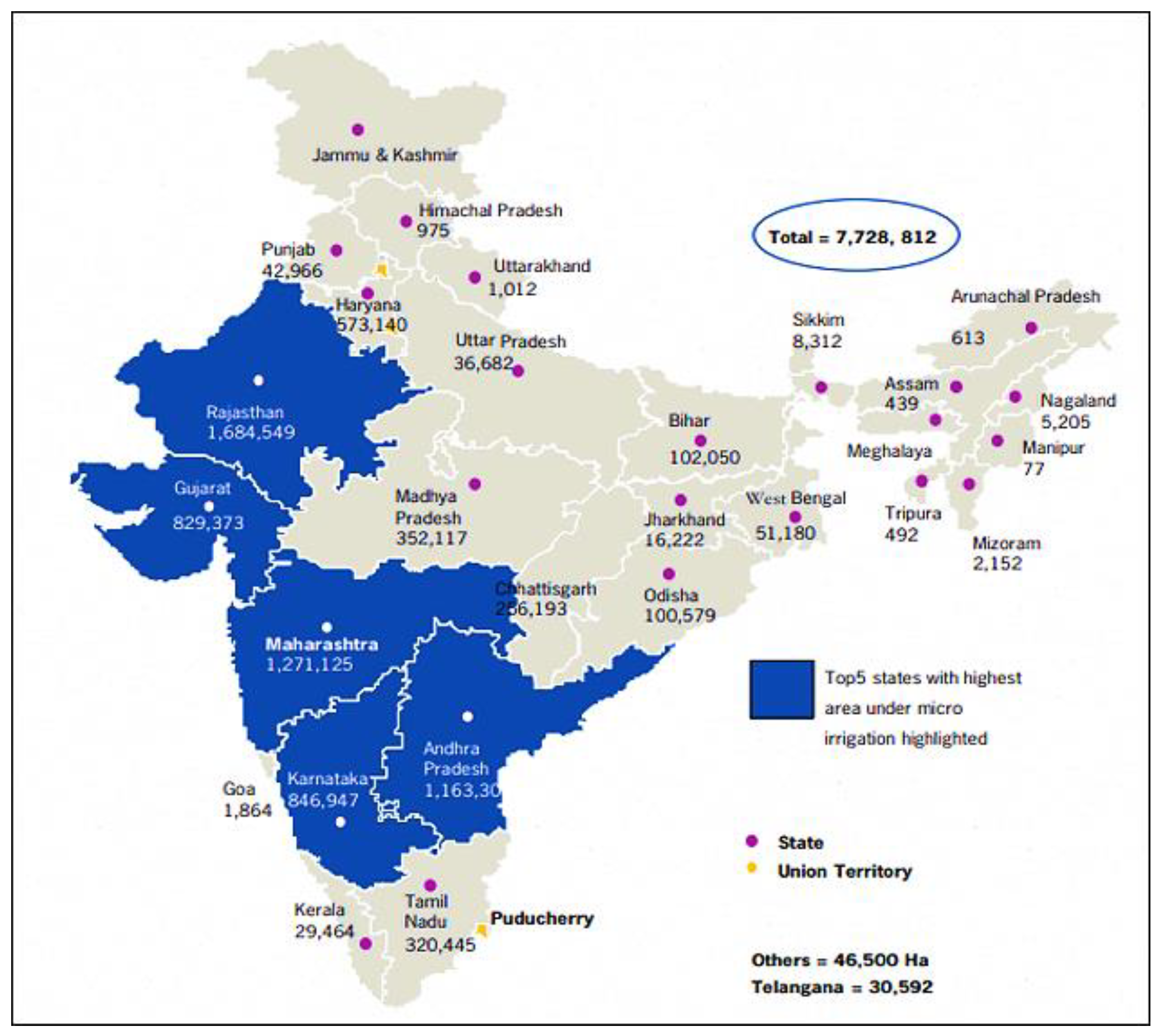
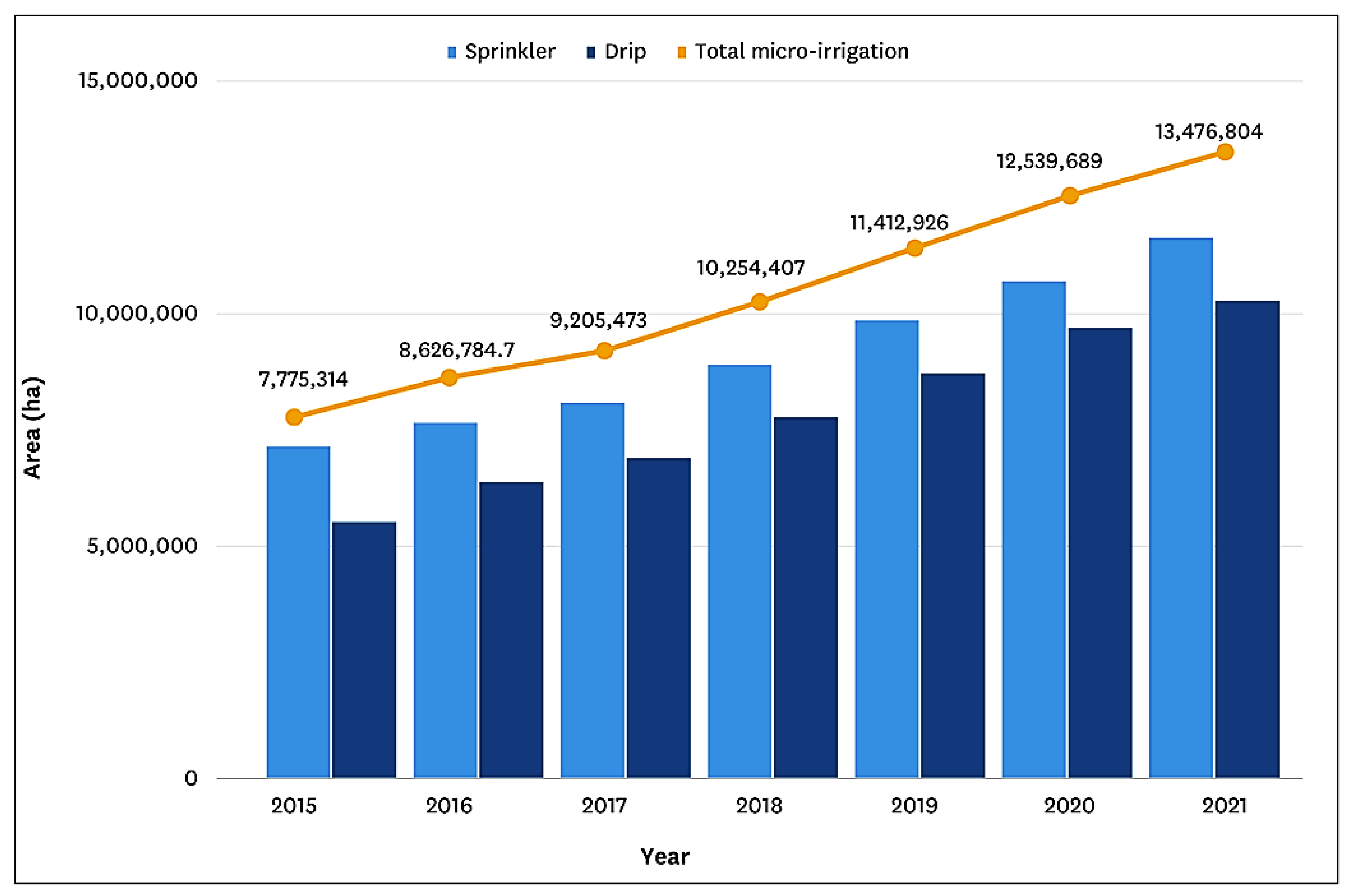
3.1.1. India’s Perspective
3.1.2. African Perspective
Micro-Irrigation Uptake in North Eastern Africa (Egypt)
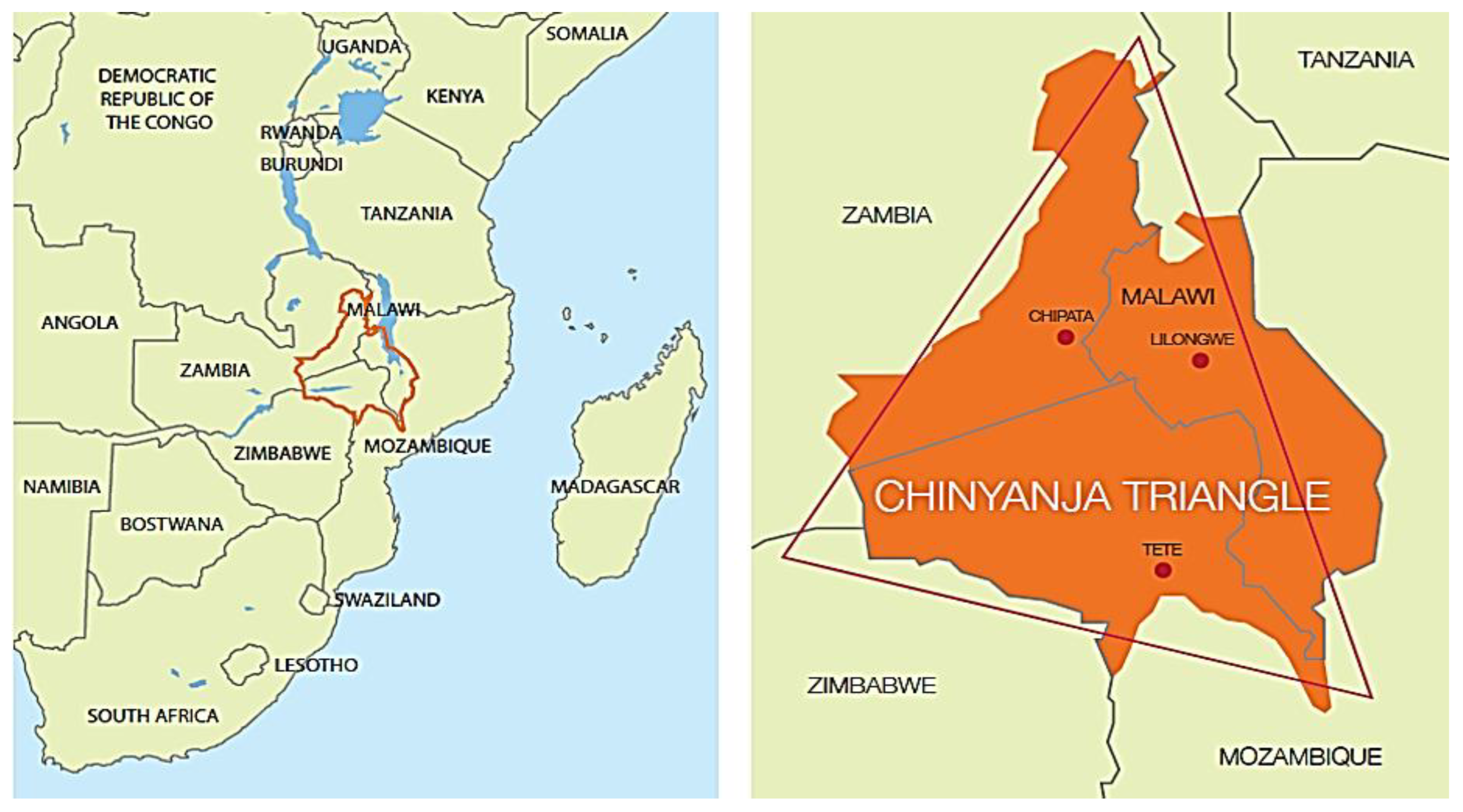
Micro-Irrigation Uptake in Southern Africa
Micro-Irrigation Uptake in Eastern Africa
Micro-Irrigation Uptake in Western Africa
3.2. Renewable Energy-Powered Irrigation Technologies
3.3. Flood Recession Agriculture
3.4. Underground Taming of Floods for Irrigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koech, R.K.; Langat, P.K. Recent Trends in Water Use Optimization of Surface Irrigation Systems in Australia. In Technological Interventions in Management of Irrigated Agriculture; Goyal, M.R., Nambuthiri, S.S., Koech, R., Eds.; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2018; 328p. [Google Scholar]
- Priyan, K.; Panchal, R. Micro Irrigation: An Efficient Technology for India’s Sustainable Agricultural Growth. Kalpa Publ. Civ. Eng. 2017, 1, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakιs, A.N.; Zaccaria, D.; Krasilnikoff, J.; Salgot, M.; Bazza, M.; Roccaro, P.; Jimenez, B.; Kumar, A.; Yinghua, W.; Baba, A.; et al. Irrigation of World Agricultural Lands: Evolution through the Millennia. Water 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, J. Drinking Water Treatment and Challenges in Developing Countries. In The Relevance of Hygiene to Health in Developing Countries; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- IWMI. Promoting Micro-Irrigation Technologies that Reduce Poverty. In Water Policy Briefing; No. 23; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Froebrich, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Rollin, D.; Coulon, C.; Belaud, G. Innovations in Irrigation Systems in Africa. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
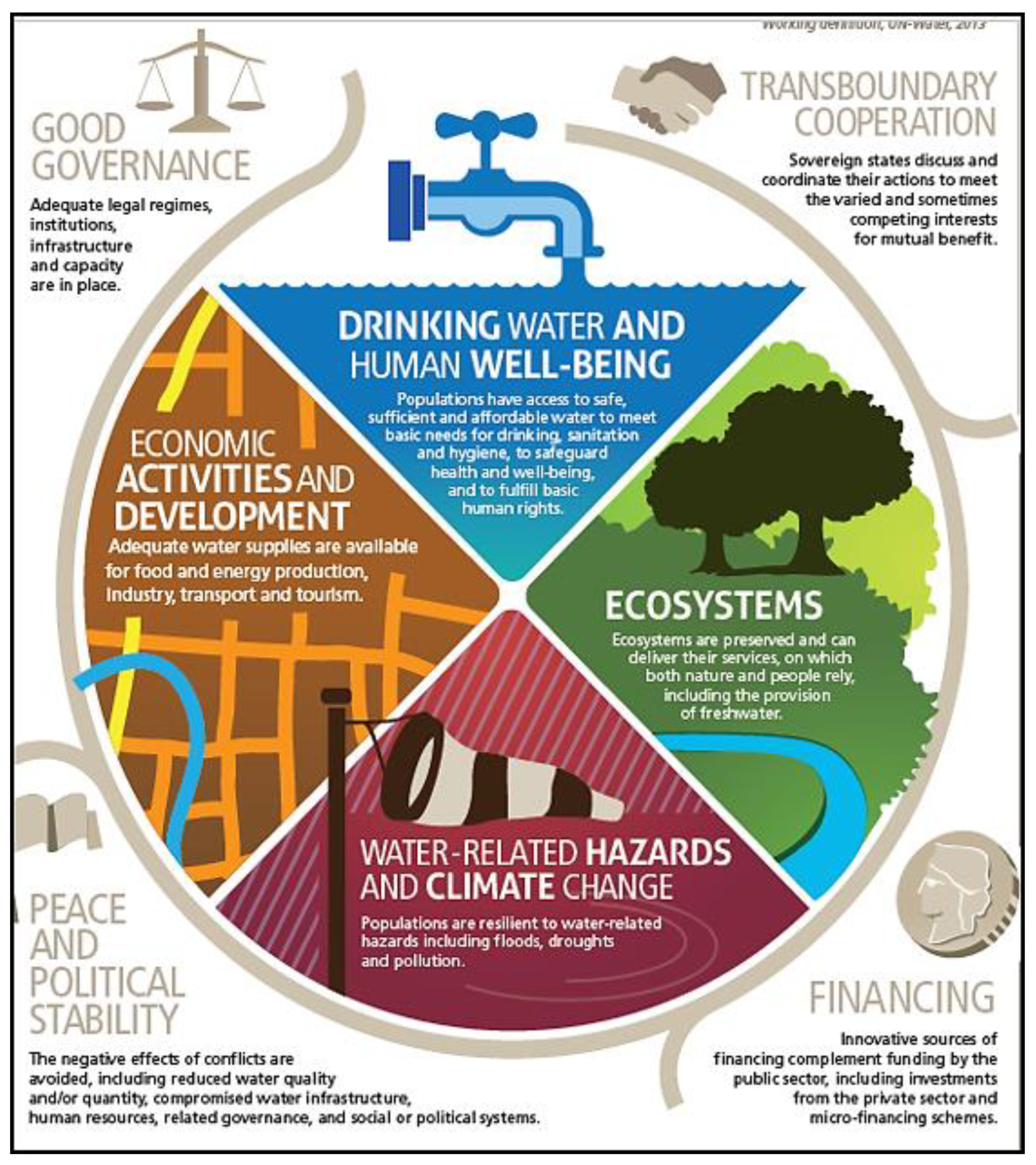
- UN-Water. What Is Water Security? Infographic. 2013. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/water-security-infographic/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- UNESCO-IHP. Strategic Plan of the Eighth Phase of IHP (IHP-VIII, 2014–2021); UNESCO-IHP: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Goal 6: Ensure Availability and Sustainable Management of Water and Sanitation for All; WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific: Manila, Philippines, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tindall, J.A.; Campbell, A.A. Water Security—National and Global Issues: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2010–3106; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2010; 6p.
- UN Water/Africa. The Africa Water Vision for 2025: Equitable and Sustainable Use of Water for Socioeconomic Development. 2020. Available online: https://www.afdb.org/fileadmin/uploads/afdb/Documents/Generic-Documents/african%20water%20vision%202025%20to%20be%20sent%20to%20wwf5.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Grantthorton. Accelerating Growth of Indian Agriculture: Micro Irrigation an Efficient Solution: Strategy Paper—Future Prospects of Micro Irrigation in India. 2016. Available online: https://www.grantthornton.in/globalassets/1.-member-firms/india/assets/pdfs/micro-irrigation-report.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Passarelli, S.; Mekonnen, D.; Bryan, E.; Ringler, C. Evaluating the pathways from small-scale irrigation to dietary diversity: Evidence from Ethiopia and Tanzania. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, L.; Thai, T.M.; Schmmiter, P. Gender mainstreaming from an institutional perspective: Cases of small and micro irrigation projects in Ethiopia. In Proceedings of the CGIAR GENDER Science Exchange, Nairobi, Kenya, 12–14 October 2022; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Macrotrends. India Population Growth Rate 1950–2021. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/countries/IND/india/population-growth-rate (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Gupta, R.; Tyagi, N.K.; Abrol, I. Rainwater Management and Indian Agriculture: A Call for a Shift in Focus from Blue to Green Water. Agric. Res. 2020, 9, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.S.; Gopinath, K.A.; Prasad, J.V.; Singh, A.K. Climate resilient villages for sustainable food security in tropical India: Concept, process, technologies, institutions, and impacts. Adv. Agron. 2016, 140, 101–214. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.K.; Gupta, S.; Sinha, R.; Densmore, A.L.; Rai, S.P.; Shekhar, S.; Mason, P.J.; van Dijk, W.M. Strongly heterogeneous patterns of groundwater depletion in Northwestern India. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajni, J.; Prabhat, K.; Kumar, S.D. Irrigation in India: Status, challenges and option. J. Soil Water Cons. 2019, 18, 354–363. [Google Scholar]
- Nations Online. Countries of Africa. 2021. Available online: https://www.nationsonline.org/oneworld/africa.htm (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Bjornlund, V.; Bjornlund, H.; Van Rooyen, A.F. Why agricultural production in sub-Saharan Africa remains low compared to the rest of the world—A historical perspective. Int. J. Water Res. Dev. 2021, 36, S20–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbottom, T.P.; Adhikari, R.; Dimova, R.; Foster, T. Performance of large-scale irrigation projects in sub-Saharan Africa. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Water Project. Poverty and Water. 2021. Available online: https://thewaterproject.org/why-water/poverty (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Holtz, L.; Golubski, C. Addressing Africa’s Extreme Water Insecurity. 2021. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/blog/africa-in-focus/2021/07/23/addressing-africas-extreme-water-insecurity/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Varma, S.; Namara, R.E. Promoting micro irrigation technologies that reduce poverty. Water Policy Brief. 2006, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, A. Can Technology Intervention Quench the Thirst of India’s Drought-Hit Areas? 2016. Available online: https://yourstory.com/2016/08/technology-irrigation-india/amp (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Bhatnagar, S. Micro Irrigation in India: Present Scenario, Types, Government Initiatives & Challenges. 2021. Available online: https://krishijagran.com/agripedia/micro-irrigation-in-india-present-scenario-types-government-initiatives-challenges/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Nakawuka, P.; Langan, S.; Schmitter, P.; Barron, J. A review of trends, constraints and opportunities of smallholder irrigation in East Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 17, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, N. Innovation: Burkina Faso Is at the Forefront of Micro-Irrigation. 2021. Available online: https://www.theafricareport.com/82432/innovation-burkina-faso-is-at-the-forefront-of-micro-irrigation/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Namara, R.E.; Upadhyay, B.; Nagar, R. Adoption and Impacts of Microirrigation Technologies: Empirical Results from Selected Localities of Maharashtra and Gujarat States of India; Research Report 93; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Q.S.W.; Dkhar, N.B. Critical Policy Interventions to Fast Forward Micro Irrigation in India; TERI Policy Brief; The Energy and Resources Institute: New Delhi, India, 2019; Available online: https://www.teriin.org/sites/default/files/2019-07/Critical-Policy-Interventions-Policy-Brief.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Viswanathan, P.K.; Kumar, M.D.; Narayanamoorthy, A. Micro Irrigation Systems in India: Emergence, Status and Impacts; India Studies in Business and Economics; Springer Science and Business Media: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barati, M.K.; Manivasagam, V.S.; Nikoo, M.R.; Saravanane, P.; Narayanan, A.; Manalil, S. Rainfall Variability and Rice Sustainability: An Evaluation Study of Two Distinct Rice-Growing Ecosystems. Land 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IWMI. Upscaling Micro-Irrigation in the Indian States of Odisha and Assam: Recommendations Based on Field Evidence. Policy Brief. 2023. Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/bitstream/handle/10568/130174/RESILIENCE%20Project%20-%20Policy%20brief.pdf?sequence=6&isAllowed=y (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Mani, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Chonabayashi, S.; Markandya, A.; Mosier, T. South Asia’s Hotspots: Impact of Temperature and Precipitation Changes on Living Standards; South Asia Development Matters; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/28723 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- ConserWater Technologies. FlyBird Farm Innovations and ConserWater Technologies Announce Partnership to Bring Precision Agriculture to Indian Farmers. 2018. Available online: https://www.pr.com/press-release/762047 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Satish, K.S. A Journey from Space to Earth. 2019. Available online: https://medium.com/ciie/a-journey-from-space-to-earth-3c76ccad87eb (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Sehgal Foundation. Micro-Irrigation for Agriculture and Sustainable Development. 2021. Available online: https://www.smsfoundation.org/micro-irrigation-for-agriculture-and-sustainable-development/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Birkenholtz, T. Assessing India’s drip-irrigation boom: Efficiency, climate change and groundwater policy. Water Int. 2017, 42, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahinipati, C.S.; Viswanathan, P.K. Can Micro-Irrigation Technologies Resolve India’s Groundwater Crisis? Reflections from Dark-Regions in Gujarat. Int. J. Commons 2019, 13, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenholtz, T. Infrastructuring drip irrigation: The gendered assembly of farmers, laborers and state subsidy programs. Environ. Plan. 2023, 6, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.; Thomas, B. Why is adoption of micro-irrigation slow in India? A review. Dev. Pract. 2023, 33, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B.; Merrey, D.J.; Kamara, A.B.; Van Koppen, B.; Penning de Vries, F.; Boelee, E.; Makombe, G. Experiences and Opportunities for Promoting Small–Scale/Micro Irrigation and Rainwater Harvesting for Food Security in Ethiopia; Working Paper 98; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005; 86p. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, R.O.C.; Kalungu, J.W.; Coelho, R.D. Irrigation technology in South Africa and Kenya. Ciência Rural Santa Maria 2010, 40, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opanda, S. How to Improve Micro Irrigation in Africa. 2021. Available online: https://intpolicydigest.org/how-to-improve-micro-irrigation-in-africa/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- International Finance Bank. Impact of Efficient Irrigation Technology on Small Farmers. 2015. Available online: https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/1f630d98-dabc-41e4-9650-b8809d620664/Impact+of+Efficient+Irrigation+Technology+on+Small+Farmers+-+IFC+Brochure.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CVID=lKbEzwG (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Altchenko, Y.; Villholth, K.G. Mapping irrigation potential from renewable groundwater in Africa—A quantitative hydrological approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinaga, J. The Adoption of Micro Irrigation Technologies (Private Sector Participation in Irrigation Development); The KickStart Experience; Kickstart International: Nairobi, Kenya, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barghouti, S.; Moigne, G.L. Irrigation in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Development of Public and Private Systems. 1990. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/603761468741626544/pdf/multi-page.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Felter, F.C.; Robinson, K. Water Stress: A Global Problem That’s Getting Worse. 2021. Available online: https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/water-stress-global-problem-thats-getting-worse (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Takouleu, J.M. EGYPT: $11.6 Million to Modernise Several Irrigation Systems in the North. 2020. Available online: https://www.afrik21.africa/en/egypt-11-6-million-to-modernise-several-irrigation-systems-in-the-north/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- The World Bank. Project Appraisal Document on A Proposed Loan in the Amount Of Us$100 Million to the Arab Republic of Egypt for A Farm-Level Irrigation Modernization Project November 16, 2010. 2010. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/656761468028446658/pdf/533490PAD0P1171OFFICIAL0USE0ONLY191.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- The World Bank. Modernizing Irrigation Improved Water Security for Farmers in Egypt. 2020. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2020/04/01/modernizing-irrigation-improved-water-security-for-farmers-in-egypt (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Mango, N.; Makate, C.; Tamene, L.; Mponela, P.; Ndengu, G. Adoption of Small-Scale Irrigation Farming as a Climate-Smart Agriculture Practice and Its Influence on Household Income in the Chinyanja Triangle, Southern Africa. Land 2018, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, N.; Makate, C.; Tamene, L.; Mponela, P.; Ndengu, G. Impact of the adoption of conservation practices on cereal consumption in a maize-based farming system in the Chinyanja Triangle, Southern Africa. Sustain. Futures 2020, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makate, C.; Makate, M.; Mango, N. Smallholder Farmers’ Perceptions on Climate Change and the Use of Sustainable Agricultural Practices in the Chinyanja Triangle, Southern Africa. Soc. Sci. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amede, T.; Desta, L.T.; Harris, D.; Kizito, F.; Cai, X. The Chinyanja Triangle in the Zambezi River Basin, Southern Africa: Status of, and Prospects for, Agriculture, Natural Resources Management and Rural Development; WLE Research for Development (R4D) Learning Series 1; CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE); International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2014; 32p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myburgh, M.; Brown, J. The Potential of Information and Communication Technology as an Enabler for Agricultural and Community Development in the Chinyanja Triangle. In Proceedings of the Agribusiness in Sustainable Natural African Plant Products (ASNAPP), Dennesig, South Africa, 14–16 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Makate, C.; Makate, M.; Mango, N. Sustainable agriculture practices and livelihoods in pro-poor smallholder farming systems in southern Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mponela, P.; Tamene, L.; Ndengu, G.; Magreta, R.; Kihara, J.; Mango, N. Determinants of integrated soil fertility management technologies adoption by smallholder farmers in the Chinyanja Triangle of Southern Africa. Land Use Policy 2016, 59, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senzanje, A.; Mapedza, E.; Lautze, J.; Van Koppen, B. Agricultural Water Management Interventions (Awmi) for Sustainable Agricultural Intensification (SAI) in the Chinyanja Triangle Area of Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia. 2015. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/4382 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Kulecho, I.K.; Weatherhead, E.K. Reasons for smallholder farmers discontinuing with low-cost micro-irrigation: A case study from Kenya. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyama, J. Irrigation Investment and Market Analysis Study. Final Report (Background Paper) Submitted to Agribusiness Initiative Trust Uganda Ltd. 2018. Available online: https://www.abi.co.ug/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Irrigation-Investment-and-Market-Analysis-Study-MAIN-REPORT-FINAL-July-18-2018.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Opio, M.; Mwesigwa, D. Embracing drip irrigation technology to stimulate smart farming: A study in Dokolo District, mid-north Uganda. Int. J. Interdiscip. Res. Innov. 2020, 9, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Byiringo, E.; Jones, M.; Kondylis, F.; Loeser, J.; Magruder, J.; Ndahimana, C. Impacts, Maintenance and Sustainability of Irrigation in Rwanda; 3ie Impact Evaluation Report 112; International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie): New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resilient Food Systems. Investment in Irrigation Unlocks Agricultural Potential for Small-Scale Farmers in Burundi. 2021. Available online: https://www.resilientfoodsystems.co/news/investment-in-irrigation-unlocks-agricultural-potential-for-small-scale-farmers-in-burundi (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Balasubramanya, S.; Buisson, M.-C.; Mitra, A.; Stifel, D. Price, credit or ambiguity? Increasing small-scale irrigation in Ethiopia. World Dev. 2023, 163, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, G.T.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Veldwisch, G.J.; Grum, B.; Ritsema, C.J. Irrigation development and management practices in Ethiopia: A systematic review on existing problems, sustainability issues and future directions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshete, D.G.; Sinshaw, B.G.; Legese, K.G. Critical review on improving irrigation water use efficiency: Advances, challenges, and opportunities in the Ethiopia context. Water-Energy Nexus 2020, 3, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitku, D.T.; Adamite, T.F.; Tefera, A.H. Verification and Demonstration of Low-Cost and Appropriate Micro-Irrigation System for Crop Production Under Smallholder Farmers Condition in Pawe District of Metekel Zone. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2022, 9, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Irrigation Policy and Strategy Guidelines for Nigeria; Report Prepared for the Federal Ministry of Water Resources, Department of Irrigation & Drainage, Abuja; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Akudugu, M.A.; Millar, K.K.; Akuriba, M.A. The Livelihoods Impacts of Irrigation in Western Africa: The Ghana Experience. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittoh, S.; Bhattarai, M.; Akuriba, M.A. Micro Irrigation-Based Vegetable Farming for Income, Employment and Food Security in West Africa. In Global Food Security: Emerging Issues and Economic Implications; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 177–200. [Google Scholar]
- Manalil, S.; Flower, K. Soil water conservation and nitrous oxide emissions from different crop sequences and fallow under Mediterranean conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 143, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, E.; El Didi, H. Considering Gender in Irrigation: Technology Adoption for Women Farmers. 2019. Available online: https://wle.cgiar.org/thrive/2019/07/01/considering-gender-irrigation-technology-adoption-women-farmers (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- AFDB; FAO; IFAD; IWMI; The World Bank. Investment in Agricultural Water for Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Collaborative Program. 2007. Available online: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/RPDLPROGRAM/Resources/459596-1170984095733/synthesisreport.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- World Bank. Africa Region: Irrigation Business Plan; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, O.; Bolarin, O.; Oyewale, A.; Kehinde, O. Impact of irrigation technology use on crop yield, crop income and household food security in Nigeria: A treatment effect approach. AIMS Agric. Food 2018, 3, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, T.V. Solar Pumps: A Nondescript Village in Gujarat Shows the Way. 2018. Available online: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/solar-pumps-a-nondescript-village-in-gujarat-shows-the-way/article22694612.ece (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Hartung, H.; Pluschke, L. The Benefits and Risks of Solar-Powered Irrigation—A Global Overview. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/I9047EN/i9047en.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- ICID. Solar Powered Irrigation Systems in India: Lessons for Africa Through a FAO Study Tour Draft Report International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage. 2019. Available online: https://www.icid.org/FAO-SPIS-Report.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Suman, S. Evaluation and Impact Assessment of the Solar Irrigation Pumps Program in Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh; Report Prepared for Shri Shakti Alternative Energy Ltd.; Sampling Research: New Delhi, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- TNN. Dhundi Farmers Receive First Payment for Their ‘Solar Crop’. 2016. Available online: http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/53920747.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Bhattacharya, P.; Banerjee, P. Solar-Powered Automatic Irrigation System: A Giant Leap towards Sustainable Agriculture. Agric. Lett. 2020, 01, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- CCAFS. Progressing towards Climate Resilient Agriculture; Top Ten Success Stories From CCAFS in South Asia; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) of South Asia: New Delhi, India, 2017; Available online: https://repository.cimmyt.org/bitstream/handle/10883/19366/59321.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Hamidat, A.; Benyoucef, B.; Hartani, T. Small-scale irrigation with photovoltaic water pumping system in Sahara regions. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REEEP. Solar-Powered Irrigation in Kenya: Future Pump. 2018. Available online: https://www.reeep.org/projects/solar-powered-irrigation-kenya-futurepump (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- ESI Africa. Solar Pumping Systems Address Dual Water and Energy Challenge. 2021. Available online: https://www.esi-africa.com/industry-sectors/renewable-energy/solar-pumping-systems-address-dual-water-and-energy-challenge/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Yahya, H.; Sambo, A. Design and installation of solar photovoltaic powered water pumping system at Usmanu Danfodiyo University, Sokoto. Renew. Energy 1995, 6, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A.; Taha, A.Z. Performance of submersible PV solar pumping systems under conditions in the Sudan. Renew. Energy 1995, 6, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoo, M.; Lefore, N.; Schmitter, P.; Barron, J.; Gebregziabher, G. Business Model Scenarios and Suitability: Smallholder Solar Pump-Based Irrigation in Ethiopia. Agricultural Water Management—Making a Business Case for Smallholders; IWMI Research Report 172; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2018; 67p. [Google Scholar]
- Gadeberg, M. Solar-Powered Irrigation Could Boost Climate Resilience for Millions. 2020. Available online: https://agrilinks.org/post/solar-powered-irrigation-could-boost-climate-resilience-millions (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Wazed, S.; Hughes, B.; O’Connor, D.; Calautit, J. A review of sustainable solar irrigation systems for Sub-Saharan Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1206–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S. Solar Pump Cooperative Supports Climate-Smart Agriculture in Gujarat. Lessons and Good Practice in Climate Action. 2020. Available online: https://cdkn.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Dhundi-solar-pumps-case-study-2.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- ESI Africa. Webinar Recording: Solar-Powered Water Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture in SSA. 2021. Available online: https://www.esi-africa.com/industry-sectors/generation/solar/solar-powered-water-solutions-for-sustainable-agriculture-in-ssa/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Otoo, M.; Schmitter, P. Opinion: How to Keep Africa’s Boom in Solar-Powered Irrigation from Going Bust. 2018. Available online: https://www.devex.com/news/opinion-how-to-keep-africa-s-boom-in-solar-powered-irrigation-from-going-bust-92398 (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Shah, T.; Durga, N.; Verma, S.; Rathod, R. Promoting Solar Power as a Remunerative Crop. Econ. Political Wkly. 2017, LII, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Ringler, C.; Mondal, M.A.H. Solar or Diesel: A Comparison of Costs for Groundwater-Fed Irrigation in Sub-Saharan Africa Under Two Energy Solutions. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.; Rijsberman, F.; Smith, M. Is Solar Irrigation Set To Take Over Africa? 2019. Available online: https://ccafs.cgiar.org/news/solar-irrigation-set-take-over-africa (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- DSUUSM. Dhundi Solar Energy Producers’ Cooperative Society; Tri-Annual Report, 2015–2018; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lankal, 2019; 28p, Available online: http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/iwmi-tata/PDFs/dhundi_solar_energy_producers_cooperative_society-tri-annual_report-2015-18.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Shim, H. Case Study: Solar-Powered Irrigation Pumps in India—Capital Subsidy Policies and the Water-Energy Efficiency Nexus; Global Green Growth Institute: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jörgensen, K.; Mishra, A.; Sarangi, G.K. Multilevel climate governance in India: The role of the states in climate action planning and renewable energies. JIE 2015, 12, 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, A.; Thiel, A.; Roggero, M. Institutional performance of collective irrigation systems: A fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis in the nile delta of Egypt. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwadzingeni, L.; Mugandani, R.; Mafongoya, P. Localized Institutional Actors and Smallholder Irrigation Scheme Performance in Limpopo Province of South Africa. Agriculture 2020, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balana, B.B.; Sanfo, S.; Barbier, B.; Williams, T.; Kolavalli, S. Assessment of flood recession agriculture for food security in northern Ghana: An optimization modelling approach. Agric. Syst. 2019, 173, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederveen, S.; van Steenbergen, A.M.F.; Almirew, T.; Geleta, Y. Flood Based Farming Practices in Ethiopia: Status and Potential. 2011. Available online: https://www.waterethiopia.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/Flood-Based-Farming-Pr3actices-in-Ethiopia-Status-and-Potential.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Singh, R.; Patel, S.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, G.S. Assessment of flood recession farming for livelihood provision, food security and environmental sustainability in the Ganga River Basin. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 3, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, B.; Kachari, A.; Das, D.N. Assessment of Water Quality in Relation to Fishery Perspective in Flood Plain Wetlands of Subansiri River Basin Assam, India. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 10, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Motsumi, S.; Magole, L.; Kgathi, D. Indigenous knowledge and land use policy: Implications for livelihoods of flood recession farming communities in the Okavango. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 50–52, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S. Challenges and Opportunities for Agricultural Water Management in West and Central Africa: Lessons from IFAD Experience. 2012. Available online: http://www.adaptationlearning.net/sites/default/files/resource-files/Challenges%20and%20opportunities%20for%20agricultural%20water%20management%20in%20West%20and%20Central%20Africa_lessons%20from%20IFAD%20experience_2.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Barbier, B.; Ouedraogo, H.; Dembélé, Y.; Yacouba, H.; Barry, B.; Jamin, J.Y. L’agriculture irriguée dans le Sahel ouest-africain. Diversité des pratiques et des performances. Cah. Agric. 2011, 20, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczewski, A.; Hertzog, T.; Dosso, M.; Jouve, P.; Jamin, J.Y. Can irrigation replace flood recession for crops? The lake Horo depression (Northern Mali). Agric. Noteb. 2011, 20, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bendsen, H. The Dynamics of Land use Systems in Ngamiland: Changing Livelihoods Options and Strategies; University of Botswana Harry Openheimer Okavango Research Centre: Maun, Botswana, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kgathi, D.L.; Bendsen, H.; Blaike, P.; Mbaiwa, J.; Ngwenya, B.; Wilk, J. Rural Livelihoods, Indigenous Knowledge Systems, and Political Economy of Access to Natural Resources in the Okavango Delta; University of Botswana: Maun, Botswana, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mavhura, E. Applying a systems-thinking approach to community resilience analysis using rural livelihoods: The case of Muzarabani district, Zimbabwe. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 25, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sall, M.; Poussin, J.-C.; Bossa, A.Y.; Ndiaye, R.; Cissé, M.; Martin, D.; Bader, J.-C.; Sultan, B.; Ogilvie, A. Water Constraints and Flood-Recession Agriculture in the Senegal River Valley. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidibé, Y.; Williams, T.O.; Kolavalli, S. Flood Recession Agriculture for Food Security in Northern Ghana: Literature Review on Extent, Challenges, and Opportunities; Working Paper 42; International Food Policy Reserach Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Traore, K.; Traore, B.; Synnevåg, G.; Aune, J.B. Intensification of Sorghum Production in Flood Recession Agriculture in Yelimane, Western Mali. Agronomy 2020, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoema. Flood Recession Cropping Area Non-Equipped. 2021. Available online: https://knoema.com/atlas/topics/Water/Irrigation-Water-Management/Flood-recession-cropping-area-non-equipped?type=maps (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Vanderpost, C. Molapo Farming in the Okavango Delta; Fact Sheet 7/2009; Harry Oppenheimer Okavango Research Centre: Maun, Botswana, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coomes, O.T.; Lapointe, M.; Templeton, M.; List, G. Amazon river flow regime and flood recessional agriculture: Flood stage reversals and risk of annual crop loss. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, P. Mitigating Floods for Managing Droughts through Aquifer Storage: An Examination of Two Complementary Approaches; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Bunsen, J.; Rathod, R. Pipe Assisted Underground Taming of Surface Floods: The Experience with Holiyas in North Gujarat; IWMI-TATA Water Policy Research Highlight 2; International Water Management Institute: Anand, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shivakoti, B.R.; Villholth, K.G.; Pavelic, P.; Ross, A. Strategic Use of Groundwater-Based Solutions for Drought Risk Reduction and Climate Resilience in Asia and Beyond; Contributing Paper to GAR 2019; UNDRR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; 20p. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.F.; Pavelic, P. Underground Transfer of Floods for Irrigation (UTFI): Exploring Potential at the Global Scale; IWMI Research Report 176; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.R.; Pavelic, P.; Hanjra, M.A. Underground taming of floods for irrigation (UTFI) in the river basins of South Asia: Institutionalising approaches and policies for sustainable water management and livelihood enhancement. Water Policy 2018, 20, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, P.; Sikka, A.; Alam, M.F.; Sharma, B.R.; Mutuwatte, L.; Eriyagama, N.; Villholth, K.G.; Shalsi, S.; Mishra, V.K.; Jha, S.K.; et al. Utilizing Floodwaters for Recharging Depleted Aquifers and Sustaining Irrigation: Lessons From Multi-Scale Assessments in the Ganges River Basin, India; Groundwater Solutions Initiative for Policy and Practice (GRIPP) Case Profile Series 04; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGWB. Guide on Artificial Recharge to Ground Water; Ministry of Water Resources; Central Ground Water Board: New Delhi, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A. Management of Groundwater as a Common Pool Resource: Case Study of Holiyas in North Gujarat; IWMI-TATA Internship Report; IWMI: Anand, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naireeta Services, Bhungroo. 2018. Available online: www.naireetaservices.com/projects/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Pavelic, P.; Sikka, A.K.; Villholth, K.G. Underground Taming of Floods for Irrigation (UTFI) Controlling Water-Related Disasters through Innovative Underground Storage. Sri Lanka. 2018. Available online: http://gripp.iwmi.org/natural-infrastructure/water-retention-3/underground-taming-of-floods-for-irrigation-utfi-2/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- IWMI, Project: Underground Taming of Floods for Irrigation (UTFI). 2015. Available online: https://utfi.iwmi.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angom, J.; Viswanathan, P.K. Irrigation Technology Interventions as Potential Options to Improve Water Security in India and Africa: A Comparative Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316213
Angom J, Viswanathan PK. Irrigation Technology Interventions as Potential Options to Improve Water Security in India and Africa: A Comparative Review. Sustainability. 2023; 15(23):16213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316213
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngom, Juliet, and P. K. Viswanathan. 2023. "Irrigation Technology Interventions as Potential Options to Improve Water Security in India and Africa: A Comparative Review" Sustainability 15, no. 23: 16213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316213
APA StyleAngom, J., & Viswanathan, P. K. (2023). Irrigation Technology Interventions as Potential Options to Improve Water Security in India and Africa: A Comparative Review. Sustainability, 15(23), 16213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316213





