The Effects of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment Resilience and Its Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Impact of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment System
2.1.1. Negative Impact
2.1.2. Positive Impact
2.2. Urban Ecosystem Resilience
2.2.1. Resilience
2.2.2. Urban Resilience
2.2.3. Urban Ecosystem Resilience
3. Research Design
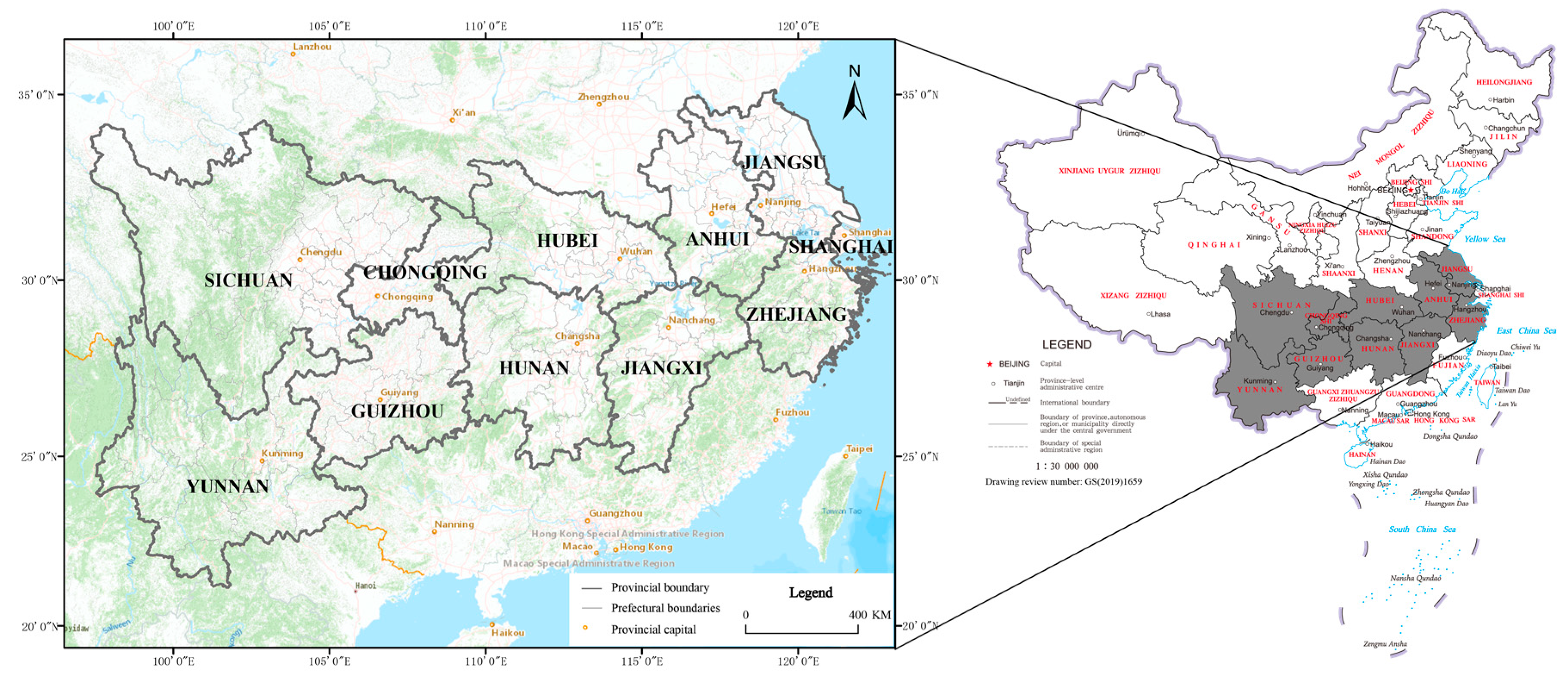
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Evaluation Indicator System of TDI and ERI
3.3.2. Comprehensive Assessment Model (CAM)
3.3.3. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis (BISA)
3.3.4. Spatial Econometric Model
3.3.5. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR)
4. Results
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the TDI and ERI
4.1.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the TDI
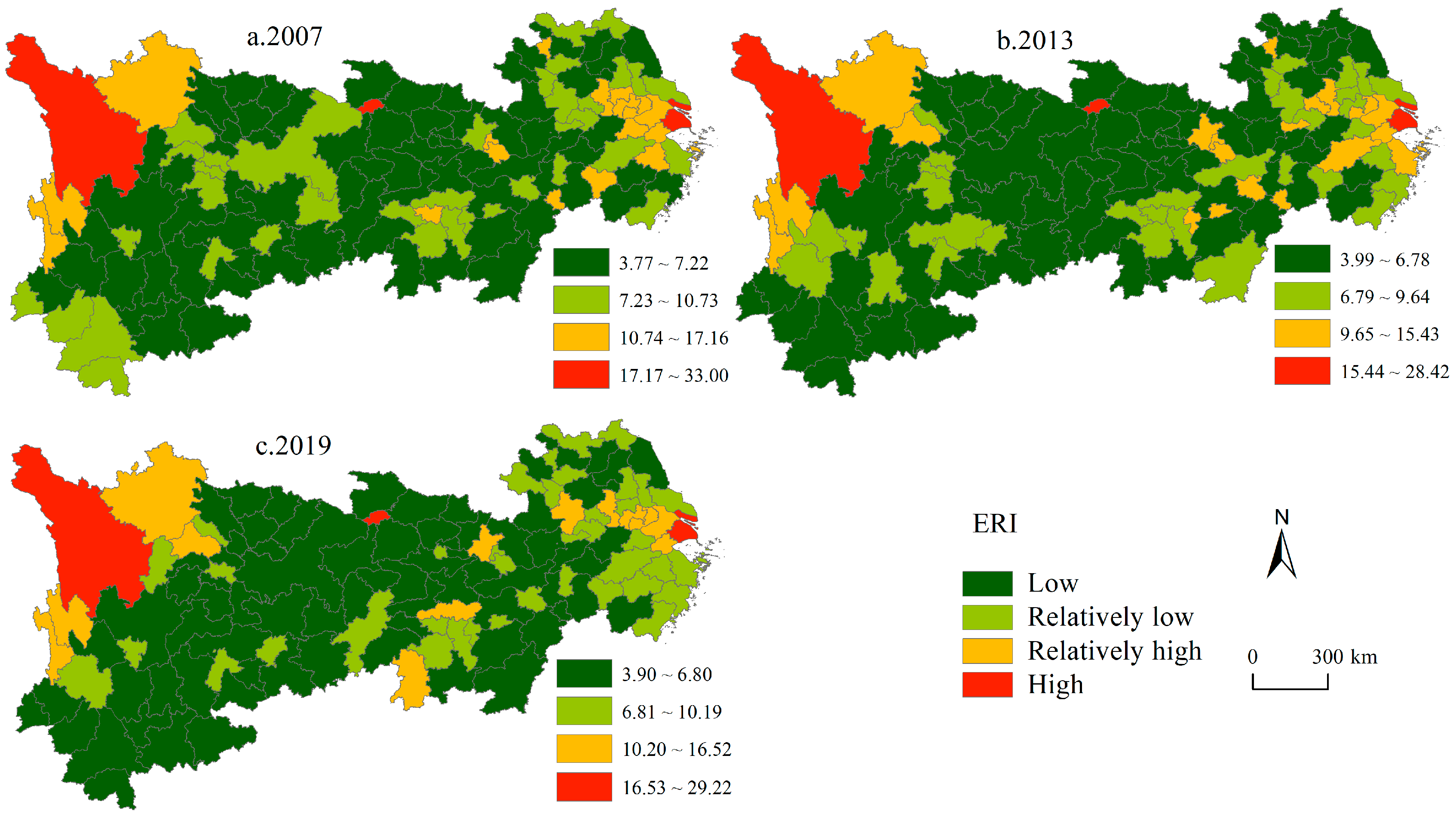
4.1.2. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the ERI
4.2. Spatial Relationship between the TDI and ERI
4.3. The Effect of the TDI on the ERI
4.3.1. Model Construction
4.3.2. Overall Effect Analysis
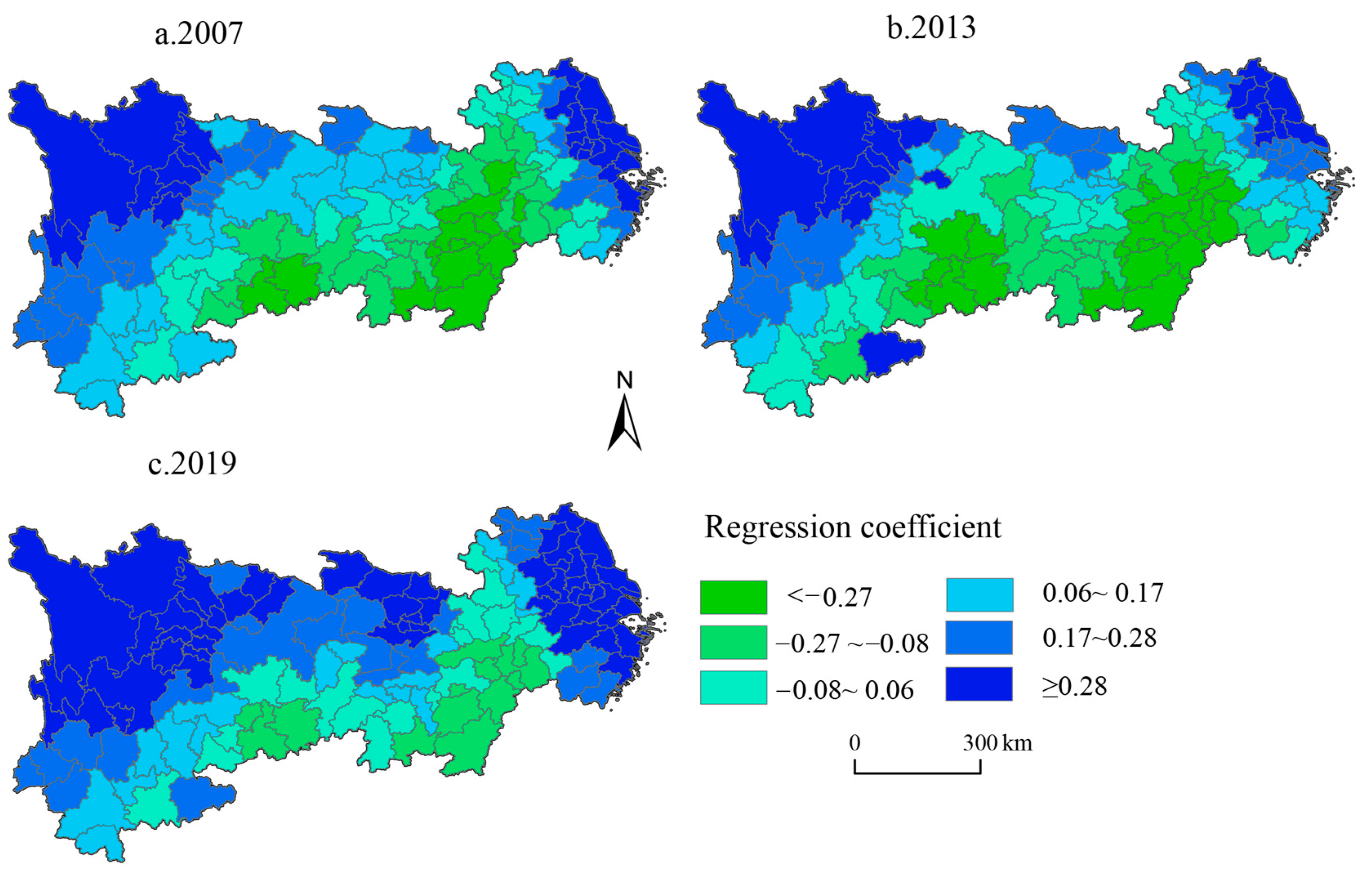
4.3.3. Heterogeneity Analysis of the Effect
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Main Conclusions
6.2. Theoretical Contributions
6.3. Policy Implications
6.4. Limitations and Avenues for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, L.; Ma, E.; Long, H.; Peng, X. Land Use Transition and Its Ecosystem Resilience Response in China during 1990–2020. Land 2023, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Li, Y.P.; Yu, L. Urban agglomeration (Guangzhou-Foshan-Zhaoqing) ecosystem management under uncertainty: A factorial fuzzy chance-constrained programming method. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, G.R.; Elkadi, H.; Meikle, H. Developing a complementary framework for urban ecology. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberley, W.R.; Albert, K. Escalating trends in the urban metabolism of Hong Kong: 1971–1997. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2001, 30, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W. Cultivated land use efficiency and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Assessment of urban ecological resilience and its influencing factors: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China. Land 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaliah, M.M.; Powell, R.B. Ecotourism resilience to climate change in Dana Biosphere Reserve, Jordan. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 26, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsiglio, S. Economic growth and environment: Tourism as a trigger for green growth. Tour. Econ. 2015, 21, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Deng, J.; Song, Z.; Ding, P. Research on environmental impacts of tourism in China: Progress and prospect. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.M.; Hill, W. Impacts of recreation and tourism on plant biodiversity and vegetation in protected areas in Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, L. Assessment of coordinated development between tourism development and resource environment carrying capacity: A case study of Yangtze River economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Brahmasrene, T. Investigating the influence of tourism on economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from panel analysis of the European Union. Tour. Manag. 2013, 38, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, A. The environment-tourism nexus: Influence of market ethics. Ann. Tour. Res. 2009, 36, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, S.A.; Wilson, J. The evolution of coastal tourism destinations: A path plasticity perspective on tourism urbanisation. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S. Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environ. Change 2002, 12, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.W. Tourism and the environment: A geographical perspective. Tour. Geogr. 2000, 2, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beladi, H.; Chao, C.C.; Hazari, B.R.; Laffargue, J.P. Tourism and the environment. Energy Econ. 2009, 31, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W. How to construct system guarantee for economic development of eco-tourism resources based on value compensation. Anthropologist 2015, 22, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushi, E. Sustainable tourism and environment protection in Albania. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2011, 12, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sarah, P.; Zhevelev, H.M. Effect of visitors’ pressure on soil and vegetation in several different micro-environments in urban parks in Tel Aviv. Landscape Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Mahmudul Alam, M.; Haroon Hafeez, M. Effect of tourism on environmental pollution: Further evidence from Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, A. Green innovation for the ecological footprints of tourism in China. Fresh evidence from ARDL approach. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraz. 2023, 36, 2172600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, M.; Sun, Y.Y.; Faturay, F.; Ting, Y.P.; Geschke, A.; Malik, A. The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphin, H.; Sheeran, P.; Pilato, M. Over-tourism and the fall of Venice as a destination. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movono, A.; Dahles, H.; Becken, S. Fijian culture and the environment: A focus on the ecological and social interconnectedness of tourism development. J. Sustain. Tour. 2018, 26, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Mahmood, T.; Idrees, M. Tourism–growth nexus in Pakistan: Evidence from ARDL bounds tests. Econ. Modell. 2013, 35, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Abosedra, S. Small sample evidence on the tourism-led growth hypothesis in Lebanon. Curr. Issues Tour. 2014, 17, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, X.; Tribe, J. Promoting green tourism: The future of environmental awards. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2001, 3, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongbuamai, N.; Bui, Q.; Yousaf, A.U.; Liu, Y. The impact of tourism and natural resources on the ecological footprint: A case study of ASEAN countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19251–19264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, S. The impact of tourism development on the environment in China. Acta Sci. Malay. 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarczyk-Raźniak, A.; Raźniak, P. Are Pueblos Mágicos Really Magic? Tourism Development Program in the Context of the Quality of Life of Town Residents. Land 2021, 10, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Paramati, S.R. The dynamic role of tourism investment on tourism development and CO2 emissions. Ann. Tour. Res. 2017, 66, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motesharrei, S.; Rivas, J.; Kalnay, E.; Asrar, G.R.; Busalacchi, A.J.; Cahalan, R.F.; Cane, M.A.; Colwell, R.R.; Feng, K.; Franklin, R.S.; et al. Modeling sustainability: Population, inequality, consumption, and bidirectional coupling of the Earth and Human Systems. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 470–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining urban resilience: A review. Landsc. Urban Plan 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raźniak, P.; Dorocki, S.; Winiarczyk-Raźniak, A. Economic resilience of the command and control function of cities in Central and Eastern Europe. Acta Geogr. Slov. 2020, 60, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raźniak, P.; Dorocki, S.; Winiarczyk-Raźniak, A. Permanence of economic potential of cities based on sector development. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masik, G.; Grabkowska, M. Practical dimension of urban and regional resilience concepts: A proposal of resilience strategy model. Miscellanea Geogr. 2020, 24, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baho, D.L.; Allen, C.R.; Garmestani, A.S.; Fried-Petersen, H.B.; Renes, S.E.; Gunderson, L.H.; Angeler, D.G. A quantitative framework for assessing ecological resilience. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Carstensen, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, E.; Duarte, C.M. Ecological thresholds and regime shifts: Approaches to identification. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, B. Problematizing resilience: Implications for planning theory and practice. Cities 2015, 43, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.R.; Angeler, D.G.; Garmestani, A.S.; Gunderson, L.H.; Holling, C.S. Panarchy: Theory and application. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, I.; Petchey, O.L.; Montoya, J.M.; Jackson, A.L.; McNally, L.; Viana, M.; Healy, K.; Lurgi, M.; O’Connor, N.E.; Emmerson, M.C. On the dimensionality of ecological stability. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adger, W.N.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.R.; Rockström, J. Social-ecological resilience to coastal disasters. Science 2005, 309, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C. Resilience: The emergence of a perspective for social–ecological systems analyses. Global Environ. Change 2006, 16, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Benayas, J.; Tilbury, D. Towards an urban resilience index: A case study in 50 Spanish cities. Sustainability 2016, 8, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Evaluating urban ecosystem resilience using the DPSIR framework and the ENA model: A case study of 35 cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C. Increasing urban ecological resilience based on ecological security pattern: A case study in a resource-based city. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.G.; Peel, D.; Duck, R.W. Towards a social–ecological resilience framework for coastal planning. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Hao, X.; Hua, D.; Hao, H. Assessment of ecosystem resilience in Central Asia. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 195, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Zhang, A.; Wen, L. Can China’s resource-saving and environmentally friendly society really improve the efficiency of industrial land use? Land 2021, 10, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Lei, Z.; Zhou, X. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of the resilience of tourism environmental systems in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Zheng, L.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of tourism development efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Z. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution of wastewater discharge in Yangtze River Economic Zone from 2002 to 2015. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 110, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; An, Y.; Jiang, C.; Tan, H.; Gong, G. Coupling and interaction between tourism eco-efficiency and new urbanization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Based on the perspective of uncoupling coordination. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 25, 13171–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Fakhraee, A.; Karami, S.; Kamari, Z.J. A quantitative approach to estimating carrying capacity in determining the ecological capability of urban tourism areas (Case study: Eram Boulevard of Hamadan city). Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2015, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Yun-Chao, L.I.; Zhang, C.P. Analysis of the effect of social support on sustainable competitive advantage in tourism industry-Based on the perspective of living-ecology-production integrated space. Rev. Cercet. Interv. Soc. 2020, 71, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, V.S.; Yang, Y.; Li, G. Where can tourism-led growth and economy-driven tourism growth occur? J. Travel Res. 2019, 58, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Aydın, S. An empirical note on tourism and sustainable development nexus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 34515–34527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.X.; Bao, J.G. Tourism gentrification in Shenzhen, China: Causes and socio-spatial consequences. Tour. Geogr. 2015, 17, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, D.; Vukoicic, D.; Milincic, M.J. Tourism and sustainable development of rural settlements in protected areas—Example NP Kopaonik (Serbia). Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F. A resource market and product analysis for marine tourism development. J. Coastal Res. 2020, 107, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, J. Spatio-temporal evolution and obstacle factors analysis of tourism ecological security in Huanggang Dabieshan UNESCO Global Geopark. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, L.; Niu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Development trajectory for the temporal and spatial evolution of the resilience of regional tourism environmental systems in 14 cities of Gansu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65094–65115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, L.; Guan, X.; Ye, S. Quantitative evaluation and prediction analysis of the healthy and sustainable development of China’s sports industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Quantitative methods and applications in GIS. Environ. Plan. 2008, 35, 757–758. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Tang, D.S. Multi-objective linear programming for optimal water allocation based on satisfaction and economic criterion. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Lv, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Ecological resilience assessment of an arid coal mining area using index of entropy and linear weighted analysis: A case study of Shendong Coalfield, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Wu, D.; Pan, S.; Chen, W. Spatial correlation among cultivated land intensive use and carbon emission efficiency: A case study in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43341–43360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, R.R. Advances in Spatial Econometrics: Methodology, Tools and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 45, pp. 866–870. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, M.C. The geography of parameter space: An investigation of spatial non-stationarity. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sys. 1996, 10, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics. Rev. Econ. Polit. 2008, 123, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fik, T. Spatial effects in regional tourism growth. Ann. Tour. Res. 2014, 46, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagonigro, R.; Martori, J.C.; Apparicio, P. Understanding Airbnb spatial distribution in a southern European city: The case of Barcelona. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 115, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, S.; Kim, J.W. Spatial is special: The need to consider spatial effects in leisure research. Leisure Sci. 2019, 44, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, L. Assessment framework of provincial carbon emission peak prediction in China: An empirical analysis of Hebei province. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Henao, J.A.; Vivanco, D.F.; Hernandez-Riveros, J.A. Technological change and the rebound effect in the STIRPAT model: A critical view. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.J.; Sun, T.; Zhang, K.; Guo, W. Research on rural nonpoint source pollution in the process of urban-rural integration in the economically-developed area in China based on the improved STIRPAT model. Sustainabilty 2015, 7, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lv, Z. Do spatial spillovers matter? Estimating the impact of tourism development on CO(2) emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 32777–32794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, B.; Pérez-Barahona, A.; Strobl, E. Dynamic implications of tourism and environmental quality. J. Pub. Econ. Theory 2019, 21, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.F.; Gan, Y.; Ferreira-Lopes, A. An empirical analysis of the influence of macroeconomic determinants on World tourism demand. Tour. Manag. 2017, 61, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkova, L.; Yukhnovska, Y. Comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the influence of factors on the formation and development of the tourism industry in Ukraine. Bus. Inform. 2020, 2, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaobin, M.; Biao, S.; Guolin, H.; Xing, Z.; Li, L. Evaluation and spatial effects of tourism ecological security in the Yangtze River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tan, H.; Zhao, P.; Gao, L.; Ma, D.; Xiao, Y. What was the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of high-quality development in China? A case study of the Yangtze River economic belt based on the ICGOS-SBM model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Baylon Verances, J.; Song, W. The tourism-environment causality. Int. J. Tour. Sci. 2009, 9, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhong, L.; Ng, P. Factors that Influence the Tourism Industry’s Carbon Emissions: A Tourism Area Life Cycle Model Perspective. Energy Policy 2017, 109, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, W.; Yang, G. Green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry from the perspective of shared inputs: Dynamic evolution and combination improvement paths. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Hou, B. The Influencing Effect of Tourism Economy on Green Development Efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Target | Guideline (Weight) | Indicator | Indicator Description (Attribute) | Weight | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism development (TDI) | Tourism Market scale (0.3093) | X1 Total tourism income | Reflecting the economic condition of tourism (+) | 0.1511 | [64] |
| X2 Total tourist trips | Reflecting the scale of visitors (+) | 0.1139 | [64] | ||
| X3 Per capita tourist consumption | Per capita tourist consumption capacity (+) | 0.0443 | [64] | ||
| Resources and products of tourism (0.3971) | X4 High-level tourist attraction | Expressed by the number of Grade 3A or above (+) | 0.1184 | [30] | |
| X5 state-level tourism resources | The sum of National Forest Park, National Geopark, National Scenic Spot, and World Heritage Site (+) | 0.0759 | [30] | ||
| X6 National intangible cultural heritage | Represents the integration of urban culture and tourism resources (+) | 0.1181 | [30] | ||
| X7 Number of museums for 10,000 people | 0.0846 | [30] | |||
| Contribution of tourism (0.2936) | X8 Tourism Industry Dependency | Total tourism income/ GDP (+) | 0.0947 | [64] | |
| X9 Elasticity of urban residents’ tourism income | Reflects the contributions that tourism makes to the revenues of urban and rural residents (+) | 0.0796 | [64] | ||
| X10 Elasticity of rural residents’ tourism income | 0.0210 | [64] | |||
| X11 Ratio of employees of tertiary industry | Tourism’s contribution to employment (+) | 0.0237 | [64] | ||
| X12The proportion of tourism income in tertiary sector income | Tourism’s contribution to the optimization of industrial structure (+) | 0.0746 | [64] | ||
| Resilience of eco- environment (ERI) | Pressure and resistance (0.5014) | Y1 Population density | The pressure of population size on the ecosystem (−) | 0.0409 | [47] |
| Y2 Economy density | Ecosystem perturbation by economic growth (−) | 0.1514 | [47] | ||
| Y3 Land use intensity | Area of built-up /Urban land area (−) | 0.0811 | [47] | ||
| Y4 Wastewater discharge intensity | The pressure of wastewater on the ecosystem (−) | 0.1040 | [47] | ||
| Y5 Exhaust emission intensity | Exhaust pressure on ecosystems (−) | 0.1240 | [47] | ||
| Adjustment and adaptability (0.1945) | Y6 Harmless disposal rate of domestic waste | Adaptation of cities to ecosystem pressures through solid waste, domestic wastewater treatment, and waste utilization (+) | 0.0029 | [65] | |
| Y7 Per capita domestic waste removal volume | 0.1778 | [65] | |||
| Y8 The rate of domestic wastewater treatment | 0.0064 | [65] | |||
| Y9 Usage rate of solid waste | 0.0074 | [65] | |||
| Flexibility and recovery (0.3041) | Y10 Excellent air quality rate | Expressed by the number of days to reach level 2 (+) | 0.0076 | [47] | |
| Y11 The rate of greenery coverage in the built-up region | Indicates the greening of the city’s environment (+) | 0.0042 | [47] | ||
| Y12 Park area per capita | Indicates the green leisure space of the city (+) | 0.0136 | [47] | ||
| Y13 Water resources per capita | Indicates the water carrying capacity (+) | 0.1925 | [47] | ||
| Y14 Investment of the Environment Fund as a percentage of financial expenditure | Indicates the environmental management level (+) | 0.0862 | [47,66] |
| Variable | 2007 | 2013 | 2019 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | SLM | SEM | SEMLD | OLS | SLM | SEM | SEMLD | OLS | SLM | SEM | SEMLD | |
| lnTDI | 0.20 *** (0.00) | 0.18 *** (0.00) | 0.17 *** (0.00) | 0.19 *** (0.00) | 0.13 ** (0.02) | 0.11 ** (0.04) | 0.10 * (0.09) | 0.12 ** (0.05) | 0.20 *** (0.00) | 0.19 *** (0.00) | 0.24 *** (0.00) | 0.20 *** (0.00) |
| lnPOP | 0.03 (0.30) | 0.02 (0.40) | 0.02 (0.48) | 0.02 (0.43) | 0.03 (0.28) | 0.02 (0.31) | 0.02 (0.32) | 0.03 (0.33) | 0.03 (0.19) | 0.03 (0.23) | 0.02 (0.30) | 0.03 (0.25) |
| lnGDP | −0.01 (0.72) | −0.03 (0.36) | −0.04 (0.31) | −0.03 (0.45) | −0.05 (0.16) | −0.05 * (0.08) | −0.06 * (0.08) | −0.05 * (0.08) | −0.01 (0.69) | −0.02 (0.45) | −0.04 (0.22) | −0.02 * (0.08) |
| lnOPEN | 0.05 ** (0.04) | 0.04 * (0.09) | 0.03 (0.21) | 0.05 * (0.06) | 0.10 *** (0.00) | 0.09 *** (0.00) | 0.10 *** (0.00) | 0.10 *** (0.00) | 0.04 * (0.06) | 0.03 (0.14) | 0.02 (0.30) | 0.08 ** (0.03) |
| Spatial-lag | 0.36 *** (0.00) | 0.35 *** (0.00) | 0.34 *** (0.00) | 0.35 *** (0.00) | 0.36 *** (0.00) | 0.37 *** (0.00) | ||||||
| Spatial-err | 0.36 *** (0.00) | 0.36 *** (0.00) | 0.34 *** (0.00) | 0.34 *** (0.00) | 0.43 *** (0.00) | 0.41 *** (0.00) | ||||||
| Constant | 1.91 *** (0.00) | 1.31 *** (0.00) | 2.09 *** (0.00) | 1.87 *** (0.00) | 2.34 *** (0.00) | 1.73 *** (0.00) | 2.50 *** (0.00) | 2.33 *** (0.00) | 1.56 *** (0.00) | 0.96 *** (0.01) | 1.68 *** (0.00) | 1.77 *** (0.00) |
| Moran’s I | 2.89 *** (0.00) | 3.37 *** (0.00) | 4.14 *** (0.00) | |||||||||
| LM (lag) | 11.96 *** (0.00) | 9.63 *** (0.00) | 14.96 *** (0.00) | |||||||||
| Robust LM (lag) | 10.26 *** (0.00) | 0.98 (0.32) | 1.52 (0.22) | |||||||||
| LM (error) | 6.33 *** (0.01) | 8.66 *** (0.00) | 13.47 *** (0.00) | |||||||||
| Robust LM (error) | 4.62 ** (0.03) | 0.02 (0.89) | 0.02 (0.87) | |||||||||
| LM (lag and error) | 16.58 *** (0.00) | 9.65 *** (0.00) | 14.99 *** (0.00) | |||||||||
| R2 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| LogL | −55.45 | −50.02 | −50.64 | −52.32 | −38.04 | −33.48 | −33.89 | −33.56 | −38.97 | −32.87 | −32.41 | −32.33 |
| AIC | 120.90 | 112.03 | 115.29 | 118.94 | 86.08 | 78.95 | 77.78 | 76.57 | 87.94 | 77.75 | 74.81 | 73.81 |
| SC | 135.24 | 129.24 | 135.36 | 133.26 | 100.42 | 96.16 | 92.12 | 89.43 | 102.28 | 94.95 | 89.15 | 88.67 |
| Obs. | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, X. The Effects of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment Resilience and Its Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152216124
Wang K, Chen X, Lei Z, Zhao S, Zhou X. The Effects of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment Resilience and Its Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(22):16124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152216124
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kun, Xiangtai Chen, Zhenxian Lei, Songxin Zhao, and Xiao Zhou. 2023. "The Effects of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment Resilience and Its Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China" Sustainability 15, no. 22: 16124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152216124
APA StyleWang, K., Chen, X., Lei, Z., Zhao, S., & Zhou, X. (2023). The Effects of Tourism Development on Eco-Environment Resilience and Its Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sustainability, 15(22), 16124. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152216124










