Analysis of the Degradation Characteristics of Chlorpyrifos in an Electrochemically Constructed Wetland Coupled System under Different Pesticide Exposure Conditions and Microbial Community Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
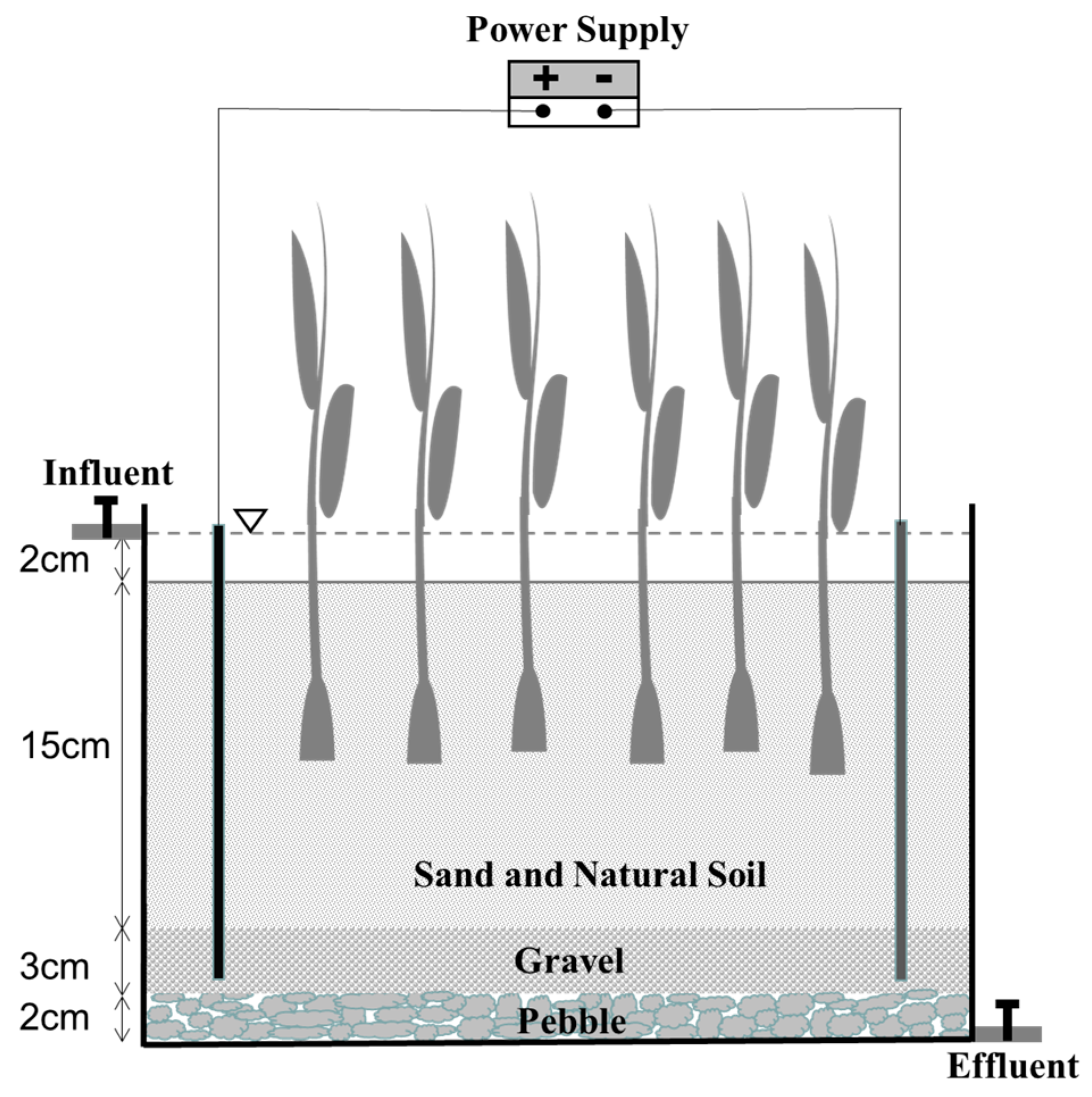
2.1. Experimental Device
2.2. Experimental Water
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Analysis and Data Processing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
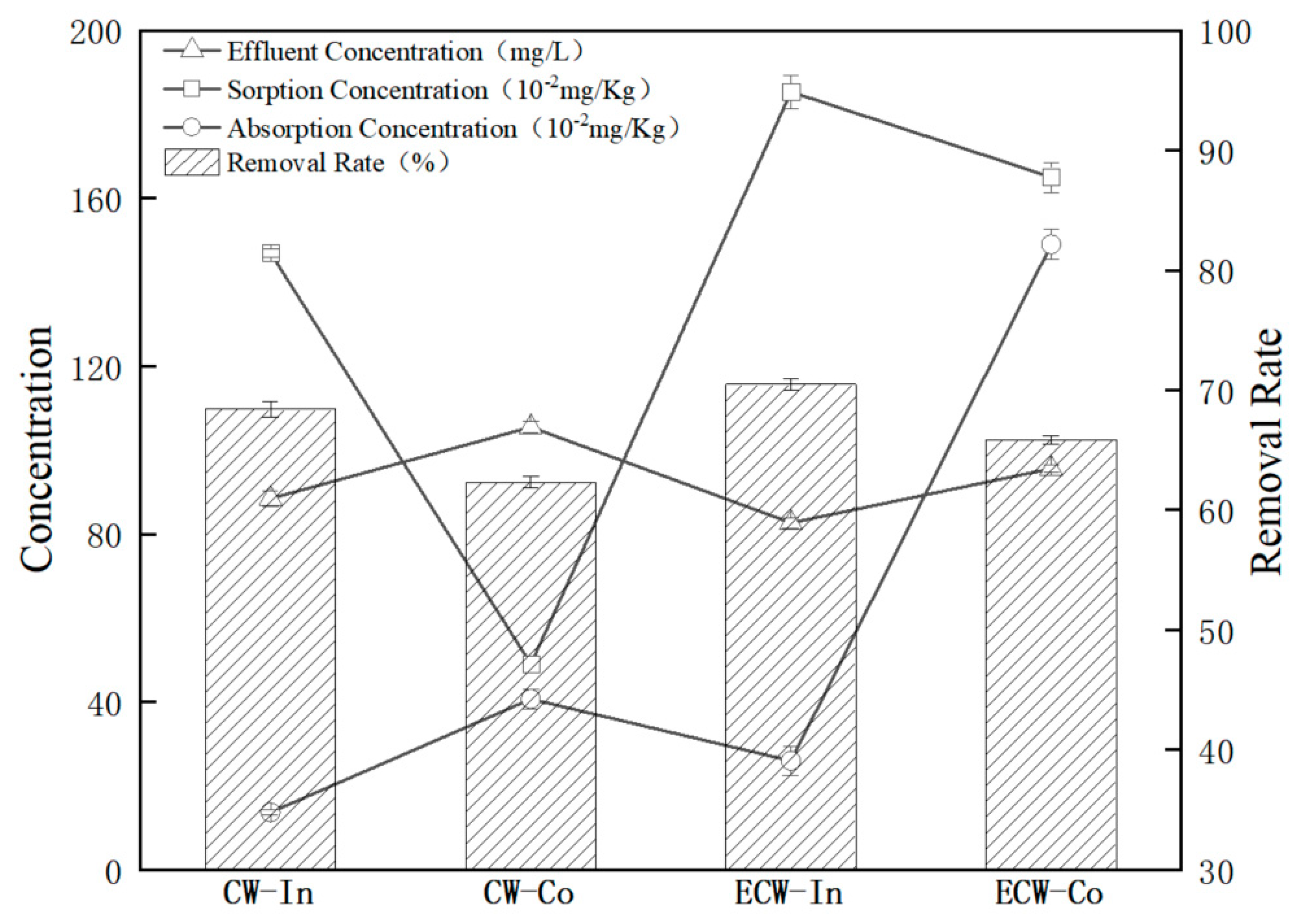
3.1. Degradation of Chlorpyrifos
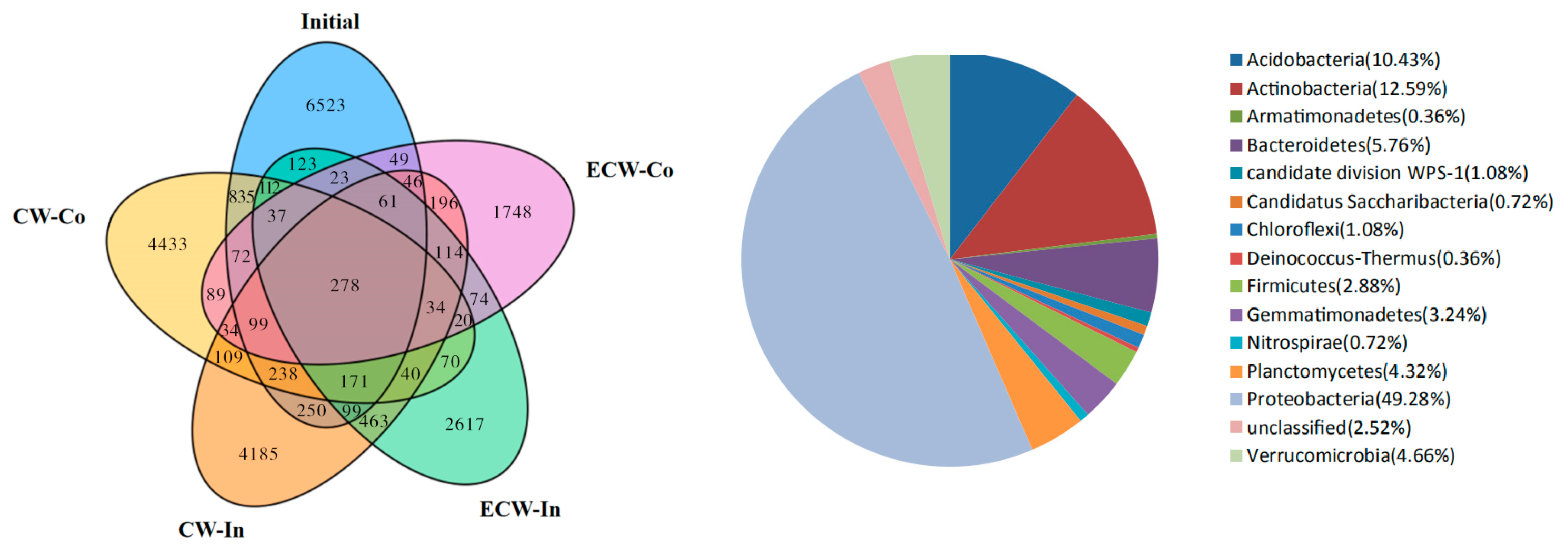
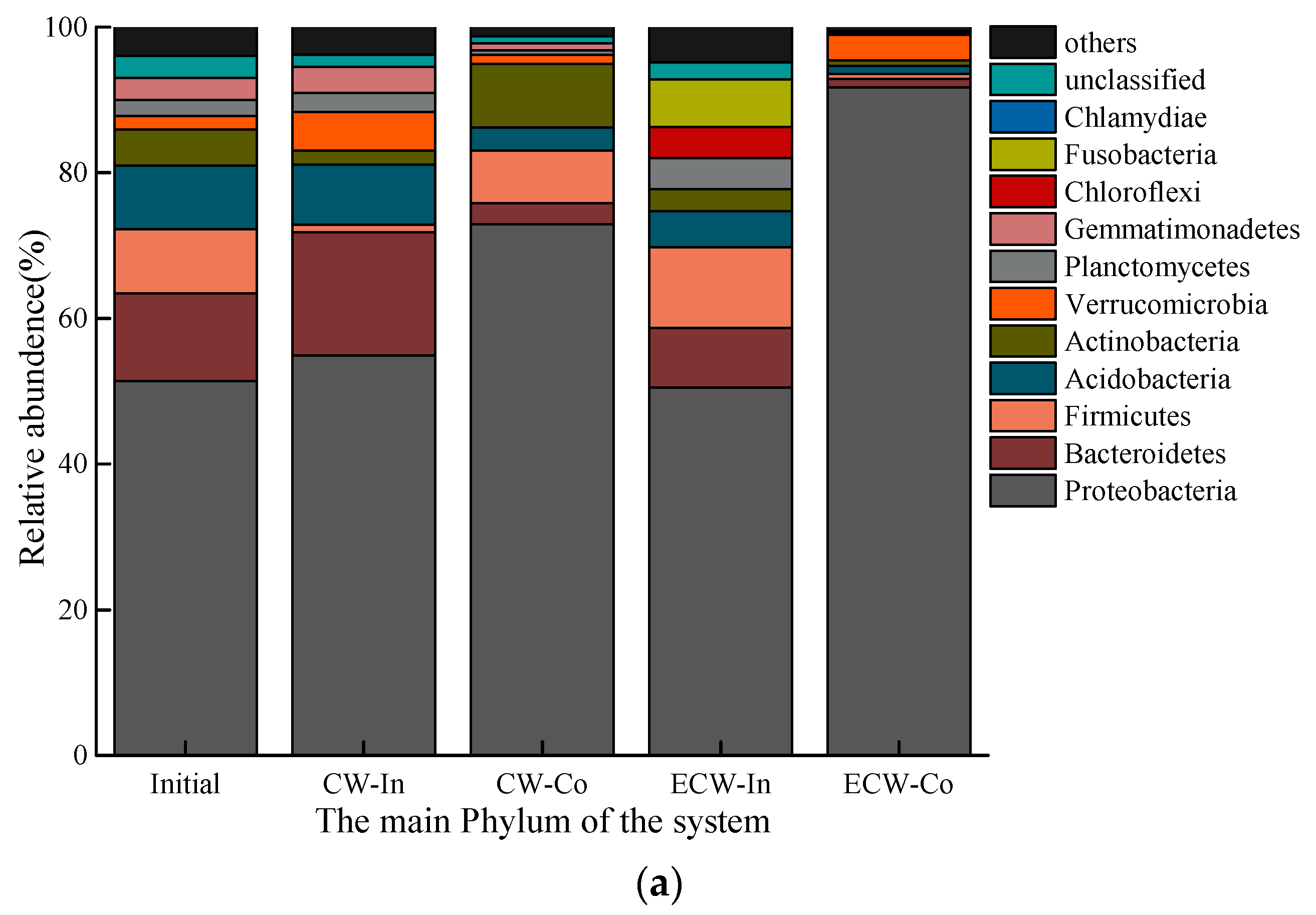
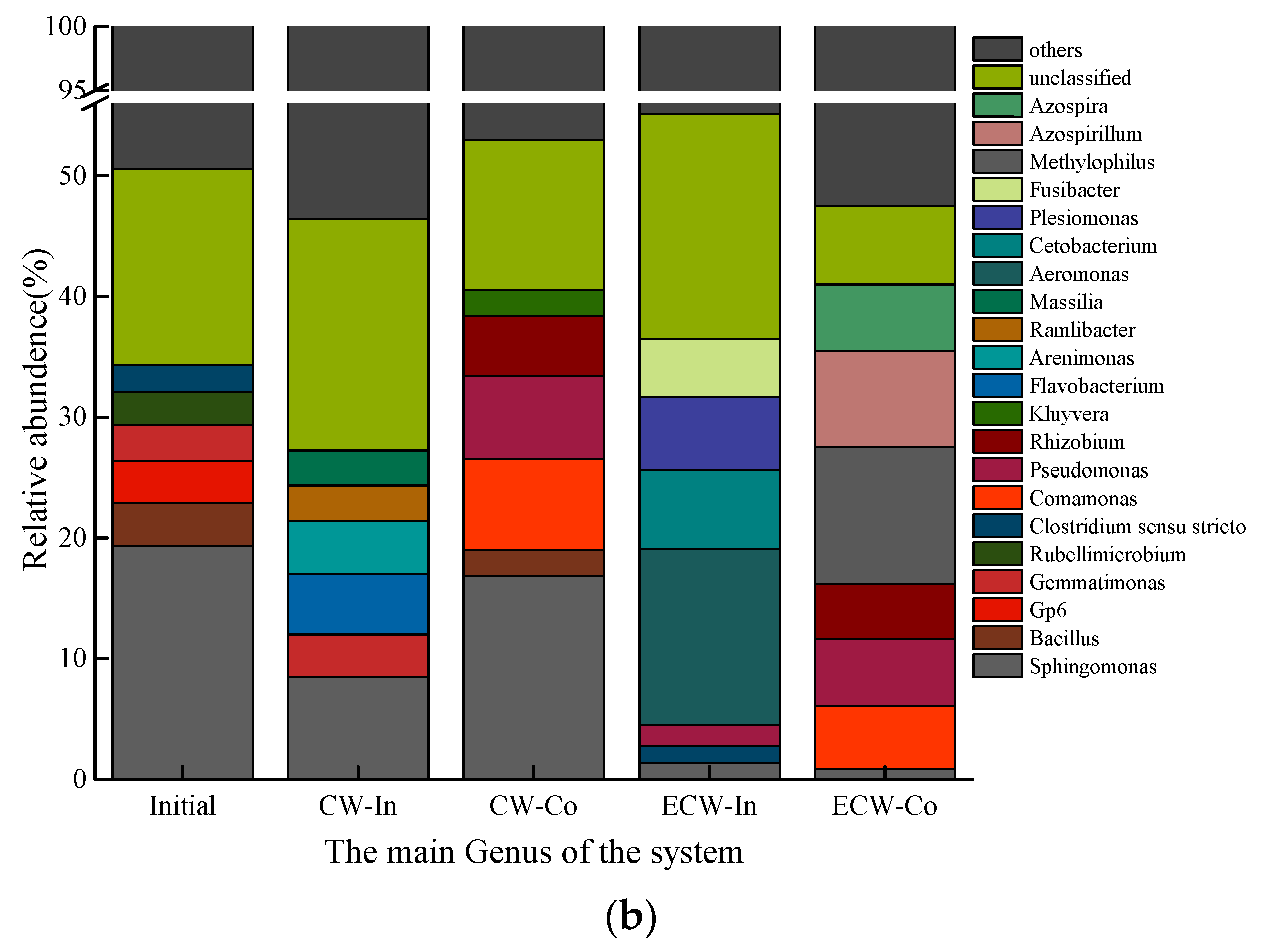
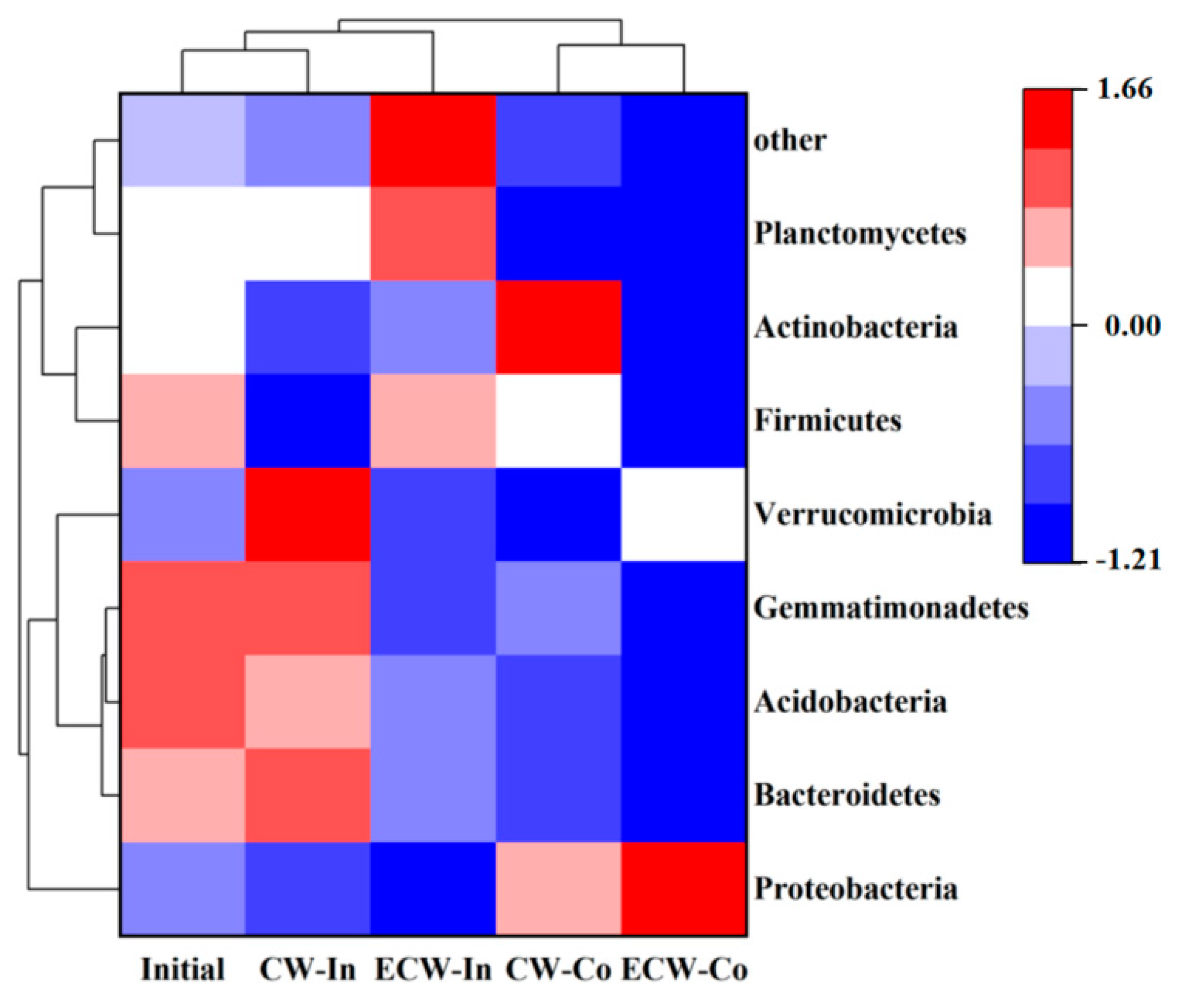
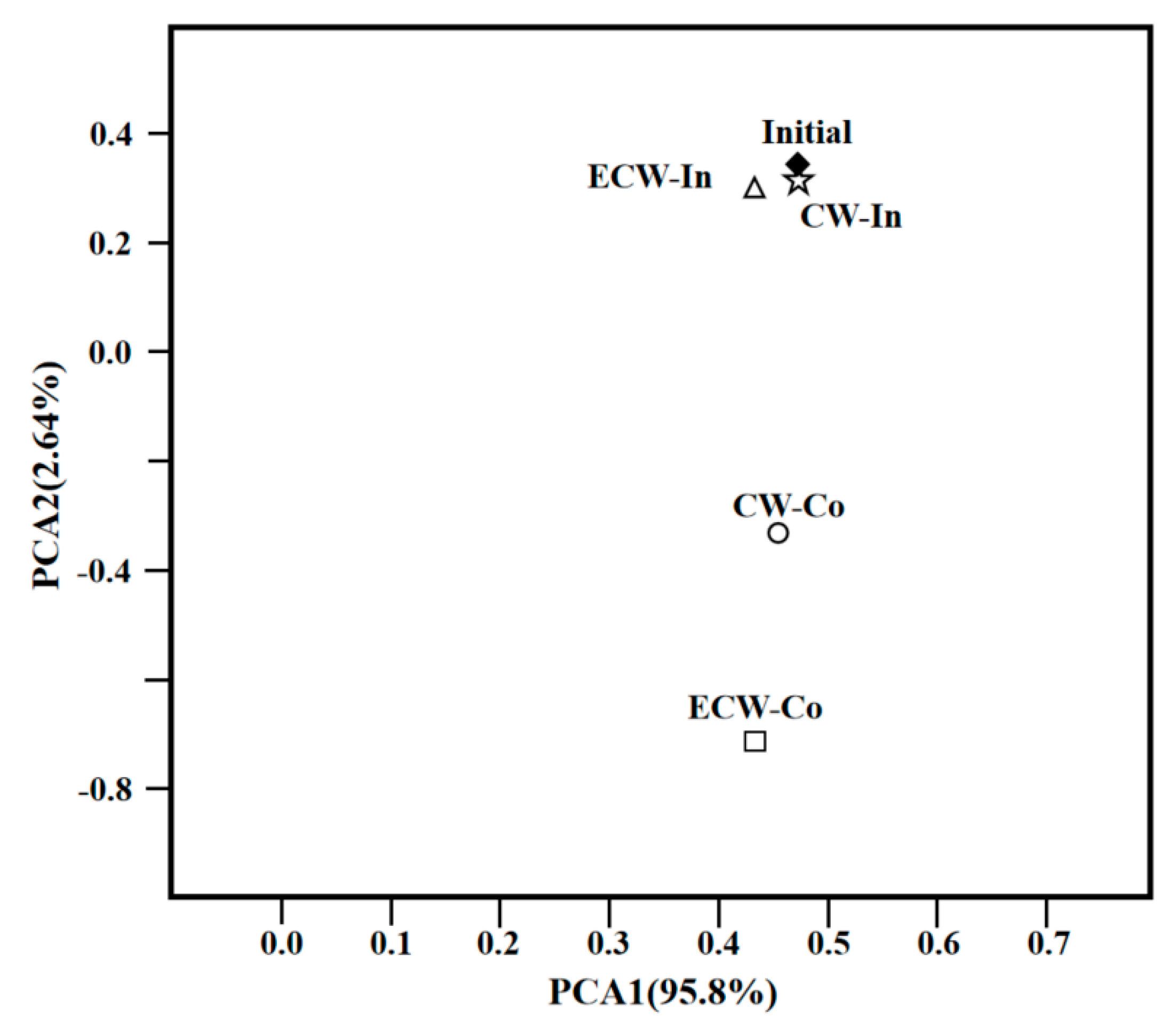
3.2. High-Throughput Sequencing
3.2.1. Microbial Community Diversity
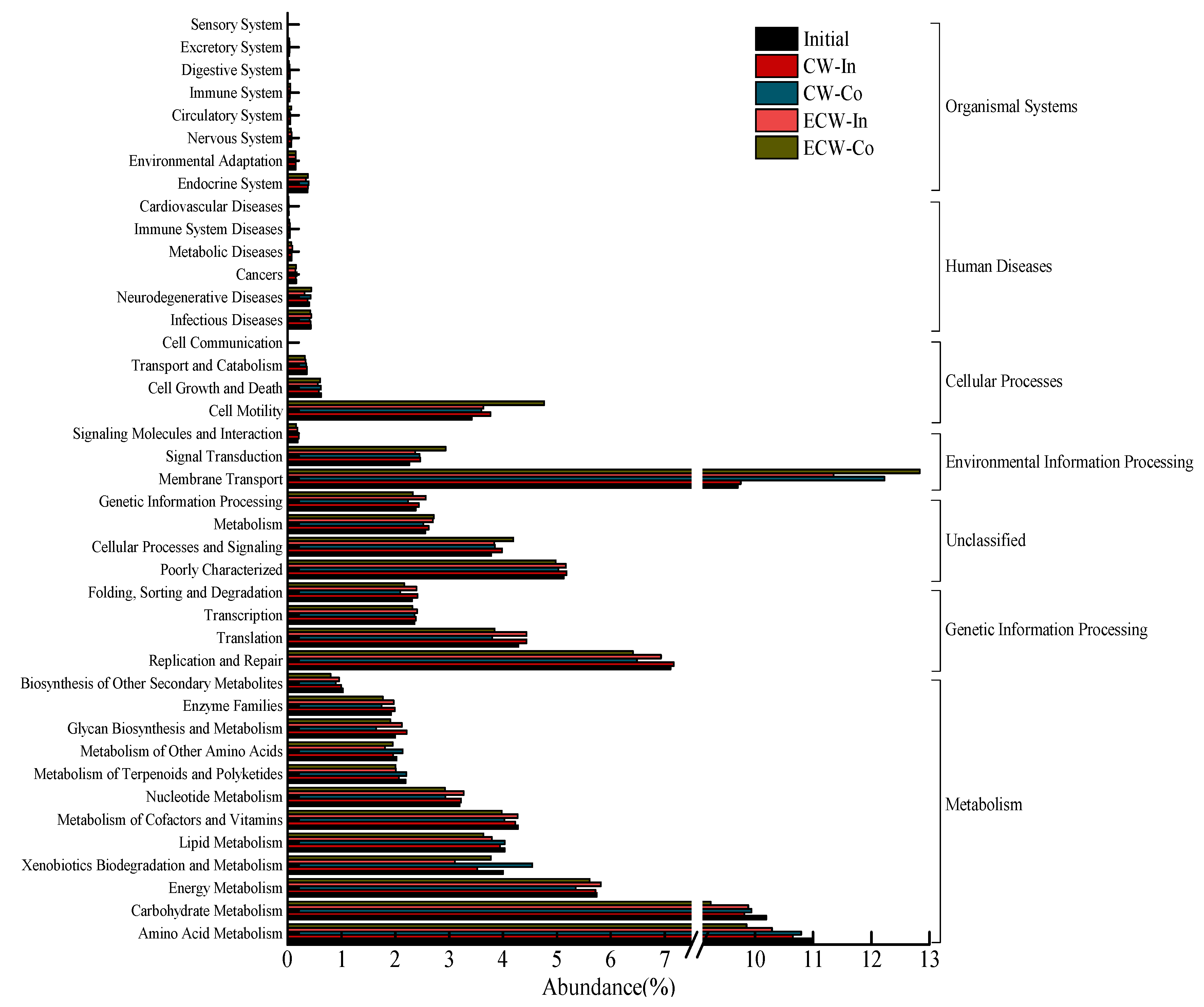
3.2.2. PICRUSt Gene Prediction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichenberger, S.; Bach, M.; Skitschak, A.; Frede, H.G. Mitigation strategies to reduce pesticide inputs into ground- and surface water and their effectiveness—A state-of-the-art review. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Yu, Z.D.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Kong, F.L. Research advances in using constructed wetlands to remove pesticides in agricultural runoff. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.J.; Niu, C.G.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, G.-M.; Wu, Z. Nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds degradation in the microbial fuel cells. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Chou, W.L.; Kuo, Y.M.; Chang, F.-L. Paired removal of color and COD from textile dyeing wastewater by simultaneous anodic and indirect cathodic oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, S.; Ocon, D.J.; Chong, N.M. Electrochemical oxidation remediation of real wastewater effluents—A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Min, Y.; Zhang, A.; Si, Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Yu, H.-Q. Electrochemical treatment of phenol-containing wastewater by facet-tailored TiO2: Efficiency, characteristics and mechanisms. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylor, G.L.; Zhao, C.; Kupferle, M.J. Synergistic enhancement of oxidative degradation of atrazine using combined electrolysis and ozonation. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 21, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.; Chiu, K.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Leu, H.-J. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater: Selectivity of the heavy metals removal process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27741–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Song, H.L.; Yu, C.Y.; Li, X.-N. Simultaneous degradation of toxic refractory organic pesticide and bioelectricity generation using a soil microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguezgaray, A.; Boltes, K.; Estevenúñez, A. Cleaning-up atrazine-polluted soil by using Microbial Electroremediating Cells. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde García, A.; Socías Viciana, M.; González Pradas, E.; Sánchez, M.V. Adsorption of chlorpyrifos on Almería soils. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 123–124, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, V.R.; Hoonhout, C.; Miller, G.C. Use of stable tracer studies to evaluate pesticide photolysis at elevated temperatures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1916–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onneby, K.; Jonsson, A.; Stenström, J. A new concept for reduction of diffuse contamination by simultaneous application of pesticide and pesticide-degrading microorganisms. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Maillacheruvu, K. Electrochemical and Biogeochemical Interactions under dc Electric Fields. In Physicochemical Groundwater Remediation; Springer: Greer, SC, USA, 2002; pp. 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, S.Y.; Burritt, D.J.; Oey, I. Utilising Pulsed Electric Fields Processing to Modify the Characteristics of Plant-Based Foods. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tomenko, V.; Ahmed, S.; Popov, V. Modeling constructed wetland treatment system performance. Ecol. Model. 2007, 205, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Adsorption of Pesticide Compound Pollution in Soil. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Conde-Cid, M.; Paradelo, R.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Pérez-Novo, C.; Nóvoa-Múñoz, J.; Arias-Estévez, M. Retention of quaternary ammonium herbicides by acid vineyard soils with different organic matter and Cu contents. Geoderma 2017, 293, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.; Rubilar, O.; Diez, M.C.; Cea, M.; da Silva, A.S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.; Tortella, G. Combined pollution of copper nanoparticles and atrazine in soil: Effects on dissipation of the pesticide and on microbiological community profiles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 361, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, L.F.; Germán, G.V.; Carmen, P.C.M.D.; Hossein, G. Adsorption of organophosphorus pesticides in tropical soils: The case of karst landscape of northwestern Yucatan. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vryzas, Z. Pesticide fate in soil-sediment-water environment in relation to contamination preventing actions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizosa, M.J.; Calderón, M.J.; Hermosín, M.C.; Cornejo, J. Organosmectites as sorbent and carrier of the herbicide bentazone. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, J. Relationship between the soil sorption constants forpesticides and their physicochemical properties. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1989, 8, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameselle, C.; Gouveia, S. Phytoremediation of mixed contaminated soil enhanced with electric current. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 361, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrard, R.M.; Bearr, J.S.; Murray-Gulde, C.L.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr.; Shah, Y.T. Feasibility of constructed wetlands for removing chlorothalonil and chlorpyrifos from aqueous mixtures. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannehl, D. Effects of electricity on plant responses. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, B.; Bañuelos, G.; Shutes, B.; Wen, Z. Removal of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolytic metabolite in microcosm-scale constructed wetlands under soda saline-alkaline condition: Mass balance and intensification strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Gabus, S.; Rohrbachbrandt, E.; Hosseini, M.; Rossi, P.; Maillard, J.; Holliger, C. Performance and microbial community composition dynamics of aerobic granular sludge from sequencing batch bubble column reactors operated at 20 °C, 30 °C, and 35 °C. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Sekiguchi, Y. Enhanced electrode-reducing rate during the enrichment process in an air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sträuber, H.; Lucas, R.; Kleinsteuber, S. Metabolic and microbial community dynamics during the anaerobic digestion of maize silage in a two-phase process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, M.; Ferraresso, S.; Ciofi, C.; Chelazzi, G.; Carrer, C.; Ferrari, G.; Pavan, L.; Patarnello, T.; Bargelloni, L. Exploring the effects of seasonality and chemical pollution on the hepatopancreas transcriptome of the Manila clam. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 2157–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Pauletto, M.; Boffo, L.; Carrer, C.; Sorrentino, F.; Ferrari, G.; Pavan, L.; Patarnello, T.; Bargelloni, L. Transcriptomic resources for environmental risk assessment: A case study in the Venice lagoon. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Matozzo, V.; Pauletto, M.; Di Camillo, B.; Giacomazzo, M.; Boffo, L.; Binato, G.; Marin, M.G.; Patarnello, T.; Bargelloni, L. Can ecological history influence response to pollutants? Transcriptomomic analysis of Manila clam collected in different Venice lagoon areas and exposed to heavy metal. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Du, L.; Yang, B. Predictive functional profiling using marker gene sequences and community diversity analyses of microbes in full-scale anaerobic sludge digesters. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Xia, Y.; Lau, F.T.K.; Tang, D.T.W.; Fung, W.C.; Fang, H.H.P.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis of sludge from full-scale anaerobic digesters operated in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5709–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type | Effluent Concentration (mg/L) | Removal Rate (%) | Sorption Concentration (mg/Kg) | Absorption Concentration (mg/Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW−In | 88.48 ± 1.83 c | 68.40 ± 0.66 b | 1.47 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.006 d |
| CW−Co | 105.47 ± 1.26 a | 62.33 ± 0.45 d | 0.49 ± 0.02 d | 0.41 ± 0.023 b |
| ECW−In | 82.67 ± 1.27 d | 70.47 ± 0.45 a | 1.85 ± 0.04 a | 0.26 ± 0.035 c |
| ECW−Co | 95.60 ± 0.96 b | 65.86 ± 0.34 c | 1.65 ± 0.036 b | 1.49 ± 0.036 a |
| Samples ID | Number of Sequences | Number of OTUs | Chao1 Index | ACE Index | Shannon Index | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 67,660 | 9016 | 41,902.62 | 85,544.22 | 6.26 | 0.03 | 0.90 |
| CW−In | 59,239 | 6417 | 15,063.84 | 21,743.44 | 6.56 | 0.01 | 0.94 |
| CW−Co | 63,033 | 6671 | 32,890.43 | 60,978.58 | 5.67 | 0.02 | 0.92 |
| ECW−In | 49,825 | 4336 | 8215.19 | 8794.71 | 5.85 | 0.03 | 0.96 |
| ECW−Co | 60,091 | 2974 | 13,310.22 | 29,259.80 | 4.70 | 0.02 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Hao, A.; Quan, Y.; Jin, M.; Piao, W. Analysis of the Degradation Characteristics of Chlorpyrifos in an Electrochemically Constructed Wetland Coupled System under Different Pesticide Exposure Conditions and Microbial Community Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15958. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215958
Wang Y, Hao A, Quan Y, Jin M, Piao W. Analysis of the Degradation Characteristics of Chlorpyrifos in an Electrochemically Constructed Wetland Coupled System under Different Pesticide Exposure Conditions and Microbial Community Analysis. Sustainability. 2023; 15(22):15958. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215958
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuhang, Aibo Hao, Yue Quan, Mingji Jin, and Wenhua Piao. 2023. "Analysis of the Degradation Characteristics of Chlorpyrifos in an Electrochemically Constructed Wetland Coupled System under Different Pesticide Exposure Conditions and Microbial Community Analysis" Sustainability 15, no. 22: 15958. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215958
APA StyleWang, Y., Hao, A., Quan, Y., Jin, M., & Piao, W. (2023). Analysis of the Degradation Characteristics of Chlorpyrifos in an Electrochemically Constructed Wetland Coupled System under Different Pesticide Exposure Conditions and Microbial Community Analysis. Sustainability, 15(22), 15958. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215958





