Abstract
With the acceleration of urbanization, the carrying capacity of urban land resources is increasingly being challenged. Thus, urban land use efficiency (ULUE) has been a crucial issue in sustainable development, and digital finance (DF) has been thought to be an effective solution for solving this dilemma. Based on panel data from 283 cities in China spanning from 2011 to 2020, this study first utilized the super-efficiency SBM model to assess ULUE across China. Then, the panel Tobit model was employed to empirically examine the overall impact of DF on ULUE, while the intermediary effect model was utilized to analyze the indirect impact of DF on ULUE. Additionally, the threshold effect model was employed to investigate the non-linear characteristics of the impact of DF on ULUE. The findings indicate that: (1) DF can enhance ULUE, with the dimension of application depth of DF exerting the most significant impact, followed by the dimensions of coverage breadth and digitization degree of DF; (2) DF can boost ULUE by promoting industrial structure upgrading (ISU); (3) the promotional effect of DF on ULUE exhibits regional variations, with a stronger impact observed in the western region and provincial capital cities, but weaker effects noted in the eastern and central regions as well as non-provincial capital cities; (4) with the improvement of economic development and DF, the impact of DF on ULUE exhibits a slightly increasing nonlinear trend. The research findings presented in this paper offer valuable insights for enhancing ULUE in emerging economies.
1. Introduction
China is undergoing a new phase of rapid urbanization. However, the expansion of such land for urbanization will encroach upon cultivated and forested areas as well as other territorial spaces [1]. Furthermore, the extensive urban land use pattern has given rise to issues such as an irrational land use structure and low efficiency in land utilization [2]. Urban land use efficiency (ULUE) reflects the extent to which economic, social, and environmental benefits are maximized in the utilization of urban land resources, and it is directly correlated with the healthy development of the social economy [3], especially under the current constraints of limited resources and the deteriorating ecological environment [4]. Given that China’s urbanization has entered a new stage, it is imperative to effectively enhance ULUE [5].
ULUE is a crucial indicator for assessing the utilization level of urban land resources [6,7]. The present studies on ULUE primarily center on the assessment methods, evolutionary traits, and influential factors. In terms of evaluation, ULUE has been analyzed by several scholars utilizing remote sensing technology. For instance, Dimov et al. investigated the utilization of land resources in Central Asia by using remote sensing data [8], and Wiatkowska et al. analyzed the ULUE in Opole city in Poland utilizing remote sensing imagery and GIS technology [9]. Some scholars also use other methods, such as the entropy method [10], stochastic frontier analysis [11], data envelopment analysis [12,13] to evaluate ULUE, and data enveloping analysis exhibits fewer drawbacks compared to the entropy method and stochastic frontier analysis [14]. The super-efficiency SBM model is a sophisticated approach in data envelopment analysis. The model assesses the ability of a region or organization to optimize its output under given input conditions [14]. The aforementioned model possesses inherent strengths in the handling of multiple output indicators [14]. The super-efficiency SBM model is increasingly favored by scholars for assessing ULUE [15,16,17]. Therefore, a prevailing approach for calculating and comparing land use efficiency across multiple cities is the super-efficiency SBM model [14].
Additionally, other scholars have examined the evolution characteristics of ULUE [18,19,20,21]. For example, the study conducted by Ahmad revealed significant regional disparities in ULUE within China [20]. Yu et al. found that ULUE in China decreased from east to west [21]. The study conducted by Schiavina et al. revealed a recent improvement in global ULUE, with urban centers demonstrating the highest levels of efficiency [22]. Existing studies have also examined the impacts and mechanisms of industrial structure upgrading (ISU) [23,24], agglomerating industries [25], decentralizing fiscal policies [26], integrating regional economies [27] and urbanizing areas [28] on enhancing ULUE. For example, Wang et al. argue that a higher level of urbanization in central and western China fosters a favorable synergy between industrial structure adjustment and ULUE [24]. Wiatkowska et al. contend that the urbanization of Opole city in Poland primarily resulted in the conversion of agricultural land and substantiate the detrimental impacts of urban expansion on ULUE [9]. Some scholars have also investigated the interrelationship between ULUE and green manufacturing systems [29], ecological carrying capacity [30], ecosystem health [6], carbon emissions [11] and other factors. It is evident that there exists an abundance of research findings on ULUE.
In fact, with the rapid growth of global financial technology, governments worldwide are placing great emphasis on DF development and formulating relevant national-level strategies to support it [31]. DF refers to a novel financial business model in which financial institutions provide financing, payment, and other related financial services by integrating internet and information and communication technologies [32]. DF, unlike traditional finance, utilizes information technology to overcome the temporal and spatial limitations of conventional counter financial services [33], thereby mitigating urban congestion. The research findings in DF evaluation are comparatively abundant in China. Currently, the primary tool for measuring DF in China is the Digital Financial Inclusion Index developed by the Institute of Digital Finance Peking University [34,35].
Based on quantitative evaluations of DF, several studies have investigated the economic impacts of digital financial services. DF has the potential to bridge the regional development gaps by addressing the inefficient allocation of financial resources [36] and enhancing resource allocation efficiency, thereby fostering high-quality economic development [37]. Daud conducted a study on 190 SMEs in Banten Province, Indonesia and found that the implementation of DF can significantly enhance their financial performance [38]. Furthermore, DF can alleviate the financial burden on enterprises and provide a solid financial foundation for their technological innovation endeavors [39]. In addition, DF can efficiently manage a vast customer base through advanced technologies while simultaneously increasing revenue and minimizing costs [40]. Jiang et al. conducted a study on 30 provinces in China and discovered that DF can stimulate entrepreneurship and economic development by relying on information technology [34].
Furthermore, DF has an undeniable ecological impact. The Ant Forest Project launched in China is an innovative approach to tree planting that integrates individual users, digital finance, and reforestation initiatives [41]. Following the DF development boom, numerous scholars believe that DF plays a crucial role in promoting technological innovation [39,42], optimizing industrial structure [43,44], upgrading consumption patterns [31,45], facilitating green and low-carbon development [46,47], and enhancing economic resilience [48,49]. Feng et al. argue that DF has the potential to enhance green technology innovation in regions characterized by high levels of pollutant emissions and robust local government governance capacity [50]. Cao et al. discovered that the advancement of green technology is a crucial conduit for DF to enhance energy and environmental performance [35].
Although plenty of studies on ULUE and DF have been conducted, the following research gaps still need to be discussed: (1) Many studies have discussed the factors affecting ULUE and investigating the economic and ecological effects of DF from multiple perspectives, but very few of them have mentioned the influential effect of DF on ULUE. (2) Very few studies have mentioned the specific influencing mechanism between DF and ULUE. (3) It is also necessary to explore the nonlinear relationship between the variables [51].
Therefore, the following research questions need to be answered:
- Does DF have any effect on ULUE?
- If yes, will this effect be influenced by other variables?
- What is the influencing mechanism between DF and ULUE?
To answer these questions, the influencing mechanisms and research hypotheses regarding variable relationships are elaborated in Section 2; the mathematic models for examining the relationships among variables and the dimensions and indicators for measuring DF and ULUE are explained in Section 3; the results of this study are described in Section 4; and the conclusions and discussions are presented in Section 5.
The objective of this study is to examine the direct effect of DF on ULUE as well as the mediating role of industrial structure upgrading on this effect, and to explore the non-linear relationship between DF and ULUE. To do that, the panel Tobit model was employed to empirically examine the overall impact of DF on ULUE, while the intermediary effect model was utilized to analyze the indirect impact of DF on ULUE. Additionally, the threshold effect model was employed to investigate the non-linear characteristics of the impact of DF on ULUE. A threshold model is a measurement model that calculates the threshold value according to the sample data and takes the threshold value as the classification standard to explore the nonlinear relationship between variables [51]. The contribution of this study lies in the following aspects: Firstly, this study examines the impact of DF on ULUE. Although some scholars have analyzed the ecological benefits of DF, they failed to investigate the impact of DF on ULUE. Given that DF possesses certain ecological effects, it is plausible to assume a potentially positive influence of DF on ULUE. Secondly, this study not only examines the direct influence of DF on ULUE, but also explores its indirect impact. In this paper, ISU is also selected as the mediating variable of DF’s influence on ULUE, which enriches the research on the mechanism of DF’s influence on ULUE. Thirdly, this paper not only examines the overall impact of DF on ULUE but also investigates the non-linear relationship between DF and ULUE through a threshold model. By setting economic development and DF as threshold variables, it becomes more evident that an improvement in both economic development and DF leads to a stronger promotion effect of DF on ULUE.
2. Mechanism Analysis and Research Hypotheses
2.1. The Overall Influence of DF on ULUE
The advent and development of DF have exerted a substantial influence on ULUE in various aspects, as illustrated in Figure 1. The transaction cost theory lends support to our analysis. In many aspects such as land information management, land valuation and land financing, digital finance can reduce transaction costs. Firstly, the development of DF has facilitated the digitization of land information. The emergence and development of DF facilitate the storage, management, and transmission of crucial information such as cadastral data, land use status, and land development planning in a digital format [52]. This advancement enhances the efficiency of land information utilization while minimizing the risk of information loss and interference. Secondly, DF has the potential to enhance the precision of land valuation. By analyzing a large amount of land data for accurate land valuation [53], DF has revolutionized the traditional approach to assessing land value, resulting in reduced mistakes and increased transparency and fairness in the land market. Thirdly, the advancement of DF can optimize land financing methods. The conventional bank loan model encounters difficulties in meeting the requirements of land development enterprises, thereby limiting the efficient utilization of land. DF has the potential to reduce transaction costs associated with land financing, enhance financing efficiency, diversify land financing channels, facilitate easier access to funds for land development enterprises, and consequently improve the overall efficiency in utilizing land [54]. Fourthly, DF can facilitate the utilization of land by generating novel forms and models that enhance ULUE. The integration and implementation of digital financial technology can expand more diversified, flexible, and efficient approaches for exploring and utilizing land value [55], thereby better satisfying market demand. To conclude, the emergence and development of DF have significantly impacted ULUE, fostering transparency, standardization, and sustainable growth in the land market. Moreover, it has enhanced the effectiveness of land utilization. To examine the overall effect of DF on ULUE, Hypothesis 1 was proposed as follows:

Figure 1.
The direct impact of DF on ULUE.
H1.
DF can enhance the efficiency of urban land utilization.
2.2. The Indirect Impact of DF on ULUE
The effect of DF on ULUE can also be indirect. DF integrates traditional finance with digital information technology to facilitate industrial structure upgrading (ISU). Firstly, as a part of the service industry, DF promotes ISU [46]. Additionally, DF has the potential to enhance information dissemination and mitigate information asymmetry. By facilitating the flow of production factors to more efficient sectors, DF can further stimulate industrial structural upgrading [43]. Secondly, DF has the potential to mitigate financing constraints faced by companies, particularly small enterprises (SEs) that have been marginalized within the conventional financial system. By offering a wider range of financing alternatives, DF effectively addresses the challenges associated with “difficult financing” encountered by SEs [56]. The easing of financing constraints can, on one hand, promote technological upgrading in enterprises [57]. On the other hand, it can enhance innovation capabilities and market competitiveness in emerging industries, thereby further optimizing the industrial structure [58]. Finally, DF can furnish enterprises with more convenient and cost-effective financing channels, expedite enterprise development, and provide support for the establishment and growth of industrial clusters [59].
ISU can enhance ULUE. Firstly, it directly boosts the economic benefits by extending the industrial chain and promoting product added value [23]. Furthermore, ISU can enhance the optimal allocation of land and labor factors through adjustments to both urban land use and employment structures [25]. Finally, ISU can facilitate the transformation of the economic structure towards services and rationalization, thereby mitigating the adverse externalities associated with environmental pollution [23]. DF has a very positive promoting effect on ISU, and ISU has a positive effect on ULUE. Therefore, it can be considered that DF can enhance ULUE by promoting ISU. The aforementioned influencing mechanisms are depicted in Figure 2. To explore the indirect impact of DF on ULUE, Hypothesis 2 was proposed as follows:
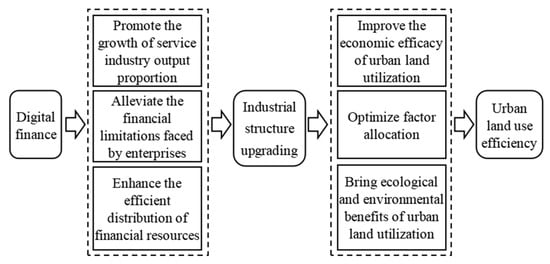
Figure 2.
The indirect impact of DF on ULUE.
H2.
By promoting ISU, DF can enhance ULUE.
2.3. The Threshold Impact of DF on ULUE
The influential effect of DF on ULUE may exhibit heterogeneity. The term heterogeneity pertains to the variations in specific characteristics among individuals [51]. Regions with varying levels of economic development will exhibit significant disparities in terms of infrastructure construction, digitalization development, and industrial advancement [60]. Cities with underdeveloped economies face challenges such as inadequate digital infrastructure, limited industry diversity, and insufficient innovation capacity [33]. Consequently, the application of DF may be constrained to some extent [33], resulting in a relatively minor impact on ULUE. In cities with better economies, digital development is more advanced and industrial support is stronger, which facilitates the further promotion of industrial upgrading, integration, and ecological optimization through DF [61], which in turn significantly enhances ULUE.
There exist notable regional disparities in the development of DF [62], and the impact of DF on ULUE is characterized by heterogeneity. Cities with underdeveloped DF may face challenges such as inadequate financial market development, limited risk management capabilities, and a narrow range of financing options [63]. In such cases, the impact of DF on ULUE may be relatively small. With the advancement of DF development, financial products will become increasingly diversified. A more comprehensive digital financial service system can offer more convenient, efficient, and flexible financing channels for land development and utilization. To elucidate the intricate non-linear correlation between DF and ULUE, the hypothesis was developed as follows:
H3.
With the advancement of economic development and DF, the promoting effect of DF on ULUE will be further enhanced.
3. Methods and Variables
To measure ULUE and DF and explore the influential effect and mechanism of DF and ULUE, we firstly designed the dimensions and indicators of ULUE and DF for their measurement. Then, the panel Tobit model was established to explore the direct and indirect influential effect of DF on ULUE. Finally, the threshold effect model is introduced to investigate the non-linear characteristics of the effect of DF on ULUE.
3.1. Measurement of ULUE and DF
3.1.1. ULUE
Referring to relevant research literature [17], the super-efficiency SBM model is employed to measure ULUE, and this takes into account undesirable outputs and maintains a constant return to scale with respect to inputs. This model is employed in this study to assess ULUE [64]. Suppose there are n decision-making units , and the quantities of input, expected output, and unexpected output contained in each DMU are denoted as , and , respectively. The ULUE value with respect to each DMU can be derived by solving the following linear program:
where represents ULUE, , and represent the input value, expected output value, and unexpected output value of in period t; , and represent relaxation variables of input, expected output, and unexpected output, respectively; and is the weight vector. Referring to relevant research literature [65,66,67], the input–output indicator system designed for ULUE measurement is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Input–output indicator.
3.1.2. DF
DF is measured by introducing the China Digital Financial Inclusion Index proposed by the Digital Finance Research Center in Peking University [35]. This index includes three dimensions: coverage breadth (Bre), application depth (Dep), and digitization degree (Dig). The coverage breadth of DF reflects the extent to which digital financial accounts are included. The application depth of DF encompasses payment, money fund management, credit services, insurance operations, investment activities and credit evaluation, thereby demonstrating the tangible impact of digital finance development. The digitization level of DF encapsulates mobile accessibility, affordability, creditworthiness and facilitation capabilities, representing a concentrated manifestation of Internet technology [68]. The logarithm of the aforementioned variables is taken in regression and represented as lnDF, lnBre, lnDep, and lnDig.
3.2. Model Setting
3.2.1. The Reference Effect Model
The adoption of least square regression may directly lead to significant bias due to the restricted nature of ULUE measured by a super-efficiency SBM model. To address this issue, the Tobit model is a better solution for dealing with dependent variables that are constrained [69]. Therefore, we employ a panel Tobit model to investigate the impact of DF on ULUE.
The model is formulated as follows:
where i represents the city, t represents time, ULUE stands for urban land use efficiency, DF indicates the level of digital finance development, and denotes the impact of DF on ULUE. A value greater than 0 signifies that DF development is conducive to promoting improvements in ULUE. represents a set of other control variables that impact ULUE, encompassing economic development (lnEd), population density (lnPi), urban transportation development (lnRs) and local government financial support (lnGov). denotes the coefficient of the control variable; stands for constant term; represents the random error term.
3.2.2. Intermediate Effect Model
To examine the potential of DF in enhancing ULUE through ISU, this study employs the Tobit model for empirical testing as follows:
where the intermediary variable represents ISU, represents the impact of DF on ISU, while represents the influence of DF on ULUE after controlling for the intermediary variable (industrial structure upgrading). signifies the effect of ISU on ULUE, while other variables and symbols remain consistent with Equation (3).
If the coefficients of , , and are statistically significant at the chosen confidence level, it suggests that the mediating effect of ISU is also significant, which implies that DF can impact ULUE through its influence on ISU.
3.2.3. Threshold Effect Model
To elucidate the intricate non-linear correlation between DF and ULUE, it is necessary to analyze the heterogeneity between these two variables. Compared with traditional heterogeneity analysis, the threshold model can accurately identify the threshold value, so as to clearly depict the nonlinear characteristics of DF affecting ULUE. Referring to relevant research literature [51], the panel threshold model is shown in Equation (6):
where represents the indicative function, in parentheses is the threshold variable, signifies the threshold value, n stands for the threshold number, represents the impact of DF on ULUE within the first threshold interval, while represents the coefficient value of digital finance affecting land use efficiency within the NTH threshold interval, while other variables and symbolic meanings are consistent with Equation (3).
3.3. Variable Selection
Dependent variable: ULUE.
Independent variable: DF Index. In the subsequent empirical research, we further examine the impact of DF on ULUE from three dimensions.
Mediating variable: ISU. Since the 1970s, the dominant feature of ISU has been the “service-oriented economic structure” propelled by information technology. Therefore, this paper employs the ratio of tertiary industry’s added value to that of secondary industry as an indicator for assessing the level of industrial structure upgrading [70], with a higher ratio indicating a more advanced stage of industrial structural transformation.
Control variables:
The evolution of ULUE is not only influenced by DF but is also closely correlated with social and economic development, population concentration, traffic conditions, government support and other factors. Control variables include: (1) Urban economic development level. The enhancement of the economic development level is not only an internal prerequisite for improving ULUE but also a significant driving force [71]. In this study, per capita GDP is employed as a measure of each city’s economic development level, with an anticipated positive coefficient. (2) Population density. The crowding effect and environmental pressure caused by population density growth may inhibit the improvement of ULUE [72]. In this study, population per square kilometer is utilized as a measure for population density. (3) Urban transportation development level. The development status of urban transportation will have an impact on the efficiency of regional economic operations and land use patterns, thereby influencing ULUE. We employ the ratio of urban road area to regional area as a measure of the level of urban transportation development [73]. (4) Local government financial support. The government’s financial expenditure will exert a significant influence on land utilization and economic valuation. Governments can improve regional transport networks and infrastructure by strengthening financial input, optimize urban planning and land management policies, and increase investment in environmental protection projects. This can not only enhance land utilization efficiency, but also establish a durable and sustainable basis for economic advancement. The ratio of general government financial expenditure to GDP is employed as an indicator to quantify the level of financial support provided by local governments. The study expresses the logarithms of the aforementioned variables as lnEd, lnPi, lnRs, and lnGov, respectively (“ln” denotes logarithm).
3.4. Sample and Data Source
This study utilizes panel data from 283 cities at the prefecture level and above in China, covering the period from 2011 to 2020, as research samples. The total samples are further divided into eastern, central, and western regions to compare the changing characteristics of ULUE and DF in both China as a whole and its respective regions [74,75]. The digital finance index is derived from the Digital Finance Research Center of Peking University (https://idf.pku.edu.cn/, accessed on 17 May 2023). Except for the DF index, other variables are obtained from various sources including China City Statistical Yearbook (2012–2021) (http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/, accessed on 17 May 2023), and the statistical yearbooks and statistical development bulletin of the cities. Cities with significant data deficiencies have been excluded. The missing data were imputed using both interpolation and mean value methods [76]. The independent variables and control variables in this paper are logarithmically transformed to address heteroscedasticity in the time series, without altering the inherent nature and relationships of the data, thereby enhancing its stability.
4. Results Analysis
In this section, we presented the descriptive statistics of variables and analyzed the evolutionary trends of ULUE and DF in China at first. Then, the direct and indirect effect of DF on ULUE were examined, respectively. After that, the robustness tests and heterogeneity analysis were conducted to further explore the effectiveness of the direct effect examination. Finally, the threshold effect was examined to explore the non-linear relationship between DF and ULUE.
4.1. The Descriptive Statistics of the Variables
The results presented in Table 2 demonstrate a wide range of lnDF values, spanning from 2.834 to 5.813, with an average value of 5.506 and a standard deviation of 0.514. These findings indicate significant variability in lnDF among different cities in China, with a few cities exhibiting lower levels. The ULUE values in Chinese cities range from 0.003 to 2.425, with an average of 0.371, indicating a generally low level of ULUE across the cities; however, a few cities exhibit high levels of ULUE. The minimum value of lnPi is 0.683, while the maximum value is 7.882, among other variables, indicating a significant imbalance in the population distribution across Chinese cities. The standard deviation of lnEd is 0.565, with a minimum value of 8.327 and a maximum value of 15.675, while the average stands at 10.959, indicating significant variations in the economic development levels among Chinese cities. The other control variables are not detailed.

Table 2.
Data descriptive statistics.
4.2. Evolutionary Trends of ULUE and DF in China
By examining the average fluctuations in ULUE across China and its various regions from 2011 to 2020, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the evolving trends in China’s urban land utilization. The eastern region includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei Province, Liaoning Province, Shanghai, Jiangsu Province, Zhejiang Province, Fujian Province, Shandong Province, Guangdong Province, Hainan Province; the central region includes Shanxi Province, Jilin Province, Heilongjiang Province, Anhui Province, Jiangxi Province, Henan Province, Hubei Province, Hunan province; and the western region includes Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Chongqing City, Sichuan Province, Guizhou Province, Yunnan Province, Tibet Autonomous Region, Shaanxi Province, Gansu Province, Qinghai Province, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. (The above classification comes from the website of China’s National Bureau of Statistics (https://data.stats.gov.cn/, accessed on 17 May 2023)). The overall trend of ULUE in the country and its three major regions is upward, as illustrated in Figure 3; however, there are fluctuations across different time periods. For example, the ULUE in both the country and the eastern region experienced a temporary decline between 2011 and 2014. From 2012 to 2014, there was a temporary decline in ULUE observed in the central and western regions. The ULUE in the central region was 0.249 in 2014. The ULUE of the country and the three major regions has been consistently increasing since 2015, with a value exceeding 0.5 by 2019. The ULUE for the eastern region in 2020 stands at 0.680. Further comparison reveals that the ULUE in the eastern region is generally superior to that of other regions, whereas the ULUE in the central region tends to be comparatively lower.
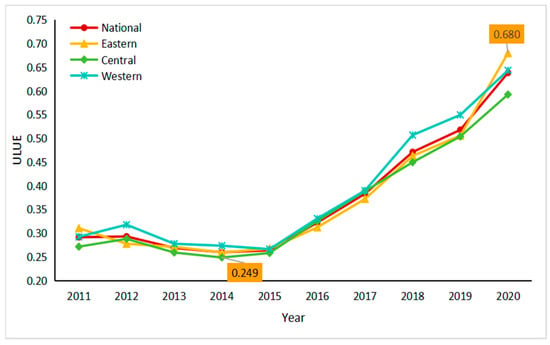
Figure 3.
Evolutionary trends of ULUE in China.
Figure 4 illustrates the average variation of the DF Index in China and its regions between 2011 and 2020, with a range from 0 to 300. The western region exhibited the lowest DF value in 2011. The overall development level of DF in the country and its three major regions has been consistently trending upwards year after year. By 2020, the DF Development Index exceeded 250 in all regions except for the western region. The DF value for the eastern region in 2020 amounts to 271.851. The level of DF development in the eastern region has consistently surpassed that of other regions, while the central and western regions have remained below the national average.
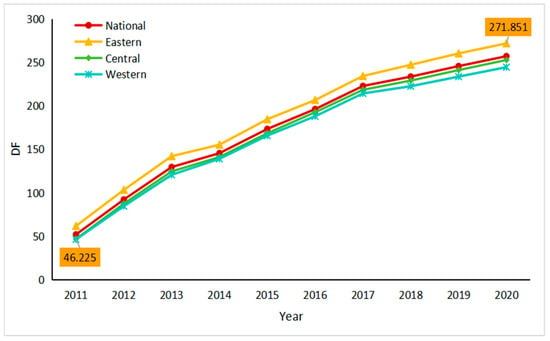
Figure 4.
Evolutionary trends of DF in China.
4.3. Direct Effect Analysis
Regarding the empirical analysis of the impact of DF development on ULUE, this paper investigates the influence of DF and its three dimensions (lnBre, lnDep, lnDig) on ULUE. Table 3 presents the regression results. Notably, column (1) reveals a significant impact coefficient of lnDF on ULUE with a significance level of p < 0.01. It indicates that a 1% increase in DF results in a 0.082 increase in ULUE. DF plays a favorable role in enhancing ULUE. In practice, DF can promote the application of land information data, enhance the accuracy of land value assessment, and optimize land financing methods. It has facilitated transparency, standardization, and sustainable development within the land market while further augmenting ULUE and the comprehensive value of land resources. As a result, hypothesis H1 is validated.

Table 3.
Benchmark regression results.
Specifically, columns (2)–(4) present the regression results for lnBre, lnDep and lnDig in relation to ULUE. The influence coefficients of the three dimensions on ULUE are 0.067, 0.101, and 0.030, respectively. Among them, the utilization depth of DF has the most significant impact on ULUE. This could be attributed to the fact that a deeper application depth of DF facilitates smoother investment flows, thereby enhancing ULUE.
As to the effect of control variables, urban economic development is an important factor in promoting ULUE improvement. The density of population exerts a significant inhibitory impact on ULUE, as the rise in population density leads to urban congestion and environmental pressure that impede the enhancement of ULUE. Urban traffic development presents a substantial positive influence on ULUE, because the enhancement of urban transportation development can bring an improvement in urban economic operational efficiency, optimize land use patterns, and consequently increase ULUE to a certain extent. Financial support from local governments has a substantial and favorable effect on the ULUE. Increasing the financial support provided to local governments can directly facilitate the rational utilization of land and enhance its economic value, thereby promoting the advancement of ULUE.
4.4. Mediating Effect Analyses
Table 4 presents the results regarding the mediating role of ISU on the effect of DF on ULUE. As indicated in Column (2) in Table 4, DF exerts a significant and positive impact on ISU, with a significance level of p < 0.01. This suggests that DF is conducive to promoting ISU. As depicted in Column (3) in Table 4, ISU exerts a positive and significant impact on ULUE, with a significance level of p < 0.01. This finding highlights the substantial intermediary effect of industrial structure upgrading. The empirical findings indicate that DF can facilitate the enhancement of ULUE by means of industrial structure upgrading. ISU can enhance economic, social, and ecological benefits by directing capital and technology towards sectors with higher land efficiency, environmental sustainability, and better industrial chains, which will further improve ULUE. As a result, hypothesis H2 is validated.

Table 4.
Mediation mechanism test results.
The significance of the mediation effect of ISU has been further demonstrated in this paper through the application of the Sobel test. The direct impact of DF on ULUE is 0.079, while its indirect impact is 0.020, constituting 20.002% of the total impact. The data indicate that 20.002% of the impact of DF on ULUE is attributed to its promotion of ISU, thereby enhancing land use efficiency.
4.5. Robustness Test
In order to enhance the reliability of the research results, it is necessary to conduct a robustness test. Adding control variables and changing the sample scope are common ways of conducting the robustness test. The robustness test is conducted using the following procedures. (1) Adding control variables, given that the intensity of real estate investment and fiscal decentralization may also exert an influence on ULUE, thereby influencing the robustness of the aforementioned research findings. Therefore, this paper selects municipal district real estate investment as the measure of real estate investment intensity, utilizes the ratio of general government fiscal expenditure to general government fiscal revenue as an indicator for measuring fiscal decentralization, and incorporates both variables as control factors for robustness testing. (2) Changing sample period. It is widely acknowledged in academia that 2013 marks the commencement of DF development in China. To ensure robustness, the sample period is subsequently narrowed down to 2013–2020 for testing purposes. (3) Excluding municipalities directly under the central government. In order to mitigate the influence stemming from substantial policy and developmental disparities between the municipalities (Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing) and other cities, this study excludes these municipalities from the sample and subsequently conducts a robustness test. (4) Using instrumental variables. To account for the potential bidirectional causal relationship between DF and ULUE, this study employs a one-stage lag of DF (L.lnDF) as an instrumental variable in the model to address possible endogeneity. DF with a one-stage lag will affect DF in the current period, but ULUE will not affect DF with a one-stage lag. Therefore, DF with a one-stage lag can be selected as an instrumental variable. These methods mainly tested the robustness of the direction of the digital financial regression coefficient from the perspectives of changing the number of samples and changing the research period. The results shown in Table 5 demonstrate that the significance level and sign for the coefficient of DF remain unchanged. This suggests that the benchmark regression findings exhibit strong robustness.

Table 5.
Robustness test.
4.6. Heterogeneity Analysis
In the baseline regression results, the influence coefficient of DF on ULUE was the average effect of 283 cities, which could not explain the heterogeneity of the effect of DF on ULUE. Heterogeneity analysis has a positive significance to provide valuable policy implications. The geographical locations of various cities vary, and it is imperative to categorize cities based on their respective regions. Furthermore, provincial capital cities exhibit a higher level of economic development compared to other cities within the province. Therefore, for the purpose of heterogeneity analysis, the sample is categorized into provincial and non-provincial capital cities. Table 6 shows that all coefficients of lnDF in these models are significantly positive. The coefficient value indicates that in the western region and provincial capital cities, the impact of DF on ULUE is significantly higher compared to other regions. The coefficients for the eastern region, central region, and non-provincial capital cities are relatively small.

Table 6.
Heterogeneity analysis results.
4.7. Threshold Effect Analysis
Based on the theoretical analysis and actual conditions of regional economic development in China, there exist certain disparities in both economic development and DF among different cities. Therefore, a nonlinear relationship between DF and ULUE can be possibly observed under varying circumstances of economic development and DF level. This paper employs the panel threshold model by selecting urban economic development and DF as threshold variables.
The bootstrap method was employed to perform 300 independent samplings for testing various threshold variables [77], and the outcomes are presented in Table 7. Among them, the results of significance tests indicate that the single threshold of urban economic development passed at a significance level of p < 0.01. In terms of DF, it successfully passed both the single and double thresholds at a level of p < 0.01 but failed to meet the criteria for the triple threshold. Therefore, utilizing the single threshold model, this paper conducts an analysis of the impact of DF on ULUE across varying levels of urban economic development. According to the double threshold model, this paper examines the impact of DF on ULUE across varying levels of DF development.

Table 7.
Threshold condition test results.
According to Table 7 and Table 8, it is evident that DF has a significant impact on ULUE at different stages of economic development. Specifically, when lnEd is below the threshold value of 11.719, the coefficient of lnDF affecting ULUE is 0.082; however, when it exceeds this threshold, its coefficient increases to 0.110, thereby enhancing the promotion effect of DF on ULUE. This is primarily attributed to the higher digitalization and more robust industrial support resulting from the advancement of economic development. These factors contribute to creating a more favorable environment for DF, facilitating its role in promoting industrial upgrading and ecological optimization, thereby further enhancing ULUE.

Table 8.
Threshold effect test results.
In conjunction with Table 7 and Table 8, it is evident that DF presents a significant threshold effect on ULUE across varying development levels of DF. When the level of lnDF falls below the threshold value of 5.315, the coefficient of lnDF affecting ULUE is −0.004, but it lacks statistical significance, indicating that a lower DF level does not have a statistically significant impact on ULUE. When the level of lnDF falls in the threshold value range of 5.315 to 5.363, it enhances the promotion effect on ULUE with a coefficient increase to 0.023. Even when lnDF exceeds the threshold value of 5.363, it has a significantly positive impact on ULUE at the p < 0.01 level with an increased coefficient up to 0.074. With the advancement of DF, its impact on ULUE shows a marginal increase. This is primarily due to the continuous innovation and maturation of DF technologies, which can lead to a greater diversification of DF products and services. As a result, they will be better equipped to meet the financing needs associated with land utilization and development. Furthermore, DF advancement can enhance the financing efficiency of land projects and mitigate financing expenses, thereby further optimizing land utilization. As a result, hypothesis H3 is validated.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
By taking 283 Chinese cities as an example, this study validated the direct effect of DF on ULUE as well as the mediating role of ISU on the indirect effect of DF on ULUE, and the nonlinear characteristic of this effect has also been proved. The findings of this study elaborated the influential mechanism of DF on ULUE, which offered new insights for optimizing land resource utilization.
5.1. Conclusions
The conclusions of this study are as follows: (1) In general, the implementation of DF can significantly facilitate the enhancement of ULUE. The empirical findings demonstrated that the lnDF had a significant positive impact on ULUE, with an estimated coefficient of 0.082; that is, a 1% increase in DF was associated with a corresponding increase in ULUE by 0.082 units. From the perspective of sub-dimensions, lnBre, lnDep, and lnDig exhibit significant enhancements on ULUE with their respective influence coefficients being 0.067, 0.101, and 0.030. Among them, the depth of DF utilization has the strongest promotional effect on ULUE, with every 1% increase in itself resulting in a 0.101 increase in ULUE, while the impact of coverage breadth and degree of digitalization is relatively weak. (2) From the perspective of intermediary mechanisms, DF can enhance ULUE by driving ISU. Of the effects of DF on ULUE, 20.002% were attributed to the promotion of ISU. (3) From the perspective of heterogeneity, it is observed that DF can significantly enhance ULUE in both eastern, central, and western regions, as well as provincial capital cities and non-provincial capital cities. However, judging by the magnitude of the numbers, the promoting effect of lnDF on ULUE is more pronounced in western cities and provincial capital cities, with influence coefficients of 0.091 and 0.238, respectively. Conversely, the impact of lnDF on ULUE is relatively small in eastern, central, and non-provincial capital cities. (4) The impact of DF on ULUE exhibits a threshold effect. With the improvement of economic development level and DF, the promoting effect of DF on ULUE will be further enhanced. Specifically, when lnEd surpasses the threshold of 11.719, the influence coefficient of lnDF on ULUE increases from 0.082 to 0.110. When DF is at a low level, it fails to facilitate the enhancement of ULUE by itself. However, once lnDF surpasses 5.315, DF can significantly increase ULUE. Moreover, when lnDF exceeds 5.363, the impact coefficient of lnDF on ULUE further escalates to 0.074; in other words, each 1% increase in DF will result in a corresponding increase of 0.074 in ULUE.
5.2. Discussion
As a novel financial development model, DF has exerted significant impacts across all aspects of economy and society. This study explored the relationship between DF and ULUE, and the empirical results confirm our hypothesis and provide a valuable supplement to existing research on factors influencing ULUE.
This paper presents the measurement, trends and evolving characteristics of ULUE across China and its three major regions, which is consistent with Xu and Su’s findings [17]. The evolution trend of ULUE in China drawn by Zhong and Li [64] also shows similar results, but there are minor discrepancies. The differences observed in the images are primarily attributed to variations between the index systems employed by Xu and Su versus those utilized in this study. Specifically, Xu and Su’s analysis focuses on China’s urban land green use efficiency, while Zhong and Li examine trends in ULUE within a specific region of China.
In the analysis of intermediary effects, this study reveals that DF presents a positive driving force on ISU, which is consistent with the findings of Ren et al. [43] and Zhang et al. [44]. Additionally, this study also demonstrates that ISU significantly promotes ULUE improvement, in line with the research results of Liu et al. [23] and Wang et al. [24]. However, unlike previous studies, this paper considers ISU as the mediating variable through which DF impacts ULUE. Empirical research reveals that DF can enhance ULUE by promoting ISU.
In the examination of the impact of control variables on ULUE, this study has ascertained that: (1) Economic development is positively correlated with ULUE, which is consistent with the findings of Shu et al. [78] and Qu et al. [79]. (2) The increase in population density impeded the enhancement of ULUE, which is consistent with Anders’ research findings [80]. (3) The degree of urban traffic development exerts a significant promoting effect on ULUE, which is in line with the findings of Cui et al. [81]. (4) Direct financial support from local governments can effectively facilitate the enhancement of ULUE, which is in line with the research findings of Fan et al. [82]. Moreover, the aforementioned literature further confirms the robustness of our study results.
The more significant finding of this study lies in the regional variations or heterogeneity in the impact of DF on ULUE. Figure 5 provides a clearer depiction of the disparities in the influence of DF on ULUE across different samples. In comparison to the eastern and central regions, the western region lags behind in terms of economic development and the construction of road transportation facilities; however, it possesses a greater abundance of land resources. The digital finance model, being an Internet-based financial service, has relatively low requirements for transportation infrastructure. Consequently, it enables the provision of financial services to the western region and facilitates the enhancement of ULUE. The western region holds immense potential for the development of DF, which can bring new economic growth points to the region and subsequently enhance ULUE. Compared to non-provincial capital cities, provincial capital cities possess a greater concentration of advantageous factors such as financial resources, innovative talents, and market demand. This creates a more expansive environment for the development of digital finance and offers a wider array of financial services and solutions for improving ULUE. Therefore, digital finance can more effectively improve ULUE in western regions and provincial capitals.
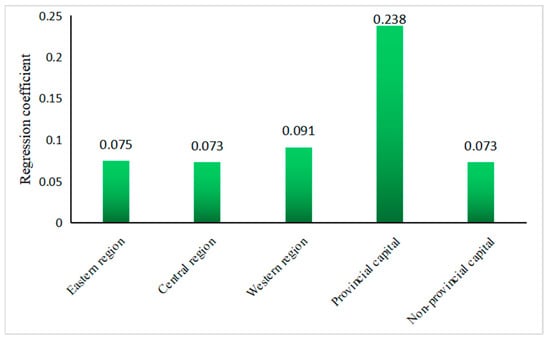
Figure 5.
Regression coefficients of different samples of lnDF to ULUE.
The findings of this study offer new insights for optimizing land resource utilization. The potential contributions lie primarily in the following aspects: (1) Through a comprehensive analysis of DF and its three dimensions, we have enriched the existing research on factors influencing ULUE by examining the influential effect and mechanism of DF on ULUE. The influential role of DF has been overlooked in previous studies. The present study examines the mechanism by which DF directly impacts ULUE, while also uncovering the underlying mechanisms through which DF influences ULUE. This paper represents a pioneering empirical investigation into the correlation between DF and ULUE. (2) It expands the existing research on DF. Although some scholars have examined the impact of DF on ISU, there has been a lack of comprehensive analysis regarding the interrelationship among DF, ISU, and ULUE. The present study not only evaluates the direct impact of DF on ULUE but also investigates the mediating effect of ISU, thereby contributing to the existing literature at the intersection of financial economics and land use science. (3) A comprehensive analysis was conducted on the heterogeneity and nonlinear characteristics of the impact of DF on ULUE. This aims to provide targeted strategies and recommendations for promoting the development of DF, enhancing ULUE, and achieving sustainable utilization of land resources both in China and around the world. Without a thorough analysis of the heterogeneity and nonlinear characteristics of DF’s impact on ULUE, valuable research findings cannot be obtained.
The results of heterogeneity analysis and threshold model have the following policy implications: Firstly, we should vigorously develop DF, fully leverage emerging digital technologies, promote balanced development across multiple dimensions such as coverage breadth, usage depth and degree of digitization in order to make DF a new driving force for improving ULUE, and enhance the deep collaboration between traditional financial institutions and digital financial platforms, facilitating diverse financial services for the prudent utilization of land. The land administration department should establish a collaborative development agency for DF and incorporate the utilization of digital finance into the performance appraisal. Currently, certain local governments are confronted with a funding shortfall and can address the financing needs for digital technology development by means of local borrowing. Secondly, we should fully leverage the exemplary role of advanced regions. The empirical research demonstrates that DF exerts the most significant impact on ULUE in provincial capitals. Therefore, we should leverage the valuable experience of advanced regions to drive improvements in ULUE across less developed areas. At the national level, a demonstration area for digital finance to promote the improvement of ULUE should be established, and the assessment should be conducted once every three years, and the assessment results should be disclosed in a timely manner. At the same time, the experience of the demonstration zones will be published in the form of blue books for cities in developing countries to learn from. Third, economic development is equally important. Empirical research shows that economic growth and DF are significant threshold variables. Therefore, while developing DF, it is also necessary to continuously promote economic growth, which is a challenging job for governments around the world. The rise of ULUE in other rapidly urbanizing BRICS countries is also noteworthy. Since there are certain similarities in the economic development of China and other BRICS countries, other countries should also focus on the synergy of economic growth and digital financial development, but more empirical investigations are still needed to validate that.
Limitations of this study still exist. Firstly, it should be noted that the focus of this research was primarily on 283 cities within China, without conducting an in-depth analysis of resource-based cities. Therefore, further investigation is required to explore potential variations in the impact of DF on ULUE. The data collection for this study did not include the period from 2021 to 2022. Once the data for these two years become available, future research can delve deeper into examining the impact of DF on ULUE. Secondly, the efficient utilization of land resources is a crucial concern among scholars. This study is based on an analysis of Chinese data, and it is expected that more researchers will utilize data from other countries to validate the hypothesis. On the basis of this study, there is a very valuable research direction in the future, which is to analyze the synergistic effect of green finance and DF on ULUE. Thirdly, the study on the relationship between DF and ULUE can further establish a theoretical model to more precisely depict the promotional impact of DF on ULUE. The intermediary variable in this study is ISU, while future research could consider other intermediary variables such as environmental regulation and science and technology expenditure, thus enabling a more comprehensive analysis of the mechanism through which DF influences ULUE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Q.; data curation and methodology, H.Q. and X.L.; formal analysis, H.Q. and X.L.; visualization, H.Q. and X.L.; writing—review and editing, H.Q. and L.Z.; revision and editing, H.Q. and L.Z.; project administration, H.Q.; funding acquisition, H.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Fund Project, Research on Green Development Mechanism and Path of the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of State Governance Modernization (22BZZ039) and the Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Z. The Border Effect on Urban Land Expansion in China: The Case of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, G.; Puga, D. Chapter 8—Urban Land Use. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Duranton, G., Henderson, J.V., Strange, W.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 467–560. ISBN 1574-0080. [Google Scholar]
- Cipoletti, N.; Jorgenson, Z.G.; Banda, J.A.; Kohno, S.; Hummel, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L. Biological Consequences of Agricultural and Urban Land-Use along the Maumee River, a Major Tributary to the Laurentian Great Lakes Watershed. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up Land Efficiency in Urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Impact of Urbanization on Cultivated Land Changes in China. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Fang, B.; Xu, H.; He, S.; Li, X. Study on the Coordinated Relationship between Urban Land Use Efficiency and Ecosystem Health in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Spatial-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of the Coordinated Relationship among Multiple Land Use Efficiencies Integrating Stakeholders’ Vision in Eastern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, D.; Löw, F.; Ibrakhimov, M.; Sarah-Schönbrodt-Stitt; Conrad, C. Feature Extraction and Machine Learning for the Classification of Active Cropland in the Aral Sea Basin. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Worth, TX, USA, 23 July 2017; pp. 1804–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Wiatkowska, B.; Słodczyk, J.; Stokowska, A. Spatial-Temporal Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Urban Areas Using Remote Sensing Images and GIS Analysis: The Case Study of Opole, Poland. Geosciences 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Huang, H.; Tian, Y. The Identification and Use Efficiency Evaluation of Urban Industrial Land Based on Multi-Source Data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jin, G.; Deng, X. Dynamic Interactive Effects of Urban Land-Use Efficiency, Industrial Transformation, and Carbon Emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, J.; Meng, L.; Qin, X.; Qi, X. Measuring the Area Green Efficiency and the Influencing Factors in Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, L. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of Urban Land Use Efficiency of China’s 35mega Cities Based on DEA: Decomposing Technology and Scale Efficiency. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W. Land Use Efficiency Assessment under Sustainable Development Goals: A Systematic Review. Land 2023, 12, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L.; Zou, L.; Zhang, H. Exploring the Eco-Efficiency of Cultivated Land Utilization and Its Influencing Factors in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt, 2001–2018. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, X. Urban Administrative Hierarchy and Urban Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 88, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sun, Y. The Impact of Industrial Agglomeration on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency and Its Spatio-Temporal Pattern: Evidence from 283 Cities in China. Land 2023, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yue, L.; Ahmad, F.; Draz, M.U.; Chandio, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Amin, W. Empirical Investigation of Urban Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Yellow River Basin Chinese Cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. Measuring the Efficiency and Driving Factors of Urban Land Use Based on the DEA Method and the PLS-SEM Model—A Case Study of 35 Large and Medium-Sized Cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Işık, C.; Jabeen, G.; Ali, T.; Ozturk, I.; Atchike, D.W. Heterogeneous Links among Urban Concentration, Non-Renewable Energy Use Intensity, Economic Development, and Environmental Emissions across Regional Development Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Urban Agglomerations in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Freire, S.; Florio, P.; Ehrlich, D.; Tommasi, P.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Land Use Efficiency of Functional Urban Areas: Global Pattern and Evolution of Development Trajectories. Habitat Int. 2022, 123, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. Study the Effect of Industrial Structure Optimization on Urban Land-Use Efficiency in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Liao, C. Urban Development Sustainability, Industrial Structure Adjustment, and Land Use Efficiency in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.D. How Does Industrial Agglomeration Affect Urban Land Use Efficiency? A Spatial Analysis of Chinese Cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Qian, Y. Does Fiscal Decentralization Promote Green Utilization of Land Resources? Evidence from Chinese Local Governments. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Z. How Regional Economic Integration Influence on Urban Land Use Efficiency? A Case Study of Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H.; Lengoiboni, M.; Zevenbergen, J.A. Urbanization and Urban Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from Regional and Addis Ababa Satellite Cities, Ethiopia. Habitat Int. 2021, 117, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jie, X.; Ning, S.; Wang, K.; Li, X. Coupling and Coordinated Development of Urban Land Use Economic Efficiency and Green Manufacturing Systems in the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, G. A Systematic Coupling Analysis Framework and Multi-Stage Interaction Mechanism between Urban Land Use Efficiency and Ecological Carrying Capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, J.J. The Impact of Digital Finance on Household Consumption: Evidence from China. Econ. Model. 2020, 86, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z. Determinants and Mechanisms of Digital Financial Inclusion Development: Based on Urban-Rural Differences. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Ma, R. How Does Digital Finance Influence Green Technology Innovation in China? Evidence from the Financing Constraints Perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Xie, Z. The Nexus between Digital Finance and Economic Development: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Nie, L.; Sun, H.; Sun, W.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Digital Finance, Green Technological Innovation and Energy-Environmental Performance: Evidence from China’s Regional Economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-J.; Tang, K.; Hu, H.-Q. The Impact of Digital Finance on Green Innovation: Evidence from Provinces in China. Innov. Green Dev. 2022, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, X. The Impact of Digital Inclusive Finance on Sustainable Economic Growth in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 50, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, I.; Nurjannah, D.; Mohyi, A.; Ambarwati, T.; Cahyono, Y.; Haryoko, A.E.; Handoko, A.L.; Putra, R.S. The Effect of Digital Marketing, Digital Finance and Digital Payment on Finance Performance of Indonesian SMEs. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2021, 6, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, M.; Li, W.; Xian, B.T.S.; Yang, A. Digital Inclusive Finance and Enterprise Innovation—Empirical Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, Y.; Qian, M.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, D.; Chen, Y. The Contribution of Fintech to Sustainable Development in the Digital Age: Ant Forest and Land Restoration in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, G. User Continuance of a Green Behavior Mobile Application in China: An Empirical Study of Ant Forest. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, P.; Hao, Y.; Dagestani, A.A. Tax Incentives and Green Innovation—The Mediating Role of Financing Constraints and the Moderating Role of Subsidies. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1067534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zeng, G.; Gozgor, G. How Does Digital Finance Affect Industrial Structure Upgrading? Evidence from Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bao, K.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. Digital Finance, Industrial Structure, and Total Factor Energy Efficiency: A Study on Moderated Mediation Model with Resource Dependence. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhai, C.; Zhao, S. Does Digital Finance Promote Household Consumption Upgrading? An Analysis Based on Data from the China Family Panel Studies. Econ. Model. 2023, 125, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, G. Research on the Impact of Digital Finance on the Green Development of Chinese Cities. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 3813474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Wei, X. The Impact of Digital Finance Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Households in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 190, 122364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J. How Does Digital Inclusive Finance Affect Economic Resilience: Evidence from 285 Cities in China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023, 88, 102709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, L. Digital Finance and Regional Economic Resilience: Theoretical Framework and Empirical Test. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 55, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, G. Environmental Decentralization, Digital Finance and Green Technology Innovation. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2022, 61, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.M. Panel Threshold Analysis of Taiwan’s Outbound Visitors. Econ. Model. 2013, 33, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, Y. Research and Application of 3D Visualization and Internet of Things Technology in Urban Land Use Efficiency Management. Displays 2021, 69, 102050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodima-Taylor, D. Digitalizing Land Administration: The Geographies and Temporalities of Infrastructural Promise. Geoforum 2021, 122, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu; Singh, A.K.; Raza, S.A.; Nakonieczny, J.; Shahzad, U. Role of Financial Inclusion, Green Innovation, and Energy Efficiency for Environmental Performance? Evidence from Developed and Emerging Economies in the Lens of Sustainable Development. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2023, 64, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, H. Does Smart City Construction Improve the Green Utilization Efficiency of Urban Land? Land 2021, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanbayev, R.; Bu, W. How Does Digital Finance Affect Industrial Transformation? JIE 2023, 1, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ren, X. Digital Finance and Upgrading of Industrial Structure: Prefecture-Level Evidence from China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 55, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhong, S. Does Digital Inclusive Finance Promote Industrial Transformation? New Evidence from 115 Resource-Based Cities in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Dong, H. Green Finance, Industrial Structure Upgrading, and High-Quality Economic Development–Intermediation Model Based on the Regulatory Role of Environmental Regulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Majeed, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sohaib, M.; Shehzad, K. Digital Financial Inclusion and Economic Growth: Provincial Data Analysis of China. China Econ. J. 2021, 14, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mo, B. Can Digital Finance Promote Urban Innovation? Evidence from China. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 2023, 23, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chong, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, S. Digital Finance and Innovation Inequality: Evidence from Green Technological Innovation in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87884–87900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luan, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, Y. Can Digital Financial Inclusion Promote China’s Economic Growth? Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 78, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, Y. Mediating Effect and Suppressing Effect: Intermediate Mechanism of Urban Land Use Efficiency and Economic Development. Land 2023, 12, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Meng, C.; Cao, Q. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Low Carbon Urban Land Use Efficiency—Based on Non-Radial Directional Distance Function. Land 2022, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.; Wong, A.K.W.; Shek, D.T.L. Social Development in Hong Kong: Development Issues Identified by Social Development Index (SDI). Soc. Indic. Res. 2010, 95, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Popp, D. International Innovation and Diffusion of Air Pollution Control Technologies: The Effects of NOX and SO2 Regulation in the US, Japan, and Germany. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2006, 51, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z. Measuring China’s Digital Finance Inclusion: Index Complilation and Spatial Characteristics. China Econ. Q. 2020, 19, 1401–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Liang, L.; Zhu, J. A Slacks-Based Measure of Super-Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis: A Comment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 204, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Shao, W. How Does Digital Economy Drive Industrial Structure Upgrading: An Empirical Study Based on 249 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, C.; Zhu, S. Do China’s Economic Development Zones Improve Land Use Efficiency? The Effects of Selection, Factor Accumulation and Agglomeration. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Li, J. Regional Difference Decomposition and Policy Implications of China’s Urban Land Use Efficiency under the Environmental Restriction. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Su, Y.; Ren, K.; Song, F.; Xue, R. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Urban Traffic Ecological Resilience in Developing Countries: A Case Study of 31 Chinese Cities. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, C.; Shu, T.; Ren, Y. Spatiotemporal Impacts of Urban Structure upon Urban Land-Use Efficiency: Evidence from 280 Cities in China. Habitat Int. 2023, 131, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; He, J. Digital Economy, Technological Innovation, and Green Economic Efficiency—Empirical Evidence from 277 Cities in China. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, L. The Convergence between Digital Industrialization and Industrial Digitalization and Export Technology Complexity: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, L.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of Government Subsidies on Renewable Energy Investments: The Threshold Effect. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Xie, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Q. Is Urban Land Development Driven by Economic Development or Fiscal Revenue Stimuli in China? Land Use Policy 2018, 77, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Long, H. The Economic and Environmental Effects of Land Use Transitions under Rapid Urbanization and the Implications for Land Use Management. Habitat Int. 2018, 82, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirén, A.H. Population Growth and Land Use Intensification in a Subsistence-Based Indigenous Community in the Amazon. Hum. Ecol. 2007, 35, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Bao, C. Spatial Relationship of High-Speed Transportation Construction and Land-Use Efficiency and Its Mechanism: Case Study of Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Qiu, S.; Sun, Y. Land Finance Dependence and Urban Land Marketization in China: The Perspective of Strategic Choice of Local Governments on Land Transfer. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).