Abstract
Arsenic (As) is a well-known toxic metalloid, but environmental risks due to excessive As content in soils or sediments depend on the chemical forms present and their relative mobility. Long-term exposure to arsenic may cause several diseases. In order to assess the possible risks in the heavily impacted Consorzio per lo Sviluppo Industriale e di Servizi Reali alle Imprese (Consortium for Industrial Development and Effective Services for Business, S.I.S.R.I.) industrial area of Brindisi (Apulia, southern Italy), 38 soil samples were collected in the area, from 18 sampling points previously determined as outliers. Total As determination, speciation analysis, and a cession test with acetic acid were performed. Speciation analysis was performed by HPLC coupled to hydride generation-atomic absorption spectroscopy (HG-AAS). Total As determination obtained by mineralization showed a concentration range between 51.8 and 169.6 mg kg−1, which is higher than the limit of 50 mg kg−1 established by D.M. (Ministerial Decree) 471/99 for industrial areas. The highest concentrations of extracted As were obtained in the top-soil layers. As(III) and As(V) were detected in all the samples, while the concentrations of the organic species monomethyl arsonic acid (MMAA) and dimethyl arsenic acid (DMAA) were always under the detection limit. The samples releasing the highest As quantities in the acetic acid cession test were in every circumstance collected from the superficial soil levels. The different amounts of As determined in the sampling sites could depend on the distance from the specific sources of pollution, even if it is very difficult to identify them in a very complex industrial zone such as the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi. In this study, As occurs mainly as relatively immobile or slowly exchangeable forms: for this reason, it is more abundant in the top-soil and is little affected by the action of rainwater, which transports only reduced quantities of As into the deeper layers.
1. Introduction
Arsenic (As) is the twentieth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust [1]. Many As compounds are present in the environment and in biological systems: arsenite (As(III)), arsenate (As(V)), monomethylarsonic acid (MMAA), dimethylarsinic acid (DMAA), arsenobetaine (AsB), arsenocholine (AsC), arsine (AsH3), arsenosugars, etc. [2]. Arsenite, arsenate, MMAA, and DMAA are the most often encountered forms and also the most studied in soils and sediments [3,4]. A very large number of sites in the world are characterized by high levels of As concentration in soils or sediments, either for geochemical reasons or due to anthropic impact [5,6], for instance, as reported in Greece and Cyprus [7], Bangladesh and West Bengal [8], India [9], and Brazil [10]. Non-contaminated soils have an As content in the 1–40 mg kg−1 range; agricultural soils subjected to direct use [11] of arsenical pesticides may reach 2550 mg kg−1; and up to 3000 mg kg−1 has been measured in the proximity of cattle pesticide dip sites [12]. In old industrial [13] or mining sites, As concentrations higher than 20 g·kg−1 may sometimes be detected [14].
However, it has long been realized that the determination of total As concentration is not sufficient for clinical and environmental considerations [15]. Environmental risks linked to the presence of an excessive As content in soils or sediments depend on the chemical forms present and their relative mobility. It is now well known that As species are not all equally toxic to humans; the most toxic forms are the inorganic As species, followed by the methylated species of intermediate toxicity, while the biomolecules are non-toxic [16]. Other As complexes, such as AsB and AsC, are also considered non-toxic [17]. These differences may modulate the toxic effects as a function of the effective bioavailability of As, for example, in food samples [18]. Differences in the mobility of ionic species also play an important role; in fact, As(III) is much more mobile in the environment than As(V) [19]. Speciation studies focus on the species that can be dissolved in water under environmentally attainable conditions such as inorganic As (i.e., arsenite and arsenate), MMAA, and DMAA [20]. Many minerals containing As (for example arsenopyrite, FeAsS) may be found in soils without presenting an immediate risk because of a very low solubility, except in specific conditions or in the long-term [21]. Therefore, sequential extractions may be needed to investigate the effective mobility and availability of the As contained in the samples [22].
Consequently, accurate As speciation studies [20] of soils [13,23], sediments [23,24], and cell cultures [25], and, in general, environmental [26] and biological samples [27,28], are required for assessments of environmental impact and health risks.
The techniques used for the detection of As species in environmental and biological samples should be sensitive and selective, with a rapid analysis of samples to prevent As species interconversion before detection [29]. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has become a favored detection technique in As analysis [27]. It provides ultra-sensitivity and multi-element capability and can be combined with separation techniques for speciation analysis. Another common technique used in As speciation is hydride generation (HG) [30]. HG provides extremely low detection limits and has been used in the quantification of the unstable trivalent arsenic metabolites MMAA and DMMA [31]. However, not all As species form hydrides; therefore, decomposition techniques are usually required.
A combination of analytical techniques is often necessary to achieve both selectivity and sensitivity. Hyphenated techniques allow for the possible separation of all soluble species in the sample and selective detection at low concentrations. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is frequently used as the separation technique in As speciation, in biological samples [27], drinking waters [32], and environmental samples [30,33].
The separation and detection techniques used in As analysis are only as reliable as the sampling procedure used. Species instability during sampling, storage, and sample pre-treatment are all very important issues that must be considered. Species may be converted from one form to another or lost from the sample [31]. If the original distribution of the species in the sample is destroyed, the result of speciation analysis is questionable. The methods of extraction of As from solid samples must be efficient and minimize the destruction or transformation of the As species present in the solid materials.
“Soft” extraction approaches (hydroxylammonium hydrochloride, ammonium oxalate, and orthophosphoric acid) have been studied and applied to the determination of As species (arsenite, arsenate, MMAA, DMAA) in different environmental solid reference materials (river sediment, agricultural soil, sewage sludge) certified for their total As content [34]. The analytical method used was ion exchange liquid chromatography coupled online to atomic fluorescence spectroscopy through hydride generation. Orthophosphoric acid was the best extractant for sediment (mixed origin) and sludge samples (recent origin), but not for the older formation soil samples, from which As was extracted efficiently only by ammonium oxalate. The inorganic forms As(III) and As(V) were both significant in all samples, with the As(V) species being predominant. Microwave-assisted extraction appears to minimize the risk of a redox interconversion of inorganic As forms [34].
With this in mind, we performed the speciation analysis of As and the cession test with acetic acid on 38 samples collected in an area heavily stressed by environmental factors, namely the Consorzio per lo Sviluppo Industriale e di Servizi Reali alle Imprese (Consortium for Industrial Development and Effective Services for Business, S.I.S.R.I.) area of Brindisi (Apulia, southern Italy), in the context of an environmental monitoring project. The S.I.S.R.I. Consortium, together with the Port of Brindisi Consortium, includes and manages an area counting various types of infrastructure: a railway network with a length of approximately 40 km and approximately 30 km of roads equipped with methane, water, sewerage, telephone, and optical fiber pipelines. The main industrial activities of the Consortium include construction and repair of aeronautical engines, pharmaceuticals, a thermoelectric power plant, sugar refining, petrochemicals, and polymer production.
The chemical speciation, defined by the European Community [35] and by I.U.P.A.C. (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) recommendations [36], was performed to determine the concentration of As(III), As(V), and the main As methyl-derivatives (MMAA and DMAA) [37]. In order to investigate the possibility of arsenic elution from superficial to deeper layers, which is strongly related to differences in soil characteristics and the availability and solubility of the arsenic species, in some sites the sampling was performed in layers at different depths. We performed (i) As extraction from soil samples; (ii) As compound separation by HPLC (ion exchange column); (iii) As compound analysis by hydride generation-atomic absorption spectroscopy (HG-AAS); and (iv) a classic cession test in acetic acid (IRSA-CNR method) [38].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sample Collection and Total As Determination
Thirty-eight soil samples were collected from different sampling points in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi (Apulia, Italy), as described in Figure 1. The sampling points were selected by the commissioning body Regione Puglia, Italy, as an additional investigation in the area following a previous survey. The samples were independently collected and supplied to our laboratory for the analysis. In some of the sites, different depth levels were considered: 0.0–0.1 m (top-soil), 0.4–1.0 m, 3.4–4.0 m, and 7.4–8.0 m.
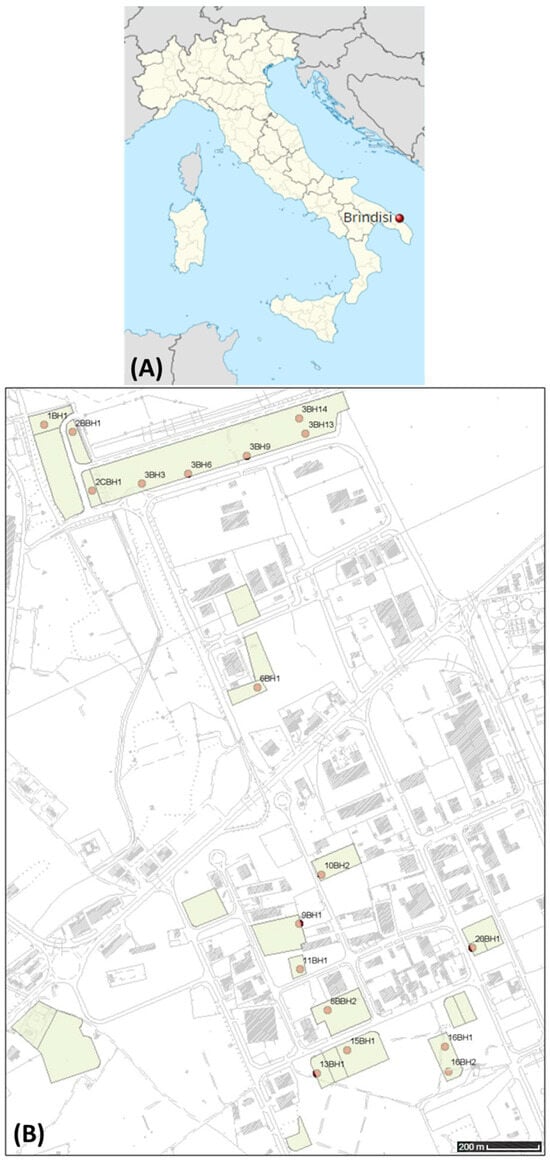
Figure 1.
(A) Map of Italy with administrative divisions. City of Brindisi is marked by a dark red dot. (B) Map showing labels for the locations of the 38 soil collection sites in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi; four different depth levels (0.0–0.1 m, 0.4–1.0 m, 3.4–4.0 m, 7.4–8.0 m) were sampled. The alphanumeric code before the slash indicates the sampling point, while the numbers after the slash indicate, for each point, the different depths of the soil sample. The coordinates of the depicted area corners, reported in decimal degrees, are as follows: 40.644261, 17.959213 top left; 40.622922, 17.959213 bottom left; 40.644261, 17.978737 top right; 40.622922, 17.978737 bottom right.
Total As determination was performed using the hyphenated technique HG-AAS after sample mineralization with one volume of nitric acid and three volumes of hydrochloric acid. The results are summarized in Table 1. The maximum level of total As concentration was detected in the sample 2CBH1/1, a top-soil sample with 169.6 mg kg−1 of As. The lowest As concentration was found in the sample 13BH1/1 at the 0.4–1.0 m depth level (51.8 mg kg−1). All the data show concentrations higher than the limit of 50 mg kg−1 established by D.M. (Ministerial Decree) 471/99 for industrial areas.

Table 1.
Results of total As determination, speciation analysis, and cession test of the 38 soil samples from the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi. Sample name is a combination of sampling site and depth of the probe. The alphanumeric code before the slash indicates the sampling point, while the numbers after the slash indicate, for each point, the different depths of the soil sample. As(III), As(V), MMAA, DMAA: speciation analysis of the ammonium oxalate extract; speciation total As: total concentration obtained from the ammonium oxalate extraction; total As: concentration obtained from mineralization; cession test As: concentration obtained from acetic acid cession test.
2.2. Ammonium Oxalate Extraction and As Speciation
Chemical speciation analysis consisted of the determination of the concentration of As(III), As(V), and the main As methyl-derivatives (MMAA and DMAA), which are the species typically detected in soil and sediment samples [37]. Before the speciation analysis, the soils were extracted with 0.2 M ammonium oxalate, a soft chemical extraction method affording very high recovery of As from soil matrices [34,39]. As(III) and As(V) were found in all the analyzed samples, whereas the concentrations of the organic species MMAA and DMAA concentrations were always lower than the detection limits (<0.11 and <0.15 mg kg−1, respectively); see Table 1.
Total inorganic As was calculated as the sum of the As(V) and As(III) concentrations (determined by ammonium oxalate extraction and speciation analysis), and was found to be, on average, 62% of the total As measured after mineralization. The ratios between the speciation total As and the total As (column 7 and 8 of Table 1, respectively) ranged from a minimum of 36% (sample 3BH14/8, 7.4–8.0 m of depth) to a maximum of 92% (sample 6BH1/0.0–0.1, top-soil) (Table 1 column 10). This result can be attributed to differences in the sample matrices. As extracted by ammonium oxalate was equal to (i) 30–40% of total As in two samples (5.3% of analyzed samples); (ii) 40–50% in six samples (15.8%); (iii) 50–60% in eight samples (21.1%); (iv) 60–70% in eleven samples (28.9%); (v) 70–80% in ten samples (26.6%); and >80% in one sample (2.6%) (Figure 2).
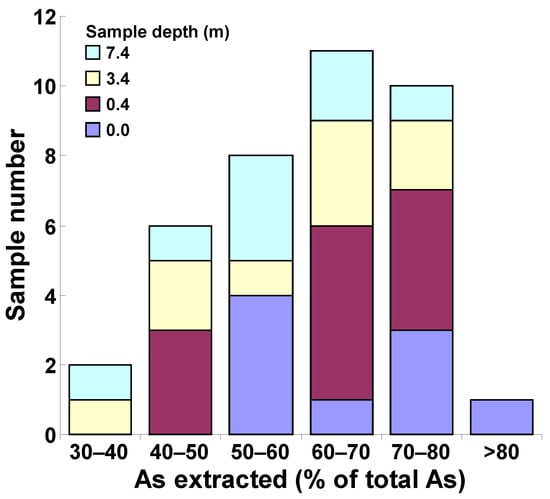
Figure 2.
Arsenic determined by oxalate extraction as a percentage of total arsenic obtained by mineralization of the 38 samples collected in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi.
The highest values of As extracted by ammonium oxalate were found in the top-soil samples and in the samples deriving from the depth of 0.4–1.0 m. A significant decrease in the As percentage extracted by ammonium oxalate was recorded in the deepest sampled layers (Figure 3). Since ammonium oxalate extraction is able to solubilize many of the arsenic coprecipitates, including those with amorphous Fe, Al, and Mn oxyhydroxide, but not their crystalline forms or sulfides [40], this result allowed us to hypothesize that a significant percentage of arsenic is strongly bound or occluded, particularly in the deeper soil layers, suggesting a natural origin of arsenic in the soil. The highest percentage of extracted arsenic, significantly increasing in the top-soil and first layer, can be possibly attributed to changes in soil makeup and texture in the deeper layers [13,41].
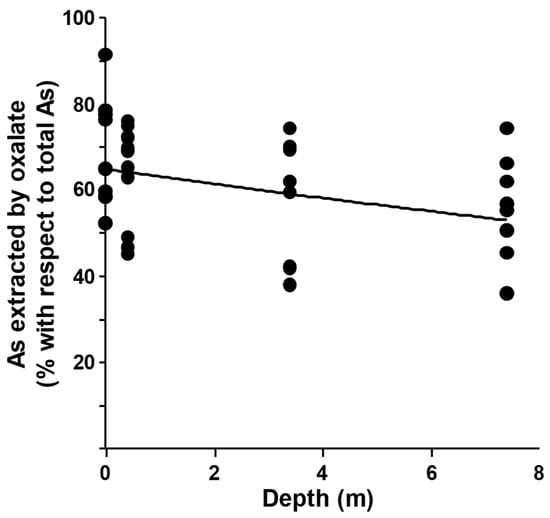
Figure 3.
Plot of quantity of arsenic extracted by ammonium oxalate expressed as percentage of total arsenic determined after mineralization, against depth of the soil samples.
Speciation analyses revealed that, in all samples, As(V) accounted for the majority of the As extracted by 0.2 M ammonium oxalate (>90%); As(V) percentages ranged from a minimum of 90.23% (sample 13BH1/1, depth 0.4–1.0 m) to a maximum of 99.97% (sample 3BH9/1, depth 0.4–1.0 m; sample 15BH1/8, depth 7.4–8.0 m). Conversely, As(III) percentage values ranged from 0.03% (sample 3BH9/1, depth 0.4–1.0 m; sample 15BH1/8, depth 7.4–8.0 m) to 9.77% (sample 13BH1/1, depth 0.4–1.0 m). In particular, (i) six samples (15.8% of the 38 analyzed samples) showed As(III) percentage values in the range 0–2% of the total As amount extracted by ammonium oxalate; (ii) eighteen samples (47.4%) were in the range 2–5%; (iii) twelve samples (31.6%) were in the range 5–8%; and (iv) two samples (5.3%) were in the range 8–10%. The highest As(III) percentage values were detected at low depth, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
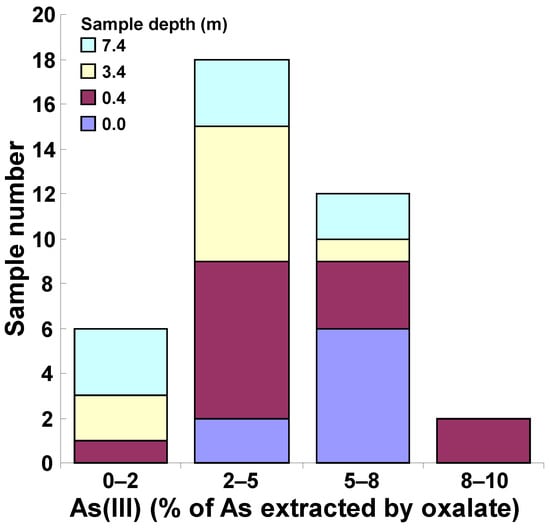
Figure 4.
As(III) obtained from the speciation analysis, expressed as percentage of total As extracted by ammonium oxalate for the 38 samples collected in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi.
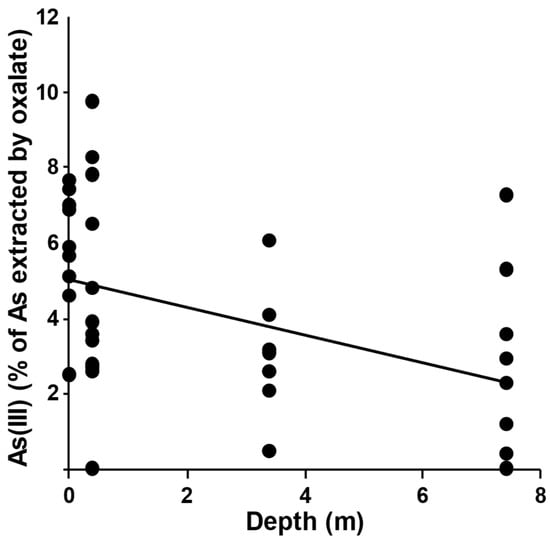
Figure 5.
Plot of As(III) as percentage of arsenic extracted by ammonium oxalate, against the depth of the soil samples.
The amount of As extracted by ammonium oxalate was found to be a linear function of both the As(V) and As(III) percentage values determined in the speciation analysis (Figure 6).
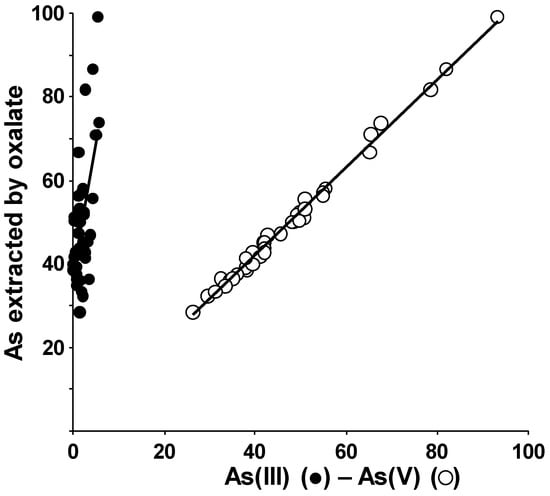
Figure 6.
Plot of total As amount extracted by ammonium oxalate vs. As(V) and As(III) percentage values as determined in the speciation analysis.
The linearity of the functions and the relationship between the As(III)/As(V) ratio and the As(III) concentration (Figure 7) indicate that As(III) and As(V) are not in equilibrium. In fact, the As(III)/As(V) ratio increases with the increase in the percentage of As(III), and the As(III)/As(V) ratio is constant only at high levels of As(III).
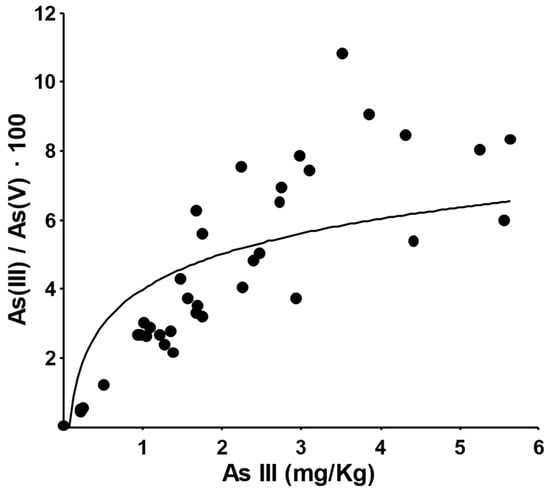
Figure 7.
Plot of As(III)/As(V) ratio against As(III) amount for each sample.
In most cases, top-soil layers are in aerobic conditions, favoring the oxidation of arsenic species to As(V), while the lack of oxygen in the deeper layers allows for higher percentages of As(III) [42]. The behavior observed here, with an almost constant As(III)/As(V) ratio having a slightly higher average value in the top-soil and first layer, can suggest either a direct anthropic contribution or the existence of anoxic conditions due to accumulation of plant material layers on the ground or other similar conditions.
2.3. Cession Test
The cession test in acetic acid was used to calculate As cession percentage values. Percentage values were calculated as the ratio between cession test As (corrected for sample mass and extraction water volume) and the total As columns (Table 1, column 11). As cession percentage values were low with respect to total As determined by sample mineralization, ranging from a minimum of 8.7 × 10−3% (16BH2/8, depth 7.4–8.0 m) to a maximum of 1.3 × 10−1% (sample 20BH1/1, top-soil), followed closely by another top-soil sample (sample 3BH9/1, 1.2 × 10−1%). Specifically, (i) six samples (15.8% of analyzed samples) released an As amount in the range of 0.5 × 10−2–2 × 10−2% with respect to the total As obtained by sample mineralization; (ii) twenty samples (52.6%) released an amount in the range of 2 × 10−2–6 × 10−2%; (iii) nine samples (23.7%) released an amount in the range of 6 × 10−2–1 × 10−1%; and (iv) three samples (7.9%) released an As amount of >1 × 10−1% (Figure 8).
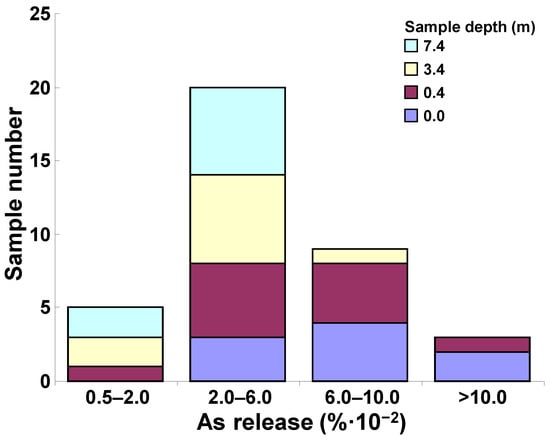
Figure 8.
Arsenic amount obtained by cession test in acetic acid (percentage of total arsenic measured by mineralization), for the 38 samples collected in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi.
The samples that released the highest As quantities in acetic acid were collected from the superficial soil levels. Moreover, the data obtained from the samples derived from the deepest soil levels were more homogeneous (Figure 9). These results parallel those obtained with the ammonium oxalate extraction.
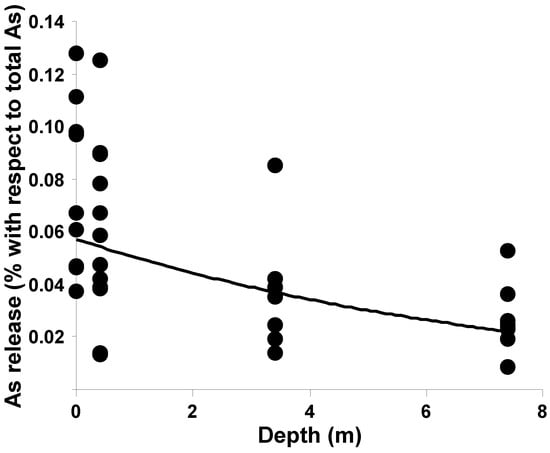
Figure 9.
Plot of percentage of As extracted by acetic acid against depth of the soil samples.
The cession test with acetic acid simulates the effect of meteoric waters, and is able to dissolve arsenic carbonate coprecipitates but not more tightly bound species [40]. Since the quantity of soluble arsenic was found to be a small part of the total arsenic, meteoric rains can evidently move a reduced quantity of this metalloid into the deeper layers of the soil.
2.4. Comparison of Sites
As speciation analysis was performed at all the depth levels (0.0–0.1 m, 0.4–1.0 m, 3.4–4.0 m, and 7.4–8.0 m) for three sampling sites: 11BH1, 15BH1, and 16BH2.
The highest quantity of total As obtained by oxalate extraction in site 11BH1 was found in the 0.4–1.0 m layer, whereas the highest As amounts from sample mineralization were found in the 0.4–1.0 m and 3.4–4.0 m layers. The highest As(III) concentration was detected in the top-soil and in the deepest layer (7.4–8.0 m), whereas the highest As(V) level and the largest As release in acetic acid was found in the 0.4–1.0 m layer. It can be hypothesized that elution through the soil layers causes higher As concentrations in the deepest levels than in the superficial layers.
For site 15BH1, speciation data showed the highest levels of As(III) and As(V) in the top-soil, with a decrease in the deeper layers more evident for As(III). The highest concentration of total As obtained by sample mineralization and the most abundant As release in the cession test were found in the 0.4–1.0 m layer. Very high As levels were also found in the top-soil and the 3.4–4.0 m layer.
Site 16BH2 showed the highest concentration of As derived from the speciation analysis in the top-soil, with a sharper decrease in As(III) than As(V) in the other layers. Total As data determined by sample mineralization showed high concentrations in both the top-soil and the deepest layer (7.4–8.0 m). The top-soil was also the layer with the largest release of As in acetic acid.
Three sites (2BBH1, 3BH14, and 3BH3) were investigated at three different depth levels: 0.4–1.0 m, 3.4–4.0 m, and 7.4–8.0 m.
At site 2BBH1, both As speciation data and total As determination by mineralization showed the highest As concentrations in the 0.4–1.0 m level and a gradual decrease in the deeper layers. As(III) percentage values decreased sharply in the deeper layers, and As release in acetic acid was highest in the 0.4–1.0 m level and gradually lower in the other deeper layers.
In the site 3BH14, As speciation analysis revealed the highest concentration in the 0.4–1.0 m level and a gradual decrease, which was sharper for As(III) with respect to As(V), in the other layers. Total As determination by sample mineralization showed the highest concentration in the 3.4–4.0 m level. The 0.4–1.0 m layer released the highest quantity of As in the cession test.
At the site 3BH3, both As speciation data and total As determination by mineralization showed the highest As levels in the 0.4–1.0 m layer and lower concentrations in the other layers. In particular, speciation analysis revealed a considerable amount of As(V) in all the soil layers. The 0.4–1.0 m layer released the highest As quantity in acetic acid.
At the four sites 16BH1, 3BH13, 6BH1, and 8BBH2, As speciation analysis was performed for two layers: 3.4–4.0 m and 7.4–8.0 m for 16BH1, 0.4–1.0 m and 3.4–4.0 m for 3BH13, 0.0–0.1 m and 0.4–1.0 m for 6BH1, and 0.0–0.1 m and 3.4–4.0 m for 8BBH2.
At site 16BH1, the highest As concentrations measured in both speciation analysis and sample mineralization were detected in the deepest layer (7.4–8.0 m). The 3.4–4.0 m level released the highest As amount in the cession test. Site 3BH13 was characterized by a higher As level in the 0.4–1.0 m layer for both speciation analysis and total As determination. The largest As release in acetic acid was obtained in the same layer. At site 6BH1, the largest As concentrations were detected in the top-soil for all analyses performed. The same situation was observed at site 8BBH2, with an important difference: although total As obtained by oxalate extraction showed high levels in the top-soil, the analysis of the two species As(III) and As(V) revealed that the former was more abundant in the top-soil, whereas the latter was more concentrated in the 3.4–4.0 m layer.
Ammonium oxalate extractions showed that, even in the deeper layers of the sampled sites, a non-negligible quantity of strongly bound or occluded arsenic is present, as already observed in other sites in the area [22], pointing at least partially to a possible natural soil origin.
Additionally, speciation analysis indicates a low prevalence of the more mobile and toxic As(III) species (always <10%). The low yields of acetic acid cession test allow us to exclude the presence of high quantities of highly mobile species that are easily migrated by meteoric waters.
However, higher values (>50%) of As extraction by ammonium oxalate were generally observed in the top-soil samples and the samples from the 0.4–1.0 m depth, suggesting additional anthropic contributions, although this was not consistently observed in all of the sampled sites.
Other recent studies that investigated the behavior of As in soil samples have reported similar results and conclusions [43]. For example, in a study of soil samples from an agricultural site near an industrial plant, As was mostly confined to the plow layer, with lower (although not negligible) amounts leached to deeper soil layers.
Extensive studies have recently been conducted to better understand the behavior of metals and metalloids (including As) in soil, assess potential exposure to toxic elements, estimate their bioavailability, and measure the health risk [44]. The results from different soils revealed that the physicochemical soil properties and the species of the analyzed elements are important factors. In particular, the health risk assessment is undertaken by considering the total concentration of an element in the soil, but only the bioavailable fraction can induce a toxic effect. The physicochemical parameters of soils, the total concentrations of elements, and their chemical forms influence their bio-accessibility. Correlations between different parameters and bioavailability in soil varied greatly for the same element due to the complexity of the soil structure and the interactions between its constituents. A better understanding of the role of these parameters can help to manage contaminated sites and soils more efficiently, leading to more effective remediation of compromised sites and more accurate assessment of the risks to public health.
Quantitative differences among the sites can be attributed to differences in the compositions of the soil sample matrices, possibly caused by variations in the original soil makeup and differences in usage over the long years of industrial activity.
The different amounts of As in the sampling sites could depend on the distance from the specific sources of pollution, although it is very difficult to identify them in an industrial zone with a complex history such as the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi. Moreover, in the previously mentioned study [43], a spatial gradient in top-soil was observed depending on the distance from the probable pollution input.
Obviously the collection of this type of data would have required a much more extensive approach. Nevertheless, the speciation analyses confirmed that most As occurs as relatively immobile or slowly exchangeable forms, suggesting that it is a naturally occurring component of the soil in the area [22]. In fact, As is generally associated with sulfide minerals, and its mobility and availability in soils are strictly related to pH, redox potential, ionic composition, and mineral type. For example, among As chemical forms, arsenite is much more soluble and mobile than arsenate, and therefore potentially more dangerous [41]. This result suggests that an approach focused on plow layer phytoremediation and monitoring industrial activity that involves arsenic derivatives could lead to significant improvements in soil conditions and mitigation of health issues.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
Thirty-eight soil samples were collected at 18 different sites of the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi (Apulia, southern Italy), dried at room temperature, and passed through a 2 mm sieve.
The area’s sampling coordinates, reported in decimal degrees, are as follows: 40.644261, 17.959213 top left; 40.622922, 17.959213 bottom left; 40.644261, 17.978737 top right; and 40.622922, 17.978737 bottom right. The soil fractions with a size <2 mm were used for total As determination, the extraction and speciation analysis, and the cession test. Blank solutions were prepared for all performed analyses using the solvent mixtures employed for extractions and speciation.
3.2. Total As Determination
Total As determination was performed by hydride generation-atomic absorption spectroscopy (HG-AAS) after sample mineralization that consisted of a digestion process of the soil sample with one volume of nitric acid and three volumes of hydrochloric acid [45].
3.3. Ammonium Oxalate Extraction and As Speciation Analysis
Speciation analysis was performed by hyphenated techniques in which the HPLC was coupled to the HG-AAS. A quantity of 0.2 M of ammonium oxalate was used for the As extraction in soft conditions [34] in order to avoid transformation of the different As forms and to save the original distribution of the chemical species in the samples. After the dehydration at room temperature and the sieving, the particles with a size <2 mm were used for the As extraction: 0.2 g of each soil sample was treated with 50 mL of ammonium oxalate 0.2 M (extraction ratio 1:250) for ten minutes in an ultrasonic bath. The resulting solutions were filtered through 0.45 µm filters. The determination of the As species was performed using an HPLC system (Waters 626 LC System, Milford, MA, USA) coupled online with an atomic adsorption spectrometer (Varian 880Z Zeeman, Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with a HG system (Varian VGA-77, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and an electrothermal temperature controller (Varian ETC-60, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The identity of arsenic species was assessed via comparison of retention times of single standards on the Hamilton PRP-X100 column (Hamilton Company, Reno, NV, USA) [24]. Stock solutions (1000 mg·L−1) were prepared from NaAsO2 (arsenite), Na2HAsO4·7H2O (arsenate), CH3AsO(OH)2 (monomethylarsonic acid, MMAA), and (CH3)2AsO(OH) (dimethylarsinic acid, DMAA). Arsenite, arsenate, MMAA, and DMAA were obtained from Sigma–Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany).
In order to assess the quality of the data collection, standard solutions with known concentrations of the species were inserted into the analysis sequences and treated as samples with unknown metalloid concentration. The experimental conditions are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental conditions for HPLC separation, HG, and AAS analysis.
3.4. Cession Test
The acetic acid cession test can be used to evaluate the impact of any solid matrix (soil, waste, etc.) on the leaching action of rainwater, with both organic and inorganic matrix types. The release test is conducted by placing the sample, reduced to the appropriate grain size, in contact with distilled water for 24 h, maintaining the pH of the solution at values not exceeding 5 by adding diluted acetic acid (0.5 M) [38].
The analyses are therefore performed on the extracting liquid phase, separated by filtration of the solid part.
The cession test was carried out respecting the following parameters:
- -
- Elution ratio of 1:20 (i.e., 50 g of sample per 1000 g of water);
- -
- Contact time of 24 h with moderate continuous stirring;
- -
- Analysis of the filtered solution (0.45 µm) carried out using atomic absorption spectrophotometry with a hydride generation system (HG-AAS).
4. Conclusions
Total As determination, performed by sample mineralization for all the samples collected in the S.I.S.R.I. area of Brindisi, showed a concentration range between 51.8 mg kg−1 and 169.6 mg kg−1. All the data were higher than the expected limit of 50 mg kg−1, established by D.M. (Ministerial Decree) 471/99 for industrial areas. As speciation analysis revealed the presence of inorganic As(III) and As(V) in all the samples studied, whereas the concentrations of the organic species MMAA and DMAA were always under the detection limit (<0.11 and <0.15 mg kg−1, respectively). This result allowed the exclusion of the water-soluble organic species from the list of health hazards. Extracted As, calculated as the sum of the As(V) and As(III) concentrations determined by the soft chemical oxalate extraction and speciation analysis, was shown to range from a minimum of 36% to a maximum of 92% of the total As obtained by mineralization, with an average value of 62%. The speciation analyses revealed that, in all samples, the lower mobility As(V) represents >90% of the extracted As, with percentages up to 99.97% of the total. The highest values of As extraction by ammonium oxalate were observed in the top-soil samples and the samples deriving from the 0.4–1.0 m depth. Since this extraction method is able to dissolve amorphous Fe, Al, and Mn oxyhydroxide but not their crystalline forms or sulfides, this result allows us to hypothesize that a significant percentage of arsenic is strongly bound or occluded, particularly in the deeper soil layers, suggesting a natural origin of arsenic in the soil. On the other hand, the relatively high percentage of As(III) in the top-soil and first layer, which decreases with depth, may suggest an anthropic contribution to the soil or possibly the development of anoxic conditions due to environmental management. The differences among the sites can be attributed to differences in the compositions of the soil sample matrices, possibly caused by variations in soil makeup and usage over time.
The cession test in acetic acid, which is able to extract lightly bound arsenic, showed low values compared to the total As extracted by ammonium oxalate, with the higher quantities of As released in acetic acid originating from samples collected from superficial soil levels.
The speciation analysis showed that the highly mobile As(III) species always had very low relative concentrations in all the sampled sites, the effect of the meteoric water on the mobility of As was limited mostly to the top-soil, and the sampled sites had a very different makeup. Nonetheless, all sampled sites and depths in the area showed a total concentration of As that was higher than the allowed legal limits for industrial areas to various degrees.
While the results could possibly indicate that a high background of strongly bound or occluded arsenic contribution is present in the area, it is apparent that the entire area would benefit from long-term monitoring in order to assess the stability of the conditions and targeted remedial actions, particularly at the sites where the top-soil and lower depth concentrations of As clearly exceeded the allowed limits.
A possible remediation strategy for the surface soil layers could involve application of phytoextraction of the pollutants, particularly concerning the most contaminated top-soil levels.
Unfortunately, the strategy of applying the widely used ornamental shrub Nerium oleander L., which has successfully been used in bioremediation strategies for various heavy metals in soils [46], would have serious drawbacks. In fact, recent concerns in the region regarding the Xylella fastidiosa epidemics affecting olive trees are amplified by the fact that N. oleander is an asymptomatic carrier that functions as a reservoir for the bacteria [47].
Another recently tested phytoremediation strategy that could be applied employs clonal populations of the endemic and highly rustic plant Dittrichia viscosa with a defined phenotype related to As tolerance, in order to obtain specific As phytoremediation in contaminated areas, with a low cost [48,49].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P.F. and D.M.; methodology, F.P.F. and D.M.; software, D.M. and P.P.; validation, F.P.F., D.M. and P.P.; formal analysis, D.M.; investigation, D.M.; data curation, D.M. and P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M.; writing—review and editing, D.M. and P.P.; visualization, D.M. and P.P.; supervision, F.P.F.; funding acquisition, F.P.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been performed in the framework of the project: “Analisi di rischio sul lotto di aree agricole adiacente al nastro trasportatore ENEL ed alla Centrale Federico II caratterizzate in stralcio al Piano di caratterizzazione delle aree agricole” financed by Regione Puglia, Italy.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The concentrations of As obtained by total As determination, speciation analysis, and cession test data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Acknowledgments
The Consorzio Interuniversitario di Ricerca in Chimica dei Metalli nei Sistemi Biologici (C.I.R.C.M.S.B.), Bari (Italy), is acknowledged for financial support and for the AAS data collection. The map of Italy in Figure 1 was derived from a file distributed by Wikimedia Commons, licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY-SA 3.0 DE license.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Medical and Biological Effects of Environmental Pollutants. Arsenic: Medical and Biological Effects of Environmental Pollutants; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Arsenic Speciation in the Environment. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 713–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, W.R.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; McKnight-Whitford, A.; Peng, H.; Popowich, A.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fricke, M.; Sun, H.; et al. Methylated and Thiolated Arsenic Species for Environmental and Health Research—A Review on Synthesis and Characterization. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, M.B. Environmental Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; ISBN 978-0-19-507011-8. [Google Scholar]
- Garelick, H.; Jones, H.; Dybowska, A.; Valsami-Jones, E. Arsenic Pollution Sources. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination Volume 197: International Perspectives on Arsenic Pollution and Remediation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 17–60. ISBN 978-0-387-79284-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic Round the World: A Review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golfinopoulos, S.K.; Varnavas, S.P.; Alexakis, D.E. The Status of Arsenic Pollution in the Greek and Cyprus Environment: An Overview. Water 2021, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickson, R.T.; McArthur, J.M.; Ravenscroft, P.; Burgess, W.G.; Ahmed, K.M. Mechanism of Arsenic Release to Groundwater, Bangladesh and West Bengal. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Ghosh, D.; Dash, A.; Bose, S. Arsenic Contamination in Soil and Sediment in India: Sources, Effects, and Remediation. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Santos, A.C.; Fernandes, C.S.; Ng, J.C. Arsenic Contamination Assessment in Brazil—Past, Present and Future Concerns: A Historical and Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Ramamoorthy, S. Impact of Heavy Metals in Natural Waters. In Heavy Metals in Natural Waters; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Naidu, R.; Alston, A.M. Arsenic in the Soil Environment: A Review. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; Volume 64, pp. 149–195. ISBN 0065-2113. [Google Scholar]
- Gleyzes, C.; Tellier, S.; Sabrier, R.; Astruc, M. Arsenic Characterisation in Industrial Soils by Chemical Extractions. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, J.; Chen, T. Effects of Environmental Governance in Mining Areas: The Trend of Arsenic Concentration in the Environmental Media of a Typical Mining Area in 25 Years. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Effect of Natural Organic Matter on Arsenic Release from Soilsand Sediments into Groundwater. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.O. Arsenic in the Environment. In Part I: Cycling and Characterization; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pongratz, R. Arsenic Speciation in Environmental Samples of Contaminated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 224, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda–Piñeiro, J.; Alonso-Rodríguez, E.; Romarís-Hortas, V.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Prada-Rodríguez, D.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Assessment of the Bioavailability of Toxic and Non-Toxic Arsenic Species in Seafood Samples. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herreweghe, S.; Swennen, R.; Vandecasteele, C.; Cappuyns, V. Solid Phase Speciation of Arsenic by Sequential Extraction in Standard Reference Materials and Industrially Contaminated Soil Samples. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.S.; Hoy, K.S.; Schofield, J.R.M.; Uppal, J.S.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Peng, H.; Le, X.C. Arsenic Speciation Analysis: A Review with an Emphasis on Chromatographic Separations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, E.A.; Li, G.C.; Fendorf, S.E. Stability of Arsenate Minerals in Soil under Biotically Generated Reducing Conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migoni, D.; Papadia, P.; Cannito, F.; Fanizzi, F.P. Sequential Extraction Analysis of Arsenic in Soil Samples Collected in an Agricultural Area of Brindisi, Apulia (Italy), in the Proximity of a Coal-Burning Power Plant. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleyzes, C.; Tellier, S.; Astruc, M. Fractionation Studies of Trace Elements in Contaminated Soils and Sediments: A Review of Sequential Extraction Procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Giráldez, I. Selective Extraction of Iron Oxide Associated Arsenic Species from Sediments for Speciation with Coupled HPLC-HG-AAS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1998, 13, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styblo, M.; Del Razo, L.M.; Vega, L.; Germolec, D.R.; LeCluyse, E.L.; Hamilton, G.A.; Reed, W.; Wang, C.; Cullen, W.R.; Thomas, D.J. Comparative Toxicity of Trivalent and Pentavalent Inorganic and Methylated Arsenicals in Rat and Human Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2000, 74, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, F.; Dan, G.; Grotti, M. Arsenic Speciation Analysis of Environmental Samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpunar, J. Bio-Inorganic Speciation Analysis by Hyphenated Techniques. Analyst 2000, 125, 963–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, K.F.; Owens, G.; Davey, D.E.; Naidu, R. Arsenic Speciation and Toxicity in Biological Systems. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Ware, G.W., Albert, L.A., Crosby, D.G., de Voogt, P., Hutzinger, O., Knaak, J.B., Mayer, F.L., Morgan, D.P., Park, D.L., Tjeerdema, R.S., et al., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 97–149. ISBN 978-0-387-27565-9. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.S.; Pandey, P.K.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Corns, W.T.; Varol, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Zhu, Y. A Review on Arsenic in the Environment: Contamination, Mobility, Sources, and Exposure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8803–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, T.; Astruc, A.; Astruc, M. Speciation of Arsenic and Selenium Compounds by HPLC Hyphenated to Specific Detectors: A Review of the Main Separation Techniques. Talanta 1999, 50, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Lu, X.; Cullen, W.R.; Chris Le, X. Unstable Trivalent Arsenic Metabolites, Monomethylarsonous Acid and Dimethylarsinous Acid. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2001, 16, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Arsenic in Drinking Water; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-309-06333-3. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, T.; Molenat, N.; Astruc, A.; Pinel, R. Arsenic Speciation in Some Environmental Samples: A Comparative Study of HG-GC-QFAAS and HPLC-ICP-MS Methods. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 14, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montperrus, M.; Bohari, Y.; Bueno, M.; Astruc, A.; Astruc, M. Comparison of Extraction Procedures for Arsenic Speciation in Environmental Solid Reference Materials by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Hydride Generation-Atomic Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 16, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ure, A.M.; Quevauviller, P.; Muntau, H.; Griepink, B. Speciation of Heavy Metals in Soils and Sediments. An Account of the Improvement and Harmonization of Extraction Techniques Undertaken Under the Auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1993, 51, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, D.M.; Ariese, F.; Cornelis, R.; Danielsson, L.-G.; Muntau, H.; van Leeuwen, H.P.; Lobinski, R. Guidelines for Terms Related to Chemical Speciation and Fractionation of Elements. Definitions, Structural Aspects, and Methodological Approaches (IUPAC Recommendations 2000). Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Lu, X.; Ma, M.; Watt, C.; Le, X.C. Arsenic Speciation Analysis. Talanta 2002, 58, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APAT—IRSA/CNR. Metodi Analitici per Le Acque; APAT—IRSA/CNR: Rome, Italy, 2003; Volume 29, ISBN 88-448-0083-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, R.R.; Basta, N.T.; Casteel, S.W.; Armstrong, F.P.; Ward, D.C. Chemical Extraction Methods to Assess Bioavailable Arsenic in Soil and Solid Media. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithongkul, C.; Krongchai, C.; Santasup, C.; Kittiwachana, S. An Investigation of the Effect of Operational Conditions on a Sequential Extraction Procedure for Arsenic in Soil in Thailand. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Blodau, C. Mobilization of Arsenic by Dissolved Organic Matter from Iron Oxides, Soils and Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 354, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-H.; Matzner, E. Mobile Arsenic Species in Unpolluted and Polluted Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosini, C.; Terzaghi, E.; Raspa, G.; Grotti, M.; Armiraglio, S.; Anelli, S.; Di Guardo, A. Arsenic Movement and Fractionation in Agricultural Soils Which Received Wastewater from an Adjacent Industrial Site for 50 Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billmann, M.; Hulot, C.; Pauget, B.; Badreddine, R.; Papin, A.; Pelfrêne, A. Oral Bioaccessibility of PTEs in Soils: A Review of Data, Influencing Factors and Application in Human Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, K.A.; Rutter, A.; Koch, I.; Smith, P.; Reimer, K.J.; Poland, J.S. Extraction and Speciation of Arsenic in Plants Grown on Arsenic Contaminated Soils. Talanta 2007, 72, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Ou, Q.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, H.; Ouyang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Organic–Inorganic Composite Modifiers Enhance Restoration Potential of Nerium Oleander L. to Lead–Zinc Tailing: Application of Phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 56569–56579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, D.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Altamura, G.; Palmisano, F.; Bosco, D.; Porcelli, F.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Saponari, M. Transmission of Xylella Fastidiosa by Naturally Infected Philaenus Spumarius (Hemiptera, Aphrophoridae) to Different Host Plants. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadia, P.; Barozzi, F.; Angilé, F.; Migoni, D.; Piro, G.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Di Sansebastiano, G.-P. Evaluation of Dittrichia Viscosa Performance in Substrates with Moderately Low Levels of As and Cd Contamination. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2020, 154, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barozzi, F.; Papadia, P.; Stefano, G.; Renna, L.; Brandizzi, F.; Migoni, D.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Piro, G.; Di Sansebastiano, G.-P. Variation in Membrane Trafficking Linked to SNARE AtSYP51 Interaction with Aquaporin NIP1;1. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).