Extraction of Fish Protein Concentrates from Discards and Combined Application with Gelatin for the Development of Biodegradable Food Packaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Isolation of Fish Protein Concentrate (FPC)
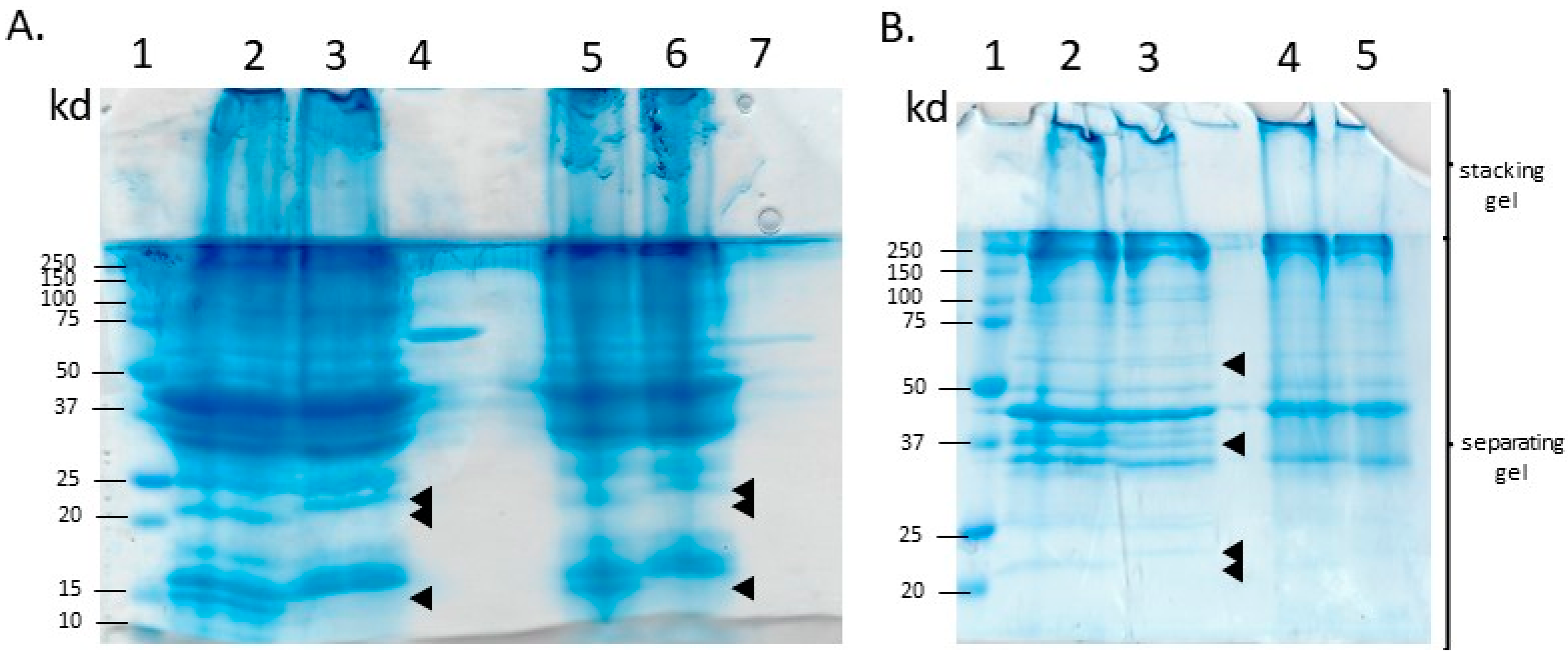
2.3. FPC Solubilization and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.4. Lipid Extraction from Fresh FPC
2.5. Film Forming Solutions
2.6. Protein, Lipid and Moisture Content of Fish Tissues and FPC
2.7. Thickness and Mechanical Properties
2.8. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP) and Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
2.9. Color
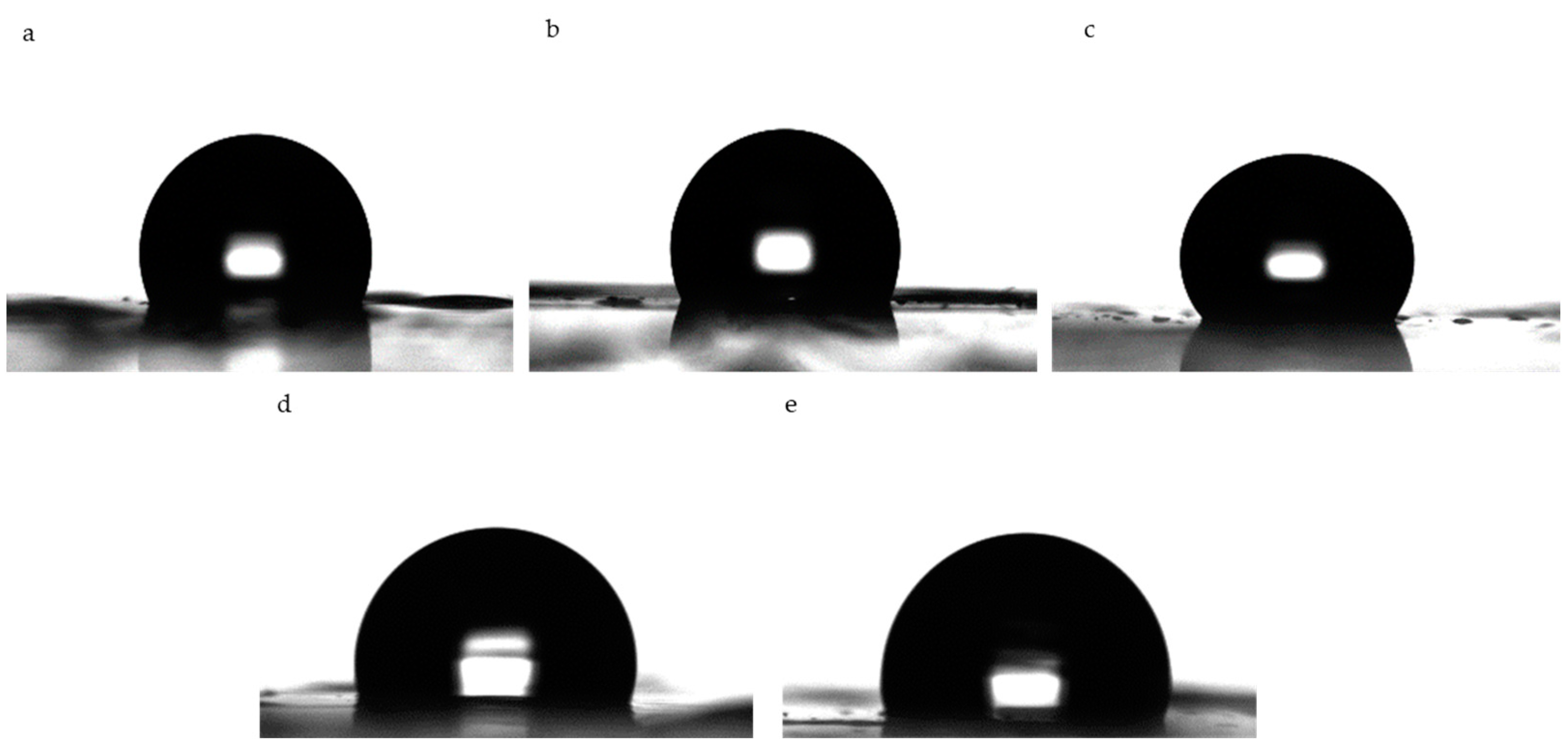
2.10. Contact Angle
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Protein, Lipid, and Moisture Content of Raw Fish Residues and FPC
3.2. SDS-PAGE Profile of the Isolated Raw Fish Proteins
3.3. Thickness and Mechanical Properties
3.4. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP) and Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
3.5. Color
3.6. Contact Angle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Wang, M.; Barba, F.J.; Bermúdez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Nutritional Profiling and the Value of Processing By-Products from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Ed.) Towards Blue Transformation. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; De Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangkheirakpam, M.R.; Mahanand, S.S.; Majumdar, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Hidangmayum, D.D.; Netam, S. Fish Waste Utilization with Reference to Fish Protein Hydrolysate—A Review. Fish Technol. 2019, 56, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, N.; Hasanin, M.S.; Abdelraof, M. Utilization of Olive Leaves Extract Coating Incorporated with Zinc/Selenium Oxide Nanocomposite to Improve the Postharvest Quality of Green Beans Pods. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2022, 28, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Business Research Company. Plastic Waste Management Global Market Report 2022. Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/p06319263/Plastic-Waste-Management-Global-Market-Report.html?utm_source=GNW (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Ibrahim, S.; Elsayed, H.; Hasanin, M. Biodegradable, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Biofilm for Active Packaging Based on Extracted Gelatin and Lignocelluloses Biowastes. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhag, R.; Kumar, N.; Petkoska, A.T.; Upadhyay, A. Film Formation and Deposition Methods of Edible Coating on Food Products: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.D.; Loiko, M.R.; Gautério, G.V.; Tondo, E.C.; Prentice, C. Influence of Heating, Protein and Glycerol Concentrations of Film-Forming Solution on the Film Properties of Argentine Anchovy (Engraulis anchoita) Protein Isolate. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitsyn, A.; Semenova, A.; Nasonova, V.; Polishchuk, E.; Revutskaya, N.; Kozyrev, I.; Kotenkova, E. Approaches in Animal Proteins and Natural Polysaccharides Application for Food Packaging: Edible Film Production and Quality Estimation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, R.D. Fish Gelatin Market by Product Type (Food Grade and Pharma Grade) and Application (Food & Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Nutraceuticals, Cosmetics, and Others): Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2021–2030. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/fish-gelatin-market-A13719 (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Kumoro, A.C.; Wardhani, D.H.; Kusworo, T.D.; Djaeni, M.; Ping, T.C.; Ma’rifat Fajar Azis, Y. Fish Protein Concentrate for Human Consumption: A Review of Its Preparation by Solvent Extraction Methods and Potential for Food Applications. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2022, 67, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.F.; Sulieman, A.M.; Soliman, N.G.; Bassiuny, S.S. Fortification of Biscuits with Fish Protein Concentrate. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2014, 9, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Phadtare, M.C.; Ranveer, R.C.; Rathod, N.B.; Sharangdhar, S.T.; Swami, S.B.; Vartak, V.R.; Koli, J.M.; Patange, S.B. Extraction, Characterization and Utilization of Fish Protein Concentrate. Aquat. Food Stud. 2021, 1, AFS47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karginov, A.; Agaphonov, M. A Simple Enrichment Procedure Improves Detection of Membrane Proteins by Immunoblotting. BioTechniques 2016, 61, 260–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A. An Analysis of Critical Factors for Quantitative Immunoblotting. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, rs2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.; Radin, N.S. Lipid Extraction of Tissues with a Low-Toxicity Solvent. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 90, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C.; Vargas, M.; Atarés, L. Edible Films and Coatings from Proteins. In Proteins in Food Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Products. J. AOAC Int. 1997, 80, 65A–66A. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D882-18; Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- ASTM E96/E96M-10; Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5946; Standard Test Method for Corona-Treated polymer films Using Water Contact Angle Measurements. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, J.L.; Green, R. Coomassie Blue Staining. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 541, pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul Syahida, S.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R.; Ainun, Z.M.A.; Nur Hanani, Z.A. Effects of Palm Wax on the Physical, Mechanical and Water Barrier Properties of Fish Gelatin Films for Food Packaging Application. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 23, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Development of Bioactive Fish Gelatin/Chitosan Nanoparticles Composite Films with Antimicrobial Properties. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Sumpavapol, P.; Songtipya, P. Physico-Mechanical Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Fish Protein Isolate/Fish Skin Gelatin-Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanocomposite Films. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewprachu, P.; Osako, K.; Rawdkuen, S. Effects of plasticizers on the properties of fish myofibrillar protein film. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Sumpavapol, P.; Songtipya, P. Properties and Antimicrobial Activity of Fish Protein Isolate/Fish Skin Gelatin Film Containing Basil Leaf Essential Oil and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, C.; Unsalan, O.; Altunayar-Unsalan, C.; Xiong, S.; Manyande, A.; Chen, H. Development and Characterization of Fish Myofibrillar Protein/Chitosan/Rosemary Extract Composite Edible Films and the Improvement of Lipid Oxidation Stability during the Grass Carp Fillets Storage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kchaou, H.; Benbettaïeb, N.; Jridi, M.; Abdelhedi, O.; Karbowiak, T.; Brachais, C.-H.; Léonard, M.-L.; Debeaufort, F.; Nasri, M. Enhancement of Structural, Functional and Antioxidant Properties of Fish Gelatin Films Using Maillard Reactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanpour, B.; Kazemi, M.; Ojagh, S.M.; Pourashouri, P. Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers as Reinforce in Edible Fish Myofibrillar Protein Nanocomposite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.-L.; Tran, T.H.; Hao, L.T.; Jeon, H.; Koo, J.M.; Shin, G.; Hwang, D.S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Park, J.; Oh, D.X. Biorenewable, Transparent, and Oxygen/Moisture Barrier Nanocellulose/Nanochitin-Based Coating on Polypropylene for Food Packaging Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yakubu, S.; Tang, H.; Li, L. Active Polylactic Acid/Tilapia Fish Gelatin-Sodium Alginate Bilayer Films: Application in Preservation of Japanese Sea Bass (Lateolabrax Japonicus). Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Javidi, Z.; Rezaei, M. Efficient Gas Barrier Properties of Multi-Layer Films Based on Poly(Lactic Acid) and Fish Gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchese, C.L.; Sperotto, N.; Spada, J.C.; Tessaro, I.C. Effect of Blueberry Agro-Industrial Waste Addition to Corn Starch-Based Films for the Production of a PH-Indicator Film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Hasanin, M.; Hashem, A.H. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Superhydrophobic Antimicrobial Film Based on Cellulose Acetate/Polycaprolactone Loaded with the Green Biosynthesized Copper Nanoparticles for Food Packaging Application. J Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzati Rostami, A.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Hosseini, S.E.; Rezaei, M.; Kamali, A. Evaluation of Plasticizing and Antioxidant Properties of Silver Carp Protein Hydrolysates in Fish Gelatin Film. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Film | Protein (%) | Lipid (%) | Moisture (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw fish residues | 14.74 | 7.97 | 77.29 |
| FPC | 93.70 | 6.30 | 0 |
| Film | Thickness (μm) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | 47 ± 10 a | 16.57 ± 8.05 a | 8.82 ± 1.72 b | 108.99 ± 18.61 c |
| 1 FPC/G 1:1 | 41 ± 20 a | 9.80 ± 5.11 a | 5.96 ± 1.76 a,b | 118.99 ± 15.63 c |
| 2 FPC/G 2:1 | 42 ± 20 a | 19.81 ± 23.40 a | 3.43 ± 1.05 a | 119.30 ± 20.41 c |
| 3 wFPC 1:1 | 46 ± 30 a | 887.20 ± 416.48 b | 19.02 ± 3.97 c | 46.84 ± 26.74 b |
| 4 wFPC 2:1 | 37 ± 20 a | 1437 ± 729.45 c | 22.91 ± 6.66 d | 9.34 ± 17.58 a |
| Film | WVTR (g/day·m2) | WVP (g·mm/kPa·h·m2) | WVP (10−10 × g/m · s · Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | 1625.84 ± 221.28 c | 1.23 ± 0.17 c | 3.40 ± 0.46 c |
| 1 FPC/G 1:1 | 1021.11 ± 49.64 b | 0.67 ± 0.03 b | 1.86 ± 0.09 b |
| 2 FPC/G 2:1 | 1066.97 ± 68.43 b | 0.72 ± 0.05 b | 2.00 ± 0.13 b |
| 3 wFPC 1:1 | 953.78 ± 78.58 b | 0.70 ± 0.06 b | 1.95 ± 0.16 b |
| 4 wFPC 2:1 | 831.30 ± 83.11 a | 0.49 ± 0.05 a | 1.37 ± 0.13 a |
| Film | L | a | b | ΔΕ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | 92.43 ± 1.71 a,b | −0.34 ± 0.02 b | 2.95 ± 0.22 c | 7.56 ± 1.61 b,c |
| 1 FPC/G 1:1 | 93.29 ± 0.37 b | −0.34 ± 0.02 b | 2.72 ± 0.09 b | 6.68 ± 0.31 b |
| 2 FPC/G 2:1 | 96.35 ± 0.50 c | −0.28 ± 0.04 a | 2.29 ± 0.26 a | 3.82 ± 0.53 a |
| 3 wFPC 1:1 | 92.42 ± 1.30 a,b | −0.29 ± 0.04 a | 2.61 ± 0.35 b | 7.44 ± 1.27 b,c |
| 4 wFPC 2:1 | 91.52 ± 1.45 a | −0.31 ± 0.03 a,b | 2.53 ± 0.04 b | 8.26 ± 1.39 c |
| Film | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| Gelatin | 107.76 ± 2.70 b |
| 1 FPC/G 1:1 | 110.46 ± 5.79 b |
| 2 FPC/G 2:1 | 121.04 ± 7.05 c |
| 3 wFPC 1:1 | 90.21 ± 6.61 a |
| 4 wFPC 2:1 | 89.21 ± 2.96 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athanasopoulou, E.; Michailidi, A.; Ladakis, D.; Kalliampakou, K.I.; Flemetakis, E.; Koutinas, A.; Tsironi, T. Extraction of Fish Protein Concentrates from Discards and Combined Application with Gelatin for the Development of Biodegradable Food Packaging. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512062
Athanasopoulou E, Michailidi A, Ladakis D, Kalliampakou KI, Flemetakis E, Koutinas A, Tsironi T. Extraction of Fish Protein Concentrates from Discards and Combined Application with Gelatin for the Development of Biodegradable Food Packaging. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):12062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512062
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthanasopoulou, Evmorfia, Anna Michailidi, Dimitrios Ladakis, Katerina I. Kalliampakou, Emmanouil Flemetakis, Apostolis Koutinas, and Theofania Tsironi. 2023. "Extraction of Fish Protein Concentrates from Discards and Combined Application with Gelatin for the Development of Biodegradable Food Packaging" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 12062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512062
APA StyleAthanasopoulou, E., Michailidi, A., Ladakis, D., Kalliampakou, K. I., Flemetakis, E., Koutinas, A., & Tsironi, T. (2023). Extraction of Fish Protein Concentrates from Discards and Combined Application with Gelatin for the Development of Biodegradable Food Packaging. Sustainability, 15(15), 12062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512062






