The Role of Redundancy of Infrastructures on the Seismic Resilience (SR) of Sustainable Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Seismic Resilience of Infrastructures
- T0E is the time of occurrence of the event E;
- RT is the repair time due to system for the recovery process;
- Q(t) is the variation of the functionality over the time: it models the recovery process to reach a new level of functionality.

3. Infrastructure Redundancy
- r is the level of redundancy (variable);
- r0 is the limit level of redundancy;
- c is the exponential that represents the trend of grown of the functionality with the level of redundancy. In particular, for c bigger than 1, there is a grown of the functionality that is bigger than linear, while for 0 < c < 1, the growth is less than linear (Figure 2).
4. A Case Study
4.1. Benchmark Bridge
4.2. Seismic Scenario
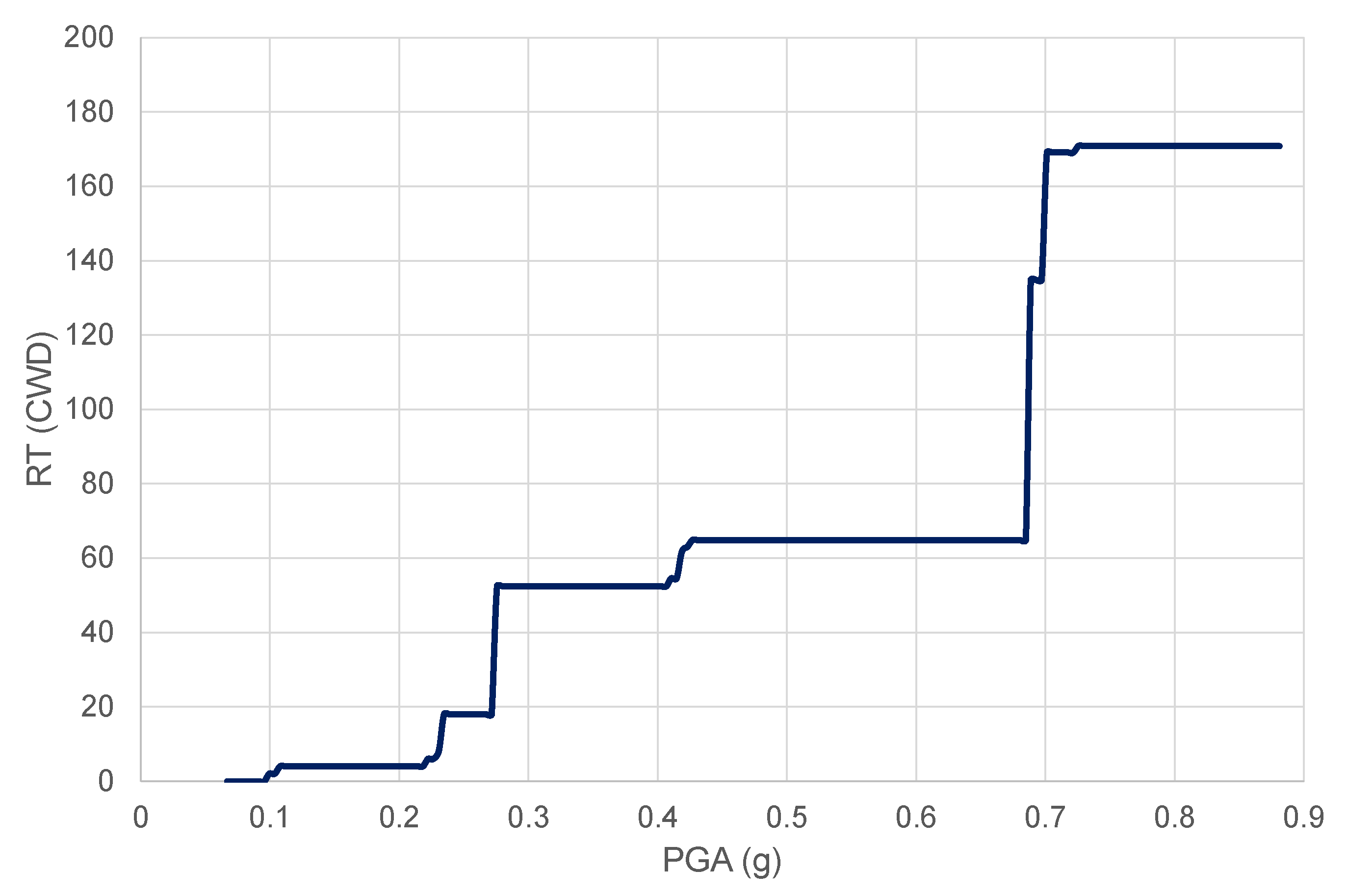
4.3. Calculation of Resilience
5. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brookshire, D.S.; Chang, S.E.; Cochrane, H.; Olson, R.A.; Rose, A.; Steenson, J. Direct and indirect economic losses from earthquake damage. Earthq. Spectra 1997, 14, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adey, B.; Hajdin, R.; Brudwile, E. Effect of common cause failures on indirect costs. J. Bridge Eng. 2004, 9, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D. A new methodology to assess indirect losses in bridges subjected to multiple hazards. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2019, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusenberry, D.O. New SEI/ASCE disproportionate collapse mitigation standard. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starossek, U. Progressive collapse of bridges, aspects of analysis and design. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Sea-Crossing Long-Span Bridges, Mokpo, Republic of Korea, 15–17 February 2006; Citeseer: State College, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Starossek, U.; Haberland, M. Disproportionate collapse: Terminology and procedures. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2010, 24, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitori, G.; Casas, J.; Ghosn, M. Redundancy and robustness in the design and evaluation of bridges: European and North American perspectives. J. Bridge Eng. 2013, 18, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn, M.; Yang, J.; Beal, D.; Sivakumar, B. Bridge System Safety and Redundancy; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bontempi, F. Elementary concepts of structural robustness of bridges and viaducts. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 9, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, G.; Ghosn, M. Structural Redundancy, Robustness, and Disproportionate Collapse Analysis of Highway Bridge Superstructures. J. Struct. Eng. 2022, 148, 04022075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D.; Alzabeebee, S. Seismic fragility assessment of geotechnical seismic isolation (GSI) for bridge configuration. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 3969–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D. Assessment of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation (GSI) as a Mitigation Technique for Seismic Hazard Events. Geosciences 2020, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimellaro, G.P. Urban resilience for emergency response and recovery. In Fundamental Concepts and Applications, Geotechnical, Geological and Earthquake Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 41, ISBN 978-3-319-30656-8. [Google Scholar]
- Venkittaraman, A.; Banerjee, S. Enhancing resilience of highway bridges through seismic retrofit. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyroudis, S.A.; Nasiopoulos, G.; Mantadakis, N.; Mitoulis, S.A. Cost-based resilience assessment of bridges subjected to earthquakes. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. 2021, 12, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, M.; Chang, S.E.; Eguchi, R.T. A Framework to Quantitatively Assess and Enhance the Seismic Resilience of Communities. Earthq. Spectra 2003, 19, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Shinozuka, M. Measuring improvements in the disaster resilience of communities. Eng. Struct. 2004, 20, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renschler, C.; Frazier, A.; Arendt, L.; Cimellaro, G.P.; Reinhorn, A.M.; Bruneau, M. Framework for Defining and Measuring Resilience at the Community Scale: The PEOPLES Resilience Framework; Technical Report MCEER-10-006; University at Buffalo: Buffalo, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Pitilakis, K.; Tsinidis, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Argyroudis, S. Resilience assessment of tunnels: Framework and application for tunnels in alluvial deposits exposed to seismic hazard. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 162, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D. A Resilience-Based Methodology to Assess Soil Structure Interaction on a Benchmark Bridge. Infrastructures 2020, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimellaro, G.P.; Reinhorn, A.M.; Bruneau, M. Framework for analytical quantification of disaster resilience. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelaschi, C.; De Angelis, G.; Giardi, F.; Forcellini, D.; Monteiro, R.; Papadrakakis, M. Performance based earthquake engineering approach applied to bridges in a road network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering (ECCOMAS), Crete Island, Greece, 25–27 May 2015; pp. 900–910. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, P.R.; Naderpour, H. Probabilistic evaluation of seismic resilience for typical vital buildings in terms of vulnerability curves. Structures 2020, 23, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, V.; Becker, N.; Markantonis, V.; Schwarze, R.; van den Bergh, J.C.J.M.; Bouwer, L.M.; Bubeck, P.; Ciavola, P.; Genovese, E.; Green, C.; et al. Review article: Assessing the costs of natural hazards—State of the art and knowledge gaps. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1351–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechler, R.; Linnerooth-Bayer, J.; Peppiatt, D. Microinsurance for Natural Disasters in Developing Countries: Benefits, Limitations and Viability; ProVention Consortium: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegatte, S.; Dumas, P. Can Natural Disasters Have Positive Consequences? Investigating the Role of Embodied Technical Change. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 68, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Ghil, M. Natural Disasters Impacting a Macroeconomic Model with Endogenous Dynamics. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 68, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Tuite, P.M. A comparison of transportation network resilience under simulated system optimum and user equilibrium conditions. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2006; pp. 1398–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Beiler, M.O.; McNeil, S.; Ames, D.; Gayley, R. Identifying resiliency performance measures for megaregional planning: Case study of the transportation corridor between Boston, Massachusetts, and Washington, DC. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2397, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavathrathan, B.K.; Patil, G.R. Quantifying resilience using a unique critical cost on road networks subject to recurring capacity disruptions. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2015, 11, 836–855. [Google Scholar]
- NSerulle, U.; Heaslip, K.; Brady, B.; Louisell, W.; Collura, J. Resiliency of transportation network of Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic: Case Study. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2234, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-Y.; Hu, T.-Y.; Ko, Y.-N. A resilience optimization model for transportation networks under disasters. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, P.; Frangopol, D.M.; Ummenhofer, T.; Zinke, T. Resilience and sustainability of civil infrastructure: Toward a unified approach. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2013, 20, 04014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D.; Kalfas, K.N. Inter-story seismic isolation for high-rise buildings. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D. Seismic resilience of isolated bridge configurations with soil–structure interaction. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2017, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellini, D. 3D Numerical simulations of elastomeric bearings for bridges. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2016, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubesic, T.H.; Timothy, C.; Matisziw, T.C.; Murray, A.T.; Snediker, D. Comparative Approaches For Assessing Network Vulnerability. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2008, 31, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duenas-Osorio, L.; Craig, J.I.; Goodno, B.J. Seismic response of critical interdependent networks. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2007, 36, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltrans (California Department of Transportation). Seismic Design Criteria Version 1.3; Caltrans: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Forcellini, D.; Tarantino, A.M. Assessment of stone columns as a mitigation technique of liquefaction-induced effects during Italian earthquakes (May 2012). Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 216278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, S.; McKenna, F.; Scott, M.H.; Fenves, G.L. Open System for Earthquake Engineering Simulation, User Command-Language Manual; OpenSees Version 2.0; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; Available online: http://opensees.berkeley.edu/OpenSees/manuals/usermanual (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Forcellini, D. Seismic resilience of bridges isolated with traditional and geotechnical seismic isolation (GSI). Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 21, 3521–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, R.F.; Forcellini, D.; McManus Warnell, J.; Walsh, K.Q. Relationship between Coastal Hazard Countermeasures and Community Resilience in the Tohoku Region of Japan Following the 2011 Tsunami. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2023, 24, 04023017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K.R.; Wong, J.-M.; Stojadinovic, B. Post-earthquake bridge repair cost and repair time estimation methodology. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2010, 39, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Number | Earthquake | Station | Duration (s) | PGA (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A-ELC | 1968 Borrego Mountain | 40.00 | 0.13 |
| 2 | A2E | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.18 |
| 3 | FMS | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.76 | 0.20 |
| 4 | HVR | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.14 |
| 5 | SJW | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.10 |
| 6 | SLC | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.58 | 0.20 |
| 7 | BAD | 1989 Loma Prieta | 35.00 | 0.11 |
| 8 | CAS | 1994 Northridge | 39.80 | 0.10 |
| 9 | CEN | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.49 |
| 10 | DEL | 1994 Northridge | 35.36 | 0.15 |
| 11 | DWN | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.17 |
| 12 | JAB | 1994 Northridge | 35.00 | 0.11 |
| 13 | L01 | 1994 Northridge | 32.00 | 0.09 |
| 14 | LOA | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.09 |
| 15 | LV2 | 1994 Northridge | 32.00 | 0.10 |
| 16 | PHP | 1994 Northridge | 60.00 | 0.07 |
| 17 | PIC | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.11 |
| 18 | SOR | 1994 Northridge | 36.48 | 0.07 |
| 19 | SSE | 1994 Northridge | 35.00 | 0.14 |
| 20 | VER | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.13 |
| 21 | AGW | 1989 Loma Prieta | 40.00 | 0.18 |
| 22 | CAP | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.55 |
| 23 | G03 | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.59 |
| 24 | G04 | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.45 |
| 25 | GMR | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.24 |
| 26 | HCH | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.10 | 0.27 |
| 27 | HAD | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.64 | 0.29 |
| 28 | SVL | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.26 | 0.21 |
| 29 | CNP | 1994 Northridge | 25.00 | 0.39 |
| 30 | FAR | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.30 |
| 31 | FLE | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.17 |
| 32 | GLP | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.37 |
| 33 | LOS | 1994 Northridge | 20.00 | 0.44 |
| 34 | NYA | 1994 Northridge | 30.00 | 0.20 |
| 35 | PEL | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.25 |
| 36 | RO3 | 1994 Northridge | 30.28 | 0.31 |
| 37 | Z-PEL | 1954 Ferndale | 28.00 | 0.22 |
| 38 | B-ICC | 1987 Superstition Hills | 40.00 | 0.38 |
| 39 | B-IVW | 1987 Superstition Hills | 44.00 | 0.17 |
| 40 | B-WSM | 1987 Superstition Hills | 40.00 | 0.18 |
| 41 | H-PVB | 1983 Coalinga | 39.96 | 0.40 |
| 42 | H-AEP | 1979 Imperial Valley | 11.16 | 0.36 |
| 43 | H-BCR | 1979 Imperial Valley | 37.62 | 0.63 |
| 44 | H-CXO | 1979 Imperial Valley | 37.82 | 0.29 |
| 45 | H-E05 | 1979 Imperial Valley | 39.30 | 0.55 |
| 46 | H-ECC | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.23 |
| 47 | H-SHP | 1979 Imperial Valley | 15.72 | 0.30 |
| 48 | I-ELC | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.33 |
| 49 | G02 | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.39 |
| 50 | GOF | 1989 Loma Prieta | 39.96 | 0.30 |
| 51 | Z-HVR | 1984 Morgan Hill | 39.98 | 0.17 |
| 52 | 637 | 1994 Northridge | 47.78 | 0.81 |
| 53 | JEN | 1994 Northridge | 28.62 | 0.62 |
| 54 | NWH | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.63 |
| 55 | RRS | 1994 Northridge | 19.92 | 0.89 |
| 56 | SCS | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.66 |
| 57 | SYL | 1994 Northridge | 40.00 | 0.65 |
| 58 | C08 | 1966 Parkfield | 26.12 | 0.24 |
| 59 | A-JAB | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 34.30 | 0.24 |
| 60 | A-SOR | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 28.72 | 0.15 |
| 61 | B-ELC | 1968 Borrego Mountain | 40.00 | 0.07 |
| 62 | H-C05 | 1983 Coalinga | 40.00 | 0.16 |
| 63 | H-C08 | 1983 Coalinga | 32.00 | 0.10 |
| 64 | H-CC4 | 1979 Imperial Valley | 28.54 | 0.12 |
| 65 | H-CMP | 1979 Imperial Valley | 36.00 | 0.20 |
| 66 | H-DLT | 1979 Imperial Valley | 99.92 | 0.24 |
| 67 | H-NIL | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.12 |
| 68 | H-PLS | 1979 Imperial Valley | 18.76 | 0.05 |
| 69 | H-VCT | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.13 |
| 70 | A-STP | 1980 Livermore | 33.00 | 0.05 |
| 71 | SJB | 1984 Morgan Hill | 28.00 | 0.05 |
| 72 | Z-CAP | 1984 Morgan Hill | 36.00 | 0.11 |
| 73 | Z-HCH | 1984 Morgan Hill | 28.34 | 0.08 |
| 74 | H06 | 1986 North Palm Springs | 40.00 | 0.07 |
| 75 | INO | 1986 North Palm Springs | 30.00 | 0.07 |
| 76 | A-BIR | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 28.62 | 0.26 |
| 77 | A-CTS | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 39.96 | 0.05 |
| 78 | A-HAR | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 40.00 | 0.06 |
| 79 | A-SSE | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 22.94 | 0.05 |
| 80 | A-STC | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 40.00 | 0.17 |
| 81 | H-CAL | 1979 Imperial Valley | 39.54 | 0.14 |
| 82 | H-CHI | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.29 |
| 83 | E-E01 | 1979 Imperial Valley | 39.04 | 0.15 |
| 84 | H-E12 | 1979 Imperial Valley | 39.02 | 0.15 |
| 85 | H-E13 | 1979 Imperial Valley | 39.52 | 0.12 |
| 86 | H-WSM | 1979 Imperial Valley | 40.00 | 0.08 |
| 87 | A-KOD | 1980 Livermore | 20.98 | 0.17 |
| 88 | A-SRM | 1980 Livermore | 40.00 | 0.06 |
| 89 | Z-AGW | 1984 Morgan Hill | 59.96 | 0.03 |
| 90 | Z-G02 | 1984 Morgan Hill | 29.98 | 0.17 |
| 91 | Z-G03 | 1984 Morgan Hill | 39.98 | 0.21 |
| 92 | Z-GMR | 1984 Morgan Hill | 29.98 | 0.20 |
| 93 | PHN | 1946 Point Mugu | 23.20 | 0.12 |
| 94 | BRA | 1966 Westmore | 28.42 | 0.17 |
| 95 | NIL | 1966 Westmore | 40.00 | 0.11 |
| 96 | A-CAS | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 31.18 | 0.36 |
| 97 | A-CAT | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 32.92 | 0.05 |
| 98 | A-DWN | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 40.00 | 0.24 |
| 99 | A-W70 | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 31.94 | 0.21 |
| 100 | A-WAT | 1987 Whittier Narrows | 29.70 | 0.11 |
| r/r0 | c = 0.5 | c = 1.0 | c = 2.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.938 | 0.750 | 0.500 |
| 0.50 | 0.750 | 0.500 | 0.293 |
| 0.75 | 0.438 | 0.250 | 0.134 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forcellini, D. The Role of Redundancy of Infrastructures on the Seismic Resilience (SR) of Sustainable Communities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11849. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511849
Forcellini D. The Role of Redundancy of Infrastructures on the Seismic Resilience (SR) of Sustainable Communities. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11849. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511849
Chicago/Turabian StyleForcellini, Davide. 2023. "The Role of Redundancy of Infrastructures on the Seismic Resilience (SR) of Sustainable Communities" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11849. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511849
APA StyleForcellini, D. (2023). The Role of Redundancy of Infrastructures on the Seismic Resilience (SR) of Sustainable Communities. Sustainability, 15(15), 11849. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511849







