A Bibliometric Review on Safety Risk Assessment of Construction Based on CiteSpace Software and WoS Database
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Software Selection
2.2. Database Selection and Paper Search
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Selected Publications
3.1.1. Average Annual Publication
3.1.2. Major Sources
3.2. Co-Authorship Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of Country
3.2.2. Analysis of Authors
3.3. Co-Term Analysis
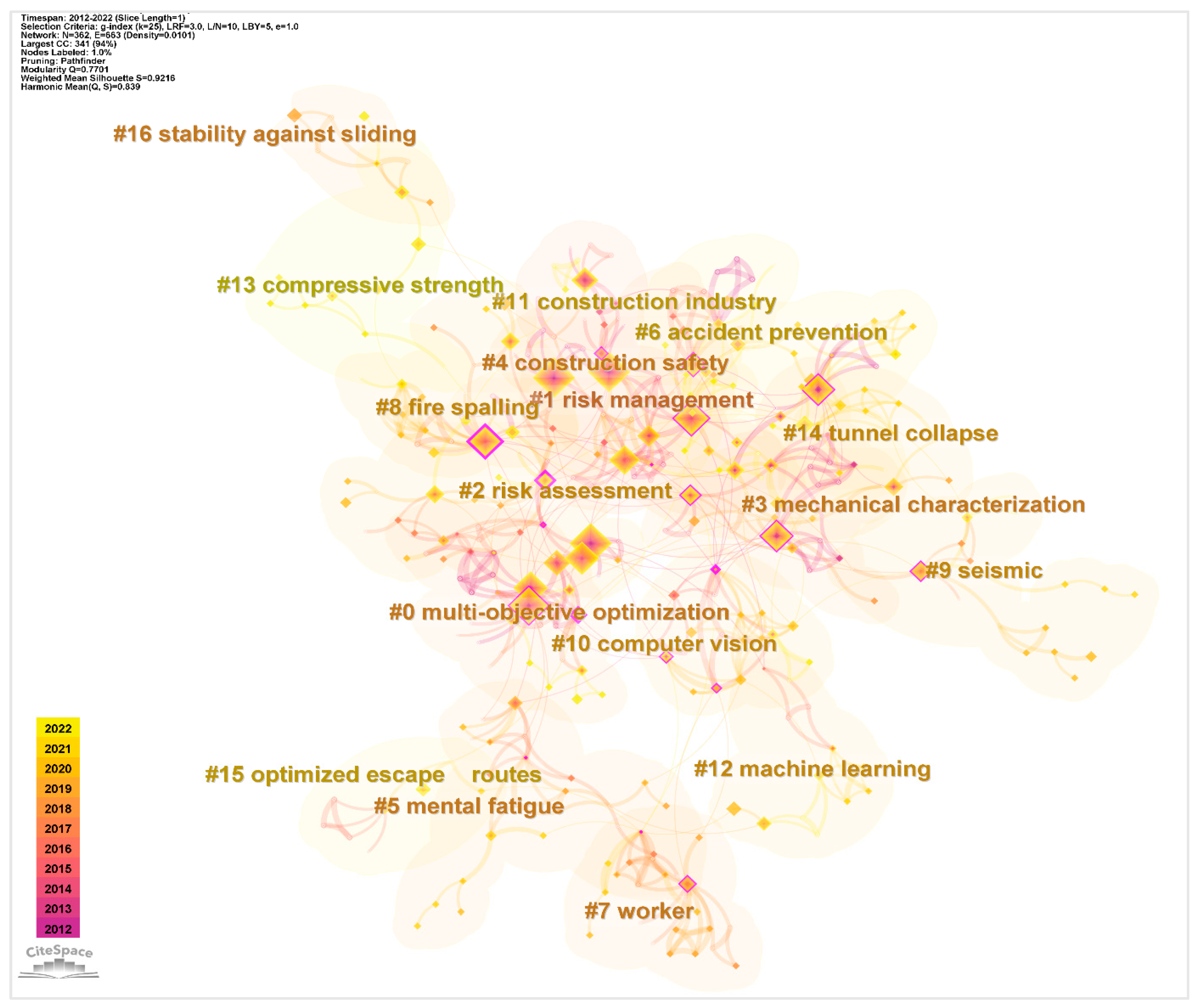
3.3.1. Analysis of Keyword Cluster
3.3.2. Analysis of Keyword Evolution
3.3.3. Analysis of Partner Institutions
3.4. Co-Citation Analysis
3.4.1. Analysis of Co-Cited Authors
3.4.2. Analysis of Co-Cited Clusters
4. Discussion
- Data-driven and AI: The increased availability of data and the adoption of digital tools such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable more comprehensive risk assessments [145,146]. Real-time data on project schedules, environmental factors, and equipment performance can provide valuable insights for effective risk identification and the mitigation to AI [141,147].
- Blockchain and cloud computing: More construction project data are becoming available, and cloud computing makes it possible to find new ways to collect, analyze, and visualize large amounts of data for construction risk assessment [148,149,150]. Blockchain technology can also make secure, transparent, and tamper-proof systems for recording and tracking information about construction risk [151,152].
- Enhanced collaboration and stakeholder engagement: Effective risk assessment requires the collaboration and input of a variety of stakeholders, including contractors, architects, engineers, and owners [153,154]. Future approaches to risk assessment are likely to emphasize improved collaboration and stakeholder engagement using cloud-based platforms, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) tools [155,156]. These technologies can facilitate real-time communication, the better visualization of risks, and enhance the decision-making process.
- Focus on sustainability and resilience: The construction industry is placing increasing emphasis on sustainability and resilience in building design and construction practices. Risk assessment needs to address these factors by considering the potential risks associated with climate change, extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and social impacts [157,158]. Assessing the resilience of buildings and infrastructure regarding these risks is essential to ensure long-term performance and minimize adverse impacts.
- Regulatory requirements and the impact on the insurance industry: As regulatory regulations in the construction industry evolve, risk assessment methods need to be accordingly adapted [159,160]. Regulators may require more stringent risk assessment practices to enhance safety, environmental protection, and compliance. In addition, insurers may influence risk assessment practices by requiring comprehensive risk assessments to accurately assess premiums.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, H.-M.; Sun, W.-J.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A.-N. Risk Assessment Using a New Consulting Process in Fuzzy AHP. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04019112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, L. Multi-Objective Optimization for Improved Project Management: Current Status and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Z.; Ding, L.Y.; Zhou, C.; Luo, H.B. Analysis of Factors Influencing Safety Management for Metro Construction in China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 68, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Karim, M.S.B.A.; Mosa El Nawawy, O.A.; Abdel-Alim, A.M. Identification and Assessment of Risk Factors Affecting Construction Projects. HBRC J. 2017, 13, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baloi, D.; Price, A.D.F. Modelling Global Risk Factors Affecting Construction Cost Performance. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2003, 21, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalaisami, C.D.; Kuppuswamy, A. Managing Cost Risks: Toward a Taxonomy of Cost Overrun Factors in Building Construction Projects. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2021, 7, 04021021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarkas, A.M.; Haupt, T.C. Major Construction Risk Factors Considered by General Contractors in Qatar. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2015, 13, 165–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.; Chapman, C. Transforming Project Risk Management into Project Uncertainty Management. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2003, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Bertsch, B.; Dale, B.; van der Wiele, T.; van Iwaarden, J.; Smith, M. Visser, RQuality and Risk Management: What Are the Key Issues? TQM Mag. 2006, 18, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayegh, S.M.; Manjikian, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Abouelyousr, A.; Jabbour, R. Risk Identification and Assessment in Sustainable Construction Projects in the UAE. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2018, 21, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chileshe, N.; Boadua Yirenkyi-Fianko, A. An Evaluation of Risk Factors Impacting Construction Projects in Ghana. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2012, 10, 306–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; Khoiry, M.A.; Hamzah, N. Assessment of the Effect of External Risk Factors on the Success of an Oil and Gas Construction Project. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2020; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q. Critical Success Factors for Modular Integrated Construction Projects: A Review. Build. Res. Inf. 2019, 48, 763–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharef, A.; Banerjee, S.; Uddin, S.M.J.; Albert, A.; Jaselskis, E. Early Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the United States Construction Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, S. Early Warning of the Construction Safety Risk of a Subway Station Based on the LSSVM Optimized by QPSO. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.A.; Warnakulasooriya, B.N.F.; Arachchige, B. Critical Success Factors for Construction Projects: A Literature Review. SSRN Electron. J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Huang, M. Statistical Analysis of Major Tunnel Construction Accidents in China from 2010 to 2020. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Irizarry, J.; Li, Q. Using Network Theory to Explore the Complexity of Subway Construction Accident Network (SCAN) for Promoting Safety Management. Saf. Sci. 2014, 64, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Nepal, M.P.; Skitmore, M.; Attarzadeh, M. Current Research Trends and Application Areas of Fuzzy and Hybrid Methods to the Risk Assessment of Construction Projects. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2017, 33, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aven, T.; Renn, O. The Role of Quantitative Risk Assessments for Characterizing Risk and Uncertainty and Delineating Appropriate Risk Management Options, with Special Emphasis on Terrorism Risk. Risk Anal. 2009, 29, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aven, T. Risk, Surprises and Black Swans; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781315755175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Ai Lin Teo, E.; Lee, K.-P. Construction Risk Assessment Using Site Influence Factors. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2012, 26, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, F.; Yunfei, S.; Nazir, M.; Bhatti, S.M. A Review of Artificial Intelligence Based Risk Assessment Methods for Capturing Complexity-Risk Interdependencies. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2019; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y. Distinguishing Investment Changes in Metro Construction Project Based on a Factor Space Algorithm. Clust. Comput. 2018, 22, 9357–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
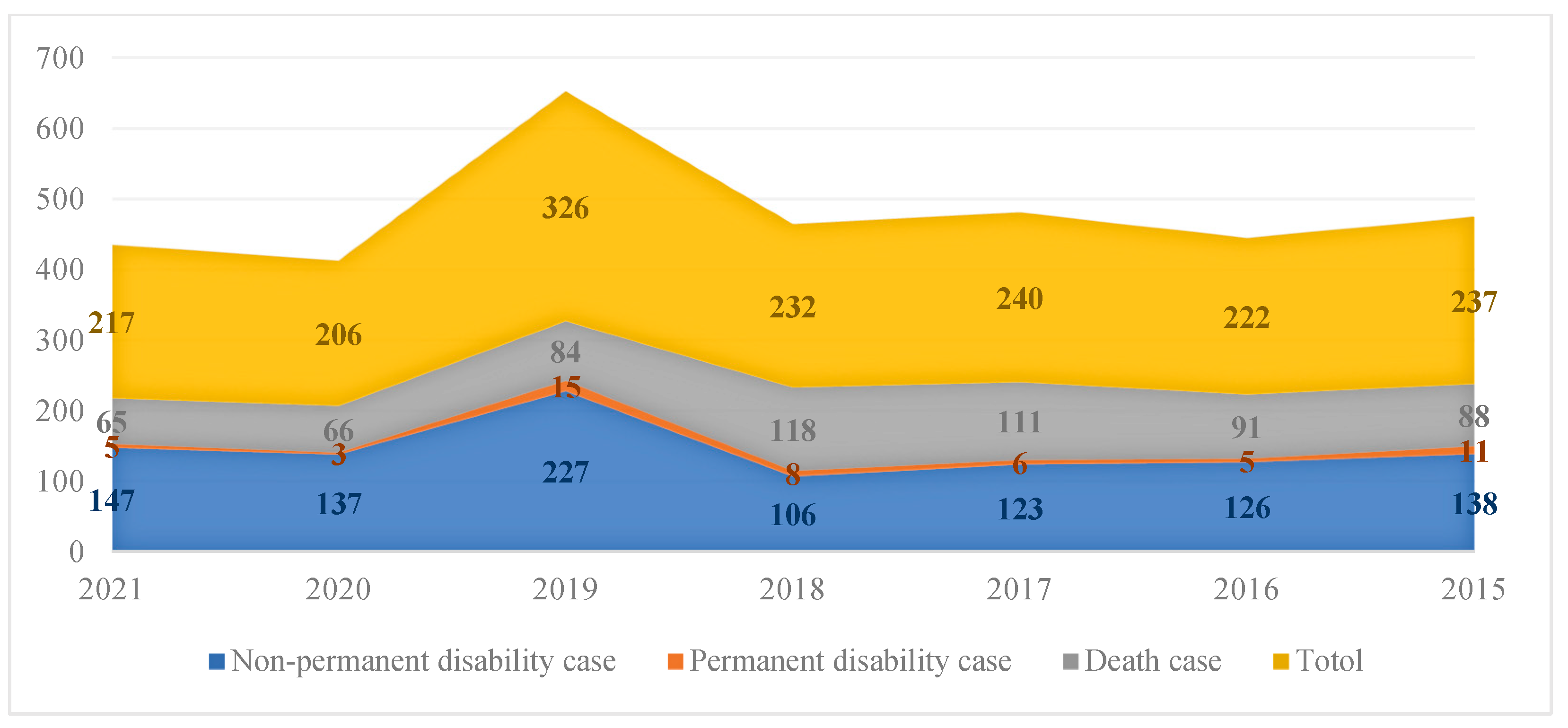
- DOSH. Occupational Accident Statistics. Available online: https://www.dosh.gov.my/index.php/statistic-v/occupational-accident-statistics (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Chellappa, V.; Srivastava, V.; Salve, U.R. A Systematic Review of Construction Workers’ Health and Safety Research in India. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2021; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Gao, C.; Elzarka, H.; Mostafa, K.; Tang, W. Risk Assessment for Construction of Urban Rail Transit Projects. Saf. Sci. 2019, 118, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Nunes, I.L.; Ribeiro, R.A. Occupational Risk Assessment in Construction Industry—Overview and Reflection. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni-Anibire, M.O.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Hassanain, M.A.; Salami, B.A. A Risk Assessment Approach for Enhancing Construction Safety Performance. Saf. Sci. 2020, 121, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.; Thakur, A.; Singh, S.; Salunkhe, A. Risk Assessment in Construction of Highway Project. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroun, A. Towards a Better Modelling and Assessment of Construction Risk: Insights from a Literature Review. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, L.; Cai, H. Risk Assessment and Management via Multi-Source Information Fusion for Undersea Tunnel Construction. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.P.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Risk Assessment of Tunnel Construction Based on Improved Cloud Model. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2020, 34, 04020028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprowicz, T. Quantitative Assessment of Construction Risk. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2017, 63, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio de los Pinos, A.J.; González García, M.d.l.N. Critical Analysis of Risk Assessment Methods Applied to Construction Works. De La Construcción 2017, 16, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardito, E.; Purba, H.H.; Purba, A. System Dynamic Modeling of Risk Management in Construction Projects: A Systematic Literature Review. Oper. Res. Eng. Sci. Theory Appl. 2021, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H. A Visual Analysis of Research on Information Security Risk by Using CiteSpace. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 63243–63257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-S.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A.; Xu, Y.-S. Risk Assessment and Management of Excavation System Based on Fuzzy Set Theory and Machine Learning Methods. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Kyei, R.; Narbaev, T.; Ampratwum, G. A Scientometric Analysis of Studies on Risk Management in Construction Projects. Buildings 2022, 12, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and Visualizing Emerging Trends and Transient Patterns in Scientific Literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace: A Practical Guide for Mapping Scientific Literature; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781536102802. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y. Review of Construction Safety Studies from a Behavioral Perspective: New Evidence from Mapping Knowledge Domains. Int. J. Innov. Manag. Technol. 2020, 11, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Dong, J.-W. Knowledge Atlas on the Relationship between Water Management and Constructed Wetlands—A Bibliometric Analysis Based on CiteSpace. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Construction of Inclusive Leadership Knowledge Graph Based on Citespace and WOS Core Database. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Engineering (MLKE), Guilin, China, 25–27 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBurney, M.K.; Novak, P.L. What Is Bibliometrics and Why Should You Care? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Professional Communication Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 20 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Li, R.Y.M.; Crabbe, M.J.C.; Pu, R. Economic Development and Construction Safety Research: A Bibliometrics Approach. Saf. Sci. 2022, 145, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Tseng, H. Emerging Trends in Regenerative Medicine: A Scientometric Analysis InCiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sang, P. A Bibliometric Review of Studies on Construction and Demolition Waste Management by Using CiteSpace. Energy Build. 2022, 258, 111822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, Q. A Literature Analysis of Construction Workers’ Safety Training Based on Narrative Review and Citespace. Available online: https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/bads-22/125981721 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Synnestvedt, M.; Chen, C.; Holmes, J. CiteSpace II: Visualization and Knowledge Discovery in Bibliographic Databases. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2005, 2005, 724–728. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhou, H. Scientometric Analysis of Public Health Emergencies: 1994–2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Zhou, X. Study on Sustainable Urbanization Literature Based on Web of Science, Scopus, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure: A Scientometric Analysis in CiteSpace. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X. Hot Topics and Trends in Zero-Energy Building Research—A Bibliometrical Analysis Based on CiteSpace. Buildings 2023, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A Tale of Two Databases: The Use of Web of Science and Scopus in Academic Papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X. Research on the Literature of Green Building Based on the Web of Science: A Scientometric Analysis in CiteSpace (2002–2018). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Shin, S. Bibliometric Analysis on Research Trend of Accidental Falls in Older Adults by Using Citespace—Focused on Web of Science Core Collection (2010–2020). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Ma, Q.; Yang, X.; Song, Y. Study on Pain Catastrophizing from 2010 to 2020: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 759347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Maimaituerxun, M. Bibliometric Review of Carbon Neutrality with CiteSpace: Evolution, Trends, and Framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76668–76686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Kamphuis, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Kim, J.H. A Visualization Analysis of Crisis and Risk Communication Research Using CiteSpace. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W. A Review of Emerging Trends in Global PPP Research: Analysis and Visualization. Scientometrics 2016, 107, 1111–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcael, E.; Ferrari, I.; Opazo-Vega, A.; Pulido-Arcas, J.A. Construction 4.0: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Trindade, E.; Alencar, L.; Alencar, M.; Silva, L. Sustainability in the Construction Industry: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C. Bibliometrical Analysis of International Big Data Research: Based on Citespace and VOSviewer. In Proceedings of the 2018 14th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), Huangshan, China, 28–30 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1 July 2018; pp. 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, L. Multi-Objective Optimization in Tunnel Line Alignment under Uncertainty. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Qi, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, W. Reducing Noise Pollution by Planning Construction Site Layout via a Multi-Objective Optimization Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.R.; Zhang, X. Developing a Holistic Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Model: An Application to a Case of Sustainable Construction Project. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantra, C.; Datta, S.; Mahapatra, S.S. Fuzzy Based Risk Assessment Module for Metropolitan Construction Project: An Empirical Study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 65, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, F.; Chinniah, Y.; Burlet-Vienney, D.; Aucourt, B.; Larouche, S. Risk Assessment in Safety of Machinery: Impact of Construction Flaws in Risk Estimation Parameters. Saf. Sci. 2018, 109, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.W.; Jung, I.S.; Lee, C.S. Risk Assessment for Reducing Safety Accidents Caused by Construction Machinery. J. Korean Soc. Saf. 2013, 28, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bluff, E. Safety in Machinery Design and Construction: Performance for Substantive Safety Outcomes. Saf. Sci. 2014, 66, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, B.U.; Tokdemir, O.B. Accident Analysis for Construction Safety Using Latent Class Clustering and Artificial Neural Networks. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04019114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Shariatfar, M.; Rashidi, A.; Lee, H.W. Evidence-Driven Sound Detection for Prenotification and Identification of Construction Safety Hazards and Accidents. Autom. Constr. 2020, 113, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chew, D.A.S.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Q. Design and Implementation of an Identification System in Construction Site Safety for Proactive Accident Prevention. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 48, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, S.; Han, S. Analyses of Systems Theory for Construction Accident Prevention with Specific Reference to OSHA Accident Reports. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2013, 31, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Arifai, A.M.; Gheisari, M. Exploring Empirical Rules for Construction Accident Prevention Based on Unsafe Behaviors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wu, Z. A Human-Centered Risk Model for the Construction Safety. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 154072–154086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Accident Causing Theory in Construction Safety Management. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 638, 012097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Huang, S.-S.; Onaizi, A.M.; Murali, G.; Abdelgader, H.S. Fire Spalling Behavior of High-Strength Concrete: A Critical Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeiml, M.; Pichler, C.; Lackner, R. Model-Based Risk Assessment of Concrete Spalling in Tunnel Linings under Fire Loading. Eng. Struct. 2014, 77, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirchian, E.; Kumari, V.; Jadhav, K.; Raj Das, R.; Rasulzade, S.; Lahmer, T. A Machine Learning Framework for Assessing Seismic Hazard Safety of Reinforced Concrete Buildings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Angelosanti, M.; Bernardini, G.; Severi, L.; Quagliarini, E.; Currà, E. Factors Influencing the Intrinsic Seismic Risk of Open Spaces in Existing Built Environments: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdiyar, A.; Hasanipanah, M.; Armaghani, D.J.; Gordan, B.; Abdullah, A.; Arab, H.; Majid, M.Z.A. A Monte Carlo Technique in Safety Assessment of Slope under Seismic Condition. Eng. Comput. 2017, 33, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Ding, L.; Love, P.E.D.; Luo, H.; Li, H.; Peña-Mora, F.; Zhong, B.; Zhou, C. Computer Vision Applications in Construction Safety Assurance. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Leite, F. Transforming Inherent Safety Risk in the Construction Industry: A Safety Risk Generation and Control Model. Saf. Sci. 2020, 124, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegboyega, A.A.; Eze, C.E.; Sofolahan, O. Health and Safety (Hs) Risks Normalization in the Construction Industry: The SMEs Perspective. Indep. J. Manag. Prod. 2021, 12, 1466–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-L. Defect Risk Assessment Using a Hybrid Machine Learning Method. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.R.; Nalluri, M.R.; Anand, K.B. Application of Ensemble Machine Learning for Construction Safety Risk Assessment. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 2022, 103, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, X.; Hou, J.; Li, X. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Predicting the Consequences of Construction Accidents in China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 145, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğan, V.; Mostofi, F.; Ayözen, Y.E.; Behzat Tokdemir, O. Customized AutoML: An Automated Machine Learning System for Predicting Severity of Construction Accidents. Buildings 2022, 12, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.-C.; Plé, O.; Weiss, J.; Amitrano, D. Revisiting the Concept of Characteristic Compressive Strength of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asteris, P.G.; Mokos, V.G. Concrete Compressive Strength Using Artificial Neural Networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 32, 11807–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Sarkar, P.; Davis, R. Quantification of Uncertainty in Compressive Strength of Fly Ash Brick Masonry. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 26, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekle, B.H.; Al-Deen, S.; Anwar-Us-Saadat, M.; Willans, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, C.K. Use of Maturity Method to Estimate Early Age Compressive Strength of Slab in Cold Weather. Struct. Concr. 2021, 23, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, G.Z.; Jiao, Y.-Y.; Zhang, G.-H.; Zou, J.; Tan, F.; Zhang, W. Collapse Risk Assessment of Deep-Buried Tunnel during Construction and Its Application. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 115, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cai, N.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Dong, T. Risk Assessment of Loess Tunnel Collapse during Construction Based on an Attribute Recognition Model. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 6205–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Shi, S.; Cheng, S.; Hu, H.; Wen, T. Dynamic Risk Assessment Method of Collapse in Mountain Tunnels and Application. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Huang, X.T.; Xue, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Flow Characteristics and Escape-Route Optimization after Water Inrush in a Backward-Excavated Karst Tunnel. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04016096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, B.; Huang, X.T. Escape Route Analysis after Water Inrush from the Working Face during Submarine Tunnel Excavation. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2017, 36, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhou, X.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Simulation of Emergency Evacuation from Construction Site of Prefabricated Buildings. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z. Platform Development of BIM-Based Fire Safety Management System Considering the Construction Site. Buildings 2022, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Nadim, F.; Xue, Y. Quantitative Risk Assessment of Cut-Slope Projects under Construction. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Xu, C. Longitudinal Sliding Event during Excavation of Feng-Qi Station of Hangzhou Metro Line 1: Postfailure Investigation. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2018, 32, 04018039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, P.; Xiao, J.; Xu, F. Risk Assessment Model of Expansive Soil Slope Stability Based on Fuzzy-AHP Method and Its Engineering Application. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Gong, P.; Tang, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, Q. BIM-Integrated Construction Safety Risk Assessment at the Design Stage of Building Projects. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Qureshi, A.H.; Alaloul, W.S. Barriers to Building Information Modeling (BIM) Deployment in Small Construction Projects: Malaysian Construction Industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminbakhsh, S.; Gunduz, M.; Sonmez, R. Safety Risk Assessment Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) during Planning and Budgeting of Construction Projects. J. Saf. Res. 2013, 46, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Visualization Analysis of High-Speed Railway Research Based on CiteSpace. Transp. Policy 2020, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Ghahramani, A.; Becerik-Gerber, B. Monitoring Fatigue in Construction Workers Using Physiological Measurements. Autom. Constr. 2017, 82, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Skibniewski, M.J.; Wang, Y. Prospective Safety Performance Evaluation on Construction Sites. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 78, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raviv, G.; Shapira, A.; Fishbain, B. AHP-Based Analysis of the Risk Potential of Safety Incidents: Case Study of Cranes in the Construction Industry. Saf. Sci. 2017, 91, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallowell, M.R.; Hinze, J.W.; Baud, K.C.; Wehle, A. Proactive Construction Safety Control: Measuring, Monitoring, and Responding to Safety Leading Indicators. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2013, 139, 04013010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbahar, E.; Karaşan, A.; Cebi, S.; Kahraman, C. A Novel Approach to Risk Assessment for Occupational Health and Safety Using Pythagorean Fuzzy AHP & Fuzzy Inference System. Saf. Sci. 2018, 103, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Ding, L.; Luo, H.; Love, P.E.D. Falls from Heights: A Computer Vision-Based Approach for Safety Harness Detection. Autom. Constr. 2018, 91, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ke, J. A Proactive Workers’ Safety Risk Evaluation Framework Based on Position and Posture Data Fusion. Autom. Constr. 2019, 98, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, J.; Ahn, C. Construction Worker’s Awkward Posture Recognition through Supervised Motion Tensor Decomposition. Autom. Constr. 2017, 77, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Teizer, J.; Lee, J.-K.; Eastman, C.M.; Venugopal, M. Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Safety: Automatic Safety Checking of Construction Models and Schedules. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Goh, Y.M.; Li, Q. Overview and Analysis of Safety Management Studies in the Construction Industry. Saf. Sci. 2015, 72, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Cheng, W.; Hussain, A.B.; Chen, X.; Wajid, B.A. Knowledge Mapping of Research Progress in Vertical Greenery Systems (VGS) from 2000 to 2021 Using CiteSpace Based Scientometric Analysis. Energy Build. 2022, 256, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L. Bibliometric Analysis of Monte Carlo Based on Citespace. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Xiamen, China, 5–7 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1 July 2019; pp. 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y. Foreign STEAM Education Research Based on Visual Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Education, Information Management and Service Science (EIMSS 2022), Changsha, China, 22–24 July 2022; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 December 2022; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, W.; Montavon, G.; Lapuschkin, S.; Anders, C.J.; Muller, K.-R. Explaining Deep Neural Networks and Beyond: A Review of Methods and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, S.; Cadene, R.; Celona, L.; Napoletano, P. Benchmark Analysis of Representative Deep Neural Network Architectures. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 64270–64277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Alsaadi, F.E. A Survey of Deep Neural Network Architectures and Their Applications. Neurocomputing 2017, 234, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, V.; Chen, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-J.; Emer, J.S. Efficient Processing of Deep Neural Networks: A Tutorial and Survey. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2295–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montavon, G.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.-R. Methods for Interpreting and Understanding Deep Neural Networks. Digit. Signal Process. 2018, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Mittal, M.; Battineni, G. Generative Adversarial Network: An Overview of Theory and Applications. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irsoy, O.; Cardie, C. Deep Recursive Neural Networks for Compositionality in Language. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Obonyo, E. Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Model for Recognizing Construction Workers’ Postures from Wearable Inertial Measurement Units. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, M.A.; Kim, B.-S. Assessment of Risk Impact on Road Project Using Deep Neural Network. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 26, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Asghari, V.; Cheung, C.M.; Hsu, S.-C.; Lee, C.-J. Assessing Effects of Economic Factors on Construction Cost Estimation Using Deep Neural Networks. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofi, F.; Toğan, V.; Ayözen, Y.E.; Tokdemir, O.B. Construction Safety Risk Model with Construction Accident Network: A Graph Convolutional Network Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Lim, K.-K.; Yum, S.-G.; Son, S. A Deep Learning Model Development to Predict Safety Accidents for Sustainable Construction: A Case Study of Fall Accidents in South Korea. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Mitigating Tunnel-Induced Damages Using Deep Neural Networks. Autom. Constr. 2022, 138, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bae, J.; Park, H.; Yum, S.-G. Predicting Financial Losses due to Apartment Construction Accidents Utilizing Deep Learning Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Bae, J.; Son, S.; Son, K.; Yum, S.-G. Development of Model to Predict Natural Disaster-Induced Financial Losses for Construction Projects Using Deep Learning Techniques. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.; Oyedele, L.; Owolabi, H.; Akinade, O.; Bilal, M.; Davila Delgado, J.M.; Akanbi, L. Deep Learning Models for Health and Safety Risk Prediction in Power Infrastructure Projects. Risk Anal. 2019, 40, 2019–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Z. Early Warning Control Model and Simulation Study of Engineering Safety Risk Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regona, M.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Xia, B.; Li, R.Y.M. Opportunities and Adoption Challenges of AI in the Construction Industry: A PRISMA Review. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.-J. Risk Factor Recognition for Automatic Safety Management in Construction Sites Using Fast Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Construction Project Risk Prediction Model Based on EW-FAHP and One Dimensional Convolution Neural Network. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejani, M.M.; Ghatee, M. A Systematic Review on Overfitting Control in Shallow and Deep Neural Networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 6391–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, M.; Ham, Y. AI-Based Risk Assessment for Construction Site Disaster Preparedness through Deep Learning-Based Digital Twinning. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Roles of Artificial Intelligence in Construction Engineering and Management: A Critical Review and Future Trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, M.A.; Ansari, R.; Hassannayebi, E.; Jeong, J. Cost Overrun Risk Assessment and Prediction in Construction Projects: A Bayesian Network Classifier Approach. Buildings 2022, 12, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, J.; Hwang, B.-G.; Zhang, C. Factor-Based Big Data and Predictive Analytics Capability Assessment Tool for the Construction Industry. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Big Data in Safety Management: An Overview. Saf. Sci. 2021, 143, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. HSE Risk Assessment of Major Sewage Transport Tunnel Projects at the Construction Stage Based on the StructuralEntropy Weight Method and the Cloud Model. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8882903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.J.; Broyd, T.; Ma, L. Exploratory Literature Review of Blockchain in the Construction Industry. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Chen, Z.; Xue, F. A Blockchain 3.0 Paradigm for Digital Twins in Construction Project Management. Autom. Constr. 2023, 145, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylan, O.; Bafail, A.O.; Abdulaal, R.M.S.; Kabli, M.R. Construction Projects Selection and Risk Assessment by Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS Methodologies. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 17, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R.; Dehghani, P.; Mahdikhani, M.; Jeong, J. A Novel Safety Risk Assessment Based on Fuzzy Set Theory and Decision Methods in High-Rise Buildings. Buildings 2022, 12, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, W.; Chi, H.-L.; Wang, X.; Chan, A.P.C. A Critical Review of Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) Applications in Construction Safety. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, P.; Proeger, E.; Kergel, R.; Lungfiel, A. Development of a vr Planning Model of a River Lock for Risk Assessment in the Construction and Machinery Industry. In Proceedings of the EuroVR 2014—Conference and Exhibition of the European Association of Virtual and Augmented Reality, Bremen, Germany, 8–10 December 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N. Risk Evaluation of a UHV Power Transmission Construction Project Based on a Cloud Model and FCE Method for Sustainability. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2885–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Mohandes, S.R. Occupational Health and Safety in Green Building Construction Projects: A Holistic Z-Numbers-Based Risk Management Framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Nagai, Y.; Gao, C. Design of Building Construction Safety Prediction Model Based on Optimized BP Neural Network Algorithm. Soft Comput. 2019, 24, 7839–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee Chattapadhyay, D.; Putta, J.; Rao, P.R.M. Risk Identification, Assessments, and Prediction for Mega Construction Projects: A Risk Prediction Paradigm Based on Cross Analytical-Machine Learning Model. Buildings 2021, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| No. | Journal | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Construction Engineering and Management | 58 | 11.69% |
| 2 | Automation in Construction | 55 | 11.09% |
| 3 | Advances in Civil Engineering | 25 | 5.04% |
| 4 | Buildings | 24 | 4.84% |
| 5 | Construction and Building Materials | 22 | 4.44% |
| 6 | Journal of Civil Engineering and Management | 22 | 4.44% |
| 7 | Tunneling and Underground Space Technology | 22 | 4.44% |
| 8 | Engineering Construction and Architectural Management | 21 | 4.23% |
| 9 | Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering | 14 | 2.82% |
| 10 | Structural Safety | 14 | 2.82% |
| 11 | KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering | 11 | 2.22% |
| 12 | Engineering Structures | 9 | 1.82% |
| 13 | Journal of Management in Engineering | 9 | 1.82% |
| 14 | Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities | 9 | 1.82% |
| 15 | Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment | 9 | 1.82% |
| 16 | ASCE-ASME Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems, Part A Civil Engineering | 8 | 1.61% |
| 17 | Building and Environment | 8 | 1.61% |
| 18 | Ocean Engineering | 8 | 1.61% |
| 19 | Journal of Building Engineering | 7 | 1.41% |
| 20 | Structure and Infrastructure Engineering | 6 | 1.21% |
| No. | Country | Frequency | Country | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 174 | England | 0.60 |
| 2 | USA | 96 | Portugal | 0.36 |
| 3 | Australia | 40 | Scotland | 0.35 |
| 4 | Canada | 36 | France | 0.24 |
| 5 | South Korea | 28 | Singapore | 0.22 |
| 6 | England | 22 | Malaysia | 0.2 |
| 7 | Iran | 20 | India | 0.19 |
| 8 | Italy | 19 | Brazil | 0.17 |
| 9 | Spain | 17 | Chile | 0.15 |
| 10 | Poland | 16 | Italy | 0.11 |
| No. | Author | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li Heng | 10 |
| 2 | Zhang Limao | 9 |
| 3 | Wu Xianguo | 7 |
| 4 | Umer Waleed | 5 |
| 5 | Antwi-afari Maxwell Fordjour | 5 |
| 6 | Al-hussein Mohamed | 5 |
| 7 | Jeong Jaewook | 5 |
| 8 | Abourizk Simaan | 5 |
| 9 | Han SangUk | 5 |
| 10 | Yu Yantao | 5 |
| No. | Institutions | Frequency | Institutions | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Huazhong University of Science and Technology | 23 | Tongji University | 0.07 |
| 2 | Hong Kong Polytechnic University | 21 | Tsinghua University | 0.07 |
| 3 | University of Alberta | 16 | Huazhong University of Science and Technology | 0.06 |
| 4 | China University of Mining and Technology | 7 | Central University of Finance and Economics | 0.06 |
| 5 | Dalian University of Technology | 7 | Hefei University of Technology | 0.06 |
| 6 | Islamic Azad University | 7 | University of Alberta | 0.05 |
| 7 | Tongji University | 7 | Broadvis Engineering Consultants | 0.05 |
| 8 | Tsinghua University | 7 | Hong Kong Polytechnic University | 0.04 |
| 9 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 6 | China University of Mining and Technology | 0.03 |
| 10 | National University of Singapore | 6 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 0.03 |
| No. | Author | Frequency | Author | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hallowell | 49 | Chan Apc | 0.23 |
| 2 | Zhang Lm | 47 | Hallowell | 0.21 |
| 3 | Hinze J | 34 | Fema | 0.19 |
| 4 | Mitropoulos P | 33 | Choudhry Rm | 0.18 |
| 5 | Ding Ly | 30 | Pearl J | 0.18 |
| 6 | Zadeh La | 26 | Ding Ly | 0.17 |
| 7 | Choudhry Rm | 25 | Zhang Lm | 0.15 |
| 8 | Zhang Sj | 23 | Abdelhamid Ts | 0.14 |
| 9 | Teizer J | 23 | Chen Cx | 0.14 |
| 10 | Fang Dp | 21 | Chi S | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Junjia, Y.; Alias, A.H.; Haron, N.A.; Abu Bakar, N. A Bibliometric Review on Safety Risk Assessment of Construction Based on CiteSpace Software and WoS Database. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511803
Junjia Y, Alias AH, Haron NA, Abu Bakar N. A Bibliometric Review on Safety Risk Assessment of Construction Based on CiteSpace Software and WoS Database. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511803
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunjia, Yin, Aidi Hizami Alias, Nuzul Azam Haron, and Nabilah Abu Bakar. 2023. "A Bibliometric Review on Safety Risk Assessment of Construction Based on CiteSpace Software and WoS Database" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511803
APA StyleJunjia, Y., Alias, A. H., Haron, N. A., & Abu Bakar, N. (2023). A Bibliometric Review on Safety Risk Assessment of Construction Based on CiteSpace Software and WoS Database. Sustainability, 15(15), 11803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511803






