Comprehensive Evaluation of the Efficient and Safe Utilization of Two Varieties of Winter Rapeseed Grown on Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Farmland under Atmospheric Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Computational Formula
2.4.1. Transfer Factor
2.4.2. Bioconcentration Factor
2.4.3. Health Risk Assessment
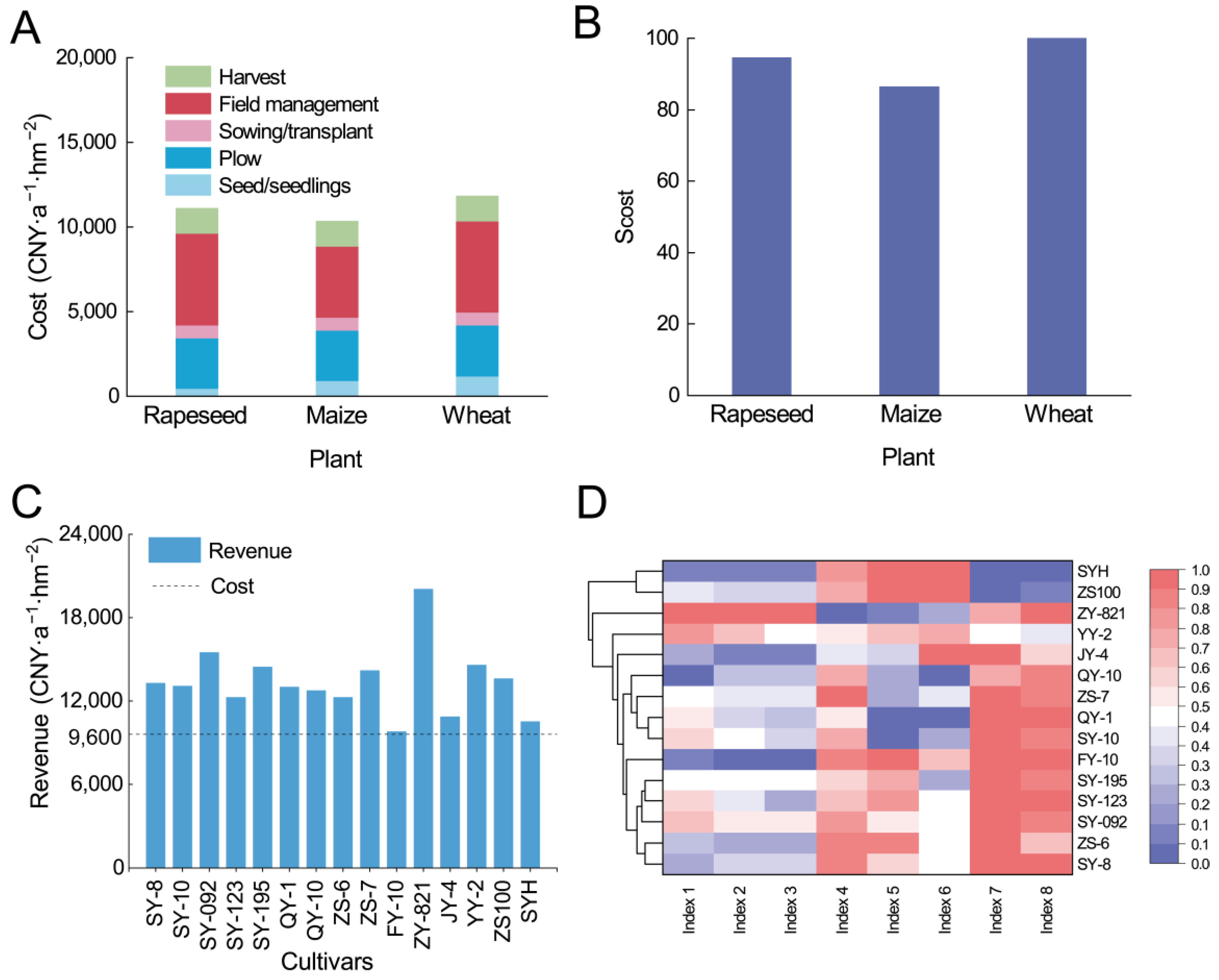
2.4.4. Economic Cost Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Biomass and Yield of Rapeseed with Cd/Pb Exposure
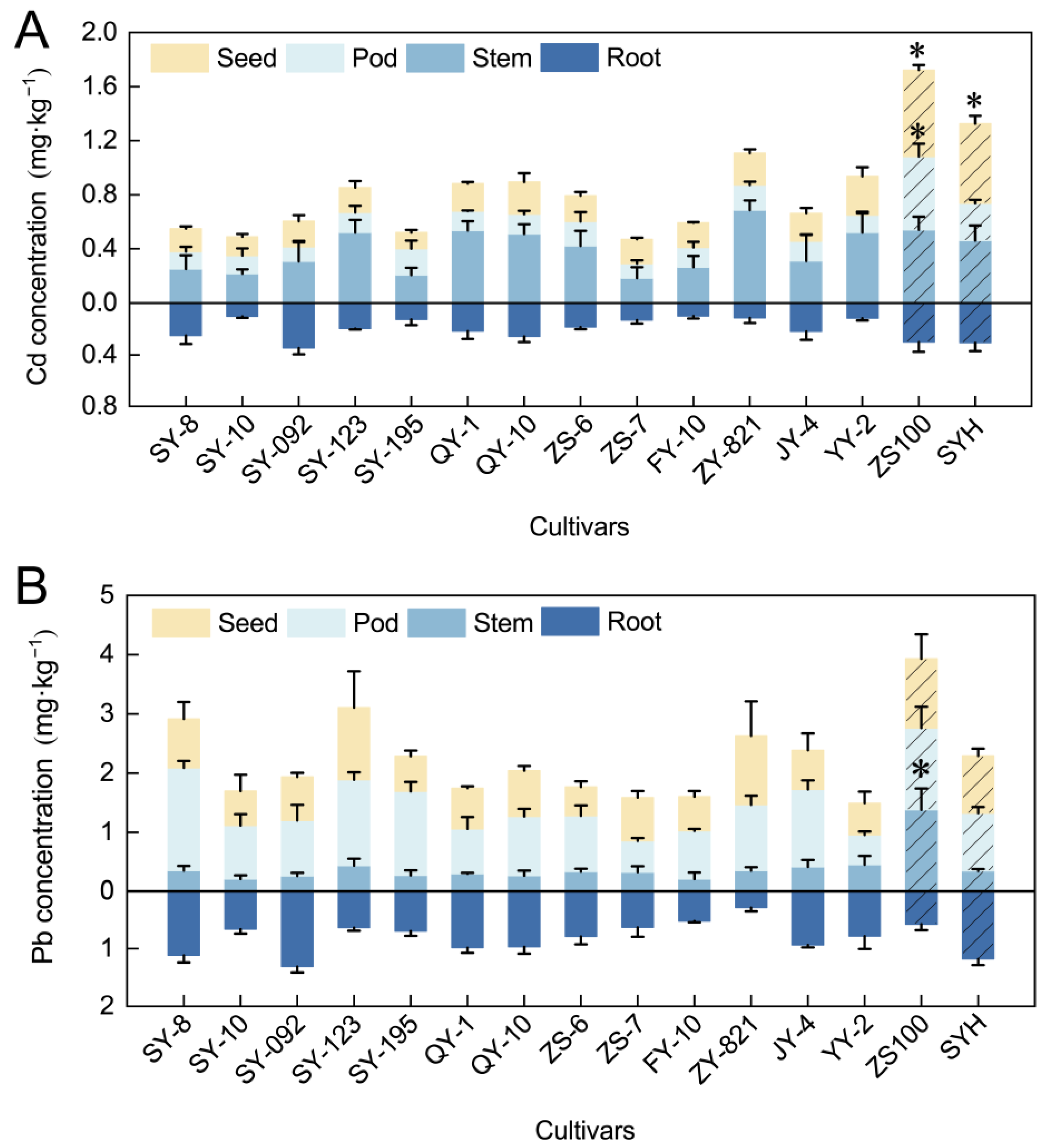
3.2. Cd/Pb Concentrations in Rapeseed Tissues
3.3. Cd/Pb Accumulation and Translocation
3.4. Rapeseed Oil/Meal Quality Assessment
| Cultivars | Oil Cd | Oil Pb | Meal Cd | Meal Pb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP 1 | SBE 2 | MP | SBE | MP | SBE | MP | SBE | |
| SY-8 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.057 | <0.001 | 0.162 | 0.249 | 0.104 | 0.133 |
| SY-10 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.040 | <0.001 | 0.133 | 0.064 | 0.500 | 0.190 |
| SY-092 | <0.002 | <0.002 | 0.051 | <0.001 | 0.168 | 0.081 | 0.472 | 0.179 |
| SY-123 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.077 | <0.001 | 0.152 | 0.403 | 0.123 | 0.146 |
| SY-195 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.132 | 0.223 | 0.105 | 0.076 |
| QY-1 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.031 | <0.001 | 0.158 | 0.243 | 0.451 | 0.578 |
| QY-10 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.053 | <0.001 | 0.244 | 0.132 | 0.362 | 0.192 |
| ZS-6 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.134 | 0.185 | 0.108 | 0.105 |
| ZS-7 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.095 | 0.160 | 0.797 | 0.575 |
| FY-10 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.040 | <0.001 | 0.196 | 0.194 | 0.361 | 0.345 |
| ZY-821 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.074 | <0.001 | 0.233 | 0.618 | 1.041 | 1.235 |
| JY-4 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.250 | 0.427 | 0.344 | 0.370 |
| YY-2 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.037 | <0.001 | 0.790 | 0.780 | 2.651 | 2.535 |
| ZS100 | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.074 | <0.001 | 0.340 | 0.468 | 2.550 | 2.479 |
| SYH | 0.002 | <0.002 | 0.067 | <0.001 | 0.462 | 0.249 | 0.752 | 0.399 |
| National Food Safety Standard Limit of Pollutants in Food (GB2762-2022) [29] | - | - | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Rapeseed oil in the market | 0.002 | 0.002 | - | - | ||||
| Feed Hygiene Standard (GB13078-2017) [31] | 1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | ||||
| Organic Fertilizer Standard (NY525-2012) [32] | 3 | 3 | 50 | 50 | ||||
3.5. Cd/Pb Extraction Amount
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in the Yield and HMs Accumulation among the 15 Winter Rapeseed Cultivars
4.2. Risk Assessment of Oil and Safe Utilization of Oil Residues and Straw
4.3. Profit Analysis and Comprehensive Assessment of Rapeseed–Maize Rotation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desboeufs, K.; Nguyen, E.B.; Chevaillier, S.; Triquet, S.; Dulac, F. Fluxes and sources of nutrient and trace metal atmospheric deposition in the northwestern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14477–14492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.; Liao, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P. Application of rapeseed residue increases soil organic matter, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity and mitigates cadmium pollution risk in paddy fields. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qin, M.; Wu, L.; Hu, P.; Li, F.; Fang, L.; Chen, C.; et al. Integrated life cycle assessment for sustainable remediation of contaminated agricultural soil in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12032–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Hou, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Paramsothy, J.; Lu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhao, L.; Han, D. Comparison of Pb and Cd in wheat grains under air-soil-wheat system near lead-zinc smelters and total suspended particulate introduced modeling attempt. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Ugarte, O.M.; Lima, L.H.V.; Silva, J.R.; do Nascimento, C.W.A. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and edible parts of vegetables grown on sites contaminated by an abandoned steel plant in Havana. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, S. Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessment of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa L.): A probabilistic-based analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5683–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.; Tian, S.; Li, X.; Xu, W. Bulk deposition and source apportionment of atmospheric heavy metals and metalloids in agricultural areas of rural Beijing during 2016–2020. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zheng, Y.; Scheckel, K.G.; Luo, Y.; Li, L. Spatial distribution of smelter emission heavy metals on farmland soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Xing, W.; Scheckel, K.G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ruan, X.; Li, L. Temporal and seasonal variations of As, Cd and Pb atmospheric deposition flux in the vicinity of lead smelters in Jiyuan, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. FAO Statistical Databases in 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, X.; Yan, G.; Hu, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Wu, X. Association mapping of cadmium-tolerant QTLs in Brassica napus L. and insight into their contributions to phytoremediation. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 155, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Peng, L.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Q. Assessment of Pb and Cd in seed oils and meals and methodology of their extraction. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Wongkaew, A.; Nakai, Y.; Rai, H.; Ohkama-Ohtsu, N. Foliar-applied glutathione activates zinc transport from roots to shoots in oilseed rape. Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Guo, S.; Tian, W.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, E.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) inoculation on the growth, antioxidant activity, Cu uptake, and bacterial community structure of rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in Cu-contaminated agricultural soil. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Bai, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Prakash, L.; Ma, L.; Lu, J.; Liu, B.; Shi, X.; et al. Spatio-temporal assessment of greenhouse gas emission from rapeseed production in China by coupling nutrient flows model with LCA approach. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Bian, J.L.; Guo, J.M.; Wang, X.D.; Yang, J.X.; Yang, J.; Chen, T.B.; Cao, L.; Chen, R.X.; Ren, Z.H.; Wang, J.; et al. Tolerance Mechanism and Cadmium Enrichment Abilities in Two Brassica napus L. Cultivars. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.F.; Guo, J.M.; Yang, J.X.; Hu, J.; Zheng, G.D.; Bian, J.L.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, T.B.; Liu, J. Mechanism of the two cultivars of rapes with different Pb enrichment ability. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 4479–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils. Methods Chem. Anal. Water Wastes. 1996. Available online: www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3050b.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- GBW07401—GBW07408; Certified Reference Materials for the Chemical Composition of Soils. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- GBW07601–GBW07605; Certified Reference Materials for the Chemical Composition of Vegetable and Human Hair. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1990.
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); EPA 540/1-89/002; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume I, p. 154.
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (Part A: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Park E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment; EPA/540/1-89/002; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume I.
- USEPA. Risk-Based Concentration Table; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Gill, R.T.; Thornton, S.F.; Harbottle, M.J.; Smith, J.W.N. Sustainability assessment of electrokinetic bioremediation compared with alternative remediation options for a petroleum release site. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, P.C.; Skaar, C.; Brattebø, H.; Fet, A.M. Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) method for assessing the sustainability of end-of-life alternatives for waste plastics: A case study of Norway. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB2762-2022; National Food Safety Standards—Limit of Pollutants in Food. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- GB/T11762-2006; Rapeseed. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB13078-2017; Hygienical Standard for Feeds. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- NY525-2012; Organic Fertilizer. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Tong, W.; Gurajala, H.; Lu, M.; Hamid, Y.; Feng, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Distribution, availability and translocation of heavy metals in soil-oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) system related to soil properties. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Joo, J.C.; Du, D.; Li, G.; Kim, J.Y. Modelling heavy-metal phytoextraction capacities of Helianthus annuus L. and Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. An overview of fieldscale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res. 2018, 147, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, R.; Awasthi, S.; Indoliya, Y.; Chauhan, A.S.; Mishra, S.; Agrawal, L.; Srivastava, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Singh, P.C.; Mallick, S.; et al. Transcriptome and proteome analyses reveal selenium mediated amelioration of arsenic toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirahmadi, E.; Ghorbani, M.; Moudry, J. Effects of Zeolite on Aggregation, Nutrient Availability, and Growth Characteristics of Corn (Zea mays L.) in Cadmium-Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, F.J.; Gao, M.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Song, Z.G. Mechanisms of trehalose-mediated mitigation of Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, S.L.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.; Pan, Y.Z. Screening ornamental plants to identify potential Cd hyperaccumulators for bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.K.; Xie, T.Z.; Yao, H.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, H.Q.; Dai, X.R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, L.; Luo, Y.T. Lead responses and tolerance mechanisms of Koelreuteria paniculata: A newly potential plant for sustainable phytoremediation of Pb-contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.D.; Ran, R.L.; Nao, W.Q.S.; Feng, Y.; Jia, L.Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, R.F.; Feng, H.Q. Physiological effects of short-term copper stress on rape (Brassica napus L.) seedlings and the alleviation of copper stress by attapulgite clay in growth medium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Zhou, T.; Tang, T.J.; Song, H.X.; Guan, C.Y.; Huang, J.Y.; Hua, Y.P. Multiomics approach reveals the pivotal role of subcellular reallocation in determining rapeseed resistance to cadmium toxicity. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5437–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.Y.; Zou, D.S.; Wang, A.D.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.R.; Xiao, Z.H. Remediation of cadmium-contaminated soils using Brassica napus: Effect of nitrogen fertilizers. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109885.1–109885.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Le, S.X.; Wang, M.L.; Zhao, Y. Variations in cadmium accumulation and distribution among different oilseed rape cultivars in Chengdu Plain in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3415–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Pan, H.; Wang, S. Transcriptome sequencing and expression analysis of Cadmium (Cd) transport and detoxification related genes in Cd-accumulating Salix integra. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Le, S.X.; Zhao, Y. Overexpression of three duplicated BnPCS genes enhanced Cd accumulation and translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana mutant cad1-3. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyadate, H.; Adachi, S.; Hiraizumi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Katou, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wan, H.; Qian, J.; Guo, J.; Sun, C.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Song, L.; et al. Genome-wide association study of cadmium accumulation at the seedling stage in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Meng, J.G.; Zhao, K.X.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.M. Annotation and characterization of Cd-responsive metal transporter genes in rapeseed (Brassica napus). Biometals 2018, 31, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Song, J. Geochemical cadmium anomaly and bioaccumulation of cadmium and lead by rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) from noncalcareous soils in the Guizhou Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Zhu, J.; Wang, P.; Zeng, J.; Tan, R.; Yang, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.M. Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, H.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Z. Boron alleviates cadmium toxicity in Brassica napus by promoting the chelation of cadmium onto the root cell wall components. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jin, H.; Zhong, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Xie, M. Estimating the contribution of atmosphere on heavy metals accumulation in the aboveground wheat tissues induced by anthropogenic forcing. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha, S.M.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Rabbani, F.; Khalid, S.; Dumat, C. Risk assessment and biophysiochemical responses of spinach to foliar application of lead oxide nanoparticles: A multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Peng, J.W.; Fei, J.C.; Yu, P.Y.; Wang, M.D.; Tan, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Zhran, M.; Fahmy, A. The contribution of atmospheric deposition of cadmium and lead to their accumulation in rice grains. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Gao, M.; Sun, C.; Weng, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Li, Y. Uptake of atmospherically deposited cadmium by leaves of vegetables: Subcellular localization by nanosims and potential risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, F.; Xie, P.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.X.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Mechanism of Pb absorption in wheat grains. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, B.; Liu, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, W.; Fan, X.; Cui, J.; Zhou, J. The bioavailability and contribution of the newly deposited heavy metals (copper and lead) from atmosphere to rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.; Xu, W. Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X.; Bai, Y.; Hong, J. Carbon, energy and water footprints analysis of rapeseed oil production: A case study in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wei, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, T.; Zheng, G.; Qian, T.; Liu, X.; Meng, X.; He, M. Cultivars and oil extraction techniques affect Cd/Pb contents and health risks in oil of rapeseed grown on Cd/Pb-contaminated farmland. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, T. Three-year field experiment on the risk reduction, environmental merit, and cost assessment of four in situ remediation technologies for metal(loid)-contaminated agricultural soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Physicochemical properties and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of fragrant rapeseed oils in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, F.; Liu, G. Physicochemical properties and energy production potential of agricultural residues in Anhui Province (Central China). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 8, 18476–18483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, F.; Wu, M.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. Cadmium accumulation, availability, and rice uptake in soils receiving long-term applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw return. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31243–31253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.D.; Ros, G.H.; de Vries, W. Impacts of agronomic measures on crop, soil, and environmental indicators: A review and synthesis of meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.K.; Ou, Q.Q.; Wang, H.Q.; Dai, X.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Luo, Y.T.; Yao, H.S.; Ouyang, D.X.; Li, Z.S.; Wang, Z.X. Organic–inorganic composite modifiers enhance restoration potential of Nerium oleander L. to lead–zinc tailing: Application of phytoremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 56569–56579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, T.; Meng, X.; Xia, T. Safe utilization of cadmium-and lead-contaminated farmland by cultivating a winter rapeseed/maize rotation compared with two phytoextraction approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.Z.; Guo, Z.H.; Shi, L.; Feng, W.L.; Xiao, X.Y. Cadmium bioavailability in agricultural soil after mixed amendments combined with rice-rape cropping: A five-season field experiment. J. Soils Sediments, 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.X.; Liu, Q.Q.; Zhao, F.H.; Li, X.F.; Tang, L.P.; Liao, X.Y. Migration and transformation of Cd in four crop rotation systems and their potential for remediation of Cd-contaminated farmland in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.P.; Kang, X.R.; Yu, J.P.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.G.; Zhuge, Y.P. Effective utilization of weak alkaline soils with Cd-contamination by wheat and rape intercropping. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 248, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Sonne, C.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals and arsenic stress in food crops: Elucidating antioxidative defense mechanisms in hyperaccumulators for food security, agricultural sustainability, and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatim, M.; Majidian, M.; Tahmasebi, M.; Nabavi-Pelesaraei, A. Life cycle assessment, life cycle cost, and exergoeconomic analysis of different tillage systems in safflower production by micronutrients. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.B.; Zhang, H.Y. Mapping annual 10 m rapeseed extent using multisource data in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China (2017–2021) on Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 117, 103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type | Cultivar | Seed Color | Place of Origin | Yield (kg·hm−2) | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brassica napus | Shuangyou 8 | Black | Henan Province, China | 2700 | SY-8 |
| Shuangyou 10 | Black | Henan Province, China | 2700 | SY-10 | |
| Shuangyou 092 | Black | Henan Province, China | 2700 | SY-092 | |
| Shuangyou 123 | Black | Henan Province, China | 3000 | SY-123 | |
| Shuangyou 195 | Black | Henan Province, China | 3000 | SY-195 | |
| Qinyou 1 | Black brown | Henan Province, China | 3300 | QY-1 | |
| Qinyou 10 | Black | Shaanxi Province, China | 2625 | QY-10 | |
| Zashuang 6 | Black brown | Henan Province, China | 2790 | ZS-6 | |
| Zashuang 7 | Black | Henan Province, China | 2700 | ZS-7 | |
| Fengyou 10 | Black brown | Henan Province, China | 2700 | FY-10 | |
| Zhongyou 821 | Black | Oil crops research institute | 2250 | ZY-821 | |
| Jinyou 4 | Black | Shanxi Province, China | 2625 | JY-4 | |
| Yuyou 2 | Yellow | Henan Province, China | 3750 | YY-2 | |
| Brassica campestris | Zaoshu 100 | Black | Shaanxi Province, China | 3000 | ZS100 |
| Sanyuehuang | Yellow | Henan Province, China | 3300 | SYH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, M.; Yang, J.; Zheng, G.; Guo, J.; Ma, C. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Efficient and Safe Utilization of Two Varieties of Winter Rapeseed Grown on Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Farmland under Atmospheric Deposition. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511750
He M, Yang J, Zheng G, Guo J, Ma C. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Efficient and Safe Utilization of Two Varieties of Winter Rapeseed Grown on Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Farmland under Atmospheric Deposition. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511750
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Mengke, Junxing Yang, Guodi Zheng, Junmei Guo, and Chuang Ma. 2023. "Comprehensive Evaluation of the Efficient and Safe Utilization of Two Varieties of Winter Rapeseed Grown on Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Farmland under Atmospheric Deposition" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511750
APA StyleHe, M., Yang, J., Zheng, G., Guo, J., & Ma, C. (2023). Comprehensive Evaluation of the Efficient and Safe Utilization of Two Varieties of Winter Rapeseed Grown on Cadmium- and Lead-Contaminated Farmland under Atmospheric Deposition. Sustainability, 15(15), 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511750







