Effect of Blending Behavior on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Authors | Year | Type of Asphalt | Field of Study | Test Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun et al. [25] | 2014 | SBS modified asphalt | Asphalt aging | GPC |
| Cong et al. [26] | 2015 | Regenerated SBS modified asphalt | Asphalt recycling | FTIR, Thin-Layer Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detection (TLC-FID) |
| Chen et al. [27] | 2019 | Crumb rubber modified asphalt | Asphalt recycling | FTIR, GPC, AFM, DSR, Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR) |
| Abdelaziz et al. [28] | 2021 | Recycled asphalt | Asphalt recycling | Indirect Tensile (IDT) |
| Yang et al. [29] | 2022 | High viscosity asphalt | Asphalt aging | DSR, BBR, FTIR, AFM |
| Schwettmann et al. [30] | 2023 | Naturally and artificially aged asphalt | Asphalt aging | Pressure Ageing Vessel (PAV), DSR, FTIR |
2. Objective and Research Approach
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Materials
3.1.1. Asphalt and Mineral Material
3.1.2. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement
3.2. Test Method
3.2.1. Thin-Layer Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detection Test
3.2.2. Mix Design Test
3.2.3. Blending Degree Test
3.2.4. Wheel Track Rutting Test
3.2.5. Low-Temperature Bending Test
3.2.6. Freeze–Thaw Splitting Test and Immersion Marshall Test
3.2.7. Semi-Circular Bending Test
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Component Changes of Asphalt Mixtures
4.1.1. Component Changes during the Aging Process
4.1.2. Component Changes during the Recycling Process
4.2. Optimization Design of Hot In-Plant Recycled Asphalt Mixture
4.2.1. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Testing
4.2.2. Determining the Rejuvenator Content
4.2.3. Synthetic Gradation Design
4.2.4. Determining the Optimal Asphalt Content
4.3. Relationship between the Degree of Blending and Performance
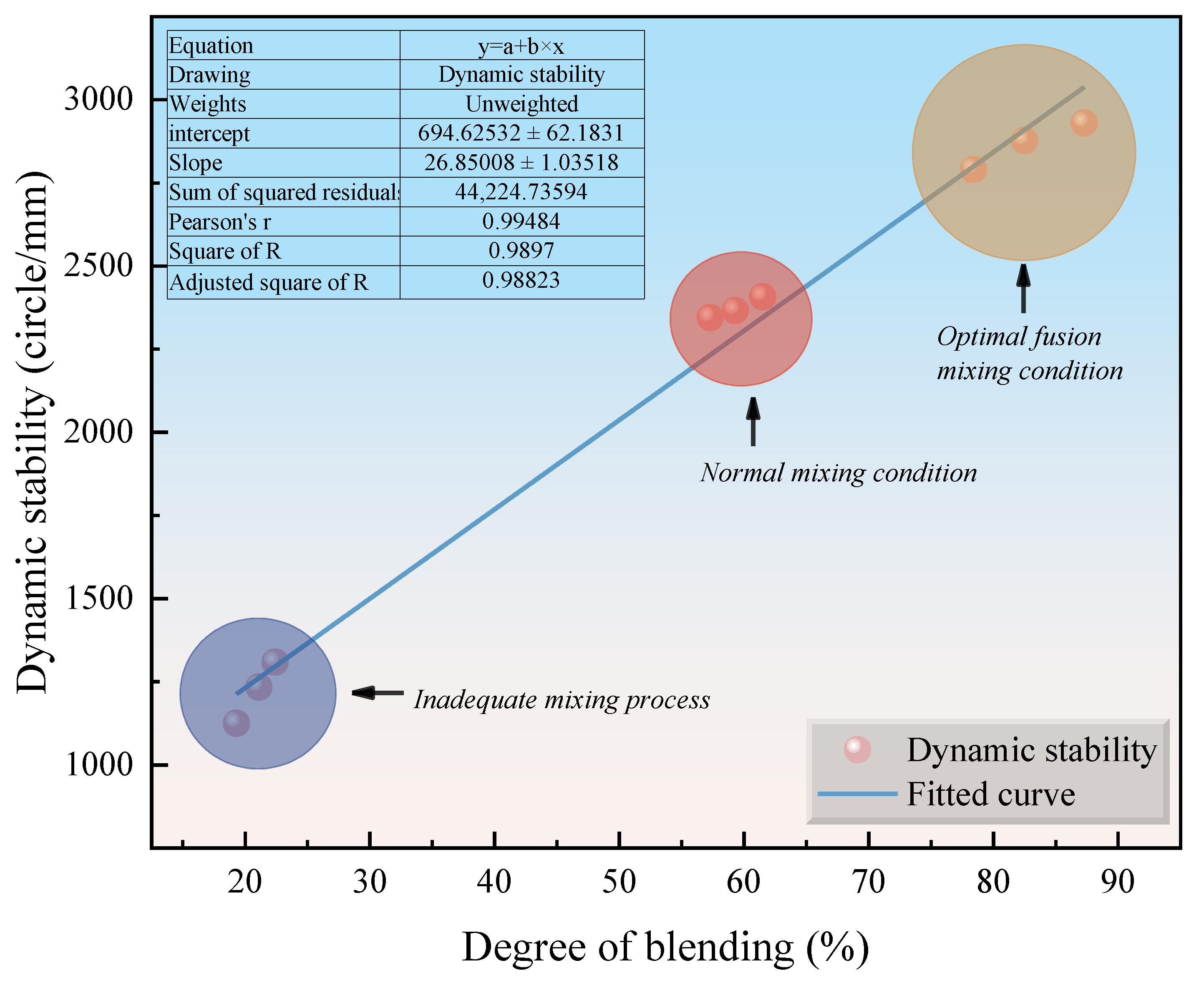
4.3.1. High-Temperature Stability
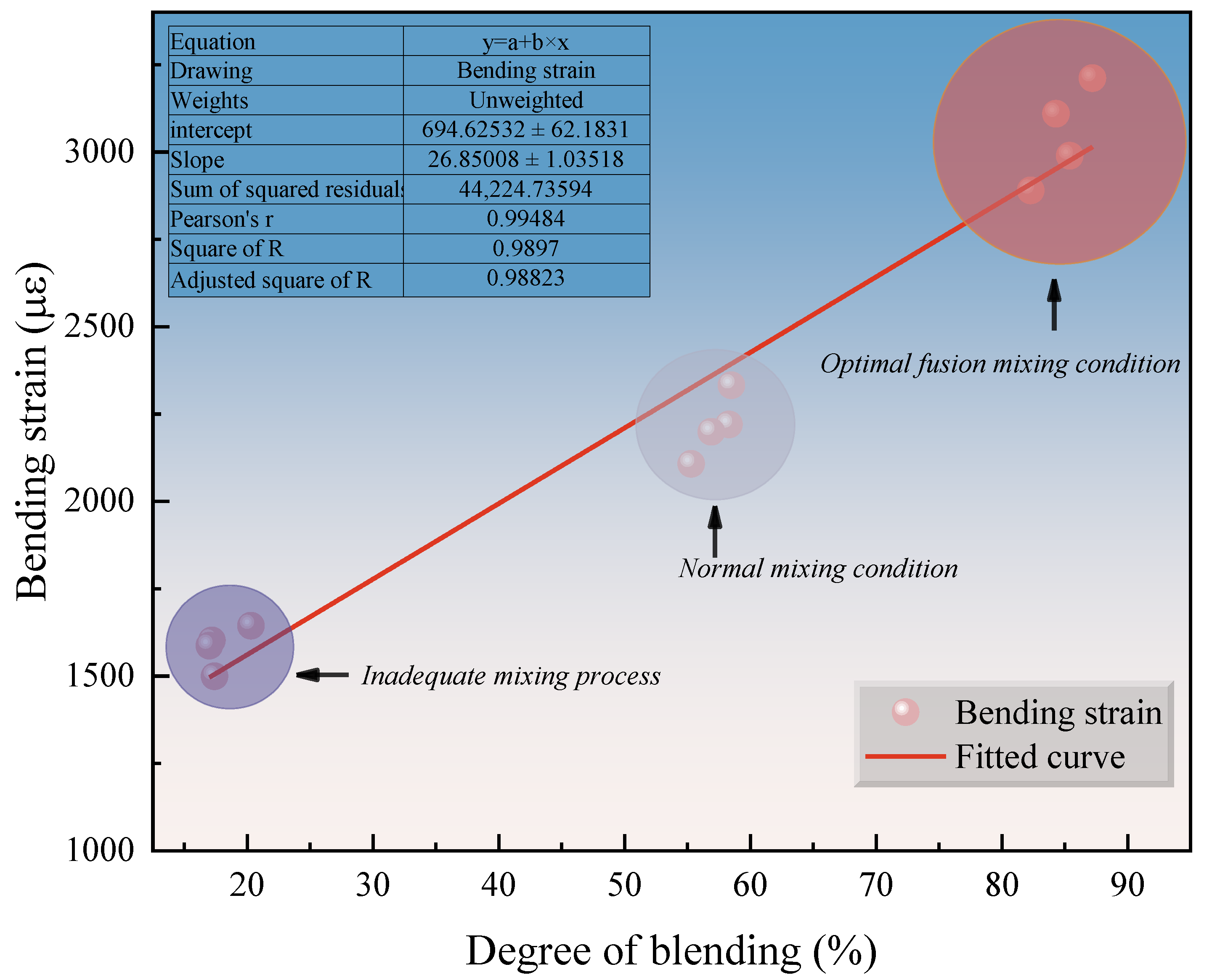
4.3.2. Low-Temperature Cracking Resistance
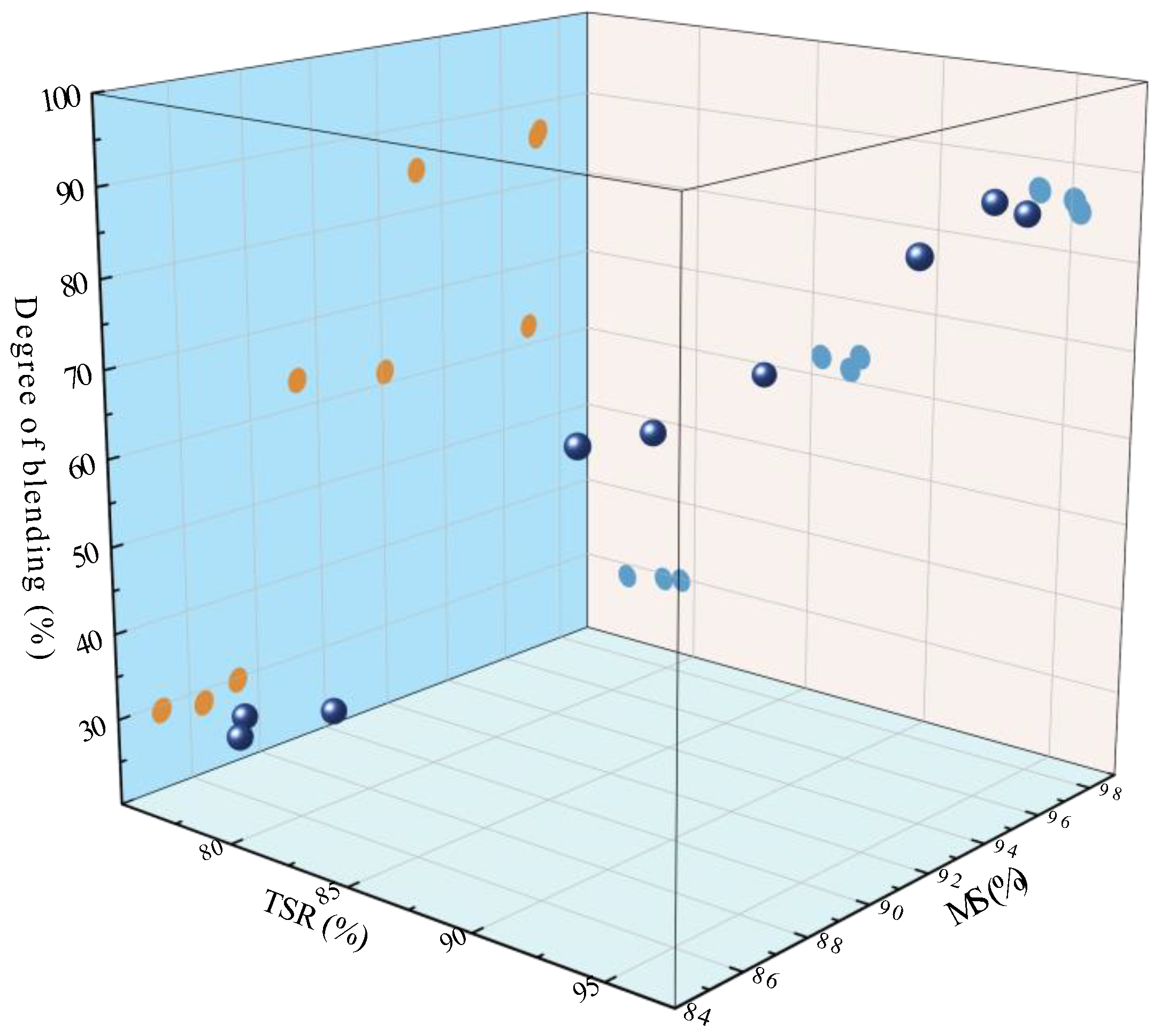
4.3.3. Water Stability
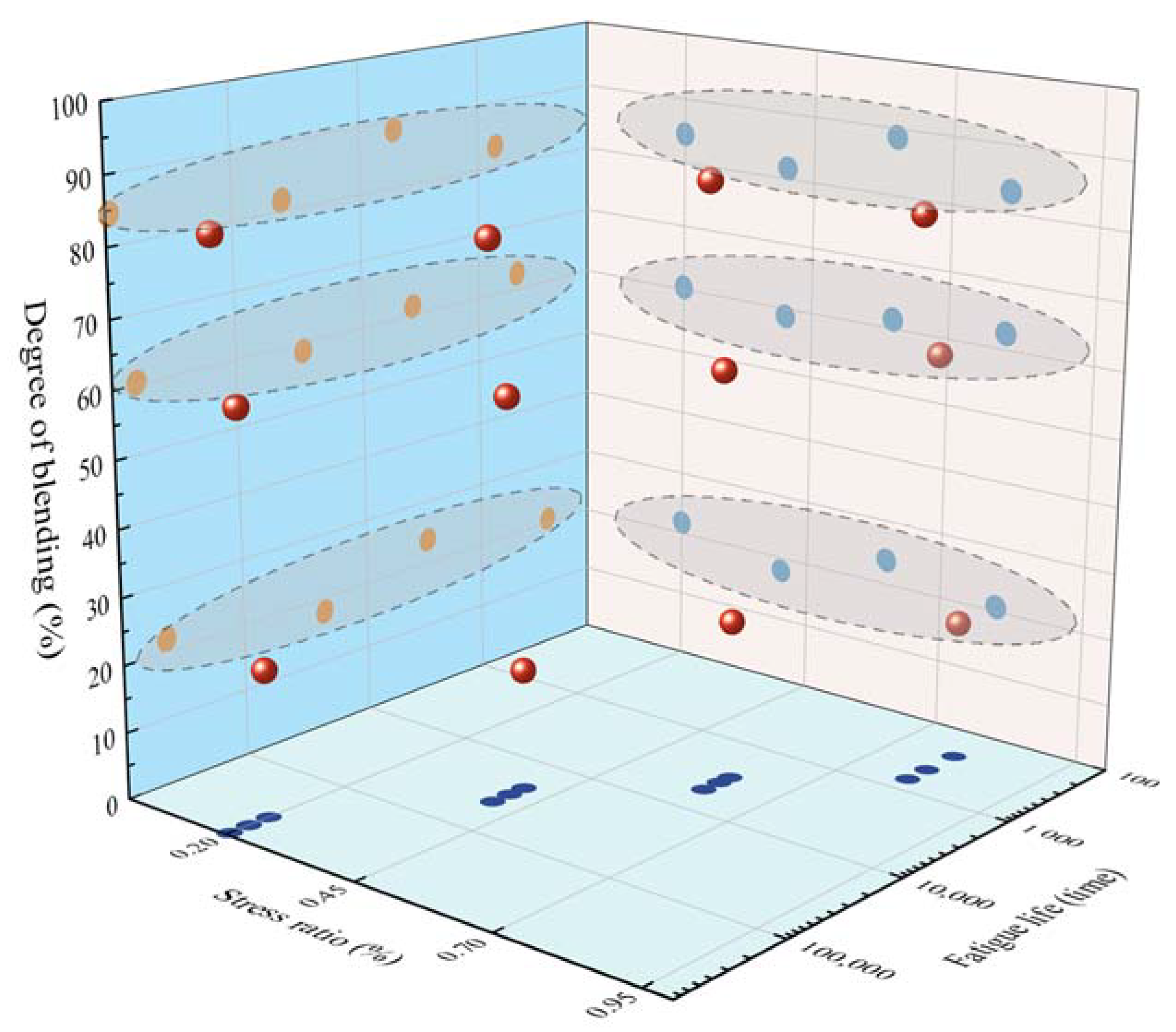
4.3.4. Fatigue Resistance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Baliello, A.; Poulikakos, L.; Vasconcelos, K.; Kakar, M.R.; Giancontieri, G.; Pasquini, E.; Porot, L.; Tušar, M.; Riccardi, C.; et al. Rheological properties of asphalt binder modified with waste polyethylene: An interlaboratory research from the RILEM TC WMR. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ruan, K.; Tao, W.; Sun, C.; Luo, L. Reducing the variability of multi-source reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: A practice in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Jiang, W.; Sha, A.; Xiao, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, T. Technology method and functional characteristics of road thermoelectric generator system based on Seebeck effect. Appl. Energy 2023, 331, 120459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Sha, A.; Li, Y.; Yuan, D.; Xiao, J.; Xing, C. Research on Pavement Traffic Load State Perception Based on the Piezoelectric Effect. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchler, S.; Falchetto, A.C.; Walther, A.; Riccardi, C.; Wang, D.; Wistuba, M.P. Wearing Course Mixtures Prepared with High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content Modified by Rejuvenators. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Zhang, C.; Cui, B.X.; Wang, D.; Tsai, J. Analysis of Impact of Transverse Slope on Hydroplaning Risk Level. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 96, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Nivitha, M.R.; Hesp, S.A.; Krishnan, J.M. Validation of empirical changes to asphalt specifications based on phase angle and relaxation properties using data from a northern Ontario, Canada pavement trial. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; Cannone Falchetto, A.; Losa, M.; Wistuba, M.P. Rheological modeling of asphalt binder and asphalt mortar containing recycled asphalt material. Mater. Struct. 2015, 49, 4167–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Yaacob, H.; Katman, H.Y.; Satar, M.; Bilema, M.; Jaya, R.P.; Eltwati, A.S.; Radeef, H.R. A Review on the Durability of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures Embraced with Rejuvenators. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperi, E.; Bocci, E. A Review on Bitumen Aging and Rejuvenation Chemistry: Processes, Materials and Analyses. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, B.; Shu, X. Blending efficiency evaluation of plant asphalt mixtures using fluorescence microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadmoro, O.F.; Kar, S.S.; Tiwari, D. Characterisation of foam bitumen mixes with diffrent RAP content at elevated mixing temperature using design of experiment (DOE) approach. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Manasrah, A.D.; Saad, A.A.; Sebakhy, K.O.; Bouhadda, Y. Adsorption of Algerian Asphaltenes onto Synthesized Maghemite Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Pet. Chem. 2021, 61, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.; Jiao, W.; Barbieri, D.M. Advances and development trends in eco-friendly pavements. J. Road Eng. 2021, 1, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Manasrah, A.D.; Carbognani, L.; Sebakhy, K.O.; Nokab ME, H.E.; Hacini, M.; Nassar, N.N. A study on the characteristics of Algerian Hassi-Messaoud asphaltenes: Solubility and precipitation. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 1279–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hesp, S.A.; Chan, S.; Li, J.Z.; Lee, S. Lessons learned from 60 years of pavement trials in continental climate regions of Canada. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalfattah, I.A.; Mogawer, W.S.; Stuart, K. Quantification of the degree of blending in hot-mix asphalt (HMA) with reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) using Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Sha, A.; Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Jiao, W. Developing a solid–solid phase change heat storage asphalt pavement material and its application as functional filler for cooling asphalt pavement. Energy Build. 2023, 285, 112935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemison, H.B.; Burr, B.L.; Davison, R.R.; Bullin, J.A.; Glover, C.J. Application and Use of the Atr, Ft-Ir Method to Asphalt Aging Studies. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 1992, 10, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Shi, C. Evaluation of aging behaviors of asphalt binders through different rheological indices. Fuel 2018, 221, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Duan, H.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z.; Luo, H. Mini-Review on the Application of Nanomaterials in Improving Anti-Aging Properties of Asphalt. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 11017–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A.; Leng, Z.; Airey, G. Micromechanics-based viscoelasticity predictions of crumb rubber modified bitumen considering polymer network effects. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2022, 2676, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; Wang, D.; Leng, Z.; Lu, G.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A. Investigating the High- and Low-temperature Performance of Warm Crumb Rubber Modified Bituminous Binders using Rheological Tests. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2021, 147, 04021067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Xiang, H. Rheological Characteristics and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Interface Regeneration Between Virgin and Aged Asphalts. China J. Highw. Transp. 2019, 32, 25. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Aging mechanism and effective recycling ratio of SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Luo, W.; Xu, P.; Zhao, H. Investigation on recycling of SBS modified asphalt binders containing fresh asphalt and rejuvenating agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, F. The performance of hot-recycling asphalt binder containing crumb rubber modified asphalt based on physiochemical and rheological measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.; Epps Martin, A.; Arámbula Mercado, E.; Sobieski, T. Study of the quantification of recycled binder activity in asphalt mixtures with RAP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Shi, J.R.; Yang, X.H.; Fang, Y. Comparative analysis of thermal aging behavior and comprehensive performance of high viscosity asphalt (HVA) from cohesion, adhesion and rheology perspectives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwettmann, K.; Nytus, N.; Radenberg, M.; Stephan, D. Ageing behaviour of naturally and artificially aged bitumen samples after the addition of rejuvenators. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.; Guo, D.; Yuan, D.; Wu, W.; Wang, W. Study on the blending behavior of asphalt binder in mixing process of hot recycling. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, F. Molecular dynamics investigation of interfacial adhesion between oxidised bitumen and mineral surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, F.; Xu, T.; Wang, H. Impact of minerals and water on bitumen-mineral adhesion and debonding behaviours using molecular dynamics simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tarefder, R.A. Investigation of asphalt aging behaviour due to oxidation using molecular dynamics simulation. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oualit, M.; Irekti, A.; Hami, B. Performance of recycled asphalt mixtures formulated with modified bitumen. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, D.; Shan, J.; Ye, W.; Lu, H.; Sha, A. Experimental study of the performance of porous ultra-thin asphalt overlay. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Bao, R.; Lu, H.; Yuan, D.; Lu, R.; Sha, A.; Shan, J. Analysis of rheological properties and aging mechanism of bitumen after short-term and long-term aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C. Investigation of aging performance of SBS modified asphalt with various aging methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.L.; Davison, R.R.; Glover, C.J.; Bullin, J.A. Asphalt aging in texas roads and test sections. Transp. Res. Rec. 1990, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Aravind, K.; Das, A. Pavement design with central plant hot-mix recycled asphalt mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Apostolidis, P.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A. Micromechanical Modeling of Complex Shear Modulus of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen. J. Mater. Des. 2020, 188, 108467. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Varveri, A.; Zhang, H.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A.; Leng, Z. Thermal aging behaviors of the waste tire rubber used in bitumen modification. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2022, 38, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Mao, Q.; Ling, N. Influence Factors of RAP Content in Plant-Mixed Hot Recycling Asphalt Pavement. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. Nat. Sci. 2020, 39, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hugener, M.; Wang, D.; Falchetto, A.C.; Porot, L.; De Maeijer, P.K.; Orešković, M.; Sa-da-Costa, M.; Tabatabaee, H.; Bocci, E.; Kawakami, A.; et al. Recommendation of RILEM TC 264 RAP on the evaluation of asphalt recycling agents for hot mix asphalt. Mater. Struct. 2022, 55, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Xing, C.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.; Wu, W.; Li, P.; Li, Y. Viscoelastic Behavior and Phase Structure of High-Content SBS-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zheng, M. Effect of RAP Content and Mixing Degree of Aged and Virgin Asphalt on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixture. Subgrade Eng. 2023, 2, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Lu, R.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.; Yuan, D. A comprehensive review on the blending condition between virgin and RAP asphalt binders in hot recycled asphalt mixtures: Mechanisms, evaluation methods, and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, S.; Wei, M.; Xie, J. Multi-scale performance evaluation and correlation analysis of blended asphalt and recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating high RAP content. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roja, K.L.; Masad, E.; Mogawer, W. Performance and blending evaluation of asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 22, 2441–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, A.; Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Mao, X.; Zhi, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F.; Liu, Z.; et al. Highway constructions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Challenge, research and practice. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ding, S. Analysis of Influence of Heating Methods on Fusion Effect of Old and New Asphalt in RAP Thermally Recycled Mixture. Eng. Technol. Res. 2022, 7, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Prosperi, E.; Bocci, E.; Bocci, M. Effect of Bitumen Production Process and Mix Heating Temperature on the Rheological Properties of Hot Recycled Mix Asphalt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Lu, C.H.; Xie, F.Z.; Wang, D.W.; Gong, H.R.; Liu, F. Study on Interfacial Fusion Characteristics of Virgin and Aged Asphalt of Warm Mix Recycled. Mixture at Micro Scale. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Yu, D.; Yang, B. Effect of Mixing Process Parameters on the Performance of Central Plant Hot Recycling Mixture. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 10032–10038. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Porot, L.; Cannone Falchetto, A.; Damen, S. Multiple stress creep and recovery test for bituminous binders—Influence of several key experimental parameters. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG F 40-2004[S]; Standard Specification for Construction and Acceptance of Highway Asphalt Pavement. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese)
- Qian, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C. Evaluation of mechanical performance of high adhesive recycled asphalt with different old asphalt content. J. Munic. Technol. 2022, 40, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.; Tong, Z.; Jia, M.; Shan, J.; Ogbon, A.W. Assessment of the Aging Process of Finished Product–Modified Asphalt Binder and Its Aging Mechanism. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
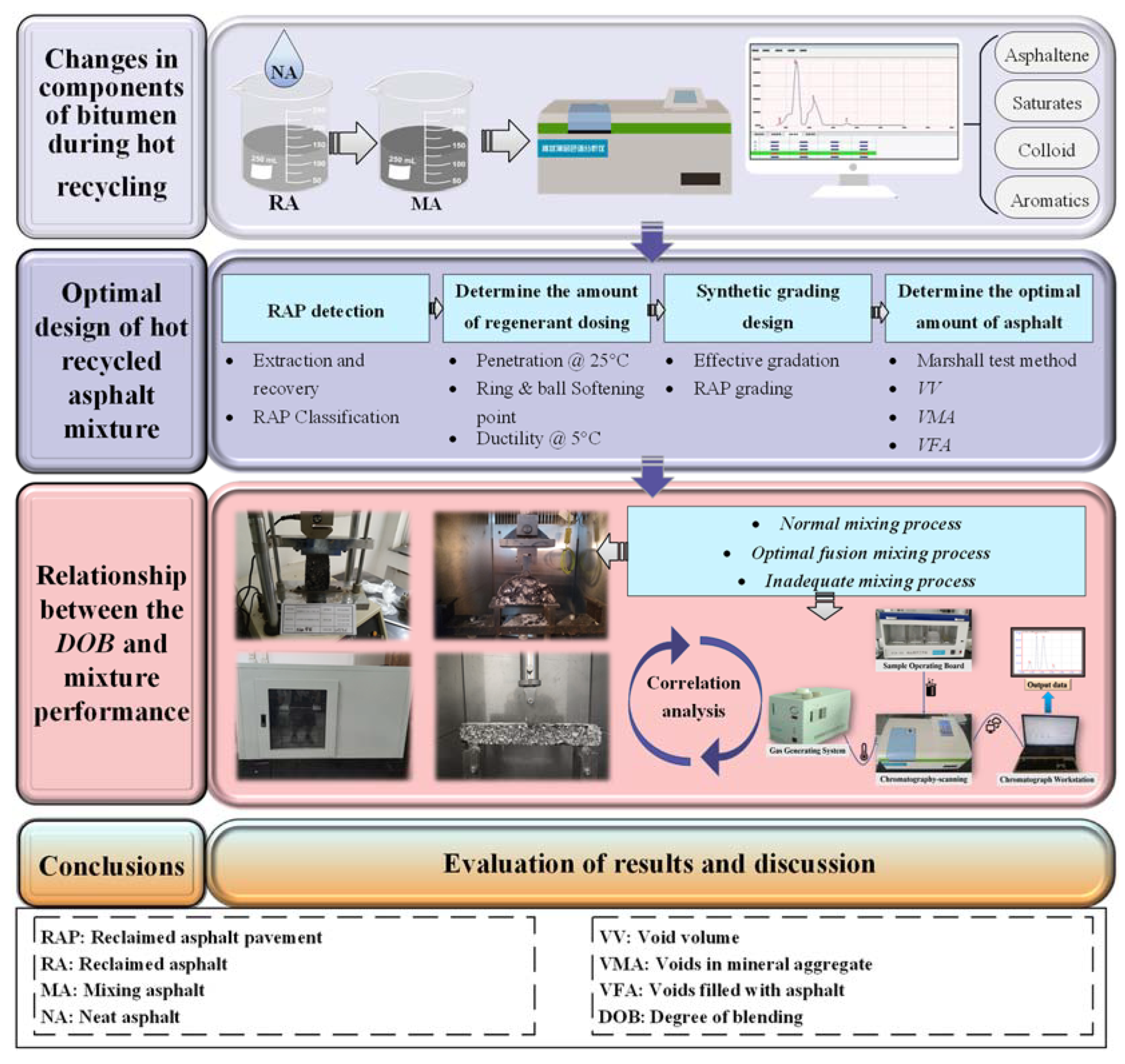

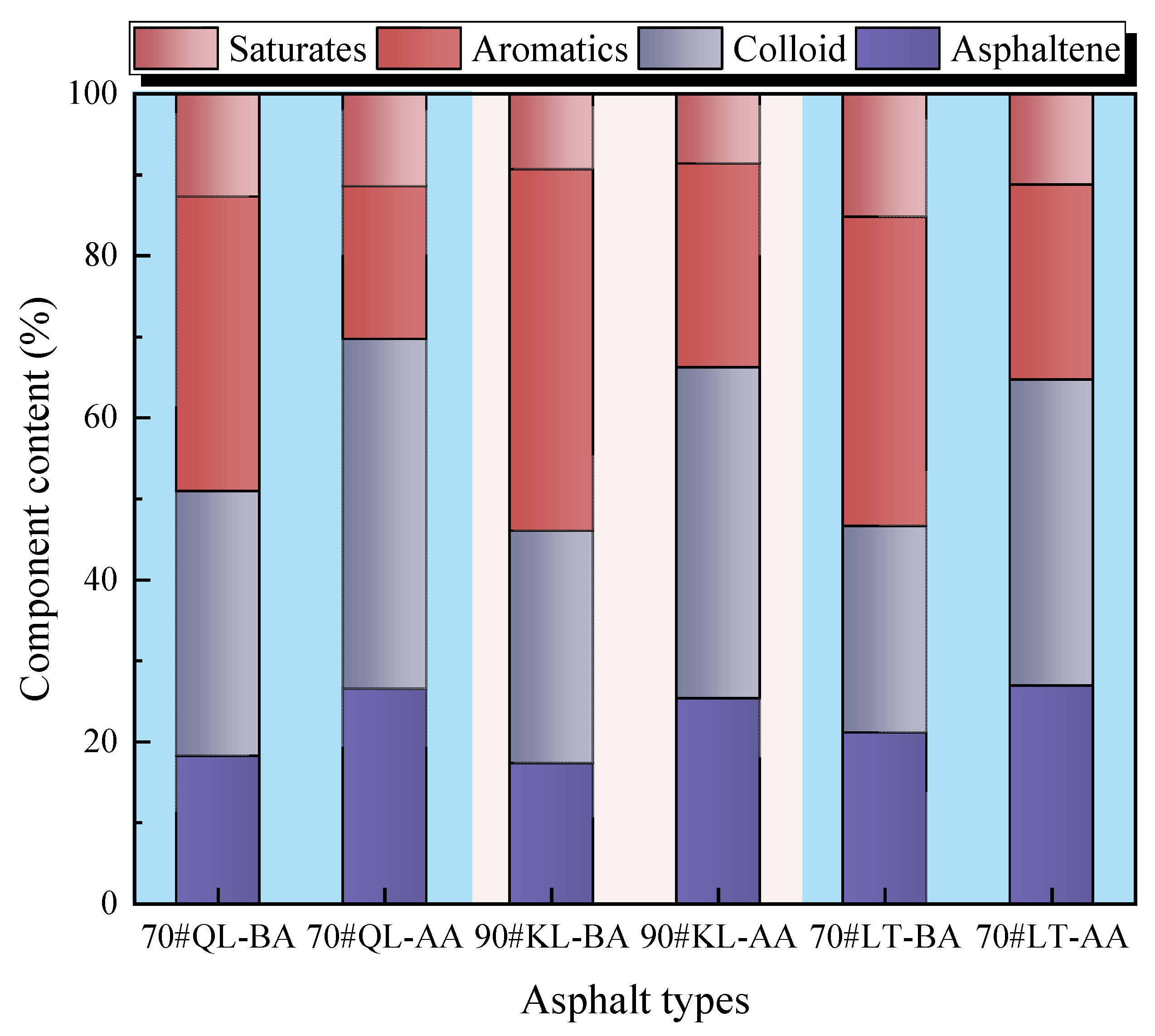
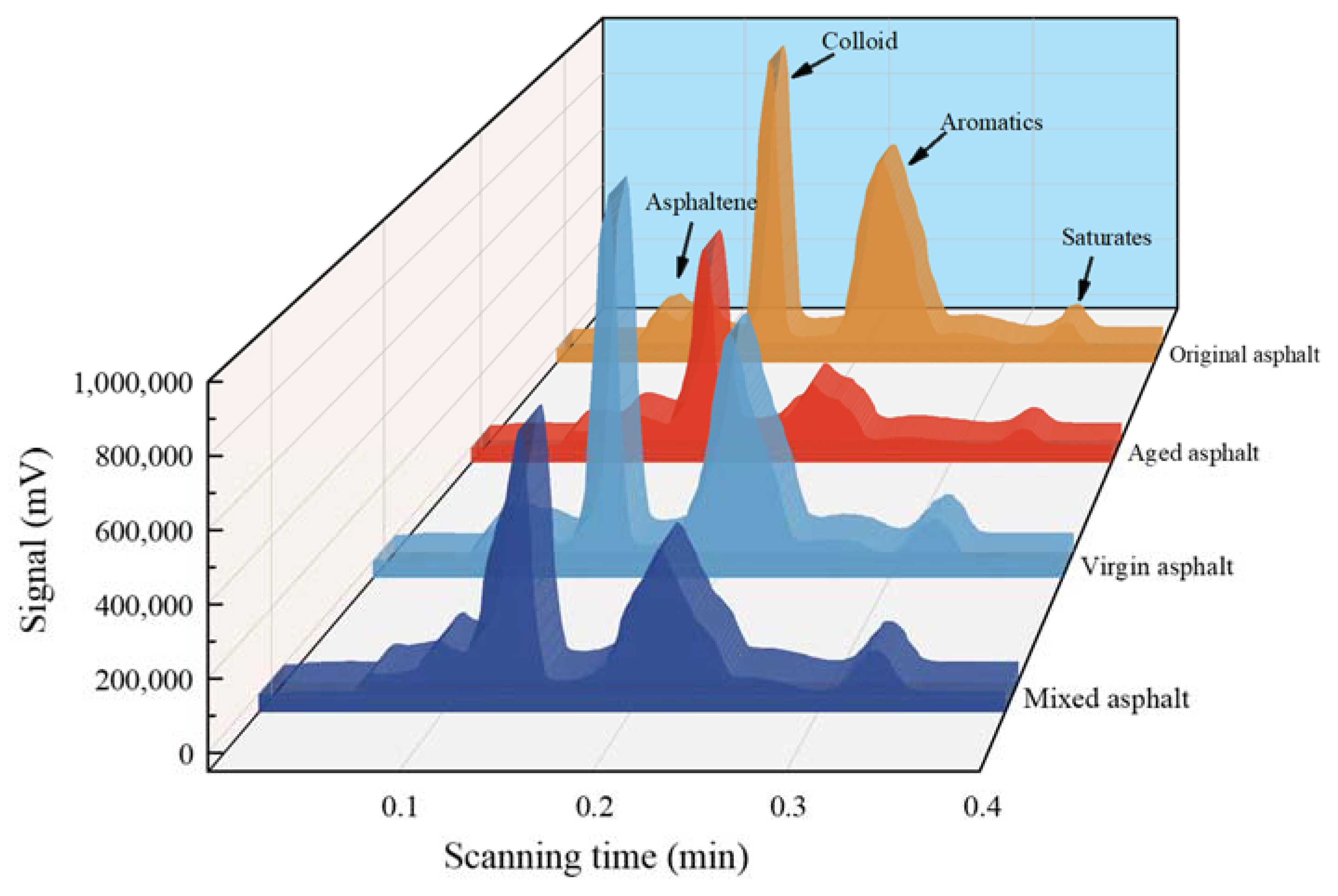
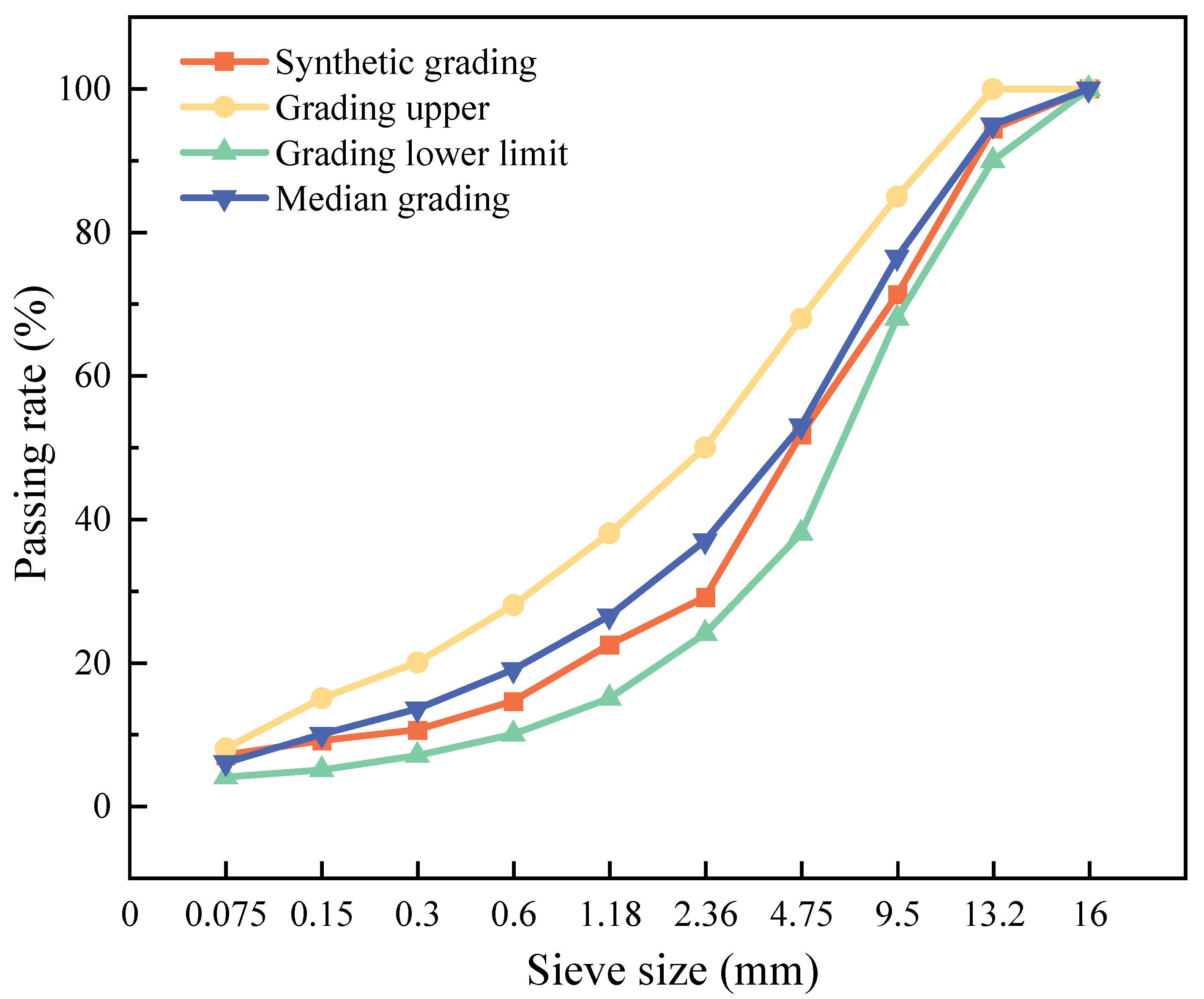

| Items | Units | 90#KL | 70#LT | 70#QL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1 mm | 89.8 | 72.0 | 74.2 |
| Ductility (10 °C) | cm | >100.0 | >100.0 | 55.1 |
| Softening Point (Ring and Ball Method) | °C | 48.4 | 49.2 | 47.6 |
| Wax Content | % | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 |
| Flash Point | °C | >260 | >260 | >260 |
| Solubility | °C | 99.5 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| Density (15 °C) | g/cm3 | 1.027 | 1.038 | 1.035 |
| Rotating Thin Film Oven Test (RTFOT) | ||||
| Mass Change | % | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.52 |
| Residual Penetration Ratio (25 °C) | % | 71.2 | 70.1 | 71.8 |
| Residual Ductility (15 °C) | cm | 2.5 | 0.7 | 15.4 |
| Testing Indexes | Limestone Aggregate | Magnetite Aggregate | Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crushing Value (%) | 14.3 | 9.8 | ≯28 |
| Abrasion Value (%) | 10.3 | 9.1 | ≯30 |
| Apparent Relative Density | 2.715 | 3.82 | ≮2.5 |
| Water Absorption (%) | 0.6 | 0.21 | ≯3.0 |
| Durability (%) | 0.5 | 0.2 | ≯12 |
| Adhesion to Asphalt | 5 | 5 | ≮4 |
| Needle-Shaped Particle Content (%) Content of Particles with Diameter > 9.5mm (%) Content of Particles with Diameter < 9.5mm (%) | 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 | ≯18 ≯15 ≯20 |
| Content of Particles Smaller than 0.075mm by Washing Method (%) | 0.36 | 0 | ≯1 |
| Polished Stone Value (PSV) | 45 | 45 | ≮42 |
| Items | Units | Test Result | Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1 mm | 25.5 | 60~80 |
| Ductility (10 °C) | cm | 4.2 | 25 |
| Softening Point (Ring and Ball Method) | °C | 64.1 | >46 |
| Asphalt Content in RAP | % | 5.6 | - |
| Sieve Size (mm) | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
| RAP | 100.0 | 99.6 | 97.4 | 65.5 | 35.9 | 27.4 | 18.4 | 13.3 | 10.4 | 8.4 |
| Mixing Conditions | Mixing Orders | Mixing Time (s) | Mixing Temperature (°C) | Film Thickness (μm) | Rejuvenator Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Mixing Process | Order 2 | 90 | 150 | 8.2 | 3 |
| The Optimal Fusion Mixing Process | Order 1 | 180 | 160 | 7 | 5 |
| Inadequate Mixing Process | Order 3 | 45 | 140 | 9 | 0 |
| Types | Aging Condition | Penetration (25 °C/0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility (10 °C/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70#QL | Before Aging (BA) | 63.5 | 49.6 | 25.0 |
| After Aging (AA) | 22.3 | 63.4 | 1.8 | |
| 90#KL | Before Aging (BA) | 89.8 | 48.4 | >100.0 |
| After Aging (AA) | 33.2 | 59.8 | 2.5 | |
| 70#LT | Before Aging (BA) | 72.0 | 49.2 | >100.0 |
| After Aging (AA) | 28.3 | 60.0 | 0.7 |
| State of Asphalt | Penetration at 25 °C (0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility at 10 °C (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Asphalt | 63.5 | 49.6 | 25.0 |
| Aged Asphalt | 22.3 | 63.4 | 1.8 |
| Virgin Asphalt | 70.1 | 47.3 | >100 |
| Mixed Asphalt | 50.1 | 54.2 | 14.8 |
| Sieve Openings (mm) | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
| RAP Coarse Material (%) | 99.8 | 92.7 | 67.5 | 27.4 | 18.4 | 14.8 | 11 | 8.1 | 6.6 | 4.8 |
| RAP Fine Material (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 89.6 | 64.7 | 50.9 | 35.2 | 25.7 | 21.6 | 17.9 |
| Content (%) | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| Penetration at 25 °C (0.1 mm) | 53.5 | 71.1 | 82.1 |
| Softening Point (°C) | 63.2 | 53.7 | 45.3 |
| Ductility at 10 °C (cm) | 28.3 | 39.2 | 49.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Ling, X.; Lin, J.; Xiang, B.; Yuan, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Guo, D. Effect of Blending Behavior on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11723. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511723
Wang T, Ling X, Lin J, Xiang B, Yuan D, Wang W, Wang D, Guo D. Effect of Blending Behavior on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11723. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511723
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Teng, Xianwu Ling, Jun Lin, Bing Xiang, Dongdong Yuan, Wentong Wang, Di Wang, and Dedong Guo. 2023. "Effect of Blending Behavior on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixtures" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11723. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511723
APA StyleWang, T., Ling, X., Lin, J., Xiang, B., Yuan, D., Wang, W., Wang, D., & Guo, D. (2023). Effect of Blending Behavior on the Performance of Hot Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability, 15(15), 11723. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511723








