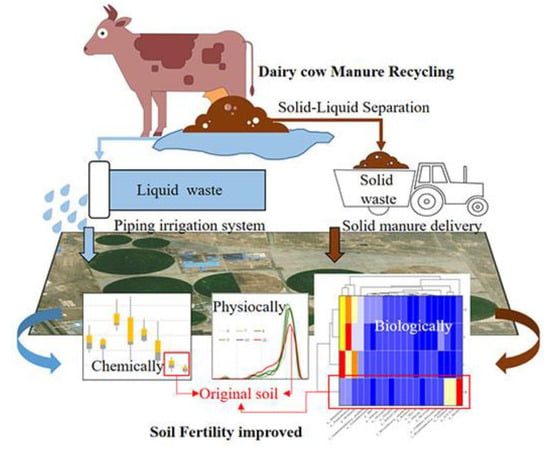
Effects of the Integrated Use of Dairy Cow Manure on Soil Properties and Biological Fertility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dairy Cow Farm Information
2.2. Materials
2.3. Detection Methods
2.3.1. Total N
2.3.2. Available P
2.3.3. Available K
2.3.4. Soil Organic Matter
2.3.5. Soil pH
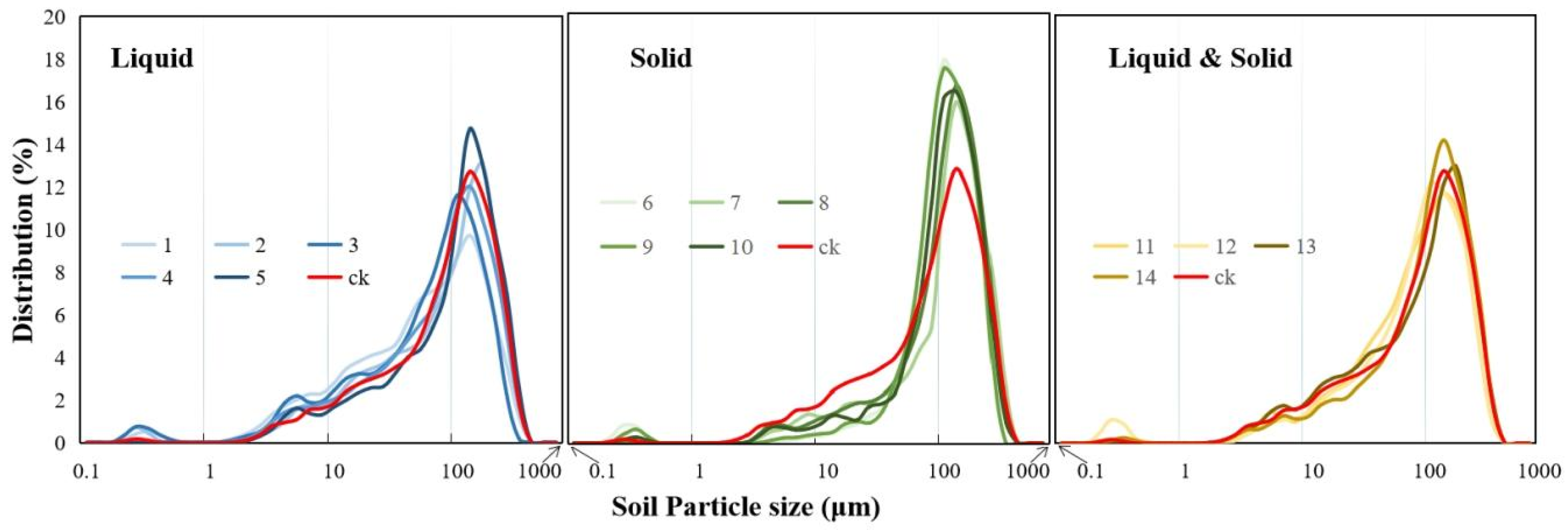
2.3.6. Soil Particle Size
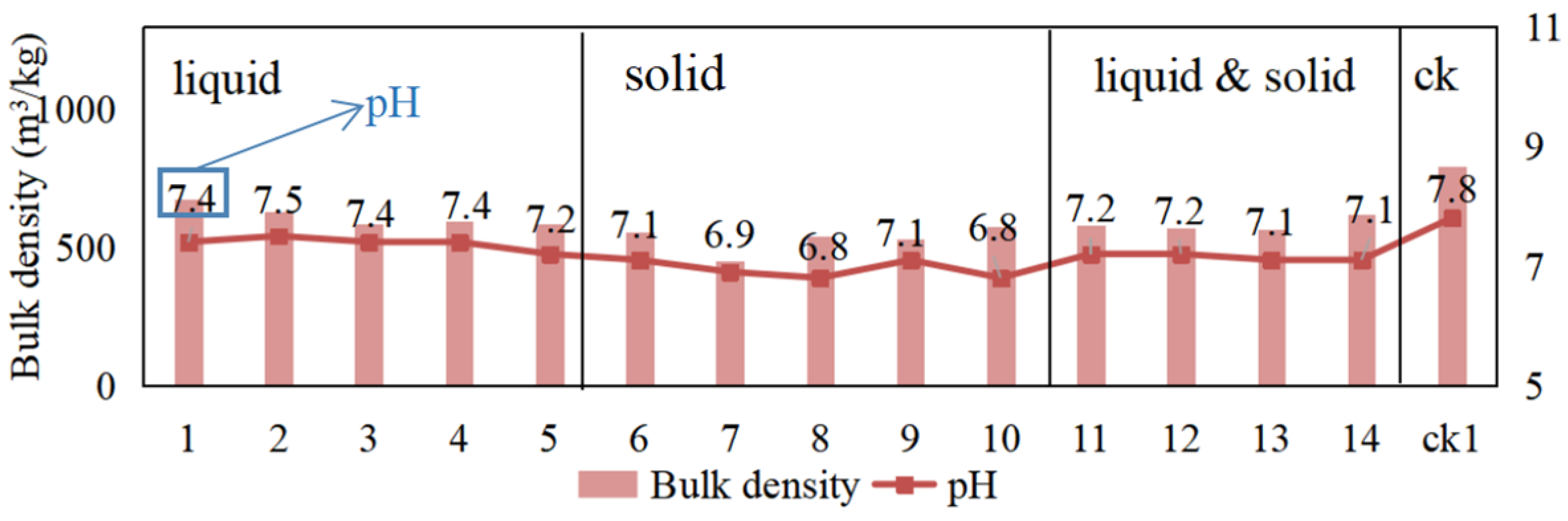
2.3.7. Soil Bulk Density
2.3.8. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Mathematical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Soil Nutrition
3.1.1. Total N
3.1.2. Available P
3.1.3. Available K
3.1.4. Organic Matter
3.1.5. Nutrient Accumulation
3.2. Changes in Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
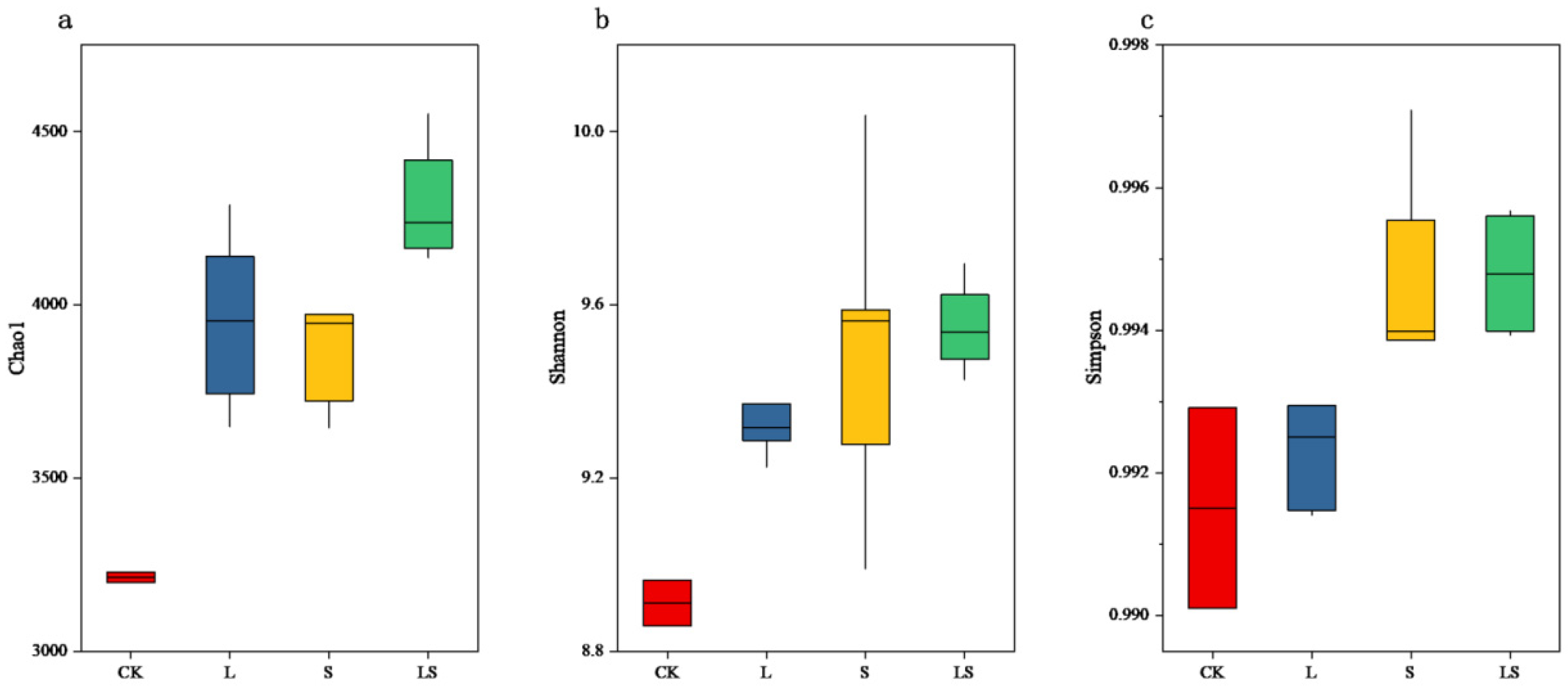
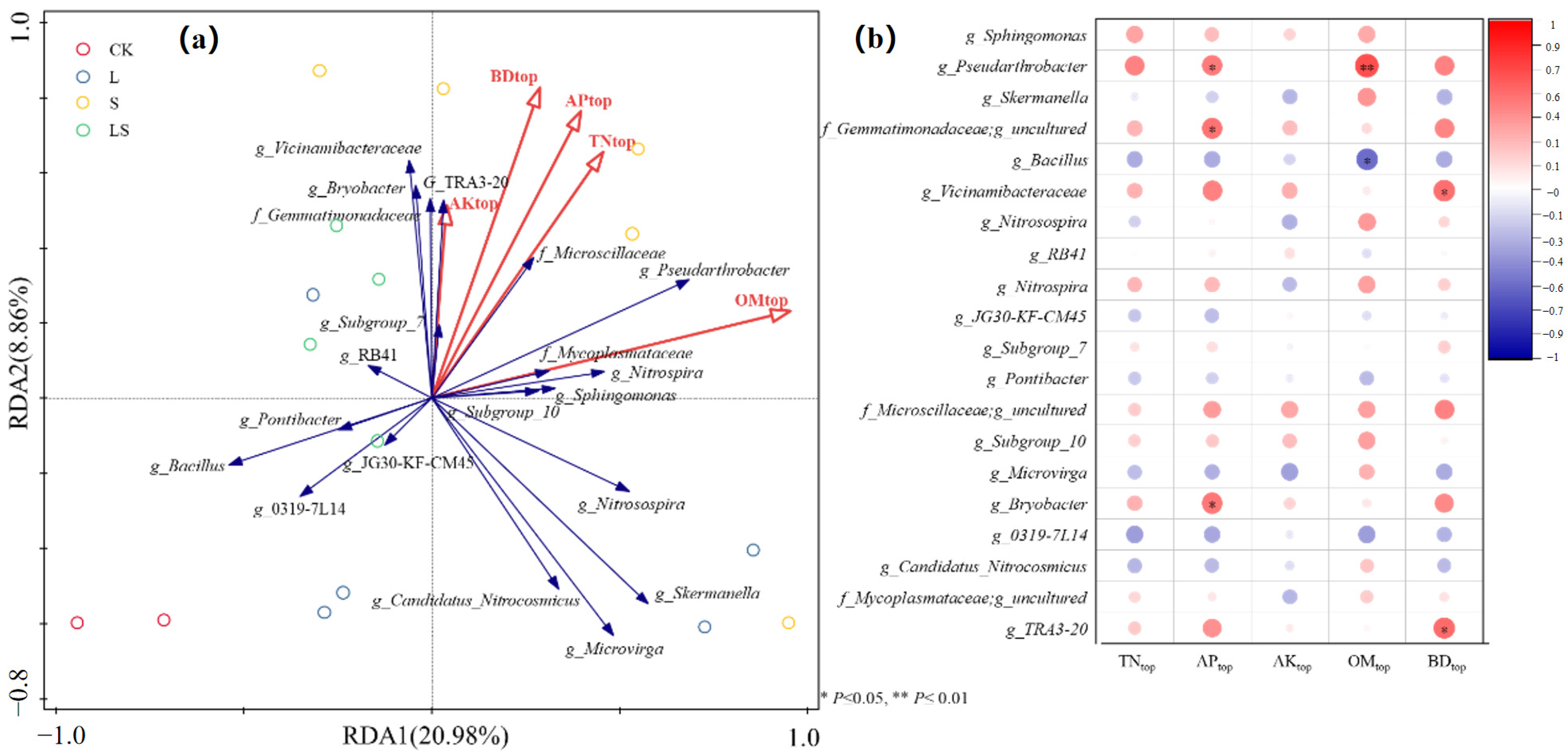
3.3. Changes to the Soil Microbial System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, P.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H. Effects of different continuous fertilizer managements on soil total nitrogen stocks in China: A meta-analysis. Pedosphere 2021, 32, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Huo, W.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Feng, G. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus can serve as an index to reflect soil phosphorus fertility. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.G.; Knudsen, L. Impact of Danish Livestock and Manure Management Regulations on Nitrogen Pollution, Crop Production, and Economy. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 658231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Antwi, P.; Deng, K.; Wang, C.; Buelna, G. Nitrogen removal from low COD/TN ratio manure-free piggery wastewater within an upflow microaerobic sludge reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Ning, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Lal, R. Crop yield and soil carbon responses to tillage method changes in North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saam, H.; Powell, J.M.; Jackson-Smith, D.B.; Bland, W.L.; Posner, J.L. Use of animal density to estimate manure nutrient recycling ability of Wisconsin dairy farms. Agric. Syst. 2005, 84, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghball, B.; Wienhold, B.J.; Gilley, J.E.; Eigenberg, R.A. Mineralization of manure nutrients. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 57, 470–473. [Google Scholar]
- Suwara, I.; Pawlak-Zaręba, K.; Gozdowski, D.; Perzanowska, A. Physical properties of soil after 54 years of long-term fertilization and crop rotation. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Li, Z.; Fan, F.; Chu, G.; Hou, Z.; Liang, Y. Soil biological activity and their seasonal variations in response to long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Plant Soil 2009, 326, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhu, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, R. Response of organic carbon fractions and microbial community composition of soil aggregates to long-term fertilizations in an intensive greenhouse system. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournel, S.; Godbout, S.; Ruel, P.; Fortin, A.; Généreux, M.; Côté, C.; Landry, C.; Pellerin, D. Production of recycled manure solids for bedding in Canadian dairy farms: I. Solid–liquid separation. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Naeth, M.A. Lignite derived humic products and cattle manure biochar are effective soil amendments in cadmium contaminated and uncontaminated soils. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, P.H.; Laboski, C.A.M. Dairy manure treatment effects on manure phosphorus fractionation and changes in soil test phosphorus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.C.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Strawn, D.G. Phosphorus Speciation in Manure-Amended Alkaline Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gavlak, R.; Mitchell, A.; Sparrow, S. Solid and Liquid Cattle Manure Application in a Subarctic Soil: Bromegrass and Oat Production and Soil Properties. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Provolo, G.; Perazzolo, F.; Mattachini, G.; Finzi, A.; Naldi, E.; Riva, E. Nitrogen removal from digested slurries using a simplified ammonia stripping technique. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liu, K.; Li, D.; Peng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H. Long-term effects of inorganic fertilizers and organic manures on the structure of a paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Wolf, A.M.; Sharpley, A.N.; Beegle, D.B.; Saporito, L.S. Survey of Water-Extractable Phosphorus in Livestock Manures. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Daniel, T.C.; Edwards, D.R. Phosphorus Movement in the Landscape. J. Prod. Agric. 1993, 6, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.J.; Han, K.J.; Muir, J.P.; Weindorf, D.C.; Lastly, L. Dairy Manure Compost Effects on Corn Silage Production and Soil Properties. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallama, M.; Pekrun, C.; Lambers, H.; Kandeler, E. Hidden miners—The roles of cover crops and soil microorganisms in phosphorus cycling through agroecosystems. Plant Soil 2018, 434, 7–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Guan, L.; Zhu, J.; Yan, L. Effects of Exogenous Humic Acids on Forms of Organic Phosphorus in Three Contrasting Types of Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, D.V.; Kavitha, P.; Naidu, M.V.S.; Maheswari, P.U. Effect of Different Levels of Potassium and Green Manure on Available K, Uptake of K and Potassium Use Efficiency of Rice (Oryza sativa, L.). Madras Agric. J. 2017, 104, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayne, N.; Aula, L. Livestock Manure and the Impacts on Soil Health: A Review. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.T.; Paradelo, R.; Moldes, A.B.; Domínguez, M.; Díaz-Fierros, F. Utilization of MSW compost for organic matter conservation in agricultural soils of NW Spain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtman, D.P.; Reid, R.J.; Ayling, S.M. Phosphorus Uptake by Plants: From Soil to Cell. Plant Physiol. 1998, 116, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Duan, Y.; Liu, G.; Shang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Zou, Z.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W. Tea plantation intercropping green manure enhances soil functional microbial abundance and multifunctionality resistance to drying-rewetting cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 810, 151282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, S.S.; Kaur, T.; Gupta, R.K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Rahman, A. Long-Term Impact of the Continuous Use of Organic Manures on Crop and Soil Productivity under Maize–Potato–Onion Cropping Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demelash, N.; Bayu, W.; Tesfaye, S.; Ziadat, F.; Sommer, R. Current and residual effects of compost and inorganic fertilizer on wheat and soil chemical properties. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2014, 100, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Nitrogen addition shapes soil enzyme activity patterns by changing pH rather than the composition of the plant and microbial communities in an alpine meadow soil. Plant Soil 2019, 440, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.F.; Qi, W.U.; Li, F.B.; Wong, J.W. Nitrogen transformations during pig manure composting. Chin. J. Env.-Ment. Sci. 2001, 13, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yin, L.; Ju, W.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Meta-analysis of green manure effects on soil properties and crop yield in northern China. Field Crop. Res. 2021, 266, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, M.G.; Tong, X.G.; Sun, F.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Zhu, P.; He, X.H. Long-term combined chemical and manure fertilizations increase soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in aggregate fractions at three typical cropland soils in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, G.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Ding, W. Long-term manure application increases soil organic matter and aggregation, and alters microbial community structure and keystone taxa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Yi, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X. Does animal manure application improve soil aggregation? Insights from nine long-term fertilization experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, F.Y.; Liang, L. Response of soil nematode ecological and maturity indexes and faunal analysis to the conservation tillage. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Yield and Nitrogen Balance of Greenhouse Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) with Conventional and Site-specific Nitrogen Management in Northern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2006, 77, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lv, L.; Liu, D.; He, X.; Wang, W.; Feng, Y.; Islam, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. A global meta-analysis of animal manure application and soil microbial ecology based on random control treatments. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Semenov, V.M.; Ksenofontova, N.; Zinyakova, N.B.; van Bruggen, A.H. Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Wemheuer, B.; Korolkow, V.; Wemheuer, F.; Nacke, H.; Schöning, I.; Schrumpf, M.; Daniel, R. Driving forces of soil bacterial community structure, diversity, and function in temperate grasslands and forests. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Y. Aggregate stability and size distribution of red soils under different land uses integrally regulated by soil organic matter, and iron and aluminum oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, H.; Parmer, Y.; Sajwan, P.; Kumari, M.; Solanki, S. Effect of organic manures and biofertilizer on plant growth, yield and quality of horticultural crop: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, A.F.M.J.; Rakibuzzaman, M.; Wasin, E.W.N.; Husna, M.A.; Mahato, A.K. Foliar application of Spirulina and Oscillatoria on growth and yield of okra as bio-fertilizer. J. Biosci. Agric. Res. 2019, 22, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imriz, G.; Ozdemir, F.; Topal, I.; Ercan, B.; Tas, M.N.; Yakısır, E.; Okur, O. Rhizobacteria (PGPRs) promoting plant growth in plant production and their mechanisms of action. Electron. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Waigi, M.G.; Sun, K.; Gao, Y. Sphingomonads in Microbe-Assisted Phytoremediation: Tackling Soil Pollution. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Alami, M.M.; Tang, H.; Zhao, J.; Nie, Z.; Hu, J.; Shu, S.; Zhu, D.; Yang, T. Applications of Streptomyces jingyangensis T. and Bacillus mucilaginosus A. improve soil health and mitigate the continuous cropping obstacles for Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 180, 114691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Fan, K.; Li, G.; Gao, S.; Chang, D.; Liang, T.; Li, S.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Che, Z.; et al. Synergistic effects of diazotrophs and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil biological nitrogen fixation after three decades of fertilization. iMeta 2023, 2, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Pathways of litter C by formation of aggregates and SOM density fractions: Implications from 13C natural abundance. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 71, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Iguchi, R.; Kataoka, R. Multifunctional food waste fertilizer having the capability of Fusarium-growth inhibition and phosphate solubility: A new horizon of food waste recycle using microorganisms. Waste Manag. 2019, 94, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Favero, C.; Creus, C.M.; Simontacchi, M.; Puntarulo, S.; Lamattina, L. Aerobic nitric oxide production by Azospirillum brasilense Sp245 and its influence on root architecture in tomato. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dai, L.; Ding, H.; Ci, D.; Qin, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z. Influence of Salt Stress on Growth of Spermosphere Bacterial Communities in Different Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.; Batstone, D.J.; Keller, J. Biological phosphorus removal from abattoir wastewater at very short sludge ages mediated by novel PAO clade Comamonadaceae. Water Res. 2015, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
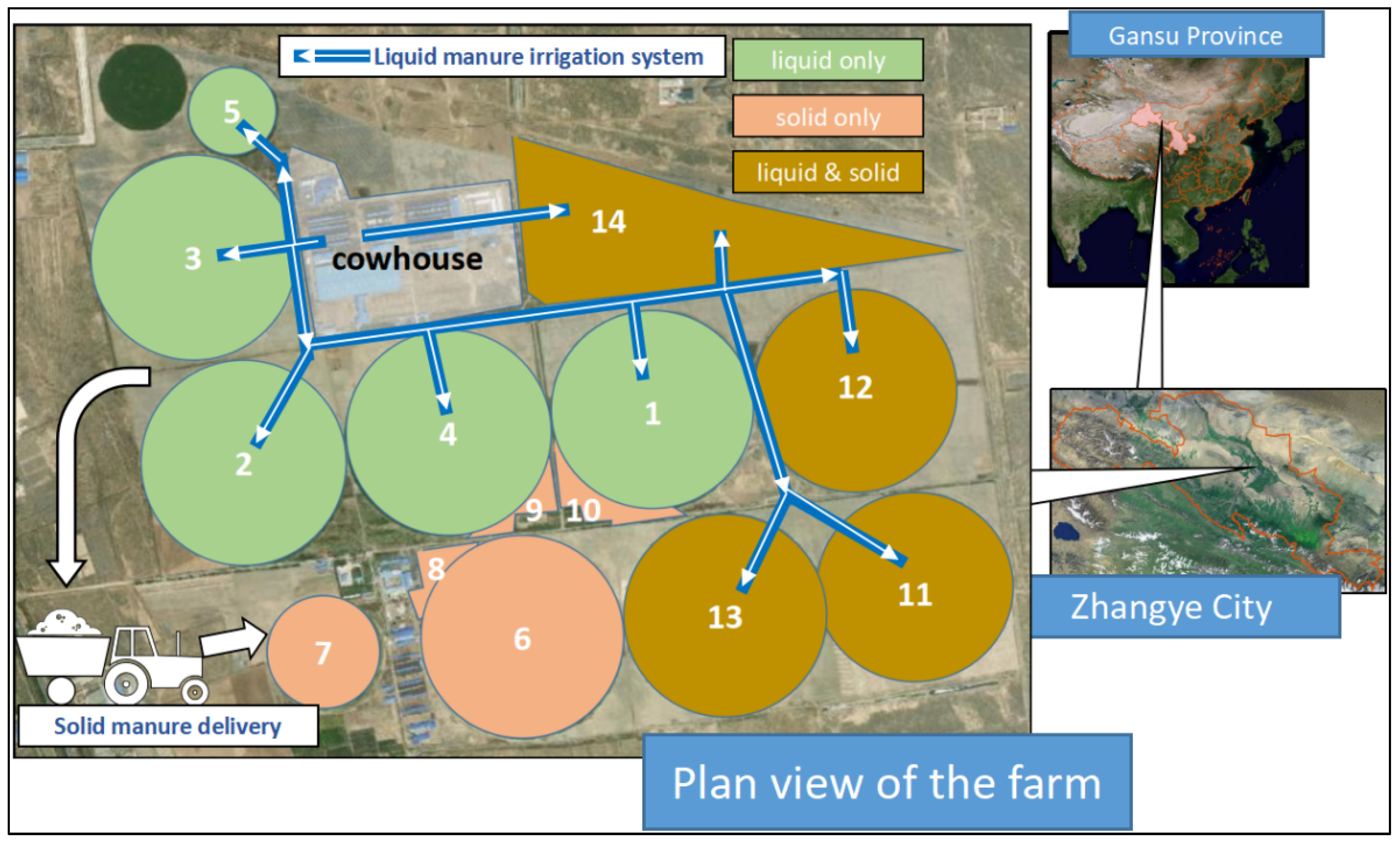




| Soil Sample Code | Manure Recycling Method | Cumulative Usage of Liquid (t/Area) | Cumulative Usage of Solid (t/Area) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liquid only (L) | 215 | 0 |
| 2 | 379 | 0 | |
| 3 | 408 | 0 | |
| 4 | 433 | 0 | |
| 5 | 465 | 0 | |
| 6 | Solid only (S) | 0 | 6.7 |
| 7 | 0 | 31.2 | |
| 8 | 0 | 44.4 | |
| 9 | 0 | 83.9 | |
| 10 | 0 | 77.5 | |
| 11 | Liquid & solid (L&S) | 17.3 | 8 |
| 12 | 352.7 | 9 | |
| 13 | 429.3 | 9.6 | |
| 14 | 69.2 | 12.8 | |
| 15 | CK | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | |
| 17 | 0 | 0 |
| Properties | pH | Bulk Density (m3/kg) | Total N (mg/kg) | Available P (mg/kg) | Available K (mg/kg) | Organic Matter (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original soil | 7.8 | 8.9 | 415.61 | 40.62 | 149.17 | 0.81 |
| Soil Fertility Properties | Liquid | Solid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −b | R2 | −b | R2 | |
| Total N | 0.0011 | 0.48 | 0.0081 | 0.16 |
| Available P | 0.0016 | <0.00001 | 0.0119 | 0.90 |
| Available K | 0.0014 | <0.00001 | 0.0142 | 0.26 |
| Organic matter | 0.0013 | <0.00001 | 0.0013 | <0.00001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Z.; He, W.; Shi, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Feng, Y. Effects of the Integrated Use of Dairy Cow Manure on Soil Properties and Biological Fertility. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511693
Han Z, He W, Shi H, Wang C, Liu C, Feng Y. Effects of the Integrated Use of Dairy Cow Manure on Soil Properties and Biological Fertility. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511693
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ziyu, Wenjun He, Huading Shi, Chen Wang, Chenfeng Liu, and Yao Feng. 2023. "Effects of the Integrated Use of Dairy Cow Manure on Soil Properties and Biological Fertility" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511693
APA StyleHan, Z., He, W., Shi, H., Wang, C., Liu, C., & Feng, Y. (2023). Effects of the Integrated Use of Dairy Cow Manure on Soil Properties and Biological Fertility. Sustainability, 15(15), 11693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511693