How Does the Digital Economy Affect Green Development?—Evidence from 284 Cities in China
Abstract
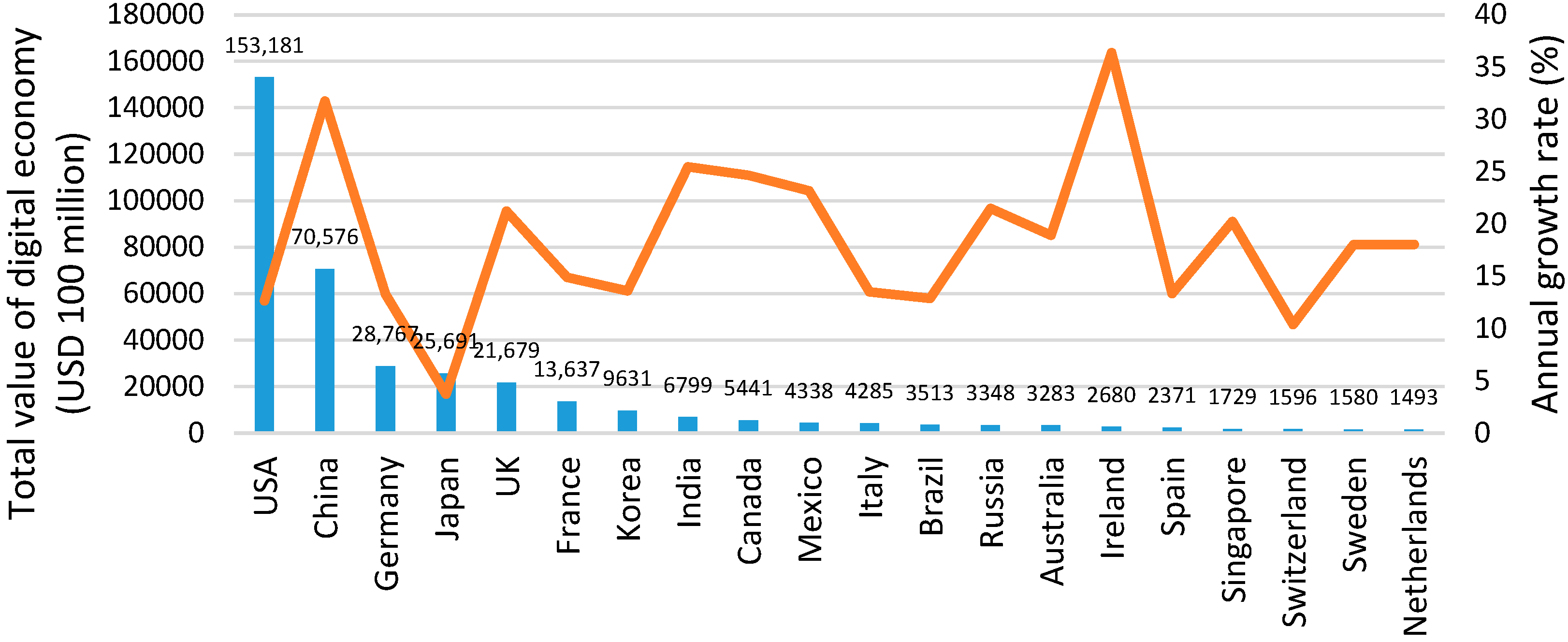
:1. Introduction
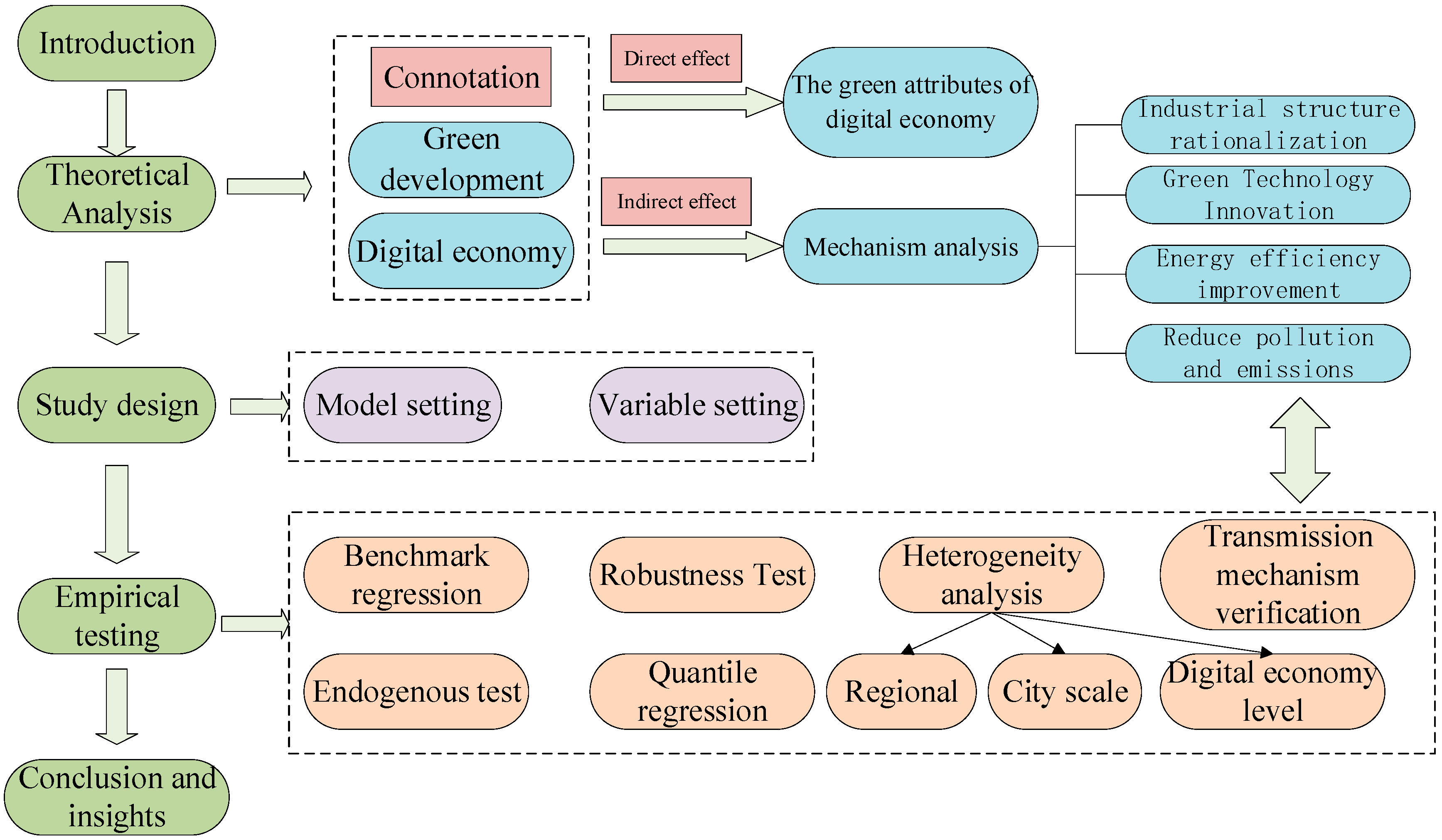
2. Theoretical Mechanism Analysis
2.1. The Connotation of Green Development
2.2. The Connotation and Green Attributes of the Digital Economy
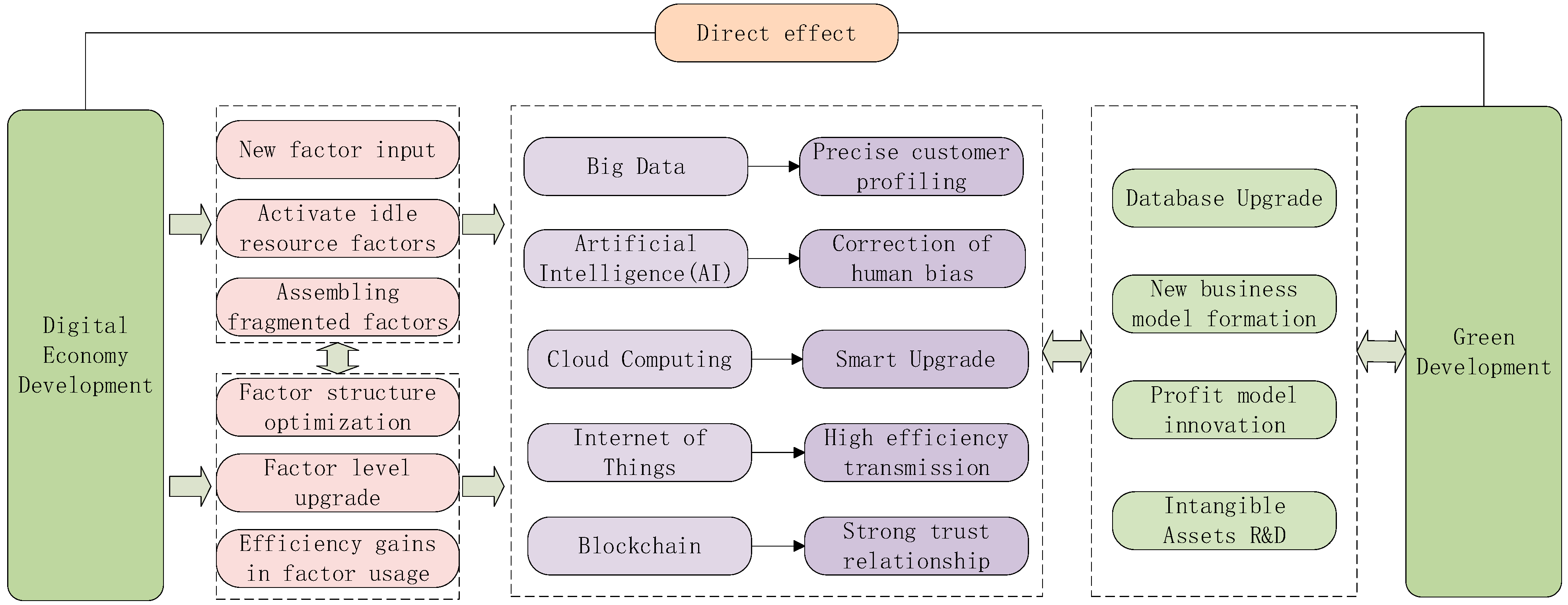
2.3. Mechanism Analysis
3. Study Design
3.1. Model Setting
3.2. Variable Setting
3.2.1. The Explained Variable
3.2.2. The Core Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Mechanism Variables
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Data Description
4. Empirical Results and Discussion
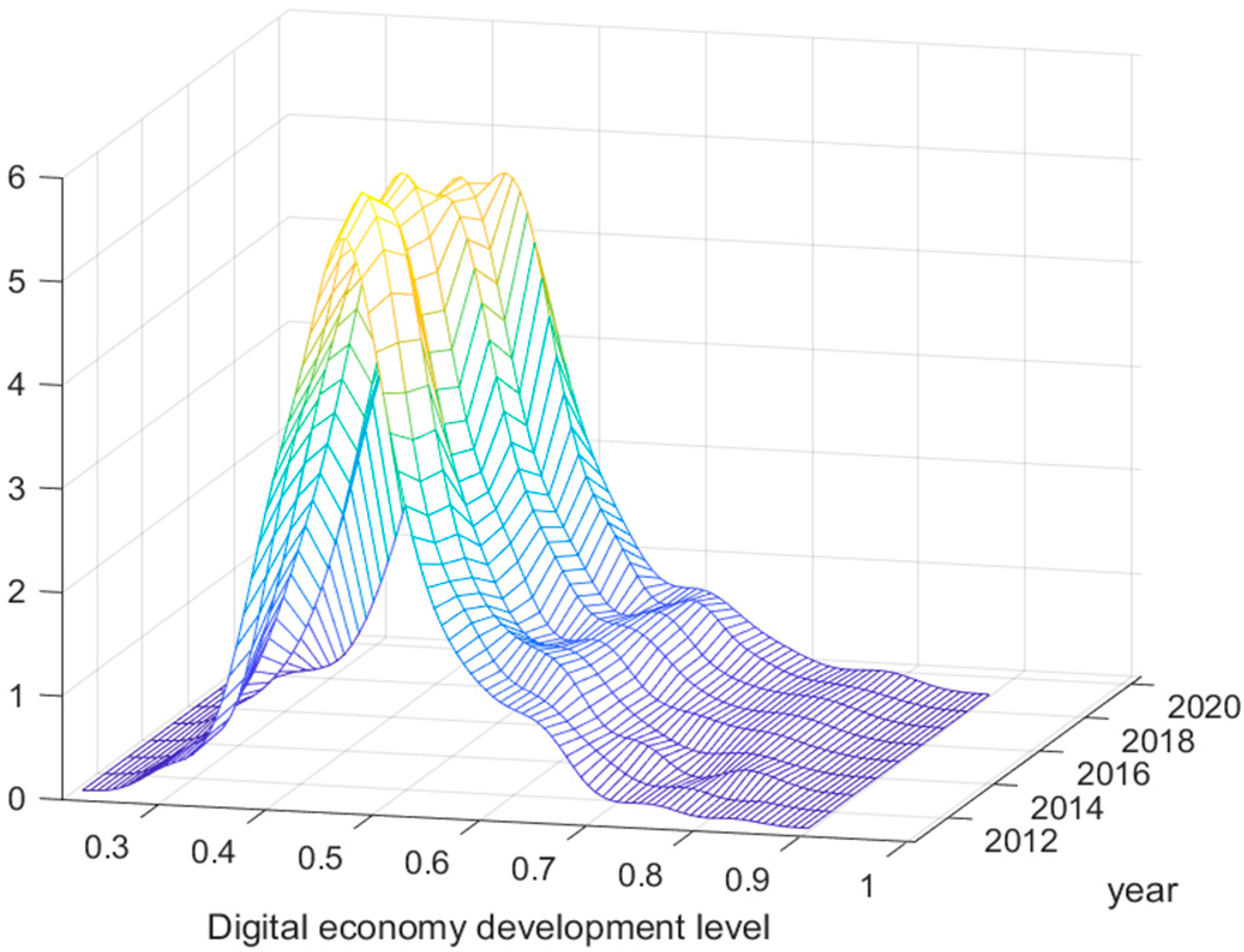
4.1. Distribution Dynamics of the Digital Economy
4.2. Benchmark Model
4.3. Endogeneity Test
5. Robustness Test
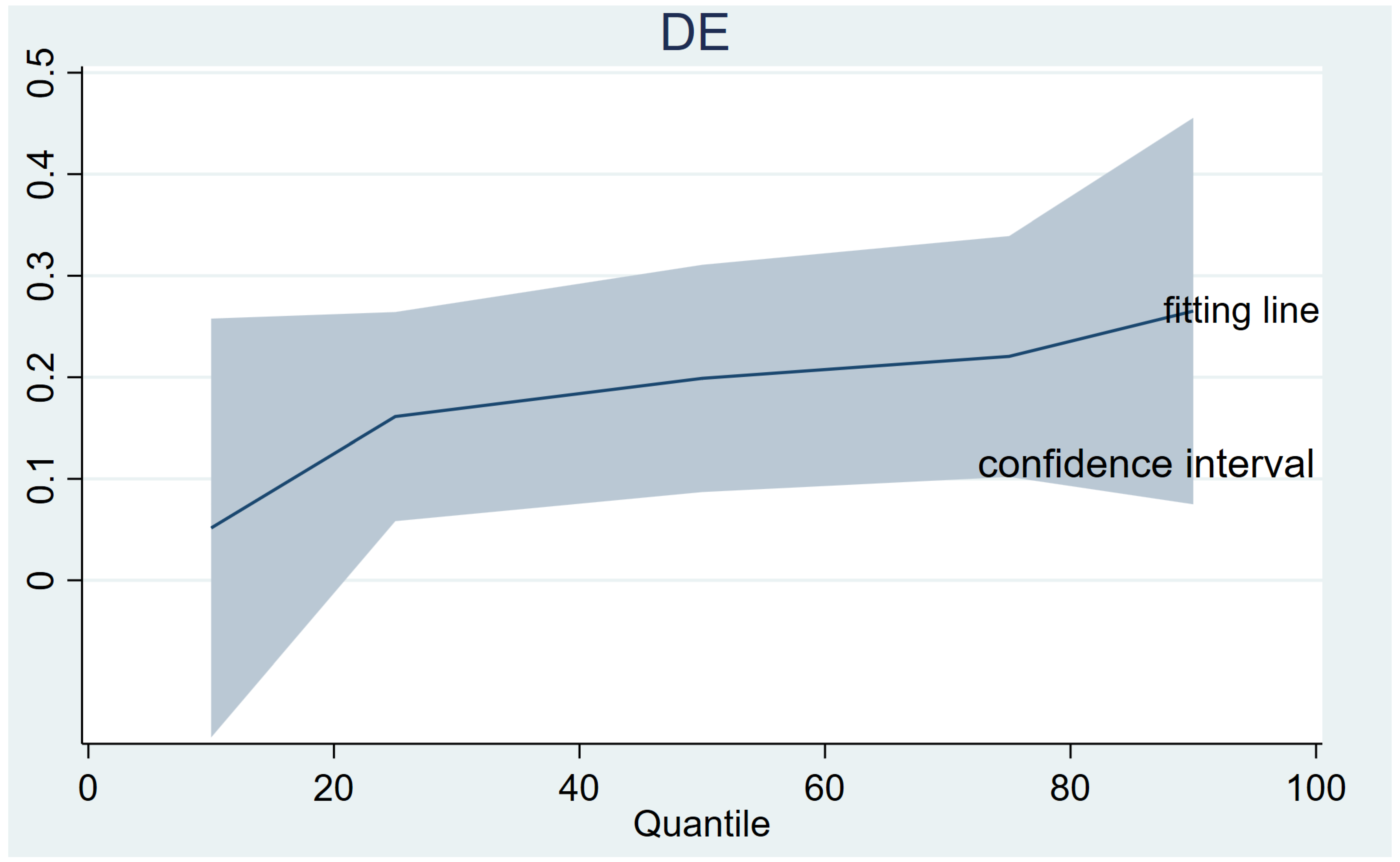
5.1. Quantile Regression Results and Analysis
5.2. Long-Term Impact Analysis
5.3. Excluding the Impact of Municipalities
6. Heterogeneity Analysis
6.1. Regional Heterogeneity
6.2. City Scale Heterogeneity
6.3. Digital Economy Level Heterogeneity
7. Transmission Mechanism Verification
8. Conclusions and Insights
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, B. Green Development: Environment and Sustainability in a Developing World; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, K. Digital Economy Development, Industrial Structure Upgrading and Green Total Factor Productivity: Empirical Evidence from China’s Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G20 Digital Economy Development and Cooperation Initiative. 2016. Available online: http://www.g20chn.org/English/Documents/Current/201609/P020160908736971932404.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Heymann, E.; Koerner, K.; Schattenberg, M. Digital Economics: How AI and Robotics Are Changing Our Work and Our Lives. Deutsche Bank Research. 2018. ISSN: 1612-0272/ISSN (Online): 1612-0280. Available online: https://www.dbresearch.com (accessed on 14 May 2018).
- Karpovich, O.G.; Diakonova, O.S.; Pozharskaya, E.L.; Grigorenko, V.V. Digital Growth Points of the Region’s Green Economy in Industry 4.0: Finance and Security Issues; Industry 4.0 Palgrave Macmillan, Cham: London, UK, 2021; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, L.; Han, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wu, H. The emerging driving force of inclusive green growth: Does digital economy agglomeration work? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 1656–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Chatti, W.; Majeed, M.T. Information communication technology (ICT), smart urbanization, and environmental quality: Evidence from a panel of developing and developed economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESCAP. The State of the Environment in Asia and the Pacific. 2005. Available online: https://www.unescap.org/sites/default/d8files/knowledge-products/SOE2005fullmainpub%20%281%29.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- OECD. Towards Green Growth: Monitoring Progress. 2011. Available online: https://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/envAccounting/ceea/meetings/UNCEEA-6-11.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- World Bank. Inclusive Green Growth: The Pathway to Sustainable Development, Washington; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Albagoury, S. Inclusive Green Growth in Africa: Ethiopia Case Study; University Library of Munich: Munich, Germany, 2016; Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/id/eprint/74364 (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Yuan, R. Regional green development level and its spatial relationship under the constraints of haze in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 210, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Kang, J.-G.; Zhao, C.-H.; Hu, Z.-G. Energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from China at both aggregated and disaggregated levels. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 3077–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Liu, S. Spatial-Temporal Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and Green Development in the Coastal Cities of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolliver, C.; Fujii, H.; Keeley, A.R.; Managi, S. Green Innovation and Finance in Asia. Asian Econ. Policy Rev. 2020, 16, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Ruangkanjanases, A. Understanding the Antecedents and Consequences of Green Human Capital. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 2158244020988867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Nie, L.; Sun, H.; Sun, W.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Digital finance, green technological innovation and energy-environmental performance: Evidence from China’s regional economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Sheng, J.; He, K.; Wei, Y.-M.; Xie, R. Exploring the effect of industrial structure adjustment on interprovincial green development efficiency in China: A novel integrated approach. Energy Policy 2019, 134, 110946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Barua, A.; Whinston, A.B. Virtual field experiments for a digital economy: A new research methodology for exploring an information economy. Decis. Support Syst. 2002, 32, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcan, V.; Gribincea, A.; Birca, I. Digital economy-a premise for economic development in the 20th century. Econ. Si Soci-Ologie Rev. Teor. Stiintifica 2014, 2, 109–115. Available online: https://www.elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=24502923 (accessed on 8 April 2014).
- Bukht, R.; Heeks, R. Defining, conceptualising and measuring the digital economy. Dev. Inform. Work. Pap. 2017, 13, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milosevic, N.; Dobrota, M.; Barjaktarovic-Rakocevic, S. Digital economy in Europe: Evaluation of countries’ performances. Bornik Rad. Ekon. Fak. Rij. 2018, 36, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. Is the digital economy driving clean energy development? -New evidence from 276 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, A.; Tucker, C. Digital Economics. J. Econ. Lit. 2019, 57, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwanholz, J.; Leipold, S. Sharing for a circular economy?—An analysis of digital sharing platforms’ principles and business models. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Li, Y. Understanding the new shape of the economy: A microeconomic perspective. China’s Ind. Econ. Ics 2020, 12, 159–177. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xiang, Q. Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: Based on an extended CDM model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Kazlauskas, A. Digital ecosystems: ICT’s contribution to addressing climate change. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd IEEE International Conference on Digital Ecosystems and Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 1–3 June 2009; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauliuk, S.; Koslowski, M.; Madhu, K.; Schulte, S.; Kilchert, S. Co-design of digital transformation and sustainable development strategies—What socio-metabolic and industrial ecology research can contribute. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 343, 130997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucak, R.; Danish; Khan, S.U. Does information and communication technology affect CO2 mitigation under the pathway of sustainable development during the mode of globalization? Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Gu, S. The Impact of Rationalization and Upgrading of Industrial Structure on Carbon Emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güler, M.; Büyüközkan, G. Analysis of Digital Transformation Strategies with an Integrated Fuzzy AHP-Axiomatic Design Methodology. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Bai, G.; Shen, Z.; Xia, L. Digital economy and its spatial effect on green productivity gains in manufacturing: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liao, F. Input digitalization and green total factor productivity under the constraint of carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, M.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, A.; Zhang, P. Resource abundance, industrial structure, and regional carbon emissions efficiency in China. Resour. Policy 2019, 60, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Peng, C.; Song, M. Macroeconomic uncertainty, high-level innovation, and urban green development performance in China. China Econ. Rev. 2019, 55, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P. Digital Futures †an Agenda for a Sustainable Digital Economy. Corp. Environ. Strat. 2001, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Yu, Y. An adoption-implementation framework of digital green knowledge to improve the performance of digital green innovation practices for industry 5.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chong, Y.; Yu, H.; Ye, X.; Li, G. Digital financial development and ecological footprint: Evidence from green-biased technology innovation and environmental inclusion. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.G.; Jaffe, A.B.; Stavins, R.N. The Induced Innovation Hypothesis and Energy-Saving Technological Change. Q. J. Econ. 1999, 114, 941–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, J.A.G.; Busso, C.M.; Gobbo, S.C.O.; Carreão, H. Making the links among environmental protection, process safety, and industry 4.0. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.; Murad, W. The impacts of economic growth, trade openness and technological progress on renewable energy use in organization for economic co-operation and development countries. Renew. Energy 2019, 145, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Shang, Y. A review of industrial big data for decision making in intelligent manufacturing. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 29, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J. The Dynamic Impact of Digital Economy on Carbon Emission Reduction: Evidence City-level Empirical Data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Ran, Q.; Wu, H.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. Energy structure, digital economy, and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64606–64629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Strasser, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Gram, W.K.; Budden, A.E.; Batcheller, A.L.; Duke, C.S.; Porter, J.H. Big data and the future of ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.-H.; Choi, M.J. Ecological views of big data: Perspectives and issues. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G. Regression Quantiles. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Development of an SBM-ML model for the measurement of green total factor productivity: The case of pearl river delta urban agglomeration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, J.-F. Energy efficiency analysis on Chinese industrial sectors: An improved Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-H. A global Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J. Prod. Anal. 2010, 34, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Du, J.; Tan, K.H. Impact of fiscal decentralization on green total factor productivity. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 205, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Academy of Information and Communication Research. China Digital Economy Development Report. 2022. Available online: http://www.caict.ac.cn/kxyj/qwfb/bps/202207/P020220729609949023295.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Tencent Research Institute. China “Internet+” Digital Economy Index. 2018. Available online: https://www.tisi.org/5025 (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- Xu, X.C.; Zhang, M.H. Research on the scale measurement of China’s digital economy—Based on the perspective of interna-tional comparison. China’s Ind. Econ. 2020, 5, 23–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Luo, X. Measuring the level of development and evolution of China’s digital economy. J. Quant. Tive Technol. Econ. 2021, 38, 26–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cui, J.B. Low carbon city and enterprise green technology innovation. China’s Ind. Econ. 2020, 12, 178–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, M. Urbanization, economic growth and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Sustain. Comput. Informatics Syst. 2019, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, F.; Kong, T.; Cheng, Z.Y. Measuring China’s digital financial inclusion: Index compilation and spatial characteristics. China Econ. Q. 2020, 19, 1401–1418. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Z.; Kong, F.X. Study on the Impact of Digital Economy Development on Green Transformation of Cities in Yangtze River Economic Zone: A Perspective of “Three Life” Space. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2021, 43, 64–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Qian, N. US Food Aid and Civil Conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 1630–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.H.; Yu, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.L. Internet development and productivity growth in manufacturing industry: Internal mecha-nism and China experiences. China’s Ind. Econ. 2019, 35, 5–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, D.K. Air pollution, government regulations and high-quality economic development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. Available online: http://jtp.cnki.net/Bilingual/detail/html/jjyj201802003?view=2 (accessed on 18 May 2018).
- Wang, H. Research on the Role and Mechanism of Digital Finance in Improving the Performance of Industrial Green Innovation. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasiga, P.; Onyeaka, H.; Ouassou, E.H. Unlocking the Green Economy in African Countries: An Integrated Framework of FinTech as an Enabler of the Transition to Sustainability. Energies 2022, 15, 8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhu, J.; Luo, S. The impact of fintech innovation on green growth in China: Mediating effect of green finance. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 193, 107308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Zhou, X.L. Can Promoting the Digital Economy Improve Environmental Pollution in China: A Quasi-natural 424 Experiment Based on the ‘Broadband China’ Strategy. Macroeconomics 2021, 7, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Level | Criterion Level | Index Level | Unit | Indicator Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital economy development level | Digital Infrastructure Development | Number of international Internet users per 100 people | Household/ 100 people | Positive |
| Number of mobile phone subscribers per 100 people | Department/ 100 people | Positive | ||
| Digital Scientific Research Support | Proportion of scientific expenditure in financial budget expenditure | % | Positive | |
| Proportion of education expenditure in financial budget expenditure | % | Positive | ||
| Number of college students | per 10,000 people | Positive | ||
| Digital Industry Development | Total telecom business | 108 yuan | Positive | |
| Proportion of employees in information transmission, computer services, and software industries in urban employment | % | Positive | ||
| Proportion of employees in scientific research, technical services, and geological exploration in urban employment | % | Positive | ||
| Total postal business per capita | yuan/person | Positive | ||
| Number of employees in transportation, storage, post, and telecommunications industry | 104 | Positive | ||
| Digital Financial Development | Coverage breadth—electronic account coverage | __ | Positive | |
| Usage depth—payments, money funds, credit, insurance, investment, credit business | __ | Positive | ||
| Digitization level—mobile, creditworthy, and convenient financial services | __ | Positive |
| Variable | Symbol | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green development | GTFP | 2556 | 1.0057 | 0.0566 | 0.5012 | 1.8724 |
| Digital economy | DE | 2556 | 0.0592 | 0.0580 | 0.0093 | 0.6721 |
| Industrial structure rationalization level | ISR | 2556 | 1.6621 | 1.0670 | −0.5434 | 8.8298 |
| Green technology innovation | Invention | 2556 | 4.8795 | 1.8040 | 0 | 10.8765 |
| Electricity consumption | ElE | 2556 | 6.7133 | 0.6074 | 5.0799 | 11.2003 |
| Environmental pollution | Pollution | 2556 | 0.0363 | 0.0380 | 0.0002 | 0.5858 |
| SO2 | SO2 | 2556 | 10.0322 | 1.1979 | 0.6931 | 13.1832 |
| Wastewater | Water | 2556 | 8.1720 | 1.1171 | 1.9459 | 11.4773 |
| Smoke | Smoke | 2556 | 9.6941 | 1.1597 | 4.0254 | 15.4582 |
| Economic development level | Pgdp | 2556 | 11.0146 | 0.6633 | 8.9870 | 13.1851 |
| Living standard of the residents | Liv | 2556 | 7.0176 | 1.2355 | 4.4699 | 12.0098 |
| Degree of government fiscal intervention | Gov | 2556 | 1.3565 | 1.2270 | 0.0455 | 30.1087 |
| Regional tax base size | Rtax | 2556 | 0.1071 | 0.1220 | 0 | 1 |
| Population size | Popul | 2556 | 4.6814 | 0.7906 | 2.7147 | 7.8156 |
| Infrastructure | Inf | 2556 | 7.1083 | 0.9682 | 2.7344 | 10.0061 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP |
| DE | 0.239 *** | 0.209 *** | 0.183 *** | 0.197 *** | 0.217 *** | 0.151 *** |
| (0.02) | (0.03) | (0.03) | (0.05) | (0.07) | (0.04) | |
| Pgdp | 0.008 ** | 0.010 *** | 0.016 *** | 0.014 *** | ||
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |||
| Liv | 0.000 | −0.008 ** | −0.010 *** | −0.009 *** | ||
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |||
| Inf | −0.005 * | −0.004 ** | −0.007 *** | −0.005 ** | ||
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |||
| Popul | 0.005 | 0.011*** | 0.016*** | 0.013*** | ||
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |||
| Gov | −0.002 ** | −0.001 | −0.001 | −0.001 ** | ||
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |||
| Rtax | −0.010 | 0.019 | −0.005 | 0.024 * | ||
| (0.01) | (0.01) | (0.01) | (0.01) | |||
| _cons | 0.992 *** | 0.923 *** | 0.995 *** | 0.920 *** | 0.866 *** | 0.884 *** |
| (0.00) | (0.03) | (0.00) | (0.03) | (0.03) | (0.03) | |
| Region FE | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region × Year | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| N | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2511 |
| R-squared | 0.060 | 0.066 | 0.165 | 0.154 | 0.173 | 0.305 |
| F-statistic | 163.044 | 25.722 | 48.702 | 15.650 | 15.062 | 18.499 |
| IV1: Tel | IV2: Post | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Variables | DE | GTFP | DE | GTFP |
| DE | 2.412 *** | 1.353 *** | ||
| (0.37) | (0.29) | |||
| IV1 | 0.022 *** | |||
| (0.00) | ||||
| IV2 | 0.023 *** | |||
| (0.00) | ||||
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | 22.470 [0.000] | 28.121 [0.000] | ||
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | 131.509 {16.38} | 155.767 {16.38} | ||
| Cragg–Donald Wald F statistic | 165.114 {16.38} | 225.912 {16.38} | ||
| F-statistic | 17.811 | 17.785 | ||
| N | 1998 | 1998 | 2223 | 2223 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantile | Q10 | Q25 | Q50 | Q75 | Q90 |
| DE | 0.052 | 0.161 *** | 0.199 *** | 0.221 *** | 0.265 *** |
| (0.11) | (0.05) | (0.06) | (0.06) | (0.10) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 |
| R-squared | 0.127 | 0.114 | 0.129 | 0.178 | 0.212 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | Non-Key |
| DE | 0.151 *** | 0.129 ** | ||||
| (0.04) | (0.06) | |||||
| L.DE | 0.185 *** | |||||
| (0.04) | ||||||
| L2.DE | 0.179 *** | |||||
| (0.05) | ||||||
| L3.DE | 0.157 ** | |||||
| (0.07) | ||||||
| L4.DE | 0.094 | |||||
| (0.09) | ||||||
| _cons | 0.884 *** | 0.906 *** | 0.875 *** | 0.852 *** | 0.828 *** | 0.898 *** |
| (0.03) | (0.03) | (0.04) | (0.04) | (0.04) | (0.02) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region × Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2511 | 2232 | 1953 | 1674 | 1395 | 2376 |
| R-squared | 0.305 | 0.297 | 0.315 | 0.310 | 0.329 | 0.284 |
| F-statistic | 18.499 | 20.959 | 17.525 | 16.772 | 11.480 | 7.513 |
| East | Northeast | Central | West | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) |
| DE | 0.194 *** | 0.184 ** | 0.414 *** | 0.325 | 0.160 *** | 0.126 | 0.062 *** | 0.111 ** |
| (0.03) | (0.08) | (0.09) | (0.23) | (0.03) | (0.09) | (0.02) | (0.05) | |
| _cons | 0.993 *** | 0.816 *** | 0.992 *** | 0.889 *** | 0.995 *** | 0.867 *** | 0.998 *** | 0.978 *** |
| (0.00) | (0.12) | (0.00) | (0.07) | (0.00) | (0.04) | (0.00) | (0.03) | |
| Control variables | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region × Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 747 | 747 | 306 | 306 | 720 | 720 | 738 | 738 |
| R-squared | 0.273 | 0.294 | 0.350 | 0.364 | 0.332 | 0.341 | 0.266 | 0.274 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Small City | Big City | Low-Level | High-Level |
| DE | 0.201 | 0.150 *** | 0.135 | 0.226 ** |
| (0.21) | (0.05) | (0.18) | (0.10) | |
| _cons | 0.909 *** | 0.838 *** | 0.897 *** | 0.872 *** |
| (0.03) | (0.05) | (0.02) | (0.12) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region × Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1071 | 1386 | 1953 | 459 |
| R-squared | 0.344 | 0.373 | 0.303 | 0.428 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | GTFP | ISR | GTFP | Invention | GTFP | ElE | GTFP |
| DE | 0.217 *** | 4.097 *** | 0.142 *** | 2.110 * | 0.219 *** | −0.983 * | 0.198 *** |
| (0.07) | (1.17) | (0.04) | (1.09) | (0.07) | (0.58) | (0.05) | |
| ISR | 0.002* | ||||||
| (0.00) | |||||||
| Invention | −0.001 | ||||||
| (0.00) | |||||||
| ElE | 0.001 | ||||||
| (0.00) | |||||||
| _cons | 0.866 *** | −4.561 *** | 0.894 *** | −4.855 *** | 0.860 *** | 10.456 *** | 0.914 *** |
| (0.03) | (1.57) | (0.03) | (0.98) | (0.03) | (0.67) | (0.03) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 |
| R-squared | 0.173 | 0.596 | 0.306 | 0.886 | 0.173 | 0.134 | 0.154 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Pollution | GTFP | SO2 | GTFP | Water | GTFP | Smoke | GTFP |
| DE | −0.139 *** | 0.171 ** | −7.570 *** | 0.174 *** | −2.152 * | 0.206 *** | −6.202 *** | 0.180 ** |
| (0.05) | (0.07) | (1.32) | (0.07) | (1.25) | (0.07) | (1.91) | (0.07) | |
| Pollution | −0.326 *** | |||||||
| (0.05) | ||||||||
| SO2 | −0.006 *** | |||||||
| (0.00) | ||||||||
| Water | −0.005 *** | |||||||
| (0.00) | ||||||||
| Smoke | −0.006 *** | |||||||
| (0.00) | ||||||||
| _cons | −0.100 *** | 0.834 *** | 5.187 *** | 0.895 *** | 2.769 ** | 0.880 *** | 4.675 *** | 0.894 *** |
| (0.03) | (0.03) | (1.13) | (0.03) | (1.07) | (0.03) | (1.23) | (0.03) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Region FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 | 2556 |
| R-squared | 0.512 | 0.196 | 0.627 | 0.178 | 0.613 | 0.177 | 0.463 | 0.181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y. How Does the Digital Economy Affect Green Development?—Evidence from 284 Cities in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511596
Zhao P, Guo J, Wang Y. How Does the Digital Economy Affect Green Development?—Evidence from 284 Cities in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511596
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Pei, Junhua Guo, and Yang Wang. 2023. "How Does the Digital Economy Affect Green Development?—Evidence from 284 Cities in China" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511596
APA StyleZhao, P., Guo, J., & Wang, Y. (2023). How Does the Digital Economy Affect Green Development?—Evidence from 284 Cities in China. Sustainability, 15(15), 11596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511596


_Li.png)



