Statistical Design of Eco-Friendly Mortar Mixtures Containing Scheelite Tailings and Quartzite Sand: Evaluation of Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Their Characterizations
2.2. Experimental Design, Mortar Production, and Curing
2.3. Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction
3. Results and Discussions
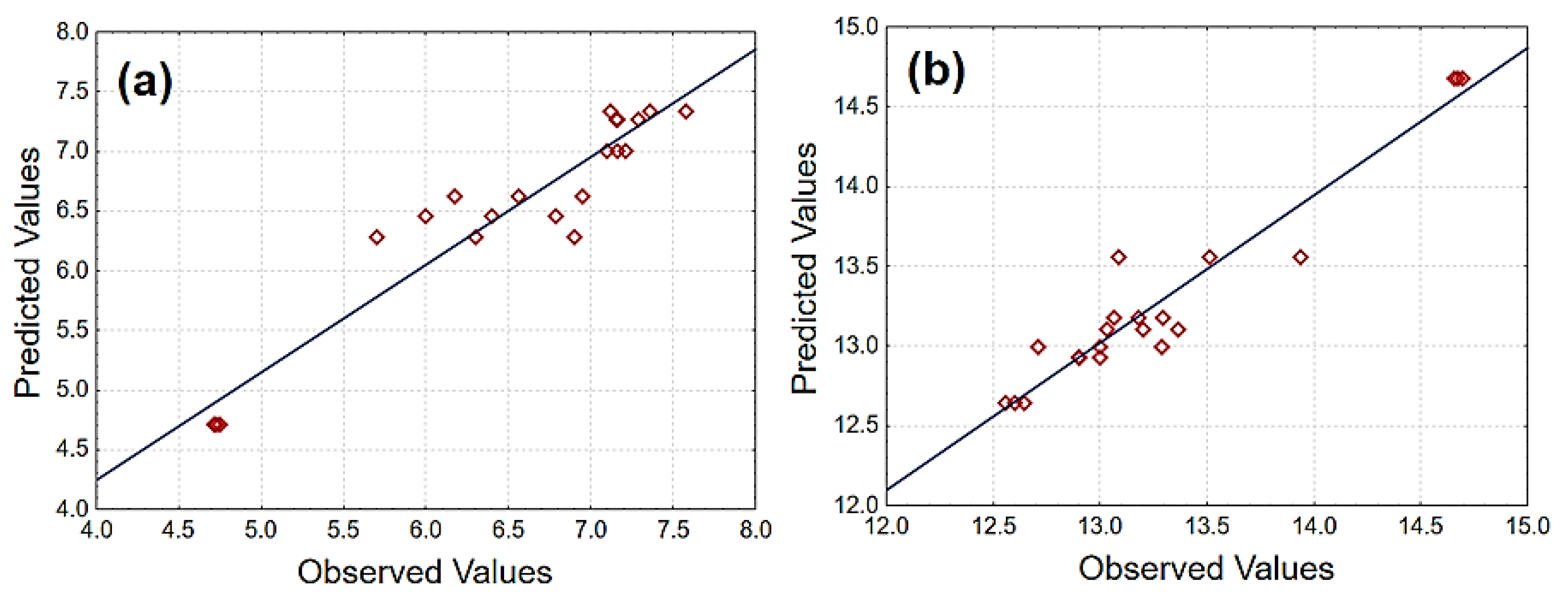
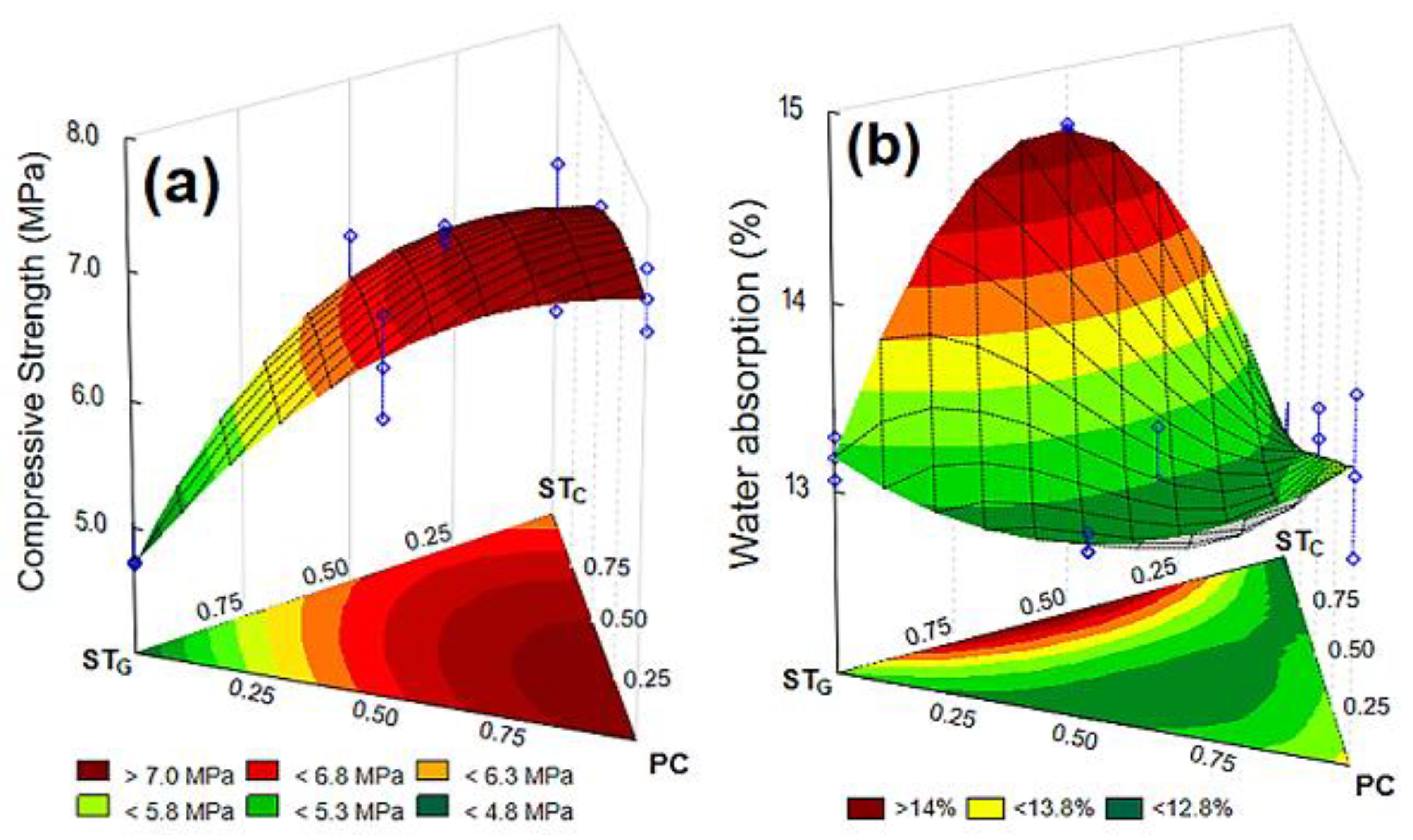
3.1. Experimental Design Results
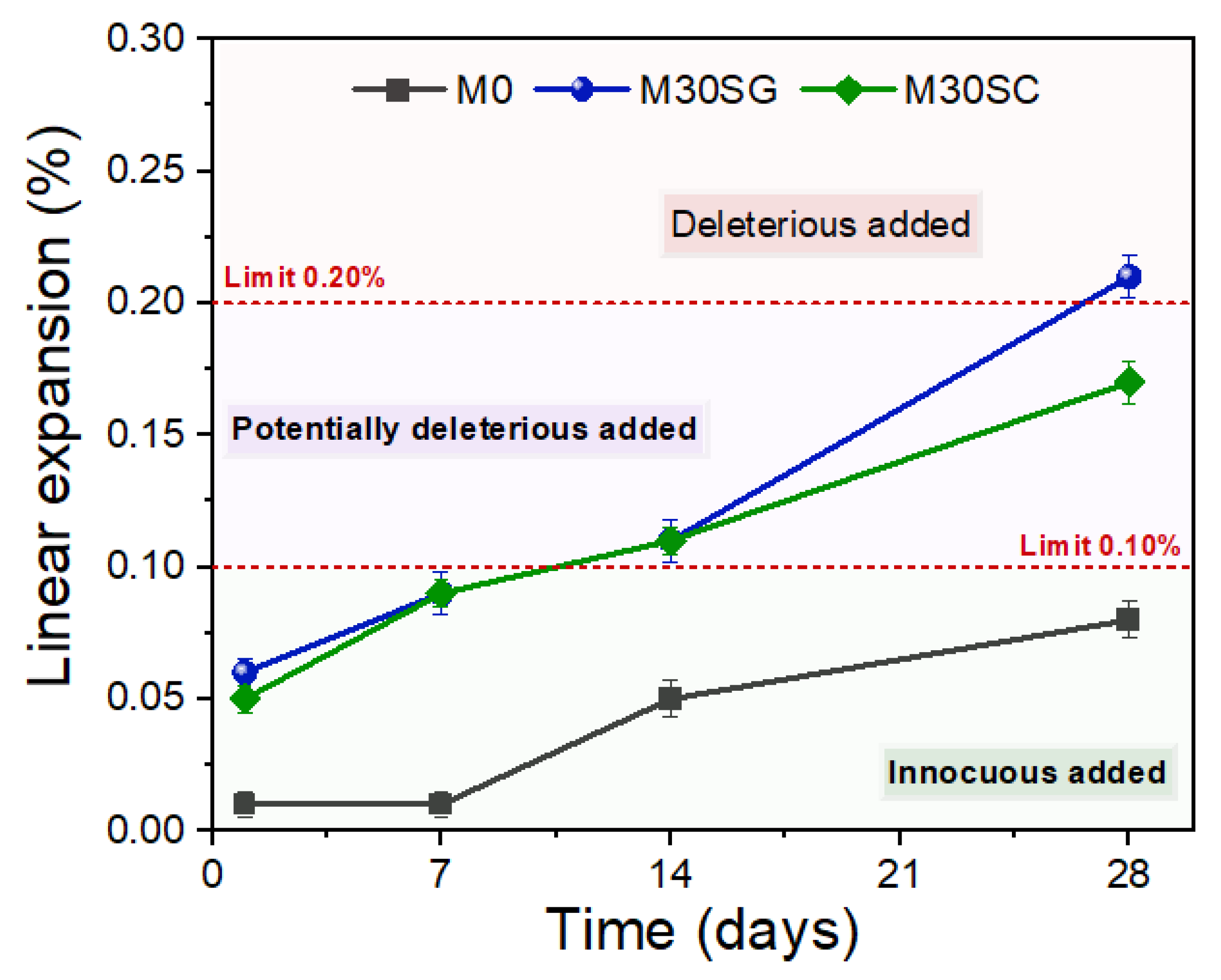
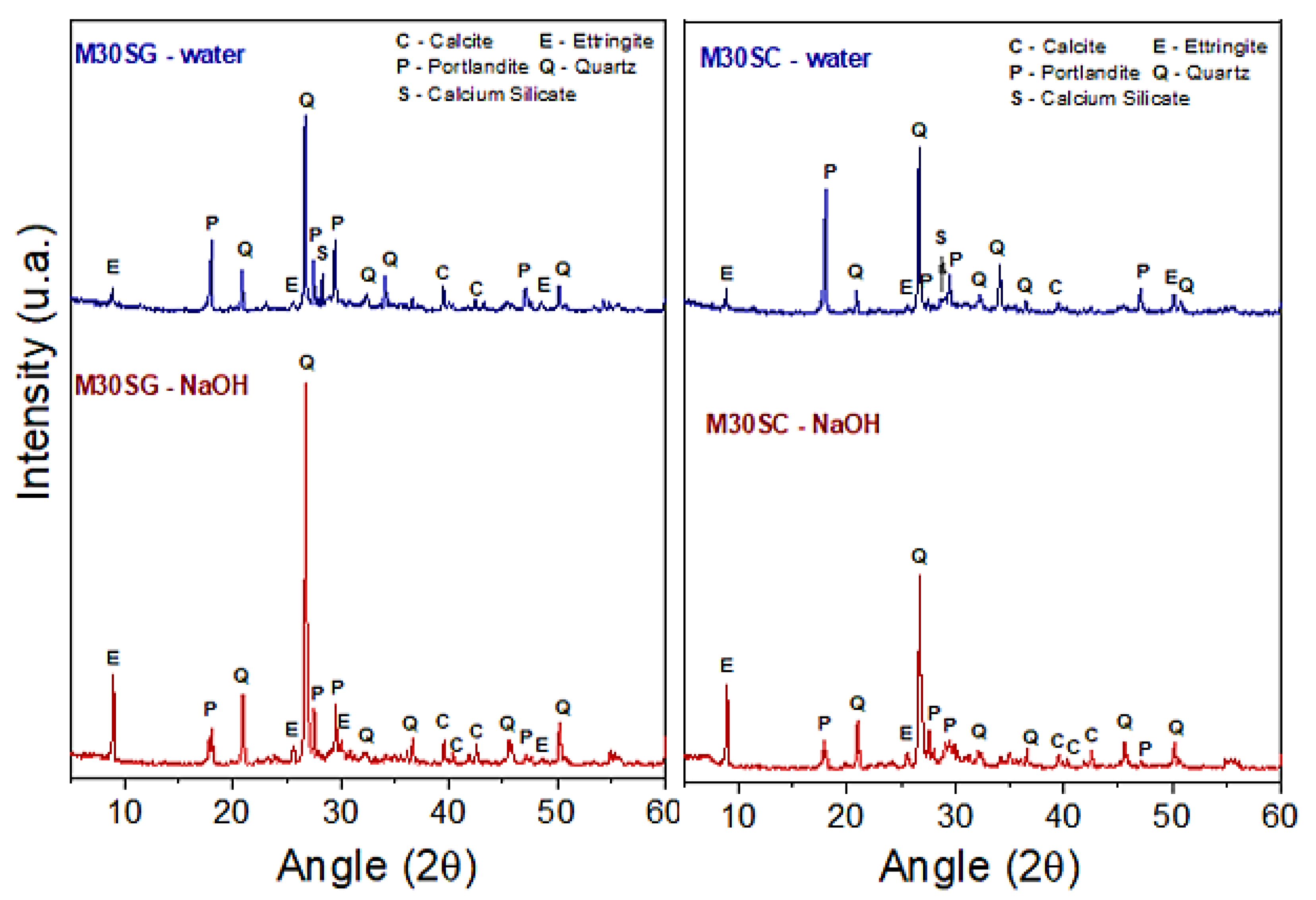
3.2. Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, K.; Loreau, M. A Model of Sustainable Development Goals: Challenges and Opportunities in Promoting Human Well-Being and Environmental Sustainability. Ecol. Model. 2023, 475, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Y.; Iizuka, A.; Ho, H.J. Calculation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions for a Carbon Recycling System Using Mineral Carbon Capture and Utilization Technology in the Cement Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proaño, L.; Sarmiento, A.T.; Figueredo, M.; Cobo, M. Techno-Economic Evaluation of Indirect Carbonation for CO2 Emissions Capture in Cement Industry: A System Dynamics Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.S.; Lynam, J.G. Embodied Energy of Rice Husk Ash for Sustainable Cement Production. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Muthusamy, K.; Embong, R.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Hashim, M.H. Environmental Impact of Cement Production and Solutions: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neto, R.E.; de Melo Cartaxo, J.; Rodrigues, A.M.; de Araújo Neves, G.; Menezes, R.R.; da Costa, F.P.; Barros, S.V.A. Durability Behavior of Mortars Containing Perlite Tailings: Alkali–Silicate Reaction Viewpoint. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Costa, F.P.D.; Beltrão, S.L.D.; Fernandes, J.V.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.D.A. Development of Eco-Friendly Mortars Produced with Kaolin Processing Waste: Durability Behavior Viewpoint. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.; Amann, M.; Borgford-Parnell, N.; Leonard, S.; Kuylenstierna, J.; Shindell, D. Short-Lived Climate Pollutant Mitigation and the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.P.; Carreiro, M.E.A.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Ferreira, H.S.; Santana, L.N.L.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A. A New Eco-Friendly Mass Formulation Based on Industrial Mining Residues for the Manufacture of Ceramic Tiles. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 11340–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.V.; Guedes, D.G.; da Costa, F.P.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Neves, G.D.A.; Menezes, R.R.; Santana, L.N.D.L. Sustainable Ceramic Materials Manufactured from Ceramic Formulations Containing Quartzite and Scheelite Tailings. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, İ.B. Characterization of Copper Tailings in Murgul Copper Plant, Turkey, and Its Utilization Potential in Cement Mortar with Nano-and Micro-Silica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36938–36950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, H.F.; Klein, N.S.; Filho, J.M.; Bianchini, M. Low-Cement High-Strength Concrete with Partial Replacement of Portland Cement with Stone Powder and Silica Fume Designed by Particle Packing Optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzerini, M.; Luti, L.; Aquino, A.; Gallello, G.; Pagnotta, S. Effect of Marble Waste Powder as a Binder Replacement on the Mechanical Resistance of Cement Mortars. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, Q.; Qu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, S. Study of Water Absorption and Corrosion Resistance of the Mortar with Waste Marble Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. An Overview of Pumice Stone as a Cementitious Material—The Best Manual for Civil Engineer. Silicon 2021, 13, 551–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Motahari, S.M.; Vosoughi, P.; Pilvar, A.; Isapour, S.; Moodi, F. Effects of Calcined Perlite Powder as a SCM on the Strength and Permeability of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.C.D.A.; Marcos, A.S.; De Sá, M.V.V.A.; De Souza, N.S.L.; De Farias, E.C. Effect of High Temperatures on Self-Compacting Concrete with High Levels of Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Metakaolin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, J.C.; Lucena, L.F.L.; Henriques, G.F.; Ferreira, R.L.S.; Marcos, A.S. Use of Banana Leaf Ash as Partial Replacement of Portland Cement in Eco-Friendly Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.U.D.; Singh, N.; Varsha, S.; Sai, A.R.; Sufyan-Ud-Din, M. Strength, Electrical Resistivity and Sulfate Attack Resistance of Blended Mortars Produced with Agriculture Waste Ashes. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.G.; Gurgel, M.T.; da Silva, W.G.; de Oliveira, M.P.; Ferreira, R.L.S.; de Lima, F.J.N. Evaluation of the Mechanical and Durability Properties of Eco-Efficient Concretes Produced with Porcelain Polishing and Scheelite Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, B.A.; Neves, G.A.; Barbosa, N.P.; Menezes, R.R.; Ferreira, H.C. Mechanical Properties of Mortar Produced with the Replacement of Natural Sand by Scheelite Residue. Ceramic 2019, 65, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueirêdo, J.M.R.D.; Costa, F.P.D.; Fernandes, J.V.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Neves, G.D.A.; Menezes, R.R.; Santana, L.N.D.L. Development of Scheelite Tailings-Based Ceramic Formulations with the Potential to Manufacture Porcelain Tiles, Semi-Stoneware and Stoneware. Materials 2020, 13, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.S. Mortar Produced with Scheelite Residue and Cassava Wastewater. In Use of Cassava Wastewater and Scheelite Residues in Ceramic Formulations; Acchar, W., da Silva, V.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 53–83. ISBN 978-3-030-58782-6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, O.; Lee, K.M.; Lachemi, M. Utilization of Tailings from Tungsten Mine Waste as a Substitution Material for Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2481–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.W. An Experimental Research on Self-Consolidating Concrete Using Tungsten Mine Tailings. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C150/C150M-20; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C618-22; Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Data Science Workbench; TIBCO Software Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2020.
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xu, R.; Gurkalo, F. Stress Distribution in Direct Shear Loading and Its Implication for Engineering Failure Analysis. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2023, 15, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, G.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Lateral Abutment Pressure Distribution and Evolution in Wide Pillars under the First Mining Effect. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1437-20; Standard Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C642-21; Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C39/C39M-21; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1260-21; Standard Test Method for Potential Alkaline Reactivity of Aggregates (Mortar-Bar Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Neto, R.E.; Cartaxo, J.D.M.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Barros, S.V.A.; da Costa, F.P.; Neves, G.D.A.; Menezes, R.R. New Sustainable Mortar Compositions Containing Perlite Waste. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C270−19a; Standard Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–14.
- Barros, S.V.A.; Marciano, J.E.A.; Ferreira, H.C.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.D.A. Addition of Quartzite Residues on Mortars: Analysis of the Alkali Aggregate Reaction and the Mechanical Behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 118, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Guo, R.; Lin, Z.; Xia, H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q. Effect of Nanosilica and Silica Fume on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Lightweight Engineered Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, D.; Ji, W.; Zhao, X. Experiment on the Properties of Soda Residue-Activated Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Mortars with Different Activators. Materials 2022, 15, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burciaga-Díaz, O.; Betancourt-Castillo, I.E.; Montes-Escobedo, M.E.; Escalante-García, J.I. One-Part Pastes and Mortars of CaO-Na2CO3 Activated Blast Furnace Slag: Microstructural Evolution, Cost and CO2 Emissions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; Shi, B. Activation of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag by Using Calcined Dolomite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobiszewska, M.; Bagcal, O.; Beycioğlu, A.; Goulias, D.; Köksal, F.; Niedostatkiewicz, M.; Ürünveren, H. Influence of Rock Dust Additives as Fine Aggregate Replacement on Properties of Cement Composites—A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, V.; Cristina, L.; Costa, B.; Pereira, F.; Cesar, A.; De Carvalho, F.; Andre, R. Performance of Low-Energy Steel Slag Powders as Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; He, F. Microstructural Insight into the Deterioration Mechanism of the Mortar Subject to the Combined Action of External Sulfate Attack and Cyclic Wetting–Drying. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 317, 125484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Jeong, Y.; Bae, S.; Jun, Y.; Yoon, S.; Oh, J.E. A Study of Thermal Decomposition of Phases in Cementitious Systems Using HT-XRD and TG. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Geiker, M.R.; Lothenbach, B.; De Weerdt, K.; Garzon, S.F.; Enemark-Rasmussen, K.; Skibsted, J. Friedel ’ s Salt pro Fi Les from Thermogravimetric Analysis and Thermodynamic Modelling of Portland Cement-Based Mortars Exposed to Sodium Chloride Solution. Cem. Concr. Compos. J. 2017, 78, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
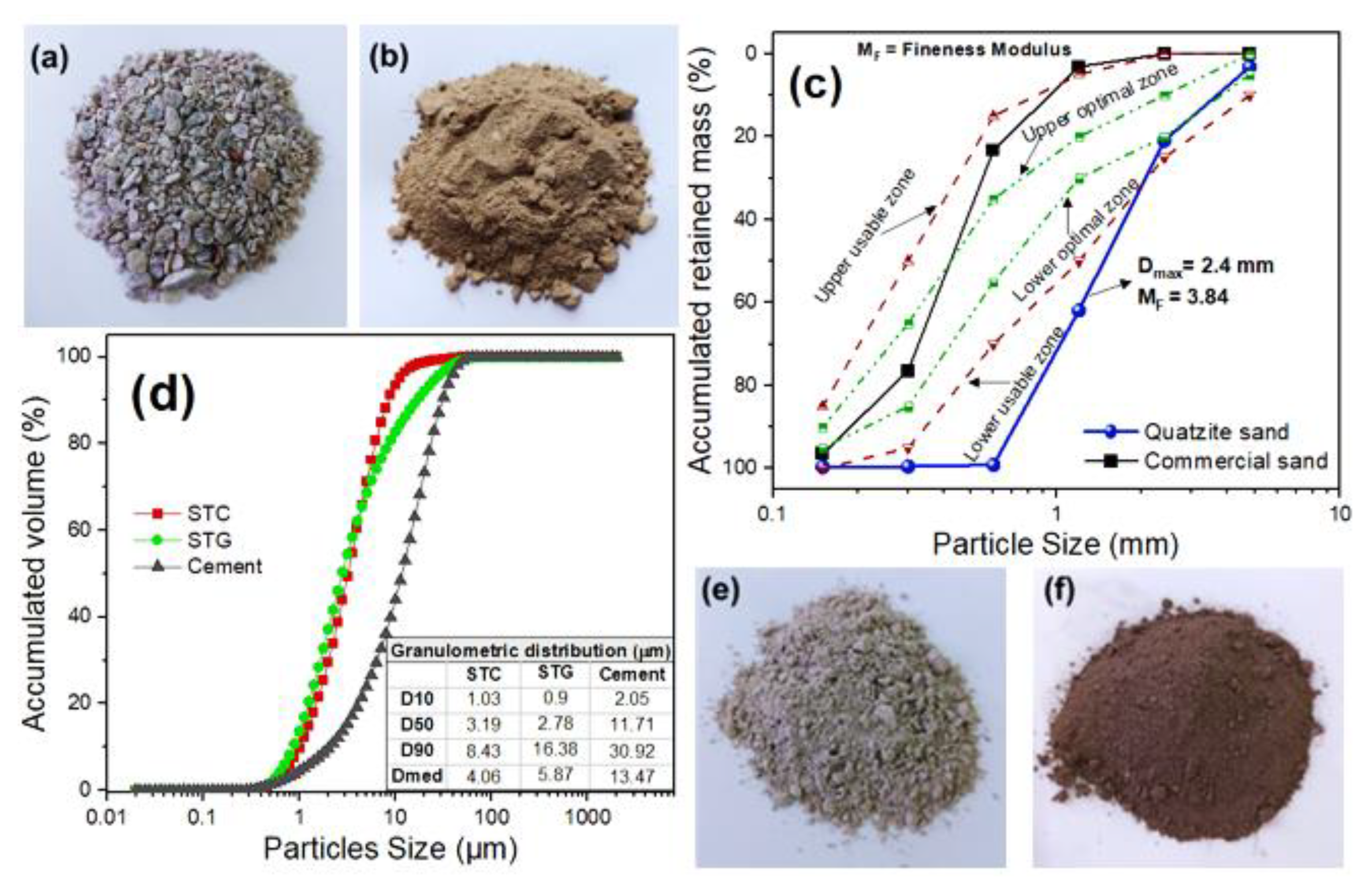
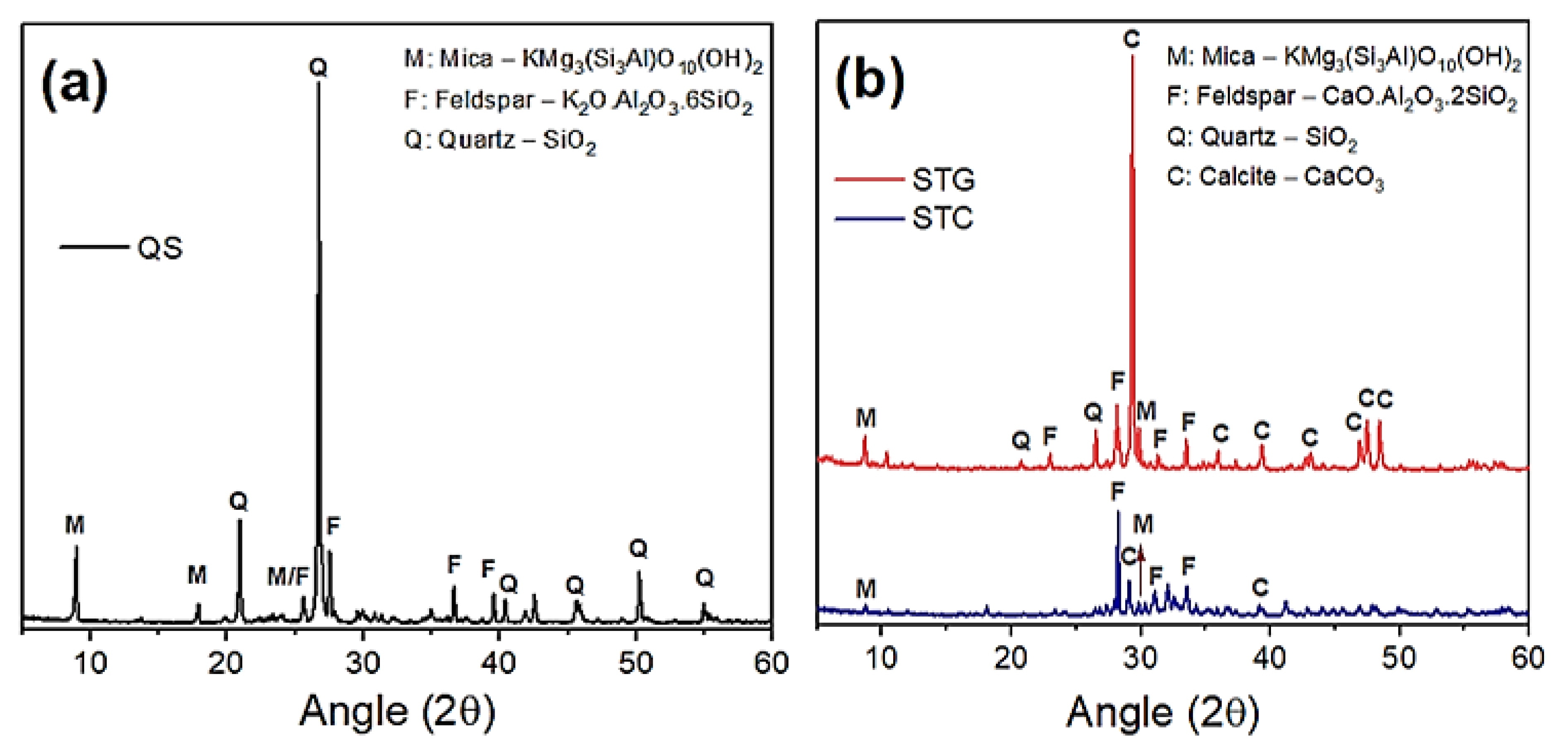
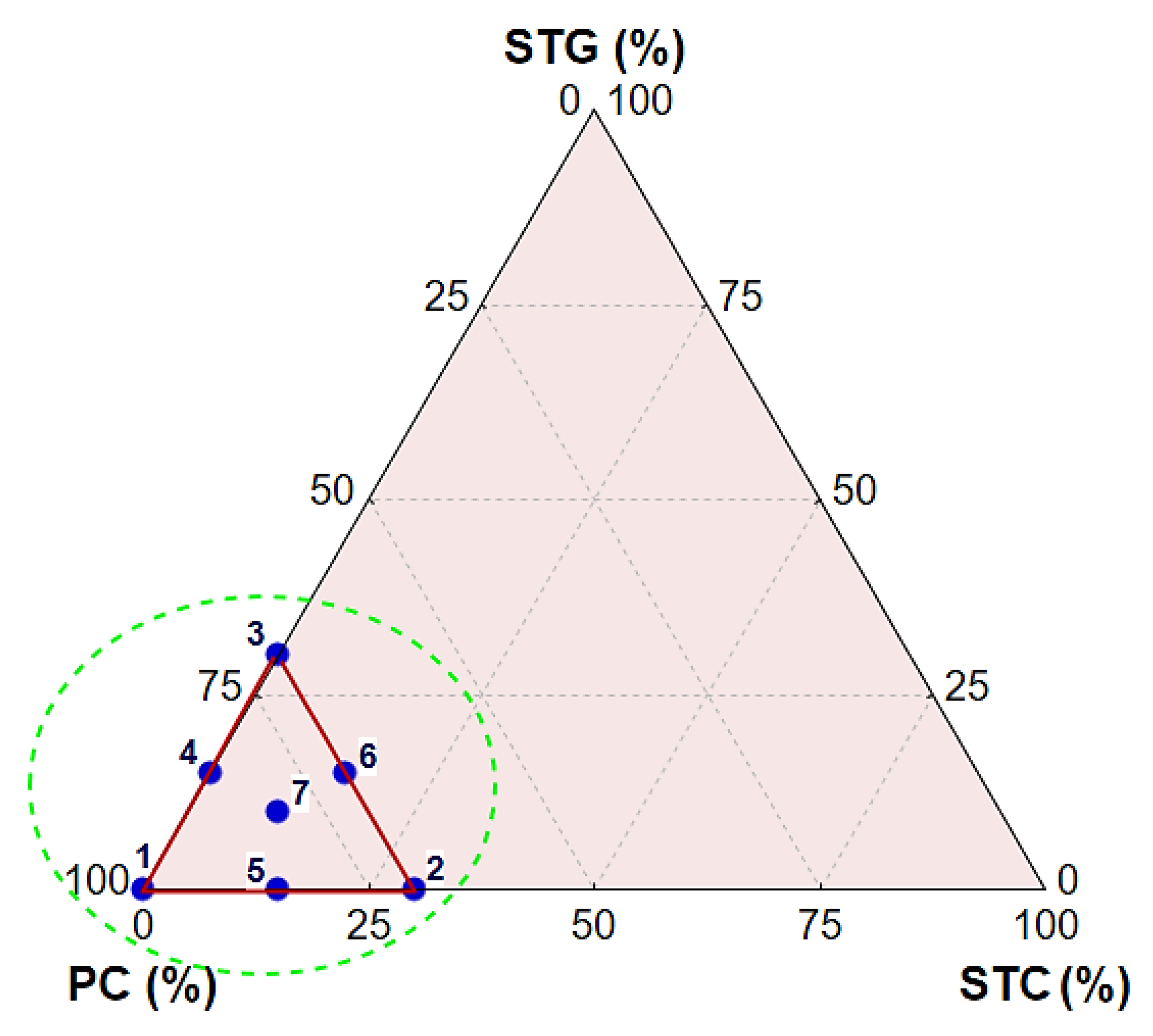




| Raw Materials | Oxides (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | SO3 | MnO | Others | * LOI | |
| QS | 66.4 | 17.2 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 7.7 | 1.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| PC | 15.0 | 4.0 | 3.1 | 66.9 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 4.8 | – | 0.3 | 3.2 |
| STG | 16.4 | 6.1 | 5.0 | 48.1 | 1.0 | 3.4 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 19.0 |
| STC | 20.3 | 6.3 | 6.1 | 57.3 | 0.3 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 2.6 |
| Components (%) | Compositions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| PC | 100 | 70 | 70 | 85 | 85 | 70 | 80 |
| STC | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 15 | 10 |
| STG | 0 | 0 | 30 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 10 |
| Compositions | Components (%) | CS Values * (MPa) | WA Values * (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | STC | STG | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 6.56 | 7.41 | 8.25 | 13.1 | 13.9 | 13.5 |
| 2 | 70 | 30 | 0 | 8.89 | 10.39 | 9.46 | 12.6 | 12.6 | 12.6 |
| 3 | 70 | 0 | 30 | 3.56 | 4.48 | 5.07 | 13.3 | 13.1 | 13.2 |
| 4 | 85 | 0 | 15 | 6.95 | 6.17 | 6.56 | 12.9 | 13.0 | 12.9 |
| 5 | 85 | 15 | 0 | 7.29 | 7.16 | 7.15 | 13.4 | 13.0 | 13.2 |
| 6 | 70 | 15 | 15 | 6.79 | 6.00 | 6.40 | 14.7 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
| 7 | 80 | 10 | 10 | 7.21 | 7.10 | 7.16 | 12.7 | 13.3 | 13.0 |
| Regression Models | Ftest | Fcal/Ftab | Pvalue | * R2 (%) | ** R2ajust (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | Linear | 10.13 | 2.85 | 0.00002 | 70.26 | 66.95 |
| Quadratic | 21.26 | 6.46 | 0.00067 | 90.17 | 86.90 | |
| Special Cubic | 1.02 | 0.22 | 0.32915 | 90.84 | 86.92 | |
| WA | Linear | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.73367 | 3.38 | 0.01 |
| Quadratic | 19.33 | 5.88 | 0.00002 | 80.14 | 73.53 | |
| Special Cubic | 24.88 | 5.41 | 0.00012 | 92.85 | 89.79 |
| MR | M0 | M30SG | M30SC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g·cm−3) | 2.05 ± 0.01 c | 1.95 ± 0.01 d | 2.11 ± 0.01 b | 2.19 ± 0.01 a |
| Porosity (%) | 17.2 ± 0.4 b | 11.5 ± 0.6 c | 18.9 ± 0.5 a | 17.7 ± 0.3 b |
| Condition | Mortar | Weight Loss (%) | Estimated Amount (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Free Water, C-S-H, AFt, and AFm * | Ca(OH)2 | CaCO3 | ||
| Water | M0 | 17.5 | 10.0 | 14.4 | 6.1 |
| MS30G | 17.9 | 6.9 | 10.7 | 15.4 | |
| M30SC | 17.0 | 8.8 | 15.6 | 7.0 | |
| 1N NaOH solution | M0 | 17.1 | 9.3 | 11.1 | 9.8 |
| MS30G | 9.3 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 7.5 | |
| M30SC | 10.7 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 4.8 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arruda, T.d.L.; Costa, F.P.d.; Diniz, R.C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.d.A. Statistical Design of Eco-Friendly Mortar Mixtures Containing Scheelite Tailings and Quartzite Sand: Evaluation of Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11544. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511544
Arruda TdL, Costa FPd, Diniz RC, Rodrigues AM, Menezes RR, Neves GdA. Statistical Design of Eco-Friendly Mortar Mixtures Containing Scheelite Tailings and Quartzite Sand: Evaluation of Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11544. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511544
Chicago/Turabian StyleArruda, Thainara de Lima, Fabiana Pereira da Costa, Rebeca Cavalcante Diniz, Alisson Mendes Rodrigues, Romualdo Rodrigues Menezes, and Gelmires de Araújo Neves. 2023. "Statistical Design of Eco-Friendly Mortar Mixtures Containing Scheelite Tailings and Quartzite Sand: Evaluation of Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11544. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511544
APA StyleArruda, T. d. L., Costa, F. P. d., Diniz, R. C., Rodrigues, A. M., Menezes, R. R., & Neves, G. d. A. (2023). Statistical Design of Eco-Friendly Mortar Mixtures Containing Scheelite Tailings and Quartzite Sand: Evaluation of Resistance to Alkali-Aggregate Reaction. Sustainability, 15(15), 11544. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511544









