Evaluating the Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on Climate Change Signal and Extreme Indices in the Jemma Sub-Basin of Blue Nile Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
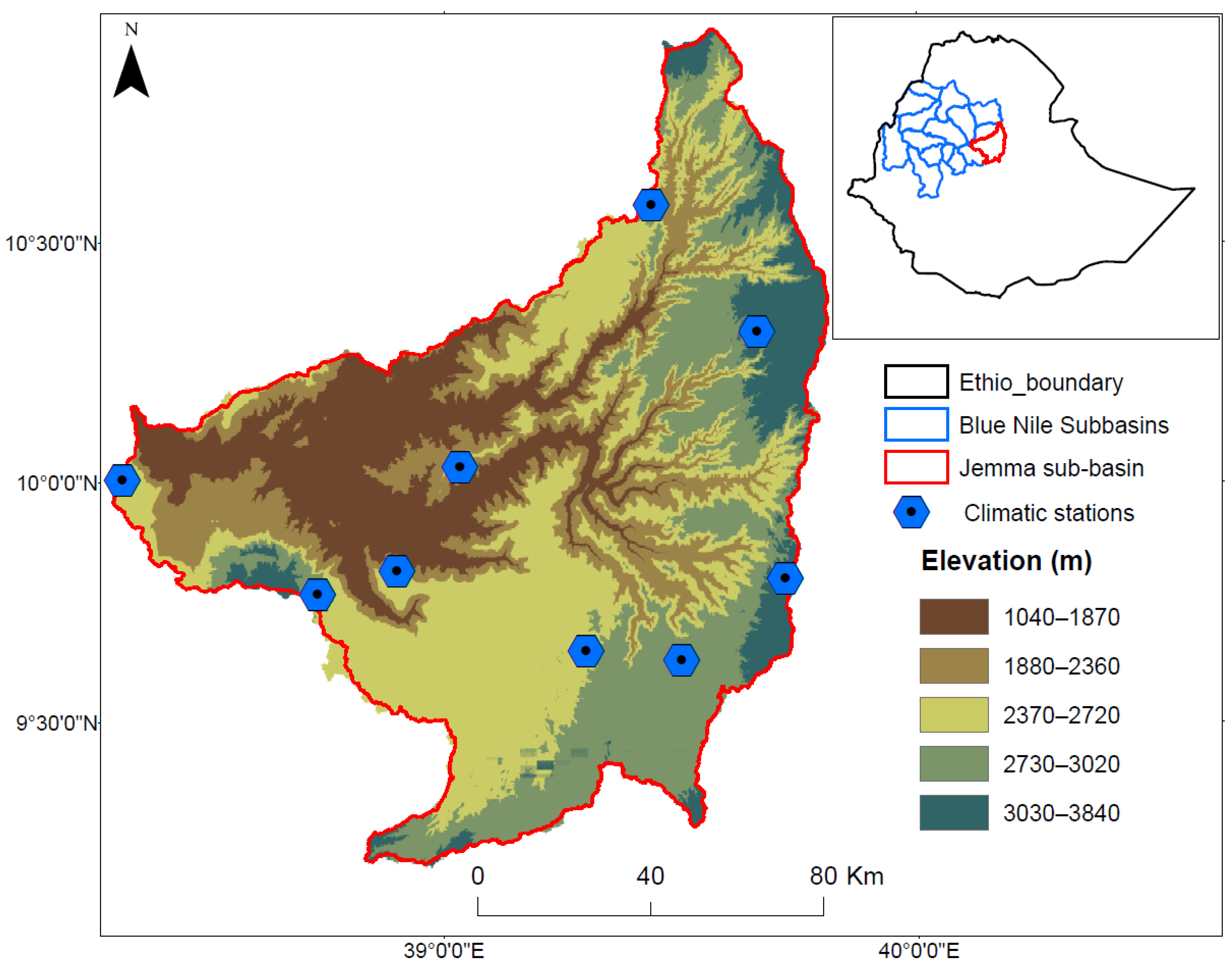
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Climate Data
2.3. Regional Climate Model Simulations Data
2.4. Statistical Bias Correction Techniques
- Vo is an observed variable;
- Vm is modeled variable;
- Fm is the CDF related to Vm;
- Fo−1 is the inverse CDF of Vo [19].
2.5. Future Rainfall and Temperature Extremes Analysis
2.6. Evaluation Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
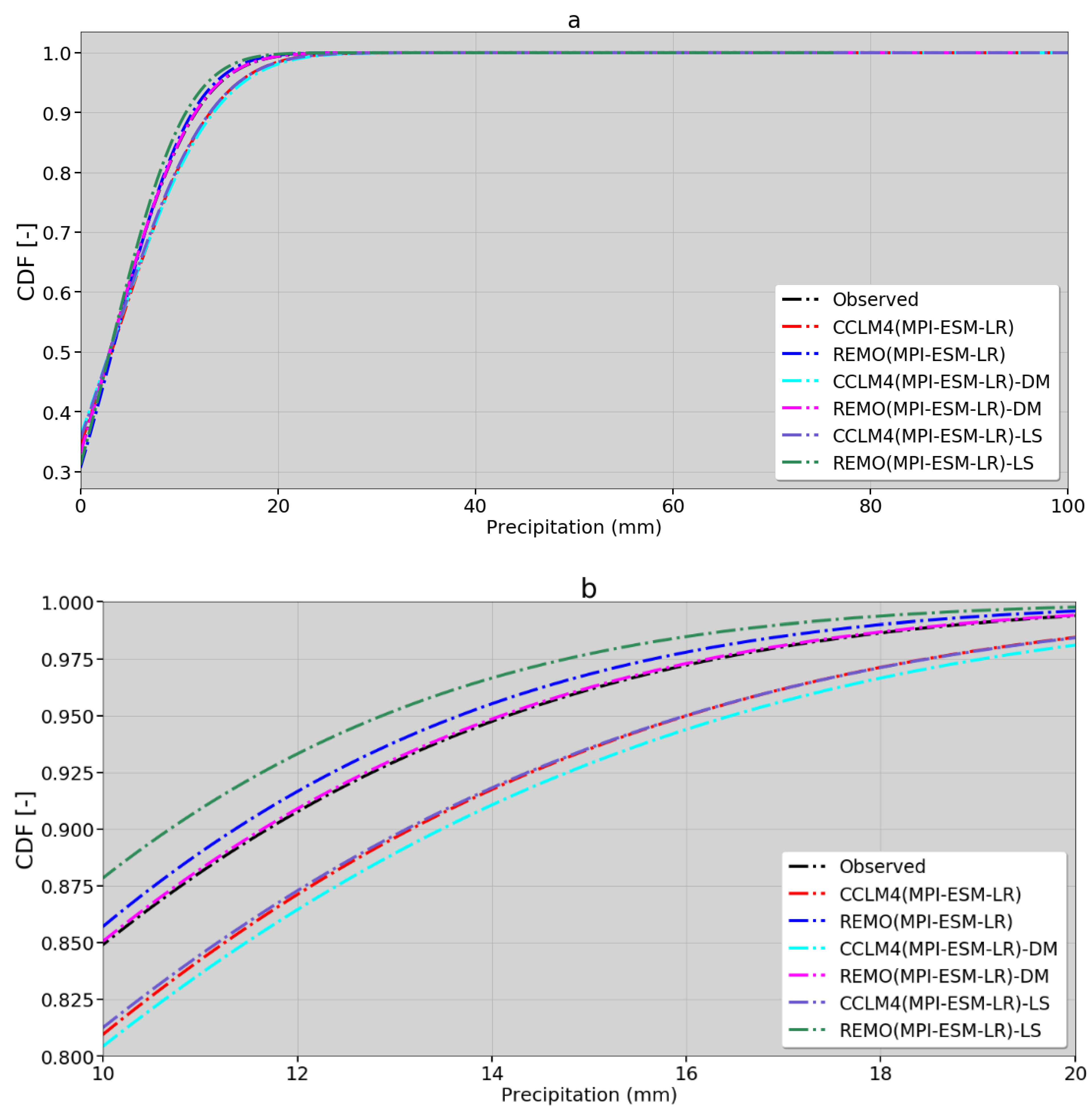
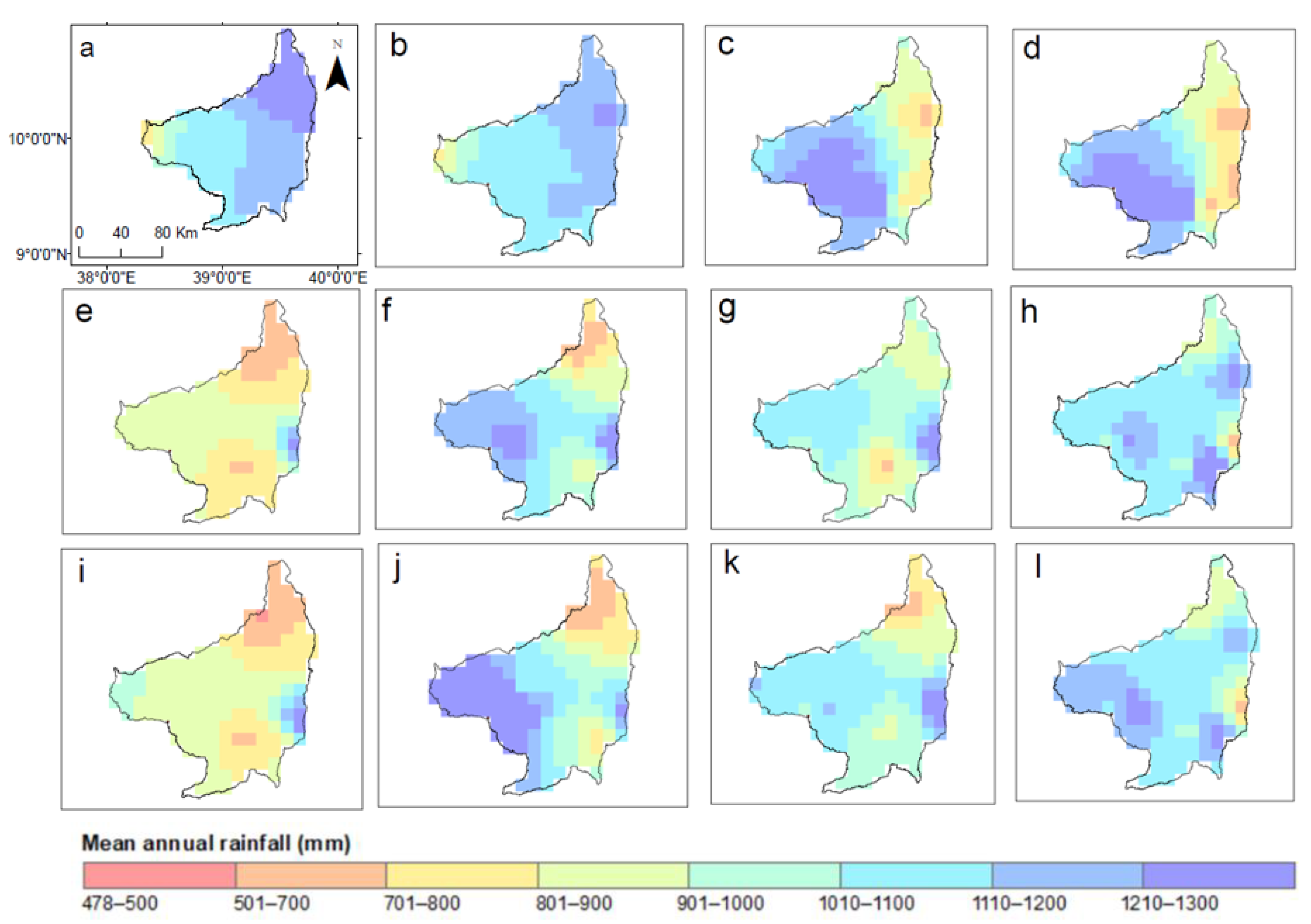
3.1. Evaluation of Bias Correction Techniques
3.2. Effect of Bias Correction Techniques on Climate Change Signal
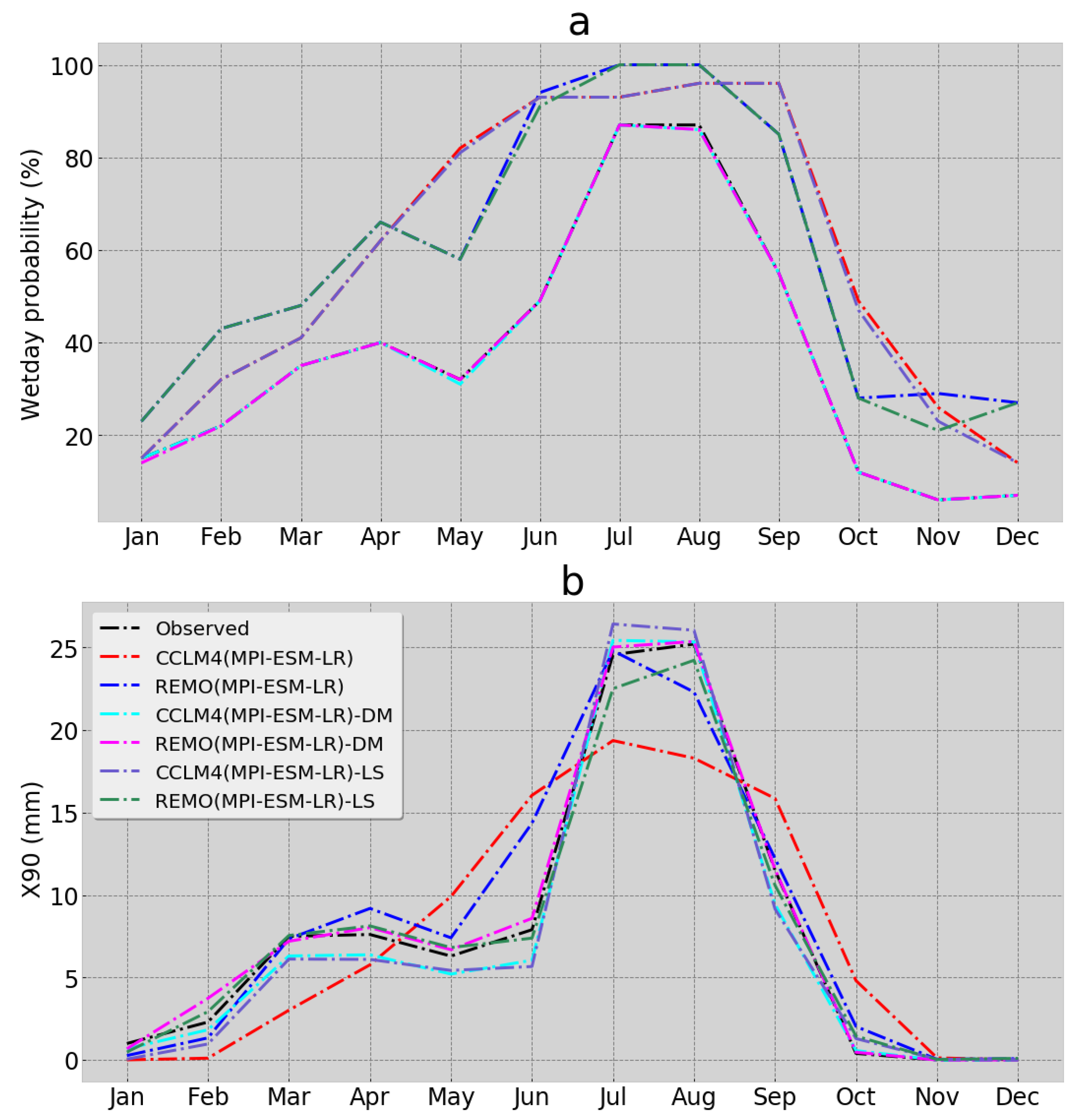
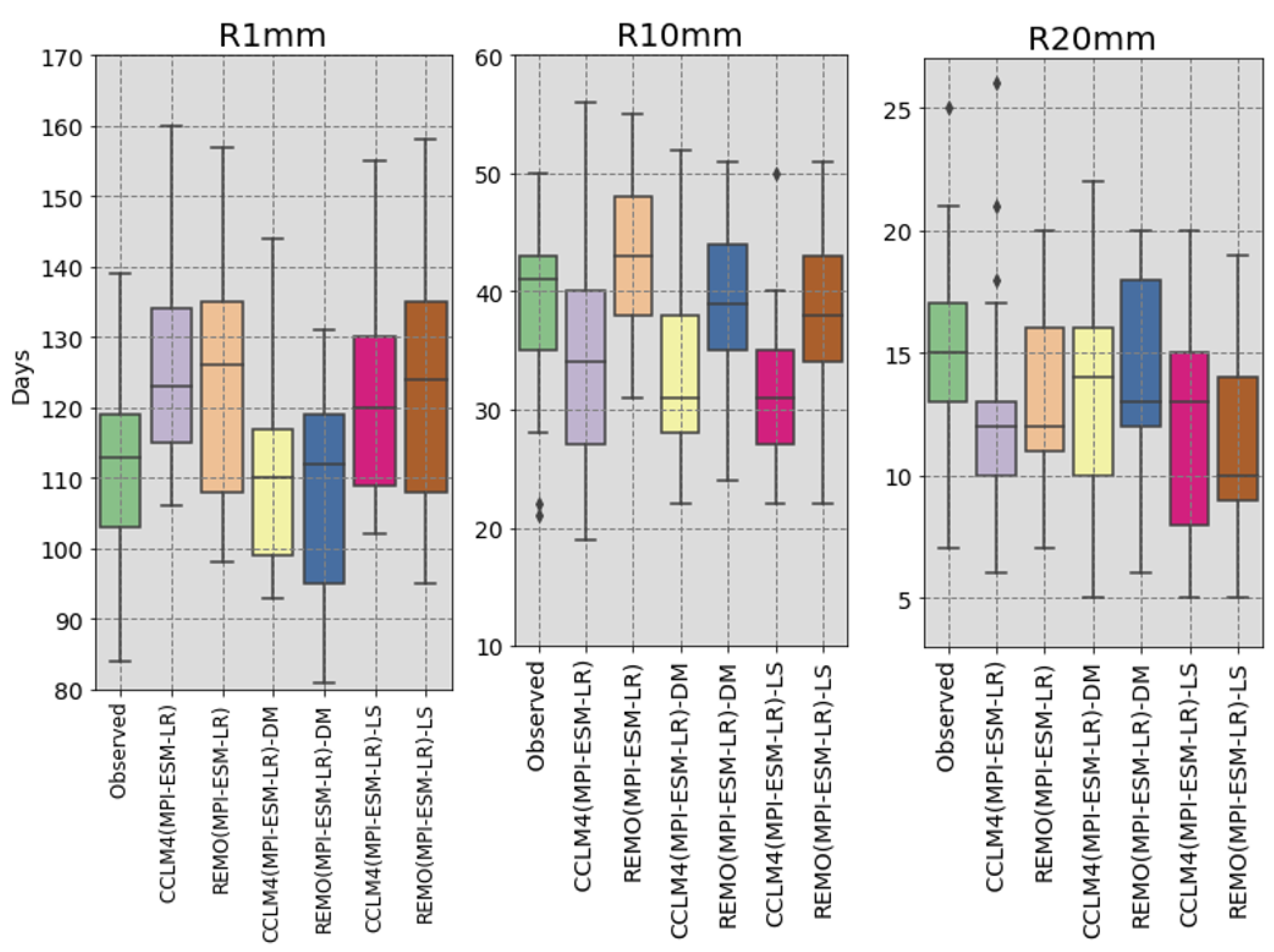
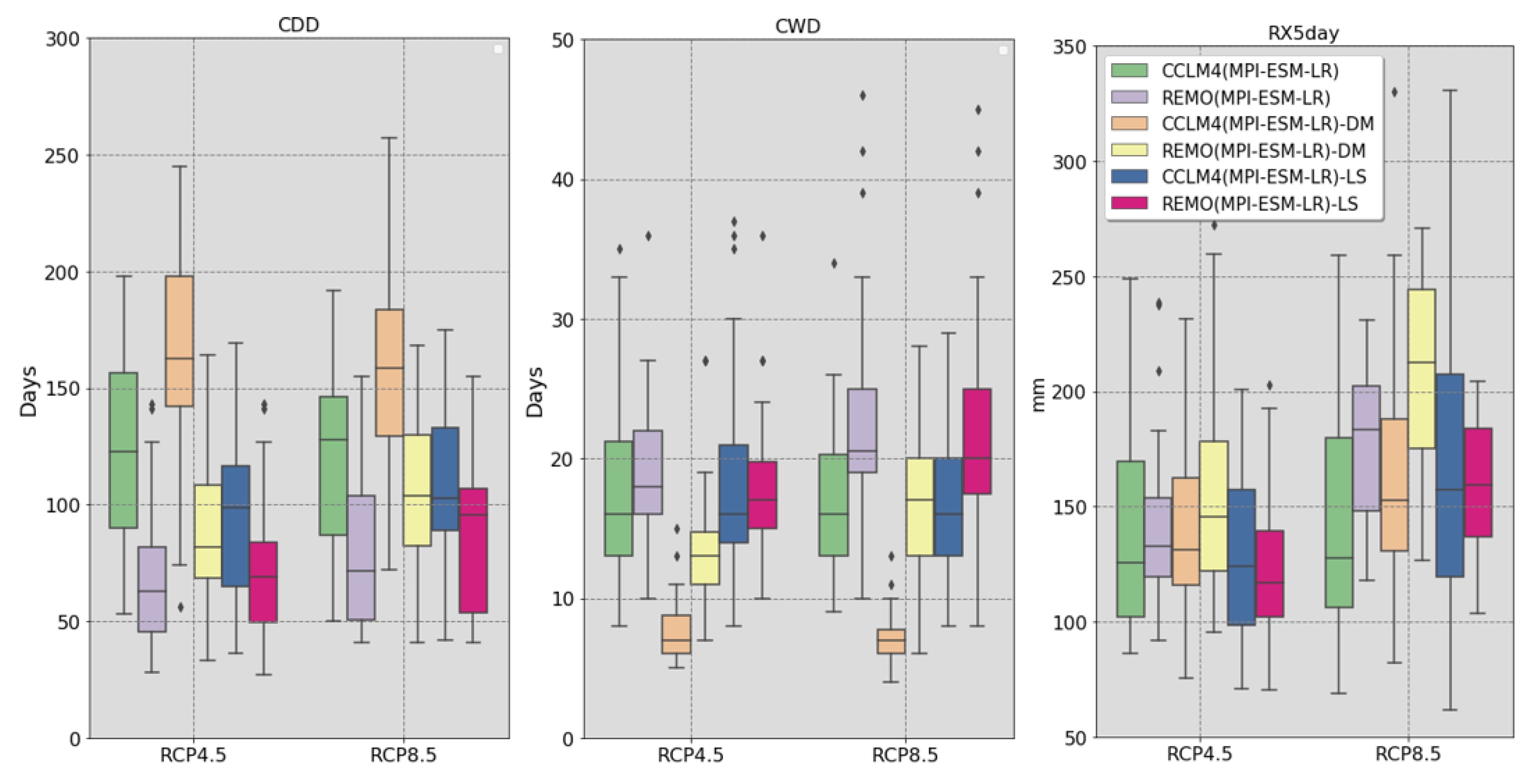
3.3. Effect of Bias Correction Techniques on Rainfall Extreme Indices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flato, G.; Marotzke, J.; Abiodun, B.; Braconnot, P.; Chou, S.C.; Collins, W.; Cox, P.; Driouech, F.; Emori, S.; Eyring, V.; et al. Evaluation of Climate Models. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; Volume 53, ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, B.; Kundzewicz, Z.; Wu, S.; Palutikof, J. Climate Change and Water; Technical Paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; 210p, ISBN 9789291691234. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781139899642. [Google Scholar]
- Flato, G.M. Earth System Models: An Overview. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemeskel, F.M.; Sharma, A.; Sivakumar, B.; Mehrotra, R. Quantification of Precipitation and Temperature Uncertainties Simulated by CMIP3 and CMIP5 Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 107, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wood, E.F.; Sheffield, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. Bias Correction of Historical and Future Simulations of Precipitation and Temperature for China from CMIP5 Models Bias Correction of Historical and Future Simulations of Precipitation and Temperature for China from CMIP5 Models. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosio, A.; Panitz, H.J.; Schubert-Frisius, M.; Lüthi, D. Dynamical Downscaling of CMIP5 Global Circulation Models over CORDEX-Africa with COSMO-CLM: Evaluation over the Present Climate and Analysis of the Added Value. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 2637–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.; Roberts, N.; Lean, H.; Ballard, S.P.; Charlton-Perez, C. Convection-Permitting Models: A Step-Change in Rainfall Forecasting. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummukainen, M. Added Value in Regional Climate Modeling. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2016, 7, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnitou, G.T.; Tan, G.; Ma, T.; Akinola, E.O.; Nooni, I.K.; Babaousmail, H.; Al-Nabhan, N. Added Value in Dynamically Downscaling Seasonal Mean Temperature Simulations over West Africa. Atmos. Res. 2021, 260, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.J.; Sobie, S.R.; Murdock, T.Q. Bias Correction of GCM Precipitation by Quantile Mapping: How Well Do Methods Preserve Changes in Quantiles and Extremes? J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6938–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanueva, A.; Herrera, S.; Iturbide, M.; Lange, S.; Jury, M.; Dosio, A.; Maraun, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Testing Bias Adjustment Methods for Regional Climate Change Applications under Observational Uncertainty and Resolution Mismatch. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, G.; Teferi, E.; Bantider, A.; Dile, Y.T.; Taye, M.T. Evaluation of Regional Climate Models Performance in Simulating Rainfall Climatology of Jemma Sub-Basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2018, 83, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kang, W.; Li, W.; Luo, J.J.; Zhu, Y. The Optimal Bias Correction for Daily Extreme Precipitation Indices over the Yangtze-Huaihe River Basin, Insight from BCC-CSM1.1-M. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Haerter, J.O.; Coppola, E. Statistical Bias Correction for Daily Precipitation in Regional Climate Models over Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.B.; Haugen, J.E.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical Note: Downscaling RCM Precipitation to the Station Scale Using Statistical Transformations – A Comparison of Methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D. Bias Correcting Climate Change Simulations - a Critical Review. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2016, 2, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhellambam, B.S.; Srivastava, P.; Lamba, J.; McGehee, R.P.; Kumar, H.; Tian, D. Temporal Disaggregation of Hourly Precipitation under Changing Climate over the Southeast United States. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Tang, J. Bias Correction of Surface Air Temperature and Precipitation in CORDEX East Asia Simulation: What Should We Do When Applying Bias Correction? Atmos. Res. 2022, 280, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Chen, J.; Cannon, A.J.; Xie, P.; Guo, Q. Multi-Site Bias Correction of Climate Model Outputs for Hydro-Meteorological Impact Studies: An Application over a Watershed in China. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2575–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, T.; Kotlarski, S.; Ewen, T.; Schär, C. Spectral Representation of the Annual Cycle in the Climate Change Signal. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Buishand, A.; van Deursen, W. Estimates of future discharges of the river Rhine using two scenario methodologies: Direct versus delta approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Kwon, H.H.; Han, D. Bias Correction Methods for Regional Climate Model Simulations Considering the Distributional Parametric Uncertainty Underlying the Observations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias Correction of Regional Climate Model Simulations for Hydrological Climate-Change Impact Studies: Review and Evaluation of Different Methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.H.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.N.; Zammit, C. Comparing Bias Correction Methods in Downscaling Meteorological Variables for a Hydrologic Impact Study in an Arid Area in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, G.; Teferi, E.; Bantider, A.; Dile, Y.T. Statistical Bias Correction of Regional Climate Model Simulations for Climate Change Projection in the Jemma Sub-Basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 1569–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.A.; Kotlarski, S. Assessing Distribution-Based Climate Model Bias Correction Methods over an Alpine Domain: Added Value and Limitations. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2633–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, D.C.; Sriver, R.L.; Nicholas, R.E.; Hertel, T.W.; Keller, K.; Nicholas, R.E. Statistically Bias-Corrected and Downscaled Climate Models Underestimate the Adverse Effects of Extreme Heat on U.S. Maize Yields. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhellambam, B.S.; Srivastava, P.; Lamba, J.; McGehee, R.P.; Kumar, H.; Tian, D. Projected Mid-Century Rainfall Erosivity under Climate Change over the Southeastern United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kotamarthi, V.R. High-Resolution Dynamically Downscaled Projections of Precipitation in the Mid and Late 21st Century over North America. Earth’s Future 2015, 3, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addor, N.; Rössler, O.; Köplin, N.; Huss, M.; Weingartner, R.; Seibert, J. Robust Changes and Sources of Uncertainty in the Projected Hydrological Regimes of Swiss Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7541–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Is Bias Correction of Regional Climate Model (RCM) Simulations Possible for Non-Stationary Conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5061–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terink, W.; Hurkmans, R.T.W.L.; Torfs, P.J.J.F.; Uijlenhoet, R. Evaluation of a Bias Correction Method Applied to Downscaled Precipitation and Temperature Reanalysis Data for the Rhine Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaye, M.L.; Haensler, A.; Hagemann, S.; Gaye, A.T.; Moseleyd, C.; Afouda, A. Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on the Projected Climate Change Signals of the Regional Climate Model REMO over the Senegal River Basin.Pdf. Int. J. Clim. 2016, 36, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, A.M.; Dixon, K.W.; Adams-Smith, D.J.; McPherson, R.A. Statistically Downscaled Precipitation Sensitivity to Gridded Observation Data and Downscaling Technique. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 980–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, A. Application of the Bias Correction and Spatial Downscaling Algorithm on the Temperature Extremes From CMIP5 Multimodel Ensembles in China. Earth Sp. Sci. 2019, 6, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmokhtarian, A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Campbell, J.L.; Hayhoe, K.; Stoner, A.M.K. The Effects of Climate Downscaling Technique and Observational Data Set on Modeled Ecological Responses. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Melesse, A.M. Comparison of Trend Preserving Statistical Downscaling Algorithms Toward an Improved Precipitation Extremes Projection in the Headwaters of Blue Nile River in Ethiopia. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Z.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Daily Precipitation and Temperature for 2021–2050 over China: Multiple RCMs and Emission Scenarios Corrected by a Trend-Preserving Method. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, H.I.; Cannon, A.J. Intercomparison of Projected Changes in Climate Extremes for South Korea: Application of Trend Preserving Statistical Downscaling Methods to the CMIP5 Ensemble. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3381–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viste, E.; Sorteberg, A. Moisture Transport into the Ethiopian Highlands. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 33, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, G.; Teferi, E.; Bantider, A.; Dile, Y.T. Observed Changes in Extremes of Daily Rainfall and Temperature in Jemma Sub-Basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilma, A.D.; Awulachew, S.B. Characterization and Atlas of the Blue Nile Basin and Its Sub Basins; International Water Management Institute: Delhi, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Y.S.A.; Crosato, A.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Abdalla, S.H.; Wright, N.G. Sediment Balances in the Blue Nile River Basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2014, 29, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team Core. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Chan, R. Introduction to RClimDex; Climate Research Division, Environment Canada: Downsview, ON, Canada, 2018; pp. 1–26.
- WMO. Guidelines on Analysis of Extremes in a Changing Climate in Support of Informed Decisions for Adaptation; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Cham, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Gutowski, W.J. Regional Dynamical Downscaling and the CORDEX Initiative. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2015, 40, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Weedon, G.P.; Best, M.; Gomes, S.M.; Viterbo, P.; Hagemann, S.; Haerter, J.O. Statistical Bias Correction of Global Simulated Daily Precipitation and Temperature for the Application of Hydrological Models. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.T.; Rientjes, T. Evaluation of Regional Climate Model Simulations of Rainfall over the Upper Blue Nile Basin. Atmos. Res. 2015, 161–162, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endris, H.S.; Omondi, P.; Jain, S.; Lennard, C.; Hewitson, B.; Chang’a, L.; Awange, J.L.; Dosio, A.; Ketiem, P.; Nikulin, G.; et al. Assessment of the Performance of CORDEX Regional Climate Models in Simulating East African Rainfall. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8453–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.A.; Luterbacher, J.; Kotlarski, S. Climate Model Biases and Modification of the Climate Change Signal by Intensity-Dependent Bias Correction. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 6591–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
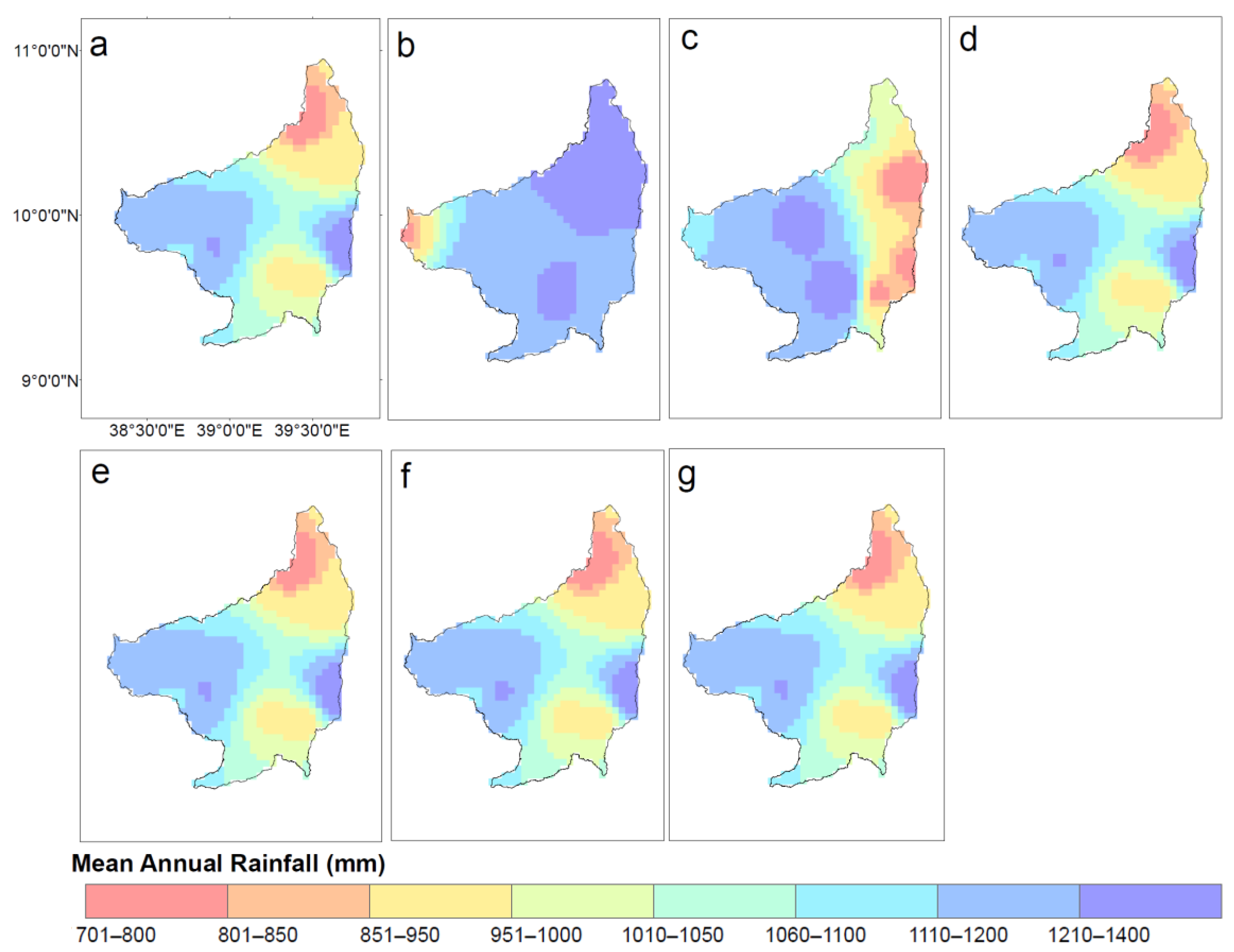

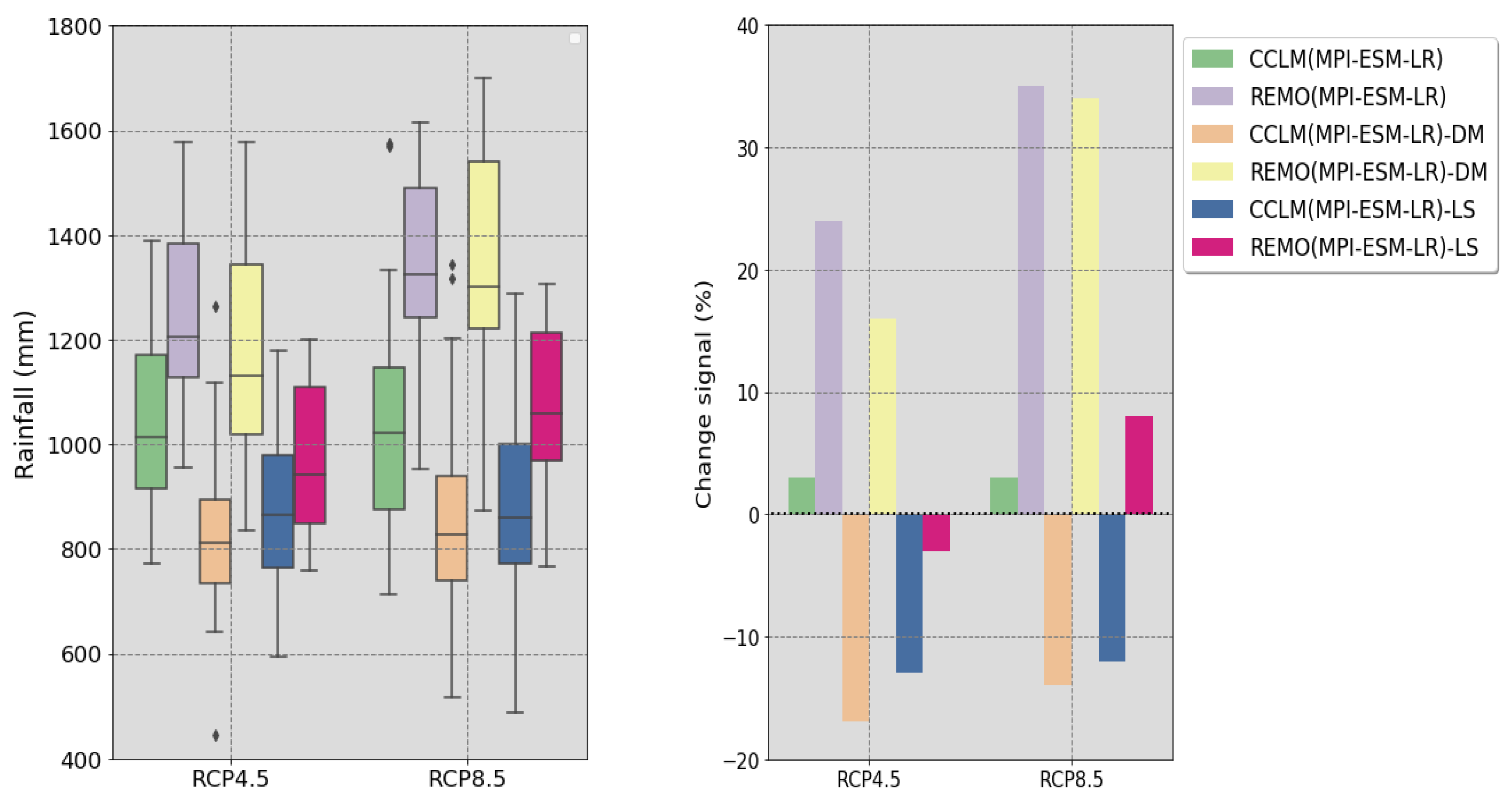

| Emission Scenario | RCMs | Mean Annual Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| RCP4.5 | Observed | 1001 (-) |
| CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR) | 1034 (3) | |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR) | 1240 (24) | |
| CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR)-DM | 829 (−17) | |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR)-DM | 1166 (16) | |
| CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR)-LS | 875 (−13) | |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR)-LS | 967 (−3) | |
| RCP8.5 | CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR) | 1035 (3) |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR) | 1348 (35) | |
| CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR)-DM | 858 (−14) | |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR)-DM | 1344 (34) | |
| CCLM4(MPI-ESM-LR)-LS | 879 (−12) | |
| REMO(MPI-ESM-LR)-LS | 1078 (8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tefera, G.W.; Dile, Y.T.; Ray, R.L. Evaluating the Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on Climate Change Signal and Extreme Indices in the Jemma Sub-Basin of Blue Nile Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310513
Tefera GW, Dile YT, Ray RL. Evaluating the Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on Climate Change Signal and Extreme Indices in the Jemma Sub-Basin of Blue Nile Basin. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310513
Chicago/Turabian StyleTefera, Gebrekidan Worku, Yihun Taddele Dile, and Ram Lakhan Ray. 2023. "Evaluating the Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on Climate Change Signal and Extreme Indices in the Jemma Sub-Basin of Blue Nile Basin" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310513
APA StyleTefera, G. W., Dile, Y. T., & Ray, R. L. (2023). Evaluating the Impact of Statistical Bias Correction on Climate Change Signal and Extreme Indices in the Jemma Sub-Basin of Blue Nile Basin. Sustainability, 15(13), 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310513







